Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
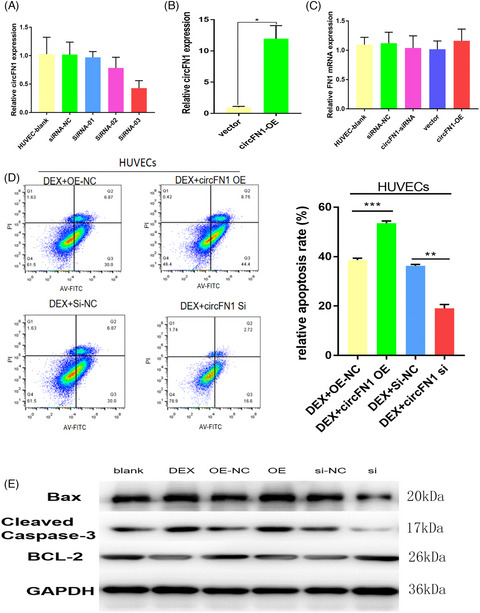
hsa_circ_0058122 knockdown prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting human umbilical vein endothelial cells apoptosis via the miR-7974/IGFBP5 axis
- First Published: 11 March 2022
Alinity hq platelet count is not impacted by severe microcytosis
- First Published: 11 March 2022
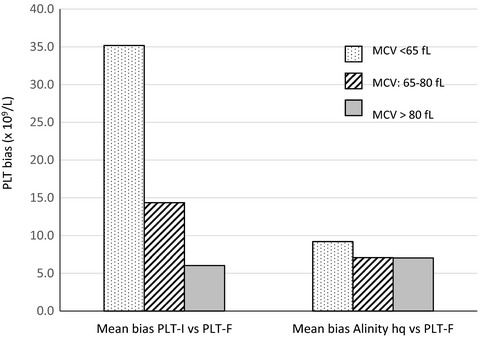
Increasing PLT count bias was seen between Sysmex PLT-I and PLT-F methods with decreasing MCV values in a study on 464 samples. Mean bias was 35.2 × 109/L in severe microcytosis (MCV < 65 fl). Consistent mean bias was observed between Alinity hq and PLT-F across all MCV ranges. The Sysmex PLT-I method overestimated the PLT count in samples with severe microcytosis, while Alinity hq PLT count was not impacted.
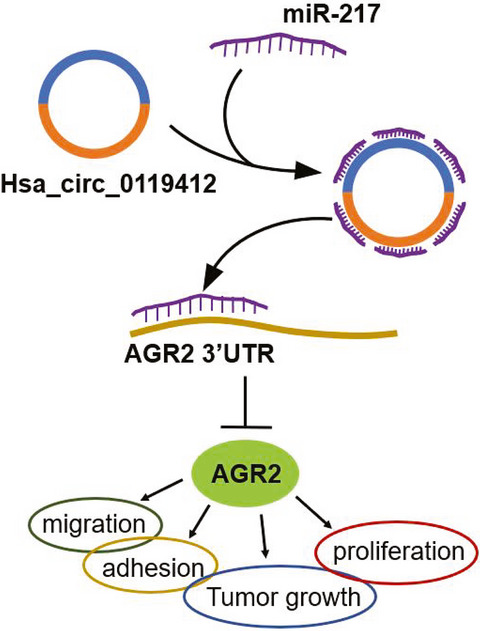
hsa_circ_0119412 overexpression promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting miR-217 to upregulate anterior gradient 2
- First Published: 11 March 2022
Downregulation of Talin-1 is associated with the increased expression of miR-182-5p and miR-9-5p in coronary artery disease
- First Published: 14 February 2022
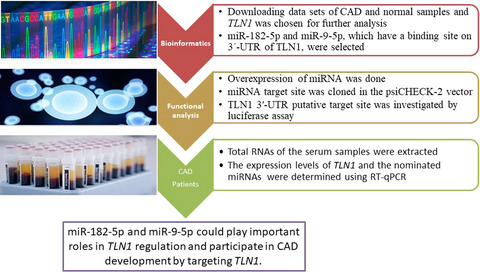
Data sets of CAD and normal samples were downloaded, and TLN1 was chosen as one of the genes with differential expressions. miR-182-5p and miR-9-5p, which have a binding site on 3´-UTR of TLN1, were selected by bioinformatics tools. miR-182-5p was cloned into the downstream of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene of the pEGFP-N1 vector and was overexpressed in the HEK293T cell line. Then, the miRNA target site was cloned in the psiCHECK-2 vector, and direct interaction between the miRNA target site and the TLN1 3′-UTR putative target site was investigated by luciferase assay. A real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction was done to assess the expression of miR-182-5p, miR-9-5p, and TLN1 in the serum samples of CAD and non-CAD individuals. So, miR-182-5p and miR-9-5p could play important roles in TLN1 regulation and participate in CAD development by targeting TLN1.
MALDI-TOF-MS analysis in low molecular weight serum peptidome biomarkers for NSCLC
- First Published: 25 February 2022
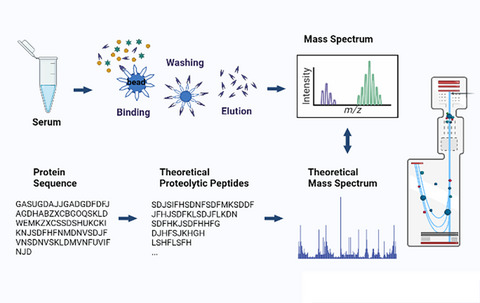
The aim of this study was to explore the differential peptides of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) based on the late-model mass spectrometry technology of proteomics. We established the diagnostic prediction model that distinguished NSCLC samples from the healthy controls, found the potential tumor markers that can assist the early diagnosis of NSCLC, and provide new clues for the screening of high-risk groups of NSCLC and the evaluation of postoperative efficacy.
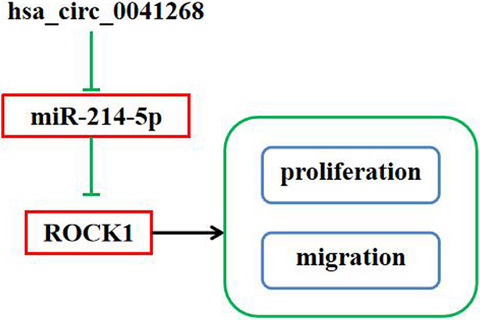
Hsa_circ_0041268 promotes NSCLC progress by sponging miR-214-5p/ROCK1
- First Published: 25 February 2022
Clinical value of serum JKAP in acute ischemic stroke patients
- First Published: 10 March 2022
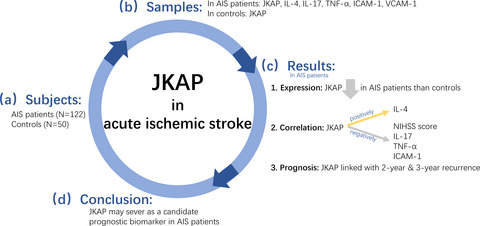
This study detected JKAP, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17, TNF-α, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1 in 122 AIS patients and JKAP in 50 controls to evaluate the association of JKAP with disease severity, Th1, 2, 17 secreted cytokines, adhesion molecules, and prognosis of AIS patients. Interestingly, it was found that JKAP was decreased in AIS patients than controls. Besides, JKAP negatively correlated with NIHSS score, IL-17, TNF-α, and ICAM-1 in AIS patients, while it was positively related to IL-4. Additionally, declined JKAP was linked with 2-year recurrence and 3-year recurrence in AIS patients.
Expression and clinical significance of circular RNA hsa_circ_0003416 in pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with congenital heart disease
- First Published: 15 February 2022
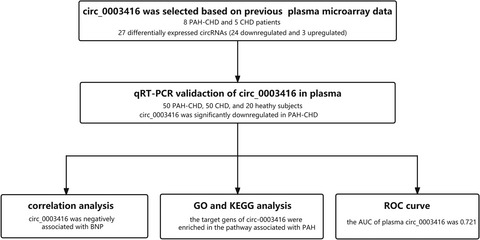
This study evaluated the expression and clinical significance of the circular RNA hsa_circ_0003416 in children with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with congenital heart disease (PAH-CHD). The expression levels of hsa_circ_0003416 in plasma were lower in the PAH-CHD group than in the CHD and healthy control groups. Hsa_circ_0003416 was found to be negatively associated with B-type natriuretic peptide. In addition, the area under the curve of hsa_circ_0003416 levels in plasma was 0.721, suggesting that it had a promising diagnostic value.
