Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture
- Page: i
- First Published: 05 February 2025

The cover image is based on the article ‘Generation of transgenic chicken through ovarian injection’ (DOI: 10.1002/ame2.12514) reported by Jinghua Jiang, Caiying Wang, Xuguang Du, Fei Gao, Sen Wu. The article presents a technique for generating transgenic chickens in a single generation by injecting DNA into immature oocytes. This method holds immense promise for advancing the genetic manipulation capabilities of avian species that lack primordial germ cell (PGC) lines. The research not only showcases the chicken as a pivotal model organism in developmental biology but also underscores the significant value of genetic modification models in chickens.
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Embarking on a new journey, exploring infinite possibilities—Welcoming the 2025 edition of Animal Models and Experimental Medicine
- Page: 3
- First Published: 05 February 2025
Building an international platform for the research, development, and dissemination of new knowledge in the field of laboratory animal science, technology, and experimental medicine
- Page: 4
- First Published: 05 February 2025
THEMED SECTION: FRONTIER EXPLORATION OF IMMUNOLOGY AND CELL THERAPY
THEMED SECTION: REVIEW
Improving dexamethasone drug loading and efficacy in treating rheumatoid arthritis via liposome: Focusing on inflammation and molecular mechanisms
- Pages: 5-19
- First Published: 03 December 2024

Liposomal dexamethasone formulations offer targeted delivery and enhanced efficacy in treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Dex@FA-ROS-Lips utilize folic acid targeting to accumulate in inflamed joints, reducing cartilage destruction and joint swelling while improving circulation time and bioavailability. hPG-Dex liposomes enhance regulatory T cells and increase IL-10 expression, leading to systemic tolerance and reduced arthritis progression. Polymerized stealth liposomes preferentially accumulate in inflamed joints, decreasing TNF-α and IL-1β levels, thus mitigating arthritis symptoms. DP-SAL liposomes target neutrophils via sialic acid modification, enhancing anti-inflammatory effects and drug accumulation in joints. Dex-Lips reduce paw swelling, TNF-α, and IL-1β levels, showing superior therapeutic efficacy and fewer side effects compared to free DEX. These liposomal formulations demonstrate significant potential in improving RA treatment by providing targeted delivery and sustained release of DEX. Future research should focus on optimizing particle size, exploring advanced targeting strategies, and addressing scalability and regulatory challenges. Additionally, combining liposomal DEX with other therapies could further enhance treatment outcomes. Overall, liposomal DEX represents a promising approach for effective and safe RA therapy.
Unwanted disorders and xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease in experimental immunodeficient mice: How to evaluate and how to report
- Pages: 20-29
- First Published: 27 November 2024
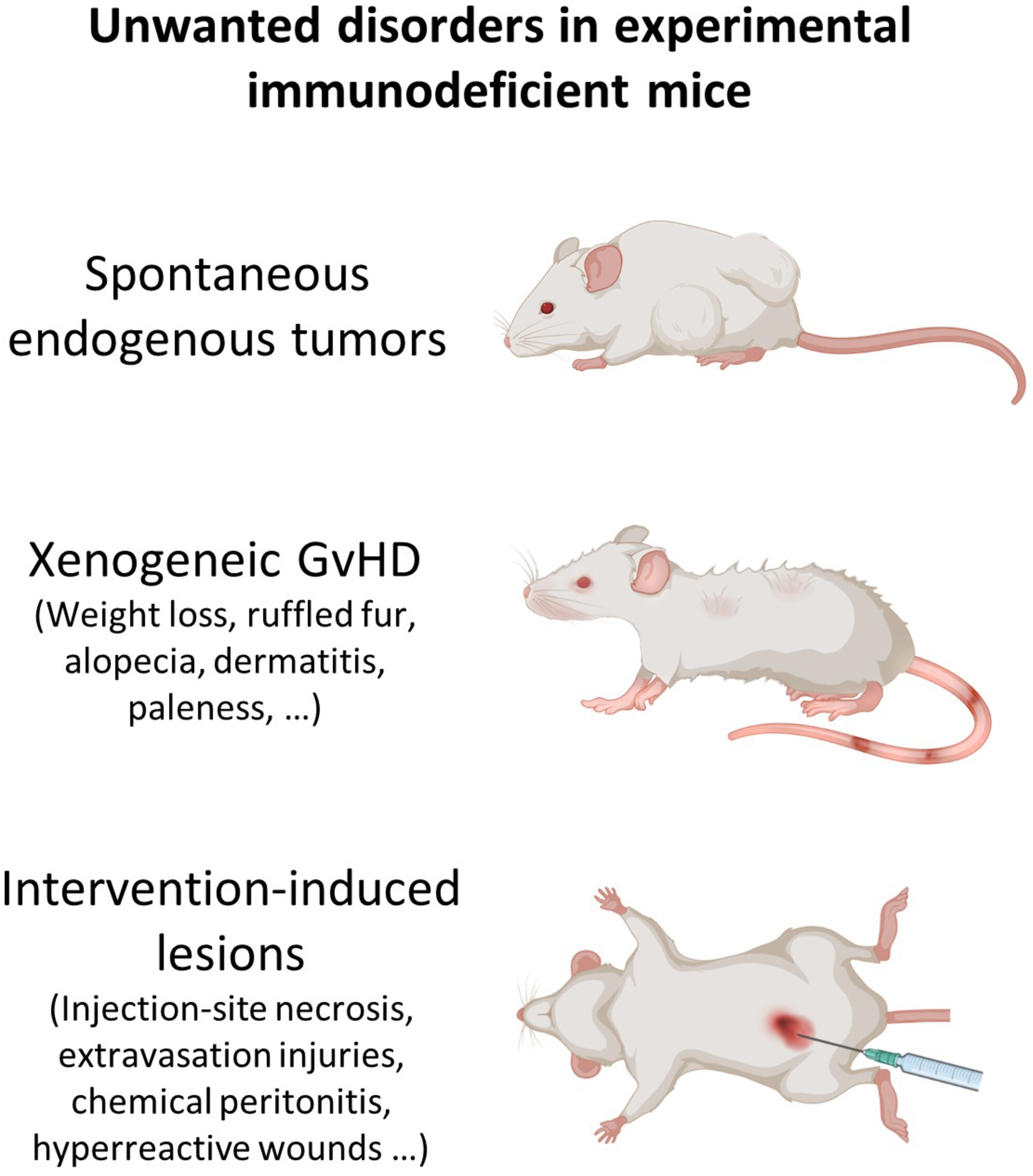
Xenograft-bearing immunodeficient mice are susceptible to developing unwanted disorders primarily irrelevant to nature of the xenografted tumor; and if get involved with such disorders, they do not produce reliable results, inevitably confounding the research outputs. This article reviews clinical signs of common unwanted disorders in experimental immunodeficient mice, and how to examine and report them.
