Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
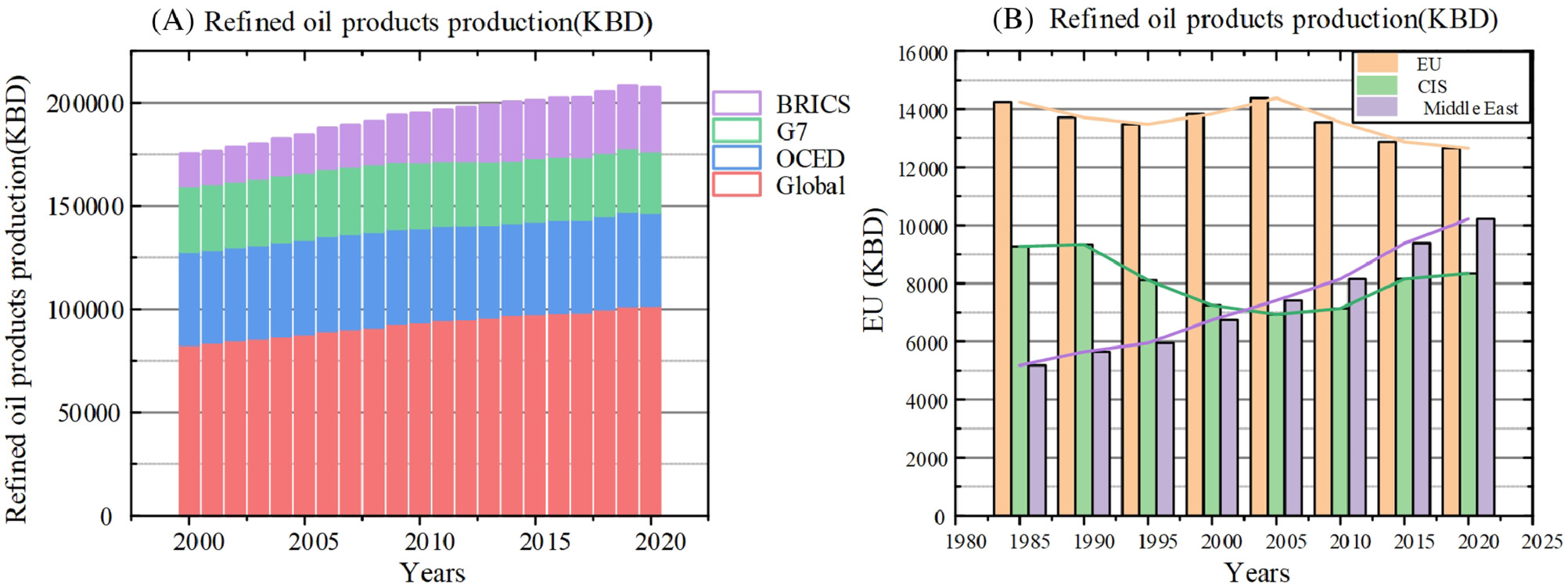
Review and outlook of global energy use under the impact of COVID-19
- First Published: 06 November 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
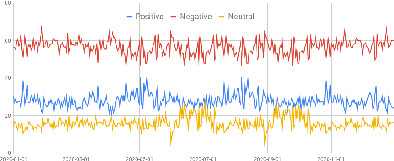
Leveraging machine learning to analyze sentiment from COVID-19 tweets: A global perspective
- First Published: 18 September 2022
Sentiment analysis on social media tweets using dimensionality reduction and natural language processing
- First Published: 11 October 2022
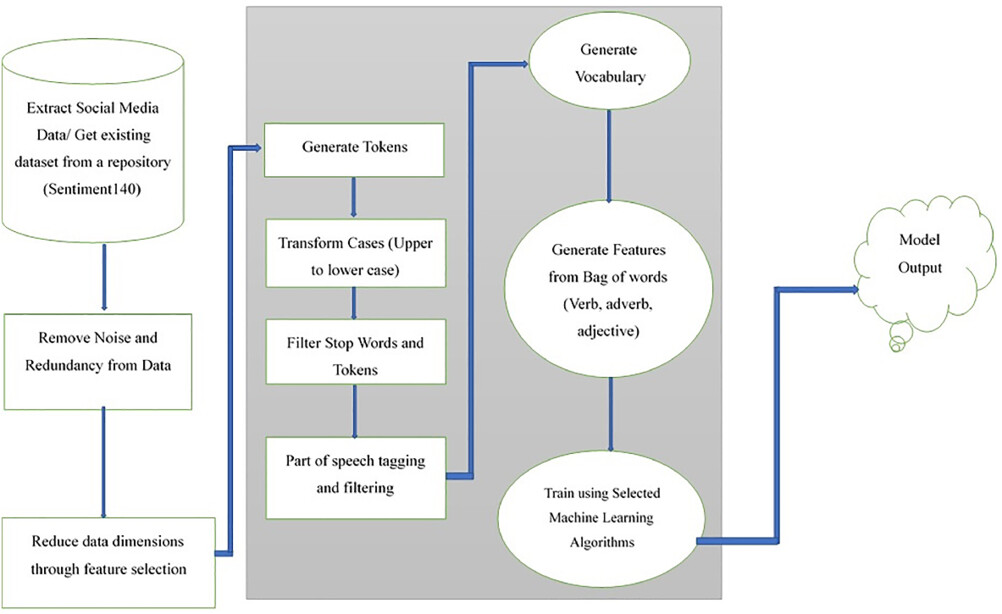
This research aims at developing a model for sentiment analysis of social media data in which dimensionality reduction and natural language processing with part of speech tagging