Methylation- and homologous recombination deficiency-related mutant genes predict the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 03 March 2022

This study aimed to investigat the prognostic value of methylation- and homologous recombination deficiency (HRD)-associated gene signatures in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). A novel prognostic model for LUAD was developed based on methylation and HRD. Methylation-associated DMEGs may function as both biomarkers and therapeutic targets for LUAD, and further studies are planned to elucidate their roles in the carcinogenesis of LUAD.
Study on the value of small dense low-density lipoprotein in predicting cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in the high-risk stroke population
- First Published: 02 March 2022
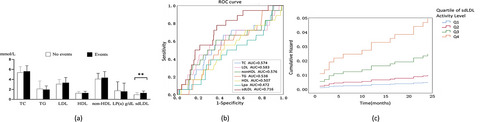
(a) The difference of 7 indicators between the group without cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events and the group with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, **p < 0.01. (b) Predictive values of serum lipids for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. The ROC curves and AUCs regarding risk are depicted in Figure 5. AUCs: 0.716 for sdLDL, 0.574 for TC, 0.583 for LDL, 0.576 for nonHDL, 0.538 for TG, 0.507 for HDL, 0.472 for Lpa. (c) sdLDL quartile grouping hazard function diagram. Q1: sdLDL ≤ 0.659 mmol/L; Q2: 0.659 mmol/L< sdLDL <0.926 mmol/L; Q3: 0.926 mmol/L≤ sdLDL <1.235 mmol/L; Q4: sdLDL ≥ 1.235 mmol/L.
Long non-coding RNA screening and identification of potential biomarkers for type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 07 March 2022
Aberrant expression of long non-coding RNA PVT1 in allergic rhinitis children: Correlation with disease risk, symptoms, and Th1/Th2 imbalance
- First Published: 11 March 2022
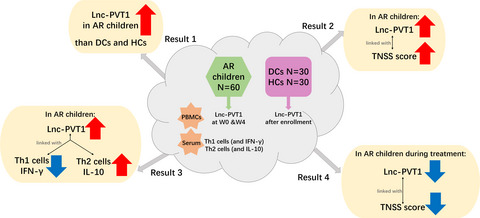
The current study enrolled 60 AR children, 30 DCs, and 30 HCs and then detected their lnc-PVT1 in PBMC. For AR children only, serum IFN-γ, IL-10, Th1, and Th2 cells at W0 and lnc-PVT1 in PBMC at W4 were also analyzed. Interestingly, lnc-PVT1 was upregulated in AR children compared with DCs and HCs. Lnc-PVT1 was positively related to nasal rhinorrhea score, itching score, congestion score, and TNSS in AR children. Moreover, lnc-PVT1 was negatively associated with Th1 cells in AR children and also exhibited a negative correlation trend with IFN-γ (but without statistical significance). Differently, lnc-PVT1 was positively related to Th2 cells and IL-10 in AR children. Besides, lnc-PVT1 and TNSS were reduced at W4 after treatment in AR children; notably, lnc-PVT1 decline was correlated with TNSS decline during treatment.
Low levels of serum IL-39 are associated with autoimmune thyroid disease
- First Published: 19 February 2022
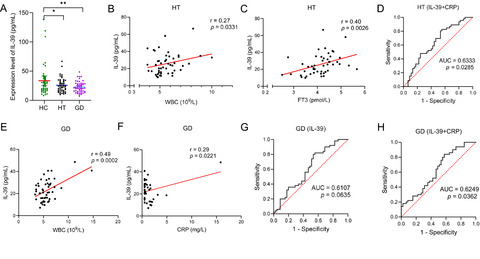
Serum IL-39 levels in patients with HT and GD were significantly lower than those of HCs (A). In patients with HT, serum IL-39 level was positively correlated with WBC count (B) and FT3 level (C). We assessed the value of IL-39 and IL-39 combined with CRP for diagnosis of HT using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. The area under the curve (AUC) of IL-39 combined with CRP for diagnosis of HT was 0.6333 (D). In patients with GD, serum IL-39 level was positively correlated with WBC count (E) and CRP level (F). The AUC of IL-39 for diagnosis of GD was 0.6107 (G), while the AUC of IL-39 combined with CRP for diagnosis of GD was 0.6249 (H).
Comparison of next generation diagnostic systems (NGDS) for the detection of SARS-CoV-2
- First Published: 17 February 2022
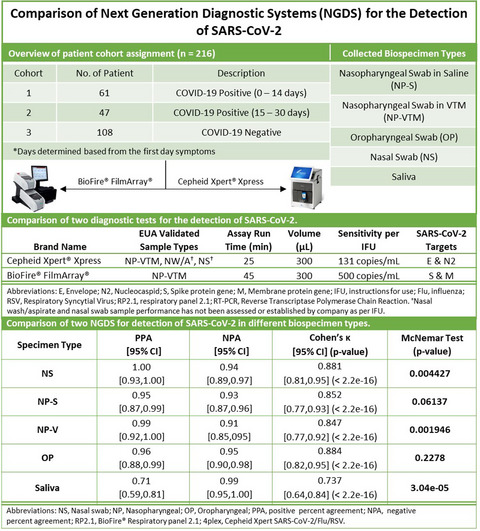
Limit of detection (LoD) and comparative testing, performed on BioFire® FilmArray® and Cepheid GeneXpert® Xpress, demonstrated increased sensitivity with the Cepheid compared with the BioFire® in detecting SARS-CoV-2 in NP VTM and saline, nasal, and OP swabs. Conversely, saliva testing on the Cepheid showed statistically significant lower sensitivity compared with the BioFire®. Finally, NP swabs in saline showed no significant difference comparedwith NP swabs in VTM on both platforms. The Cepheid and BioFire® NGDS are viable options to address a variety of public health needs providing rapid and reliable, point-of-care testing using a variety of clinical matrices.
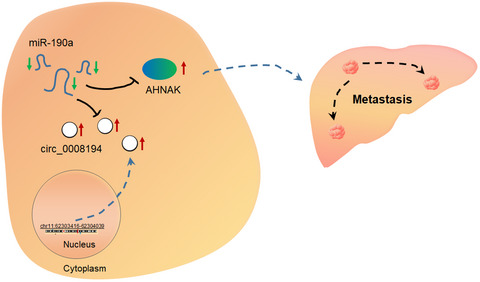
CircRNA_0008194 functions as a ceRNA to promote invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibiting miR-190a/AHNAK signaling pathway
- First Published: 24 February 2022
CASE REPORT
Chronic neutrophilic leukemia complicated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: A case report and literature review
- First Published: 16 February 2022
BRIEF REPORT
Comparative performance of ELISA and dot blot assay for TSH-receptor antibody detection in Graves’ disease
- First Published: 20 February 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Oncogenic and tumor suppressor genes expression in myeloproliferative neoplasms: The hidden side of a complex pathology
- First Published: 17 February 2022
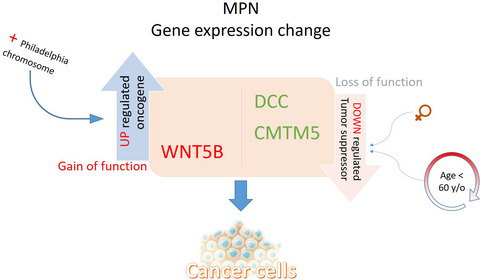
The presence of the Philadelphia chromosome led to a significant upregulation of WNT5B with non-significant changes in other genes. Two tumor suppressor genes, DCC and CMTM5, were downregulated in MPN patients especially in females and patients younger than 60 years old. WNT5B, a known oncogenesis gene, was upregulated in CML patients.