THEMED SECTION: ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Single-cell sequencing reveals the features of adaptive immune responses in the liver of a mouse model of dengue fever
- Pages: 30-43
- First Published: 11 July 2024
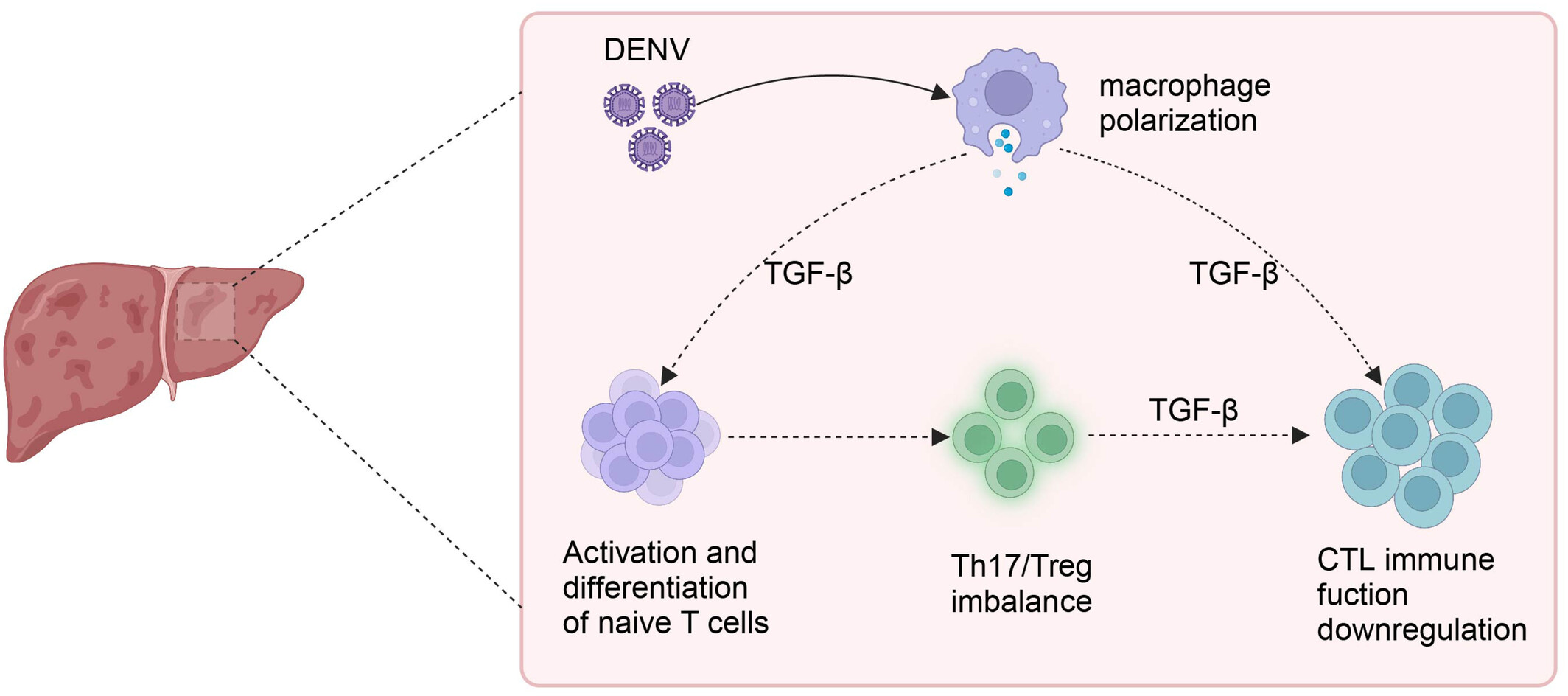
Single-cell sequencing revealed that the number and immune function of effector T cells in the livers of severe liver injury mice model were lower than those in the livers of dengue fever mice model with mild liver damage. This finding may be related to the disruption of Th17/Treg homeostasis and macrophage polarization caused by dengue virus infection.
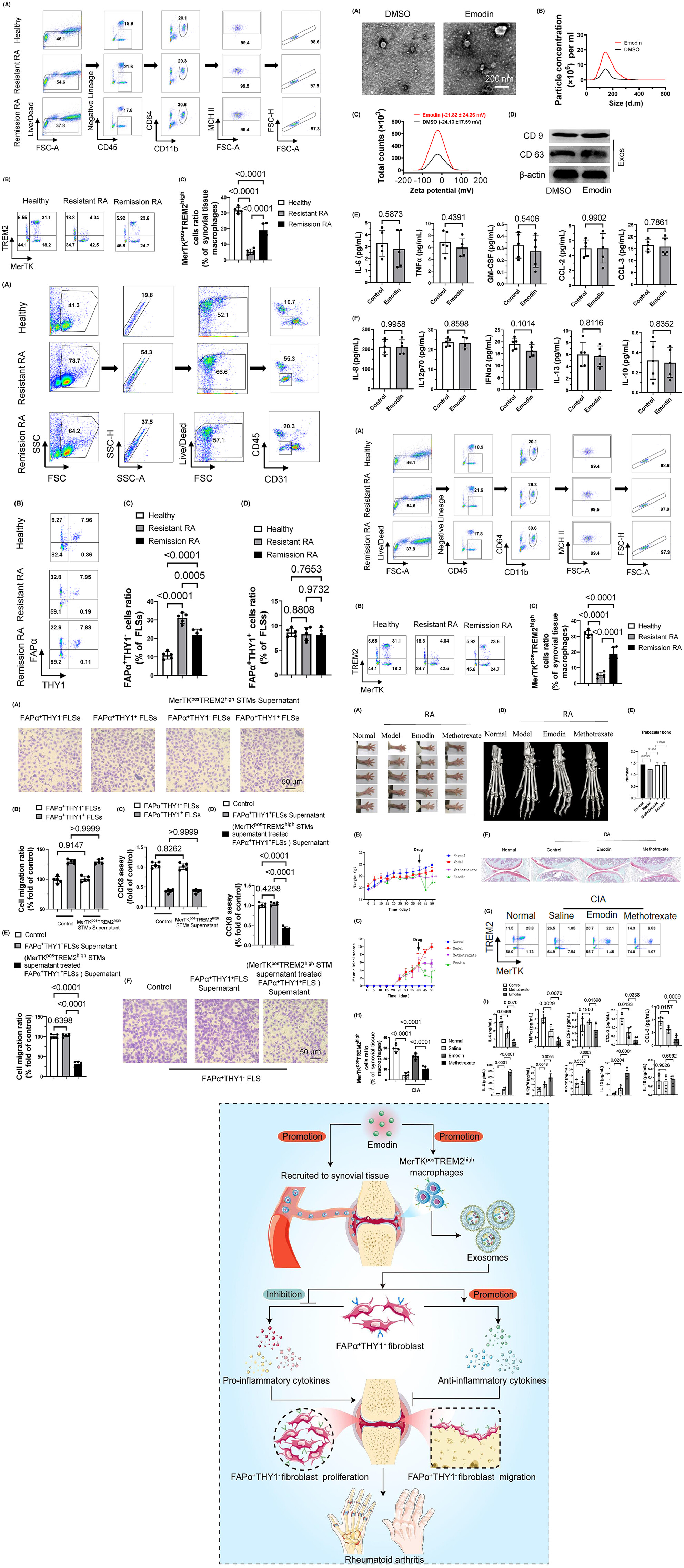
Emodin promotes the recovery of rheumatoid arthritis by regulating the crosstalk between macrophage subsets and synovial fibroblast subsets
- Pages: 44-56
- First Published: 18 February 2024
THEMED SECTION: SHORT COMMUNICATION
The transcriptome of MHV-infected RAW264.7 cells offers an alternative model for macrophage innate immunity research
- Pages: 57-66
- First Published: 11 July 2024
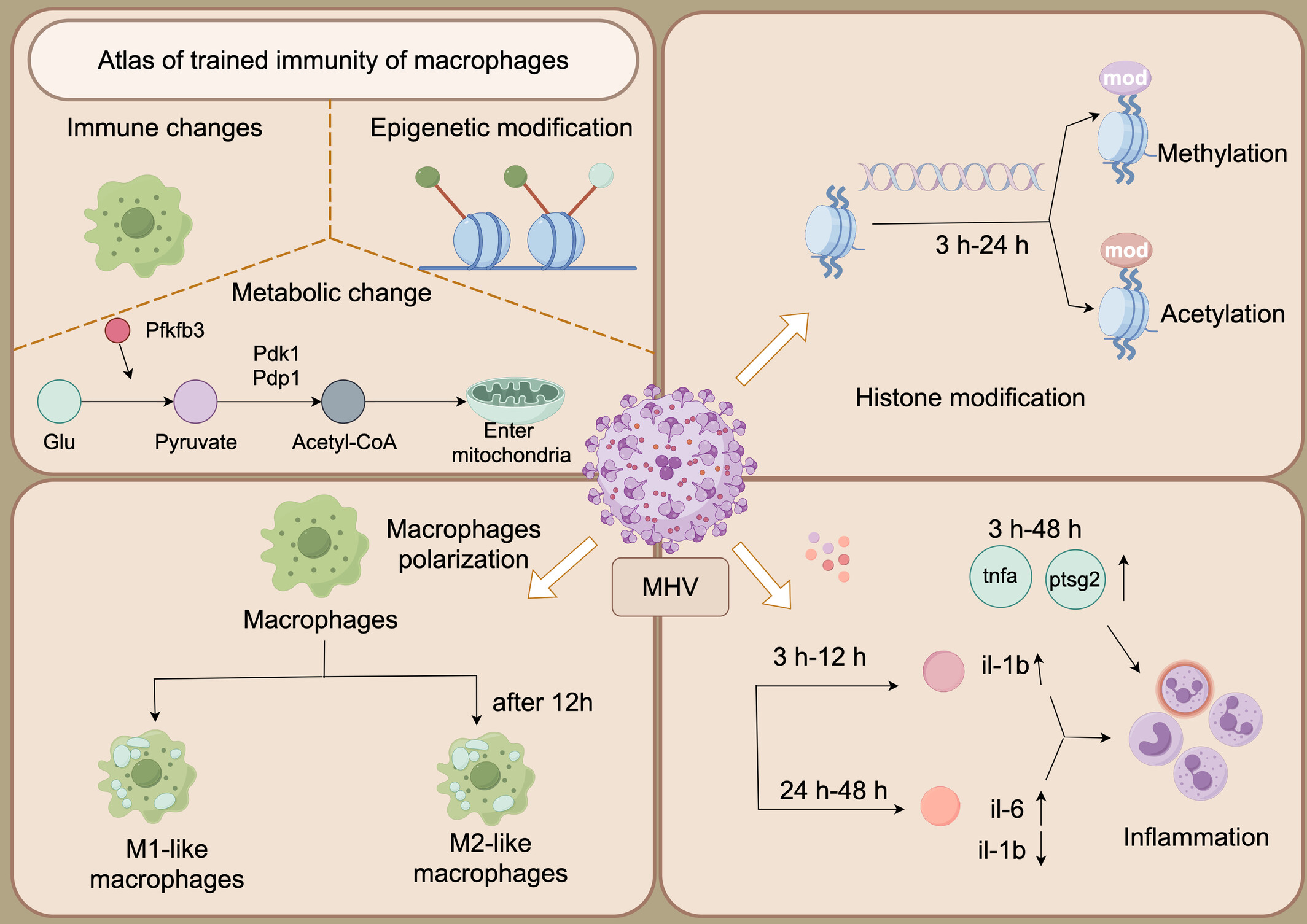
