hsa_circ_0058122 knockdown prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting human umbilical vein endothelial cells apoptosis via the miR-7974/IGFBP5 axis
Abstract
Background
Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head (SONFH) is a serious complication of glucocorticoid overused. Recent evidence has demonstrated that circRNAs exert key pathophysiological roles in a variety of disease processes. However, the role of circRNA in SONFH remains largely unknown. The current study sought to evaluate how hsa_circ_0058122 affects SONFH in dexamethasone (DEX) treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) model.
Methods
RT-PCR was used to demonstrate the hsa_circ_0058122 expression level in Dex-treated HUVECs cells. The effects of hsa_circ_0058122 on HUVECs apoptosis were evaluated via overexpression plasmid and siRNA. Using dual-luciferase and fluorescence in situ hybridization assays, we demonstrated that hsa_circ_0058122 binds to miR-7974 thereby facilitating HUVECs apoptosis. Bioinformatics analysis and western blot were performed to confirm target genes of hsa-miR-7974.
Results
In our previous work, we revealed the top 20 elevated circRNAs in SONFH patients were hsa_circ_0010027, hsa_circ_0058115, hsa_circ_0010026, hsa_circ_0058839, hsa_circ_0056886, hsa_circ_0056885, hsa_circ_0058146, hsa_circ_0058105, hsa_circ_0058112, hsa_circ_0058143, hsa_circ_0058102, hsa_circ_0058090, hsa_circ_0075353, hsa_circ_0058126, hsa_circ_0058130, hsa_circ_0058140, hsa_circ_0058122, hsa_circ_0058123, hsa_circ_0058103, and hsa_circ_0058121. Among these, hsa_circ_0058122 was finally selected for further investigation. We found hsa_circ_0058122 expression was markedly elevated in Dex-treated HUVECs cells, and the Dex-mediated HUVEC apoptosis was impaired in hsa_circ_0058122-silenced cells and increased in hsa_circ_0058122-overexpressing cells. hsa_circ_0058122 competitively binds to hsa-miR-7974, which in turn interacts with insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5).
Conclusions
hsa_circ_0058122/miR-7974/IGFBP5 was proposed to be a key regulatory pathway for SONFH. DEX treatment upregulated hsa_circ_0058122 expression in HUVECs, which sponged miR-7974, thereby increasing IGFBP5 expression, the hsa_circ_0058122/miR-7974/IGFBP5 axis contributed to the Dex-mediated apoptosis. These findings may identify novel targets for SONFH molecular therapy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) is a commonly occuring progressive disease that may induce femoral head collapse and rapid destruction of the hip joint. It is primarily observed in young- and middle-aged people.1-3 Steroid-induced ONFH (SONFH) is a form of ONFH that results from long-term or high-dosage glucocorticoids intake.4, 5 In a majority of SONFH cases, the patient ultimately needs a hip replacement, which is both costly and burdensome for families and societies. At present, not much is known about the pathogenesis of SONFH. However, emerging evidences suggest that the damaged femoral head blood supply contributes to SONFH.6, 7 In this study, we aim to add the existing knowledge of SONFH etiology, by examining the direct effect of steroid hormones on human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) apoptosis.
