Hsa_circ_0041268 promotes NSCLC progress by sponging miR-214-5p/ROCK1
Abstract
Circular RNAs hold significant regulatory functions during various tumors. However, the exact hsa_circ_0041268 roles in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) along with regulatory mechanism are unknown. In this study, RT-qPCR was used to perceive hsa_circ_0041268 expressions in NSCLC cell lines. Our team constructed small interfering RNA for hsa_circ_0041268. NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and tumorigenesis in nude mice were assayed to confirm hsa_circ_0041268 activities in NSCLC cells. We then used bioinformatics and luciferase reporter analyses to characterize the hsa_circ_0041268 downstream targets. The result shows that the expressions of hsa_circ_0041268 incremented in NSCLC cell lines and hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation decreased cell proliferation and migration. ROCK1 and miR-214-5p were hsa_circ_0041268 downstream targets. miR-214-5p downregulation or ROCK1 overexpression restored migration and proliferation abilities after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing. ROCK1 overexpression renovated migration and proliferation abilities after miR-214-5p overexpression. In vivo investigations confirmed that hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation inhibited tumor formation and metastasis in nude mice xenografts. Together, results demonstrated that hsa_circ_0041268 acted as tumor promoter through novel hsa_circ_0041268/miR-214-5p/ROCK1 axis, which highlighted its potential as NSCLC therapeutic agent.
1 INTRODUCTION
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a major reason for cancer mortality all over the globe. It accounts for 80–85% lung cancer cases.1 Improvements for the treatment and diagnosis of early-stage NSCLC have increased patient survival.2 Although there have been studies reporting NSCLC carcinogenesis molecular mechanisms, the mechanisms are still unclear. It is, therefore, important to better understand the mechanisms of NSCLC tumorigenesis and to identify novel NSCLC therapeutic targets as well as diagnostic biomarkers.
Circular RNAs (circ/circRNAs) constitute a class of covalently closed RNA molecules.3-5 Increasing study has found that circRNAs play an important role in tumorigenesis and metastasis and thus may be used as therapeutic targets of cancers.6, 7 circRNA expression is tissue-specific, and the majority of circRNAs introduce differential expression patterns in various species, cells, and tissues.8, 9 Most circRNAs have lengths of <1500 nucleotides, which have mean length ~500 nucleotides.10, 11 Many circRNAs are inferred to be closely associated with NSCLC prognosis and recurrence.12, 13 A former investigation advised that hsa_circRNA_012515 expressed highly and was associated with NSCLC patient prognoses.14 The circP4HB enhances NSCLC metastasis and aggressiveness via sponging miR-133a-5p.15 This study also reported that shsa_circ_0041268 was abnormally expressed, although hsa_circ_0041268 role in NSCLC remains unknown. The present research, therefore, identified hsa_circ_0041268 molecular mechanism in the progression of NSCLC.
2 MATERIALS & METHODS
2.1 Ethics statement
Our team obtained BALB/c nude mice aged 4 weeks (15–20 g) from SLARC (Shanghai, China). Ethics committee in Renji Hospital oversaw the animal experiments.
2.2 Cell culture
Our team obtained human pulmonary epithelial cell line BEAS-2B as well as NSCLC cell lines, H1755, H1650, PC9, and A549 from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). Our team cultured all cell lines in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) (Gibco, Grant Island, NY, USA), which included fetal bovine serum (FBS) of 10% in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37 °C.
2.3 Cell proliferation and clone formation assays
Cell proliferation was analyzed using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Our laboratory seeded transfected cells in 96-well plates in triplicate with 2000 cells/well, which we assayed the viabilities at 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 day after seeding. We analyzed colony formation of transfected cells, which we seeded in 96-well plates with 2000 cells/well and cultured them in DMEM with 10% FBS for 10 day. Technician determined cell numbers and photographed colonies after fixation and staining.
2.4 Cell migration assay
Our laboratory assayed cell migration in Transwell 24-well chambers (Corning, Corning, NY, USA) using 8-μm pore membranes (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Technician added 1 × 105 cells in 200 µL serum-free medium to upper chamber, while lower chamber comprised 500 µL of complete medium as chemoattractant. Cells invading lower chamber were fixed after 1 day using 4% paraformaldehyde of 4% for half of an hour, which were stained using crystal violet for 10 min.
