Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Original Articles
COVID-19 pandemic impact on cytopathology practice in the post-lockdown period: An international, multicenter study
- First Published: 10 January 2022
A persistent reduction in the cytological specimen volume during the post-lockdown period has been observed. The relative increase in the cytological workload in the late part of the post-lockdown period is a promising finding of a slow return to normality.
REVIEWS
Alzheimer's disease: An evolving understanding of noradrenergic involvement and the promising future of electroceutical therapies
- First Published: 01 May 2021
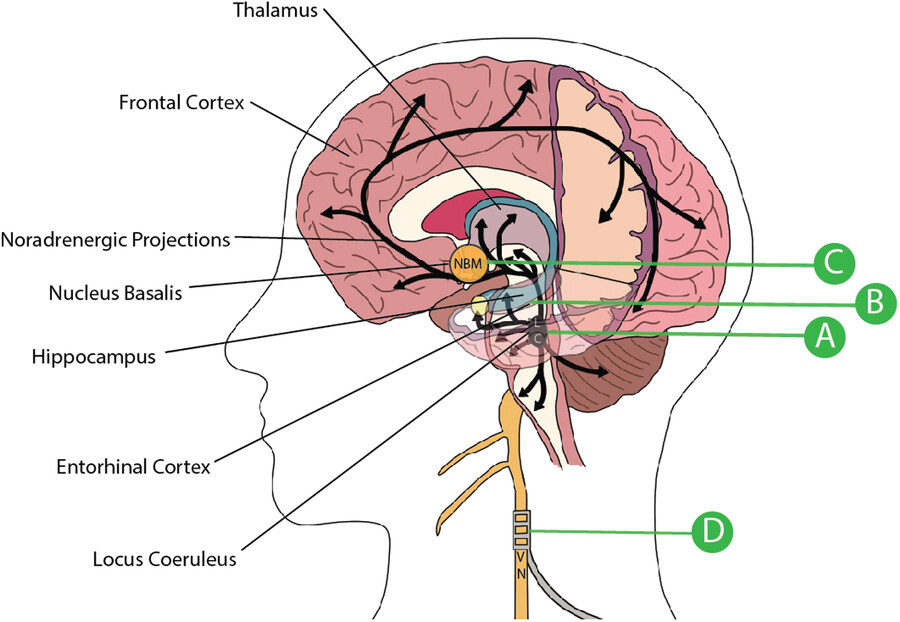
In this review, we provide a brief overview of several of the most thoroughly researched pathogenic hypotheses for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and assess their clinical impact to-date. We focus specifically on recent research into the role of the locus coeruleus norepinephrine (LC-NE) system, in both AD pathogenesis and symptom exacerbation, as well as the potential to use advanced neural stimulation techniques as a novel therapeutic option in the earliest stages of neuropathology.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Impacts of delta and omicron variants on inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-induced T cell responses in patients with autoimmune diseases and healthy controls
- First Published: 13 January 2023
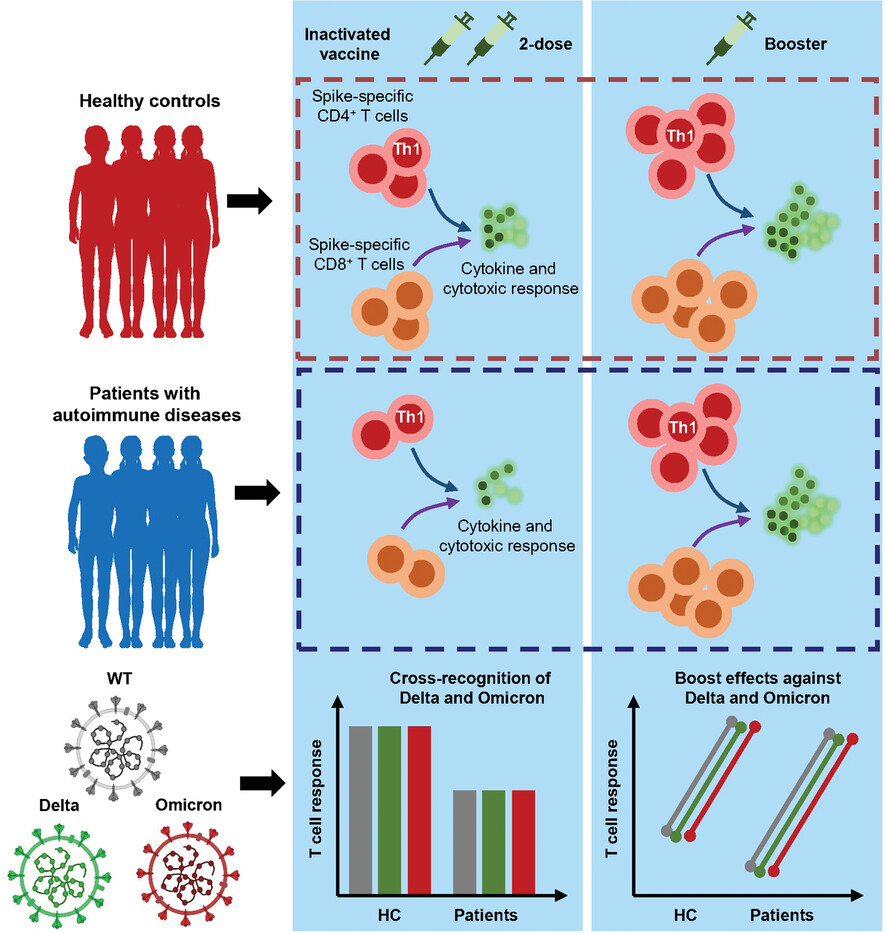
Inactivated vaccine-induced-spike specific T cell cross-recognize delta and omicron strains.
