Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editor's Choice
EDITORIAL
Patient engagement with the BJD: encouraging the patient voice and readership
- Pages: 835-836
- First Published: 04 December 2022
COMMENTARIES
Psoriasis treatment: no more room on the summit?
- Page: 837
- First Published: 05 September 2022
Linked Article: Blauvelt et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:866–877.
How will brepocitinib cream compare with established treatments for mild-to-moderate eczema?
- Page: 838
- First Published: 05 October 2022
Linked Article: Landis et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:878–887.
Differences in cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19 during the Delta and Omicron waves revealed using the ZOE app
- Page: 839
- First Published: 23 September 2022
Linked Article: Visconti et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:900–908.
Understanding the impact of life with vulval lichen sclerosus
- Page: 840
- First Published: 02 September 2022
Linked Article: Arnold et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:909–918.
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced cutaneous toxicities: they are not just random
- Pages: 840-841
- First Published: 02 September 2022
Linked Article: Nikolaou et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:962–969.
Follicular T helper cells and cutaneous T-cell lymphomas
- Pages: 841-842
- First Published: 31 August 2022
Linked Article: Wang et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:970–980.
Sensitization to epoxy resin systems in the wind turbine industry: an undesirable side-effect of renewable energies
- Pages: 842-843
- First Published: 05 October 2022
Linked Article: Christiansen et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:988–996.
Atypical clinical manifestation and protracted latency are observed in the emerging variant of checkpoint inhibitor-associated bullous pemphigoid
- Pages: 843-844
- First Published: 30 September 2022
Linked Article: Kawsar et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:981–987.
Transcriptomic analysis identifies regulators of the Wnt signalling and hypoxia-inducible factor pathways as possible mediators of androgenetic alopecia
- Page: 845
- First Published: 05 October 2022
Linked Article: Liu et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:936–947.
Evidence-Based Dermatology
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Pain measurement in painful skin conditions and rheumatoid arthritis randomized controlled trials: a scoping review to inform pain measurement in hidradenitis suppurativa
- Pages: 846-854
- First Published: 12 August 2022
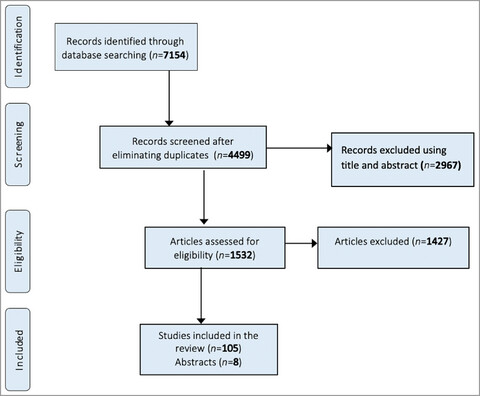
The review looked at the tools used to measure pain in painful skin conditions and how Pain NRS and VAS were used in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of painful skin conditions and rheumatoid arthritis. The results showed a discrepancy in how pain NRS/VAS were measured in the trials. In addition, the mean difference was the most common method of reporting pain.
Plain language summary available online
CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC
Topical treatments in the management of keloids and hypertrophic scars: a critically appraised topic
- Pages: 855-856
- First Published: 17 August 2022
Is routine laboratory testing in healthy young patients taking isotretinoin necessary: a critically appraised topic
- Pages: 857-865
- First Published: 20 August 2022
Original articles
CLINICAL TRIALS
Efficacy and safety of mirikizumab in psoriasis: results from a 52-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized withdrawal, phase III trial (OASIS-1)
- Pages: 866-877
- First Published: 06 July 2022
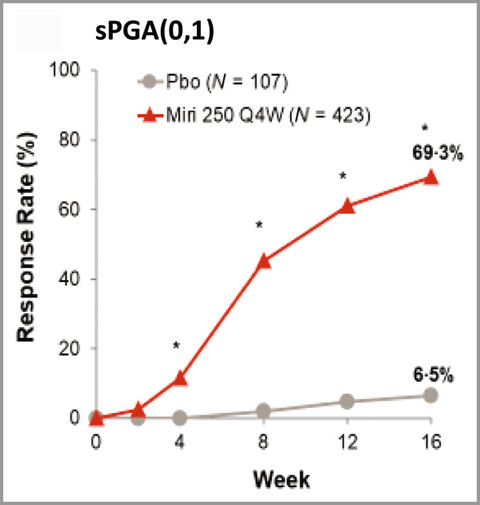
The primary efficacy endpoints were met, with significantly greater improvements in clinical response observed with mirikizumab than with placebo at the end of the induction period. sPGA(0,1) response rates were superior in the mirikizumab arm (n(%) [95% confidence interval; CI], mirikizumab: 293(69.3) [64.9-73.7]; placebo: 7(6.5) [1.9, 11.2]; P < 0.001) compared with placebo at Week 16.