2.5 Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
Our team obtained RNA through TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) as well as synthesized cDNA utilizing pTRUEscript First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Aidlab, Beijing, China). Our team designed RT-qPCR utilizing a 2× SYBR Green qPCR mix (Invitrogen) and ABI 7900HT qPCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). We decided fold changes through 2−ΔΔCT method. RT-qPCR amplification used the primers: hsa_circ_0041268, forward, 5′-GATGGCTTGTCATCCTG-3′, reverse, 5′-CATGTTGGGGTCATGC-3′; miR-214-5p, forward, 5′-TCTCTTGCTATAGAAGCACAAC-3′, reverse, 5′-TCCTCCACAATCATGCTGTGT-3′; ROCK1, forward, 5′-AACATGCTGCTGGATAAATCTGG-3′, reverse, 5′-TGTATCACATCGTACCATGCCT-3′; U6, forward, 5′-GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT-3′, reverse, 5′-CGCTTCAGAATTTGCGTGTCAT-3′; glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), forward: 5′-AATCCCATCACCATCTTCC-3′, reverse, 5′-CATCACGCCACAGTTTCC-3′. Levels of ROCK1 and hsa_circ_0041268 were normalized to GAPDH. We normalized miR-214-5p levels to U6.
2.6 Metastasis assay and tumor xenograft formation
Our team employed BALB/c nude mice. H1650 cells with or not transfected siRNA against hsa_circ_0041268 were applied for in vivo experiments. We injected 5 × 106 viable cells into nude mice right flanks. Our team detected tumor sizes each 5 day utilizing vernier caliper and computed the tumor magnitude by equation: 0.5 × length × width2. At 30-day post-implantation, we euthanized mice, followed by Ki-67 staining.
2.7 The dual luciferase reporter assay
Our team constructed reporter plasmids through putting hsa_circ_0041268 or ROCK1 3′-UTR sequence into pmirGLO vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Our laboratory co-transfected reporter plasmids along with miR-214-5p mimics into human embryonic kidney (HEK) 239T cells employing Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). After 2-day culturing, technician detected firefly and Renilla luciferase activities leveraging Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega).
2.8 Statistical analyses
Results are denoted by mean ± standard deviation (SD). We used Prism (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA) to analyze the significance between groups. P value ≤0.05 was assumed to be statistically significant.
3 RESULTS
3.1 hsa_circ_0041268 expression incremented in NSCLC cells and hsa_circ_0041268 knockdown inhibited cell migration and proliferation
Increasing studies have reported important functions of circRNA in regulating cancer progression, including in breast cancer,16 lung cancer,17 prostate cancer,18 and gastric cancer.19 Our data suggested that hsa_circ_0041268 expressed abnormally in NSCLC cells. RT-qPCR analyses showed that hsa_circ_0041268 expression incremented in NSCLC cell lines, H1755, H1650, PC-9, and A549, when compared to HEAS-2B cells (Figure 1A). In addition, H1650 and A549 cells had significantly higher expressions of hsa_circ_0041268. We then constructed a siRNA against hsa_circ_0041268 (si-circ-0041268), which was transfected into H1650 and A549 cells. The RT-qPCR results illustrated that hsa_circ_0041268 expression decreased significantly in H1650 and A549 cells after si-circ-0041268 transfection (Figure 1B). CCK-8 detection (Figure 1C, D) and analysis of cloning formation (Figure 1E, F) showed that hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation suppressed A549 and H1650 cell proliferations. Transwell migration analyses verified that hsa_circ_0041268 silencing decremented migration capabilities in A549 and H1650 cells (Figure 1E-F), saying that hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation suppressed NSCLC cell proliferation as well as migration. Bioinformatics results showcased that hsa_circ_0041268 was located in chromosome chr17:1553922–1554250 and that hsa_circ_0041268 combined with the exon from the PRPF8 gene having a length of 328 bp, which we named hsa_circ_0046701 as circ-PRPF8 (Figure 1G).
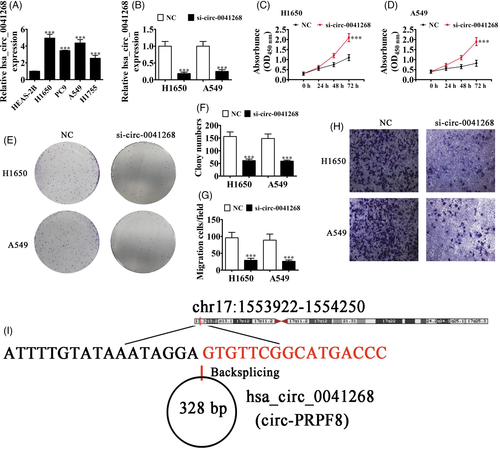
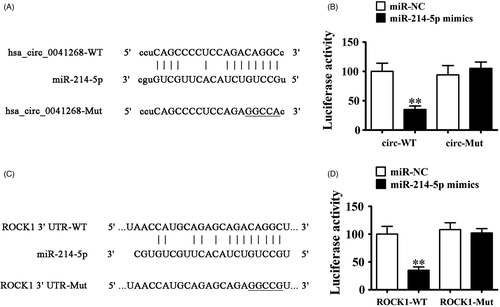
3.2 miR-214-5p and ROCK1 are downstream targets of hsa_circ_0041268
To better characterize the hsa_circ_0041268 regulatory mechanism, bioinformatics analyses were used to predict hsa_circ_0041268 downstream targets. Data showcased that miR-214-5p was possible hsa_circ_0041268 downstream target. We then made luciferase reporter vector with miR-214-5p wild-type (WT) and mutant (MUT) sites using hsa_circ_0041268 sequence (Figure 2A). Luciferase reporter assay verified that luciferase activity decreased after hsa_circ_0041268 WT vector and miR-214-5p mimic transfections (Figure 2B), advising that hsa_circ_0041268 interacted with miR-214-5p directly. More studies confirmed that ROCK1 was miR-214-5p downstream target (Figure 2C). In addition, luciferase reporter results verified that miR-214-5p interacted with ROCK1 3′-UTR (Figure 2D).
