Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
A novel STING agonist with systemic and durable anti-tumour activity
- First Published: 04 September 2023
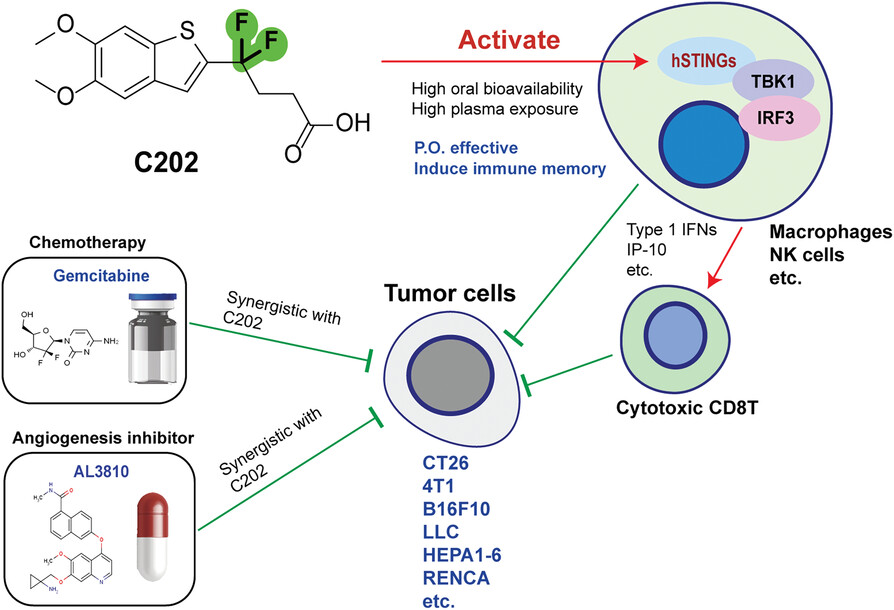
- C202 specifically activates various STING isoforms and its downstream signalling, and exhibited high oral bioavailability and plasma exposure and displayed broad-spectrum anti-tumor activity either by local or oral administration.
- C202 activated both innate and adaptive anti-tumor immunity, and importantly it induced complete tumor regression and immune memory,C202 exerts synergistic effects with chemotherapy (gemcitabine) or angiogenesis inhibitor (AL3810) in anti-tumor.
COMMENTARY
Live lean and CRISPR – Engineering metabolism with FGF21 and FNDC5
- First Published: 05 September 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Translational implications of targeting annexin A2: From membrane repair to muscular dystrophy, cardiovascular disease and cancer
- First Published: 05 September 2023
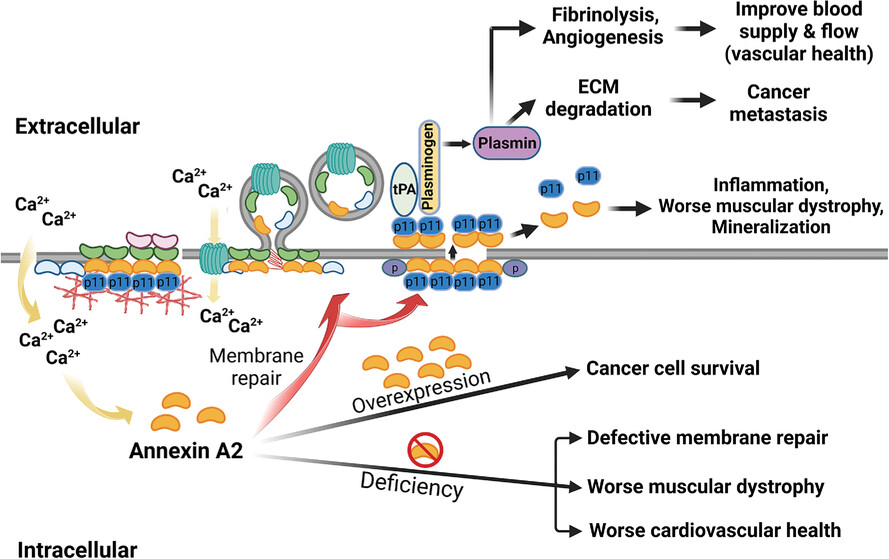
- 1. Annexin A2 is a key repair protein that works with S100A10 and other S100 proteins to execute its membrane repair and extracellular roles.