Linked Comment: L. Puig. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:837.
Plain language summary available online
Efficacy and safety of topical brepocitinib for the treatment of mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis: a phase IIb, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, dose-ranging and parallel-group study
- Pages: 878-887
- First Published: 20 August 2022
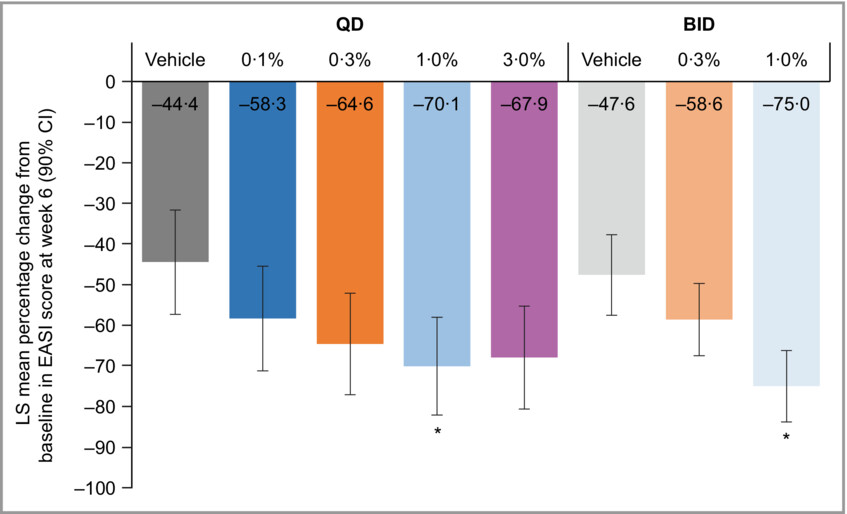
Brepocitinib, a TYK2/JAK1 inhibitor, is being investigated as a topical cream treatment for atopic dermatitis (AD). In a phase IIb, randomised, double-blind study, brepocitinib was effective and well tolerated in participants with mild-to-moderate AD, although further study with a larger population and longer treatment duration is required.
Linked Comment: S.J. Lax and A.M. Drucker. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:838.
Plain language summary available online
Safety of tralokinumab in adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: pooled analysis of five randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II and phase III trials
- Pages: 888-899
- First Published: 09 September 2022
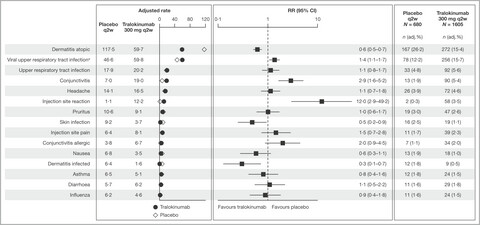
Tralokinumab, an anti-interleukin-13 biologic for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD), has provided significant and early improvements in signs and extent of AD in key Phase 3 clinical trials and was well tolerated, with a safety profile comparable to placebo. This study comprehensively assessed the safety profile of tralokinumab using data from five placebo-controlled trials in adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD, finding that overall incidence and rate of adverse events (AEs) was similar between tralokinumab and placebo in the initial treatment period (16 weeks) and did not increase over 52 weeks of continued treatment. Common AEs occurring more frequently with tralokinumab included conjunctivitis and injection site reaction.