The macrophages were infected with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV). The transcriptome analysis showed the immediate up regulation of different expressed genes (DEGs) related to inflammation. DEGs related to M2 differential polarization showed up regulation at 24 hpi, the late term after viral infection. In addition, DEGs related to metabolism and histone modification, like Ezh2 were detected, which might correlate with the trained immunity of macrophages. The current in vitro viral infection study showed the key innated immunity character of macrophages, which suggested the replacement value of viral infection cells model, to reduce the animal usage in preclinical researches.
REGULAR ARTICLE
REVIEW
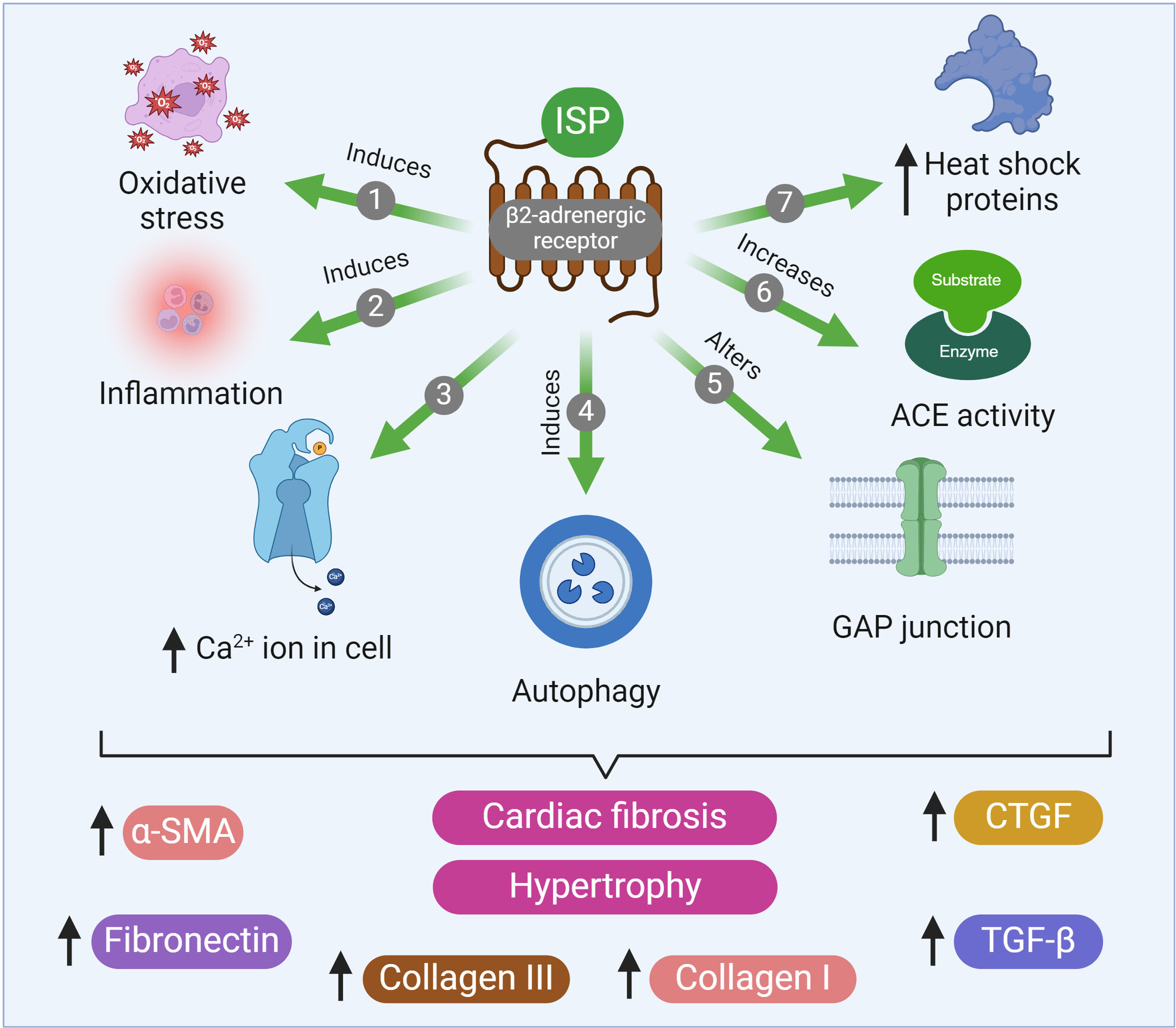
Isoproterenol mechanisms in inducing myocardial fibrosis and its application as an experimental model for the evaluation of therapeutic potential of phytochemicals and pharmaceuticals
- Pages: 67-91
- First Published: 17 December 2024
Rat models of frozen shoulder: Classification and evaluation
- Pages: 92-101
- First Published: 03 December 2024
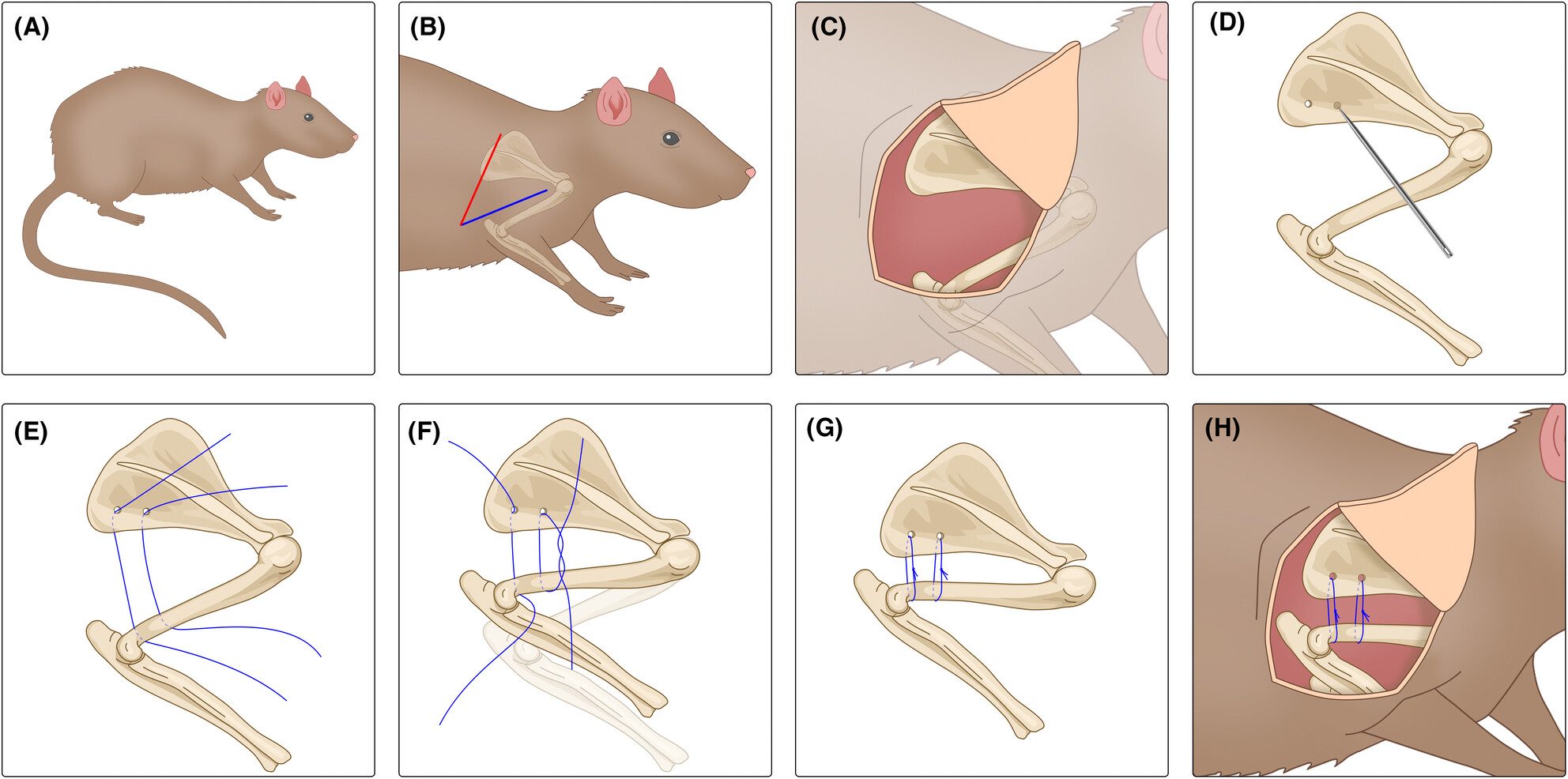
