Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Hotspots of zoonotic disease risk from wildlife hunting and trade in the tropics
野生动物狩猎和贸易引发人畜共患病风险的热带热点地区
- Pages: 165-175
- First Published: 23 January 2024
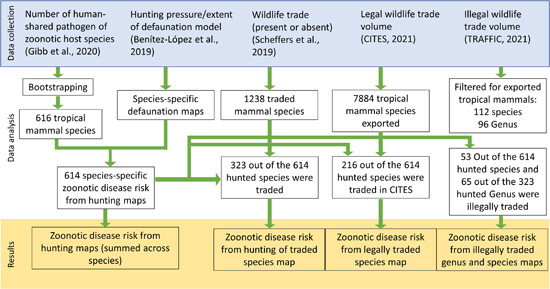
There is a lack of knowledge of which species and areas have a high risk of zoonotic disease spillover due to wildlife hunting and trade. We combined maps of hunting pressure, recent data sets on human-shared pathogens, and trade volumes for 614 mammalian host species to map zoonotic disease risk from wildlife hunting and trade pantropically. We identified hotspots of zoonotic disease risk from hunting in central America, China and central Africa.
Sustainability of medicinal animal products: Tokay geckos and pangolin scales as traditional Chinese medicine
药用动物制品的可持续性:作为传统中药的大壁虎和穿山甲片
- Pages: 176-186
- First Published: 29 January 2024
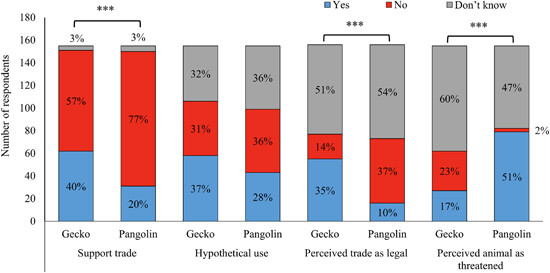
Public opinion toward pangolin and tokay gecko medicinal trade reveals significant differences in attitude and knowledge aspects but not in the percentage of hypothetical users. It is thus interesting to investigate hypothetical user profiles and the driving factors behind their choices. Setting up legal protection status for species is found to be the most influential factor in shaping public attitudes and is thus more likely to change behaviors. With the high demand for gecko products, the need for up-to-date NDFs is becoming increasingly urgent.
The cooperative development relationship between Nature Reserves and local communities
自然保护区与社区的协同发展关系
- Pages: 187-200
- First Published: 23 January 2024
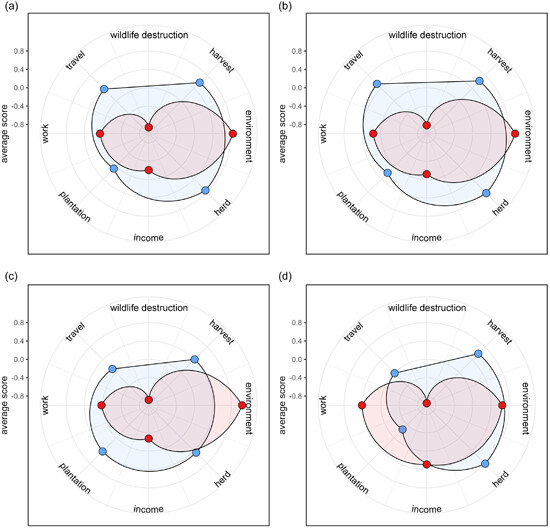
The incongruous relationship between Nature Reserves (NRs) and adjacent communities has a significant impact on both these communities and conservation management practices. However, the precise relationship between NRs and their surrounding communities remains poorly understood. Is the relationship between the two entities coordinated or unbalanced? Our research provides an empirical evidence of the adverse effects resulting from the establishment of NRs on community development. In response, we advocate for a model that actively involves the public in future development strategies, with a view to fostering coordinated progress between the NRs and local communities.
Impacts of livestock grazing on blue-eared pheasants (Crossoptilon auritum) survival in subalpine forests of Southwest China
散放家畜对中国西南山地亚高山森林雉类蓝马鸡的影响
- Pages: 201-213
- First Published: 22 January 2024
Social and cultural aspects of human–wildlife conflicts: Understanding people's attitudes to crop-raiding animals and other wildlife in agricultural systems of the Tibetan Plateau
社会和文化视角下的人与野生动物冲突:青藏高原农区居民对肇事动物与其他野生动物的态度研究
- Pages: 214-225
- First Published: 04 December 2023
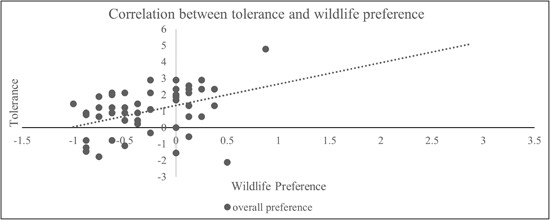
In this case study from the eastern Tibetan area of China, we used a multi-year data set from a novel compensation insurance initiative in five Buddhist villages, coupled with an extensive questionnaire-based survey. Our aim was to elucidate the local people's tolerance to crop-raiding species. Wildlife tolerance was generally high and predominantly shaped by wildlife preference rather than by economic incentives or mitigation interventions. This finding provides valuable insight for practitioners, underscoring the necessity to consider the local context and the engagement of all stakeholders in conservation strategy.