are incorporated. The model is tested using Naïve Bayes, support vector machine, and K-nearest neighbors algorithms, and its performance compared with that of two other sentiment analysis models. Experimental results show that the model improves sentiment analysis performance using machine learning techniques.
Automatic work-order assignment method for Chinese government hotline
- First Published: 17 October 2022
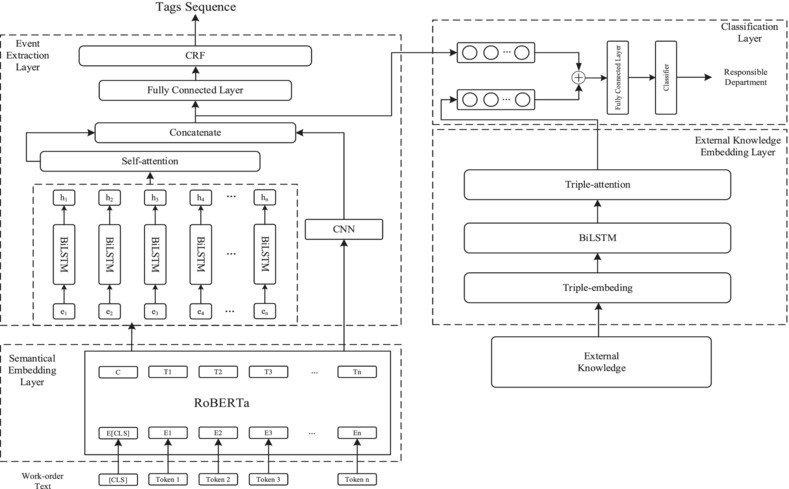
We propose a work-order assignment method based on event extraction and external knowledge to address the problem of low efficiency with manual allocation. The assignment method is composed of four parts: (1) semantic encoding layer, (2) event extraction layer, (3) external knowledge embedding layer, (4) assignment layer.
