Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
The synergistic ameliorative activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and gamma agonists, fenofibrate and pioglitazone, on hippocampal neurodegeneration in a rat model of insulin resistance
- Pages: 251-263
- First Published: 08 August 2022
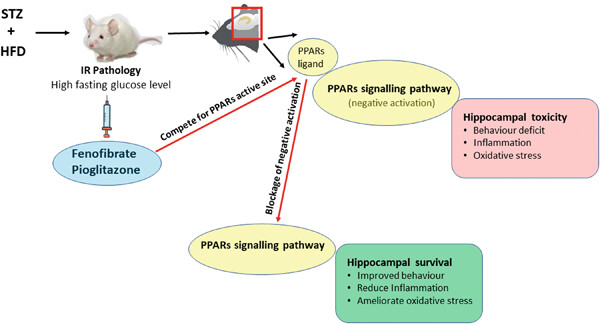
Induction of symptoms of insulin insensitivity with the concomitant administration of streptozotocin (STZ) and a high-fat diet (HFD) increased the fasting glucose level. This alters the neural activities and morphology of the hippocampus via negative activation of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARs)-regulated signaling pathways needed for synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival. However, the use of fenofibrate and pioglitazone (PPARs agonists) results in competition for similar active sites and leads to modulation of the respective signaling pathways altered by insulin insensitivity to mitigate alterations of the hippocampus and improve its functionality and neuronal survival.
Treadmill training improves cognitive function by increasing IGF2 targeted downregulation of miRNA-483
- Pages: 264-275
- First Published: 21 July 2022
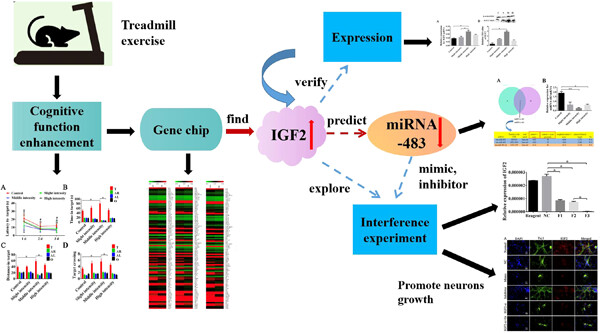
After 6 weeks of treadmill training, the Morris water maze experiment was used to study the effects of treadmill exercise on the spatial learning and memory of rats. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot results confirmed that insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) expression was significantly upregulated in the hippocampus of rats after moderate-intensity treadmill exercise. Its function is to repair neurons, but the growth of neurons is inhibited after silencing IGF2. MicroRNA-483-inhibitor can repair the damage of hippocampal neurons induced by silencing IGF2 and promote the growth of hippocampal neurons.
Study on painless gastroscopy and POCD of smoking patients under general anesthesia
- Pages: 276-284
- First Published: 25 May 2022
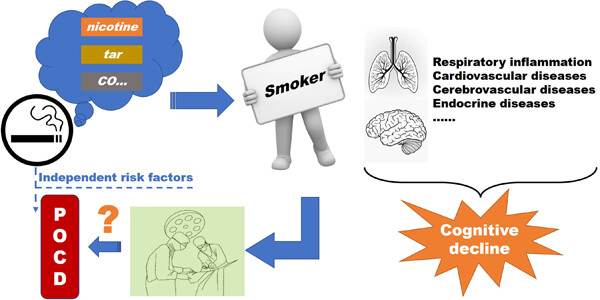
The purpose of this article was to explore whether smoking is an independent risk factor for postoperative cognitive impairment. A double-blind, parallel, and controlled study was conducted on 112 patients who met the standard and planned to undergo painless gastroscopy under general anesthesia. The changes in mini-mental state examination (MMSE) scores after waking up and 3 days after anesthesia and the adverse events were observed. The study found that in patients with chronic smoking after undergoing general anesthesia, the MMSE score would decline after they awoke, it indicated that smoking patients with traumatic stimulus in the absence of general anesthesia would display transient mild cognitive function, smoking is probably an independent risk factor for post-operative cognitive dysfunction in early postoperative patients.
