Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Evaluation of albumin and lactate dehydrogenase in comparison with cytokeratin 19 fragments and neuron-specific enolase as diagnostic biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 227-237
- First Published: 16 October 2024
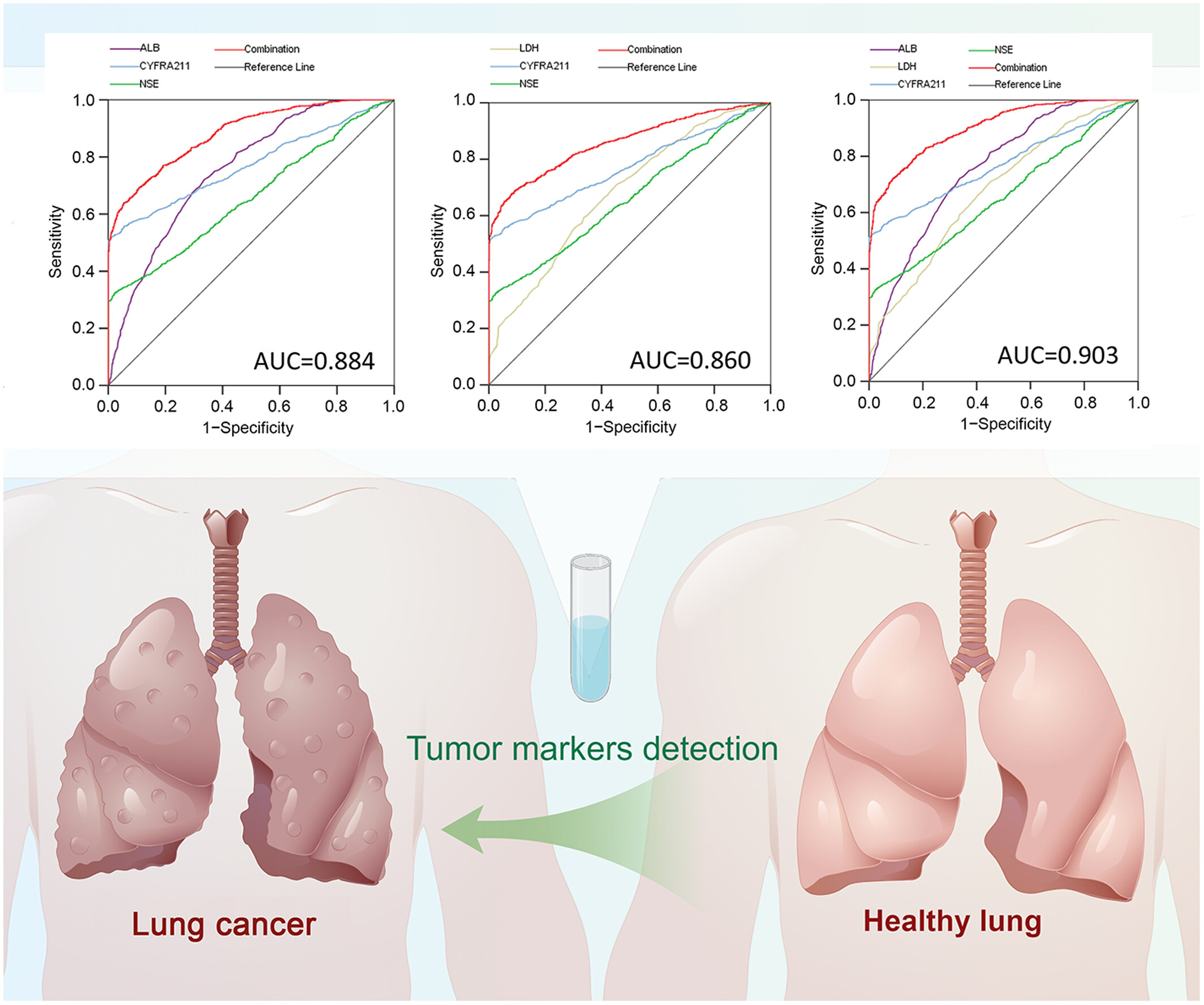
This research analyzed 1048 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, 503 benign pulmonary diseases patients and 1125 healthy controls. It was found that there were significant differences in the concentrations of albumin (ALB) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) between NSCLC patients and healthy controls. The combination of them with cytokeratin 19 fragments and neuron-specific enolase, the AUC was moreover improved to 0.903. In this study, we found ALB and LDH in NSCLC patient serum, which have the potential to improve the diagnostic efficiency of traditional biomarkers of NSCLC.
