Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 15 March 2021

The cover image is based on the Short Communication Elucidating the role of lattice thermal conductivity in Π-phases of IV-VI monochalcogenides for highly efficient thermoelectric performance by Sajid Ur Rehman et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/er.6174.
A perspective on the use of ammonia as a clean fuel: Challenges and solutions
- Pages: 4827-4834
- First Published: 25 November 2020
The German hydrogen regulation, codes and standards roadmap
- Pages: 4835-4840
- First Published: 01 December 2020
Different kinds of energy harvesters from human activities
- Pages: 4841-4870
- First Published: 04 February 2021
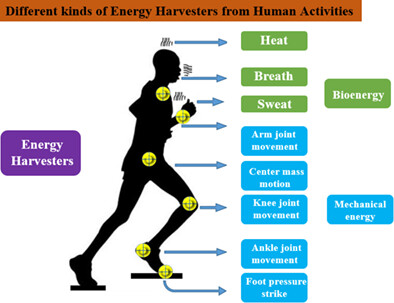
Human has abundant energy and can achieve energy from different daily activities. Energy sources are divided into mechanical energy and biochemical energy. The biochemical energy harvesters based on cell and molecular level is an innovative method which can be used for low-power devices. While mechanical energy harvesters can achieve more energy. This paper provides useful information for researchers to develop energy harvesters suitable for practical application in daily life.
Advanced modification of scandia-stabilized zirconia electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells application—A review
- Pages: 4871-4887
- First Published: 17 November 2020
Techno-economic planning of local energy systems through optimization models: a survey of current methods
- Pages: 4888-4931
- First Published: 23 November 2020
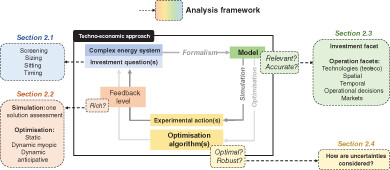
This paper proposes an original framework to analyse the simulation and optimization methods of more than 60 research papers that deal with the planning of complex energy systems including multiple energy carriers, technologies, intermittent energy sources and storages. The focus is on local energy systems that are discussed and optimized through the lens of techno-economic approaches. It intends to bring valuable insights about the variety of methodologies used within this area of the energy system planning literature.
A review on passive methods for thermal performance enhancement in parabolic trough solar collectors
- Pages: 4932-4966
- First Published: 16 November 2020
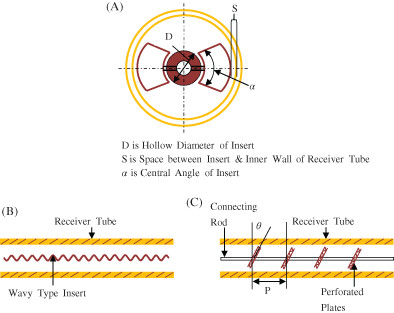
The passive techniques such as provision of inserts and geometrical changes of receiver tube are efficient strategies for increasing thermal performance. The thermal and fluid flow properties of various insert geometries have been studied for different parameters such as insert height, insert thickness, insert orientation, insert shape, number of inserts on receiver tube, porosity, twist ratio, pitch value, length etc. The passive method of heat transfer enhancement helps in uniform distribution of heat flux on absorber tube surface.
Thermal behavior of lithium-ion battery in microgrid application: Impact and management system
- Pages: 4967-5005
- First Published: 22 November 2020

Second-life lithium-ion batteries are used in the microgrid to extend their useful life, where these batteries are expected to generate more heat than their new counterparts. Additionally, further abuse by charging/discharging the batteries at high rates impose safety risk associated with fire and explosion. This review article outlines the adverse effects of temperature, followed by approaches used to monitor the internal battery temperature, and finally currently available battery thermal management systems that are possible candidates for microgrid application.
A comprehensive review of distribution generation integrated DC microgrid protection: issues, strategies, and future direction
- Pages: 5006-5031
- First Published: 01 December 2020

The major focal point on which this paper is devoted are:
- To summarize the challenges faced by the protection system of conventional networks at the presence of DGs in DC microgrid.
- To provide the major pros and cons of the existing protection strategy needed for improvement in DC microgrid protection.
- To analyze the feasibility of the protection strategy for futuristic large-scale penetration of DGs.
- To provide supplementary suggestions for an enhanced and innovative approach toward future DC microgrid protection development.
Fuel cells as an advanced alternative energy source for the residential sector applications in Malaysia
- Pages: 5032-5057
- First Published: 02 December 2020
Review of vibration-based electromagnetic–piezoelectric hybrid energy harvesters
- Pages: 5058-5097
- First Published: 11 December 2020
A comprehensive review of experimental investigation procedures and thermal performance enhancement techniques of solar air heaters
- Pages: 5098-5164
- First Published: 02 December 2020
Alkali metal modified iron-nickel oxygen carrier to produce hydrogen-rich synthesis gas by chemical looping gasification with pine sawdust
- Pages: 5165-5176
- First Published: 23 October 2020
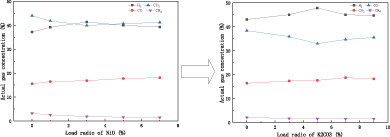
- Alkali metal modified low-load 3% NiO iron-nickel-oxygen carrier can prepare hydrogen-rich synthesis gas with a volume concentration of 47%.
- The modification of alkali metal can strengthen the preparation of hydrogen-rich synthesis gas, and the efficiency has decreased after 15 cycles. We found that it is because of the loss of alkali metal.
MgSO4 composites in a ferroaluminophosphate for enhancement of volumetric heat storage capacity at a low charging temperature
- Pages: 5177-5189
- First Published: 29 October 2020
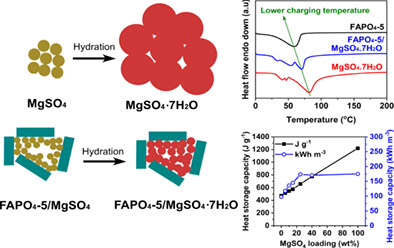
Composites with various MgSO4 contents (5-40 wt%) in the micropore and textural pore of a ferroaluminophosphate (FAPO4-5) were prepared using a wet impregnation method. Limited swelling of the confined MgSO4 salt particles in the pore allowed the composites to exhibit highly improvement of volumetric heat storage capacity. Moreover, the dehydration temperature of MgSO4 in the composites decreased due to the easier dehydration of FAPO4-5 and thus heat storage recovery at low temperature was improved.
New insight on the open-circuit voltage of perovskite solar cells: The role of defect-density distribution and electric field in the active layer
- Pages: 5190-5200
- First Published: 26 October 2020
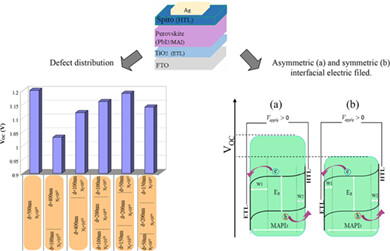
The J-V characteristic of the fabricated perovskite solar cells is studied by modified dynamic electrical model and SCAPS package. Results show that modified dynamic electrical model with an asymmetric electric field inside the perovskite layer can properly describe the performance of the prepared cells.
Performance evaluation of a high concentrator photovoltaic integrating a Fresnel lens in Saudi Arabia: A case study
- Pages: 5201-5213
- First Published: 19 December 2020
Manganese and graphene oxide composite as highly effective sulfur host for enlightening electrochemical kinetics of lithium-sulfur batteries
- Pages: 5214-5223
- First Published: 02 November 2020
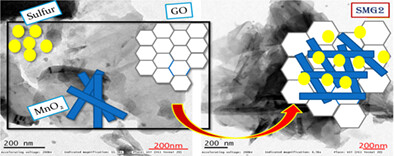
- S/MnO2/GO ternary composite was prepared by solid state reaction and used as a cathode for Li-S battery.
- Shuttle effect is controlled by the mesoporous MnO2 layer composed with GO sheets.
- GO/MnO2 matrix providing fast electron and Li+ transport and the formation of polythionate complex enhances electrochemical behavior of SMG2 composite.
Co/Eu co-doped electron transport layer enhances charge extraction and light absorption for efficient carbon-based HTM-free perovskite solar cells
- Pages: 5224-5234
- First Published: 11 December 2020
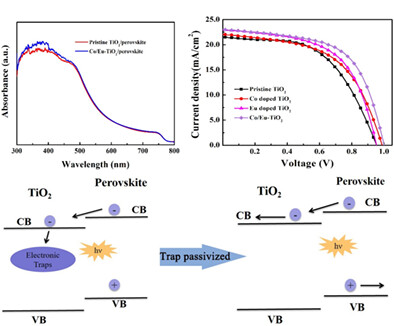
This work reports a bimetal Co/Eu co-doping strategy to modify the electron transport layer for carbon based hole-transport-materials-free perovskite solar cells. Co/Eu co-doping could not only improve the device charge extraction but also enhance device light absorption. Improving the power conversion efficiencies from 11.12 to 14.06% was obtained by optimizing the doping concentration, while keeping a superior device stability.
