Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
Emerging role of RNF2 in cancer: From bench to bedside
- Pages: 5453-5465
- First Published: 05 January 2021
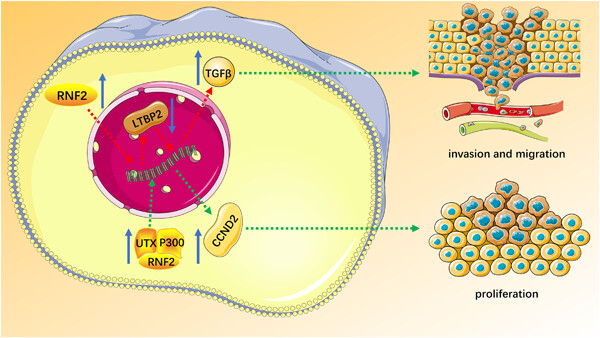
- (1).
Elevated expression of RNF2 is closely related to the occurrence and progression of cancer.
- (2).
RNF2 is involved in a variety of cellular signaling pathways associated with cancer occurrence and progression.
- (3).
RNF2 may serve as a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker and therapeutic target.
The direct and indirect regulation of follicular T helper cell differentiation in inflammation and cancer
- Pages: 5466-5481
- First Published: 09 January 2021
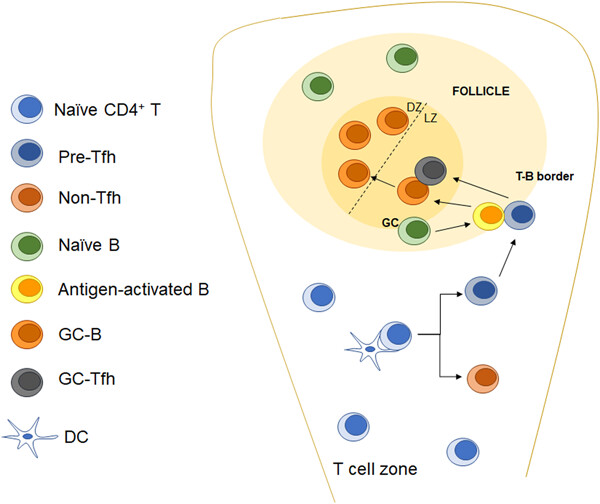
The process of naïve CD4+ T cells differentiating into follicular T helper (Tfh) cells and inducing the formation of germinal centers (GCs). Naïve CD4+ T cells differentiate into pre-Tfh cells under the activation of dendritic cells (DCs). The pre-Tfh cells migrate to the T-B bounder and combine with activated B cells to further differentiate into GC-Tfh cells. GC-Tfh cells induce the maturation of GC-B cells to form GCs.
Extracellular vesicles mediate cellular interactions in renal diseases—Novel views of intercellular communications in the kidney
- Pages: 5482-5494
- First Published: 11 January 2021
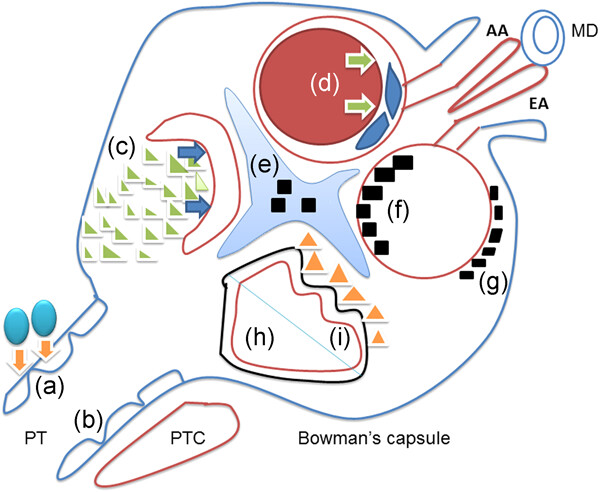
Graphical abstract
In the past several decades, the role of extracellular vesicles (EV) in intercellular communications, and the uptake of EVs by recipient cells through phagocytosis and endocytosis have been elucidated. The new knowledge on EVs expands over the classical mechanisms of cellular interaction, and may change our way of thinking of renal pathophysiology in the subcellular scale. Based on some ultrastructural discoveries in the kidney, this review will focus on the role of EVs in intercellular communications, their internalization by recipient cells, and their relationship to renal pathology.
Gold digging: Searching for gut microbiota that enhances antitumor immunity
- Pages: 5495-5511
- First Published: 16 January 2021
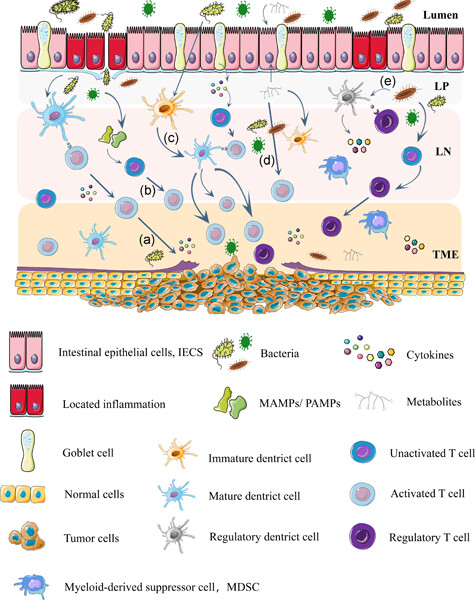
In this review, we classified the relative microbes according to their taxonomic information and aimed to clarify their modulatory functions and potent effects on immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) immunotherapy by focusing on recent trials investigating the relationships between the gut microbiota and ICIs. MAMP, microbe-associated molecular patterns; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern.