Plain language summary available online
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Cutaneous manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection during the Delta and Omicron waves in 348 691 UK users of the UK ZOE COVID Study app
- Pages: 900-908
- First Published: 22 July 2022
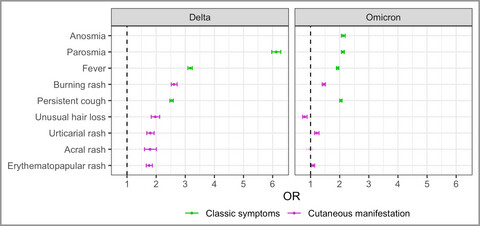
Odds ratios in adults testing positive for COVID-19 of self-reporting some of the typical COVID-19 symptoms and skin signs of COVID-19 infection. Results are based on 198 609 users of the ZOE COVID Study App that self-reported their symptoms during the Delta wave and 198 609 users matched for age, sex, vaccination status and self-reported eczema diagnosis that self-reported their symptoms during the Omicron wave. The OR for anosmia (13·4, 95% confidence interval 13·1–13·8) is not shown for the Delta wave to improve visualization.
Linked Comment: M. Grau-Pérez and I. Garcia-Doval. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:839.
Plain language summary available online
OUTCOMES AND QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Living with vulval lichen sclerosus: a qualitative interview study
- Pages: 909-918
- First Published: 13 July 2022

Vulval lichen sclerosus can have a profound impact on quality of life and self-identity but is relatively under-explored from the perspective of those living with the condition. Using qualitative methods, the aim of this study was to explore individuals’ experiences of vulval lichen sclerosus and its impact on their lives. We developed three themes to interpret the experience of living with vulval lichen sclerosus: missed opportunities, learning to live with a long-term condition, and a secret life.
Linked Comment: V. Sivalingam and K. Tamber. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:840.
Plain language summary available online
Content validity of the Recap of atopic eczema (RECAP) instrument in Dutch, English and German to measure eczema control in young people with atopic eczema: a cognitive interview study
- Pages: 919-926
- First Published: 16 July 2022
Factors associated with treatment satisfaction in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: results from the Global VOICE project
- Pages: 927-935
- First Published: 30 July 2022
Plain language summary available online
TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH
Insights into male androgenetic alopecia using comparative transcriptome profiling: hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathways
- Pages: 936-947
- First Published: 21 July 2022
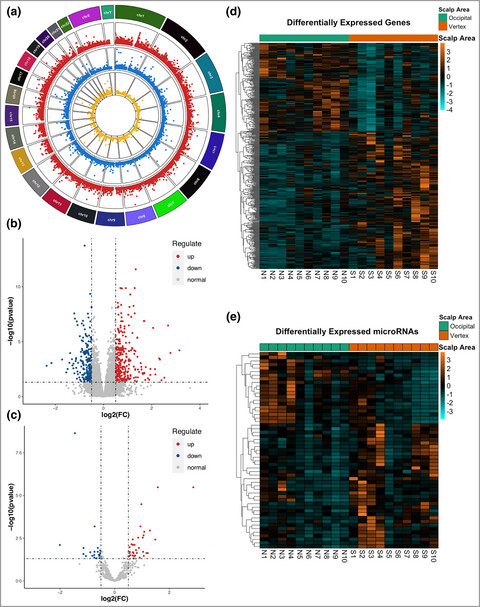
We identified a number of differentially expressed genes and pathways between balding vertex and non-balding occipital AGA HFs by using whole transcriptome analyses. We identified pathways not previously reported in AGA, such as the HIF-1 signaling pathway. Moreover, we verified that HIF-1 pathway-related genes (EGLN1, EGLN3) and Wnt pathway inhibitors (PEDF, SFRP2) played important roles in DPC activity, hair growth, and hair cycle, suggesting that these genes may be potentially utilized as therapeutic targets for AGA.
Linked Comment: M. Philpott. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:845.