- A bimetal Co/Eu co-doping strategy was reported to modify the electron transport layer for carbon based hole-transport-materials-free perovskite solar cells.
- Co/Eu co-doping could improve the device charge extraction and light absorption.
- Improving the power conversion efficiencies from 11.12% to 14.06% was obtained by optimizing the doping concentration.
Electrochemical behavior of a spinel zinc ferrite alloy obtained by a simple sol-gel route for Ni-MH battery applications
- Pages: 5235-5247
- First Published: 27 October 2020
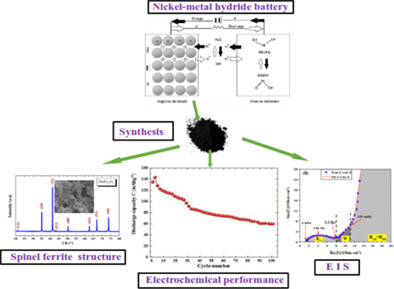
Zinc ferrite spinel (ZnFe2O4) is employed as an innovative anode material in Ni-MH batteries. The ZnFe2O4 particles were synthesized by the sol gel technique. The electrochemical behavior of ZnFe2O4 is better in front of certain compounds studied. The ZnFe2O4 electrode has an excellent stability during a long cycling. The electrolyte/ZnFe2O4 electrode interface is studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The electrochemical results of the ZnFe2O4 electrode show the strong potentiality for an electrochemical application of the Ni-MH batteries.
Enhanced thermal energy storage of nitrate salts by silica nanoparticles for concentrating solar power
- Pages: 5248-5262
- First Published: 30 October 2020
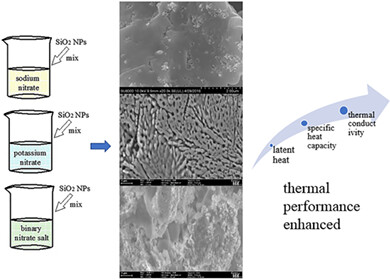
- Nine nanofluids of NaNO3, KNO3, and binary salt with SiO2 nanoparticles are tested.
- Increase of 34.08% and 39.24% in specific heat and thermal conductivity is obtained.
- Increase of 36.1°C in decomposing temperature is reached.
- Cloud nuclei are proposed and responsible for thermal performance improvement.
- Mass ratio of NaNO3 and KNO3 determines effect of SiO2 nanoparticles on binary salt.
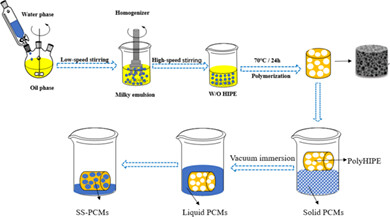
Shape stabilization of phase change material by polymerized high internal phase emulsion for thermal energy storage
- Pages: 5263-5271
- First Published: 09 December 2020
Enhanced electrochemical performance of lanthanum ferrite decorated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite electrodes prepared by in situ microwave irradiation for energy storage applications
- Pages: 5272-5282
- First Published: 27 October 2020
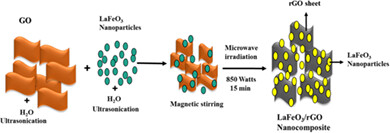
Novelty of the present investigation is to synthesis LaFeO3/rGO nanocomposite by low cost in-situ microwave irradiation method. Uniform decoration of LaFeO3 nanoparticles on the 2D graphene sheets provides more stability of the electrode. The prepared composite electrode material demonstrates higher specific capacitance, Strong cyclic stability and improved capacitive retention.
Dual coating strategy of CoS2@Co@C toward fast insertion/extraction anode material for sodium-ion batteries
- Pages: 5283-5292
- First Published: 14 November 2020
Role of SEI layer growth in fracture probability in lithium-ion battery electrodes
- Pages: 5293-5308
- First Published: 27 October 2020
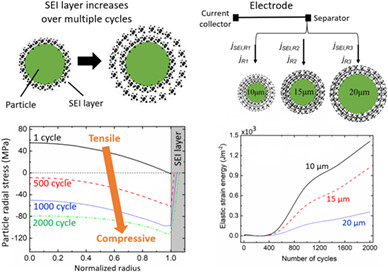
The effect of the SEI layer growth on the fracture probability of the electrode particles is investigated using a coupled electrochemical and core-shell particle model. The simulations reveal that as the SEI layer grows, the tensile stress inside the particle is transformed into compressive stress, which reduces the fracture probability inside the particles. Moreover, in the multi-size particle electrode, the SEI layer on the small particles tends to be more fractured than that on large particles.
Experimental investigation of hydrogen insertion in copper oxide on photovoltaic performance of p-type dye-sensitized solar cell
- Pages: 5309-5317
- First Published: 27 October 2020
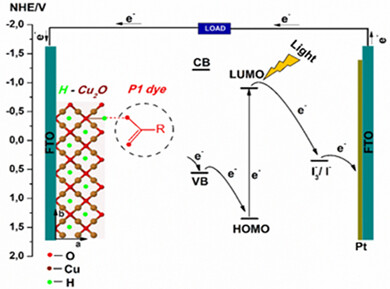
Hydrogenation promotes a strong chemisorption of COOH-anchoring groups of the dye onto Cu2O substrate, leading to higher dye absorption and a beneficial effect on the solar energy conversion efficiency, also in case of p-type DSSC. Even if the hydrogenation was performed only in 2% H2 atmosphere, the significant increase in JSC (98%) confirms that the hydrogenation of p-type semiconductors should not be excluded as an effective and low-cost way to augment the efficiency of p-DSSCs.
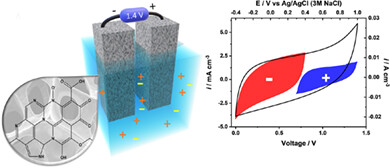
A selection strategy for enhancing exoelectrogenic consortium towards improved power generation in microbial fuel cells
- Pages: 5318-5324
- First Published: 09 November 2020
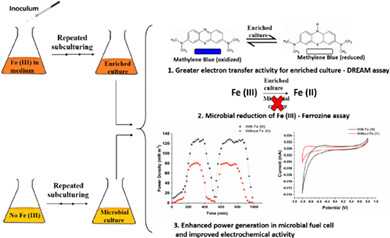
The manuscript presents a selection method to enrich electrochemically active bacteria for use in microbial fuel cells. Using the methods described, these bacteria can be enriched from commonly used inocula in a reasonably short span of time. The enriched consortium of electrochemically active bacteria significantly boosts the current output and can be used for future studies with lesser start-up times.
Electrodeposited NiRh alloy as an efficient low-precious metal catalyst for alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction
- Pages: 5325-5336
- First Published: 29 October 2020
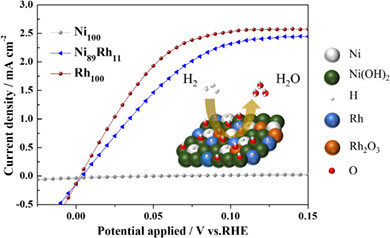
In this study, Ni100-xRhx electrocatalysts are fabricated via electrodeposition as a low Pt-group metal-containing (low-PGM) hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) catalyst for anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs). Through alloying, substantial changes are observed, such as enlarged surface area and development of different textures. The dramatically enhanced HOR activity of NiRh alloy is because of the surface segregation of Rh and its balanced composition with the oxide. The initial high HOR activity of 1.5 mA/cm2 for Ni89Rh11 at 0.05 VRHE, though it requires a further improvement in the durability, suggests the practical feasibility of it as a low PGM alkaline HOR catalyst.
Characterization of SrFe0.9-xCuxMo0.1O3-δ (x = 0, 0.1 and 0.2) as cathode for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells
- Pages: 5337-5346
- First Published: 01 December 2020
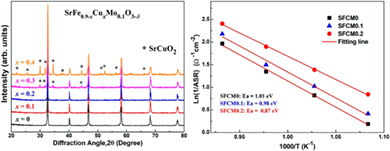
Cu and Mo co-doped SrFeO3-δ perovskite SrFe0.9-xCuxMo0.1O3-δ (SFCM, x = 0, 0.1, and 0.2) perovskites as cathodes for solid oxide fuel cells. Cu doping can accelerate the loss of lattice oxygen, leading to the enhancement of ORR activity of SFCM perovskites. SFCM0.2 is chemically compatible with LSGM electrolyte and has the lowest ASR values as well as the activation energy for ORR, indicating SFCM0.2 can be a good cathode candidate for IT-SOFC.
