Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Front Cover, Volume 43, Issue 7
- Page: i
- First Published: 08 June 2022

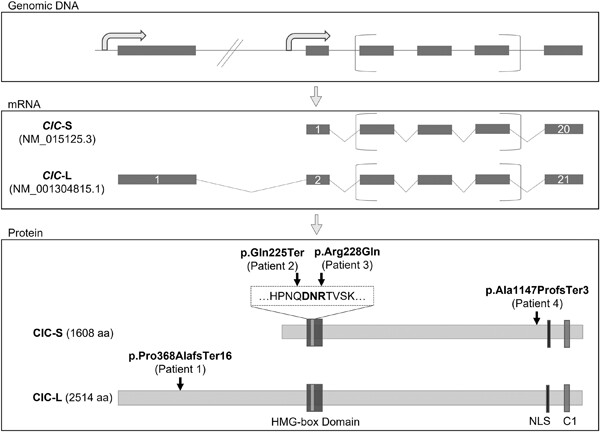
Front Cover: The cover image is based on the Research Article Novel CIC variants identified in individuals with neurodevelopmental phenotypes by Qiumin Tan et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.24346.
Back Cover, Volume 43, Issue 7
- Page: ii
- First Published: 08 June 2022
Back Cover: The cover image is based on the Research Article Phenotypic and mutational spectrum of ROR2-related Robinow syndrome by Juliana Forte Mazzeu de Araujo et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.24375.
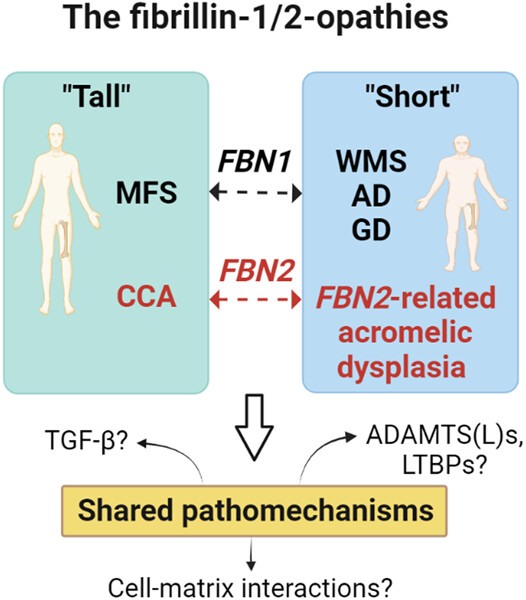
The fibrillinopathies: New insights with focus on the paradigm of opposing phenotypes for both FBN1 and FBN2
- Pages: 815-831
- First Published: 14 April 2022
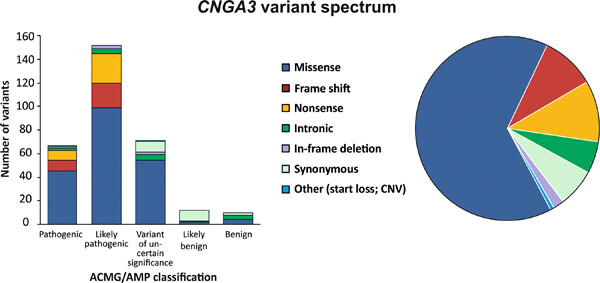
Comprehensive variant spectrum of the CNGA3 gene in patients affected by achromatopsia
- Pages: 832-858
- First Published: 25 March 2022
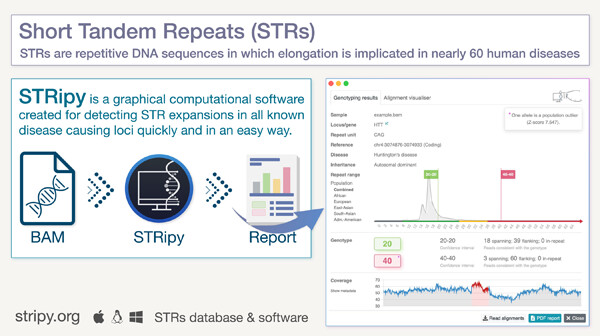
STRipy: A graphical application for enhanced genotyping of pathogenic short tandem repeats in sequencing data
- Pages: 859-868
- First Published: 08 April 2022
Pathogenic missense variants altering codon 336 of GARS1 lead to divergent dominant phenotypes
- Pages: 869-876
- First Published: 25 March 2022
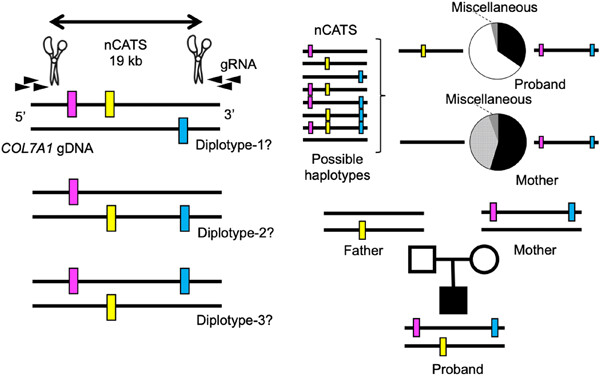