- 2. Annexin A2 is a therapeutic target because the loss of annexin A2 function enhances cellular degeneration, which exacerbates muscular dystrophy and cardiovascular disease.
- 3. Annexin A2-mediated protection is hijacked by cancer cells to enhance survival and metastasis.
COMMENTARY
Developing a mechanistic understanding of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome one cell at a time
- First Published: 10 September 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Role of the tumour microenvironment in bladder cancer pathogenesis and value of the reverse translational approach: a tale of two species
- First Published: 12 September 2023
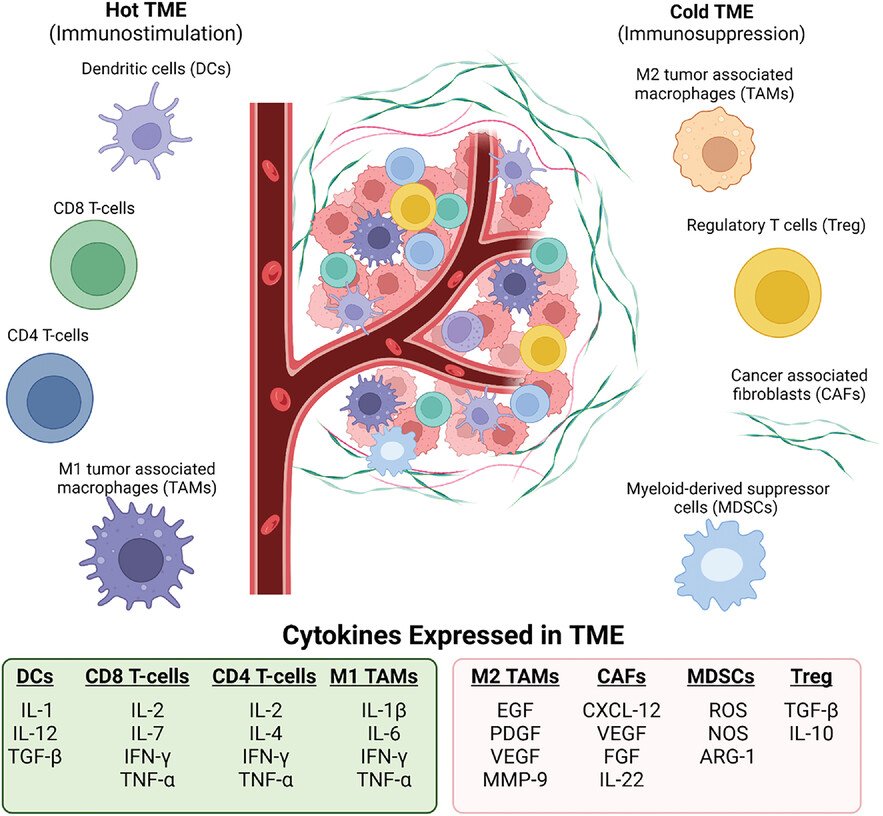
The understanding of the bladder cancer tumour microenvironment (TME) is crucial in both humans and dogs, with all clinical, molecular and histological similarities in order to select the effective treatment at the right time. There has been a recent improvement in the in vitro models that help recapitulate the immune-oncology TME elements.