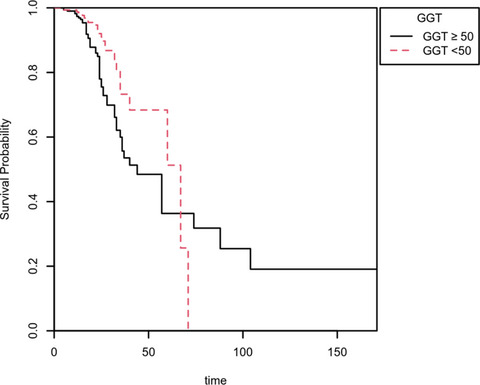
In-hospital mortality in SARS-CoV-2 stratified by gamma-glutamyl transferase levels
- First Published: 09 March 2022
Pyroptosis patterns and immune infiltrates characterization in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 14 February 2022
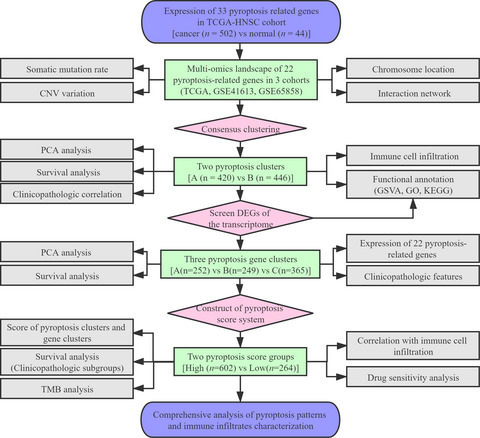
In the first stage, the expression of 33 pyroptosis-related genes (PRGs) was compared in the TCGA-HNSC datasets (cancer [n = 502] vs normal [n = 44]), 22 differentially expressed PRGs were filtered, and then, the somatic mutation, copy number variation (CNV), chromosomal location, and PRGs interactions were shown. To explore the relationship of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) characteristics and PRGs, consensus clustering analysis was performed in TCGA-HNSC, GSE41613, and GSE65858, and pyroptosis clusters A (n = 420) and B (n = 446) were defined. Overall survival, clinicopathologic features, immune cell infiltration, and functional enrichment (GSVA, GO, and KEGG) were analyzed between two pyroptosis clusters. In the second stage, consensus clustering analysis was presented based on 784 DEGs between two pyroptosis clusters; three subtypes (gene cluster A [n = 252], gene cluster B [n = 249], and gene cluster C [n = 365]) were defined; PCA analysis, survival analysis, and clinicopathologic features were performed. In the last stage, we constructed a novel pyroptosis score for each HNSCC sample by a PCA algorithm, the patients were divided into a high (n = 602) or low (n = 264) pyroptosis score groups, Sankey plots, Kaplan–Meier curves, tumor mutation burden (TMB), immune cells, and drug sensitivity were comprehensively analyzed.
Identification and molecular epidemiology of routinely determined Streptococcus pneumoniae with negative Quellung reaction results
- First Published: 16 February 2022
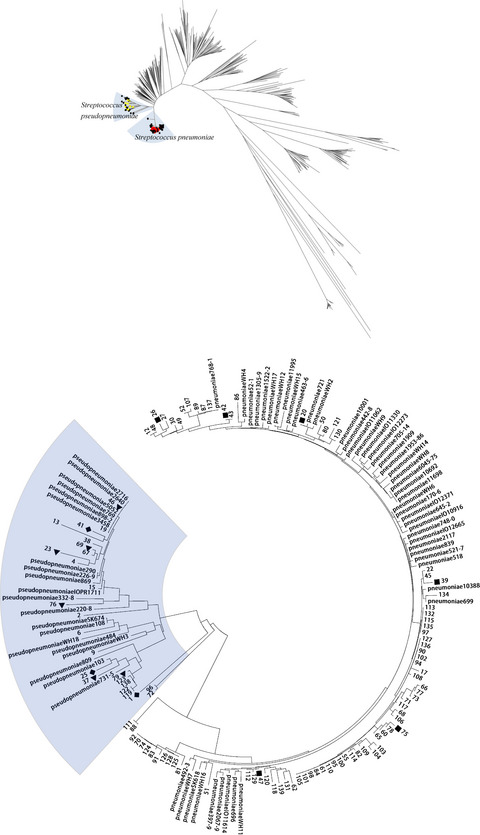
Isolates identified as Streptococcus pneumoniae by routine tests were examined by multilocus sequence analysis, multilocus sequence typing, Vitek MS, and sequential multiplex PCR. Some Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates identified by routine methods could be Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae. Most non-encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae strains have a different genetic background with capsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae strains.
Multicenter performance evaluation and reference range determination of a new one-stage factor VIII assay
- First Published: 11 March 2022
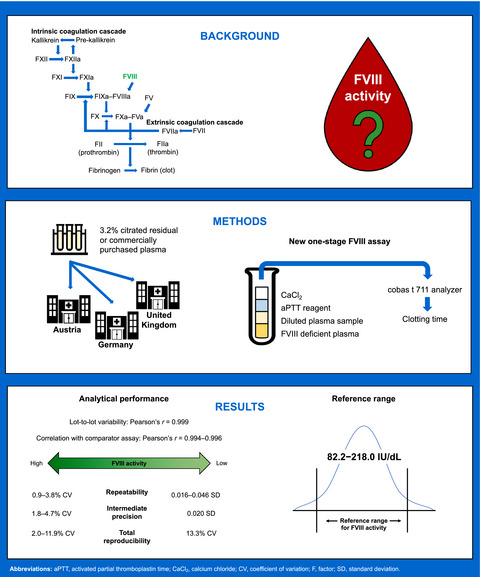
We conducted a multicenter evaluation of a new one-stage factor VIII (FVIII) assay (Roche Diagnostics), intended for the quantitative assessment of FVIII activity. The new one-stage FVIII assay demonstrated robust analytical performance on the cobas t 711 analyzer, supporting its use in routine laboratory practice.
Performance evaluation of the i-Smart 300E cartridge for point-of-care electrolyte measurement in serum and plasma
- First Published: 14 February 2022
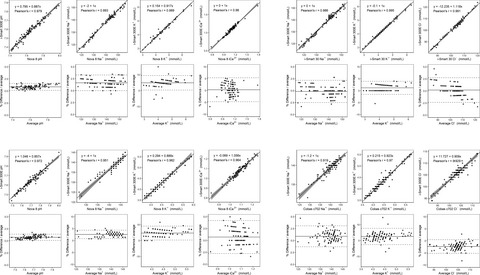
The Passing-Bablok regression and Bland-Altman plots of comparison using serum with Nova 8 and i-Smart 30, respectively. Compared with Cobas c702, K+ and Cl− showed both proportional and systematic differences. The Passing-Bablok regression and Bland-Altman plots of comparison using plasma with Nova 8 and Cobas c702 are presented, respectively. For comparisons that did not include either 1 in 95% CI of slope or 0 in 95% CI of intercept, predicted values for i-Smart 300E at medical decision levels were obtained. The i-Smart 300E demonstrated lower level of Na+ compared to that of the Nova 8 and was beyond the total allowable error in both serum and plasma for all levels. Predicted values in medical decision levels and allowable total error analytes showed proportional and/or systematic differences in the comparison analysis.
Validation of the hepatocellular carcinoma early detection screening algorithm Doylestown and aMAP in a cohort of Chinese with cirrhosis
- First Published: 26 February 2022
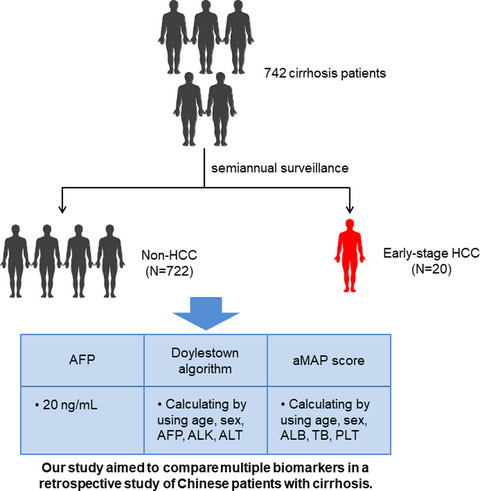
In this study, HCC surveillance was performed by radiographic imaging and testing for tumor markers every 6 months from August 21, 2018, to January 12, 2021. We conducted a retrospective study of 742 liver cirrhosis patients. Samples from these patients at three follow-up time points were tested to evaluate alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), the Doylestown algorithm, and aMAP score. Overall, 521 liver cirrhosis patients underwent semiannual longitudinal follow-up three times. Five patients were diagnosed with HCC within 0–6 months of the third follow-up. We found that for these liver cirrhosis patients, the Doylestown algorithm had the highest accuracy for HCC detection, with areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.763, 0.801, and 0.867 for follow-ups 1–3, respectively. Compared with AFP at 20 ng/ml, the Doylestown algorithm increased biomarker performance by 7.4%, 21%, and 13% for follow-ups 1–3, respectively. Our findings show that the Doylestown algorithm performance appeared to be optimal for HCC early screening in the Chinese cirrhotic population when compared to the aMAP score and AFP at 20 ng/ml.