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a relatively new class of endogenous RNAs first discovered in RNA viruses in 1970s.8 circRNAs can be divided into non-coding circRNAs and coding circRNAs based on whether they have translation products.9, 10 As the name suggests, circRNA is a circular form of RNA with no 5′ cap or 3′ polyadenylated tail, and these RNAs are generally more stable than the linear parent gene, due to their resistance to degradation by RNA exonuclease.11, 12 Emerging evidences suggest an essential role of circRNAs in the initiation and progression of diseases, likely due to their sponging of miRNA and relieve inhibitory effect of miRNA on downstream target genes.13-15 Among the established circRNAs is CDR1as, which harbors more than 70 binding sites for miR-7 and has been reported to regulate the progression of numerous cancers.16-18 Unfortunately, there are very few reports of circRNA expression and regulatory mechanism in SONFH. According to the Chen et al. report, CDR1as knockdown in SONFH-bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) dramatically elevated osteocytic differentiation while reducing adipocytic differentiation of BMSCs.19 Previously, using microarray analysis, we have demonstrated that hsa_circ_0058122 (termed circFN1) expression was significantly upregulated in SONFH tissues, relative to healthy controls.20 In the present study, we verified the expression of hsa_circ_0058122 in SONFH tissue samples and generated a dexamethasone (DEX)-induced HUVEC cell apoptosis model. Our aim was to elucidate the effects of hsa_circ_0058122 on HUVECs apoptosis via the miR-7974/IGFBP5 (insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5) axis. The findings from this study can contribute to a better understanding of the mechanism and pathogenesis of SONFH, particularly in terms of insufficient femoral head blood supply.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Tissue specimen collection
This study has been approved by Ethical Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, and every participant signed an informed consent form. Femoral heads were obtained from 10 patients who had corticosteroid usage histories and fulfilled the diagnosis of ONFH according to the guidelines of the Chinese Medical Association who were undergoing total hip arthroplasty at the Third Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. Femoral heads were cut along the coronal plane to differentiate the osteonecrosis zone and normal zone which were defined as a pair group. All the tissue samples were cut into small pieces of approximately 5 × 5 × 5 mm 3 and stored in a −80°C freezer immediately. The clinical details for the 10 patients are listed in Table 1.
| Patient | Age | Gender | Drugs used | Duration of glucocorticoid use (month) | Association Research Circulation Osseous stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 46 | Female | Prednisone | 26 | IIIC |
| 2 | 39 | Female | Prednisone | 15 | IIIC |
| 3 | 35 | Female | Prednisone | 21 | IV |
| 4 | 41 | Female | Prednisone | 18 | IIIC |
| 5 | 49 | Male | Prednisone | 16 | IV |
| 6 | 39 | Female | Prednisone | 31 | IV |
| 7 | 58 | Male | Prednisone | 17 | IIIC |
| 8 | 47 | Female | Prednisone | 19 | IV |
| 9 | 38 | Female | Prednisone | 23 | IV |
| 10 | 53 | Male | Prednisone | 17 | IV |
2.2 Cell culture
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were purchased from Cell Bank of the. Chinese Academy of Sciences and cultured in endothelial cell medium (ECM) containing 5% fetal bovine serum and 1% endothelial cell growth supplement (ECGS) under a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37ºC. HUVECs treated with 1 μM DEX (Beyotime) for 72 h were termed as the model group, and HUVECs treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) were used as the normal control.
2.3 RNA extraction and qRT-PCR
Femoral heads tissue and HUVECs total RNA were extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). One microgram total RNA was reversed to cDNA used an RTreagent kit purchased from GENESEED. Then, real-time PCR was performed using SYBR Premixsupplied by Vazyme on the AppliedBiosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR Detection Systems. U6 levels were used to normalize has-miR-7974 expression. GAPDH was endogenous control for hsa_circ_0058122 and IGFBP5 mRNA. Relative expression of each RNA was determined using the 2−ΔΔCT method. All the qRT-PCR analysis was done in triplicate. The primer sequences of used in qPCR are listed in Table 2.
| Gene name | Primer sequences (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| circFN1 |
F: TGGAGTCTTTACCACACATCAGT R: TGAATCCTGGCATTGGTCGA |
| FN1_mRNA |
F: ATGTGATCCCCGTCAACCTG R: ACTGGAGGTTAGTGGGAGCA |
| hsa-miR−7974 |
F: ATGGTTCGTGGGAGGCTGTGATGCTC R: GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACCGGGCTG |
| IGFBP5 |
F: ACCTGAGATGAGACAGGAGTC R: GTAGAATCCTTTGCGGTCACAA |
| GAPDH |
F: AGAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTTG R: GCAGGAGGCATTGCTGATGAT |
| U6 |
F: CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA R: AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT RT: AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCG |
2.4 circRNA RNase R treatment
Total RNA (2 µg) was incubated for 15 min at 37°C with or without 6 U RNase R supplied by GENESEED. Subsequently, hsa_circ_0058122 and FN1 mRNA expression was detected through qRT-PCR.