3.3 miR-214-5p inhibited or ROCK1 overexpression reversed hsa_circ_0041268 knockdown effects on H1650 and A549 cell proliferation and migration
We detected regulatory correlations with hsa_circ_0041268, miR-214-5p, and ROCK1 in H1650 and A549 cells after transfecting with si-circ-0041268, miR-214-5p inhibitor, and the ROCK1 overexpression vector singly or combined. RT-qPCR results showcased that hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation inhibited hsa_circ_0041268 expression. Inhibiting miR-214-5p or ROCK1 overexpressions could not recover hsa_circ_0041268 expression (Figure 3A, B), suggesting that miR-214-5p and ROCK1 were hsa_circ_0041268 downstream targets. For miR-214-5p, data verified that hsa_circ_0041268 silencing promoted miR-214-5p expression. After miR-214-5p inhibitor transfection, miR-214-5p expression decreased even after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing, but ROCK1 upregulation could not reverse miR-214-5p expression after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing (Figure 3C and D) revealing that ROCK1 was miR-214-5p downstream target. For ROCK1, RT-qPCR analyses elucidated that hsa_circ_0041268 silencing inhibited ROCK1 expression, but miR-214-5p downregulation partially recovered ROCK1 levels (Figure 3E and F), validating that ROCK1 was miR-214-5p downstream target.

Analysis of cloning constitution showed that hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation inhibited H1650 and A549 cell proliferations, but miR-214-5p downregulation or ROCK1 overexpression recovered proliferation abilities of H1650 and A549 cells after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing (Figure 3G-I). Transwell migration analyses also found that miR-214-5p downregulation or ROCK1 overexpression retrieved H1650 and A549 cell migration abilities after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing (Figure 3J-L), saying that hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation suppressed NSCLC cell proliferation and migration. These results illustrated that miR-214-5p and ROCK1 were hsa_circ_0041268 downstream targets and that miR-214-5p downregulation or ROCK1 overexpression retrieved proliferation and migration abilities after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing.
3.4 ROCK1 overexpression reversed the miR-214-5p overexpression effects on A549 and H1650 cell migration and proliferation
We then determined the regulatory relationships of ROCK1 and miR-214-5p in A549 and H1650 cells after miR-214-5p mimic and ROCK1 overexpression vector transfections, singly or combined. RT-qPCR verified that miR-214-5p upregulation promoted miR-214-5p expression, while ROCK1 overexpression could not recover miR-214-5p expressions in both H1650 and A549 cells (Figure 4A and B), suggesting that ROCK1 was miR-214-5p downstream target. For ROCK1, results showcased that miR-214-5p overexpression decreased ROCK1 expression. After being transfected with ROCK1 overexpression vector, ROCK1 expression incremented even after miR-214-5p upregulation (Figure 4C, D), confirming that ROCK1 was miR-214-5p downstream target.
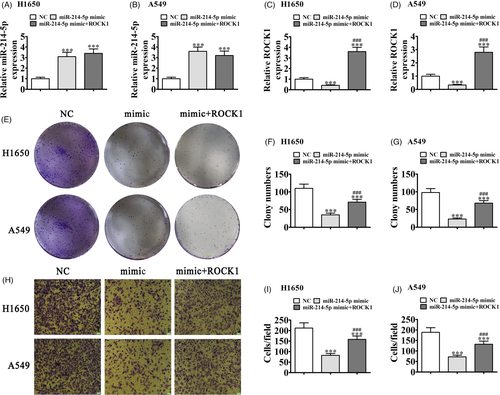
Analyses of cloning formation showed that ROCK1 overexpression recovered H1650 and A549 cell proliferation abilities after miR-214-5p upregulation (Figure 4E-G). Transwell migration also showed that miR-214-5p upregulation suppressed cell migration, though ROCK1 overexpression restored migration abilities of H1650 and A549 cells after miR-214-5p overexpression (Figure 4H-J), suggesting that ROCK1 overexpression restored proliferation and migration abilities after miR-214-5p overexpression.