Signaling, metabolism, and cancer: An important relationship for therapeutic intervention
- Pages: 5512-5532
- First Published: 12 February 2021
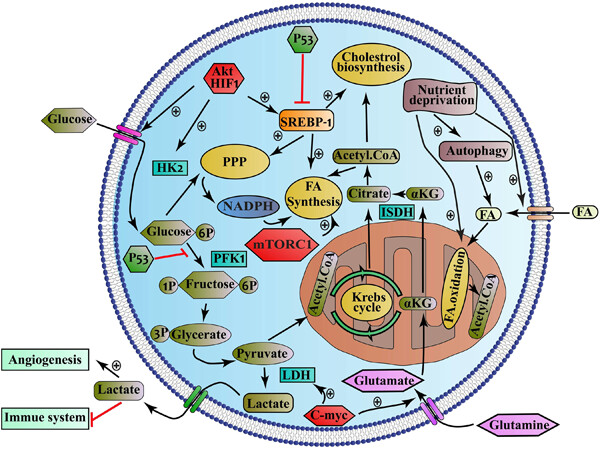
Various studies have shown that metabolism is reprogrammed in cancer cells, and this reprogramming which mediated by signaling pathways is in line with meeting the metabolic needs of cancer cells for growth, proliferation, survival, invasion, and metastasis. Antitumor compounds that have the ability to target both metabolism and signaling may be helpful in the treatment of cancer.
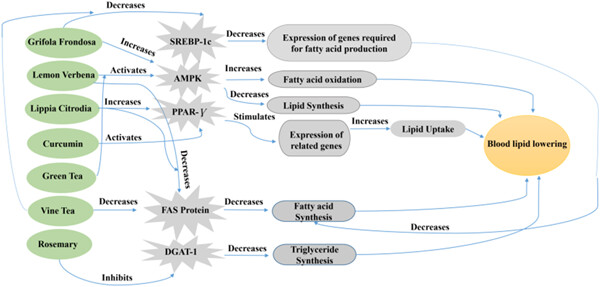
Herbal therapy as a promising approach for regulation on lipid profiles: A review of molecular aspects
- Pages: 5533-5546
- First Published: 20 January 2021
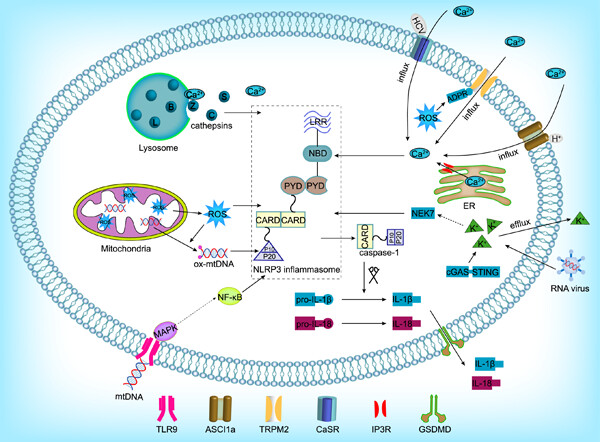
The NLRP3 inflammasome: Multiple activation pathways and its role in primary cells during ventricular remodeling
- Pages: 5547-5563
- First Published: 20 January 2021
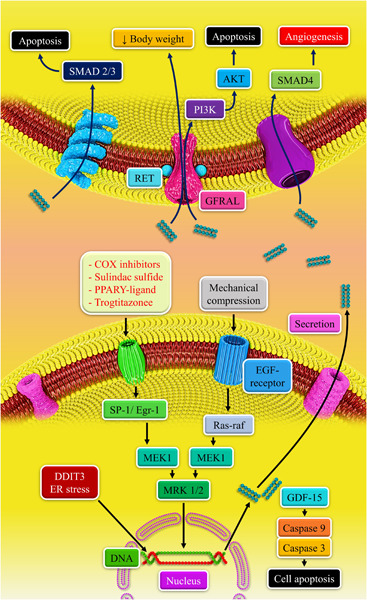
GDF-15: Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance in glioblastoma multiforme
- Pages: 5564-5581
- First Published: 12 February 2021
The role of HDAC11 in obesity-related metabolic disorders: A critical review
- Pages: 5582-5591
- First Published: 22 January 2021
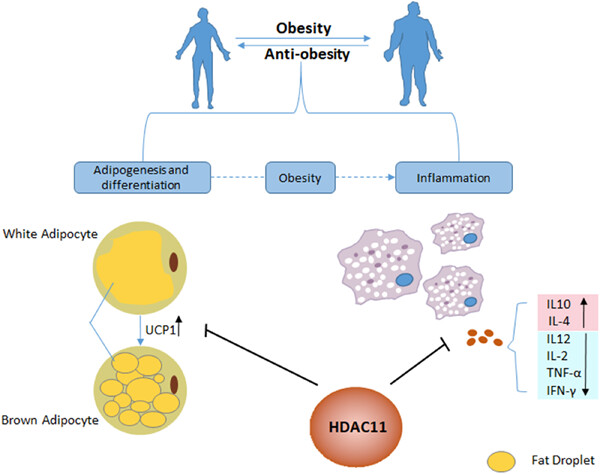
Currently, research on new key regulatory functions of histone deacetylase 11 (HDAC11) in metabolic homeostasis is receiving more and more attention, and HDAC11 has also become a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of obesity and obesity-related diseases. Here, we summarized the latest literature on the role of HDAC11 in regulating the progress of obesity-related metabolic disorders.
Comparative hematopoiesis and signal transduction in model organisms
- Pages: 5592-5619
- First Published: 25 January 2021
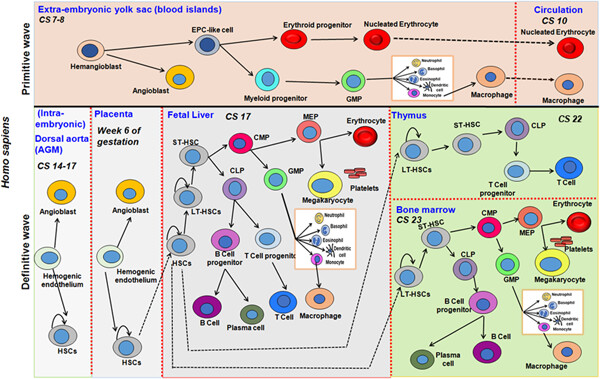
Graphical abstract
Our review article summarizes the ontogeny of hematopoiesis along with information on anatomical sites and developmental stages of hematopoiesis in four research model organisms. We further discuss the signaling pathways essential for proper hematopoietic regulation and homeostasis.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
FAM201A knockdown inhibits proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating miR-7515/GLO1 axis
- Pages: 5620-5632
- First Published: 09 March 2021
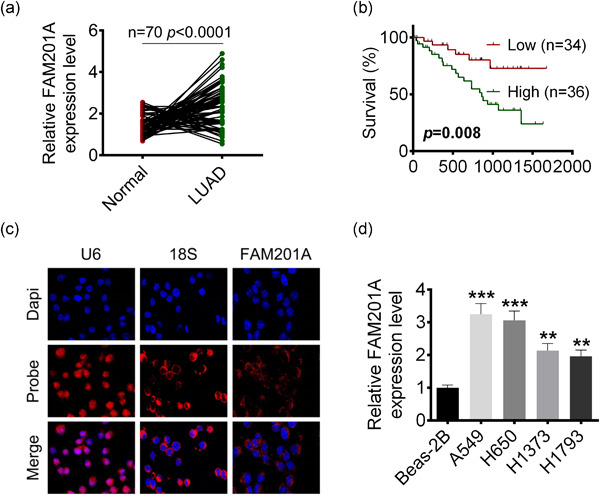
FAM201A was overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and predicted poor prognosis. FAM201A promoted cell proliferation, viability, migration and invasion and promoted cell apoptosis via competing endogenous sponging miR-7515 and accelerating GLO1 expression in LUAD. FAM201A might be a novel potential molecular target and a potential diagnostic biomarker in LUAD therapy.