Thermal performance of a thermal management system with a thin plate and a slender tube for prismatic batteries
- Pages: 5347-5358
- First Published: 29 October 2020
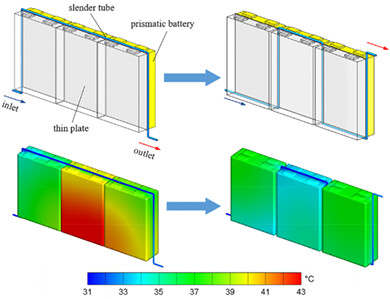
A novel liquid-cooling BTMS with a thin plate and a slender tube is proposed for prismatic batteries. Increasing the contact area between the battery and the cooling tube along the coolant flow direction can effectively improve the cooling effect, especially the temperature uniformity.The maximum temperature difference between the batteries for the optimum design is not exceed 5°C.Different impact factors are investigated.
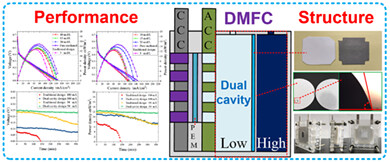
Design and experimental analysis of a dual-cavity high-concentration adaptive passive micro direct methanol fuel cell
- Pages: 5359-5368
- First Published: 09 November 2020
Energy management of islanded microgrid by coordinated application of thermal and electrical energy storage systems
- Pages: 5369-5385
- First Published: 09 November 2020
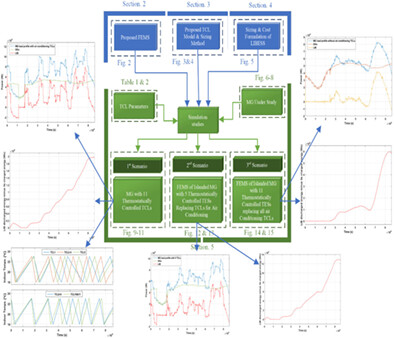
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are one of the commonly used ESS technologies for grid-based applications, which are used in this paper to always maintain the demand–supply balance in a residential MG. For this purpose, a novel frequency-based energy management scheme is proposed, which uses an LIB ESS to handle the primary frequency control and energy management during peak-load period, while the dispatchable distributed generators like microturbine and fuel cell supply the base load. The installation of an energy storage system (ESS) is vital for the Micrgorid (MG) islanded operation to ensure the maintenance of demand–supply balance. Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are one of the commonly used ESS technologies for grid-based applications, which is used in this paper to always maintain the demand-supply balance in a residential MG. For this purpose, a novel frequency based energy management scheme is proposed, which uses an LIB ESS to handle the primary frequency control and energy management during peak-load period while the dispatchable distributed generators like microturbine and fuel cell supply the base load. The air conditioning TCLs consume a significant part of the residential load profile especially during mid-summer. Unlike TCLs that instantaneously use their generated cooling thermal energy to control indoor temperatures, the Thermal Energy storages (TESSs) can also store the thermal energy and use it later. In this paper, the TESSs are used instead of TCLs to reduce the power consumption of a residential Microgrid (MG) in islanded mode.
Computational investigation and screening of [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine-based high energy materials
- Pages: 5386-5398
- First Published: 02 November 2020
Effect of coupling phase change materials and heat pipe on performance enhancement of Li-ion battery thermal management system
- Pages: 5399-5411
- First Published: 03 November 2020
Experimental evaluation of the dry coal deshaling by pneumatic vibrating FGX separator on the CO2 gasification process
- Pages: 5412-5422
- First Published: 04 November 2020
Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for efficient dye-sensitized solar cell with improved open-circuit voltage
- Pages: 5423-5432
- First Published: 05 November 2020
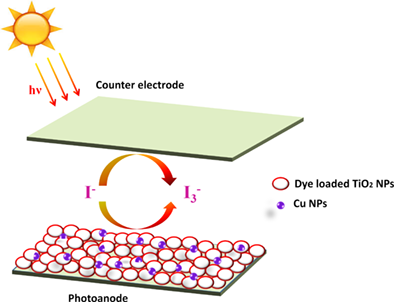
This study deals with the microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their successful incorporation in dye sensitized solar cell (DSSC) with improved power conversion efficiency and higher open-circuit voltage.It was found that the incorporation of Cu2+ into TiO2 lattice raises its conduction band (CB) edge and shifted the Fermi level upwards, which contribute towards enhanced Voc. A significant enhancement in Voc from 0.714 to 0.781 V was observed by the Cu incorporation.
An intelligent passivity-based backstepping approach for optimal control for grid-connecting permanent magnet synchronous generator-based tidal conversion system
- Pages: 5433-5448
- First Published: 10 November 2020
Combined systems based on OSOFC/HSOFC: Comparative analysis and multi-objective optimization of power and emission
- Pages: 5449-5469
- First Published: 09 November 2020
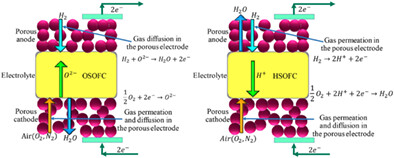
In this study, a new integrated system, including biomass gasification, a SOFC, heat pipes, and an ORC, is proposed. A comprehensive comparison analysis is performed on the performances of the systems based on OSOFC and HSOFC. The effects of parameters are studied on voltage losses, Nernst and cell voltages, powers, efficiencies, and emission. The multi-objective optimization is carried out using response surface methodology, and central composite design is utilized.
Research on matching design method of waste heat reuse system of fuel cell vehicle considering system energy consumption and waste heat exchange rate
- Pages: 5470-5485
- First Published: 16 November 2020

At present, the research on the waste heat utilization of FCV is less, and it is more based on the traditional vehicle waste heat management ideas without systematic summary of the factors affecting the system performance. As such,The novelty of this work is to provide a new idea for the matching design of waste heat reuse system of fuel cell vehicles: Considering system energy consumption and waste heat exchange rate.
Terephthalic acid-directed supramolecular Cu(II)-metallogel for photosensitive semiconducting Schottky diode with promising electronic charge transportation
- Pages: 5486-5499
- First Published: 04 November 2020
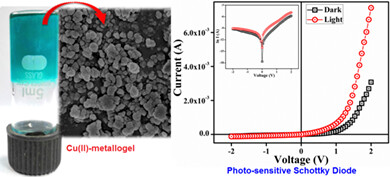
Terephthalic acid-mediated supramolecular Cu(II)-metallogel is executed to fabricate a photosensitive semiconducting Schottky diode device. The optical and electrical properties of the synthesized metallogel express the semiconducting feature of the Cu(II)-metallogel. The electrical studies explore that the conductivity of Cu(II)-metallogel increased to ~four times under illumination with respect to nonirradiation conditions. I-V characteristics of Cu(II)-metallogel-based thin-film metal-semiconductor (MS) junction devices under irradiation and nonirradiation conditions show a nonlinear rectifying behavior, characteristic of a Schottky diode.
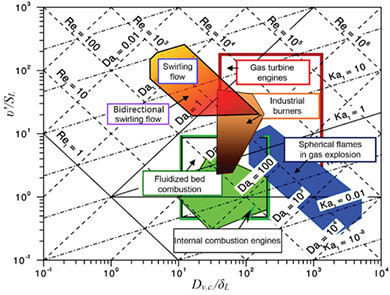
Criterion analysis and experimental study of combustion mechanisms in a bidirectional swirling flow and their relationship with pollutants emission
- Pages: 5500-5516
- First Published: 09 November 2020
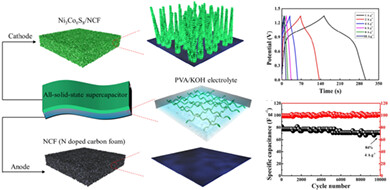
High-performance all-solid-state supercapacitor with binder-free binary transition metal sulfide array as cathode
- Pages: 5517-5526
- First Published: 15 December 2020
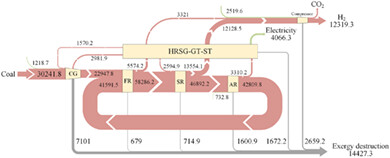
Energy quality factor and exergy destruction processes analysis for chemical looping hydrogen generation by coal
- Pages: 5527-5543
- First Published: 16 November 2020
High-efficiency solar energy conversion using infrared focusing and reflection system
- Pages: 5544-5554
- First Published: 15 December 2020
Fabrication of perovskite solar cells using novel 2D/3D-blended perovskite single crystals
- Pages: 5555-5566
- First Published: 09 November 2020
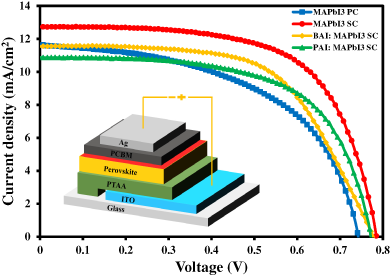
Single crystals of 2D/3D-blended perovskite were grown by inverse temperature crystallization method, and used for the fabrication of perovskite solar cells. When the 2D perovskite, possessing the long chains of hydrophobic organic molecule is incorporated in the 3D counterpart, moisture induced degradation is reduced. Perovskite solar cell with single crystal of 2D/3D-blended perovskite yielded efficiency of 5.37%.