Cas9-guided haplotyping of three truncation variants in autosomal recessive disease
- Pages: 877-881
- First Published: 21 April 2022
Estimating the proportion of pathogenic variants from breast cancer case–control data: Application to calibration of ACMG/AMP variant classification criteria
- Pages: 882-888
- First Published: 22 February 2022
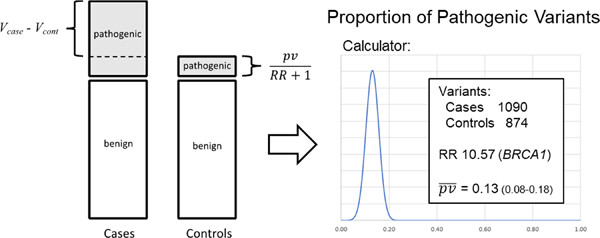
If the risk associated with pathogenic variants (PV) in a gene is known genetic case-control studies can be used to estimate how many typical PV are present in a set observed variants. We describe a simple maximum likelihood calculation for this purpose and use it to show that for breast cancer predisposition genes a small but important group of pathogenic variants are located in non-coding regions and that the proportion and location of pathogenic missense variants varies greatly between genes.
Novel CIC variants identified in individuals with neurodevelopmental phenotypes
- Pages: 889-899
- First Published: 14 February 2022
Phenotypic and mutational spectrum of ROR2-related Robinow syndrome
- Pages: 900-918
- First Published: 28 March 2022
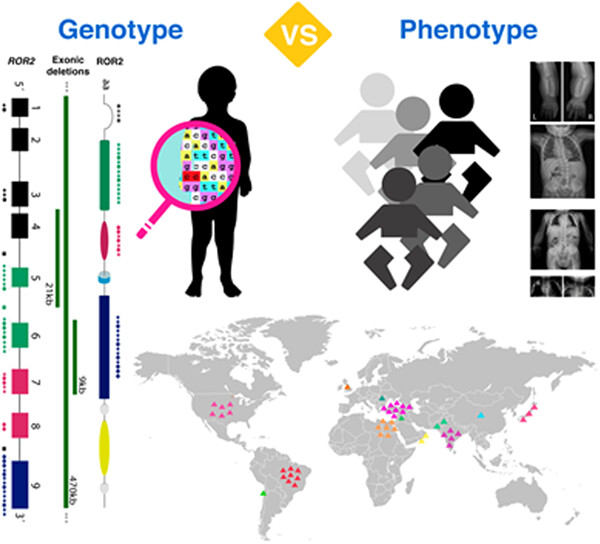
Disease-causing variants in ROR2, contribute to a clinically recognizable autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome trait phenotype with multiple skeletal defects. Molecular diagnosis and a comprehensive quantitative clinical evaluation delineated the phenotypic spectrum of ROR2-related Robinow syndrome.