Diagnostic value of exosomal N-glycan profiles for microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 238-247
- First Published: 14 October 2024
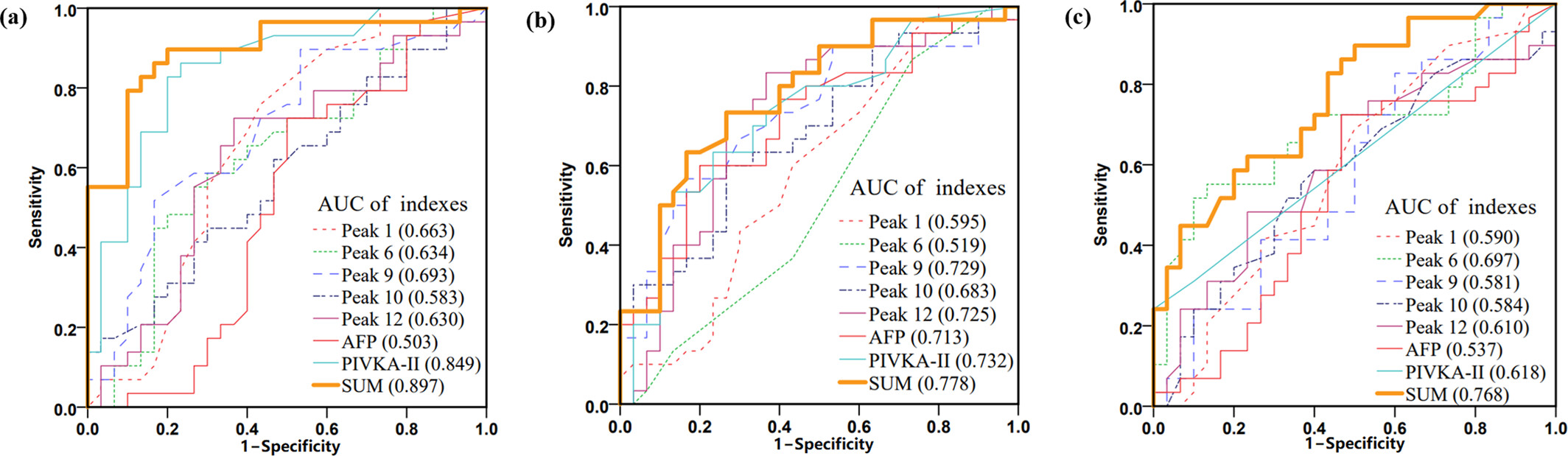
This study examined the changes in N-glycan profiles of serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients across different Microvascular invasion (MVI) grades using two datasets (the modeling cohort and the validation cohort) and developed a SUM diagnostic model. The results of this study indicate that the SUM model of serum exosomes can serve as a diagnostic indicator of MVI grade, especially for MVI grade 2 in HCC patients.
Machine learning model based on SERPING1, C1QB, and C1QC: A novel diagnostic approach for latent tuberculosis infection
- Pages: 248-265
- First Published: 16 November 2024
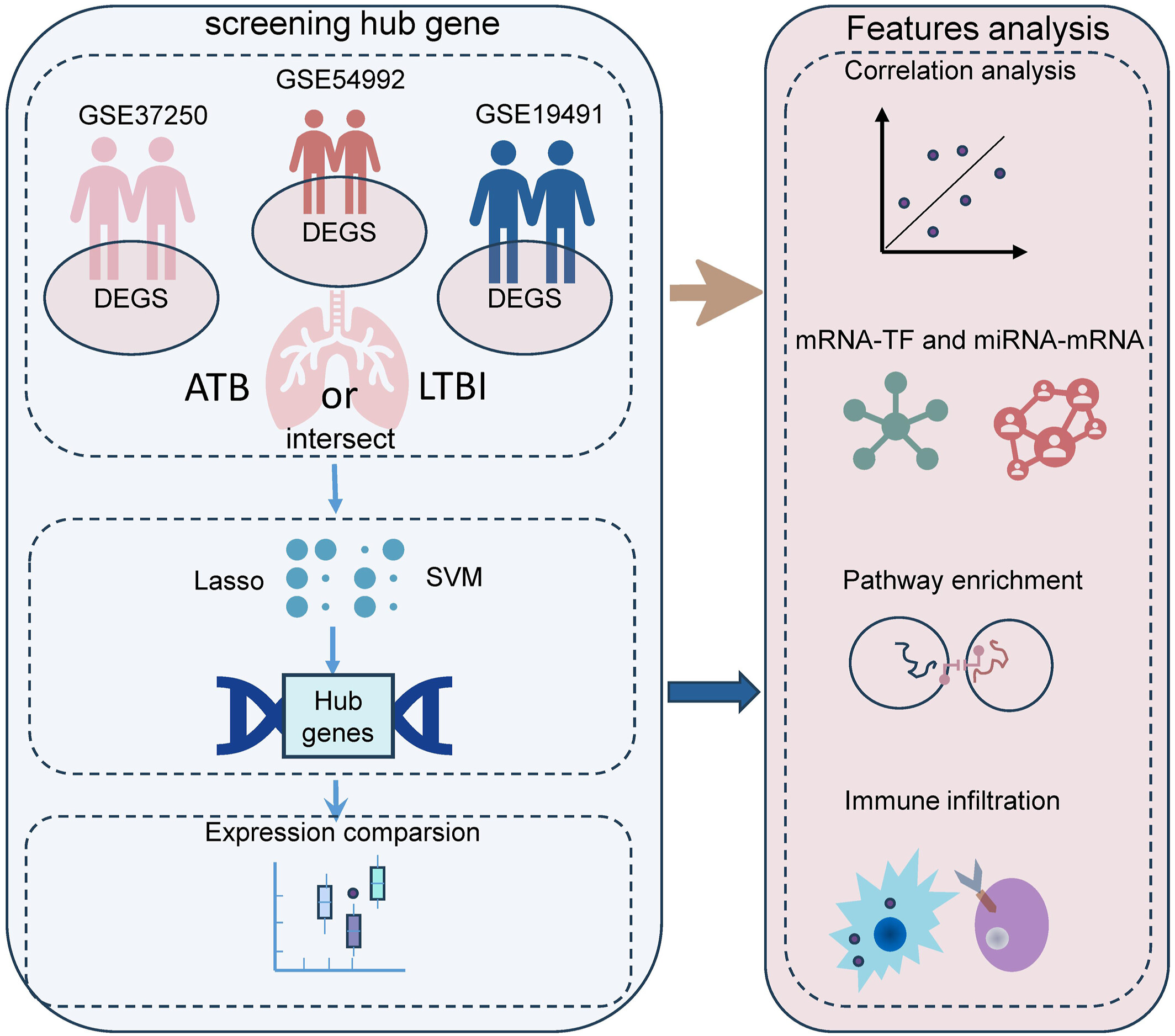
Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is an important source of active tuberculosis (ATB), but there is currently a lack of effective diagnostic tools to distinguish ATB from LTBI. In this study, by integrating transcriptome data analysis, a machine learning algorithm and protein interaction network analysis, an LTBI diagnosis model based on SERPING1, C1QB and C1QC genes was successfully constructed. The model shows good diagnostic performance in both training and validation sets. We also analyzed the functions and regulatory mechanisms of these core genes in depth, revealing the important roles they may play in the course of TB infection. In addition, through immune cell infiltration analysis, we observed significant differences in the immune microenvironment between LTBI and ATB, providing a new perspective for understanding the progression of TB.