Plain language summary available online
Germline intergenic duplications at Xq26.1 underlie Bazex–Dupré–Christol basal cell carcinoma susceptibility syndrome
- Pages: 948-961
- First Published: 20 August 2022
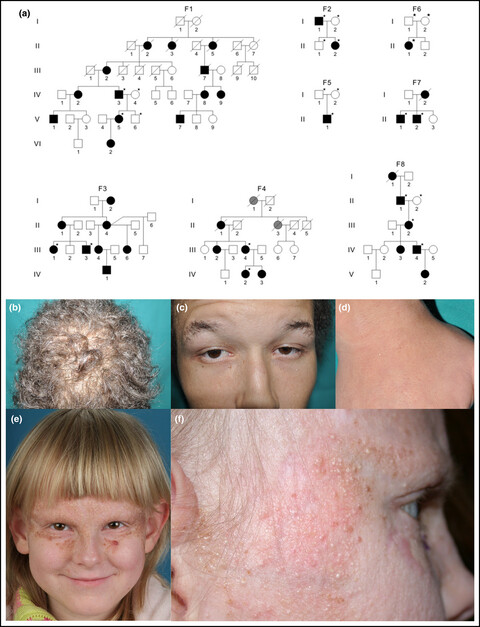
In this paper we show that Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome (BDCS), an X-linked disorder of susceptibility to basal cell carcinomas, is caused by non-coding Xq26.1 duplications that likely result in dysregulation of ARHGAP36, encoded by a flanking gene.
Plain language summary available online
MEDICAL DERMATOLOGY
Clinical associations and classification of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced cutaneous toxicities: a multicentre study from the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Task Force of Dermatology for Cancer Patients
- Pages: 962-969
- First Published: 21 July 2022
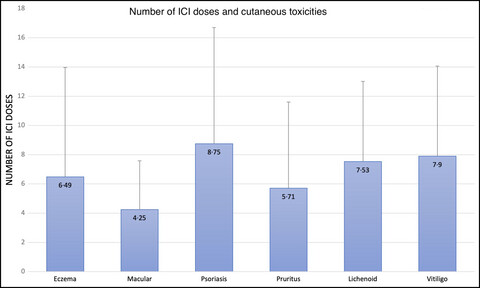
Linked Comment: H. Lee and O. Kwon. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:840-841.
Plain language summary available online
Primary cutaneous peripheral T-cell lymphomas with a T-follicular helper phenotype: an integrative clinical, pathological and molecular case series study
- Pages: 970-980
- First Published: 27 July 2022
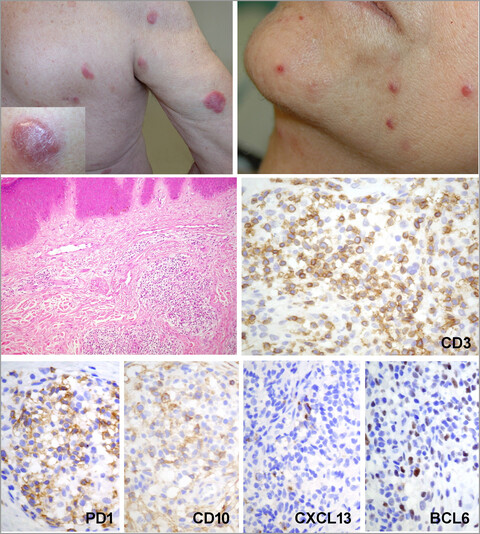
There is a group of cutaneous lymphomas that express TFH markers that do not appear to correspond to existing WHO diagnostic entities. This is the first large original series of patients with a diagnosis of primary cutaneous peripheral T-cell lymphomas with a T-follicular helper phenotype (pcTFH-PTCL) to be molecularly characterised. pcTFH-PTCL may be a standalone group of cutaneous lymphomas with clinicopathological and molecular characteristics that overlap with those of systemic TFH lymphomas, and does not belong to known diagnostic groups of cutaneous lymphoma.
Linked Comment: W. Kempf. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:841–842.
