Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
From bench to bedside: Opportunities and challenges for iLABMED
- Pages: 1-5
- First Published: 26 February 2024
REVIEW
Diagnostic approaches for monkeypox virus
- Pages: 6-13
- First Published: 07 March 2024
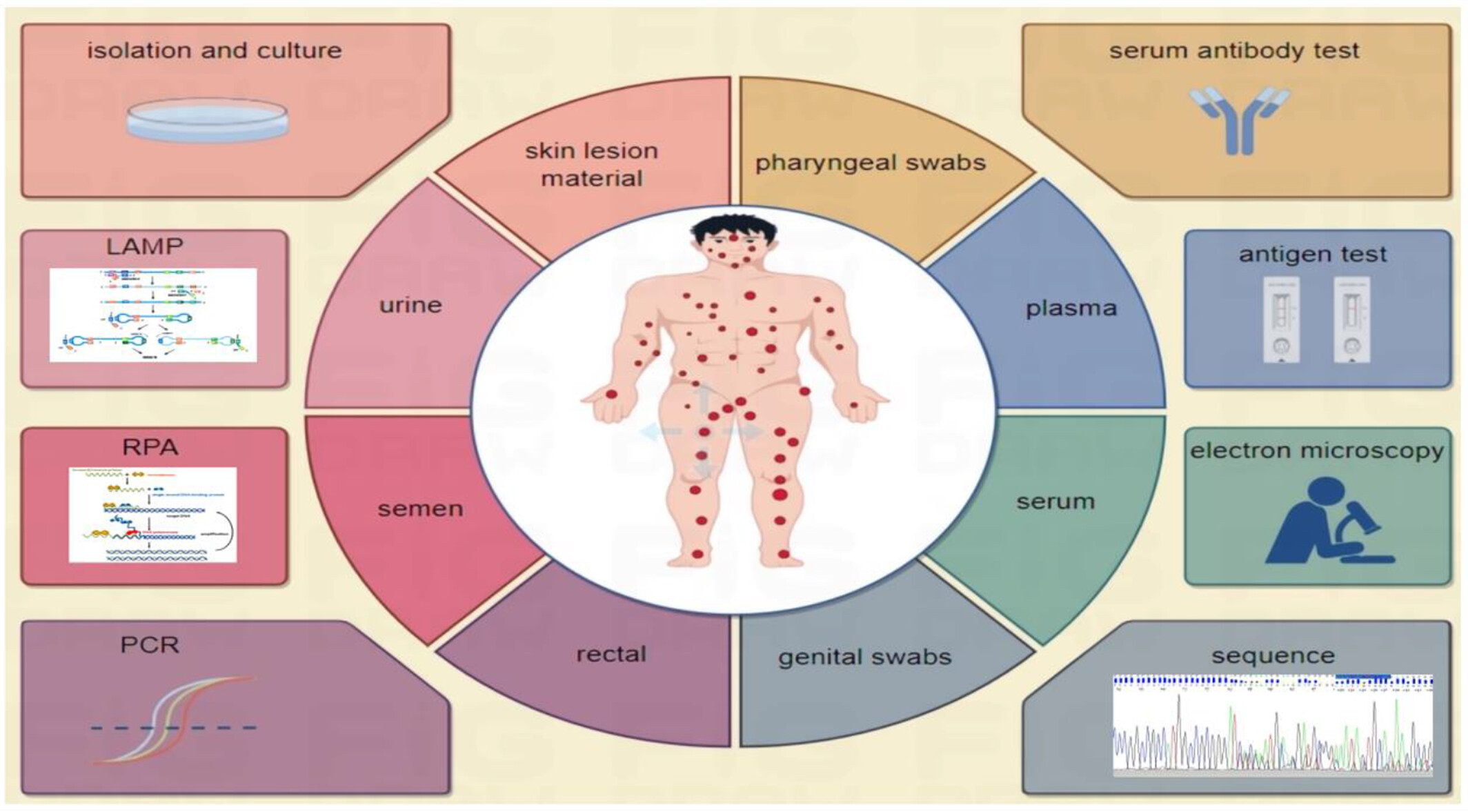
This review highlights the technical details, application scenarios, and the advantages and disadvantages of MPXV-specific diagnostic methods. The main diagnostic techniques include (1) monkeypox virus isolation and culture (2) immunoassays (3) molecular methods (4) electron microscopy. In addition, the types of specimens for MPXV detection and their uses are introduced.