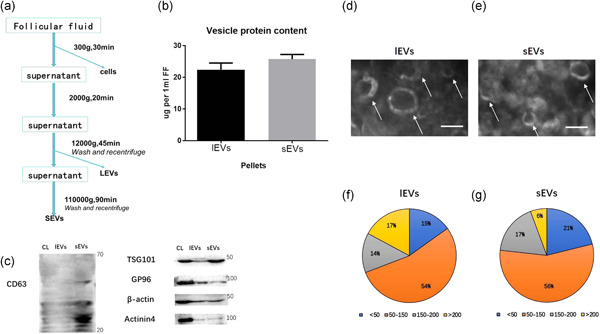
Identification of small extracellular vesicle subtypes in follicular fluid: Insights into the function and miRNA profiles
- Pages: 5633-5645
- First Published: 12 February 2021
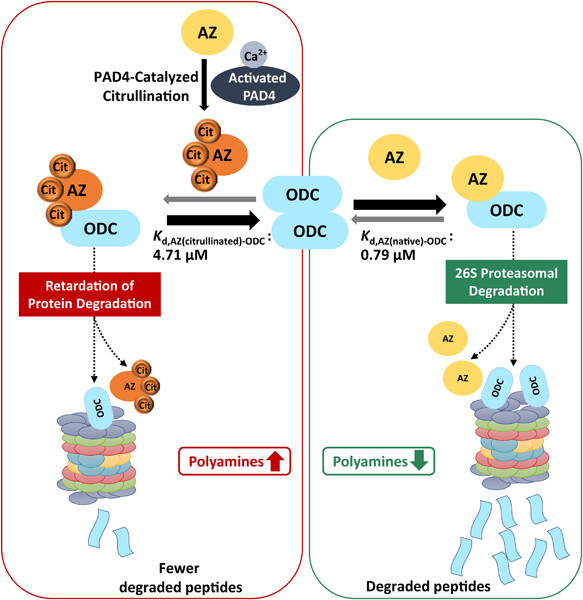
Regulation of polyamine homeostasis through an antizyme citrullination pathway
- Pages: 5646-5663
- First Published: 11 January 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Genomic integrity and mitochondrial metabolism defects in Warsaw syndrome cells: a comparison with Fanconi anemia
- Pages: 5664-5675
- First Published: 11 January 2021
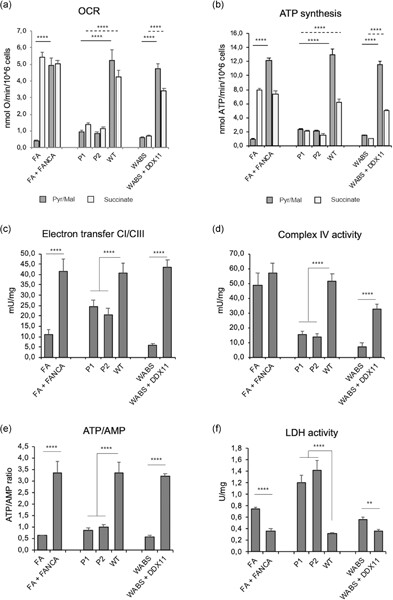
This study reports for the first time that Warsaw breakage syndrome (WABS), an ultra-rare genetic disease is characterized by an altered aerobic metabolism of mitochondria. This feature is in common with Fanconi anemia (FA), a cancer-prone genetic disease caused by genomic instability due to a defective DNA repair machinery. The association of DDX11 mutations, as well as FA ones, with defective mitochondrial activity, is intriguing not only to shed light on this fundamental process in cell physiology but also to fully understand the pathogenesis of these diseases.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
IL-37-induced activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β promotes IL-1R8/Sigirr phosphorylation, internalization, and degradation in lung epithelial cells
- Pages: 5676-5685
- First Published: 05 January 2021
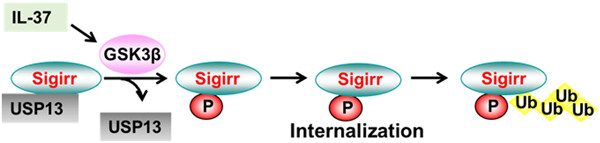
Graphical abstract
Interleukin (IL)-1R8/Sigirr plays an antiinflammatory role in innate and adaptive immunity. Glycogen synthesis kinase 3β-catalyzed IL-1R8/Sigirr phosphorylation triggers IL-1R8/Sigirr degradation through dissociation of IL-1R8/Sigirr with USP13. This study reveals a new molecular mechanism of regulation of IL-1R8/Sigirr stability.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
The transcriptional cofactor Jab1/Cops5 is crucial for BMP-mediated mouse chondrocyte differentiation by repressing p53 activity
- Pages: 5686-5697
- First Published: 03 January 2021
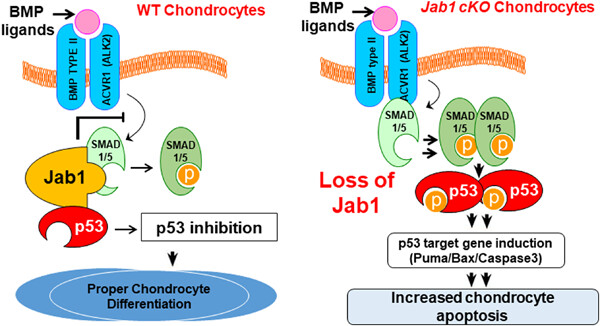
Graphical abstract
Our data showed that the delicate Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 (Jab1)-mediated crosstalk between BMP and p53 pathways is crucial to maintain proper chondrocyte survival and differentiation. Moreover, the appropriate Jab1 expression level is essential for proper skeletal development.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Calcineurin A gamma and NFATc3/SRPX2 axis contribute to human embryonic stem cell differentiation
- Pages: 5698-5713
- First Published: 03 January 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Osteoprotegerin is sensitive to actomyosin tension in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts
- Pages: 5714-5724
- First Published: 05 January 2021
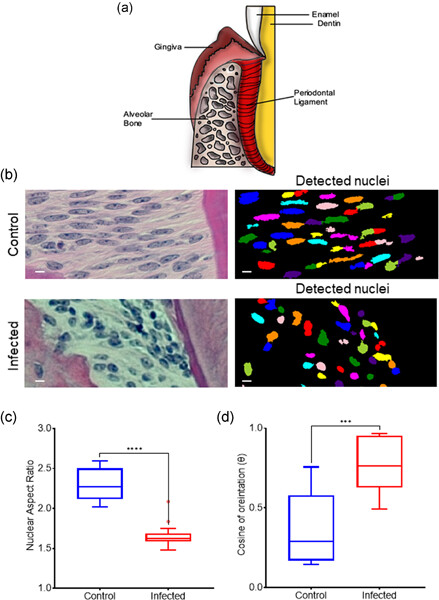
Graphical abstract