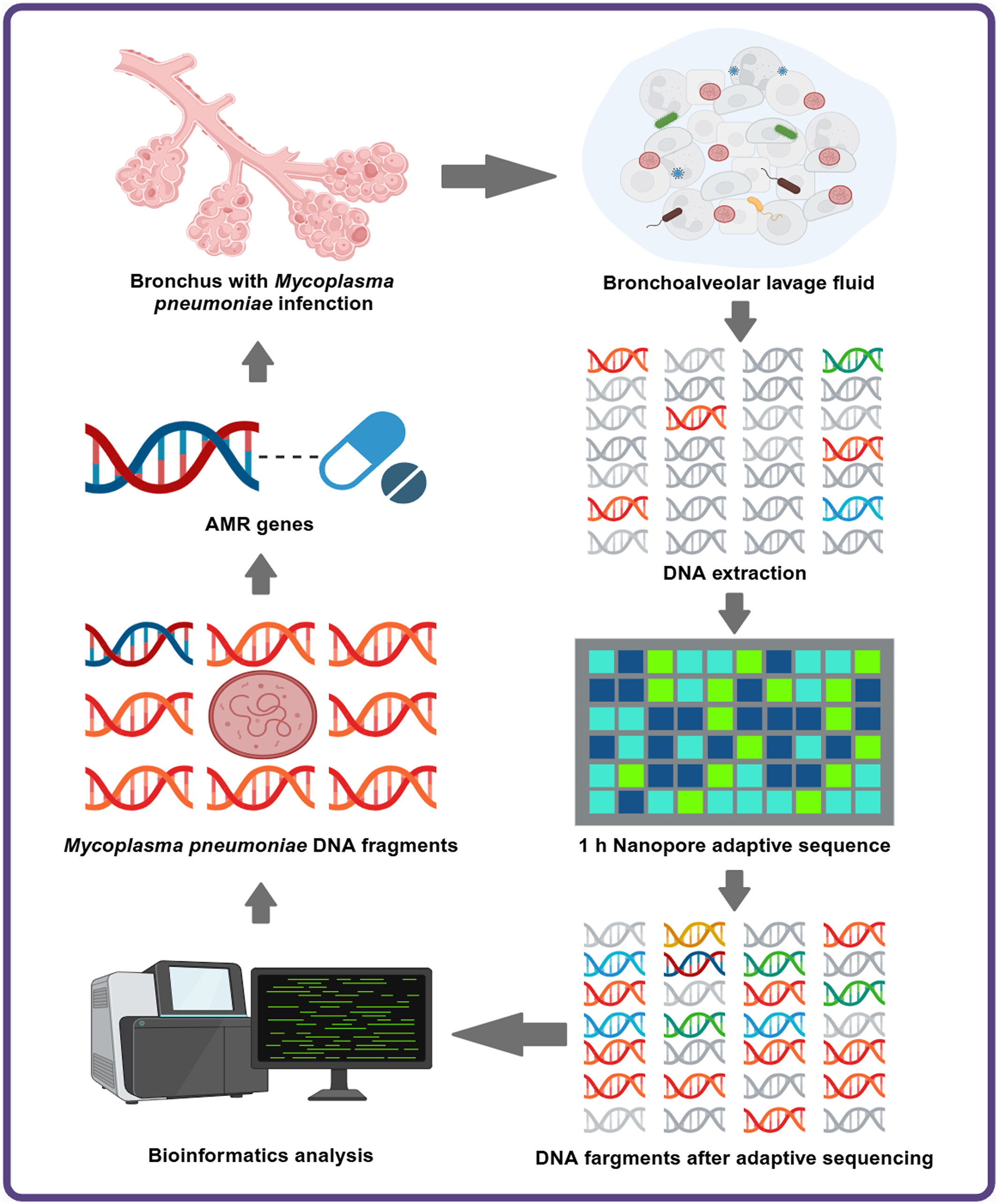
Rapid diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and prediction of antibiotic resistance by nanopore adaptive sampling
- Pages: 266-276
- First Published: 11 November 2024
Serum lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- Pages: 277-285
- First Published: 05 December 2024
This study investigates the relationship between serum lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) activity and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in a Chinese population, finding higher Lp-PLA2 activity in SLE patients, which correlates with certain clinical manifestations and disease activity. These findings provide new insights into the pathogenesis of SLE and suggest that Lp-PLA2 activity may contribute to SLE disease development.
