Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Predicting venous thromboembolism (VTE) risk in cancer patients using machine learning
- Pages: 205-222
- First Published: 13 July 2023
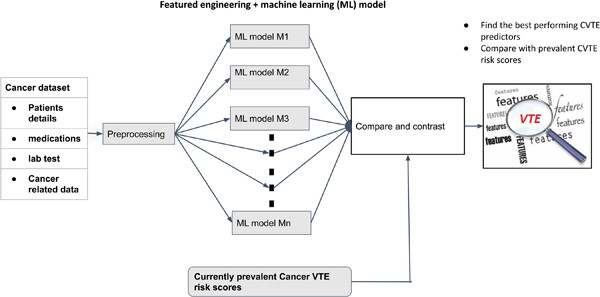
In this study, we examined the utility of using machine learning (ML) to predict venous thromboembolism (VTE) in cancer patients. It allowed us to draw insight into our feature pool and identify the features that could have the most utility in the context of developing an efficient ML classifier. Our ML-based prediction model achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.778 ± 0.006 when trained on a set of 15 features. Our result surpasses the most validated clinical scoring system for VTE risk assessment in cancer patients by 16.1%. We additionally found cancer stage information to be a useful predictor after all performed feature selection processes despite not being used in existing score-based approaches.
Healthy lifestyles in relation to cardiometabolic diseases among schoolteachers: A cross-sectional study
- Pages: 223-232
- First Published: 10 July 2023
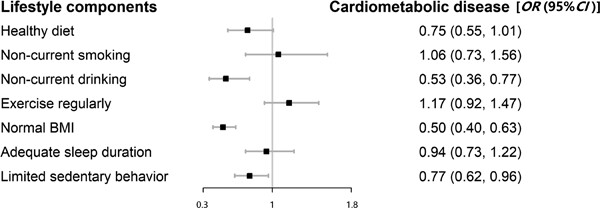
An overall healthy lifestyle (including healthy diet, noncurrent smoking, noncurrent drinking, regular exercise, normal body mass index (BMI), adequate sleep duration, and limited sedentary behavior) was significantly associated with lower odds of cardiometabolic diseases. Among specific lifestyle factors, normal BMI, noncurrent drinking, and limited sedentary behavior were the major contributors to the observed associations.
Factors underlying burnout among rural village physicians in Southwestern China
- Pages: 233-241
- First Published: 26 July 2023
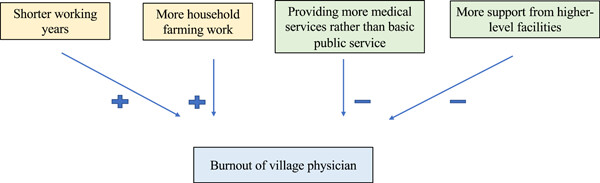
This study investigated the factors on burnout of village physicians in China, particularly exploring the effects of the medical alliance. Fewer working years, too much farming work and less workload of medical services were significantly related to exacerbation of burnout. While more supports from higher-level facilities, including transmission of images and testing results across facilities and tele-consultations, were conducive to burnout alleviation.
Exploring COVID-19 from the perspectives of healthcare personnel in Malawi
- Pages: 242-254
- First Published: 13 July 2023

This study investigates the impact of COVID-19 on healthcare workers in Malawi through a hermeneutic phenomenological approach. Findings reveal the struggles and needs of healthcare workers in a low-income nation, and highlight the role of personal biases and fear. The study provides directions for future policies and strategies to better prepare for disease outbreaks.
REVIEWS
Large language models in health care: Development, applications, and challenges
- Pages: 255-263
- First Published: 24 July 2023

The advancement of large language models (LLMs) promises to bring significant changes in health care, with extensive applications spanning pre-consultation, diagnostic, and management phases. Moreover, LLMs hold potential utility in medical education and medical writing. Concurrently, it is imperative to recognize the limitations of LLMs, strengthen review measures and enhance supervision system, thereby facilitating more effective collaboration between related personnel and LLMs.
COVID-19 retreats and world recovers: A silver lining in the dark cloud
- Pages: 264-285
- First Published: 08 August 2023
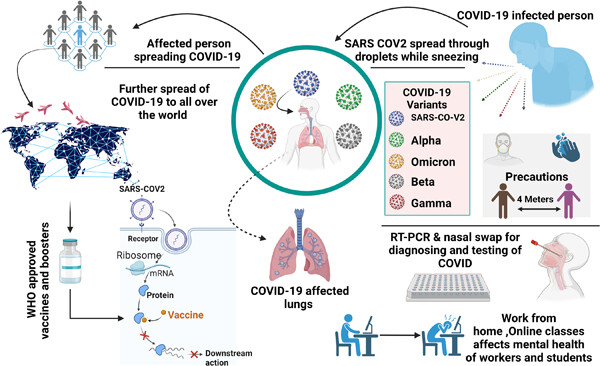
Coronavirus disease-2019 pandemic has spread across 200+ countries in a very short time span. Many have died and many are getting infected daily. But the rate has slowed down now. Improved pharmacotherapeutics and immunization with precautionary protocols have diminished its impact across the globe. The work focuses on highlighting the disease epidemiology and its socioeconomic, geopolitical, and health impact from 2019 to 2023. (Graphical abstract is created with BioRender.com)
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Differential effectiveness of COVID-19 health behaviors: The role of mental health conditions in mask-wearing, social distancing, and hygiene practice
- Pages: 286-290
- First Published: 16 July 2023