2.5 Dual-luciferase reporter assay
hsa_circ_0058122-WT and hsa_circ_0058122-MT were inserted into psiCHECK2 dual-luciferase vector (Promega). hsa-miR-7974 mimic and negative control miRNA (miR-NC) were synthesized by GenePharma. After cotransfection of the reporter vector and miR-7974 mimics or negative control in HUVEC cells for 48 h, Renilla luciferase activity was measured using a dual-luciferase assay kit (Promega) against that of firefly luciferase. Each assay was performed in triplicate and repeated three times independently.
2.6 RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization
HUVECs were seeded on cell slides at the bottom of a 24-well plate and were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. CY3-labeled probe (CY3-5′-CAATGCACTGATGTGTGGTAAAG-3′-CY3) targeted to hsa_circ_0058122 junction site and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled hsa-miR-7974 probes (FITC-5′-GGGCTCAGGAGAGCATCACAGCCT-3′-FITC) were designed and synthesized by Geneseed. Nuclei were stained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. The signals of the probes were detected by Fluorescent InSitu Hybridization Kit (GenePharma) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Images were captured with a Leica TCS-SP2-AOBS confocal microscope (Leica).
2.7 hsa_circ_0058122 knockdown and overexpression
siRNA (si-circFN1, 5′-TACCACACATCAGTGCATT-3′) targeted to back-splice junction of hsa_circ_0058122 was designed and synthesized by GenePharma. Scramble siRNA (5′-CACAGUCAAAAGAUGUUGGUU-3′) was used as a negative control. For hsa_circ_0058122 overexpression, the sequence of hsa_circ_0058122 was amplified and cloned into a circRNA overexpression vector pLO5-ciR (Geneseed) siRNA and overexpression plasmid were transfected by using Lipo3000 Transfection. Reagent (Invitrogen) into HUVECs. After 48 h, cells were harvested for qRT-PCR analysis of hsa_circ_0058122 or for other experiments.
2.8 Flow cytometry
HUVECs apoptosis was examined by flow cytometric analysis using a phycoerythrin-annexin Vapoptosis detection kit (Yeasen) according to the manufacturer's protocols. Cells were collected and rinsed using cold PBS. Subsequently, HUVEC cells were suspended in Annexin-V binding buffer, and then these cells were dyed using Annexin V combined FITC (Annexin V-FITC) and propidium iodide simultaneously in the dark for 15 min at room temperature. The apoptotic HUVEC cells were tested on a flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). Each assay was performed in triplicate and repeated three times independently.
2.9 Western blot
Western blot analysis was performed using standard procedures. Briefly, total proteins were extracted from cells and separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Millipore). To block nonspecific binding, the membranes were incubated with 5% skim milk powder at room temperature for 2 h. The membrane was then incubated with commercially available antibodies, Bax (CST; #2772T), Cleaved Caspase-3 (CST; #9661T), Bcl-2(CST; #4223T), IGFBP5 (ABclonal; #A1720), GAPDH (CST; #5174T) followed by horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody to incubate the membrane for 2 h at room temperature and then detected by chemiluminescence.
