Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Contributing to China's Biodiversity Conservation: The Role of Nature Education
助力中国生物多样性保护:自然教育的角色和作用
- First Published: 26 February 2025
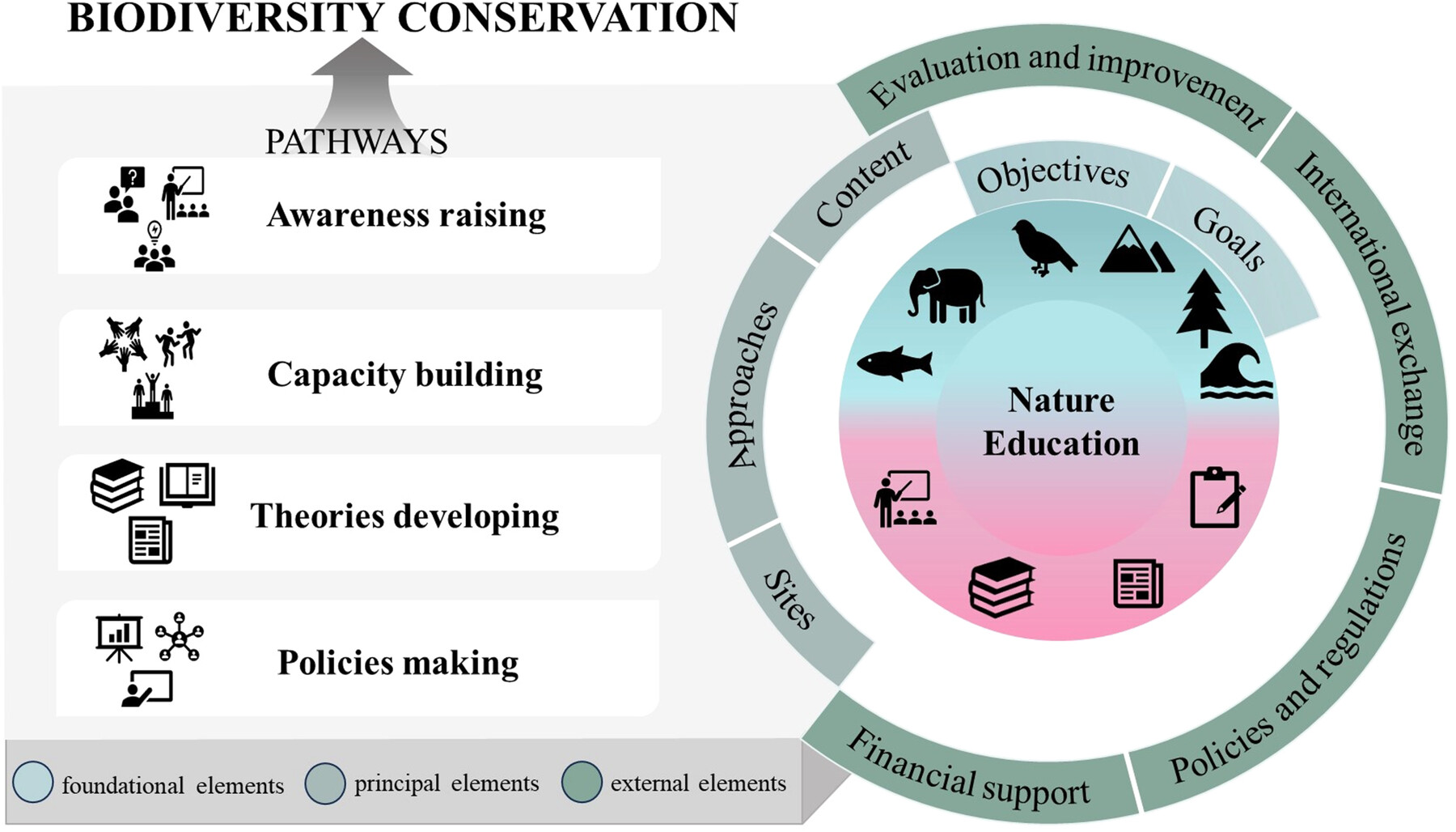
A biodiversity conservation framework integrating nature education. Note: The framework includes three types of elements: foundational, principal, and external. The elements represent the core components of nature education, while the pathways highlight the essential strategies for effectively promoting biodiversity conservation through nature education.