Design and demonstration of an islanded hybrid microgrid for an enormous motel with the appropriate solicitation of superfluous energy by using iHOGA and matlab
- Pages: 5567-5585
- First Published: 09 November 2020
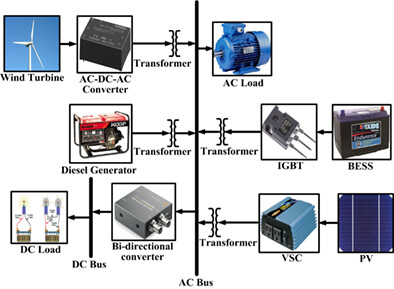
An IHMS for an enormous motel with the proper solicitation of superfluous energy has been designed and demonstrated. The estimation of the reduction of NPC, COE, CO2 emissions, Voltage, Power and Frequency responses have been presented. Sustainable development and uninterrupted power supply can be assured by this designed IHMS.
State of charge estimation framework for lithium-ion batteries based on square root cubature Kalman filter under wide operation temperature range
- Pages: 5586-5601
- First Published: 11 November 2020
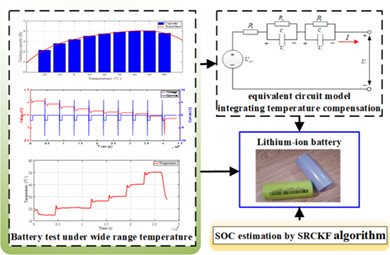
A lithium-ion battery model intergrating temperature variation in a wide range from −20°C to 60°C is constructed. A high-precision and reliable SOC estimation framework based on SRCKF is designed. The proposed framework can effectively improve the estimation accuracy of SOC under wide temperature range and time-varying temperature conditions.
Hydrogen effects on ignition delay time of methyl butanoate in a rapid compression machine
- Pages: 5602-5618
- First Published: 04 November 2020
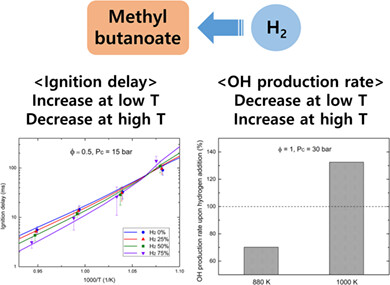
The effects of hydrogen addition on the ignition delay of methyl butanoate, a surrogate fuel of biodiesel, were investigated experimentally and numerically under engine-relevant conditions. Upon hydrogen addition, the ignition delay increased in the low-temperature region but decreased in the high-temperature region. The results of sensitivity and reaction path analysis indicated that the changes in radical-related reactions caused by the reaction of added hydrogen behave differently at low and high temperatures.
Tunable current duration in triboelectric generators via capacitive air gaps
- Pages: 5619-5628
- First Published: 15 November 2020
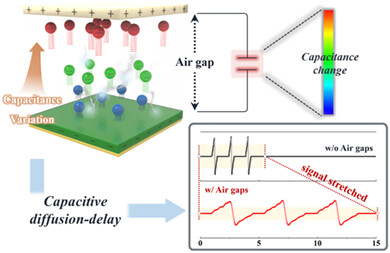
We demonstrate tunable triboelectric current duration via controlling the air-gap capacitance between two dielectric plates. In triboelectric generators with nylon/air-gap/PDMS multilayers, decreasing the vertical speed of the dielectric plates (0.5 to 0.05 cm/s) results in an increased current duration (0.10 to 0.81 s), which accompanies decreased peak current, resulting in the optimal charge density (∼0.163 nC/cm2 at the 0.25 cm/s). This study implies optimization of triboelectric generators in terms of optimal triboelectric charge density, accompanying circuit lifetime and broadened applicability.
Parametric sensitivity analysis on the cold start process of a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell
- Pages: 5629-5648
- First Published: 25 November 2020
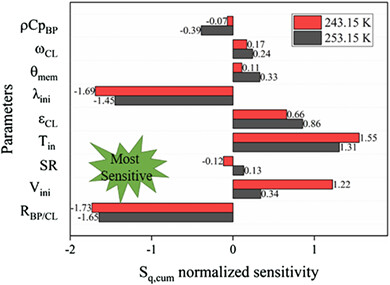
Finite difference sensitivity is used to analyze the effect of essential factors on the cold start process of a PEMFC by a 3-D multi-phase electrochemical transport coupled model in this study. Results show that the cold start process is most sensitive to RBP/CL and λini. Effective improvement of cold start performance can be achieved by appropriately adjusting RBP/CL, λini, and Tin. Appropriately increasing the Vini also can be a method to improve cold start performance, especially for the cold start from −30°C. Besides, optimized ωCL in CLs, proper θmem, and lower 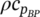 can contribute to better performance, especially for the cold start from −20°C.
can contribute to better performance, especially for the cold start from −20°C.
Location and orientation based LCOE: Simplified visual analysis and generalization of the levelized cost of electricity from storageless photovoltaic systems
- Pages: 5649-5658
- First Published: 11 November 2020
LCOE is calculated using a multivariate approach to visualize the combined effect of various parameters on the result within their specified ranges. The energy yield factor is introduced to convert the computed LCOE data into an LCOE-map and PV-system-orientation-based LCOE. The orientation-based approach to calculating LCOE reveals a new understanding of the economics of building-integrated systems by showing the degrees of freedom for the azimuthal angle and slope of the system with the little trade-off in energy cost.
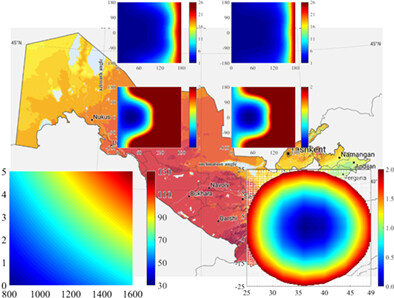
A numerical study on convection and diffusion of mass transfer in proton exchange membrane fuel cells with orientated-type flow channels
- Pages: 5659-5678
- First Published: 30 November 2020
Mass transfer in orientated-type channels with different baffles is quantitatively studied. Vapor transfer through diffusion and convection under various baffle effects are studied. Diffusion and convection of reactants and vapors affect each other. Vapor convective transfer increases the water contents in GDLs.
Solar-powered microwave pyrolysis of corn stover for value-added products and process techno-economic assessment
- Pages: 5679-5694
- First Published: 09 November 2020
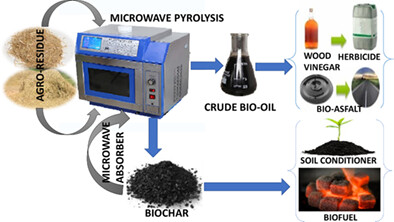
The utilization of abundantly available one agro-residue (corn stover) has been studied with an integrated approach of MAP of biomass feedstock by considering a reliable and sustainable source of energy viz. electricity from the PV source along with its techno-economic environmental assessment for adoption. The finding of the study would provide appropriate information for the planners, policymakers and environmentalists to encourage the practice among the crop growers so that the burgeoning issue of prevalent burning of crop residues in the fields can be prevented and cultivators can earn income by producing value-added products.
Rapid measurement method for lithium-ion battery state of health estimation based on least squares support vector regression
- Pages: 5695-5709
- First Published: 17 December 2020
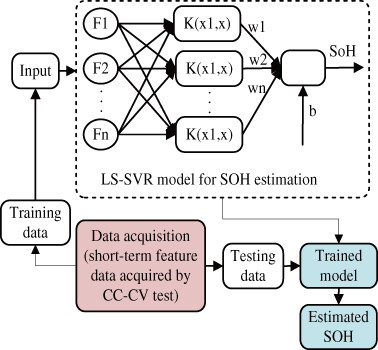
- A novel battery SoH estimation approach for LiB is proposed. The model only requires some short-term data extracted from the battery voltage response curve, which can be analyzed to effectively conduct rapid on-site measurements.
- The short-term sample collection method take only about 4 minutes to complete a sample collection. This non-destructive, non-invasive short-term feature acquisition method is convenient for engineering applications.
Characterisation of La0.9Ce0.1Ni5 alloy for the development of single-stage thermally driven sorption hydrogen compressor
- Pages: 5710-5729
- First Published: 11 November 2020
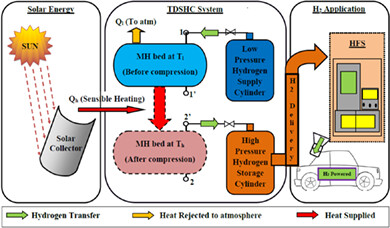
- Pressure-concentration isotherms of La0.9Ce0.1Ni5 are measured at 20°C to 140°C.
- The effect of temperature range on hydrogen storage and thermodynamic properties are investigated.
- The performance of thermally driven sorption hydrogen compressor is analysed for different discharge temperatures.