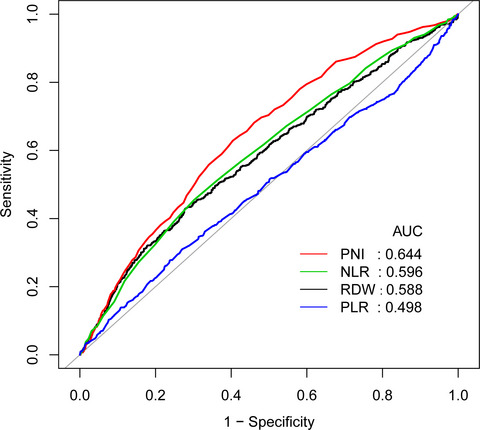
Prognostic nutrition index is associated with the all-cause mortality in sepsis patients: A retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 20 February 2022
Maternally transmitted nonsyndromic hearing impairment may be associated with mitochondrial tRNAAla 5601C>T and tRNALeu(CUN) 12311T>C mutations
- First Published: 26 February 2022
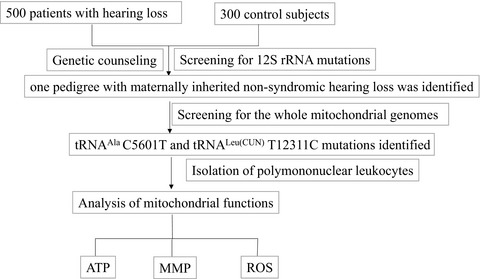
In this case–control study for genetic screening of deafness-associated mitochondrial tRNA mutations/variants, we ascertained one maternally inherited Han Chinese family harboring mitochondrial tRNAAla C5601T and tRNALeu(CUN) T12311C mutations. We further screened the whole mitochondrial genomes of the matrilineal relatives from this pedigree. In addition, the phylogenetic conservation analysis and mtDNA haplogroup analysis were performed. We further isolated the polymononuclear leukocytes and performed the mitochondrial functional analysis including ATP, mitochondrial membrane potential, and ROS in patients carrying m.C5601T and m.T12311C mutations. We found that m.C5601T and m.T12311C mutations may cause mitochondrial dysfunction, which was involved in the pathogenesis of maternally inherited hearing loss.
Prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index and its variations in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with anlotinib monotherapy
- First Published: 18 February 2022
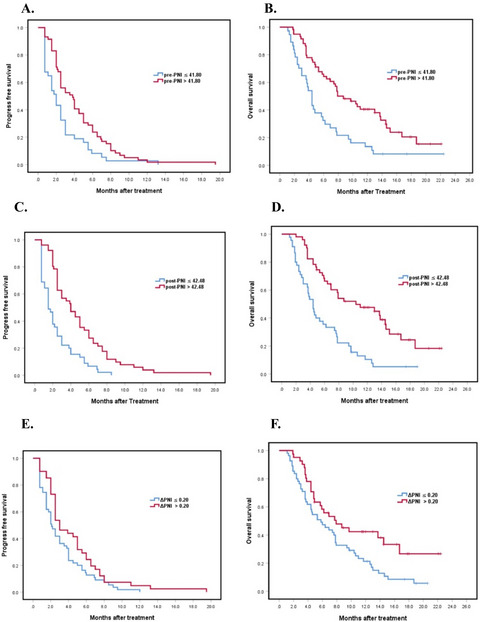
Association of pre-PNI (≤41.80 vs. >41.80), post-PNI (≤42.48 vs. >42.48), and ΔPNI (≤0.20 vs. >0.20) with progression-free survival (A, p = 0.011, C, p = 0.000 and E, p = 0.045). Association of pre-PNI (≤41.80 vs. >41.80), post-PNI (≤42.48 vs. >42.48), and ΔPNI (≤0.20 vs. >0.20) with overall survival (B, p = 0.001, D, p = 0.000 and F, p = 0.016).
BRIEF REPORT
The application of certified reference materials for clinical mass spectrometry
- First Published: 11 March 2022
Based on the problems of reference materials in clinical mass spectrometry, the precautions for the use of reference materials are summarized in the aspects of measurement method validation, calibrator usage, and quality control in this article. Additionally, combined with the previous experience of the author's laboratory, the operation mode and acceptance criteria of the new calibration solution lot replacement were formulated to ensure the continuous comparability of the measurement system.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Necroptosis-related lncRNA to establish novel prognostic signature and predict the immunotherapy response in breast cancer
- First Published: 01 March 2022
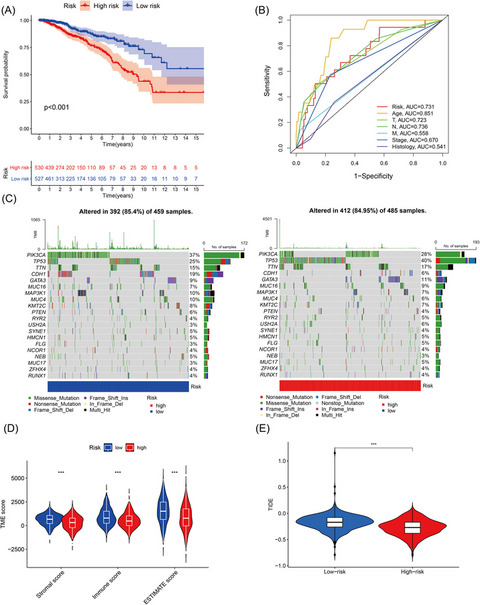
Seven necroptosis-related lncRNAs, SH3BP5-AS1, AC012073.1, AC120114.1, LINC00377, AL133467.1, AC036108.3, and AC020663.2 were involved in the risk model. In addition, the forecast performance of this model was verified and accredited. Most notably, the patients of higher risk score were characterized with increased TMB and decreased TIDE score, indicating that these patients showed better immune checkpoint blockade response.
Role of m5C RNA methylation regulators in colorectal cancer prognosis and immune microenvironment
- First Published: 25 February 2022
This study aimed to investigate the role of m5C and m1A regulators in colorectal cancer prognosis. We used multiple bioinformatics tools and databases to analyze the correlation between these regulators and differences in survival as well as the clinicopathological characteristics and tumor microenvironment in colorectal cancer tissues. We believe that our study makes a significant contribution to the literature because it explores novel biomarkers that predict the therapeutic efficacy of current treatments and benefit therapeutic modulation. We identified NSUN6 and DNMT3A as risk factors associated with prognosis, wherein the higher the expression of both genes, the lower the survival; a prognostic risk model was also constructed using these genes.
The role of platelet parameters for the diagnosis of preeclampsia among pregnant women attending at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital antenatal care unit, Gondar, Ethiopia
- First Published: 24 February 2022
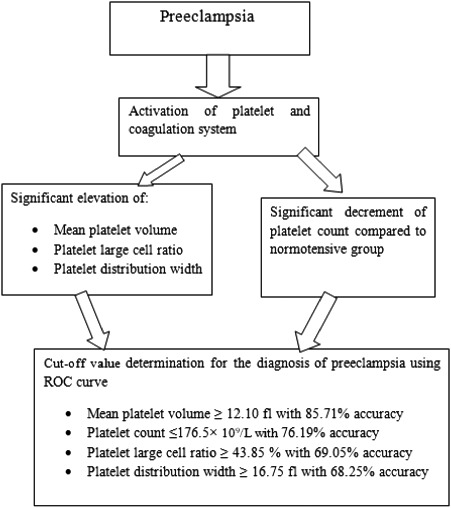
Mean platelet volume, platelet count, platelet large cell ratio, and platelet distribution width have a role in the prediction of preeclampsia as their graph on the ROC curve are above the reference line. However, their diagnostic significance (Specificity and sensitivity) are different. As indicated on the graph, mean platelet volume which covers more area of the square was the best parameter followed by platelet count, platelet count, platelet large cell ratio, and platelet distribution width, respectively.
A method comparison of three immunoassays for detection of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain in individuals with adenovirus type-5-vectored COVID-19 vaccination
- First Published: 23 February 2022
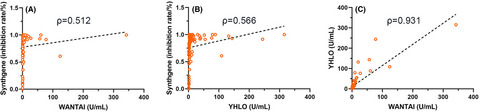
Graphic representation of correlation between the detection results of three assays. (A) The correlation of quantitative results of WANTAI ELISA with inhibition rate of Synthgene ELISA. (B) The correlation of quantitative results of YHLO CLIA with inhibition rate of Synthgene ELISA. (C) The correlation of quantitative results between WANTAI ELISA and YHLO CLIA.