Biomarkers for predicting efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy and their detection methods
- Pages: 14-26
- First Published: 16 February 2024
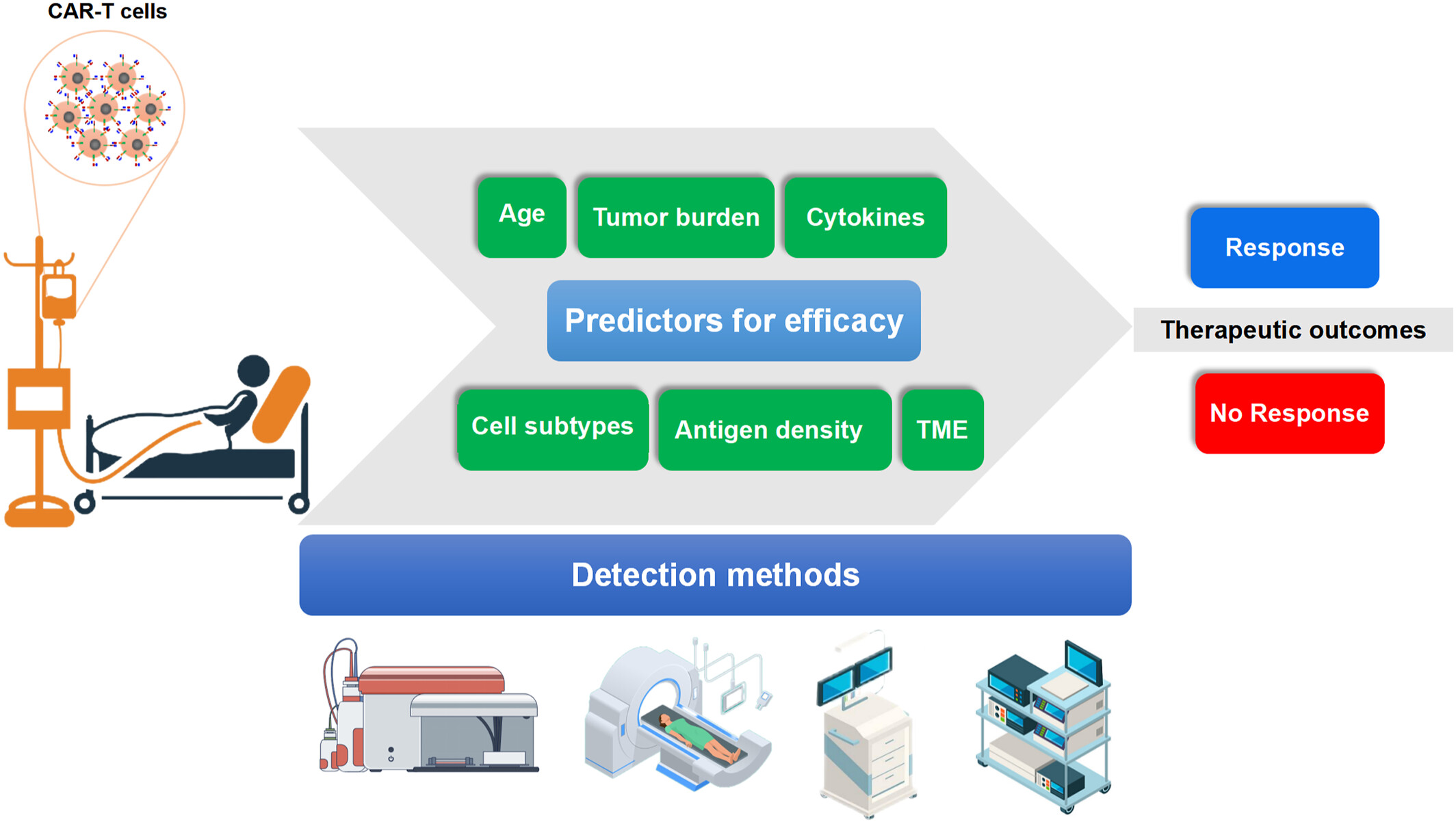
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the factors predicting the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy, with a particular focus on biomarkers and their detection methods. Six key factors were potential predictors for the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy: (1) age, (2) tumor burden, (3) cytokines, (4) cell subtypes, (5) antigen density, and (6) tumor microenvironment.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Identification of new diagnostic targets for hepatitis B virus-induced liver fibrosis