Effect of the Zushima patch combined with celecoxib on pain and inflammatory factor expression in knee osteoarthritis with cold-dampness obstruction
- Pages: 286-293
- First Published: 26 November 2024
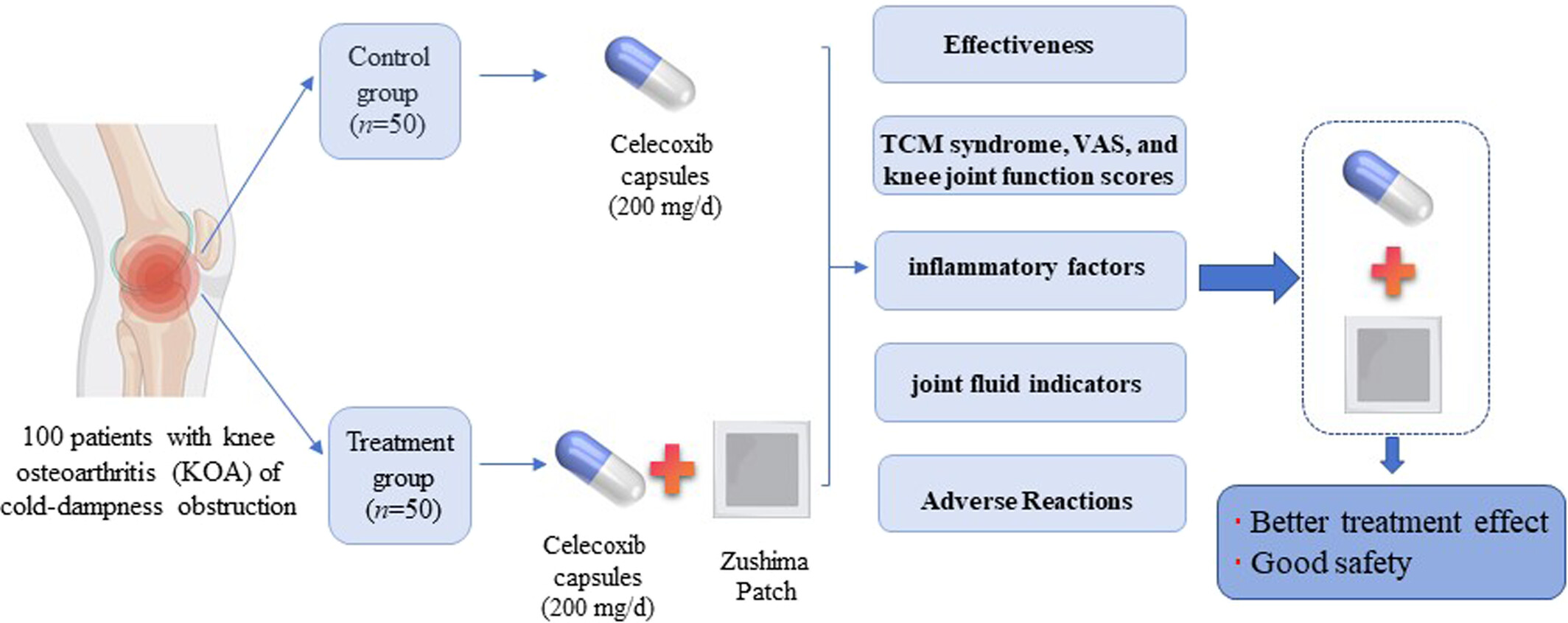
This study found that the combination of the Zushima patch and celecoxib can alleviate the pain symptoms and improve knee joint function in patients with KOA due to cold-dampness obstruction. This mechanism may be associated with the downregulation of inflammatory factors and the regulation of synovial fluid-related indicators. Additionally, their combination showed good safety with less AEs.