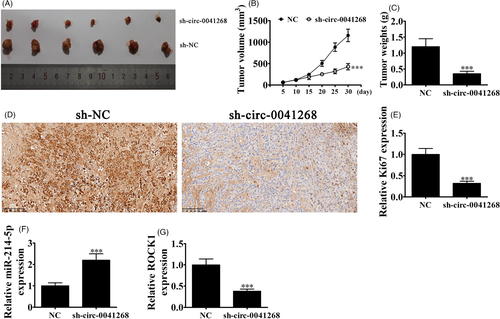
3.5 Hsa_circ_0041268 knockdown suppresses cancer growth in nude mouse xenograft model
Our team utilized H1650 cells that transfected with hsa_circ_0041268 lentiviral interference vectors to assay tumor growth in a nude mouse xenograft model. Tumor sizes 5 day after grafting were measured using vernier caliper. Knockdown of hsa_circ_0041268 decreased the xenograft weight and volume (Figure 5A-C). Immunohistochemical staining also showed decrement in Ki-67 positivity, which was consistent with tumor growth suppression by hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation (Figure 5D and E). RT-qPCR demonstrated that miR-214-5p expression incremented in tumor tissues with hsa_circ_0041268 silencing (Figure 5F), but ROCK1 expression decremented after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing (Figure 5G).
4 DISCUSSION
circRNAs are essential regulators in different pathological and physiological processes.20 Increasing evidence has shown that circRNA expression was highly associated to clinical patient identities, while abnormal expression usually resulted in malignant behaviors like metastasis and proliferation.6 Circ_0000463 absence suppressed the malignant behaviors and glutamine metabolism of NSCLC cells through mediating miR-924/SLC1A5 axis.21 CircWHSC1 is an independent indicator of poor prognosis in NSCLC patients and functions as a ceRNA of miR-296-3p to up-regulate AKT3, consequently promotes NSCLC cell growth and metastasis.22 Based on these results, it is essential to provide possible correlations between tumor progressions and the levels of circRNAs. Current research suggested that hsa_circ_0041268 functioned importantly during NSCLC progression.
Data showed that hsa_circ_0041268 expression increased in NSCLC cells. hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation inhibited cell proliferation and migration. Bioinformatics analyses showed that miR-214-5p and ROCK1 were hsa_circ_0041268 downstream targets. Increasing reports have illustrated that circRNA can regulate various physiological and pathological progressions via sponging miRNAs.23, 24 Our investigation showed that miR-214-5p was a hsa_circ_0041268 downstream target. Luciferase reporter assay confirmed that hsa_circ_0041268 interacted with miR-214-5p. Previous studies reported that miR-214-5p generated inhibitory effects upon cancer migration and proliferation.25-27 microRNA-214-5p suppression enhanced extracellular matrix formation and cell survival through targeting collagen type IV alpha 1 in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells.28 Reports also provided that miR-214-5p is tumor inhibitor.29, 30 Current study elucidated that hsa_circ_0041268 silencing promoted miR-214-5p expression. The miR-214-5p downregulation recovered migration and proliferation abilities after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing, and miR-214-5p overexpression significantly inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation as well as migration.
Further studies showed that Rho-associated kinase 1 (ROCK1) was miR-214-5p downstream target, which was validated using luciferase reporter assay. Tumor-suppressor effects of ROCK1 knockdown are reported in various tumors. For instance, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma migration and invasion were decreased in vitro through ROCK1 elimination.31 Additionally, ROCK1 regulated the TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in NSCLC cells, which was dependent on the presence of miR-335-5p.32 Increased cytoplasmic ROCK1 levels were also necessary to maintain human myeloma cell proliferation and survival.33 In prostate cancer, increased ROCK1 expression was an early biomarker of poor prognoses, because it was associated with the genetic instability of cancer cells. ROCK1 knockdown inhibits NSCLC progression through activating the LATS2-JNK signaling pathway.34 Our data found that hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation or miR-214-5p overexpression suppressed ROCK1 expression. ROCK1 overexpression recovered proliferation and migration capabilities after hsa_circ_0041268 silencing or miR-214-5p overexpression, showing that hsa_circ_0041268 downregulation inhibited NSCLC proliferation and migration via miR-214-5p/ROCK1 axis regulation.
In summary, our results found that hsa_circ_0041268 enhanced oncogenesis through functioning as miR-214-5p sponge, which could therefore be a novel NSCLC prognostic marker. Targeting hsa_circ_0041268/miR-214-5p/ROCK1 axis could be possible therapy for NSCLC patients.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82003142).
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The authors declare that all data in this study were availability.