Exploring the Impact of a Naturalist Training Camp on Biodiversity Conservation Willingness and Mental Well-Being
博物达人训练营对参与者生物多样性保护意愿和心理健康的影响
- First Published: 11 February 2025
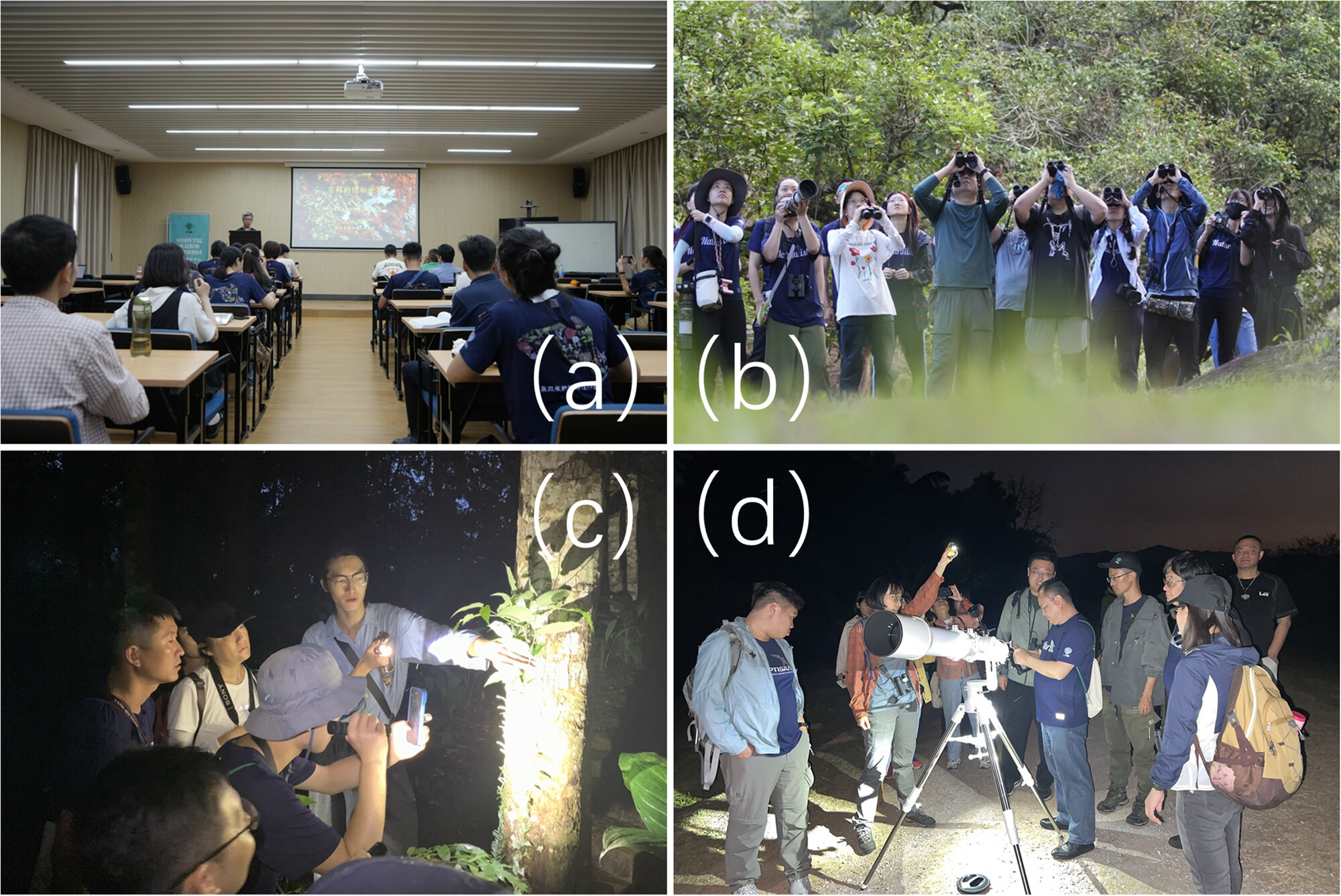

This study examined the impact of a 9-day naturalist training camp at the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden on participants' conservation attitudes and mental well-being. Findings showed significant improvements in biodiversity knowledge, social connectedness, and naturalist identity, which contributed to increased environmental stewardship and enhanced mental health.