Procedure for Surgical Internal Immobilization Modeling. After intraperitoneal anesthesia, the rat was placed on the operating table (A). In the lateral decubitus position, a longitudinal skin incision of approximately 3 cm was made along the inferior edge of the scapula, perpendicular to the spine of the scapula (B). After exposing the scapula and humerus (C), two small holes were made in the inferior angle of the scapula using a 23G needle (D). Two 2–0 sutures were then passed through the holes and around the humeral shaft, securing them tightly to fix the shoulder joint (E–H). All wounds were closed with interrupted 3–0 nylon sutures.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
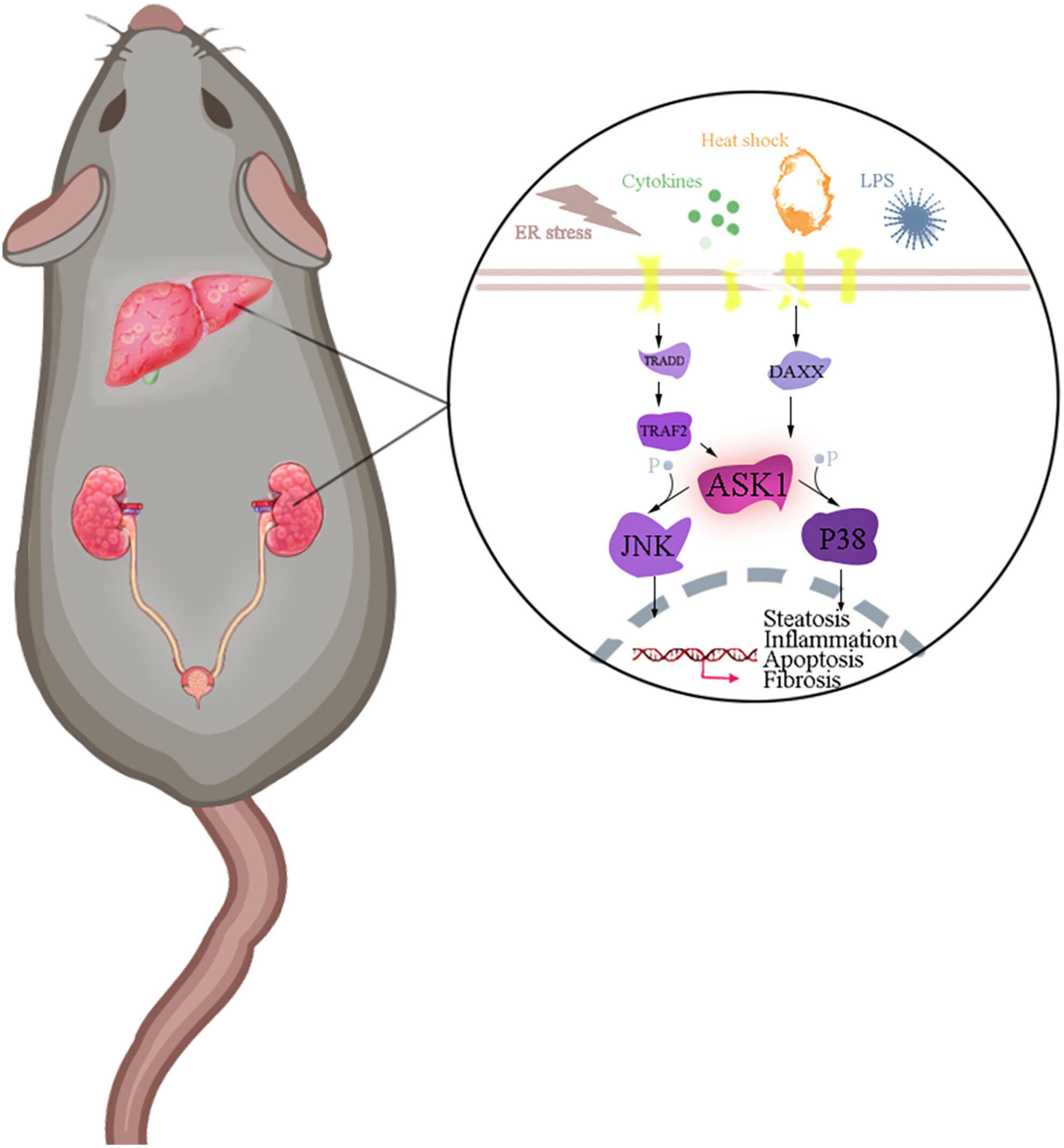
Targeting ASK1 by CS17919 alleviates kidney- and liver-related diseases in murine models
- Pages: 102-113
- First Published: 14 June 2024
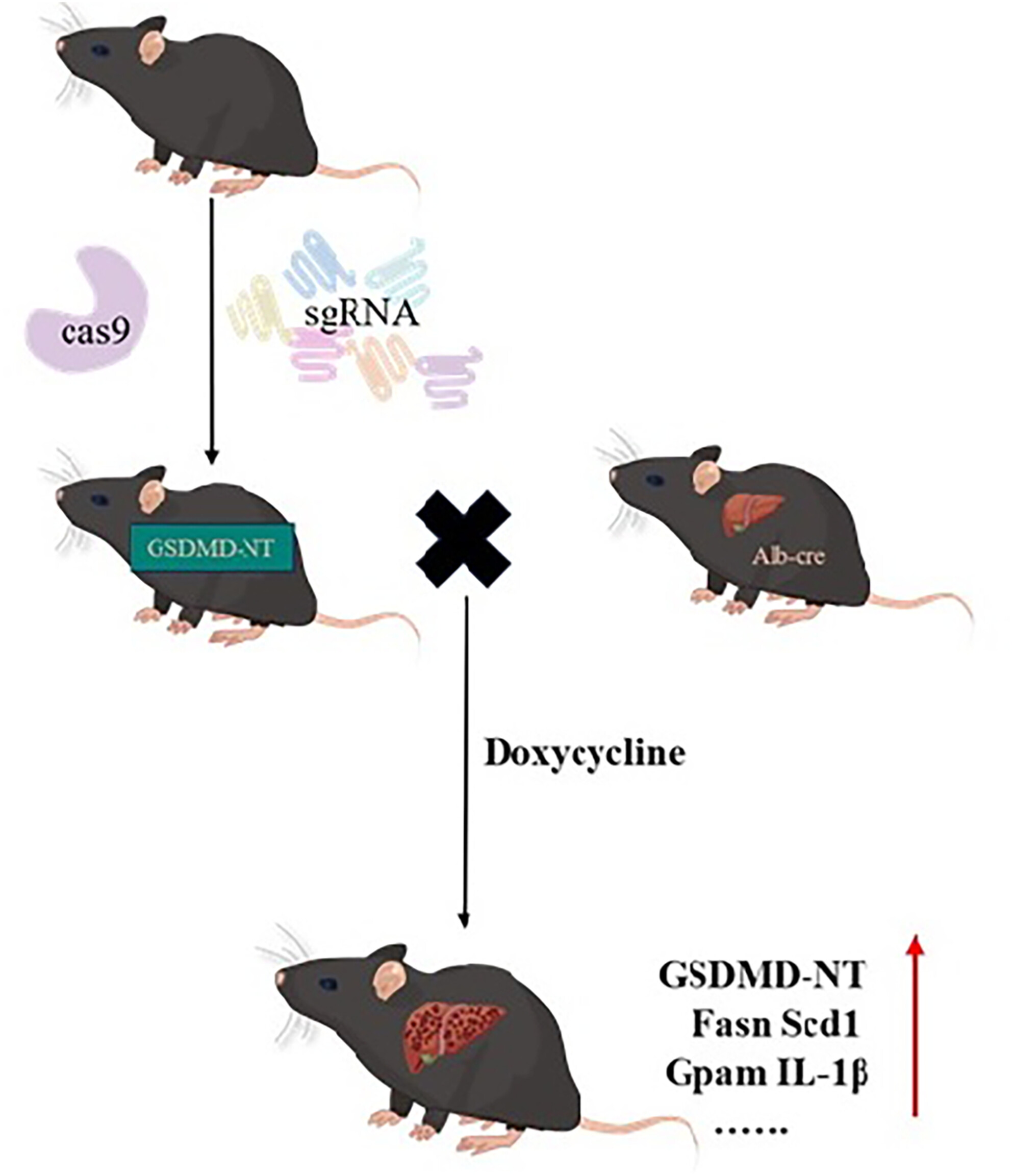
The N-terminal domain of gasdermin D induces liver fibrosis by reprogrammed lipid metabolism
- Pages: 114-125
- First Published: 27 December 2024
The collaborative cross mouse for studying the effect of host genetic background on memory impairments due to obesity and diabetes