- The cycle efficiency is increased from 1.54% to 27.57% by varying the discharge temperature from 40°C to 140°C.
- Computational fluid dynamics simulation is carried out to investigate the variations in MH bed temperature and hydrogen transmission.
An experimental study on the performance evaluation of a combined sensible-latent heat thermal energy storage
- Pages: 5730-5746
- First Published: 09 November 2020
Machine learning-based model for lithium-ion batteries in BMS of electric/hybrid electric aircraft
- Pages: 5747-5765
- First Published: 16 November 2020

An adaptive lithium-ion battery model is proposed in which models' parameters are estimated by a supervised machine learning paradigm. Moreover, a model-based fault diagnosis scheme is developed to see the effectiveness of the proposed battery model on the fault detection accuracy. Comparative verification experiments show that the proposed machine learning-based parameter estimator leads to an accurate battery model, and therefore more accurate fault detection compared with other common methods.
Optimal energy management strategy for a renewable-based microgrid considering sizing of battery energy storage with control policies
- Pages: 5766-5780
- First Published: 09 November 2020
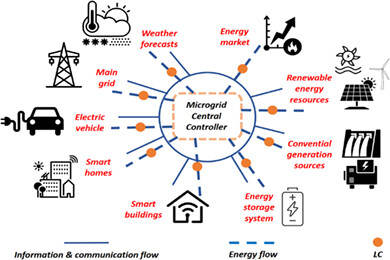
In this research study, a novel technique for meeting these requirements is suggested, utilizing the modified shuffled frog leaping algorithm, known as the MSFLA. It is noted that the search capability of the MSFLA is considerably high, compared to other optimization techniques. A formula based on the cost has been implemented in this study to specify the optimal BES size in the context of optimal day-ahead energy management of an MG.
Instability mechanism and control of hybrid electric vehicle in initial hybrid driving mode
- Pages: 5781-5794
- First Published: 11 November 2020
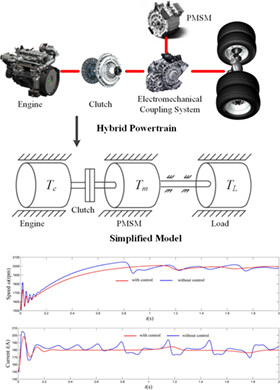
The mathematical model of the initial hybrid drive model for a series-parallel hybrid electric vehicle (SPHEV) is constructed. The local stability condition and bifurcation condition were derived to analyse the influence of engine throttle opening, and the instability threshold of the hybrid powertrain (HPT) was given. Moreover, an instability control methodology was designed to optimise the operating region of HPT for the initial hybrid drive mode, and vehicle tests of mode transition were carried out based on the existing SPHEV platform.
Thermal runaway behavior of lithium-ion batteries in different charging states under low pressure
- Pages: 5795-5805
- First Published: 11 November 2020
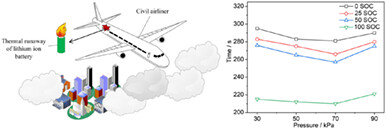
The thermal runaway (TR) time of the lithium-ion battery exhibits an U-shaped change with pressure. The novelty of this work is that we reported the low-pressure TR characteristics of lithium-ion batteries with different states of charge (SOC). And we found that the increase of SOC will shorten the voltage drop time and TR time, and increase the TR temperature and intensity. In addition, the TR time of the battery varies U-shaped with the pressure, which is the first time we found the TR law of lithium-ion batteries under different pressures.
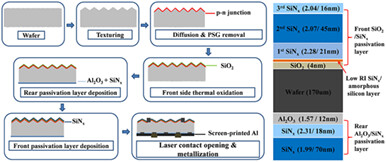
Improved Al2O3/SiNx and SiO2/SiNx stack passivation layer structure PERC sc-silicon solar cells on mass production line
- Pages: 5806-5814
- First Published: 09 November 2020
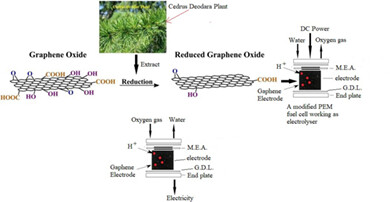
Graphene for hydrogen energy storage - A comparative study on GO and rGO employed in a modified reversible PEM fuel cell
- Pages: 5815-5826
- First Published: 25 November 2020
Using the analytical heirarchy process to select specific methanation catalysts based on their extraction impacts
- Pages: 5827-5840
- First Published: 12 November 2020
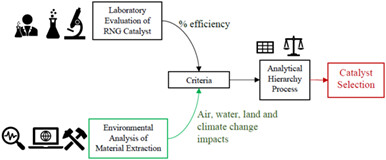
In this analysis, the authors illustrate that the environmental impacts created by certain catalysts for the production of renewable natural gas significantly exceed the benefit they provide by having a high conversion rate of CO2. Specific, catalysts that do not utilize platinum group metals have a lower environmental impact when compared on a per conversion scale. This work connects important laboratory research on catalysis with their life cycle environmental costs.
Characterization and electrocatalytic properties of electrospun Pt-IrO2 nanofiber catalysts for oxygen evolution reaction
- Pages: 5841-5851
- First Published: 11 November 2020
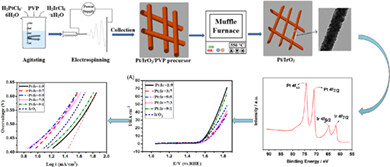
Novel Pt-IrO2 nanofiber catalysts were successfully prepared using the electrospinning method. The catalyst structure and catalytic performance of catalysts with different Pt/Ir ratios were investigated. The average diameter of nanofiber catalyst decreased evidently with the increase of Pt content and the catalysts with Pt:Ir = 1:9 and Pt:Ir = 9:1 all showed better catalytic performance than the IrO2.
Effects of flue gas recirculation on energy, exergy, environment, and economics in oxy-coal circulating fluidized-bed power plants with CO2 capture
- Pages: 5852-5865
- First Published: 17 November 2020
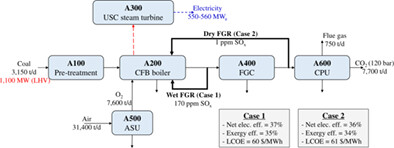
Electricity efficiency (37%) of a 500MWe oxy-coal CFB power plant with wet flue gas recirculation (FGR) was higher than that (36%) of dry FGR. Exergy efficiency was calculated 35% in the wet FGR and 34% in the dry FGR. Sulfur of dry FGR was less accumulated in recycle streams than that of wet FGR. The LCOE (61 $/MWh) of dry FGR was higher than that (60 $/MWh) of wet FGR.
Network overloading management by exploiting the in-system batteries of electric vehicles
- Pages: 5866-5880
- First Published: 16 November 2020
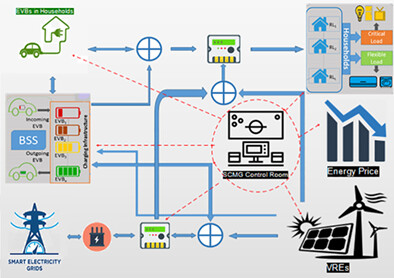
In-system exploitation of EVBs technique has been used in order to minimize network overloading. SMPC uses batteries in a sustainable way to reduce overall power consumption. Mechanism of charging/discharging of EVBs is designed in such a way that these batteries draw power from the grid during off-peak hours and they transfer energy back to network during peak hours, to reduce overall burden on the system; thereby increasing efficacy and making the grid sustainable in terms of bearing higher load demands.
Numerical analysis of a built-in thermal storage system of metal hydride and nanoparticles enhanced phase change material and nanofluid
- Pages: 5881-5893
- First Published: 25 November 2020
Energy absorption characteristics in hybrid composite materials for marine applications under impact loading: Case of tidal current turbine
- Pages: 5894-5911
- First Published: 15 November 2020
Investigations on a platinum catalyzed membrane for electrolysis step of copper-chlorine thermochemical cycle for hydrogen production
- Pages: 5912-5921
- First Published: 25 November 2020
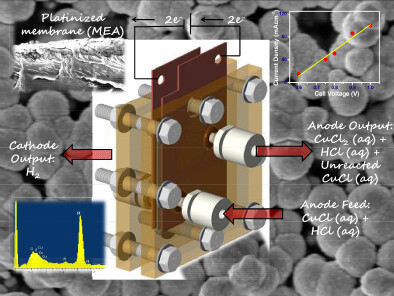
- Platinized membrane prepared by in-situ impregnation-reduction method by depositing Pt on Nafion-117.
- Monodispersed nanocrystalline Pt-particles formed a ~30 μm thick electrocatalyst layer on the Nafion-117 membrane.