Innovative Exploration of Urban Nature Education: The Mini Botanical Garden Concept
城市自然教育的创新探索:小微植物园实践
- First Published: 26 March 2025
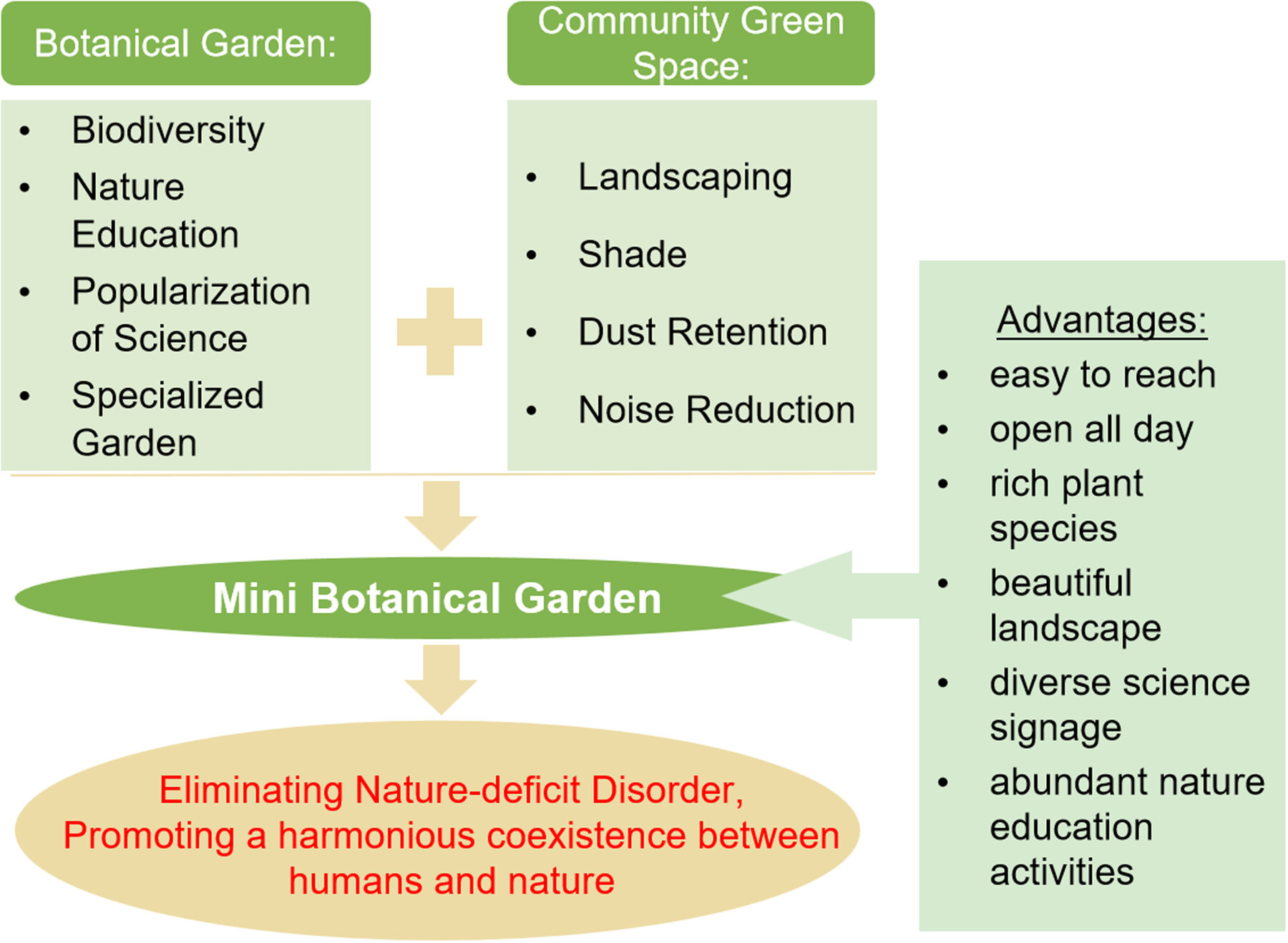
Brief summary: Urbanization is leading to “Nature-deficit Disorder” that threatens children's health and the sustainable development of humanity. This study implements a new solution—the Mini Botanical Garden, which integrates some of the functions of botanical gardens into community green spaces to popularize nature education in the city. The aim is to provide urban residents, especially children, with easily accessible nature experiences, helping them to establish a long-term connection with nature.
A Framework of Nature Education
自然教育的框架
- First Published: 10 March 2025
The framework of nature education provides guidance for educators in designing and improving their programs. Principles within this framework, categorized into foundational concepts, engagement strategies, and desired outcomes, offer a shared language for discussing nature education, and emphasize the role of nature education in human well-being and environmental stewardship.