Electroacupuncture promotes nerve regeneration and functional recovery in rats with spinal cord contusion through the coordinate interaction of CD4 and BDNF
- Pages: 285-301
- First Published: 26 July 2022
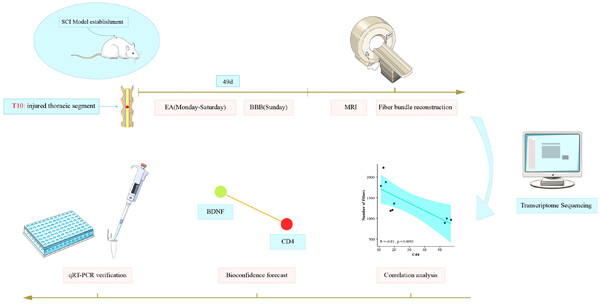
Flow chart of the study. At present, the nerve regeneration repair and treatment for spinal cord injury (SCI) patients is still in an exploratory stage, and EA has received much attention as a representative treatment for traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), but its molecular mechanism of action on functional recovery and nerve repair of SCI has not been fully elucidated. We established an SD rat spinal cord contusion (SCC) model, treated with electroacupuncture for 7 weeks, and performed Basso-Beattie-Bresnahan (BBB) score every Sunday. Rats were subsequently subjected to MRI, fiber reconstruction, and transcriptome sequencing of spinal scar samples. Using Python to write code, statistical analysis and bioinformatics analysis of the correlation between transcriptome sequencing data and fiber reconstruction results are carried out. Lastly, the expression of CD4 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in spinal cord scar was verified by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). RatsThe correlation analysis of transcriptome sequencing results with the number of reconstructed spinal cord fiber bundles revealed that the changes in expression of inflammatory factors represented by CD4 showed a strong negative correlation with the number of fibers, and the bioinformatics prediction revealed that there was a direct interaction between CD4 and a series of molecules of neural regeneration represented by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Therefore, it is inferred that the electroacupuncture treatment in spinal cord-injured rats may promote the regeneration of spinal cord fibers and recovery of motor function by reducing the inhibition of CD4 expression and thus enhancing the expression of BDNF.
The alternative 3′ splice site of GPNMB may promote neuronal survival after neonatal hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy injury
- Pages: 302-313
- First Published: 09 August 2022

Glycoprotein nonmetastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB) was the most obviously upregulated gene in differential expression genes post hypoxic–ischemic. Additionally, GPNMB was upregulated significantly in SY5Y and fetal neurons after oxygen–glucose deprivation, and GPNMB-si promoted an increase in cell viability and number. Moreover, we found that the GPNMB alternative splicing type was the alternative 3′ splice site, with the alternative splicing site in 143382985:143404102.
Brain structure analysis of different age groups of Diannan small-ear pigs
- Pages: 314-323
- First Published: 13 August 2022
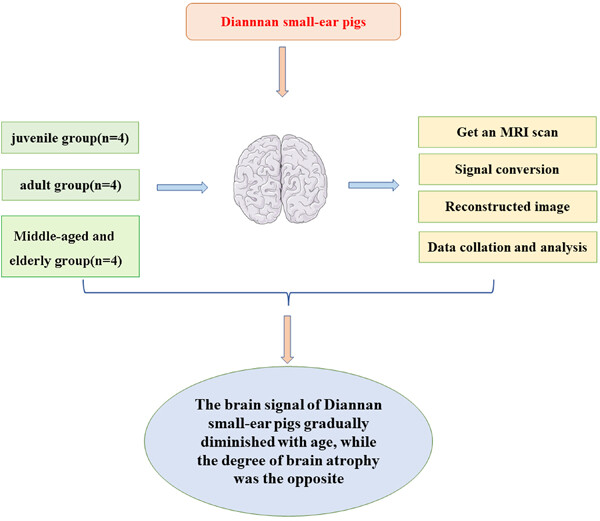
In this study, structural brain images of three groups of Diannnan small-ear pigs of different ages were scanned by magnetic resonance imaging, 3D images were constructed for whole-brain images and VBM analysis of T2 structural images was performed, and the results were compared cross-sectionally and longitudinally. The results revealed that brain development and brain atrophy were closely related to age. In this study, the basic brain tissue data were measured in Diannnan small-ear pigs to provide basic data for the development of brain test standards, related studies, and modeling of related brain diseases in Diannnan small-ear pigs.