2.10 Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The statistical significance of differences was evaluated by Student's t test using GraphPad Prism (version 7.0). p values < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 RESULTS
3.1 hsa_circ_0058122 is upregulated in the femoral head tissues of SONFH patients and HUVEC cells treated with DEX
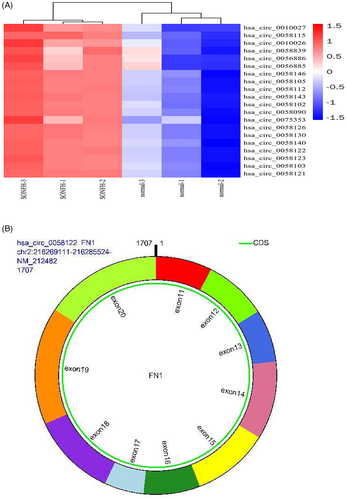
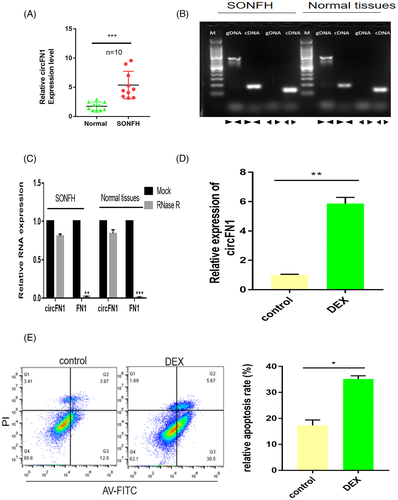
Using microarray analysis, we have previously established a circRNA expression profile in SONFH tissues versus adjacent normal tissues. According to our analysis, 647 circRNAs were differentially regulated, with 433 circRNAs highly expressed and 214 circRNAs displaying low expression.20 hsa_circ_0058122 was one of the top 20 highly expressed circRNAs in SONFH tissues(Figure 1A) and arises from the FN1 gene, which is located at chromosome 2 and consists of the head-to-tail splicing of exon 11 and exon 20 (Figure 1B). To validate our microarray results, we evaluated hsa_circ_0058122 levels in 10 pairs of SONFH tissues and adjacent normal tissues using qRT-PCR. As illustrated in Figure 2A, hsa_circ_0058122 levels were consistently elevated in all the examined SONFH tissues, resembling our previous microarray data. To prevent the likelihood of sequencing trans-splicing events, divergent and convergent primers were used to amplify hsa_circ_0058122, respectively. As a result, hsa_circ_0058122 expression was detected in the cDNA, and not in genomic DNA (gDNA) by divergent primer, whereas its linear form was detected in both cDNA and gDNA extracted from SONFH and adjacent normal tissues by convergent primers but not divergent primers (Figure 2B). The circular structure of hsa_circ_0058122 was further confirmed by treatment of RNaseR exoribonuclease. As expected, hsa_circ_0058122 resisted degradation by RNase R, whereas FN1 mRNA was easily digested by RNase R (Figure 2C). Taken together, these data demonstrated the upregulated and existence of hsa_circ_0058122 in SONFH samples. Moreover, using HUVEC cells, we demonstrated that a 72 h treatment with 1 μM DEX markedly elevated hsa_circ_0058122 expression (Figure 2D) and stimulated HUVECs apoptosis (Figure 2E).
3.2 Knockdown of hsa_circ_0058122 reverses DEX-induced apoptosis in HUVEC cells
To investigate the functional role of hsa_circ_0058122 in HUVEC cells, we performed loss- or gain-of-function experiments. We separately transfected HUVECs cells with hsa_circ_0058122 siRNA and hsa_circ_0058122 overexpressing plasmids. As depicted in Figure 3A, siRNA 3 transfection introduced the largest silencing of hsa_circ_0058122 expression, while siRNA1, siRNA 2, and si-NC exhibited no significant change in hsa_circ_0058122 expression. In cells overexpressing circFN1, the hsa_circ_0058122 expression was found to be 12-fold higher than in cells that received NC (Figure 3B). In contrast, linear mRNA FN1 expression remained the same in circFN1-silenced cells and in circFN1-overexpressed cells, suggesting that the siRNA and overexpressing plasmids does not effect levels of linear FN 1 mRNA (Figure 3C).
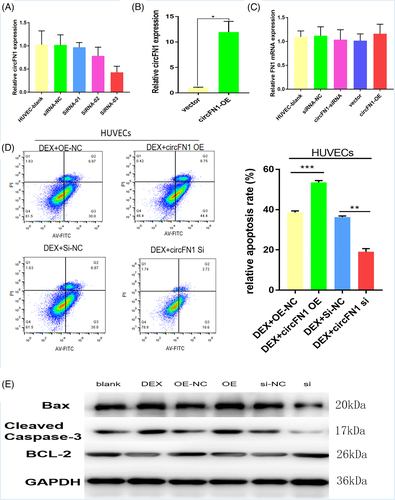
Subsequently, We evaluated HUVEC cell viability using flow cytometry. Based on our results, hsa_circ_0058122-overexpressing cells exhibited marked increase in apoptosis, relative to overexpression negetive control (OE-NC, empty vector) and the Dex-induced stimulation of apoptosis was impaired in hsa_circ_0058122-silenced cells (Figure 3D). We also examined the levels of apoptotic proteins, using western blot analysis. We demonstrated that both Dex exposure and hsa_circ_0058122 overexpression elevated the levels of pro-apoptotoc proteins Bax and cleaved caspase-3 and reduced the levels of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Conversely, hsa_circ_0058122-silenced cells displayed reduced BAX and cleaved caspase-3 expression and increased BCL-2 expression, even after exposure to Dex (Figure 3E). Taken together, these data suggest that hsa_circ_0058122-silencing can reverse DEX-induced HUVECs apoptosis.