How Does Nature-Based Education Contribute to Green and Low-Carbon Development?
基于自然的教育如何助力绿色低碳发展
- First Published: 05 May 2025
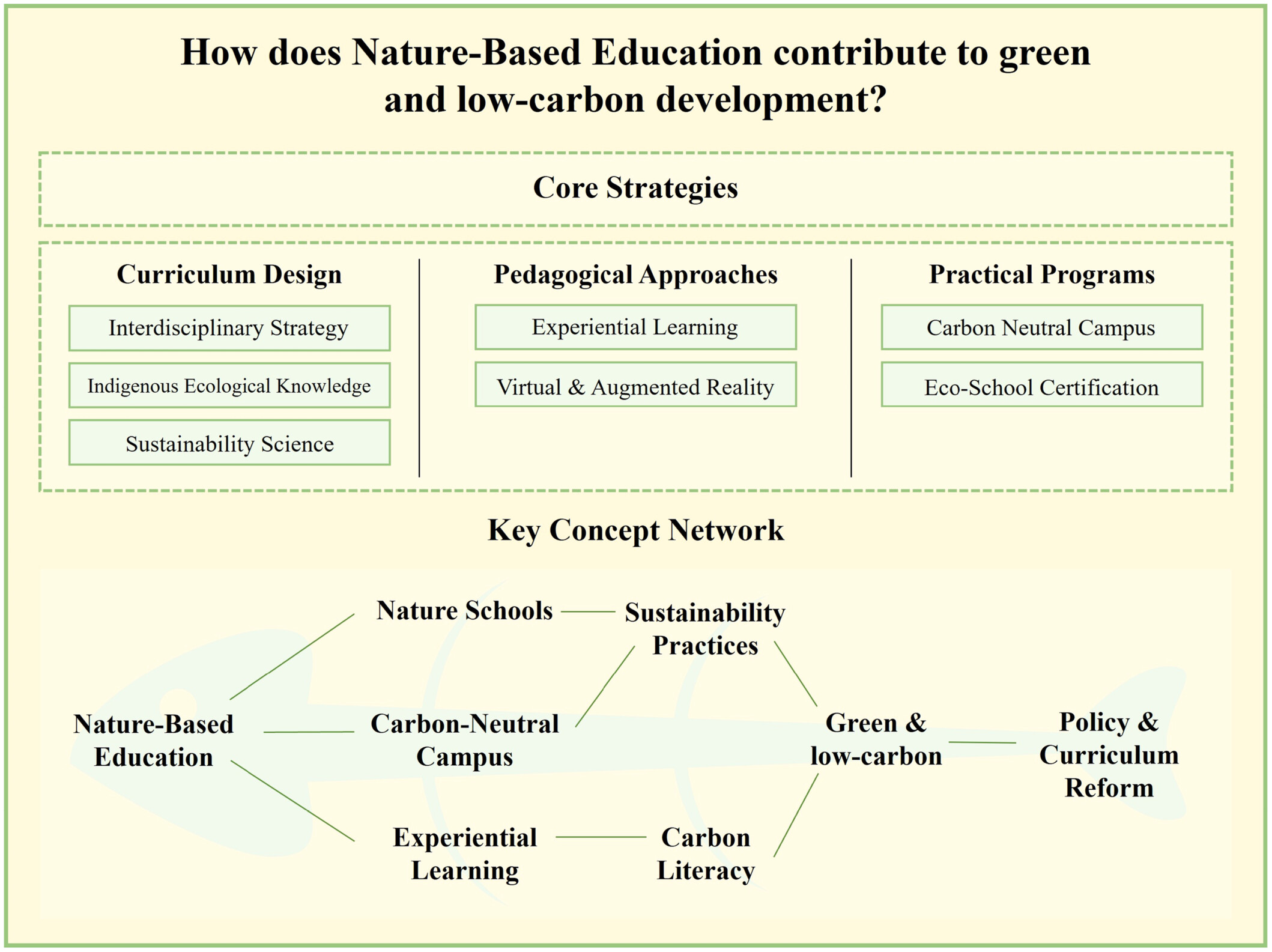
This visualization demonstrates how Nature-Based Education (NBE) supports green and low-carbon development. Key components include nature schools, carbon-neutral campus initiatives, and experiential learning, which enhance carbon literacy and sustainability practices. The study highlights the necessity of curriculum reform and policy support to ensure the integration of NBE into educational systems. By engaging students with immersive learning experiences, NBE fosters future sustainability leaders who contribute actively to sustainable development.