- A single cell PEM type electrolyser (4 cm2 active area) was designed and fabricated with graphite flow field plates
- 100 mAcm−2 at a cell voltage of 1 V with 0.2 M CuCl in ~2 M HCl solution as anolyte
- Platinized membrane: An effective MEA for CuCl/HCl electrolysis
Band gap engineering of ZnO by amino acid capping for optoelectronic and energy applications
- Pages: 5922-5938
- First Published: 30 November 2020
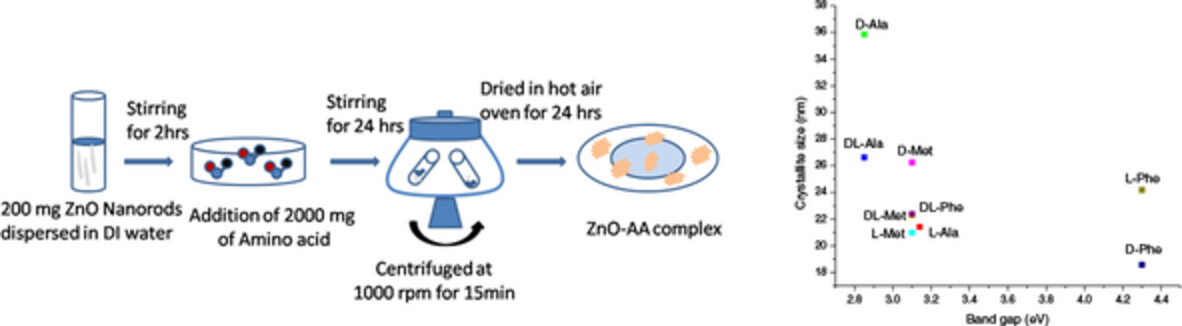
Studies on capping of ZnO NRs with aliphatic, aromatic, and heterocyclic amino acids indicate that ZnO-D-Ala and ZnO-DL-Ala complexes possess lower band gap than ZnO NRs and can be used as an viable n-type semiconductor material in optoelectronic applications such as energy harvesting devices like solar cells.
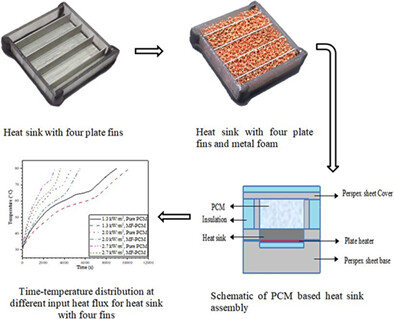
Thermal performance of phase change material–based heat sink for passive cooling of electronic components: An experimental study
- Pages: 5939-5963
- First Published: 17 November 2020
Chitosan-based fluorescein isothiocyanate film as a highly efficient metal-free photocatalyst for solar-light-mediated direct CH arylation
- Pages: 5964-5973
- First Published: 25 November 2020
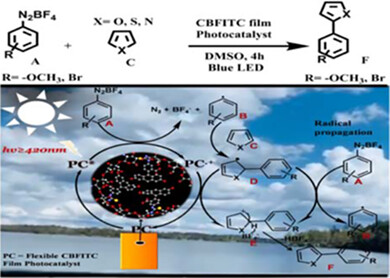
Development of eco-friendly and low-cost highly efficient photocatalysis is very importance for organic transformations. Herein, we report chitosan-based fluorescein isothiocyanate (CBFITC) film photocatalyst is the first-time design to bring new insight into direct CH bond arylation under light irradiation. Therefore, CBFITC film photocatalyst has also a potential application in the field of medicinal and phermaceutical chemistry.
Combining design of experiments, machine learning, and principal component analysis for predicting energy consumption and product quality of a natural gas processing plant
- Pages: 5974-5987
- First Published: 25 November 2020
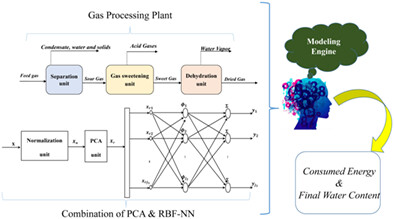
A dataset generated by ProMax 3.2 through Box-Behnken design as a three-level DoE method, is considered. Then, the variables are normalized to a standard normal distribution in order to ensure they all have balanced effects on the system function. Moreover, PCA approach is applied to the original dataset to obtain the most effective observations. Finally, a RBF-NN is designed to model the dynamics of the “consumed energy” and the “final water content” in a typical gas processing plant.
Metal-organic framework-derived carbon-cobalt oxysulfide nanocage heterostructure electrode for efficient hybrid supercapacitors
- Pages: 5988-6001
- First Published: 25 November 2020
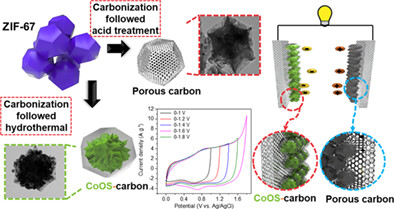
Metal-organic frameworks driven three-dimensional Co oxysulfide nanograins with carbon frame (CoOS-C) and porous carbon-based electrodes were designed and hybrid supercapacitors (HSCs) were constructed and investigated. Unique nanostructural feature with tunable defect functionality of Co oxysulfide nanograins with encapsulation of porous N- and S-doped graphitic carbon exhibited a high-energy density of 31.7 W h kg−1 and an excellent rate capability with long-term cyclic stability, with more than 93% capacity retention after 3000 cycles.
Enhanced performance of Li-S battery by constructing inner conductive network and outer adsorption layer sulfur-carbon composite
- Pages: 6002-6014
- First Published: 01 December 2020
Heat transfer study on flowing liquid film of SiO2-water nanofluid with surfactant confined by metallic foam
- Pages: 6015-6031
- First Published: 13 December 2020
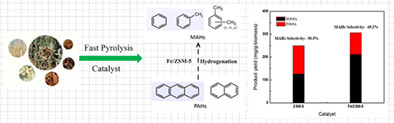
Improving the monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons production from fast pyrolysis of biomass over Fe-modified ZSM-5 catalysts
- Pages: 6032-6040
- First Published: 24 November 2020
Excellent electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 with good crystallinity and submicron primary dispersed particles
- Pages: 6041-6053
- First Published: 12 December 2020
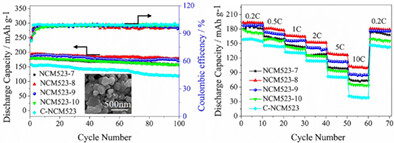
The manuscript entitled “Excellent electro chemical performance of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 with good cristallinity and submicron primary dispersed particles” is prepared by Yanfang Xie, Fuzhong Wu*, Xinyi Dai*, Yi Mai, Yijing Gu, Huixin Jin, Junqi Li. The NCM523 with submicron primary particles (NCM523-S) have been synthesized using a coprecipitation method with ethonal solution and solid-phase sintering technology. The NCM523-S exhibits a low cation mixing, high cristallinity with a well-formed layered structure, and enhanced high potential electrochemical performances.
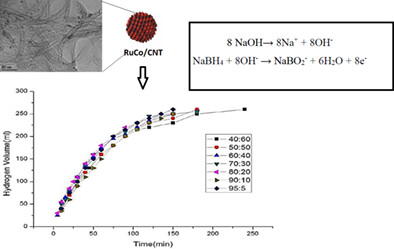
Untangling the cobalt promotion role for ruthenium in sodium borohydride dehydrogenation with multiwalled carbon nanotube-supported binary ruthenium cobalt catalyst
- Pages: 6054-6066
- First Published: 24 November 2020
Resolving mode mixing in boiling water reactors instability analysis using variational mode decomposition
- Pages: 6067-6085
- First Published: 01 December 2020
Experimental and numerical analysis of the multilayer distributed Joule-Thomson cooler with pillars
- Pages: 6086-6103
- First Published: 01 December 2020
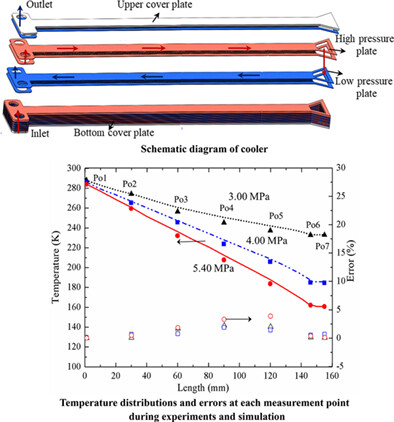
In this study, a multilayer distributed J-T cooler with staggered pillars was designed. Furthermore, a new mathmatical model of the cooler is developed and validated against the experimental data. The results show that the cooler has remarkable cooling performance. In addition, the distribution of temperature and pressure in the microchannel with staggered pillars is analyzed by the model calculation, and the influences of the axial heat conduction and heat leakage on the cooling performance are analyzed using the model.