3.3 hsa_circ_0058122 serves as sponge for hsa-miR-7974
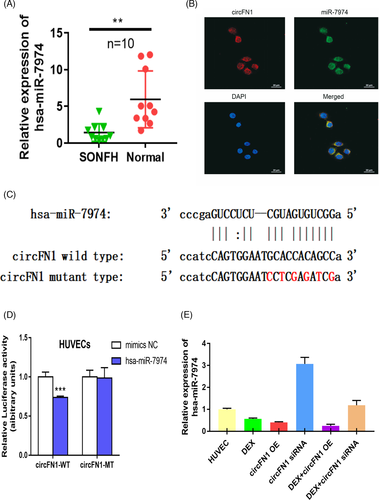
circRNAs are known to serve as miRNA sponges and regulate targeted gene expression. To elucidate the underlying mechanism of hsa_circ_0058122 action, we predicted miRNAs targets of hsa_circ_0058122 using the MiRDB21 and circBank22 databases. hsa-miR-7974 was identified by both databases as a possible target for hsa_circ_0058122. Next, we assessed miR-7974 levels in 10 pairs of SONFH tissue and adjacent normal tissues using qRT-PCR. Based on our results, miR-7974 had a very low expression in all SONFH tissues (Figure 4A). To verify whether hsa_circ_0058122 serves as an miR-7974 sponge, we firstly confirmed the co-localization of hsa_circ_0058122 and miR-7974 in the cytoplasm of HUVECs using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) (Figure 4B). Next, we performed a dual-luciferase reporter assay. The HUVECs were transiently transfected with psiCHECK2 vectors, containing either the WT or MUT hsa_circ_0058122 (Figure 4C), together with miR-7974 mimics or control. The luciferase assay revealed that the WT-hsa_circ_0058122, and miR-7974 mimic-incorporated cells had remarkably low luciferase activity, as compared to the MUT-hsa_circ_0058122 and control-incorporated cells (Figure 4D). Furthermore, in hsa_circ_0058122-overexpressed and Dex-treated HUVECs, miR-7974 had remarkably low expression. Upon transfection with hsa_circ_0058122 siRNA; however, the expression of miR-7974 increased despite exposure to Dex (Figure 4E). These results suggested that hsa_circ_0058122 might serve as a miRNA sponge for miR-7974.
3.4 hsa_circ_0058122 modulates IGFBP5 expression to promote HUVECs apoptosis
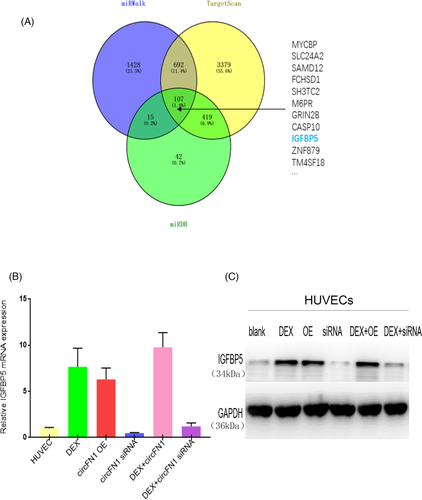
To further identify the signaling pathway whereby hsa_circ_0058122 modulates HUVECs apoptosis, we scanned 3 databases, namely miRDB,23 targetscan,24 and miRWalk,25 to predict potential targets for miR-7974. Based on our search, IGFBP5 was identified as a potential target by all algorithms (Figure 5A). Moreover, DEX-treated HUVECs produced an increase in IGFBP5 levels relative to controls. Similarly, IGFBP5 was upregulated in hsa_circ_0058122-overexpressed cells, both in the presence of or absence of Dex. In contrast, IGFBP5 was downregulated in hsa_circ_0058122-silenced cells in both DEX-stimulated HUVECs and unstimulated HUVECs (Figure 5B,C). Taken together, these results suggest a Dex stimulated hsa_circ_0058122- miR-7974-IGFBP5 axis in HUVEC cells that may explain Dex-mediated apoptosis.