Research on the generality of icon sizes based on visual attention
- First Published: 25 September 2022
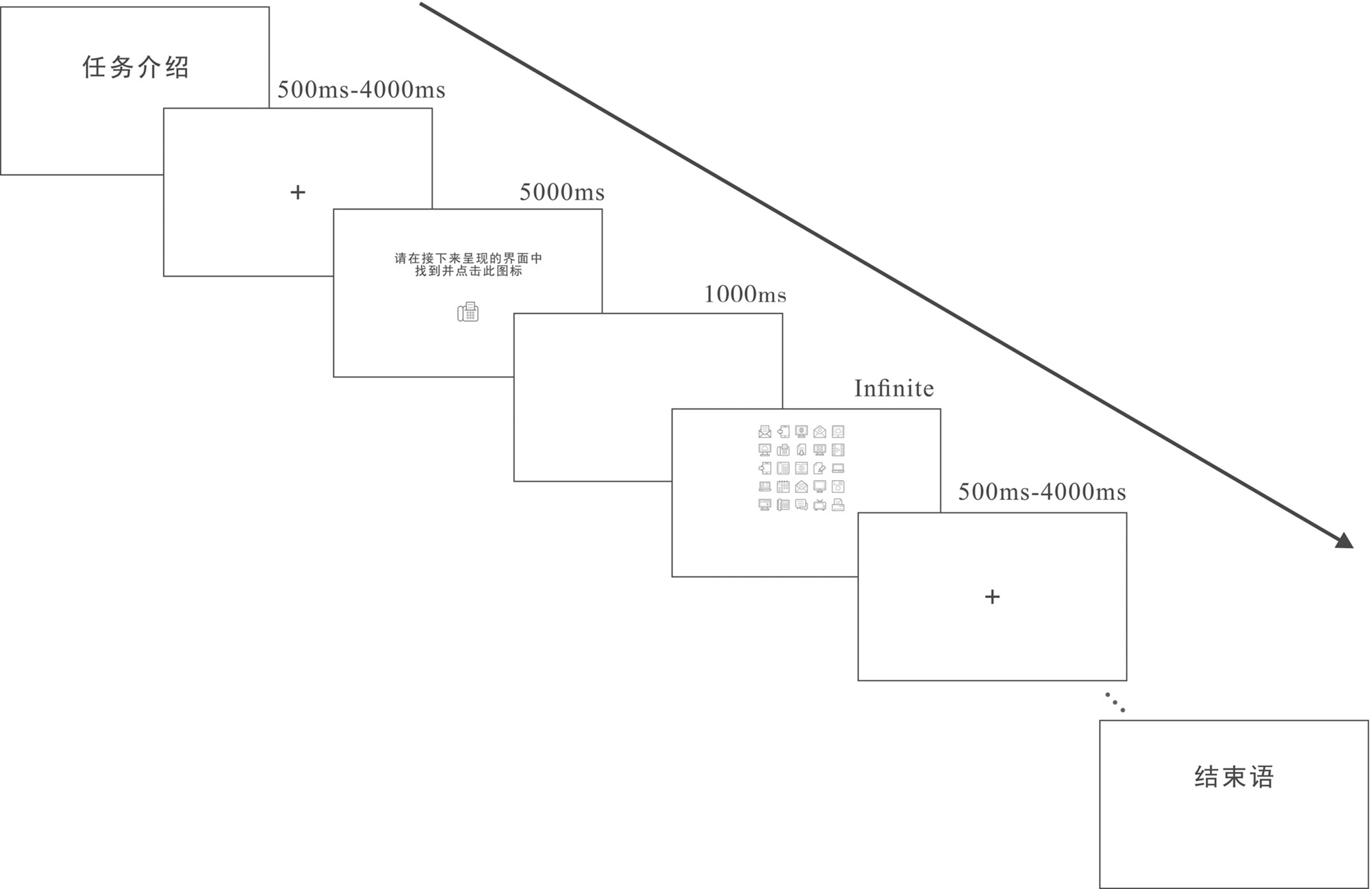
In order to meet the requirements of contactless, large amount of information and high-precision human-computer interaction in the intelligent era, as well as the continuous improvement of display resolution, we get the best ratio between icon size and display resolution and verify it by using eye tracking and EEG experiments. It is concluded that 1:309 is an effective and universal ratio. Because different display carriers have different resolutions, the use of this ratio can make icons have efficient recognition under different display resolutions, and provide a reference for icon design in different interactive interfaces based on computer software.