Dye-based recombinase-aided amplification assay with enhanced sensitivity and specificity
- Pages: 294-306
- First Published: 14 July 2024
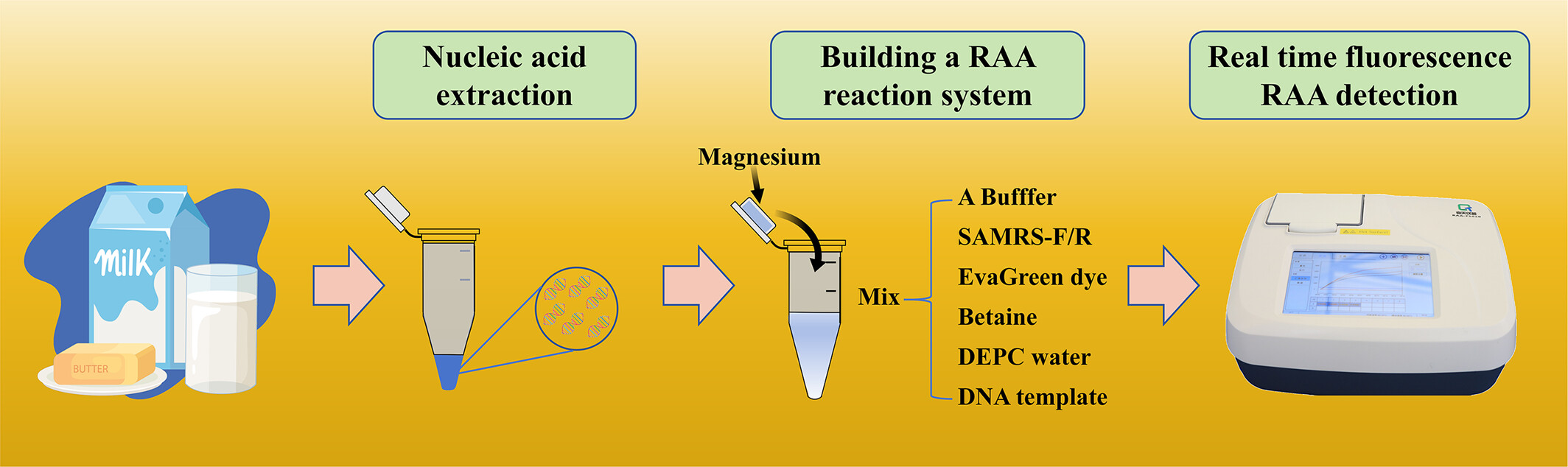
This article is based on an EvaGreen-dye based recombinase aided amplification (EvaGreen-RAA) assay using self-avoiding molecular recognition system (SAMRS) primers for Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes. The SAMRS primers effectively avoid the production of primer dimers, thus improving the detection sensitivity while eliminating the addition of fluorescent probes for RAA. The EvaGreen-RAA assays with SARMS primers provide a new strategy for simplifying fluorescence probe RAA and allowing the detection of multiple pathogens.
RT-PCR in the early detection and monitoring of pathogen residual status in neonatal bacterial meningitis
- Pages: 307-315
- First Published: 08 August 2024
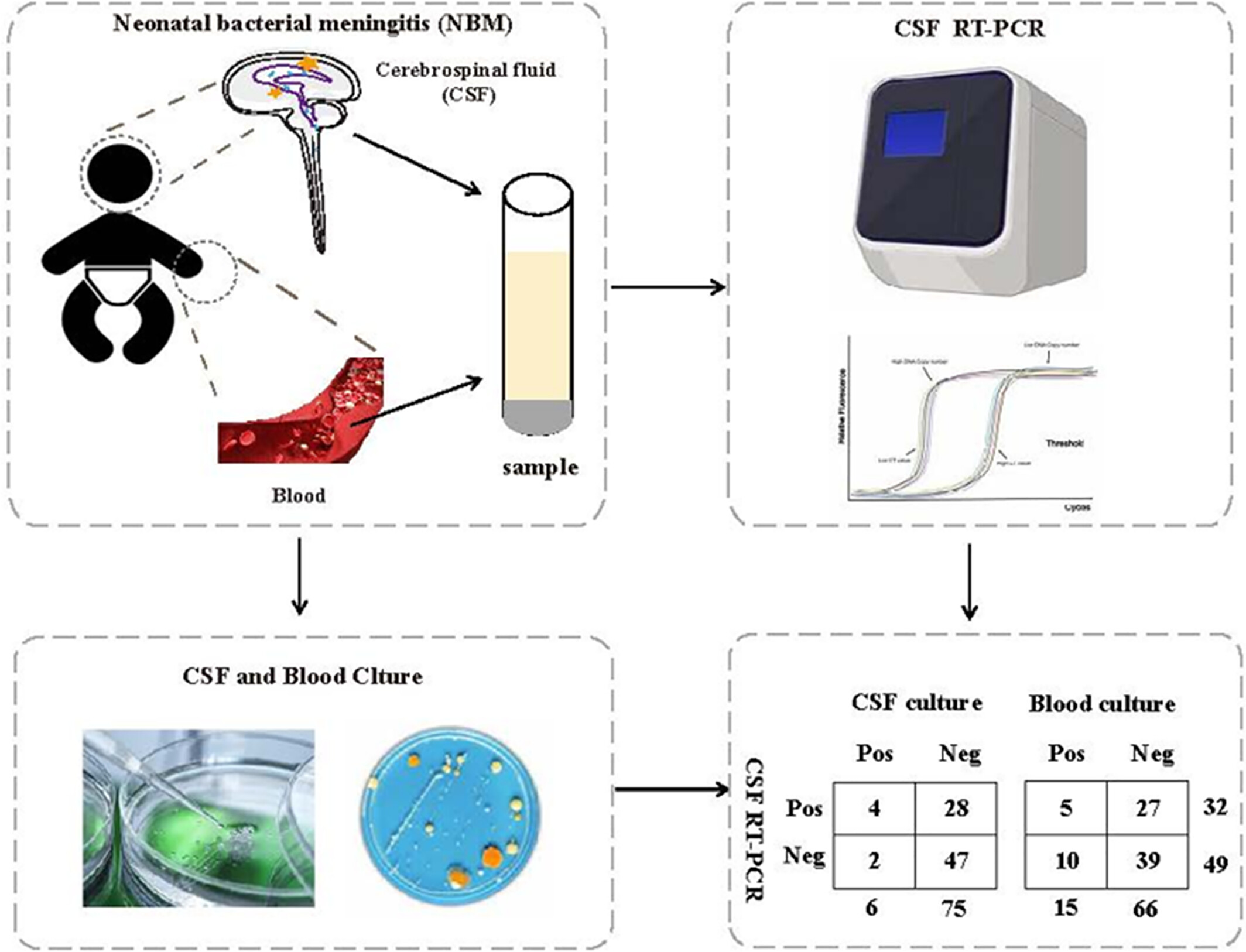
Real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is more sensitive and specific than conventional bacterial culture in detecting pathogenic bacteria in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of children with neonatal bacterial meningitis. RT-PCR is not only suitable for specimens from patients who have received antibiotic treatment before collecting CSF for the first time or for patients whose CSF bacterial culture is negative, but can also be used to dynamically monitor residual pathogenic bacterial DNA in CSF.