Comparative diagnostic utility of metagenomic next-generation sequencing, GeneXpert, modified Ziehl–Neelsen staining, and culture using cerebrospinal fluid for tuberculous meningitis: A multi-center, retrospective study in China
- First Published: 24 February 2022
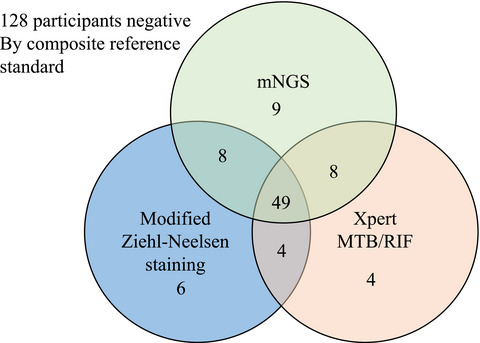
The diagnosis of tuberculosis meningitis (TBM) remains a great challenge during clinical practice. The diagnostic efficacies of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Xpert MTB/RIF (Xpert) assay, metagenomic next generation sequence (mNGS), modified Ziehl–Neelsen (ZN) stain, and mycobacterial growth indicator tube (MGIT) culture for diagnosis of TBM were evaluated. mNGS was able to detect TBM with higher sensitivity than Xpert, ZN stain, and MGIT culture. Furthermore, mNGS combined with ZN stain and Xpert could further enhance the sensitivity of diagnosis of clinical suspicious TBM.
REVIEW ARTICLE
COVID-19 in HIV-positive patients: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- First Published: 20 February 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Evaluation of LAMP assay using phenotypic tests and PCR for detection of blaKPC gene among clinical samples
- First Published: 26 February 2022
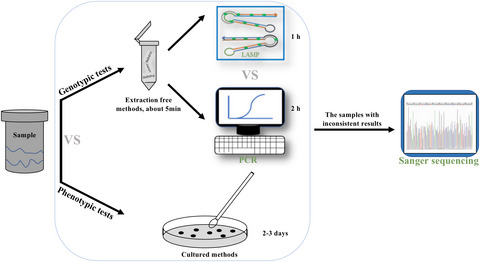
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) infection constitutes a public health threat, which blaKPC was the major carbapenemases concerned in China. However, conventional identification and susceptibility testing methods of microorganisms usually require at least 2 days from specimen collection. Timely and efficient diagnosis is of paramount importance for controlling the spread of drug-resistant bacteria. We develop an approach based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid confirmation of blaKPC within 60 min from samples collected. Five hundred forty-six clinical specimens were analyzed by the LAMP assay and compared with the phenotypic tests and PCR. The LAMP assay displayed a detection limit of 1 × 102 CFU/ml, which was 10-fold more sensitive than the PCR. The results obtained with 546 clinical samples indicate that the genotypic method and phenotypic tests have a good agreement (Kappa > 0.75). It is a reliable assay for identifying blaKPC induced CRE in China. The inconsistent results were verified by Sanger sequencing furtherly. The results of the Sanger sequencing indicate that the developed method not only has high accuracy but also meets the need for rapid diagnosis, while the PCR method is prone to false negatives. It may therefore be routinely applied for detection of blaKPC producers in routine clinical laboratories.
Combined diagnosis of QF-PCR and CNV-Seq in fetal chromosomal abnormalities: A new perspective on prenatal diagnosis
- First Published: 23 February 2022
Estimation of homocysteine concentration as an indicator of foetal death in pregnant Chinese women with preeclampsia: A case–control study
- First Published: 04 March 2022
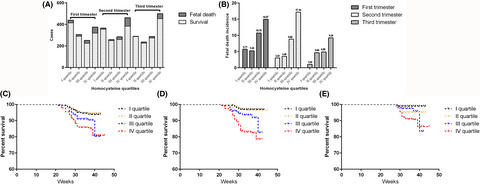
The incidence of foetal death increased evidently by quartiles of homocysteine during all the trimesters, from 5.71% quartile I to 14.97% quartile IV in the first trimester, from 3.01% quartile I to 17.14% quartile IV in the second trimester and from 1.04% quartile I to 9.24% quartile IV in the third trimester. Overall survival rate of patients with high homocysteine concentrations during pregnancy was significantly lower than those with low level.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Malaria diagnostic update: From conventional to advanced method
- First Published: 04 March 2022
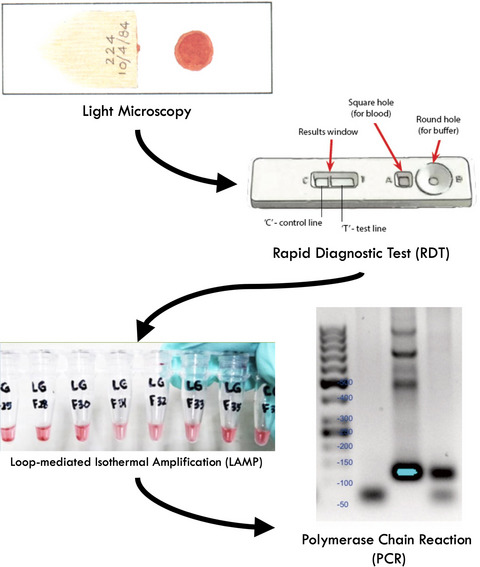
Update diagnostic methods of malaria play important roles in dealing with the current global malaria situation. There are several methods to find out the existence of parasite within the blood ranging from conventional procedures include light microscopy and RDT till advance procedures include LAMP, PCR, and POCT.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Signal transducer and activator of transcription family is a prognostic marker associated with immune infiltration in endometrial cancer
- First Published: 03 March 2022
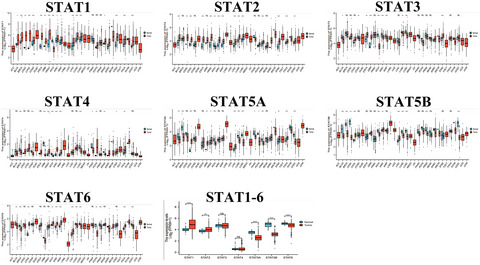
Expression of STAT family in different stages of endometrial cancer (p < 0.05 for different stages of STAT1 compared with normal tissue; p < 0.05 for STAT2 in stage 1 and stage 3 of UCEC compared with normal tissue; and no statistically significant difference in expression for different stages of STAT3 and STAT4 compared with normal tissue. STAT5A, STAT5B, and STAT6 were expressed differently at different stages compared with normal tissues, p < 0.05)
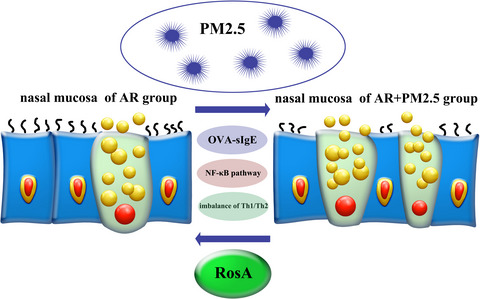
Effects of rosmarinic acid on the inflammatory response in allergic rhinitis rat models after PM2.5 exposure
- First Published: 13 March 2022
REVIEW ARTICLE
Possible effects of Treponema pallidum infection on human vascular endothelial cells
- First Published: 10 March 2022
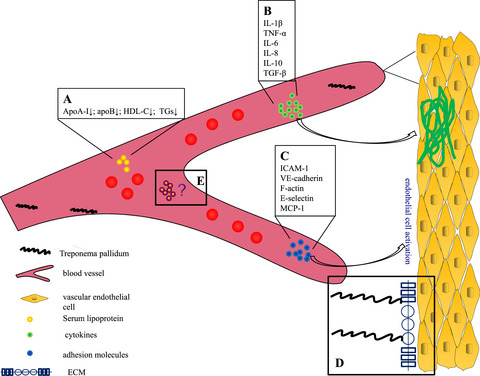
Role of Treponema pallidum in endothelial cell phenotype and functions and their direct or indirect targets. Treponema pallidum is involved in, (A) serum lipoprotein concentration, (B) cytokines in the inflammatory response to syphilis, (C) vascular endothelial cell activation by cytokines interact with chemokines, (D) binding between pathogens and lipoproteins of the intima, (E) interactions between bacteria, the immune cells, and the endothelial cells
BRIEF REPORT
Biological variation and reference change values of serum Mac-2–binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi)
- First Published: 13 March 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
A study of the moving rate of positive results for use in a patient-based real-time quality control program on a procalcitonin point-of-care testing analyzer
- First Published: 07 March 2022
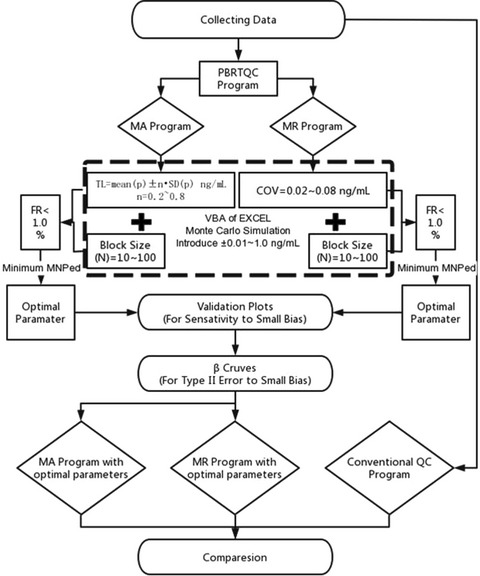
Collecting patients’ results within one year to establish PBRTQC programs of the MA and the MR. The parameter of false alarm rate (FR) 1% was eliminated. The Monte Carlo simulation within VBA was used to introduce ± 0.01 ~ 1 ng/ml at random points of the testing set. Different parameters within a specific interval were used to detect the biases, and the detection efficiency was expressed using the MNPed. The parameters of the minimum MNPeds were selected as the optimal parameters of MA and MR programs, and validation plots were generated using MNPeds and MAX of the patient samples affected. β curves were generated simultaneously, and the sensitivities were compared with that of the conventional internal quality control program. The ability of conventional QC to detect a 0.05 ng/ml bias using the 13S/22S/R4S multi-rule.