AQP4 knockout promotes neurite outgrowth via upregulating GAP43 expression in infant rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
- Pages: 324-337
- First Published: 19 August 2022
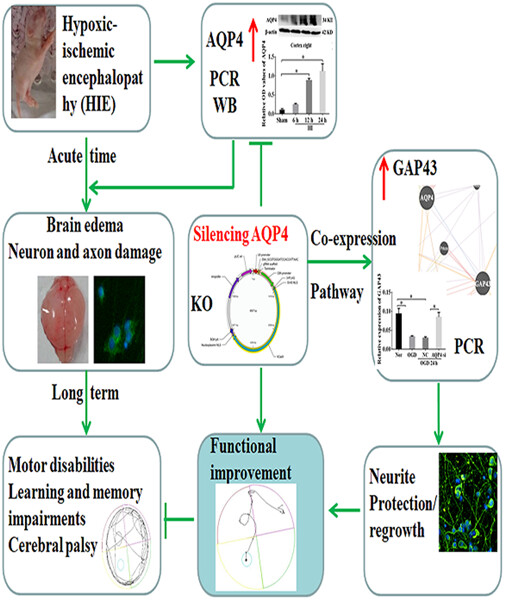
Neonatal Sprague–Dawley rats (7 days old) were applied to establish hypoxic-ischemic (HI) models; moreover, siRNA and CRISPER-/Cas9-mediated gene-editing technologies were then employed to explore the role of AQP4 in the neurological damages at 24 h after HI in vitro and in vivo. The results revealed that silencing AQP4 could promote the outgrowth of the length in oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) neurons. Moreover, AQP4-knockout could notably improve long-term neurobehavioral impairment compared with AQP4-wild type 1 month after HI reflected by the tests of neurological severity score, water maze, and Y-maze. Furthermore, growth-associated protein-43 (GAP43) was closely correlated with AQP4 in both pathway and co-expression channels via GeneMANIA prediction. As expected, OGD induced significant downregulation of GAP43, while AQP4 knockout could markedly upregulate its expression. These indicated that AQP4 silencing could enhance axon regeneration and promote long-term neurobehavioral recovery after HI; the underlying mechanism was associated with GAP43 upregulation.
Study of anxiety and job burnout, and awareness among young anesthetists during COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 338-345
- First Published: 27 August 2022
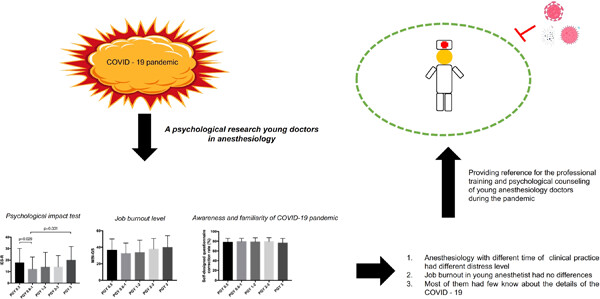
In this study, the psychological impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on young doctors and their job burnout in the Department of Anesthesiology during the initial days of the pandemic are described, using the Impact of Event Scale-Revised and Maslach Burnout Inventory General Survey and their awareness and familiarity of this pneumonia is also investigated. We found that most participants were as expected maintaining a positive mood during this hard period, yet COVID-19 has caused a mild level of distress among young doctors in anesthesia. Besides, some of them were undergoing mild work burnout. Teaching hospitals should provide timely multichannel information about the diagnostic criteria and therapeutic methods due to the lack of detailed knowledge about the COVID-19 in young doctors, which will become key teaching points in the future. Our survey can provide references for the professional training and psychological counseling of young anesthesiology doctors during the pandemic.
Normal cerebral blood vessels under ultrasound in SD rats of different ages
- Pages: 346-352
- First Published: 04 May 2022
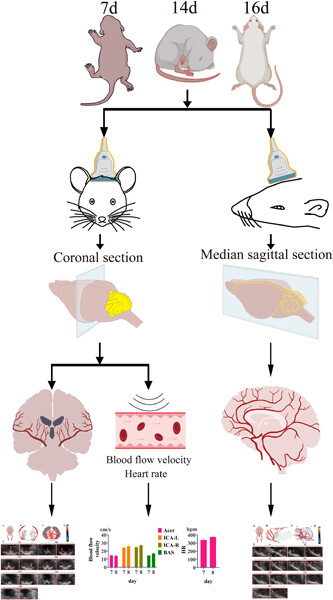
The purpose of this article mainly was to investigate whether ultrasound could also be used to monitor the brains of rats in real-time, and to know what age group of rats could be monitored by ultrasound. The correlation of cerebral vascular structure and vascular flow velocity with age was detected by transcranial ultrasound in neonatal Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats in coronal and deviated positions, respectively, which will provide a basis for the study of some brain diseases and examine whether ultrasound can examine the development of cerebral vascular structure and cerebral blood flow in SD rats by ultrasound in a noninvasive manner, which also provides a reference for ultrasound research of SD rats.