EDITORIAL
Challenges of clinical translation from single-cell sequencing to measures in clinical biochemistry of haematology: Definition of immune cell identities
- First Published: 12 September 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
COMMENTARY
Commentary: All models are wrong, but some are useful: understanding cognitive decline and dementia in atrial fibrillation through vascular computational modelling
- First Published: 21 September 2023
Understanding the interplay between N6-methyladenine RNA methylation and noncoding RNAs in kidney disease
- First Published: 29 September 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in treatment against renal fibrosis
- First Published: 02 October 2023
Lp(a) and inflammation: a new insight into atherosclerosis
- First Published: 12 October 2023
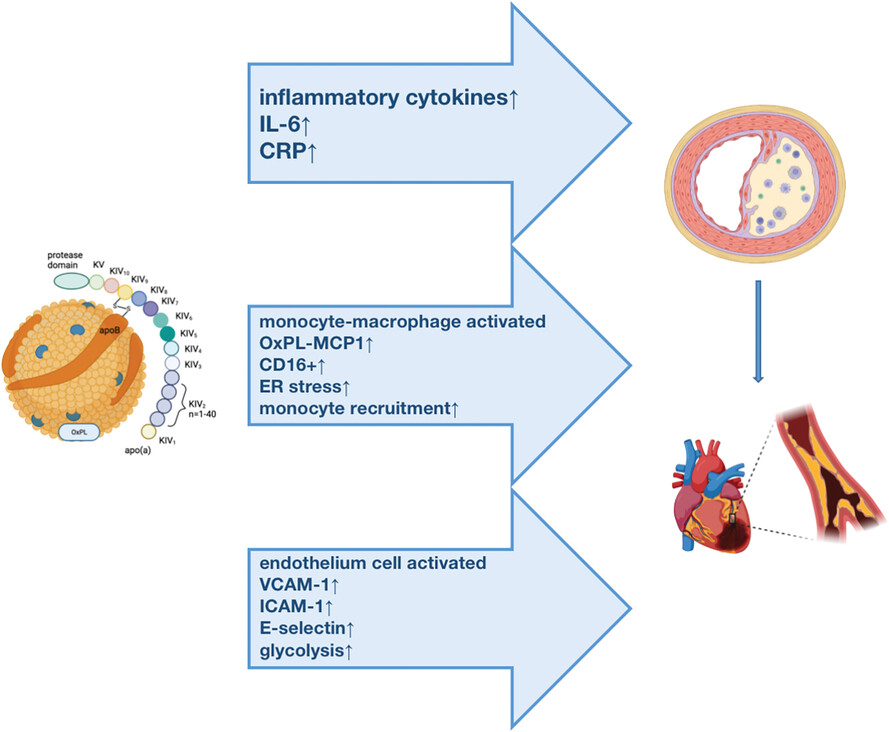
Lp(a)consists of LDL-like particles, apo(a) and OxPL. The level of Lp(a) in thehuman body is predominantly determined by genetics, with external factorshaving minimal impact. Additionally, Lp(a) levels have been found to vary amongdifferent ethnicities. There is a notable correlation between elevated levelsof Lp(a) and coronary artery disease (CAD), which is independent of otherlipoproteins. Furthermore, there exists a linear relationship between Lp(a)levels and the risk of developing ASCVD. It is now wildly believed that Lp(a) primarilycontributes to the development of cardiovascular events through pro-inflammation,pro-thrombosis and pro-atherosclerosis. From the perspective of Lp(a)influencing inflammation, it primarily promotes the release of inflammatoryfactors. This, in turn, increases levels of vascular inflammation andfacilitates the recruitment of monocytes-macrophages. Moreover, it also affectsthe function of endothelial cells during the development process ofatherosclerosis. All these aspects complement each other and contribute to theprogression of atherosclerosis. Currently, the lipid-lowering treatment used inclinical practice can partially reduce the levels of Lp(a), but its impact oninflammation is not significant.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Identification of diagnostic markers of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using transcriptomic tumour and blood sample data