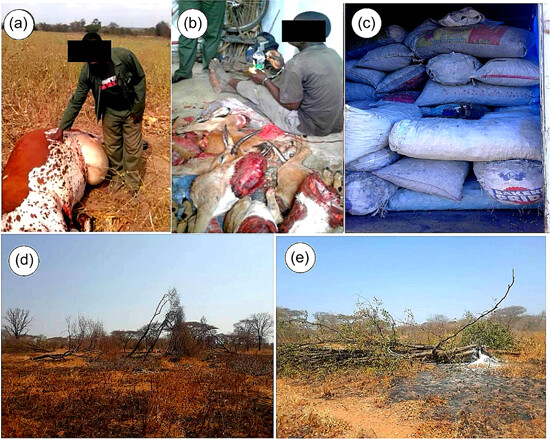
An assessment of local community engagement in wildlife conservation: A case study of the Save Valley Conservancy, South Eastern Zimbabwe
评估当地社区保护野生动物的参与度:以津巴布韦东南部的Save Valley Conservancy为例
- Pages: 226-239
- First Published: 15 December 2023
Between conflict and coexistence: Wildlife in rubber-dominated landscapes
冲突与共存之间:橡胶林主导景观中的野生动物
- Pages: 240-254
- First Published: 04 January 2024
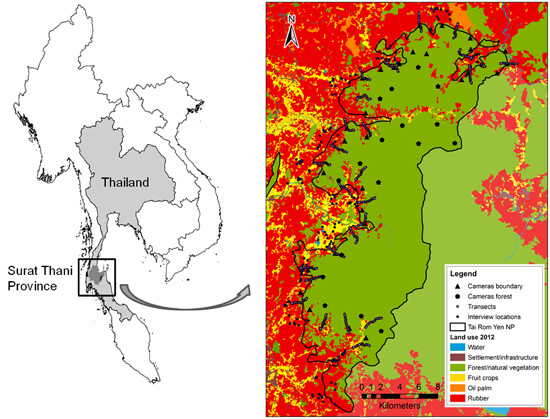
Natural habitat loss forces some wildlife species to increasingly extend their habitats into farmlands. Rubber-dominated landscapes surrounding protected areas have the potential to facilitate coexistence between people and some wildlife species if young plants are better protected and plantation management is made more wildlife-friendly.
Free-ranging dogs and their owners: Evaluating demographics, husbandry practices and local attitudes towards canine management and dog–wildlife conflict
自由放养的家犬及其主人: 评估数量、饲养方法以及当地人对家犬管理和犬与野生动物冲突的态度
- Pages: 255-270
- First Published: 28 January 2024
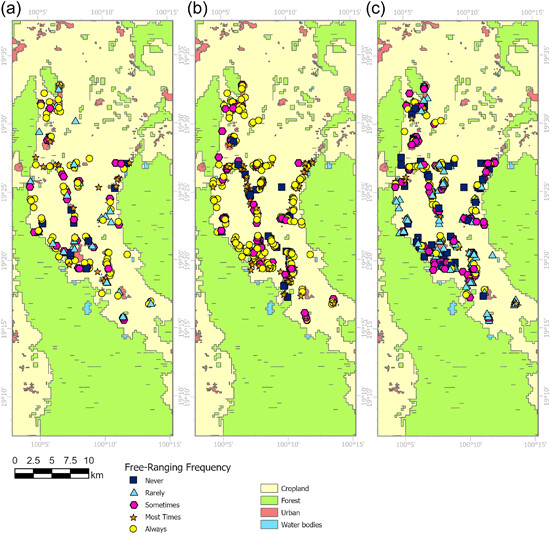
A survey in rural Thailand revealed widespread dog ownership, with most dogs unrestricted in their movements. However, there was a notable lack of awareness among the local population about the potential impact these dogs might have on wildlife. To address this issue, recommendations include enhanced education, enforcement of dog-free policies in protected areas and collaborative efforts to manage dog populations and safeguard wildlife.