From Iconic Species to Biodiversity: The Role of Zoos in Inspiring Visitors' Affinity for a Broader Range of Wild Animals
- First Published: 17 April 2025
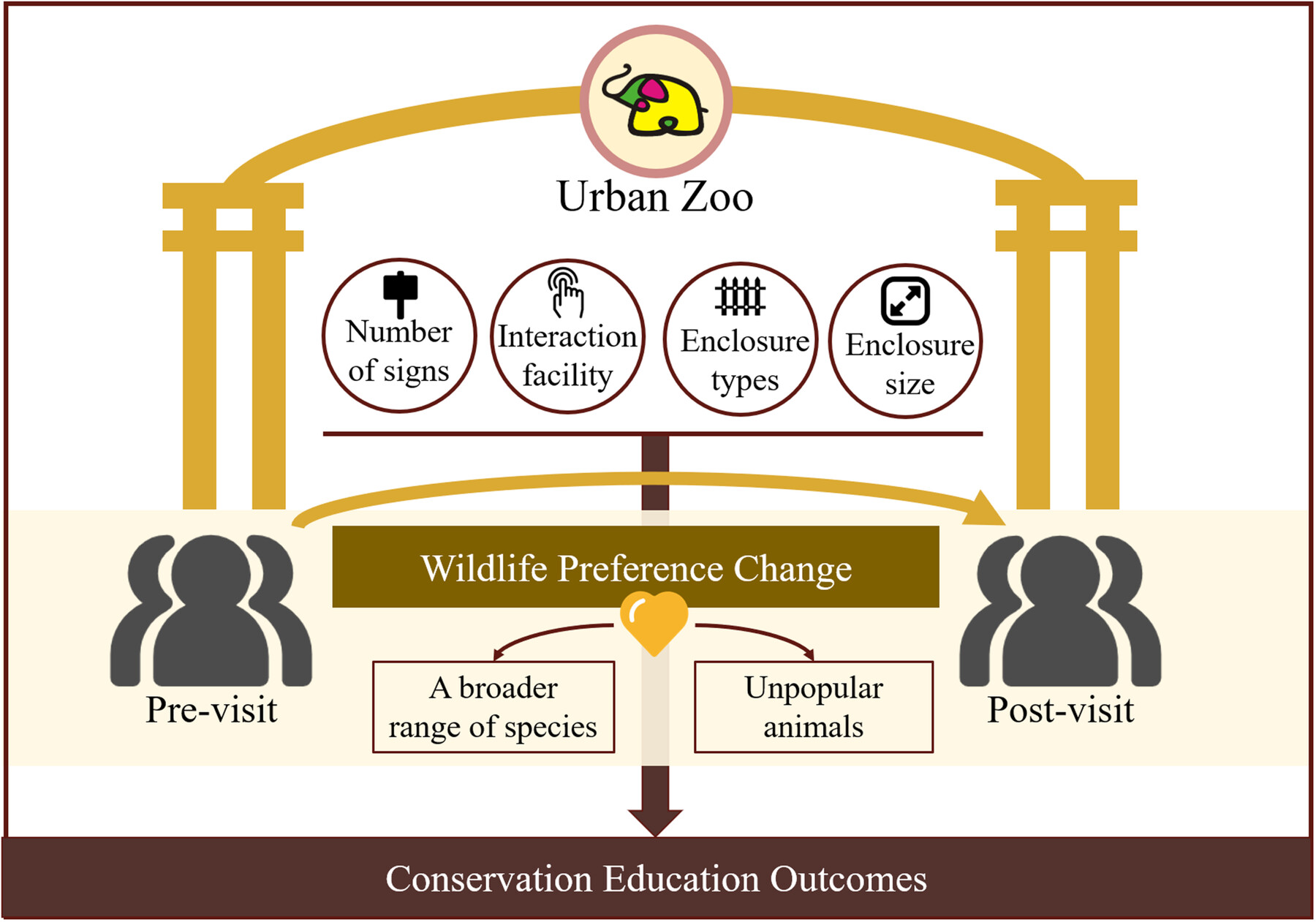
Zoo visits significantly influence wildlife preferences, enhancing fondness for a wider range of species and fostering affinity for less popular taxa. The interplay between enclosure and interpretive characteristics proved crucial in driving these changes, highlighting ways to optimize zoo conservation education.