Although alveolar bone remodeling is well known to be caused by mechanical stresses generated on the periodontal ligament (PDL), the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Here we focus on a key cell type in the PDL, the periodontal ligament fibroblast (PdLF), which is known to be contractile and plays a key role in bone remodeling through expression of bone regulatory proteins. Because external mechanical stresses are balanced by modulation of intracellular actomyosin forces, we asked here if modulating intracellular contractility can by itself alter messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of key genes in human PdLFs. Disrupting different populations of actomyosin stress fibers by inhibiting myosin light chain kinase or Rho kinase which promote nonmuscle myosin II phosphorylation, altered mRNA levels of bone regulatory protein osteoprotegerin (OPG) and matrix metalloproteinases. Infection of PdLFs by two different types of periodontal bacteria (Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum) upregulated NMMII phosphorylation while downregulating OPG. Our results add in vitro support to the concept that PdLF tensional homeostasis may be crucial for its bone regulatory functions and may become dysregulated in the response to bacterial infection. They also highlight the importance of actomyosin tension in the overall process.
Cadherin-11 deficiency mitigates high-fat diet-induced inflammatory atrial remodeling and vulnerability to atrial fibrillation
- Pages: 5725-5741
- First Published: 16 January 2021
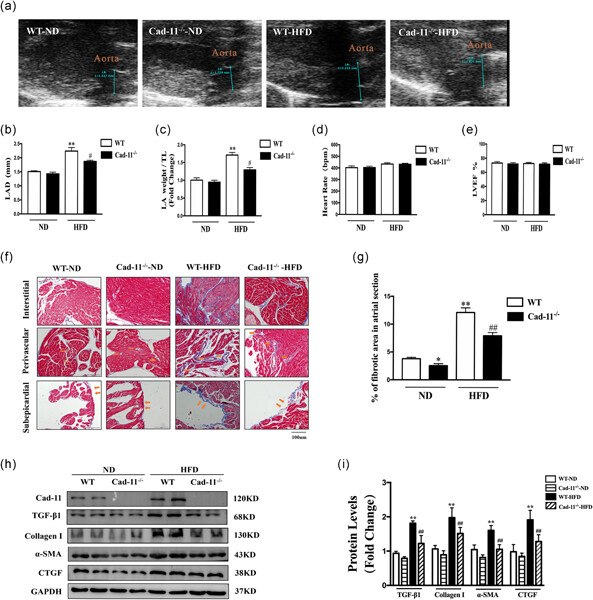
In this paper, we, for the first time, report a cadherin adhesion molecule cadherin-11 could make a contribution to diet-induced obesity and further verified how this molecule functions in clinical samples, cells, and model animals through a mechanism that involves activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways, thus finding a new treatment strategy for the pathogenesis of obesity-related atrial fibrillation.
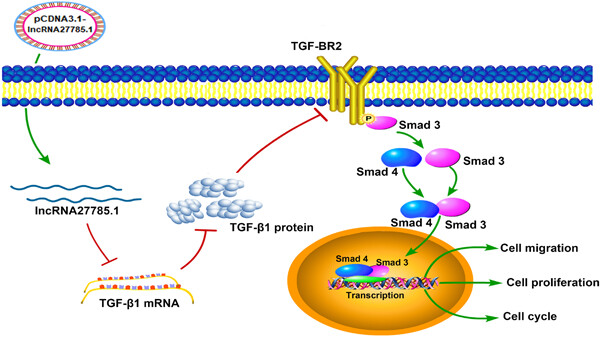
Effects and mechanism of lncRNA-27785.1 that regulates TGF-β1 of Sika deer on antler cell proliferation
- Pages: 5742-5756
- First Published: 03 January 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
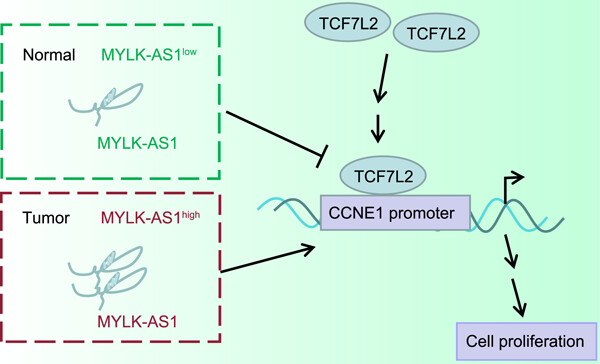
Silencing of long noncoding RNA MYLK-AS1 suppresses nephroblastoma via down-regulation of CCNE1 through transcription factor TCF7L2
- Pages: 5757-5770
- First Published: 12 January 2021
N-(3-oxododecanoyl)- l -homoserine lactone disrupts intestinal epithelial barrier through triggering apoptosis and collapsing extracellular matrix and tight junction
- Pages: 5771-5784
- First Published: 05 January 2021
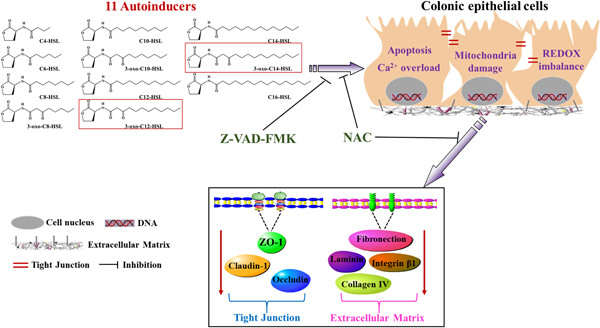
(1). 3OC12 and 3OC14 pose a significant challenge to the survival of intestinal epithelial cells. (2). 3OC12 and 3OC14 lead to apoptosis rather than necrosis and ferroptosis of intestinal epithelial cells. (3). 3OC12 and 3OC14 disrupt the ECM and TJ by triggering apoptosis and oxidative stress. (4). NAC alleviates 3OC12 and 3OC14-induced apoptosis and impairment of intestinal barrier.