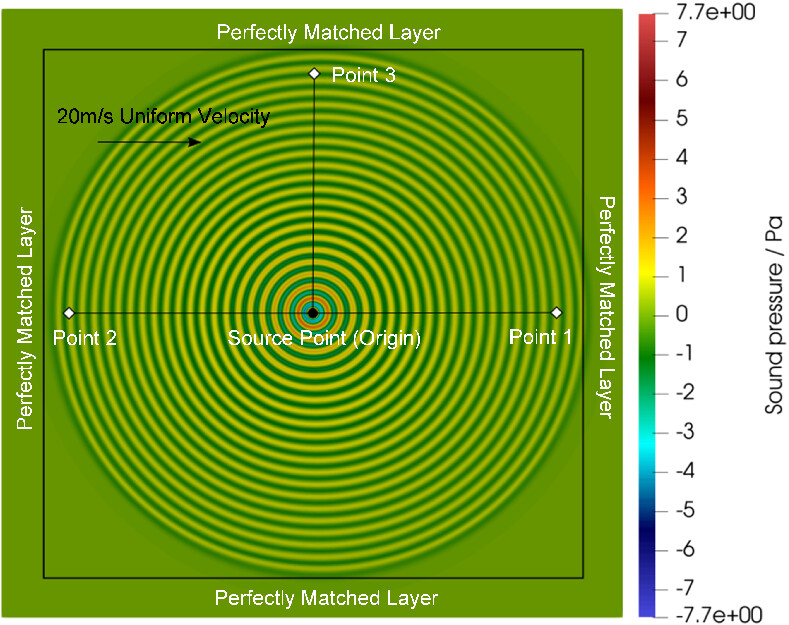
An explicit symplectic approach to solving the wave equation in moving media
- First Published: 18 September 2022
Numerical research on ablation and wear of the artillery barrel based on UMESHMOTION user-defined subroutine
- First Published: 29 September 2022
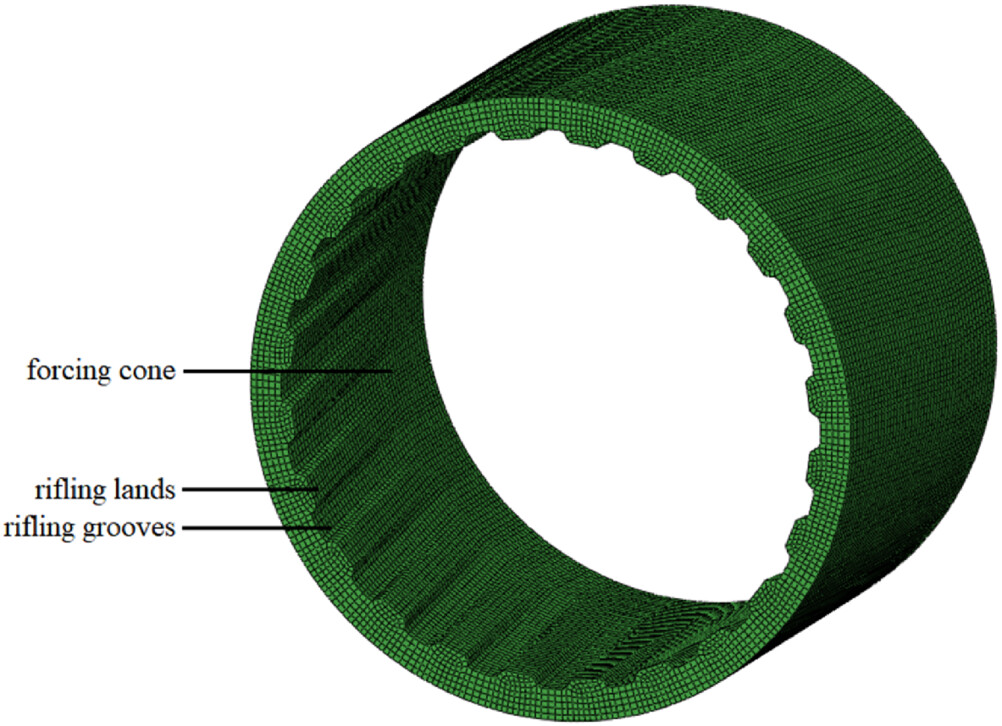
This article proposed a numerical method to calculate the ablation wear of the barrel. The research content of this article can be used to predict the life of gun steel materials in actual combat use. It includes secondary development technology, experimental verification and other steps, and the article structure is complete. This research is currently leading in the field of gun steel research.