Scutellarin protects cortical neurons against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy injury via upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor
- Pages: 353-364
- First Published: 09 July 2022
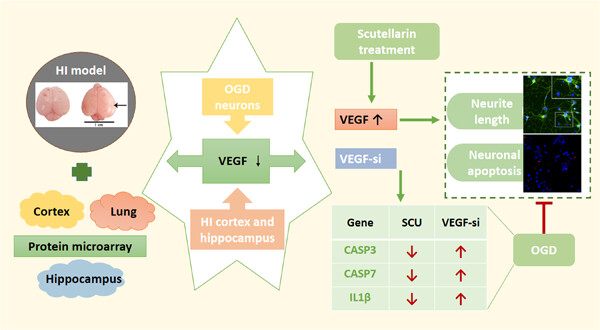
In this study, it was revealed that severe neurologic impairment and cerebral infarction were induced after hypoxia and ischemia insult, and microarray data unveiled differential expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the cortex, hippocampus, and lung tissues, along with its colocalization with neurons. Though the expression of VEGF was decreased in oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) neurons, it was obviously elevated after Scutellarin administration. Moreover, VEGF silencing depressed the effects of Scutellarin, which promoted neurite regrowth and attenuated cell apoptosis of OGD neurons. Thus, the efficacy of Scutellarin was partly abolished by interfering VEGF-triggered upregulation of caspase 3, caspase 7, and interleukin (IL)-1β, which provided a new idea for the clinical therapeutics of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
REVIEWS
Potential natural products for the management of autism spectrum disorder
- Pages: 365-376
- First Published: 21 June 2022
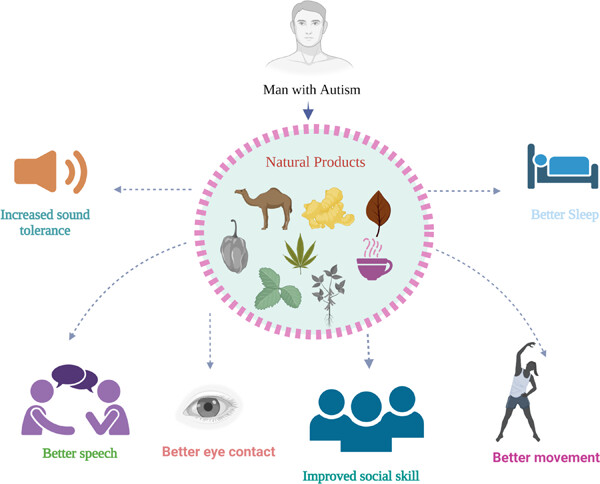
The figure explains that improvement like increased sound tolerance, better sleep pattern, better speech, improved social skills, and better eye contact and movement has been seen in patients with autism. An improvement in the symptoms can be observed by treating with natural products, such as camel's milk, luteolin, green tea, piperine, curcumin, cannabinoids, Ginkgo biloba, and Bacopa monnieri.
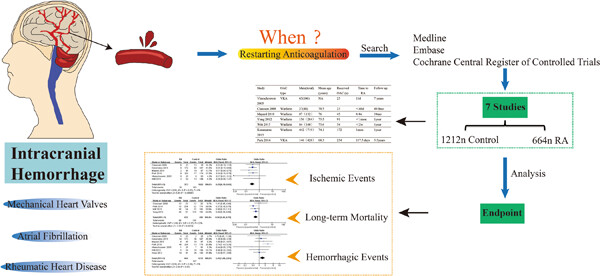
Whether it is safe to start anticoagulation after intracranial hemorrhage within 2 weeks: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 377-388
- First Published: 19 August 2022
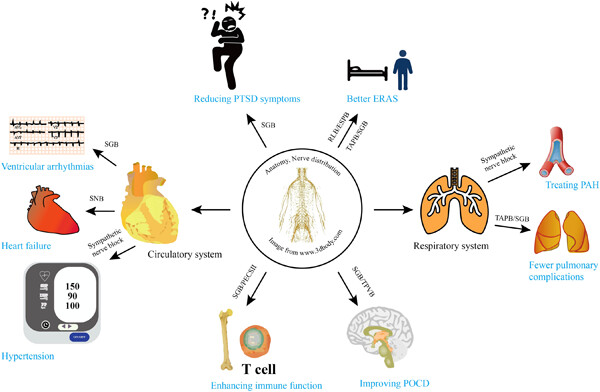
Applications of the ultrasound-guided nerve block technique for nonanalgesic effects
- Pages: 389-400
- First Published: 15 August 2022
CASE REPORTS
Invisible doppelgänger and body image disorders in right superior parietal lobule stroke, a case series