Honeycomb like copper-cobalt nanostructures and their synergy with carbon supports for electrooxidation of carbinol
- Pages: 6104-6114
- First Published: 24 November 2020
State-of-charge estimation for LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2/graphite batteries using the compound method with improved extended Kalman filter and long short-term memory network
- Pages: 6115-6138
- First Published: 01 December 2020
Optimization under uncertainty for robust fuel cycle analyses
- Pages: 6139-6151
- First Published: 14 December 2020
Novelty Statement
This work includes for the first time the coupling of multiobjective global optimization problems with uncertainties in the field of nuclear fuel cycle simulations. This problem, essential for strategy planning given the numerous assumptions and uncertainties surrounding nuclear sustainability studies, has proven to be crucial given that the optimal solutions cannot be reproduced in the presence of uncertainties. With the methodology presented, policy makers and experts can enhance confidence in their studies improving thus the sustainability of the nuclear energy.
Intelligent optimization of bioleaching process for waste lithium-ion batteries: An application of support vector regression approach
- Pages: 6152-6162
- First Published: 25 November 2020
A methanol fuel processing system with methanol steam reforming and CO selective methanation modules for PEMFC application
- Pages: 6163-6173
- First Published: 01 December 2020
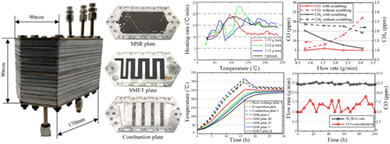
A novel methanol fuel processing system with methanol steam reforming and CO methanation modules is proposed to generate low CO concentration reformate steadily and efficiently. Experimental results show that the system can be operated for 100 hours with CO concentration below 10 ppm at the reformate flow rate of 2.5 g/min. With airbleed technology PEMFC integrated with the system can generate 100 W of electricity for 200 minutes.
Analysis of different operating strategies of thermal energy storage with radiant cooling system
- Pages: 6174-6197
- First Published: 28 December 2020
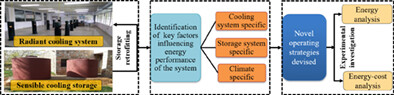
This study experimentally investigates the performance of a thermal energy storage retrofitted to a ceiling-type radiant cooling system. The key objectives are to achieve energy and energy-cost savings simultaneously by applying the novel devised operating strategies. In hot and dry climate condition, the maximum energy, and energy-cost saving up to 14% and 22.4%, respectively, can be achieved by following the novel operating strategies.
An experimental investigation for a hybrid phase change material-liquid cooling strategy to achieve high-temperature uniformity of Li-ion battery module under fast charging
- Pages: 6198-6212
- First Published: 13 December 2020
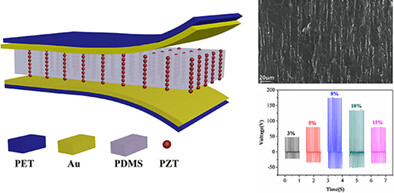
High-performance flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator based on necklace-like PZT particle chains
- Pages: 6213-6226
- First Published: 01 December 2020
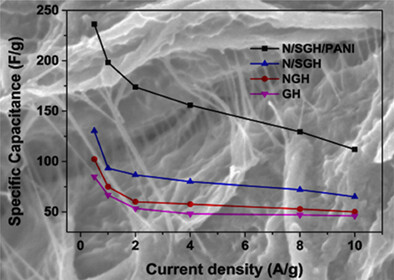
Construction of N, S-co-doped graphene/polyaniline composite as free-standing electrode material
- Pages: 6227-6238
- First Published: 01 December 2020
Sol-gel synthesized lithium orthosilicate as a reusable solid catalyst for biodiesel production
- Pages: 6239-6249
- First Published: 25 November 2020
Co-N-doped hierarchically ordered macro/mesoporous carbon as bifunctional electrocatalyst toward oxygen reduction/evolution reactions
- Pages: 6250-6261
- First Published: 10 December 2020
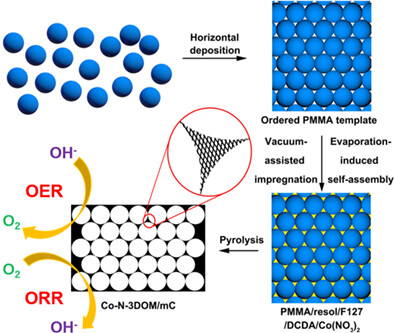
- A novel three-dimensional Co-N-doped hierarchically ordered macro/mesoporous carbon was synthesized by evaporation-induced self-assembly, vacuum-assisted impregnation and templating methods.
- The as-obtained macro/mesoporous Co-N-doped carbon endowing its 3D ordered hierarchical porosity and satisfactory surface area, leading to superior performance for ORR, OER, and rechargeable Zn-air battery.
- This work paves a new perspective in the fields of hierarchically ordered macro/mesoporous material, ORR/OER catalysis and Zn-air battery engineering.
Partial leaching effect to Pt decorated Pd-Fe/C nanoparticles for oxygen reduction reaction
- Pages: 6262-6272
- First Published: 02 December 2020
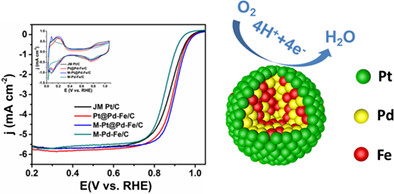
Cost-reduction and performance improvement could be combined within one Pt decoration, surface partial leaching modified Pd-Fe/C nanoparticles (NPs). Pd-Fe alloy followed by surface modification expends lattices to tune the strain and ligand effect can effectively improve catalytic performances. The M-Pt@Pd-Fe/C NPs exhibit better ORR catalytic performances and 14.1 times higher Pt mass activity than those of commercial Pt/C catalyst.
Nanoporous structured Sn-MWCNT/Cu electrodes fabricated by electrodeposition–chemical dezincification for catalytic CO2 reduction
- Pages: 6273-6284
- First Published: 15 December 2020
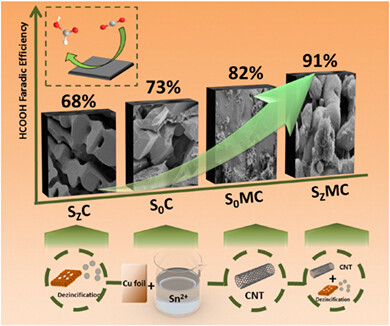
Electrochemical reduction of CO2 (ERCO2) can not only store electrical energy from renewable sources but also produce useful fuels for many applications. Thus,the cathodes with high performance are need. In this paper, a nano-porous Sn-based catalyst was synthesized by a facile two-step method. Firstly, three components of Sn, Zn and multi-walled carbon nanotubes were co-deposited, and then the Zn was removed by alkali leaching. Through the characterization and electrochemical measurements, we have proved that this material has better catalytic performance, which is attributed to the addition of carbon nanotubes and the structural vacancies.
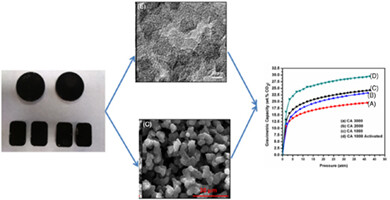
Economical synthesis of highly efficient and tunable carbon aerogels for enhanced storage of CO2 emitted from energy sources
- Pages: 6285-6292
- First Published: 23 December 2020
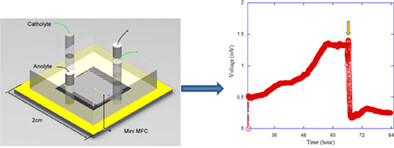
Feasibility study on a mini autonomous biosensor based on microbial fuel cell for monitoring hexavalent chromium in wastewater
- Pages: 6293-6302
- First Published: 08 December 2020
Experimental investigation on gas-liquid flow distribution in downward parallel pipes of a 660 MW ultrasupercritical CFB boiler
- Pages: 6303-6319
- First Published: 11 December 2020
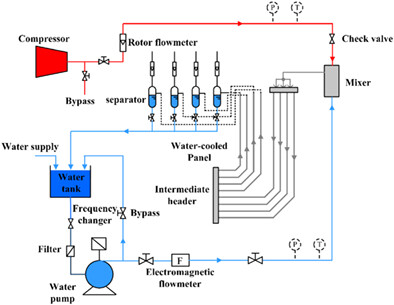
According to the similarity criterion, the reduced-scaled experimental system of a 660 MW ultrasupercritical CFB boiler was established in this study. The quick-closing valve method is used to measure the cross-sectional void fraction. The new correlation of void fraction in the downcomers is fitted.
Retracted: The impact of COVID-19 on the electricity sector in Spain: An econometric approach based on prices
- Pages: 6320-6332
- First Published: 07 December 2020
Hybrid heat sinks for thermal management of passively cooled battery chargers
- Pages: 6333-6349
- First Published: 09 December 2020
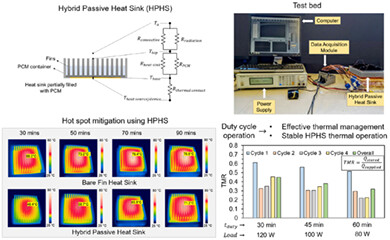
- Developed phase change material (PCM)-based hybrid passive heat sinks (HPHS) for industrial battery charger device.