- Pages: 126-141
- First Published: 28 October 2024
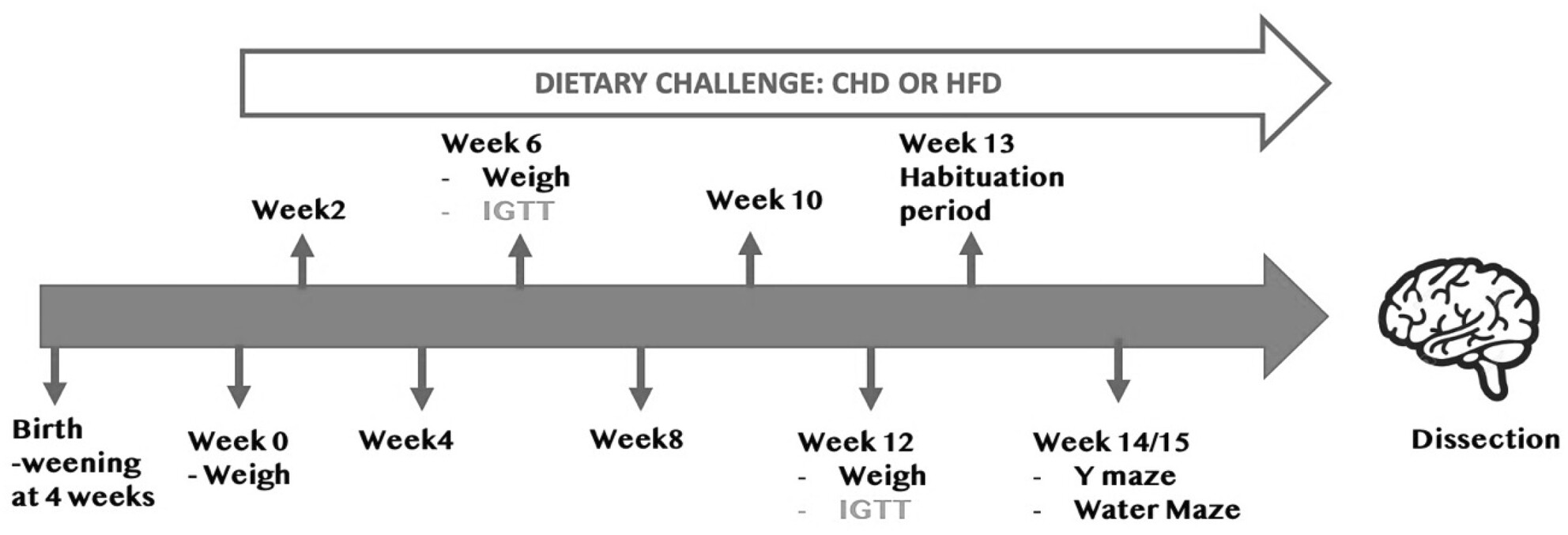
Previous studies have shown correlations between obesity, type 2 diabetes (T2D), and neurodegenerative diseases, including dementia. A wide range of illnesses can result in dementia, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). The disorders that fall under the general category of “dementia” are caused by abnormal alterations in the brain. To counteract their significant influence on public health, it is imperative to gain an in-depth understanding of the relationship between obesity, T2D, and cognitive deficits. We evaluate the cognitive impact of obesity and T2D induced by high-fat diet (HFD) in collaborative cross (CC) mice. Our findings have demonstrated differences in the assessed phenotypes between the different CC lines and the C57BL/6J reference line. These findings highlight the role the host's genetic background plays in determining the degree of obesity and T2D development, as well as how it affects different organ weights and cognitive deficiencies that could worsen into AD when faced with a HFD challenge.