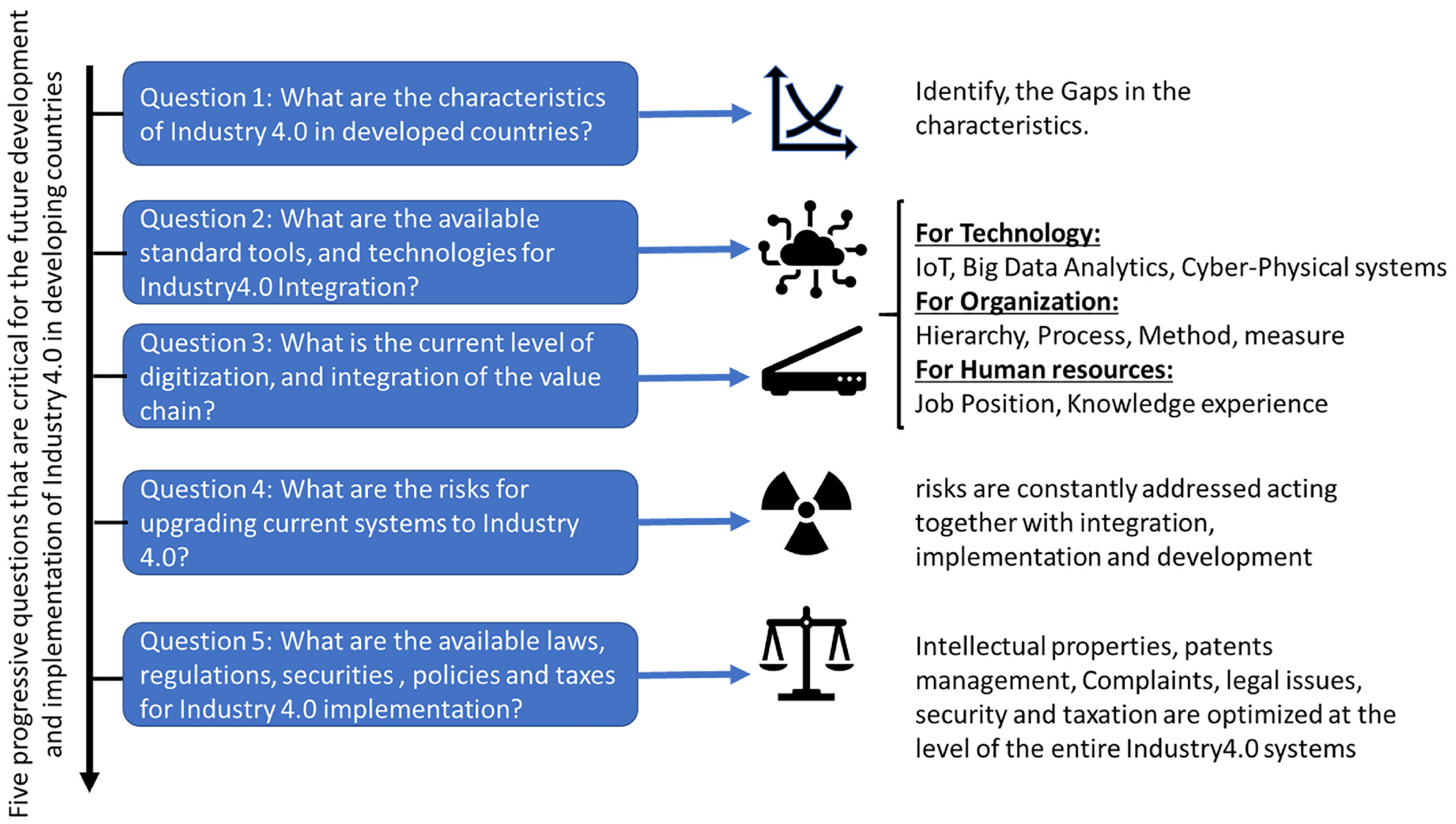
The role of intelligent manufacturing systems in the implementation of Industry 4.0 by small and medium enterprises in developing countries
- First Published: 13 October 2022
Large eddy simulation investigation of flame acceleration and deflagration to detonation transition of methane-air mixture in rectangular channel
- First Published: 11 September 2022
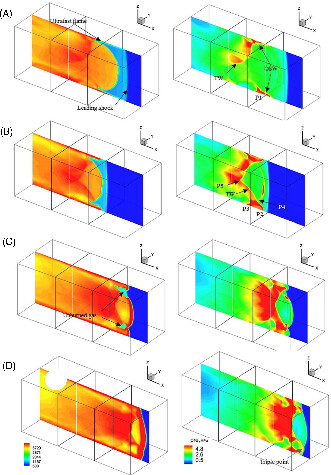
Large eddy simulation is used to simulate the process of flame acceleration and deflagration to detonation transition (DDT) of methane-air mixtures in small scale 3D channel. This study reveals a principle feature of flame acceleration in channels with no-slip walls, and the interaction between transverse waves, the pressure pulse and oblique shock waves promote DDT.
PERSPECTIVE