- Pages: 401-405
- First Published: 08 August 2022
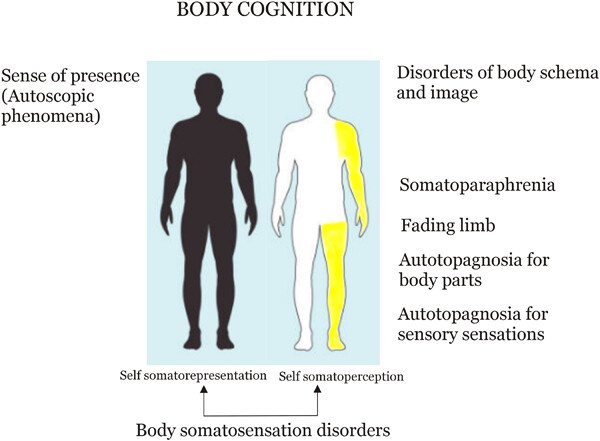
This paper describes three patients who had both the feeling of presence (FOP) and body image or body schema disorders. All patients reported almost simultaneously the invisible doppelgänger presence and at least one sense of body schema and image disorder. In terms of these cases, it is possible that body image and schema disorders may have developed in addition to FOP, especially in lesions involving the superior parietal lobule and precuneus.
Traumatic spinal cord injury caused by a dagger in the spine: A case report
- Pages: 406-412
- First Published: 25 March 2022
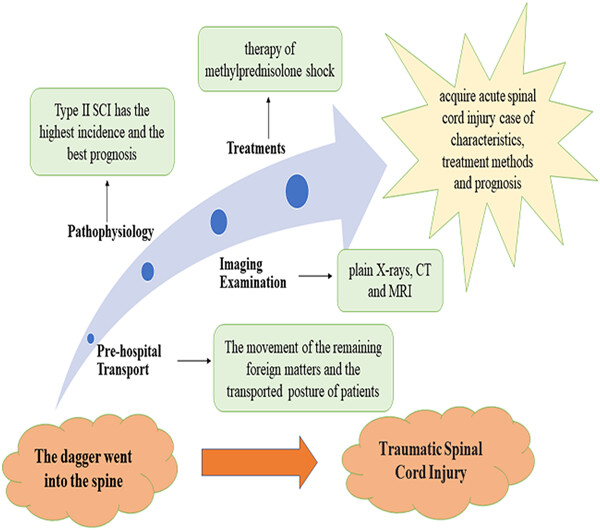
Although cases of acute spinal cord injury (SCI) combined with foreign body retention are relatively rare and are found less frequently, the possibility of extreme events that could lead to personal or even family breakdown cannot be ignored. In this study, we aimed to review and discuss prehospital transport, pathophysiology, imaging examination, and treatments for such patients sufferring from an attack of the back, causing acute SCI combined with foreign matter retention. This study shows that early surgical intervention, combined with other supportive care after surgery, and maintaining stable vital signs, prehospital transport, pathophysiology, and radiology for such patients are important to avoid secondary spinal cord injury.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Knockdown of interleukin-6 plays a neuroprotective role against hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats via inhibition of caspase 3 and Bcl-2-associated X protein signaling pathway
- Pages: 413-428
- First Published: 18 September 2022
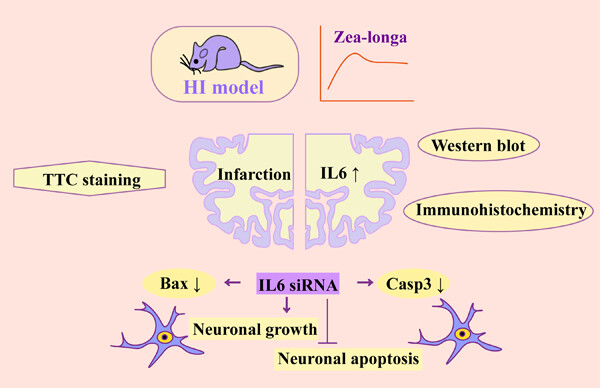
Hypoxic-ischemic (HI) induced significant brain damage, and these pathological changes were accompanied by IL-6 upregulation. Decreased Interleukin (IL)-6 improves the deficiencies in neurologic function and morphology induced by HI, and the potential mechanism may be closely related to the regulation of caspase 3 and Bcl-2 associated X protein.