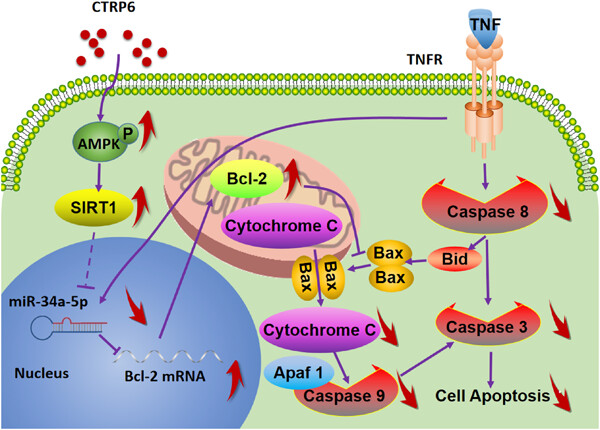
C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-6 attenuates TNF-α-induced apoptosis in salivary acinar cells via AMPK/SIRT1-modulated miR-34a-5p expression
- Pages: 5785-5800
- First Published: 05 January 2021
Vitamin C deficient reduces proliferation in a human periventricular tumor stem cell-derived glioblastoma model
- Pages: 5801-5817
- First Published: 11 January 2021
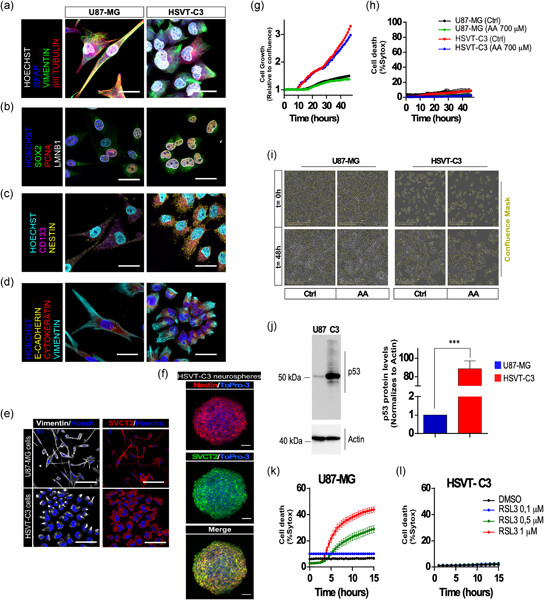
Our aim was to study the effect of vitamin C deficiency on the progression of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) using a GBM model generated by the stereotactic injection of human GBM cells (U87-MG or HSVT-C3 cells) in the subventricular zone of the guinea pig brain. Initial characterization of U87-MG and HSVT-C3 cells showed that HSVT-C3 are highly proliferative, overexpress p53, and are resistant to ferroptosis. Tumor size, proliferation, glomeruloid vasculature, microglia/macrophage infiltration, and invasion were reduced in C3 tumors carried by vitamin C-deficient guinea pigs.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
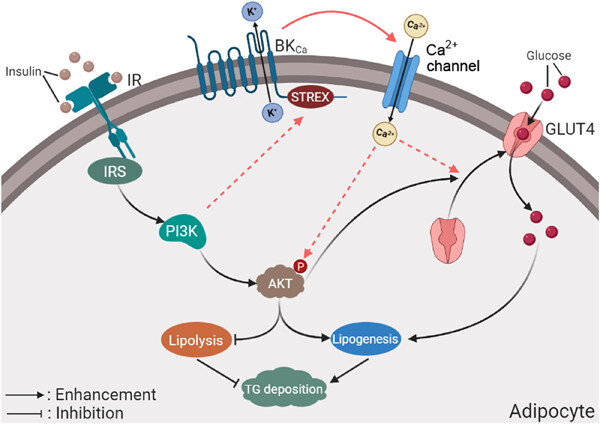
BKCa channel participates in insulin-induced lipid deposition in adipocytes by increasing intracellular calcium
- Pages: 5818-5831
- First Published: 11 January 2021
Development and functional characterization of novel fully human anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptors for T-cell therapy
- Pages: 5832-5847
- First Published: 11 January 2021
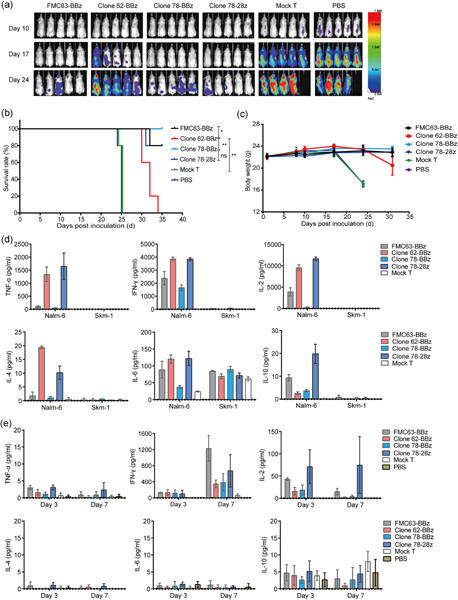
Fully human anti-CD19 single-chain variable fragment candidates were discovered through an optimized protein/cell alternative panning strategy to bypass potential immunogenicity, and their function was evaluated in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T and CD19/CD3 bispecific antibody formats. The two clones exhibited excellent cytotoxicity in CAR-T cells and bispecific antibodies in vitro compared with the benchmarks FMC63 CAR-T cells and blinatumomab.