CASE REPORT
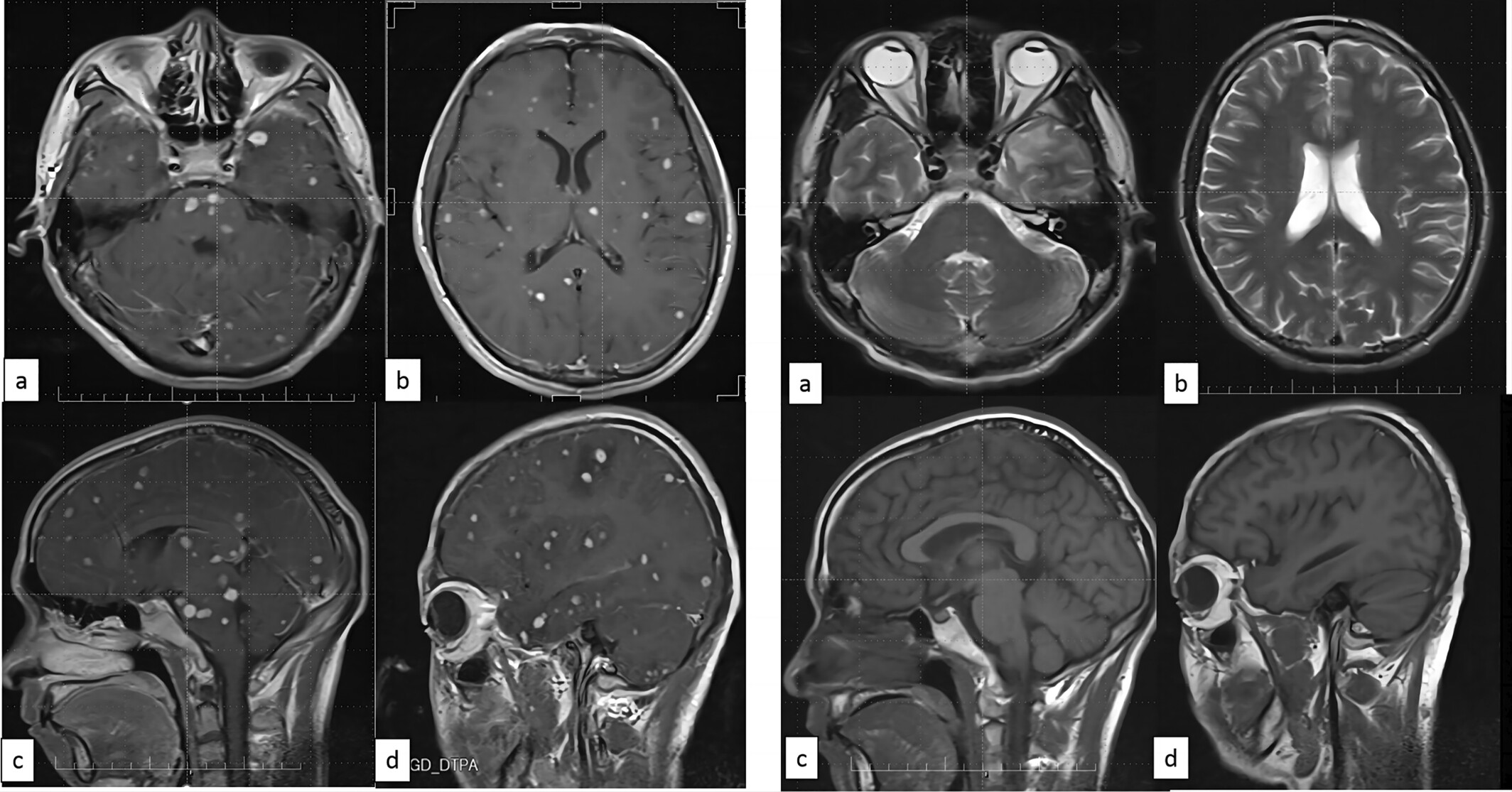
Rapid development of neurological infection in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus following schistosomiasis: A case report
- Pages: 316-322
- First Published: 22 July 2024
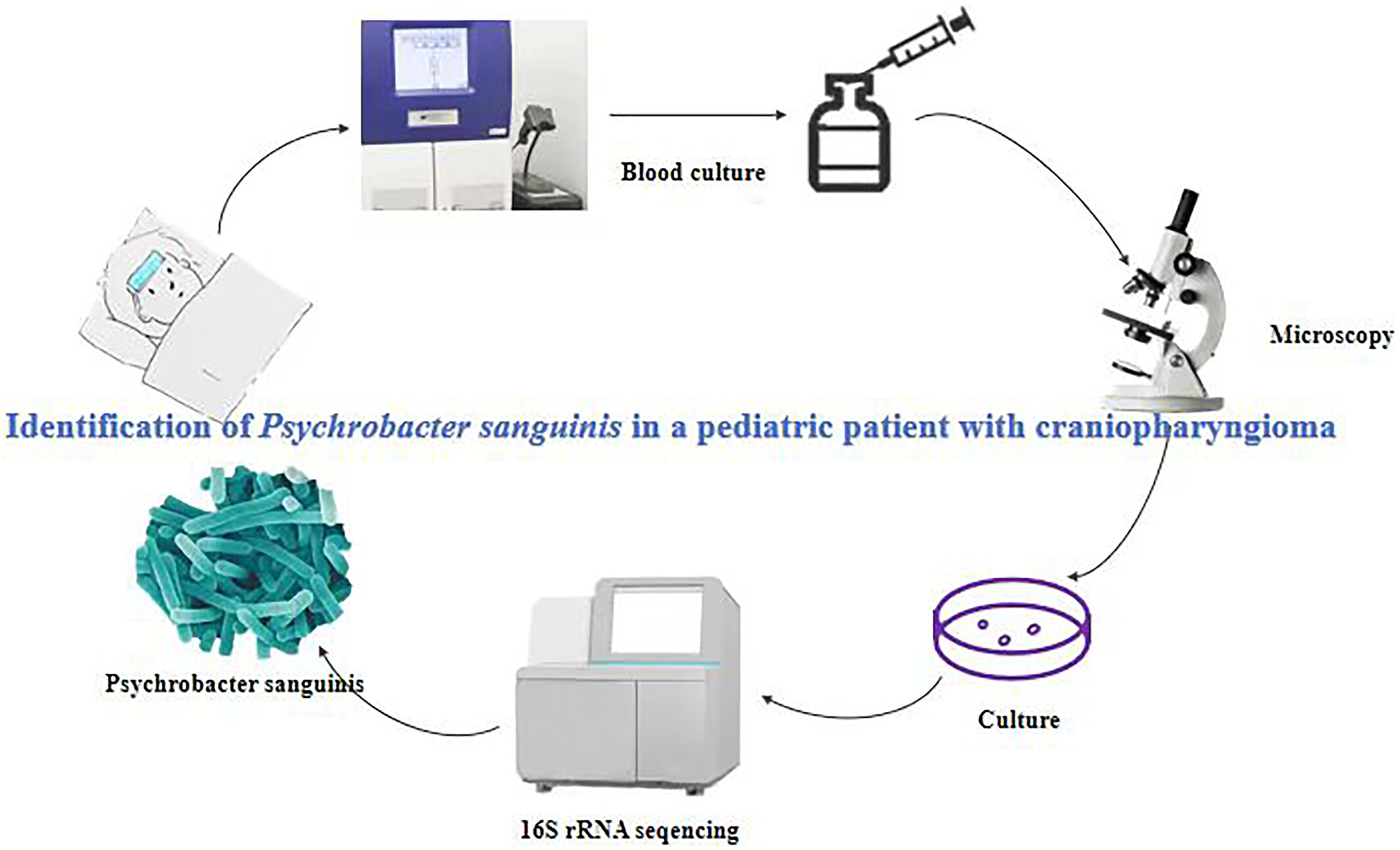
Psychrobacter sanguinis infection in a pediatric patient with craniopharyngioma identified in a blood culture by 16S rRNA sequencing
- Pages: 323-326
- First Published: 05 November 2024
REVIEW
Clinicopathological and prognostic role of CEP55 expression in cancer patients: A meta-analysis of 31 studies with 12,543 patients
- Pages: 327-340