Fostering Children's Self-Efficacy Through Nature Education: Insights From a Wildlife Education Program in Rural China
通过自然教育培养儿童的自我效能感:中国乡村自然课项目的启示
- First Published: 21 May 2025
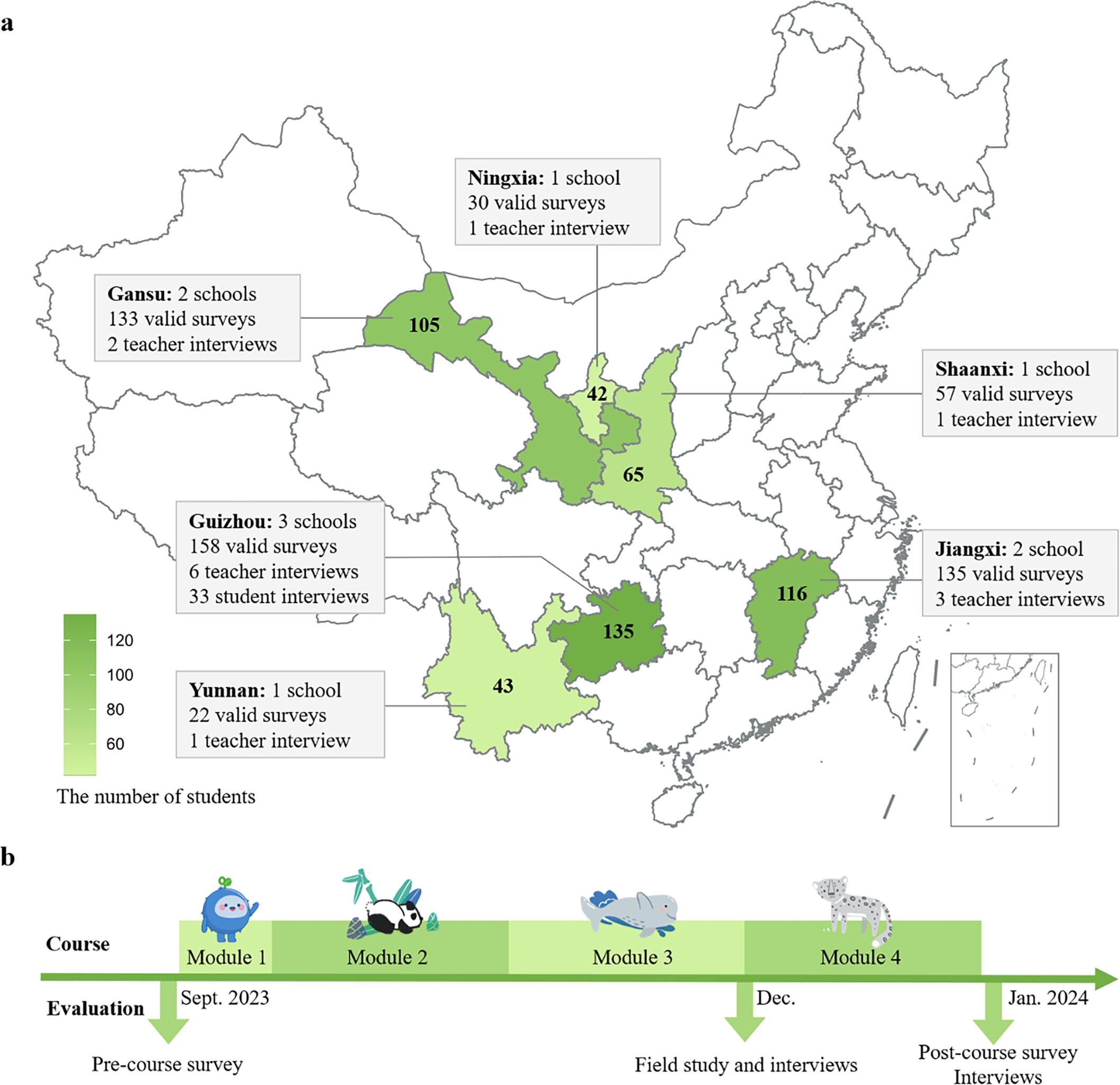
This study identified self-efficacy as a crucial outcome of nature education, with the potential for achieving long-term conservation goals. Using a mixed-methods design, we evaluated the effect of a wildlife course implemented in ten rural elementary schools in China, which significantly increased students' self-efficacy, and also contributed to pro-nature levels.