Genetic variations in ATM and H2AX loci contribute to risk of hematological abnormalities in individuals exposed to BTEX chemicals
- First Published: 02 March 2022
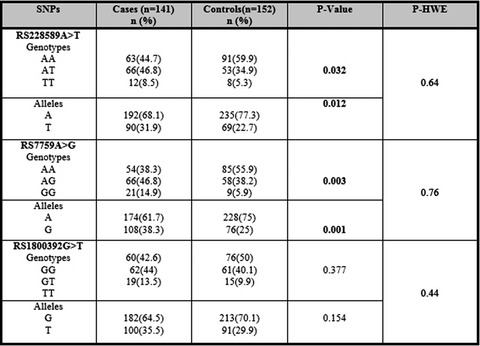
Our results demonstrated that T allele of ATM-rs228589 and G allele of H2AX-rs7759 were significantly associated with the risk of BTEX-related hematotoxicity in an Iranian subpopulation (p = 0.012 and p = 0.001, respectively). Additionally, we observed an association of reduced RBC counts with the T allele of ATM-rs228589 (p-trend = 0.010), while increased granulocyte counts and decreased lymphocyte counts were associated with the G allele of H2AX-rs7759 (p-trend = 0.008 and 0.010, respectively).
E2F4 may be a core transcription factor in the lncRNA-TF regulatory network in cervical cancer
- First Published: 09 March 2022
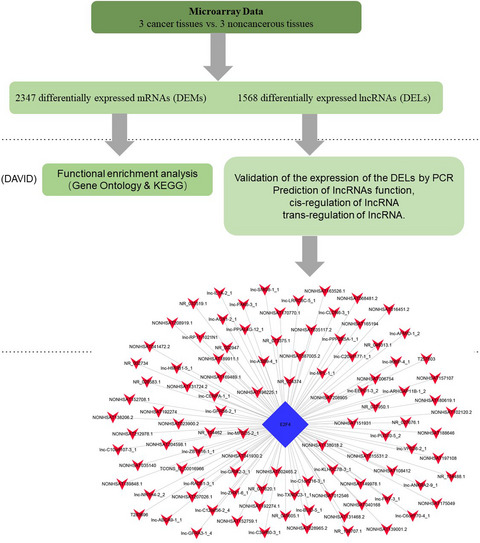
We found the differently expressed lncRNAs between cervical cancer tissues and adjacent noncancerous tissues. Through the prediction of lncRNAs function, cis-regulation of lncRNA and trans-regulation of lncRNA, we construct lncRNA-TF regulatory network and found that E2F4 may be the potential critical transcription factor in the regulatory network.
CASE REPORT
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn in the sensitizing pregnancy where anti-D was incorrectly identified as RhIG
- First Published: 03 March 2022
CORRIGENDUM
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Dynamic observation of SARS-CoV-2 IgM, IgG, and neutralizing antibodies in the development of population immunity through COVID-19 vaccination
- First Published: 02 March 2022
REVIEW ARTICLE
The effect of probiotics on gestational diabetes and its complications in pregnant mother and newborn: A systematic review and meta-analysis during 2010–2020
- First Published: 03 March 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The prognostic effect of PNN in digestive tract cancers and its correlation with the tumor immune landscape in colon adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 08 March 2022
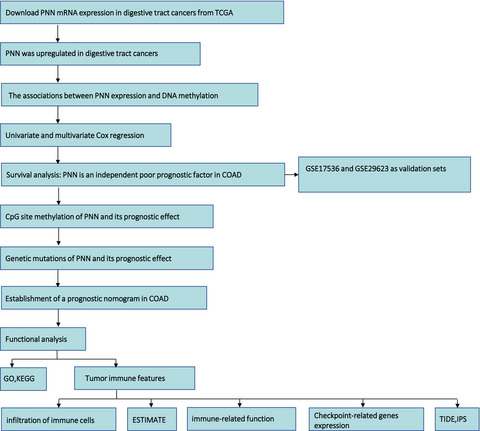
We downloaded the PNN mRNA expression in digestive tract cancers from TCGA database. PNN was upregulated and remarkably related to tumor stage in esophageal cancer, gastric adenocarcinoma, COAD and rectal adenocarcinoma. PNN expression was identified as an independent prognostic factor in COAD, high expression of PNN was positively associated with poor progression-free survival and overall survival time, the predictive value for survival was validated in two GEO datasets, GSE17536 and GSE29623. A prognostic nomogram was established for better prognosis prediction in patients with COAD. Furthermore, GO and KEGG enrichment analysis were performed to investigate the enriched biological functions and pathways in COAD. Also, several acknowledged bioinformatic algorithms were employed to assess the correlation between PNN expression and the tumor immune landscape in COAD. PNN expression was significantly associated with tumor infiltrating immune cells, immune cell functions, and several immune checkpoints in COAD.
CASE REPORT
Identification of sacrococcygeal and pelvic abscesses infected with invasive Mycoplasma hominis by MALDI-TOF MS
- First Published: 13 March 2022
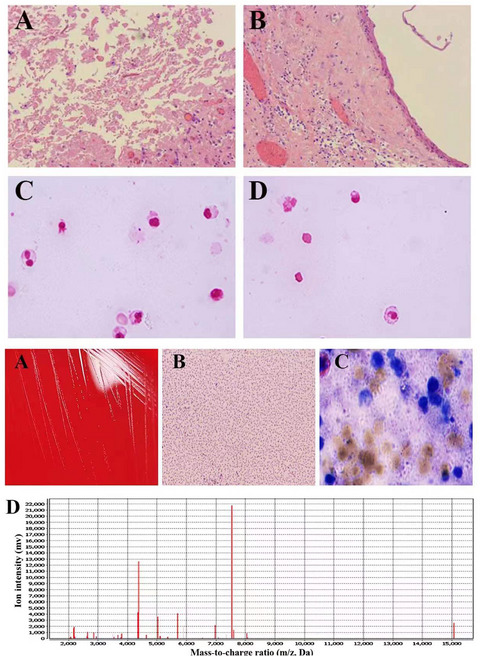
It is generally considered that M. hominis is a low virulence opportunistic pathogen and rarely invades tissue. We report a case of extra-urogenital cystic abscesses infected by M. hominis, in order to improve clinicians' comprehensive understanding of the pathogenicity of Mycoplasma. No pathogens were found after pathological and smear microscopic examination of the puncture fluid from the sacrococcygeal and pelvic abscesses. Until 48 hours later, small, translucent and gray white colonies were observed in the blood plate culture results. The laboratory physician ultimately determined that the pathogen was M. hominis by MALDI-TOF MS.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Blood long non-coding RNA intersectin 1–2 is highly expressed and links with increased Th17 cells, inflammation, multiple organ dysfunction, and mortality risk in sepsis patients
- First Published: 04 March 2022
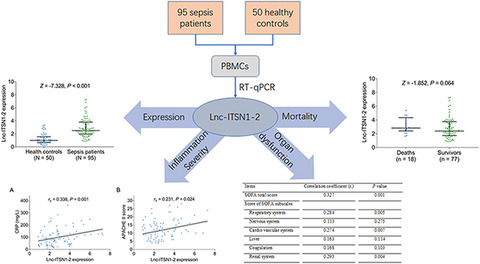
Long non-coding RNA intersectin 1-2 (lnc-ITSN1-2) exacerbates inflammation and promotes T-helper (Th) cell differentiation, also serves as biomarker in critical illness diseases. However, its clinical role in sepsis remains obscure. The findings of this study indicates that lnc-ITSN1-2 reflects sepsis progression and unfavorable prognosis to some extent, which may serve as a potential biomarker to improve the management of sepsis patients.