- First Published: 19 August 2024
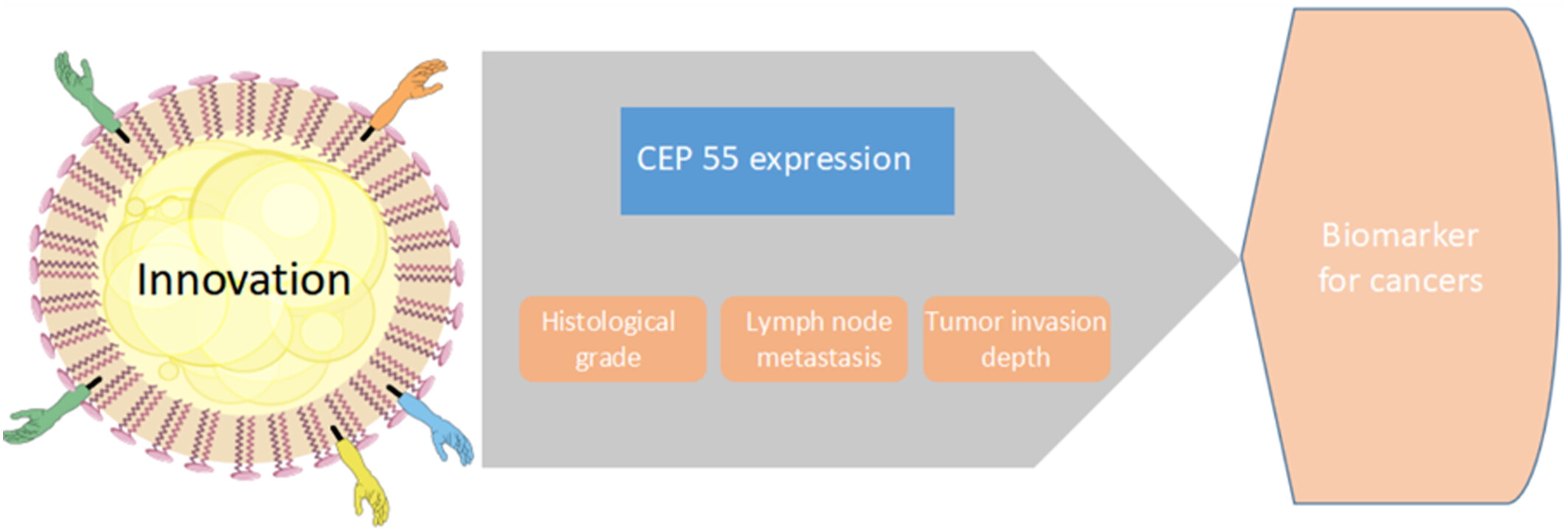
This study was the first quantitative assessment of the association between CEP55 expression and clinical outcomes in human cancers. The correlation between CEP55 expression and clinicopathological features of cancers, including histological grade, lymph node metastasis and tumor invasion depth were investigated. We found that CEP55 overexpression was correlated with poor differentiation, deeper tumor invasion, and increased lymph node metastasis, which suggested that CEP55 may serve as a predictive and prognostic biomarker for cancers, especially for lung cancer.