Plain language summary available online
Checkpoint inhibitor-associated bullous cutaneous immune-related adverse events: a multicentre observational study
- Pages: 981-987
- First Published: 17 August 2022
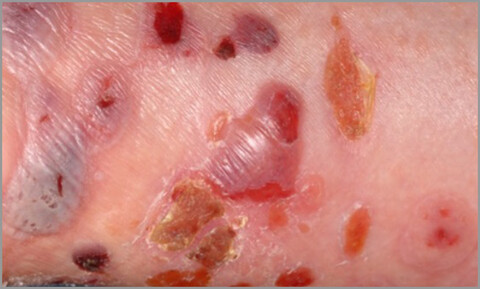
This is the largest multicentre, observational study conducted in the UK, demonstrating an overall incidence of bullous cutaneous irAEs associated with CPI of 0·3%. Clinical presentation may vary, with pruritus and non-bullous variants appearing similar to other cutaneous toxicities. Time to onset appears later than with other cutaneous toxicities (12 months) and can occur after discontinuation of therapy. Interruption of CPI is often needed. Our study demonstrates this occurs mostly in men, older age groups and is associated with BRAF wildtype in MM patients. It is important for clinicians to recognize this condition promptly, so early optimal management is initiated to reduce interruptions to CPI and improve overall patient outcomes and tumour response.
Linked Comment: K. Kridin and C.M. Hammers. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:843–844.
Plain language summary available online
Prevalence of skin sensitization and dermatitis among epoxy-exposed workers in the wind turbine industry
- Pages: 988-996
- First Published: 16 August 2022
Linked Comment: R. Brans. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:842–843.
Plain language summary available online
Correspondence
PERSPECTIVES
Multicentre Selective Lymphadenectomy Trial 1: key primary data remain unavailable
- Pages: 997-998
- First Published: 22 June 2022
Safeguarding online research integrity: concerns from recent experience
- Pages: 999-1000
- First Published: 13 July 2022
Where’s the colour? Advocating for morphological and antioppressive fluencies in dermatology
- Pages: 1001-1002
- First Published: 03 August 2022
Dermatological considerations and culturally sensitive recommendations for women who wear the hijab
- Pages: 1003-1004
- First Published: 03 August 2022
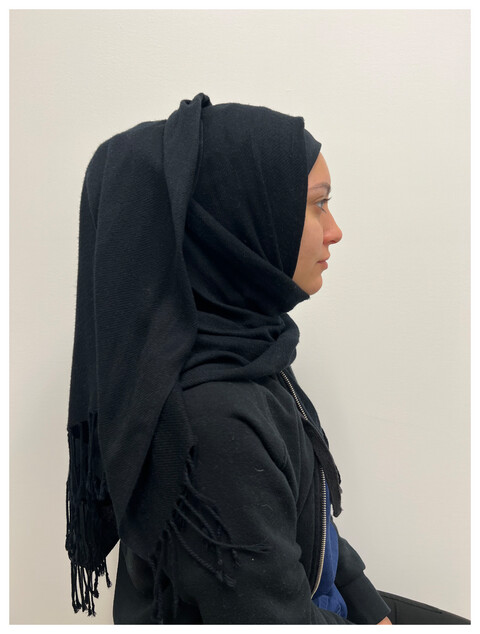

Currently, there is little guidance in the literature on how to advise patients who wear the hijab on hijab-related dermatoses. This manuscript describes hijab-related dermatoses and provides culturally sensitive recommendations that can be used in conjunction with standard treatments to provide more holistic care for these patients.
The sound of silence: where are the voices of patients in eczema guideline development?