- First Published: 18 October 2023
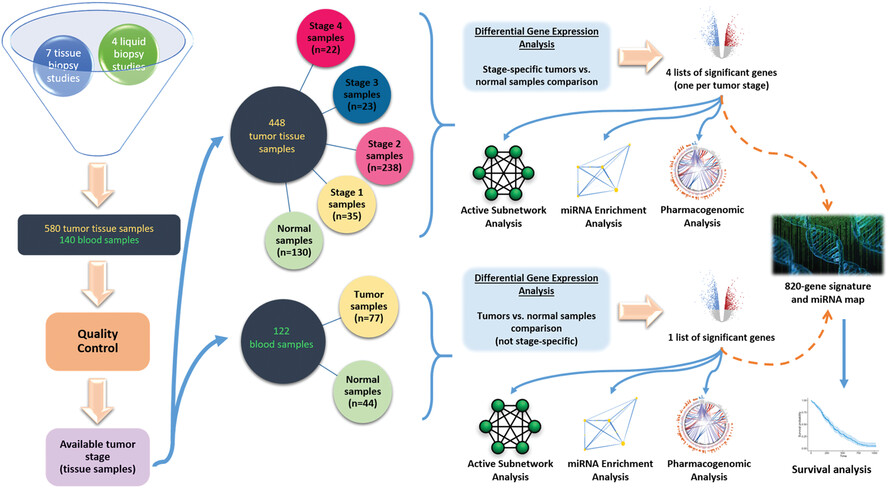
In this study, we pool publicly available gene expression data from clinical samples (tissue biopsies and blood samples) and derive and validate a signature of consistently deregulated genes across pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) samples. We identify molecular processes which are aberrated in PDAC and investigate microRNA involvement in pathology and progression. Finally, we harness documented pharmacogenomic interactions and results from our analysis to propose potential pharmacological interventions.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status in urothelial bladder carcinoma: Frequency, genomic patterns and clinical significance
- First Published: 27 October 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Review–Vibrational spectroscopy-aided diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
- First Published: 27 October 2023
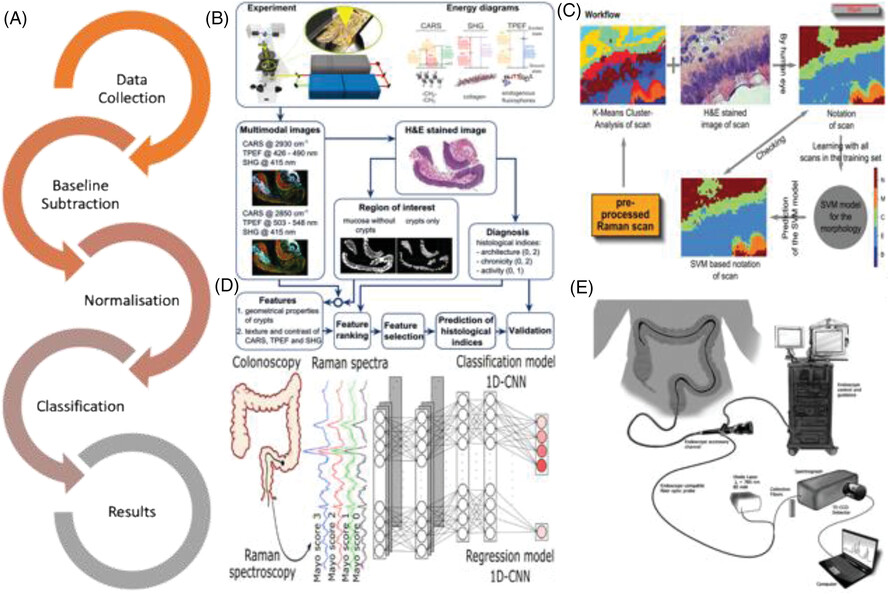
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of chronic inflammatory intestinal conditions that affect an estimated 10 million people worldwide, and currently, there is no known cure for the disease. This review is focussed on the potential of Raman spectroscopy (RS) in the diagnosis and differentiation of IBD as well as the disease-indicative biomarkers, overviewing the different Raman methodologies currently applied within clinical IBD research as well as their ability to act as monitoring and therapeutic tools in the future. Additional synopsis includes the use of RS in the identification of biomarkers and how these may contribute to the non-invasive and early detection of IBD, with further in-depth summary of the primary methodologies applied in Raman-IBD analyses and a comprehensive spectral library with corresponding peak assignments from the current Raman-IBD literature, collectively, laying a platform for the introduction of new tools for advancing the understanding of the overall biochemical changes of IBDs and the development of timely diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.