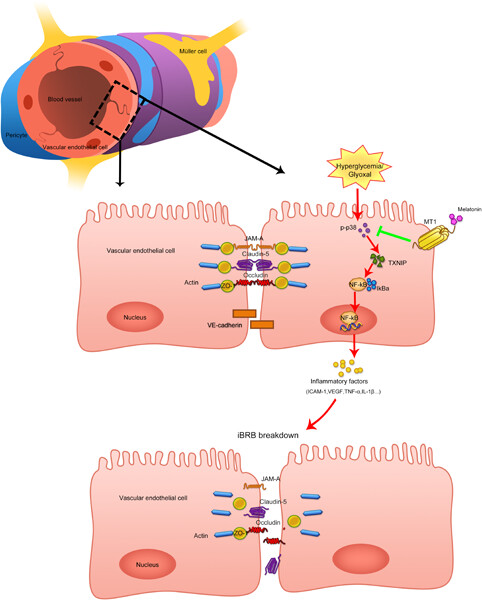
Melatonin maintains inner blood-retinal barrier via inhibition of p38/TXNIP/NF-κB pathway in diabetic retinopathy
- Pages: 5848-5864
- First Published: 11 January 2021
Synergistic effect of three-dimensional coculture and photobiomodulation therapy on vascularized liver spheroid formation by stem cells
- Pages: 5865-5874
- First Published: 11 January 2021
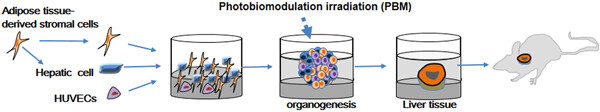
Despite studies reporting functional differentiation of liver cells, a three-dimensional, vascularized liver organ has yet to be developed from mesenchymal stem cells. We investigated whether treatment with photobiomodulation before three-dimensional liver spheroid transplantation improved the recovery of liver function via stimulation of angiogenesis and hepatocyte differentiation. These photobiomodulation-liver spheroids may be useful in designing artificial three-dimensional hepatic tissue constructs and in cell therapy with limited numbers of human hepatocytes.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
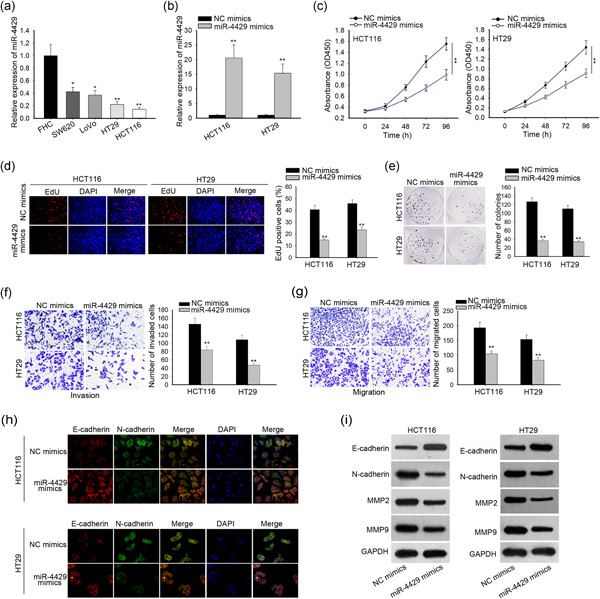
Retracted: MicroRNA-4429 restrains colorectal cancer cell invasion and migration via regulating SMAD3-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Pages: 5875-5884
- First Published: 03 March 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Hepatocyte size fractionation allows dissection of human liver zonation
- Pages: 5885-5894
- First Published: 16 January 2021
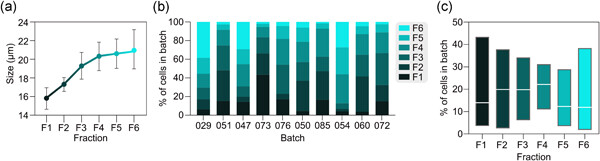
In this study, we used an elutriation-based approach to study human liver zonation. We separated human hepatocytes into six size fractions and performed proteomic analysis, which showed that proteins that were enriched in different size fractions largely represented biological processes of known zonal specificity. Together with the strong correlations that we observed between expression and metabolic function of CYP enzymes with known zonation in vivo, we conclude that elutriation-based size fractionation enables studies of zonated human liver functions in vitro.