4 DISCUSSION
Multiple studies have reported tissue-specific expressions of circRNAs, which when disrupted, can contribute to the pathogenesis and progression of multiple diseases,26, 27 including cardiovascular diseases,28 neurological disorders,29 and cancers.30, 31 In recent years, several studies examined differentially expressed miRNAs in SONFH tissues and established a long list of miRNAs associated with the disease.32-35 However, only a few studies have explored the role of circRNAs in the pathophysiology of SONFH. One such study by Zhu et al. recognized a circRNA expression profile, using peripheral blood samples from SONFH patients and healthy volunteers. They discovered 345 differentially regulated circRNAs in SONFH relative to healthy controls.36 However, the Zhu et al. study lacked a large sample size and in-depth mechanism research.
In our study, we demonstrated highly hsa_circ_0058122 expression and simultaneous low miR-7974 levels in SONFH tissues relative to normal tissues. Additionally, we revealed that DEX stimulation of HUVECs markedly increased hsa_circ_0058122 expression, decreased miR-7974 expression, and increased IGFBP5 expression. Moreover, using hsa_circ_0058122 overexpression, we verified that the DEX-induced apoptosis was facilitated by hsa_circ_0058122. Alternately, we demonstrated that hsa_circ_0058122-silencing suppressed apoptosis in DEX-treated HUVECs. Taken together, these evidences suggest that the Dex-induced apoptosis involves hsa_circ_0058122, miR-7974, and IGHBP5 in HUVEC cells.
Much of the circRNA-mediated mechanism in SONFH still remains unclear. circRNAs can exert their biological functions by sponging miRNAs or by acting as a scaffold for RNA binding proteins.37, 38 Several reports also suggest that they can translate into polypeptides and regulate downstream gene expression.39-42 To elucidate the Dex-mediated apoptotic mechanism in our study, we performed luciferase reporter and FISH assays. Based on our result, hsa_circ_0058122 physically interacted with miR-7974 to inhibit its actions. Subsequently, we identified IGFBP5 as a target gene of miR-7974 and confirmed high IGFBP5 expression levels in SONFH tissues and hsa_circ_0058122-overexpressed cells. IGFBP5 is a highly conserved member of the IGFBP family and is involved in multiple physiological processes such as cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion. In a study by Kim et al., IGFPB5 was found to be highly expressed in senescent HUVECs, resulting in a p53-mediated cell apoptosis.43 In previous studies of IGFBP5 regulating bone growth, IGFBP5 has been reported to have the behavior of enhancing and inhibiting IGF.44-46 Till now, there have been no reports on the association between IGFBP5 and SONFH. However, based on our study, Dex upregulated hsa_circ_0058122 expression, which sponged miR-7974, thereby increasing IGFBP5 expression, which contributed to the Dex-mediated apoptosis.
Our study has certain limitations. Firstly, our investigation was only conducted in vitro and will need to be repeated in vivo. Secondly, we had a low clinical sample size. In summary, we demonstrated that DEX modulated the hsa_circ_0058122/miR-7974/IGFBP5 axis to drive apoptosis of HUVECs. This finding provides further insights into blood supply insufficiency contributing to SONFH pathogenesis. Furthermore, hsa_circ_0058122, due to its tight link to SONFH, may serve as a potential diagnostic biomarker or a drug target for SONFH therapy.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We appreciate the Third Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University for offering the equipment and experiment condition.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.