- Pages: 27-37
- First Published: 02 January 2024
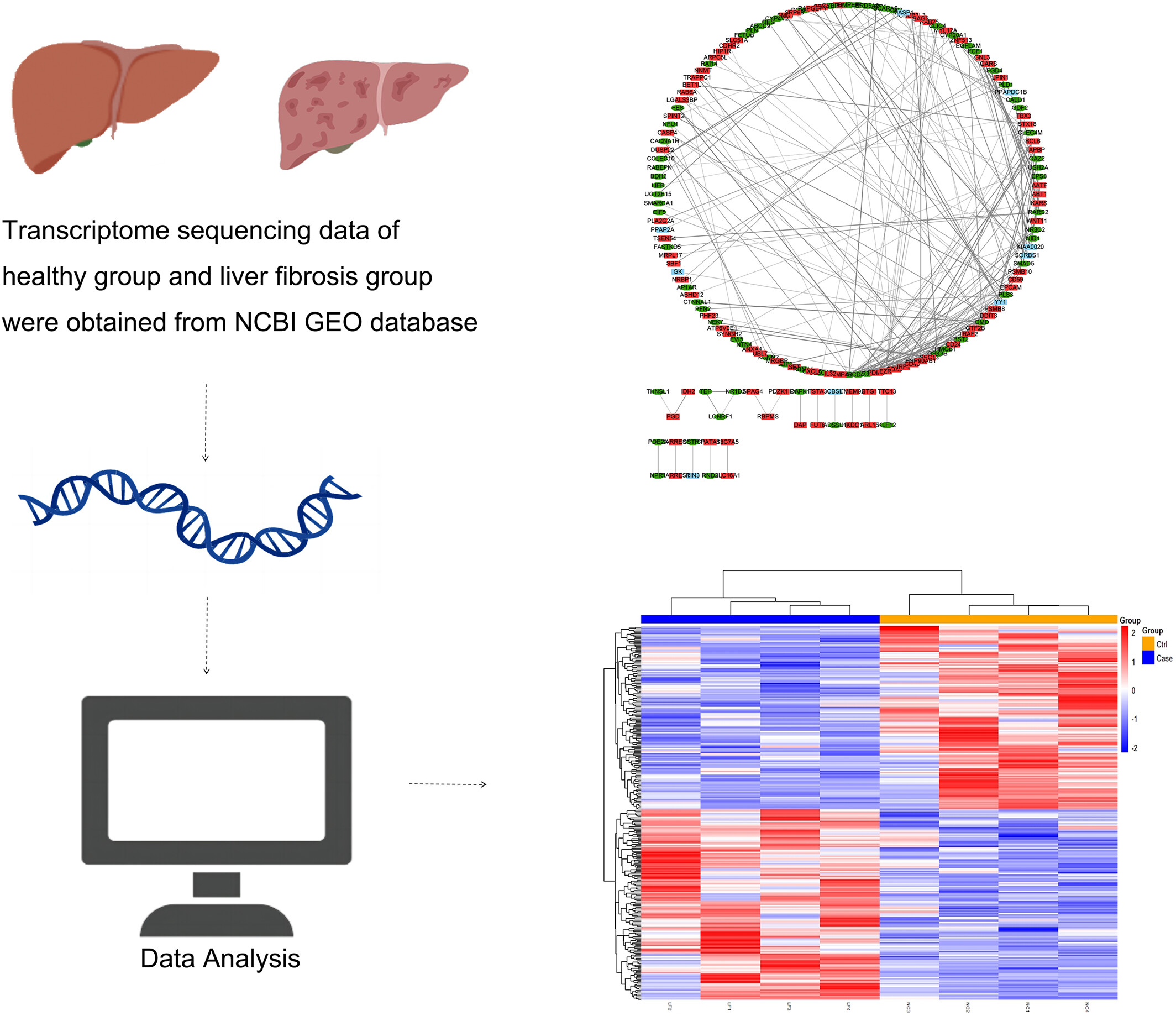
The GSE171294 human liver fibrosis sequencing matrix (mRNA matrix obtained through high-throughput sequencing technology) from the NCBI GEO database was utilized in this study to analyze healthy human liver tissue and hepatitis B virus induced liver fibrosis tissues. Differentially expressed mRNAs were identified using R software aiming to identify potential therapeutic targets for hepatitis B virus induced liver fibrosis through functional enrichment and protein interaction analysis.