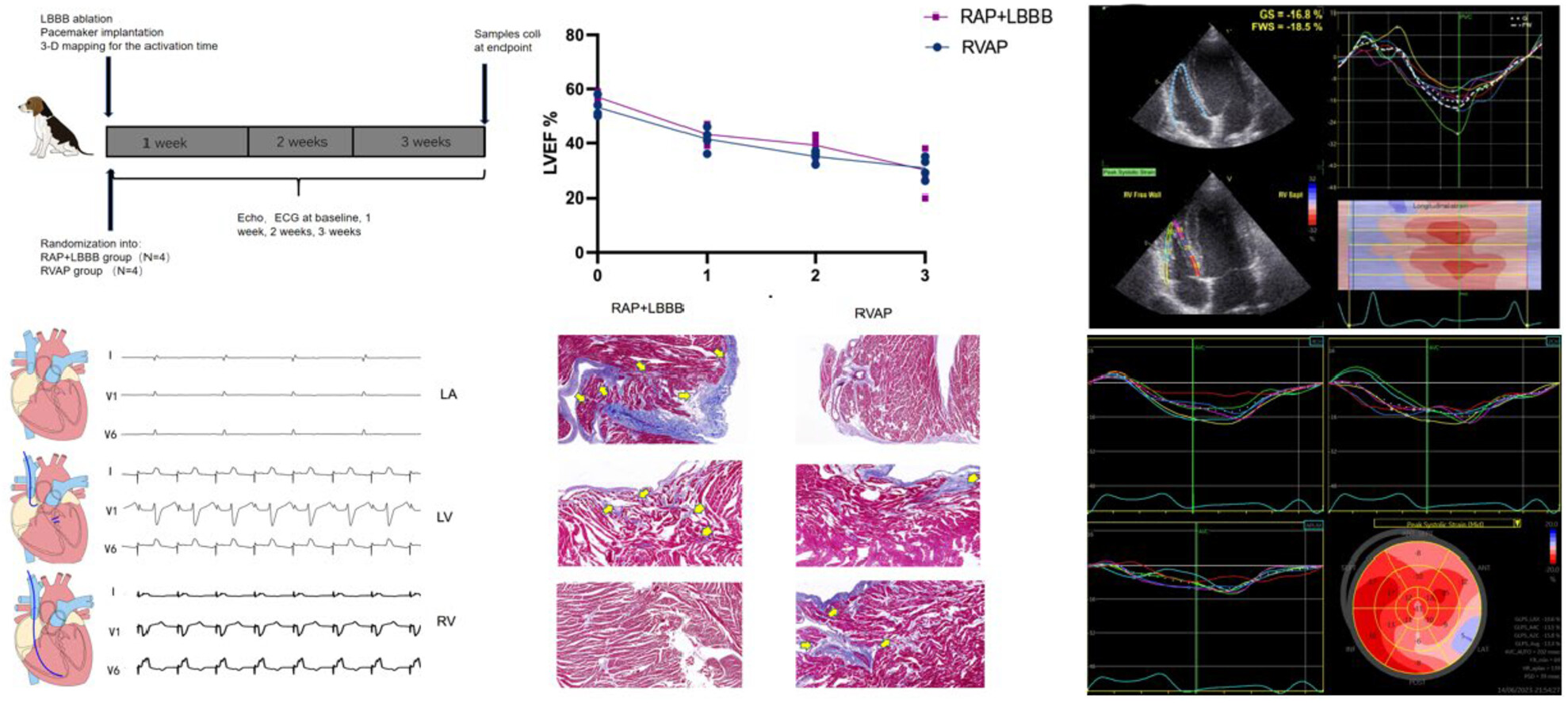
Dyssynchronous heart failure models in canines: New insights into electrocardiographic, echocardiographic and histological features
- Pages: 142-153
- First Published: 19 February 2024
Causal relationship between lipid profile and muscle atrophy: A bi-directional Mendelian randomization study
- Pages: 154-161
- First Published: 28 December 2023

Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis assumptions for lipid profile and muscle atrophy. Findings of this MR analysis suggest that hyperlipidemia may affect muscle mass and lead to muscle atrophy, but has no significant effect on muscle strength. On the other hand, increased muscle mass may reduce the incidence of dyslipidemia.