- Pages: 1005-1006
- First Published: 16 August 2022
Using the upgrade criteria of the European Psoriasis Consensus is best practice care according to the people-centred healthcare concept of the World Health Organization
- Pages: 1007-1008
- First Published: 16 August 2022
RESEARCH LETTERS
Cutaneous manifestations of lymphoid-variant hypereosinophilic syndrome
- Pages: 1011-1013
- First Published: 21 July 2022
Psychosocial burden of frontal fibrosing alopecia: a qualitative interview study
- Pages: 1013-1015
- First Published: 22 July 2022
Low predictive value of questionnaire-based diagnosis of hidradenitis suppurativa
- Pages: 1015-1017
- First Published: 23 July 2022
Nailfold videocapillaroscopy and serum vascular endothelial growth factor in probable COVID-19-induced chilblains: a cross-sectional study to assess microvascular impairment
- Pages: 1017-1019
- First Published: 02 August 2022
Time to next treatment and safety assessment in cutaneous-T-cell lymphomas: a retrospective analysis on patients treated with bexarotene and acitretin
- Pages: 1019-1021
- First Published: 13 July 2022
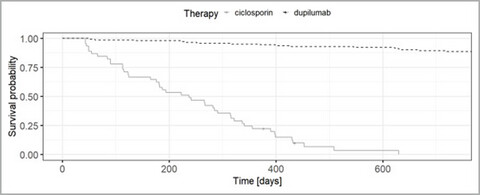
Real-world data on the effectiveness, safety and drug survival of dupilumab: an analysis from the TREATgermany registry
- Pages: 1022-1024
- First Published: 27 July 2022
Patient and disease characteristics associated with psychiatric symptoms and impaired quality of life in pityriasis rubra pilaris
- Pages: 1024-1026
- First Published: 27 July 2022
Folliculitis decalvans and dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: a significant association
- Pages: 1026-1028
- First Published: 29 July 2022
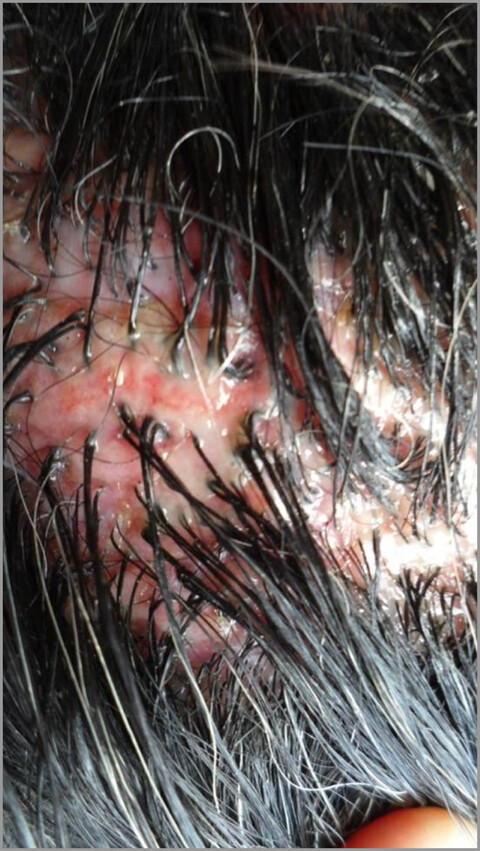
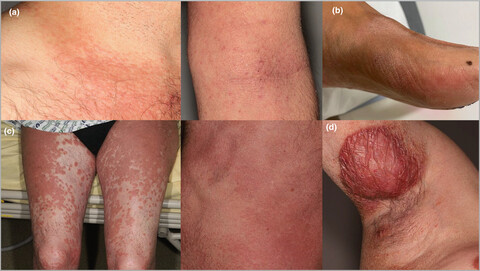
This work reports 30 cases of folliculitis decalvans (FD) in patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) among a cohort of 125 DEB patients seen between 2010 and 2021 in 2 French expert centers for the management of inherited epidermolysis bullosa. Such an association between two rare diseases cannot be fortuitous and implies a physiopathological link that we discuss in this paper. This association is a new significant fact to add to the reflexion on FD causes, suggesting that skin abnormality of DEB could act as a factor of a specific skin barrier alteration which could favor FD. Scarring alopecia with tufted folliculitis and pustules on inflamed skin at the vertex of a woman with dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.