- Inactivated vaccine-induced CD4+/CD8+ T cells respond to delta and omicron variants;
- Polyfunctionality of spike-specific T cells is preserved in response to delta and omicron variants;
- A third dose of inactivated vaccine expands spike-specific T cells that recognize delta and omicron variants;
- Spike-specific T cell responses are lower after two-dose, but boosted to a greater magnitude by a third dose in PAD.
EDITORIAL
Transfer or tailor? Implementing a technology-supported intervention for noncommunicable diseases across contexts
- First Published: 07 November 2022
RADIATION ONCOLOGY
Original Articles
Equity should know no borders: The role of Australasian radiation oncologists in supporting radiation oncology services in low- and middle-income countries in the Asia-Pacific
- First Published: 10 May 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
A potent neutralizing nanobody against SARS-CoV-2 with inhaled delivery potential
- First Published: 04 March 2021
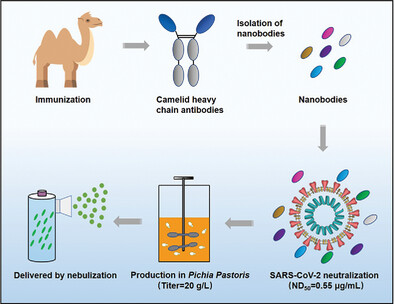
We reported nanobody (Nb) phage display libraries derived from four camels immunized with the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD), from which 381 Nbs were identified to recognize SARS-CoV-2-RBD including several mutants. Nb11-59 exhibited potent antiviral activity against authentic SARS-CoV-2 with 50% neutralizing dose (ND50) of 0.55 μg/ml, and it can be produced on large scale in Pichia pastoris with titers reached 20 g/L. Importantly, Nb11-59 showed a good stability and could be developed as an inhaled drug to treat COVID-19.
REVIEWS
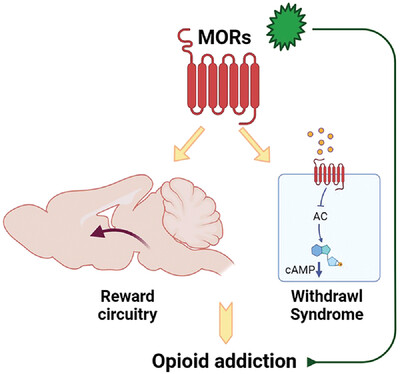
Mechanism of opioid addiction and its intervention therapy: Focusing on the reward circuitry and mu-opioid receptor
- First Published: 22 June 2022
REVIEW ARTICLE
SARS-CoV-2 modulation of RIG-I-MAVS signaling: Potential mechanisms of impairment on host antiviral immunity and therapeutic approaches
- First Published: 11 December 2022
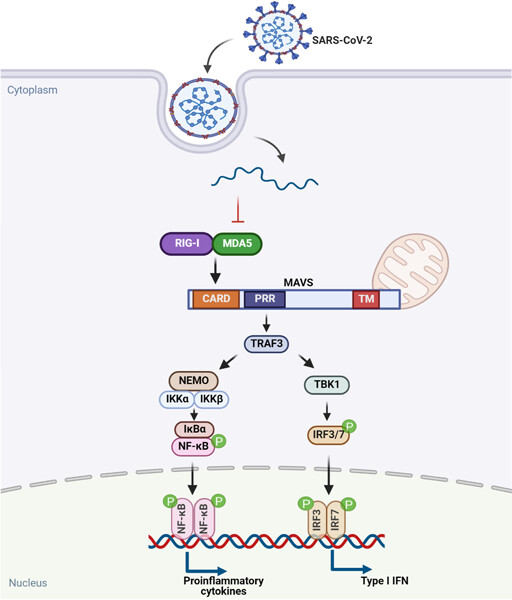
The retinoic acid-inducible gene I mitochondrial antiviral signaling (RIG-I-MAVS) axis is designated as a major signaling pathway in the innate immune response for RNA viruses. This review summarized the role of various proteins derived from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on the RIG-I-MAVS pathway and explored the underlying mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 to escape the host antiviral response. Regulation of RIG-I-MAVS pathway might be a potentially therapeutic strategy to boost immunity against COVID-19.