High expression of SULF1 is associated with adverse prognosis in breast cancer brain metastasis
- Pages: 162-170
- First Published: 08 April 2024
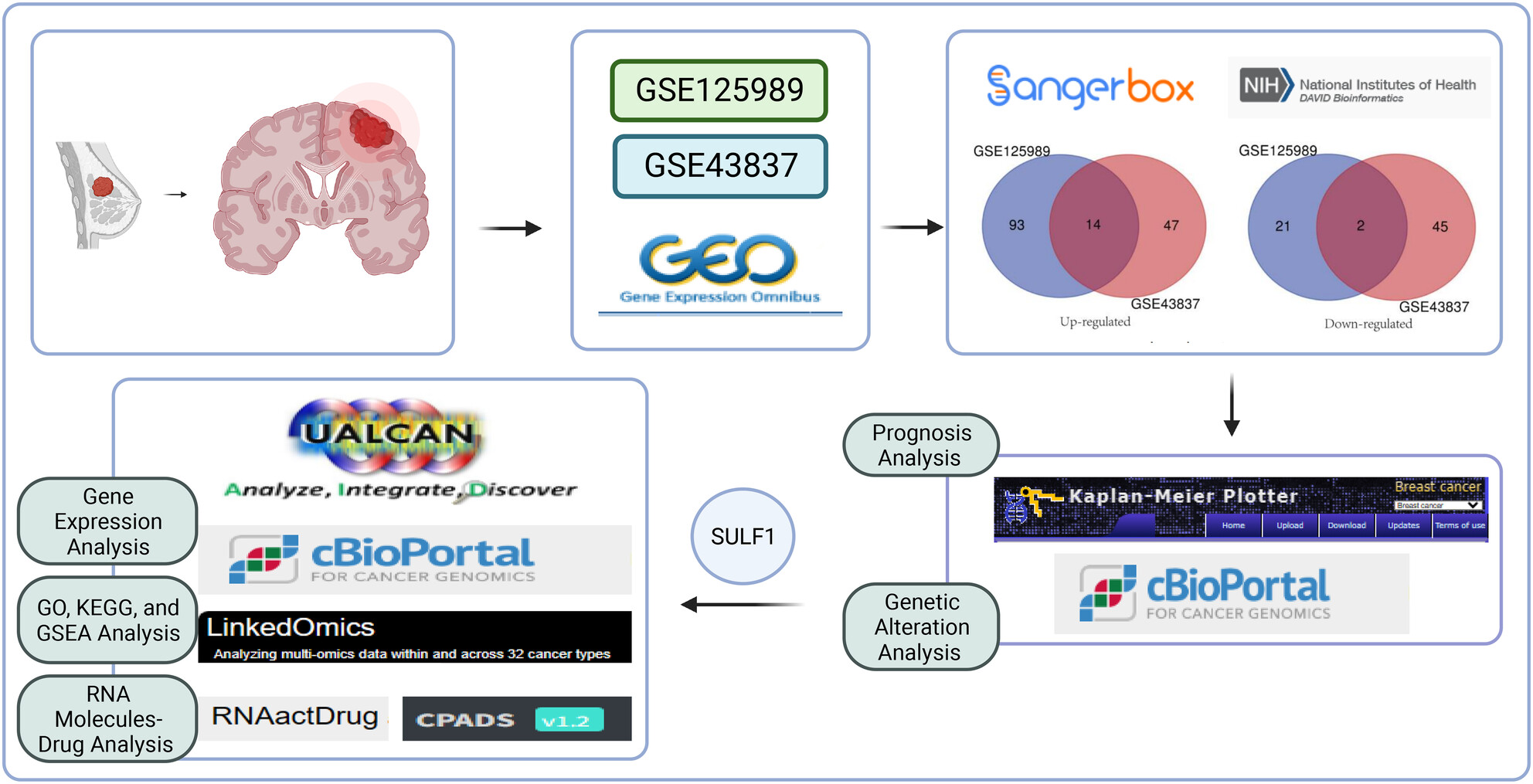
Through mining public databases, up-regulated and down-regulated differential gene expression analysis on 70 patient samples was conducted. Through prognosis survival analysis and genetic variation analysis, SULF1 was identified as a core gene. Then, related biological mechanisms were explored by mining co-expressed genes. Finally, combined clinical diagnosis and treatment potential drugs were explored.
SHORT COMMUNICATION
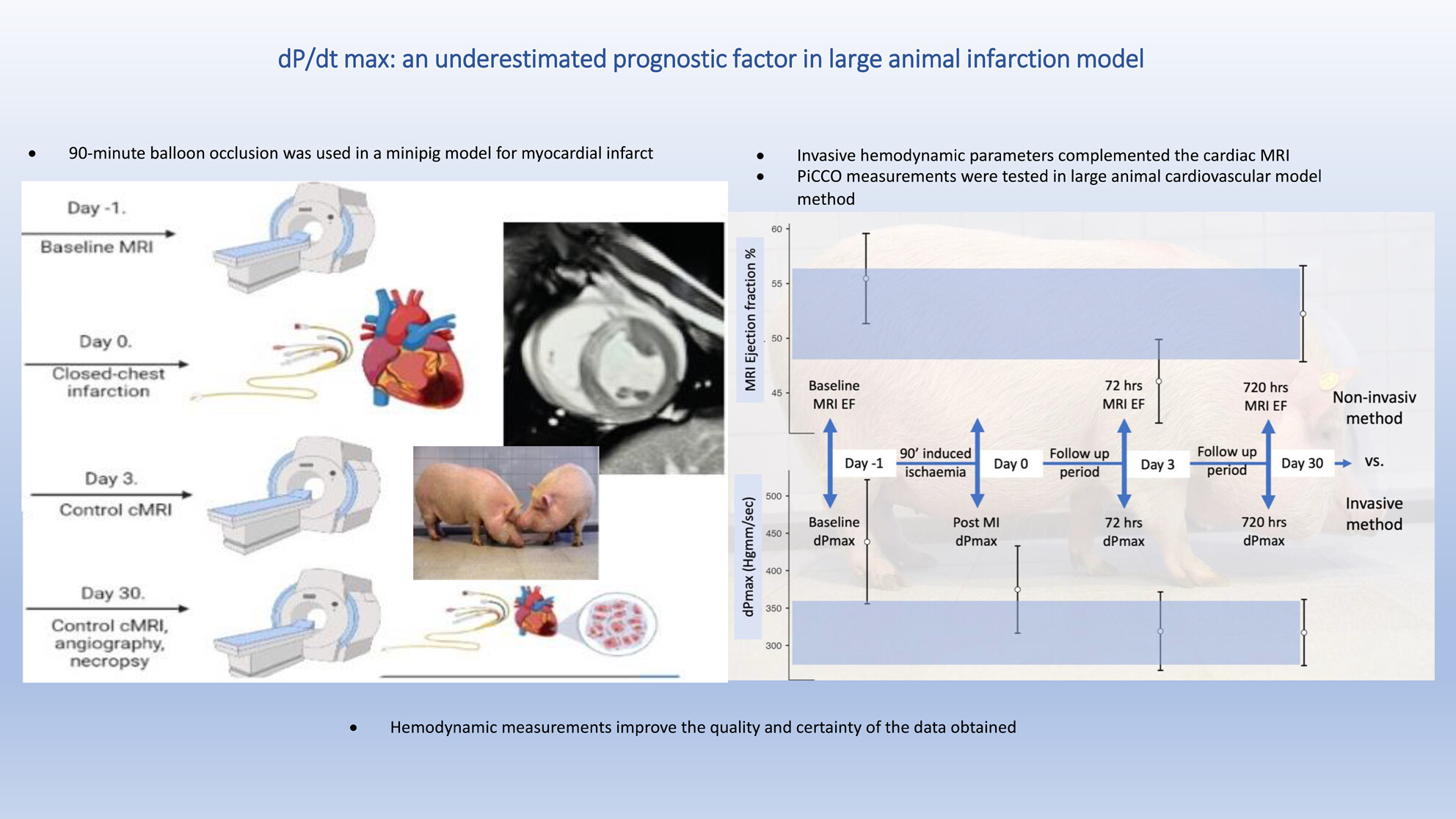
dP/dtmax: An underestimated prognostic factor in large animal infarction model
- Pages: 171-178
- First Published: 27 November 2024
Evaluation of a user-friendly CSDS cage apparatus for studying depressive-like behaviors in rodents
- Pages: 179-186
- First Published: 03 December 2024
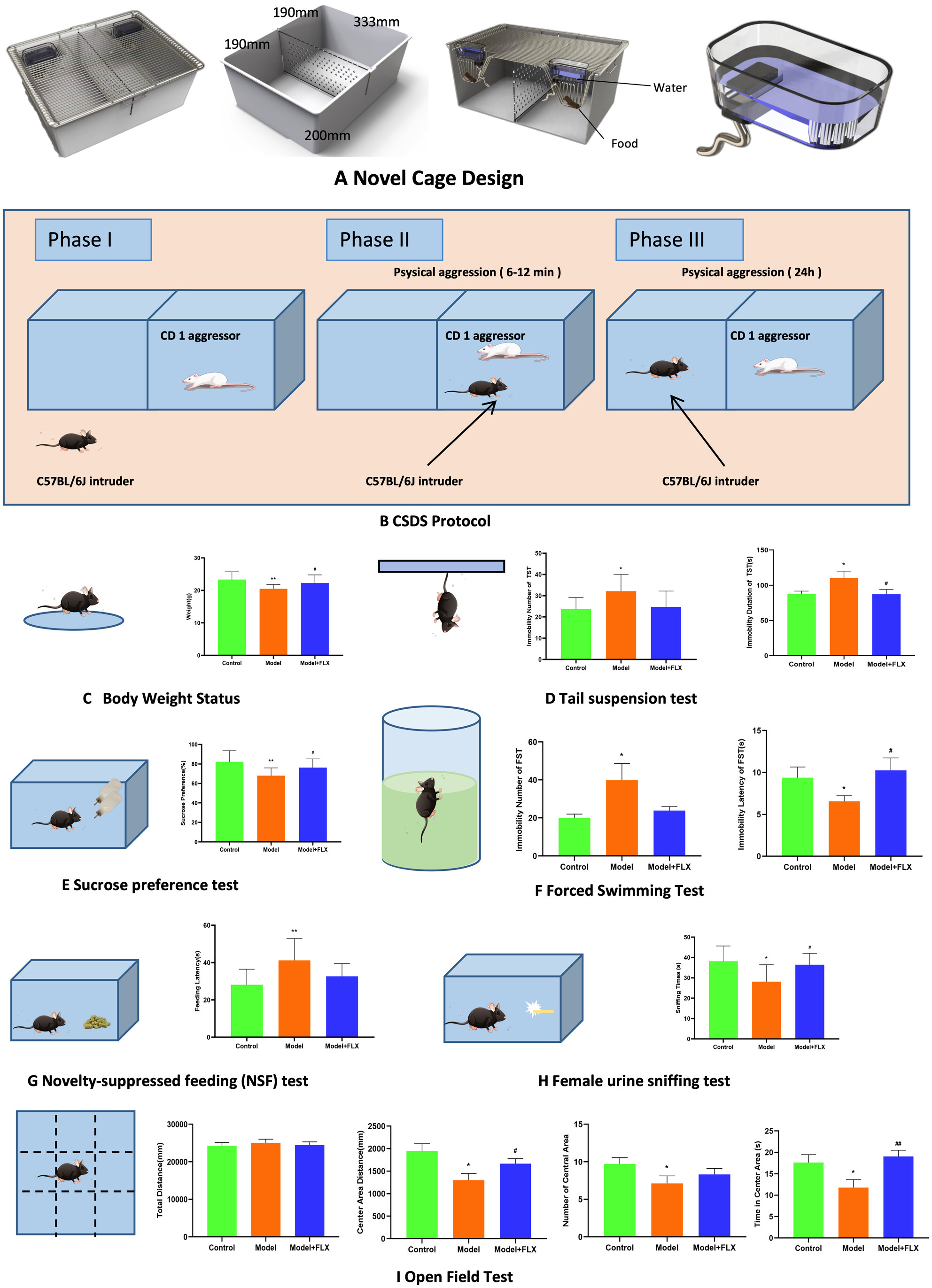