Regaining adequate treatment responses in patients with psoriasis who discontinued dose reduction of adalimumab, etanercept or ustekinumab
- Pages: 1028-1030
- First Published: 27 July 2022
Lichen sclerosus in female patients is associated with an increased risk of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular comorbidities: a retrospective cohort review
- Pages: 1030-1032
- First Published: 10 August 2022
COVID-19 pandemic-associated chilblains: more links for SARS-CoV-2 and less evidence for high interferon type I systemic response
- Pages: 1032-1035
- First Published: 16 August 2022
A qualitative study of patients’ experiences of screening for psoriatic arthritis
- Pages: 1035-1037
- First Published: 17 August 2022
Progression of in situ and early invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas concurrent with successful target tumour response to a programmed death-1 inhibitor
- Pages: 1037-1038
- First Published: 17 August 2022
Qualitative analysis of the impact of atopic dermatitis on caregivers
- Pages: 1038-1041
- First Published: 16 August 2022
The quantitative impact of atopic dermatitis on caregivers across multiple life domains
- Pages: 1041-1043
- First Published: 03 September 2022
Three new founder mutations in Chinese patients with Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratoderma
- Pages: 1043-1045
- First Published: 17 August 2022
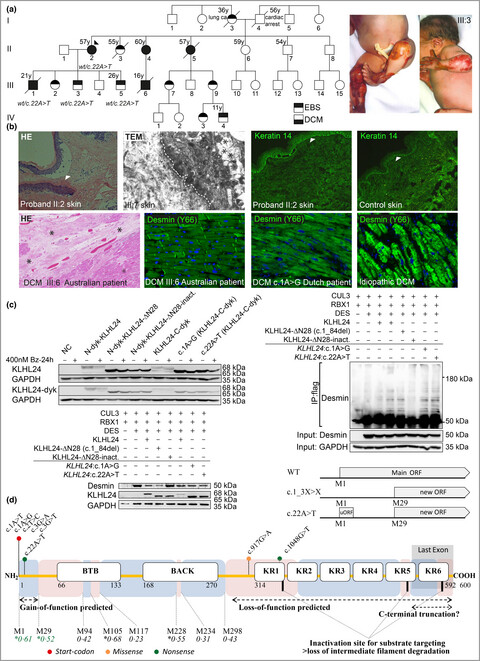
A translation re-initiation variant in KLHL24 also causes epidermolysis bullosa simplex and dilated cardiomyopathy via intermediate filament degradation
- Pages: 1045-1048
- First Published: 17 August 2022
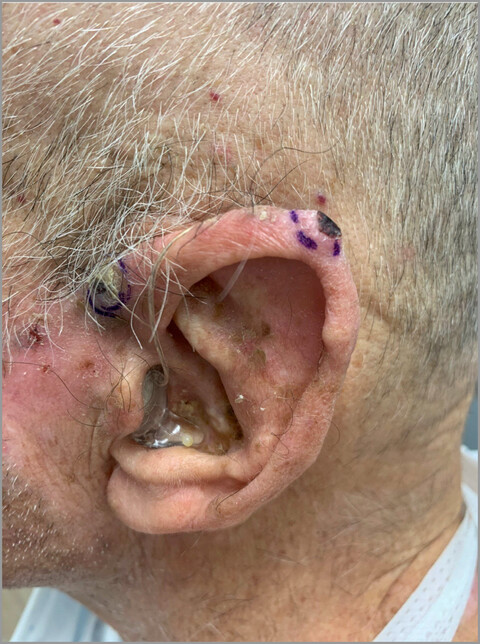
Plasma cells and acute rejection of a near-total face transplant: an incidental finding or an evolving plasma-cell-mediated rejection?
- Pages: 1048-1050
- First Published: 17 August 2022
Monkeypox: a new differential diagnosis when addressing genital ulcer disease
- Pages: 1050-1052
- First Published: 17 August 2022
Giant congenital melanocytic naevus with a novel CUX1–BRAF fusion mutation treated with trametinib
- Pages: 1052-1054
- First Published: 28 August 2022
Consensus on the clinical management of chronic radiation dermatitis and radiation fibrosis: a Delphi survey
- Pages: 1054-1056
- First Published: 01 September 2022
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
On the potential beneficial effects of indoor tanning
- Page: 1057
- First Published: 16 August 2022
Linked Article: Eden et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:105–14.