Aberrant blood MALT1 and its relevance with multiple organic dysfunctions, T helper cells, inflammation, and mortality risk of sepsis patients
- First Published: 09 March 2022
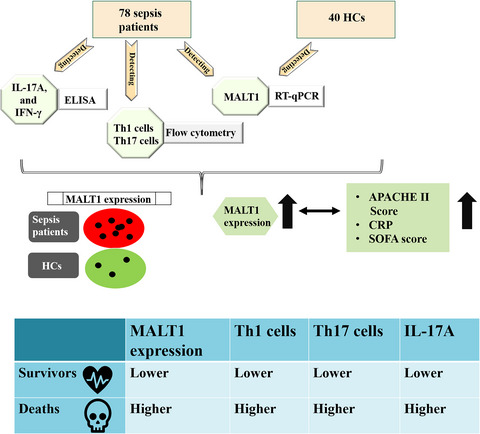
In general, 78 sepsis patients and 40 HCs were enrolled. MALT1 expression was detected in PBMCs from all subjects by RT-qPCR. Besides, Th1 and Th17 cells were measured in PBMCs from sepsis patients by flow cytometry; IL-17A and IFN-γ were determined in serum from sepsis patients by ELISA. MALT1 expression was higher in sepsis patients than HCs. MALT1 expression was positively correlated with Th17 cells and IL-17A, but not with Th1 cells or IFN-γ in sepsis patients. MALT1 expression was positively correlated with APACHE II score, CRP, SOFA respiratory system score, and SOFA liver score. MALT1 expression, Th1 cells, Th17 cells, and IL-17A elevated in sepsis deaths compared with sepsis survivors.
The expression and significance of p4E-BP1/4E-BP1 in prostate cancer
- First Published: 08 March 2022
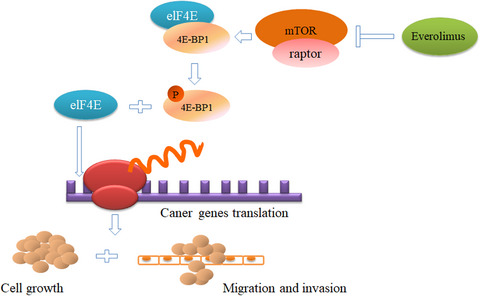
The patients with high expression of p4E-BP1 may benefit from Everolimus treatment. The mTOR inhibitor Everimos could inhibit the phosphorylation of 4EB-P1, thereby suppressing the elF4E complex assembly and translation, eventually leading to the cell death and the weakening of their migration and invasion ability in prostate cancer cells.
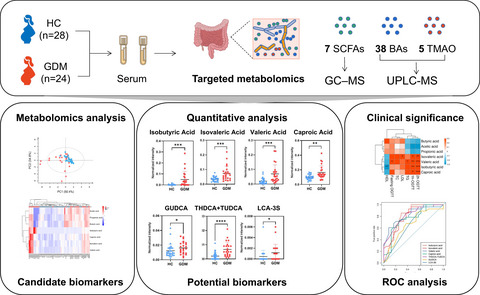
Alterations of gut microbiota-derived metabolites in gestational diabetes mellitus and clinical significance
- First Published: 13 March 2022
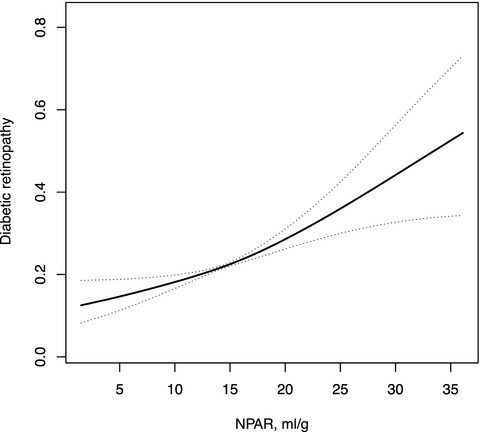
The neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio is related to the occurrence of diabetic retinopathy
- First Published: 13 March 2022
Evaluation of a cardiac troponin process flow at the chest pain center with the shortest turnaround time
- First Published: 09 March 2022
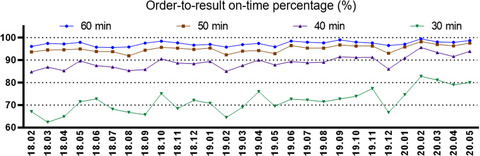
The process flow evaluated in this study had the shortest turnaround time for cardiac troponin test as ever reported. This study presented an example how process improvement could shorten the turnaround time of laboratory tests and increase clinical outcomes. The findings in this study suggested that the sampling location and floor plan should be taken seriously in optimizing the process flow of laboratory testing.
Serum hsa_circ_0079480 is a novel prognostic marker for acute myeloid leukemia
- First Published: 17 March 2022
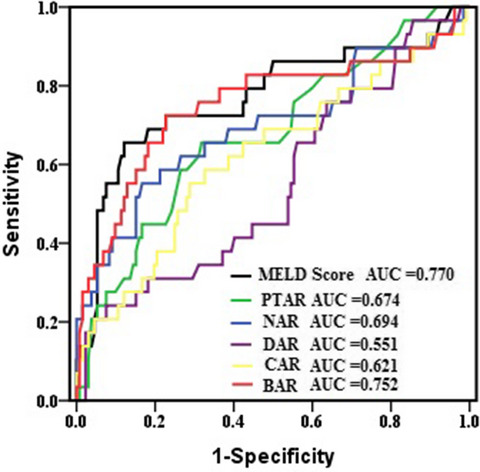
Prognostic value of albumin-related ratios in HBV-associated decompensated cirrhosis
- First Published: 17 March 2022
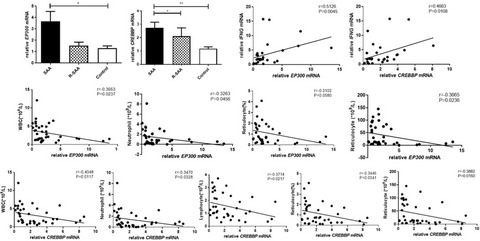
Abnormal expression of histone acetylases in CD8+ T cells of patients with severe aplastic anemia
- First Published: 10 March 2022
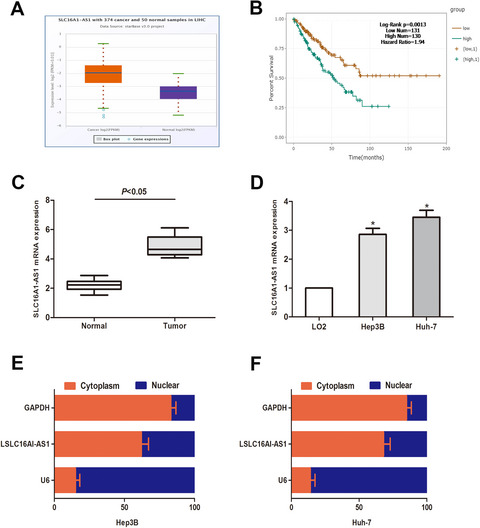
LncRNA SLC16A1-AS1 contributes to the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by modulating miR-411/MITD1 axis
- First Published: 15 March 2022
A multi-omics-based investigation of the immunological and prognostic impact of necroptosis-related genes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 15 March 2022
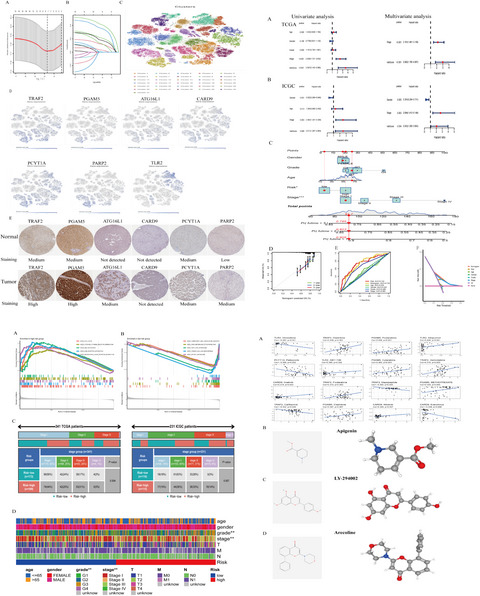
A prognostic model for necroptosis-related genes was first constructed by Lasso regression, followed by validation at the single cell and protein levels. This is followed by clinical correlation analysis to verify whether the model can be used independently as a prognostic factor. At the end, chemotherapy drug sensitivity analyses are performed and drugs that reduce the risk to patients are identified.