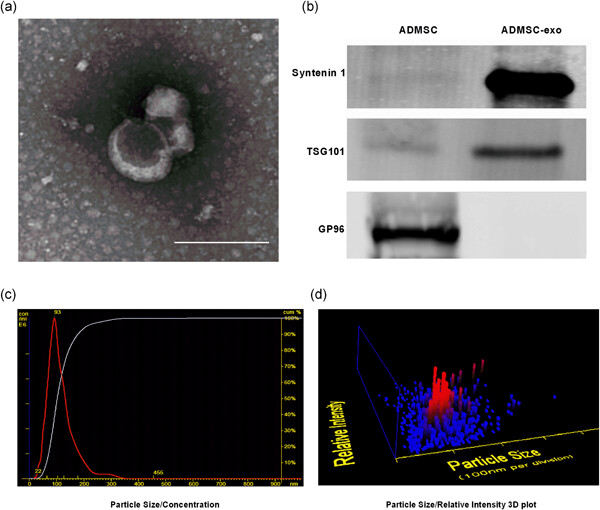
Exosomes from donor-derived adipose mesenchymal stem cells prolong the survival of vascularized composite allografts
- Pages: 5895-5905
- First Published: 16 January 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
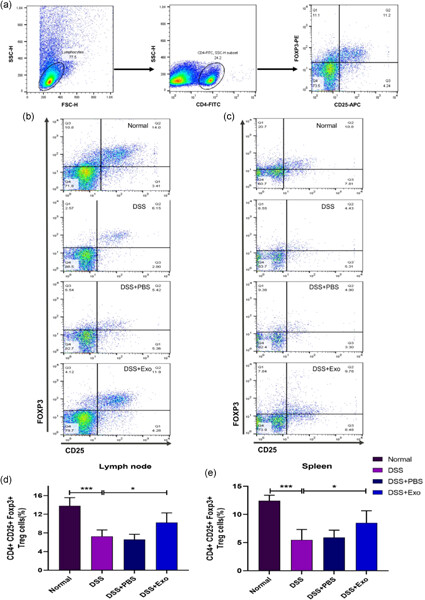
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-secreted exosome alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis by Treg cell induction and inflammatory cytokine reduction
- Pages: 5906-5920
- First Published: 16 March 2021
Silencing of a LIM gene in cotton exhibits enhanced resistance against Apolygus lucorum
- Pages: 5921-5936
- First Published: 22 January 2021
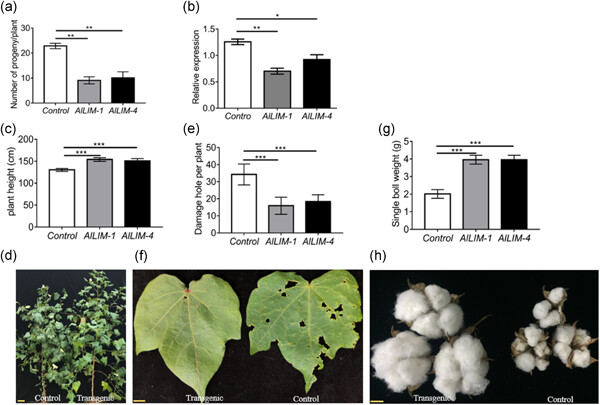
Graphical abstract
We isolated and characterized a lethal gene of Apolygus lucorum and named it Apolygus lucorum LIM (AlLIM), which produced A. lucorum mortality rates ranging from 38% to 81%. dsAlLIM transgenic cotton was protected from A. lucorum damage with high efficiency, with almost no detectable yield loss. Therefore, our study successfully provides a promising genetically modified strategy to overpower A. lucorum attack.
Oscillating calcium signals in smooth muscle cells underlie the persistent basal tone of internal anal sphincter
- Pages: 5937-5952
- First Published: 16 January 2021
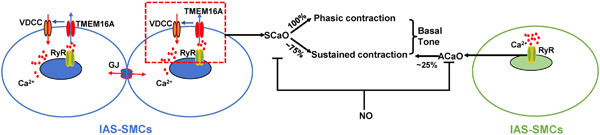
In this study, we found internal anal sphincter smooth muscle cells generate two forms of contractions (i.e., phasic and sustained contraction) and Ca2+ signals (i.e., synchronized Ca2+ oscillations [SCaOs] and asynchronized Ca2+ oscillations [ACaOs]). RyRs, TMEM16A, L-type Ca2+ channels, and gap junctions are required for SCaOs, which account for phasic contraction and 75% of sustained contraction. Nevertheless, only RyRs are required for ACaOs, which contribute 25% of sustained contraction. Nitric oxide, the primary neurotransmitter of defecation reflex, blocks both types of Ca2+ signals, leading to IAS's full relaxation. Our study provides insight into fecal continence and normal defecation.
Circular RNA circHECTD1 facilitates glioma progression by regulating the miR-296-3p/SLC10A7 axis
- Pages: 5953-5965
- First Published: 09 February 2021
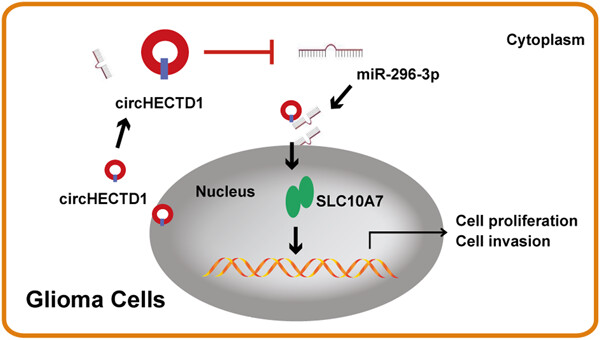
This study demonstrated that circHECTD1 functions as an oncogene in glioma. Mechanically, circHECTD1 suppresses miR-296-3p, which results in the upregulation of SLC10A7, and thus glioma progression. We elucidated a critical circHECTD1/miR-296-3p/SLC10A7 regulatory network in glioma progression, providing a new strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of glioma.
Roles of apoptotic chondrocyte-derived CXCL12 in the enhanced chondroclast recruitment following methotrexate and/or dexamethasone treatment
- Pages: 5966-5979
- First Published: 12 January 2021
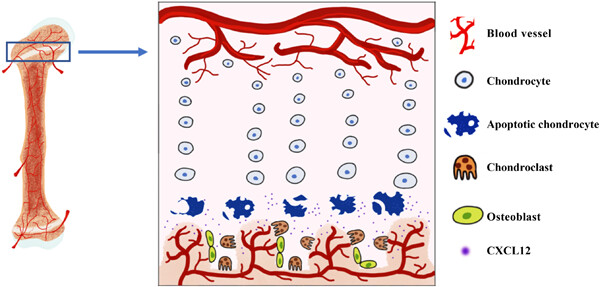
Graphical abstract
Intensive use of methotrexate (MTX) and/or dexamethasone (DEX) for treating childhood malignancies is known to cause growth plate dysfunction leading to bone growth impairments. However, the mechanisms remain vague and it is not clear whether MTX and DEX combination treatment could have additive effects in the growth plate defects. MTX and/or DEX therapy causes growth plate chondrocyte apoptosis and apoptotic chondrocytes have increased expression of CXCL12 which can enhance recruitment of cartilage-resorbing chondroclasts.