A preliminary study of the mechanism of compound hearing loss caused by ototoxic drugs combined with impulse noise
- Pages: 38-52
- First Published: 13 March 2024
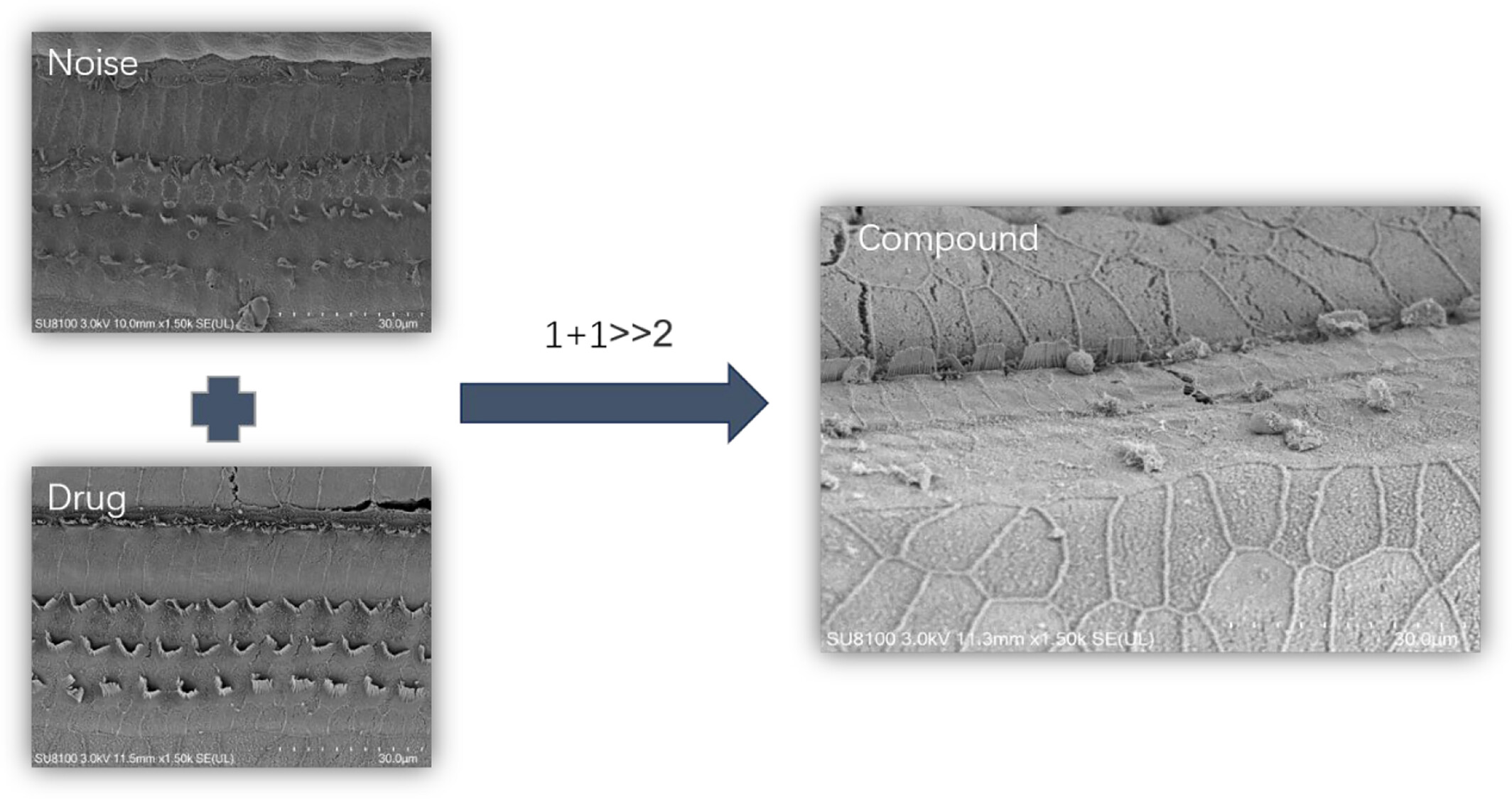
We confirmed a synergistic effect between ototoxic drugs and impulse noise that could significantly enhance the signal transduction pathway of apoptosis, including the initiation of p38MAPK, increase the level of oxidative stress and the waterfall response of inflammatory factors in the cochleae, resulting in severe hair cell damage and even severe compound HL.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections and improper storage conditions influence the performance of 1,3-β-d-glucan in diagnosis of invasive fungal infections
- Pages: 53-59
- First Published: 20 February 2024

This research investigates BDG false-positivity during bacterial infections and false-negativity during storage. Four key thrusts should be considered when diagnosing IFI based on BDG testing. (1) Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces extremely high yields of BDG in culture supernatants. (2) Streptococcus pneumoniae produces low yields of BDG in culture supernatants. (3) The degradation rates of BDG increase with increasing temperatures. (4) Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections and improper storage conditions have a higher risk of influencing BDG test results.