On the potential beneficial effects of indoor tanning: reply from the authors
- Pages: 1057-1058
- First Published: 16 September 2022
Response to ‘Multicentre Selective Lymphadenectomy Trial 1: key primary data remain unavailable’
- Pages: 1058-1059
- First Published: 20 August 2022
Linked article: Dixon et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.21712
CORRIGENDA
ERRATUM
CORRESPONDENCE: IMAGE GALLERY
A monkeypox virus infection mimicking primary syphilis
- Pages: e194-e195
- First Published: 25 August 2022
PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARIES
A review of how pain is measured in painful skin conditions and rheumatoid arthritis studies, to determine pain measurement in future hidradenitis suppurativa trials
- Page: e196
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Hasan et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:846–854.
Skin reactions to immune checkpoint inhibitors used in cancer treatment
- Page: e197
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Nikolaou et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:962–969.
Insights into the biological differences in hair follicles of men with androgenetic alopecia
- Page: e198
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Liu et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:936–947.
The effectiveness and safety of topical brepocitinib for the treatment of mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis
- Page: e199
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Landis et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:878–887.
Blistering skin side-effects associated with checkpoint inhibitor treatment for cancer
- Page: e200
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Kawsar et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:981–987.
Safety of tralokinumab for the treatment of atopic dermatitis
- Page: e201
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Simpson et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:888–899.
Patient experiences of living with vulval lichen sclerosus
- Page: e202
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Arnold et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:909–918.
Skin-related symptoms found in people with COVID-19 during the Delta and Omicron waves
- Page: e203
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Visconti et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:900–908.
Patient satisfaction with treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa
- Page: e204
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Midgette et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:927–935.
The effectiveness and safety of mirikizumab for treatment of psoriasis
- Page: e205
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Blauvelt et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:866–877.
The genetic cause of a rare skin cancer syndrome, Bazex–Dupré–Christol syndrome
- Page: e206
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Liu et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:948–961.
Skin sensitization and dermatitis among epoxy-exposed workers in the wind turbine industry
- Page: e207
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Christiansen et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:988–996.
Skin lymphomas of the T-follicular helper type
- Page: e208
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Wang et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:970–980.
关于如何在疼痛性皮肤病和类风湿关节炎研究中测量疼痛,以确定未来化脓性汗腺炎试验中的疼痛测量的综述
- Page: e209
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Hasan et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:846–854.
对癌症治疗中使用的免疫检查点抑制剂的皮肤反应
- Page: e210
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Nikolaou et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:962–969.
对雄激素性脱发男性毛囊生物学差异的见解
- Page: e211
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Liu et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:936–947.
外用 Brepocitinib 治疗轻中度特应性皮炎的有效性和安全性
- Page: e212
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Landis et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:878–887.
与癌症检查点抑制剂治疗相关的皮肤水疱副作用
- Page: e213
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Kawsar et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:981–987.
曲罗芦单抗治疗特应性皮炎的安全性
- Page: e214
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Simpson et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:888–899.
外阴硬化性苔藓患者的疾病体验
- Page: e215
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Arnold et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:909–918.
在德尔塔和奥密克戎疫情波次期间在新冠肺炎患者中发现的皮肤相关症状
- Page: e216
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Visconti et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:900–908.
患者对化脓性汗腺炎治疗的满意度
- Page: e217
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Midgette et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:927–935.
Mirikizumab 治疗银屑病的有效性和安全性
- Page: e218
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Blauvelt et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:866–877.
罕见皮肤癌综合征: Bazex-Dupré-Christol 综合征的遗传原因
- Page: e219
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Liu et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:948–961.
风力涡轮机行业暴露于环氧树脂的工人的皮肤过敏和皮炎
- Page: e220
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Christiansen et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:970–980.
T 滤泡辅助型皮肤淋巴瘤
- Page: e221
- First Published: 04 December 2022
Linked Article: Wang et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:988–996.











2690-442X.cover.png)