Comparison of the frequency of loss-of-function LZTR1 variants between schwannomatosis patients and the general population
- Pages: 919-927
- First Published: 07 April 2022
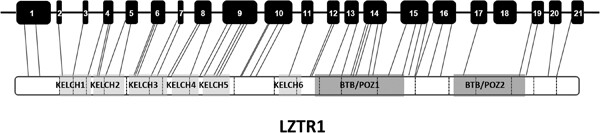
Loss-of-function (LoF) LZTR1 variants have been associated with schwannomatosis. However, many LoF LZTR1 variants exist in Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) in people who do not have clinical symptoms of schwannomatosis. We show here that LoF LZTR1 variants are strongly enriched in schwannomatosis patients, but the high frequency of LoF LZTR1 variants in gnomAD data suggest a reduced risk of schwannomas in comparison to other schwannoma predisposing genes.
Effects of 14 F9 synonymous codon variants on hemophilia B expression: Alteration of splicing along with protein expression
- Pages: 928-939
- First Published: 07 April 2022
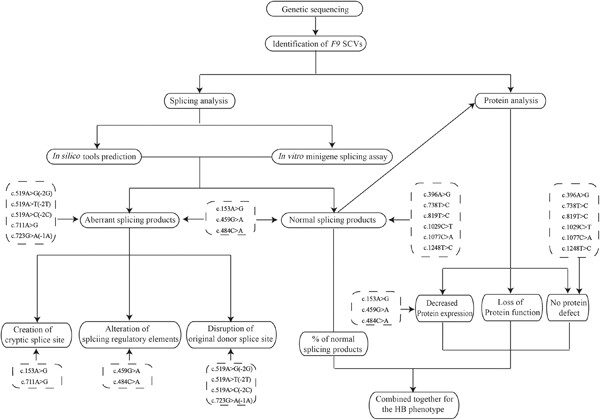
Effects of 14 F9 synonymous codon variants on hemophilia B expression: alteration of splicing along with protein expression. The impacts of 14 F9 SCVs on splicing and protein expression were detected using a combination of in silico prediction, in vitro minigene assay and cell expression detection. 5 SCVs produced almost all aberrant splicing isoforms, and 3 SCVs presented a partial defect in both splicing and protein secretion. The rest 6 SCVs had no effect on neither splicing nor protein expression.
DNAH14 variants are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders
- Pages: 940-949
- First Published: 19 April 2022
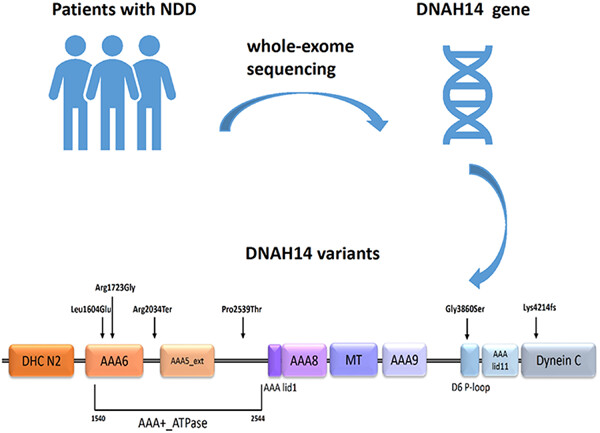
Genetics plays a substantial role in the etiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. By trio whole-exome sequencing, three unrelated patients with a spectrum of neurological and developmental phenotypes carrying compound heterozygous variants in DNAH14 were identified, which indicated that variants in DNAH14 could lead to previously unrecognized neurodevelopmental disorders.
Feasibility and limitations of cultured skin fibroblasts for germline genetic testing in hematologic disorders
- Pages: 950-962
- First Published: 14 April 2022
Short amplicon reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction detects aberrant splicing in genes with low expression in blood missed by ribonucleic acid sequencing analysis for clinical diagnosis
- Pages: 963-970
- First Published: 27 April 2022