Pharmacological modulation of dual melanocortin-4 receptor signaling by melanocortin receptor accessory proteins in the Xenopus laevis
- Pages: 5980-5993
- First Published: 26 January 2021
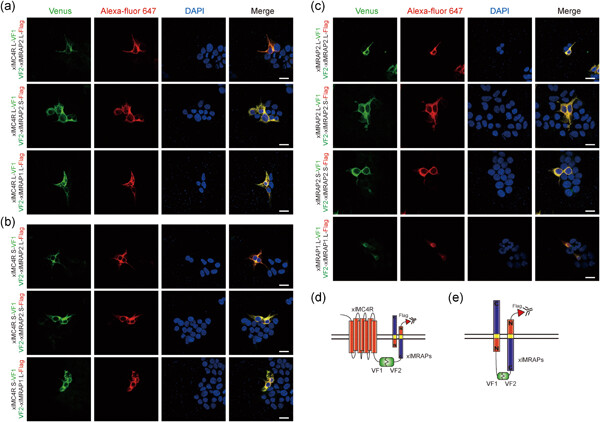
Elucidation of the pharmacological modulation of dual melanocortin-4 receptor signaling by melanocortin receptor accessory proteins in the tetrapod amphibian, Xenopus laevis. X. laevis MC4Rs (xlMC4Rs) directly interacted with xlMC4Rs on the cell surface as a functional antiparallel dimeric topology and pharmacological studies suggested a homology specific regulatory pattern of the melanocortin system in X. laevis.
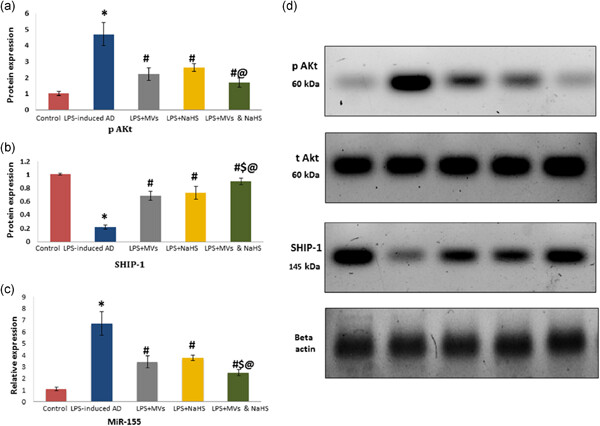
Hydrogen sulfide and mesenchymal stem cells-extracted microvesicles attenuate LPS-induced Alzheimer's disease
- Pages: 5994-6010
- First Published: 22 January 2021
Homogentisic acid induces cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix alteration in alkaptonuric cartilage
- Pages: 6011-6024
- First Published: 20 January 2021
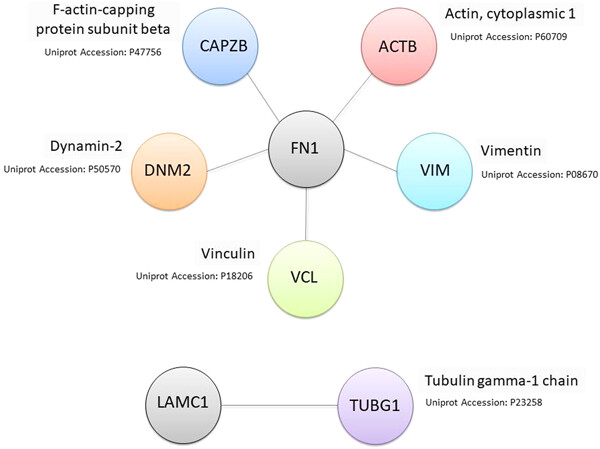
In chondrocyte cells, there is a close correlation and physical interconnection between cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM). Therefore, the alterations in the cytoskeletal structure lead to the impairment of the structure and the activity of ECM. In this study, the role of HGA metabolite accumulation in chondrocytes, which is responsible for the ultra-rare disease alkaptonuria (AKU), was evaluated as inducer of structural alteration of cellular cytoskeleton and of the cartilage ECM, contributing to the manifestation of AKU pathology.
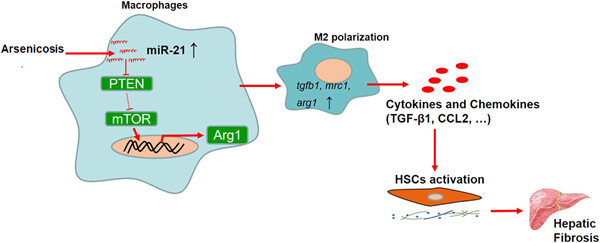
miR-21-regulated M2 polarization of macrophage is involved in arsenicosis-induced hepatic fibrosis through the activation of hepatic stellate cells
- Pages: 6025-6041
- First Published: 22 January 2021
Chemerin located in bone marrow promotes osteogenic differentiation and bone formation via Akt/Gsk3β/β-catenin axis in mice
- Pages: 6042-6054
- First Published: 25 January 2021
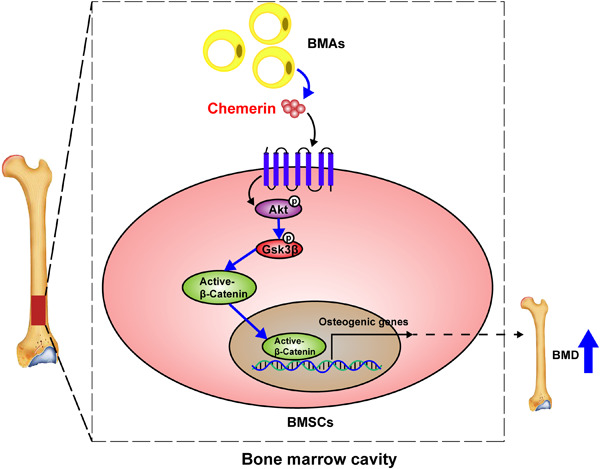
Graphical abstract
We found that chemerin promotes osteogenic differentiation and bone formation via activating Akt/Gsk3β/β-catenin axis, and this promoting effect attributes to the chemerin in bone marrow locally, not in the serum. Our findings provide new insight into the effects of chemerin on bone metabolism, and chemerin might be a new potential target for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis.
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles conditionally ameliorate bone marrow failure symptoms in an immune-mediated aplastic anemia mouse model
- Pages: 6055-6067
- First Published: 25 January 2021