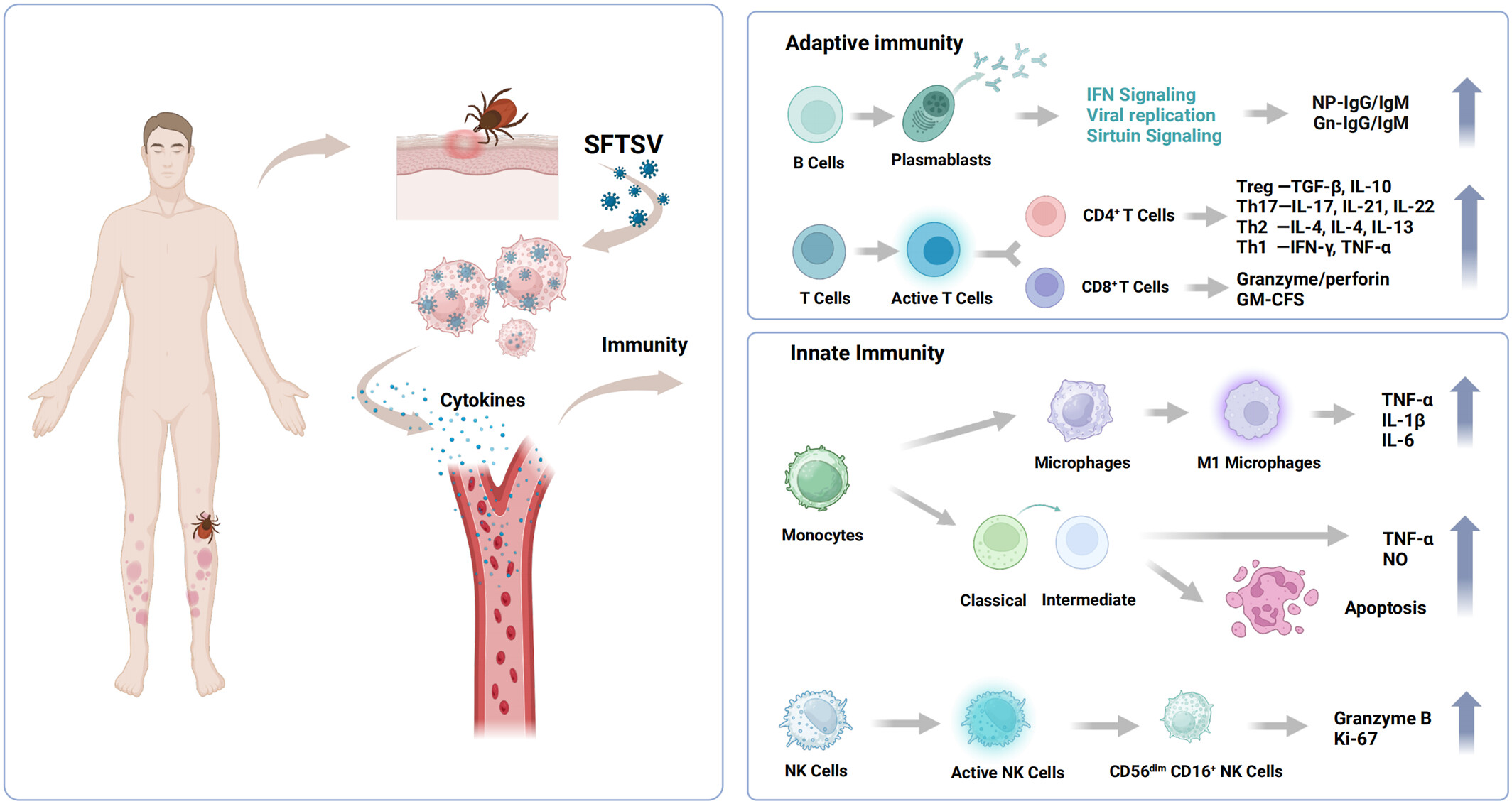
Early prognosis biomarkers of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
- Pages: 341-351
- First Published: 08 December 2024