- Studied the performance of inclined interrupted, pin, and straight interrupted fin-based HPHS geometries.
- Improved heat sink thermal management for HPHS operation was achieved during continuous and duty-cycle thermal loading.
Heat capacity and viscosity of ternary carbonate nanofluids
- Pages: 6350-6359
- First Published: 28 October 2020
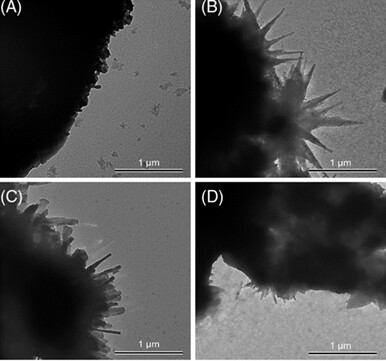
A ternary carbonate salt eutectic (Li2CO3-Na2CO3-K2CO3) based nanofluid doped with Al2O3 nanoparticles (1 wt%) was tested to investigate the effect of the synthesis protocol on the resultant heat capacity enhancement. The result shows the heat capacity enhancement decreased with an increase of heat rates from 2 °C/min to 10 °C/min. A significant shear thinning behavior was observed for those with high heat capacity enhancement.
Photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen production on ternary Co-Pi/Ag/TiON nanotube array photocatalysts
- Pages: 6360-6368
- First Published: 04 November 2020
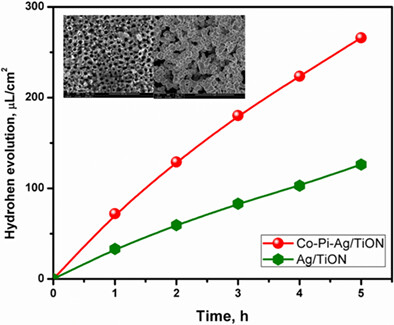
Ternary Co-Pi-Ag/TiON photocatalysts exhibit extraordinary photoelectrochemical performance due to the synergy between nitrogen doping, Co-Pi functionalization, Ag loading, and the unique structural features of the synthesized photoelectrodes. The transient photocurrent (J-t) records indicated the high stability of the fabricated photoanodes with a photocurrent density reaching 5.5 mA/cm2. This was further confirmed via the exceptionally high hydrogen generation rate of the Co-Pi-Ag/TiON ternary catalyst (54 µL h-1 cm-2), which is much higher than that reported for most of the TiO2-based photocatalysts.
Elucidating the role of lattice thermal conductivity in π-phases of IV-VI monochalcogenides for highly efficient thermoelectric performance
- Pages: 6369-6382
- First Published: 09 November 2020
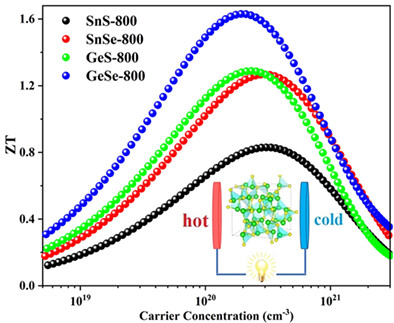
For the first time lattice thermal conductivities are considered to systematically investigate the thermoelectric performance of π-polymorphs. In present work, the high values of ZT highlights the potential of newly discovered π-phases chalcogenides towards highly efficient thermoelectric materials for practical applications.
Incorporation of heteroatoms into reticulated vitreous carbon foams derived from sucrose to improve its energy storage performance
- Pages: 6383-6394
- First Published: 12 November 2020
Pencil-traced-graphite on cellulose: A rapid and solvent-less approach for solar steam generation
- Pages: 6395-6404
- First Published: 09 December 2020
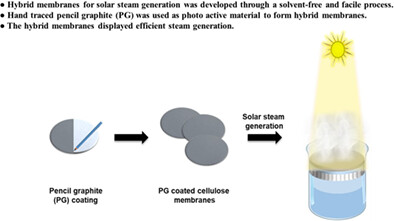
Graphite-coating method on cellulose paper with a commercial pencil was proposed as a facile and effective fabrication technique for photothermal layer of solar steam generation. The membrane coated with pencil-traced-graphite demonstrated repeatability with an efficient generation of steam at various solar intensities.
Evaluating the drop of electrochemical performance of Ni/YSZ and Ni/ScSZ solid oxide fuel cells operated with dry biogas
- Pages: 6405-6417
- First Published: 08 December 2020
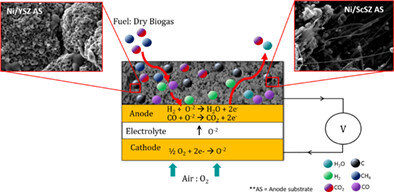
Three times higher amount of carbon found on Ni/ScSZ despite significantly better performance as compared to Ni/YSZ. Catalytic activity tests reveal a low carbon oxidation rate compared to an initially higher methane decomposition reaction, leading to carbon deposition. Methane decomposition reaction of Ni/ScSZ was higher which release more hydrogen, inevitably accompanied by more carbon deposited. Different carbon formed on the cells where graphitic carbon formed on Ni/ScSZ while amorphous carbon formed on Ni/YSZ.
MoO2/C hybrid synthesized by a facile molten-salt-assisted approach for high-performance lithium-ion batteries
- Pages: 6418-6425
- First Published: 10 December 2020
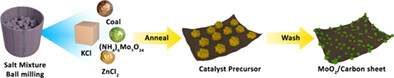
- Coal-based porous carbon decorated with MoO2 nanoparticles were fabricated by the facile and scalable molten-salt-assisted methods.
- The MoO2/C hybrid demonstrated excellent electrochemical performance as anodes for LIBs.
- Converting coal into functional nanomaterials improve its utilization efficiency with added-value.
Optoelectronic and photo-charging properties of CH3NH3PbI3/LiFePO4 system
- Pages: 6426-6435
- First Published: 01 December 2020
Bioremediation analysis of sediment-microbial fuel cells for energy recovery from microbial activity in soil
- Pages: 6436-6445
- First Published: 04 November 2020
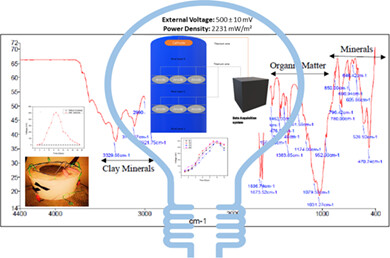
Microbial activity creates natural voltage gradients in soil, using sediment Microbial Fuel Cell or s-MFC, the biochemical pathway of microbes serves bioremediation and generates bioelectricity. Present work analyzed bioremediation activity using FTIR and bioelectricity production using standard electro-biochemical methods. Analysis showed significant reduction of complex organic material, and power generation of 2122 ± 80 mW/m2 owing to stable biofilm formation and effective microbial colonization of the anode.
Design and development of a low-cost solar parabolic dish concentrator system with manual dual-axis tracking
- Pages: 6446-6456
- First Published: 03 November 2020
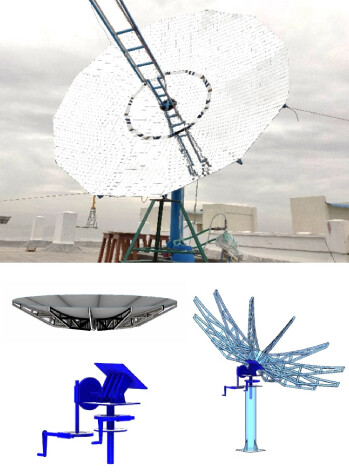
A novel approach of designing and development of a solar parabolic dish collector is elaborated in this article. Solutions to major issues which are normally encountered during fabrication of dish concentrator are also highlighted which helps researchers who are new to this field. The concentrator extracts solar thermal energy which can also be converted into electrical power by implementing suitable energy conversion devices such as concentrated photovoltaic system or high-temperature range thermoelectric generator with a suitable tracking mechanism.
Sequential biofuel production from seaweeds enhances the energy recovery: A case study for biodiesel and bioethanol production
- Pages: 6457-6467
- First Published: 04 November 2020
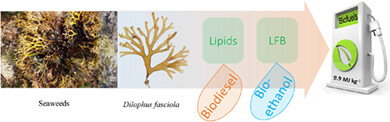
Dilophus fasciola showed a biodiesel yield of 35.04 mg g-1 dw. Lipid-free biomass showed the maximum reducing sugar content (37.2 g L-1) and bioethanol productivity at 72 h (0.165 g L-1 h-1), which were 16.3% and 27.9%, respectively, higher than that from the whole biomass. Therefore, the maximum estimated total energy output (9.96 MJ kg-1) was recorded using the suggested sequential route.





![Computational investigation and screening of [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine-based high energy materials](/cms/asset/7211ed61-d0f3-4c3e-a009-5eda887caff1/er6161-toc-0001-m.jpg)