Applying a unified process kinetic equation to advanced materials process analysis: Characterization of the kinetics of isothermal microwave-assisted chemical syntheses
- First Published: 20 June 2022
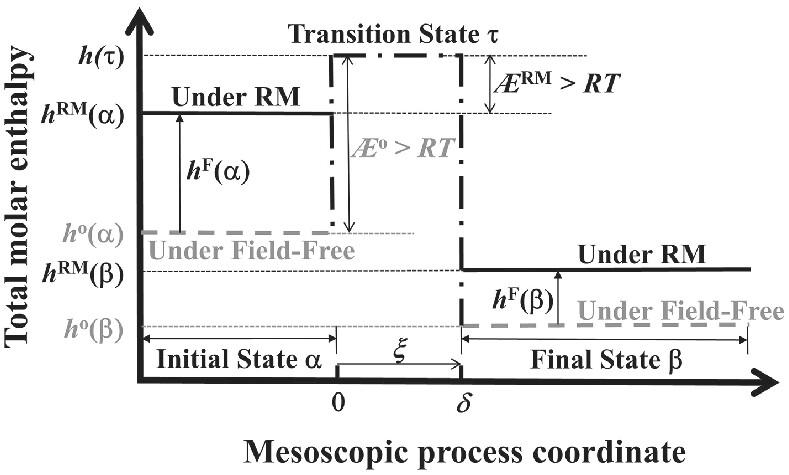
According to meso-irreversible-thermodynamics, kinetics- enhancements observed in isothermal microwave-assisted chemical syntheses are caused by a major non-thermal microwave effect (NTME). Creation of this NTME is attributed to a total enthalpy augmentation inside the resonant microwave (RM)-irradiated chemical system: RM energy-input first promotes the total molar enthalpy of the irradiated reactant(s) at temperature, which consequently motivates a reduction in activation enthalpy of the process along its mesoscopic reaction coordinate for remarkable rate-enhancement.