CASE REPORT
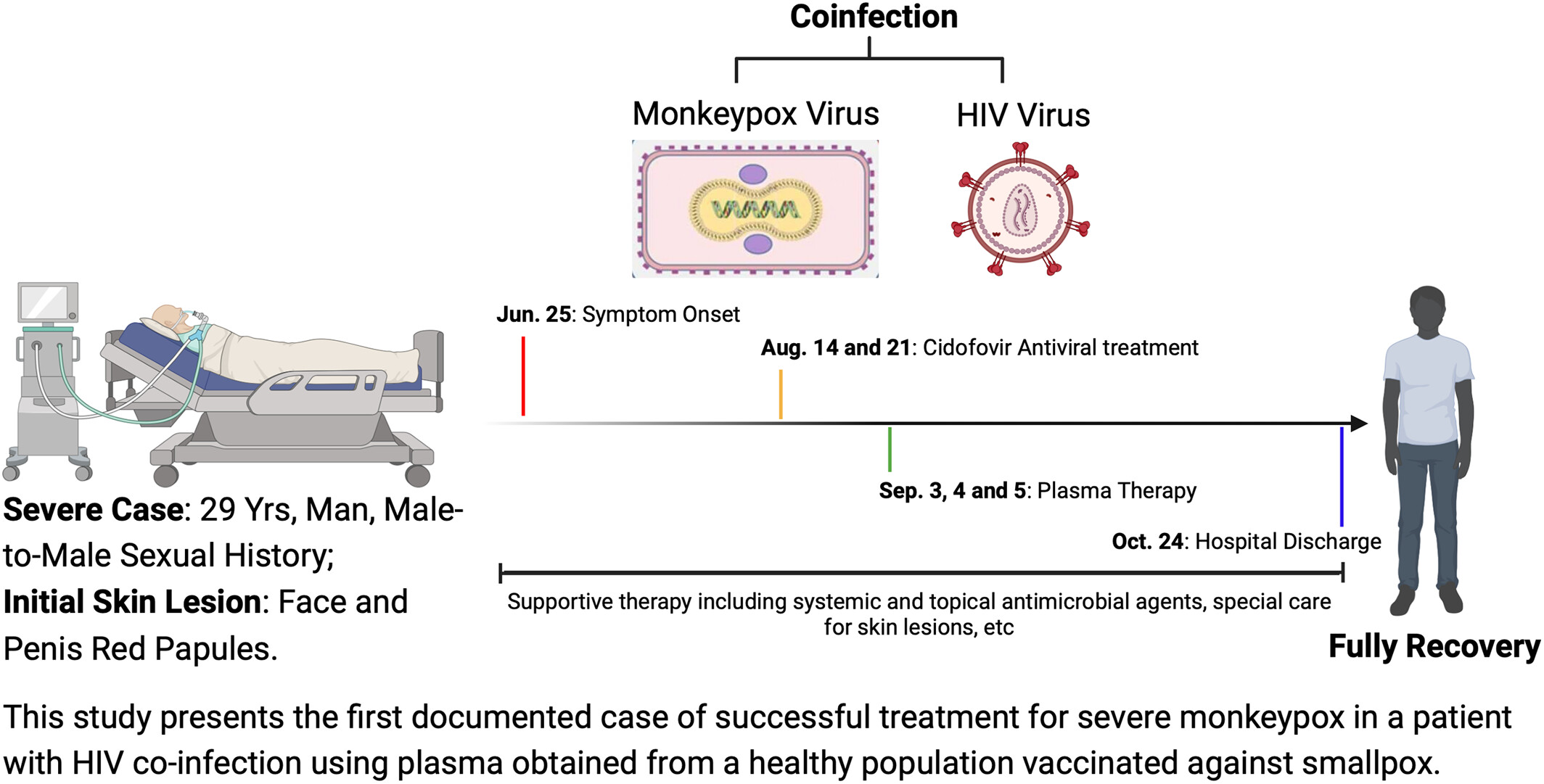
Successful treatment of severe monkeypox case with advanced HIV infection using plasma from smallpox-vaccinated healthy population: A case report
- Pages: 60-66
- First Published: 10 March 2024