Using chronic social defeat stress cage apparatus, the model mice exhibited characteristic behaviors resembling depression, including a significant decrease in preference for sugar-water, a notable reduction in the time spent sniffing female urine, a prolonged delay in initiating feeding, a substantial decrease in total distance traveled, residence time, and entries into the central zone in open field test, a significant decrease in the time taken to become immobile in forced swimming test (FST), a considerable increase in immobility time and the number of instances of immobility in FST and tail suspension test. These aforementioned behavioral manifestations were found to be reversible through drug intervention.
Generation of transgenic chicken through ovarian injection
- Pages: 187-193
- First Published: 27 December 2024
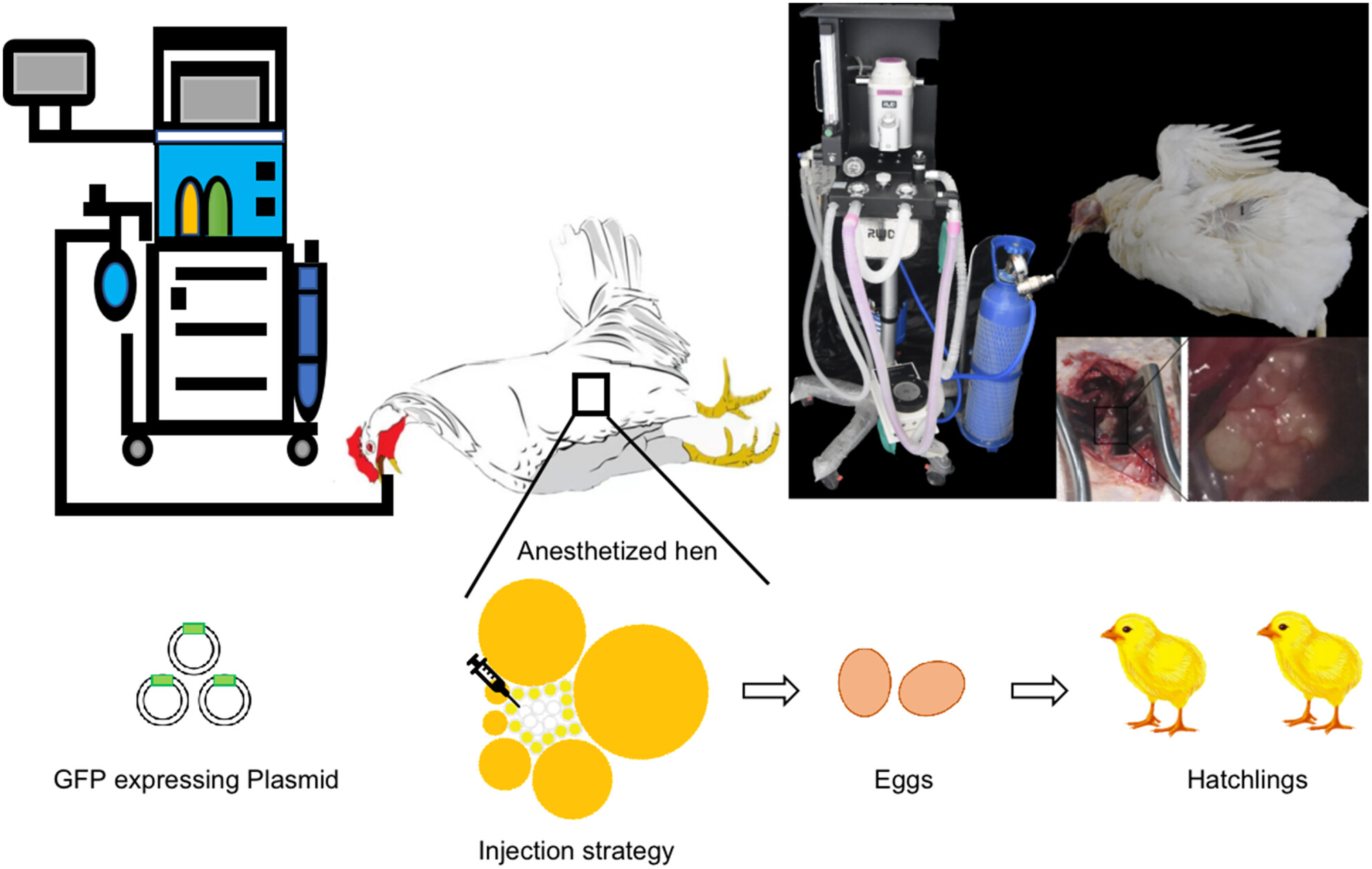
Gene modification of chickens through ovarian injection. The left section illustrates the schematic of the ovarian injection process, whereas the right section displays an actual image. Surgical procedure: anesthesia of hens and the surgical steps involved in accessing and injecting ovarian follicles were demonstrated. Lipo 2000 was utilized for delivery of DNA.