HIGHLIGHT
Phylogenomic characterization of the 2022 outbreak of monkeypox virus—The importance of sustained genetic surveillance
- First Published: 16 August 2022
REVIEW ARTICLE
Precision health in Alzheimer disease: Risk assessment-based strategies
- First Published: 01 March 2021

Precision medicine in Alzheimer's disease (AD) focuses on stratifying individuals according to their risk factors and disease susceptibility then applying preventative strategies and personalized treatment approaches for a better outcome. Identifying high-risk individuals by concentrating on a few modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors has tremendous value in slowing the progression of the disease. Future mitigation approaches rely on evidence-based research for early detection of validated biomarkers, clinical genomics sequencing and ‘omics’ molecular profiling. We present recommendations for consideration to implement for mitigation in high risk populations.
REVIEWS
The landscape of investigator-initiated oncology trials conducted in mainland China during the past decade (2010–2019)
- First Published: 01 March 2023
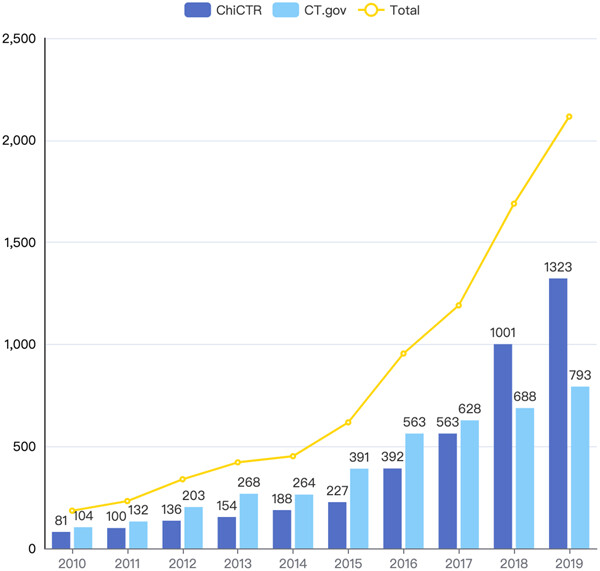
The current published studies related to the landscape of cancer-related clinical trials are mainly limited to industry-initiated trials. This is the first cross-sectional study that analyzes the landscape of cancer-related investigator-initiated trials (IITs) in the mainland China. The findings showed that the registration number of IITs increased significantly over time, but there is still a long way to go for strictly controlling the quality of clinical trials, solving regional imbalances, and deliberate funding allocation.
Application of informatics in cancer research and clinical practice: Opportunities and challenges
- First Published: 15 June 2022
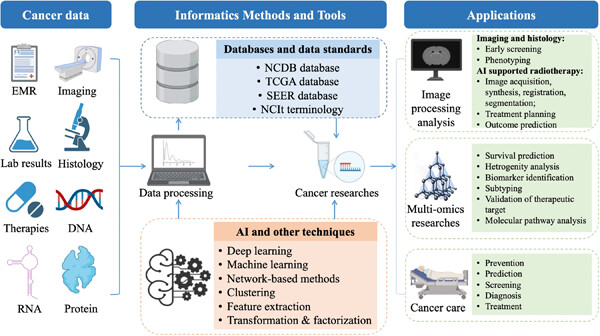
This review summarized the progress of cancer informatics in the big data era. Various informatics methods and tools that are widely applied in cancer research and practices were discussed. This review further addressed the informatics challenges and opportunities for the comprehensive cancer field. It is expected that this review is instrumental for cancer researchers and clinicians with an informatics-specific insight.