Hsa_circRNA_0017620 regulated cell progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via miR-520a-5p/KRT5 axis
- First Published: 18 March 2022
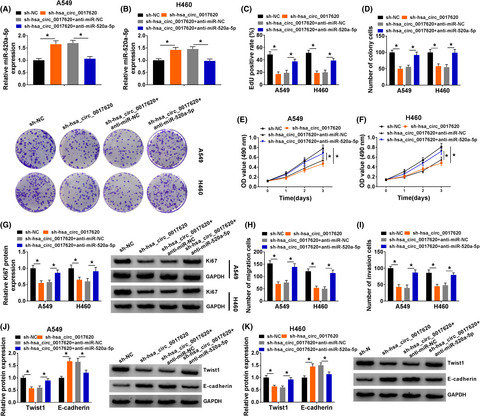
Hsa_circ_0017620 regulated cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through targeting miR-520a-5p in NSCLC. (A and B) The expression of miR-520a-5p was detected in sh-NC, sh-hsa_circ_0017620, sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-NC, and sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-520a-5p groups with qRT-PCR in A549 and H460 cells. (C) DNA synthesis was analyzed by EdU assay in A549 and H460 cells transfected with sh-NC, sh-hsa_circ_0017620, sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-NC, and sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-520a-5p. (D) The number of colony cells was measured in sh-NC, sh-hsa_circ_0017620, sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-NC, and sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-520a-5p groups using colony formation assay in A549 and H460 cells. (E and F) Cell proliferation was measured using MTT assay in sh-NC, sh-hsa_circ_0017620, sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-NC, and sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-520a-5p groups in A549 and H460 cells. (G) The protein expression of Ki67 was detected with western blot in sh-NC, sh-hsa_circ_0017620, sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-NC, and sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-520a-5p groups in A549 and H460 cells. (H and I) Cell migration and invasion were measured with transwell assay in sh-NC, sh-hsa_circ_0017620, sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-NC, and sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-520a-5p groups in A549 and H460 cells. (J and K) The protein expression of Twist1 and E-cadherin was detected with western blot in sh-NC, sh-hsa_circ_0017620, sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-NC, and sh-hsa_circ_0017620+anti-miR-520a-5p groups in A549 and H460 cells. *p<0.05.
Serum lutein is a promising biomarker for type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic kidney disease in the elderly
- First Published: 15 March 2022
To investigate the relationship between serum lutein and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in elderly individuals. A total of 60 T2DM patients over 60 years were subgrouped into a DKD group and a non-DKD group according to their urinary microalbumin to creatinine ratio (UACR), while 30 age-matched non-T2DM patients were recruited in the control group. Baseline characteristics, laboratory examination results and serum lutein levels were compared, and their correlations were analyzed. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted to identify the diagnostic potential of lutein in T2DM and DKD. The lutein level in the T2DM group was significantly lower than that in the control group and was also significantly lower in the DKD group than in the non-DKD group (p < 0.001). Lutein levels were negatively correlated with body mass index, glycosylated hemoglobin, fasting blood glucose, triglyceride, and UACR and positively correlated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (p < 0.05). T2DM patients were divided into four groups according to the quartile of their lutein level. The proportion of T2DM and DKD gradually decreased with increasing lutein levels (p < 0.001). The area under the ROC curve of serum lutein in diagnosing T2DM and DKD was 0.880 and 0.779, respectively, with corresponding cutoff values of 0.433 μmol/L and 0.197 μmol/L (p < 0.001). The serum level of lutein is negatively correlated with the incidence of T2DM and DKD in the elderly and can serve as a diagnostic marker for T2DM and DKD.
Association between red blood cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio and diabetic retinopathy
- First Published: 13 March 2022
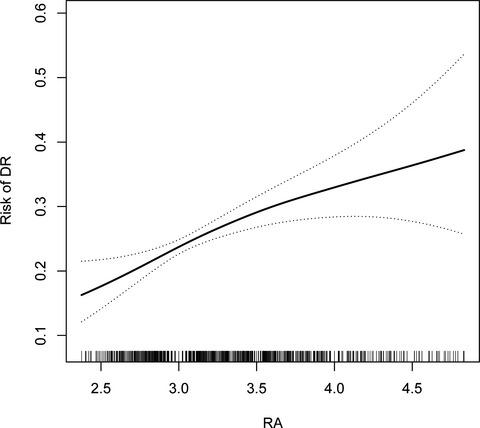
Diabetes mellitus (DM) has shown a trend of reaching pandemic levels in the world. Chronic inflammation is a key factor in the development of diabetic retinopathy (DR). Red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio (RA) is used to assess immune status and the immune response. Our study was conducted to assess the association between DR and RA levels to determine the value of RA in predicting DR. The data came from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) between 1999 and 2006, The RA was calculated as the red blood cell distribution width/albumin ratio. Multivariable logistic regression and propensity score matched analysis were used to examine the association between RA and DR levels. The clinical and demographic features of the 1751 patients with DM. The eligible participants included 874 female and 870 males with mean age 62.2 ± 14.0 years, and mean RA 3.2 ± 0.5. RA ≥ 2.9659 was a risk factor for DR (OR = 1.66 95% CI: 1.31–2.11, p < 0.0001). After adjusting for age, sex, race, education, marital status, ratio of family income to poverty, body mass index, fasting glucose, hypertension, and coronary heart disease, RA ≥ 2.9659 was an independent risk factor for DR (OR = 1.64, 95% CI: 1.23–2.19, p = 0.0008). The propensity score-matched analysis also shown that high RA was an independent risk factor for DR. Our study shown that RA is a risk factor for patients with DR. The findings of this study should be validated the role of RA in DR in diabetic patients.
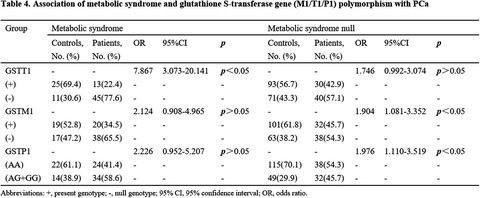
GSTT1, an increased risk factor for prostate cancer in patients with metabolic syndrome
- First Published: 15 March 2022
REVIEW ARTICLE
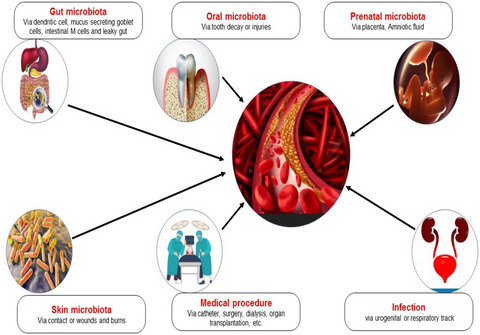
Exploring blood microbial communities and their influence on human cardiovascular disease
- First Published: 15 March 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLE
MiR-363-3p promotes prostate cancer tumor progression by targeting Dickkopf 3
- First Published: 18 March 2022
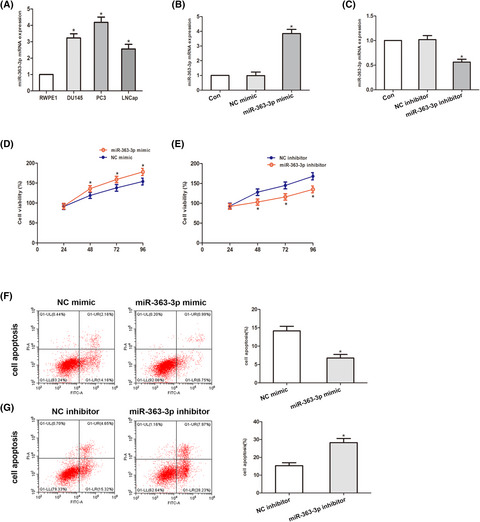
MiR-363-3p was found to be negatively associated with the expression of DKK3 in clinical PCa specimens. Further studies revealed that DKK3 was a direct target of miR-363-3p. Moreover, overexpression of miR-363-3p downregulated the expression of DKK3, promoted cell viability, migration and invasion, and reduced cell apoptosis, while knockdown of miR-363-3p led to the opposite result. Upregulation of miR-363-3p decreased E-cadherin levels but increased vimentin and N-cadherin protein levels in PC3 cells; in contrast, miR-363-3p downregulation produced the opposite result.