Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
CONSENSUS
Consensus statement on the exploration of clinical translation and application of electron ultra-high dose rate FLASH radiotherapy
- Pages: 4-12
- First Published: 03 March 2025
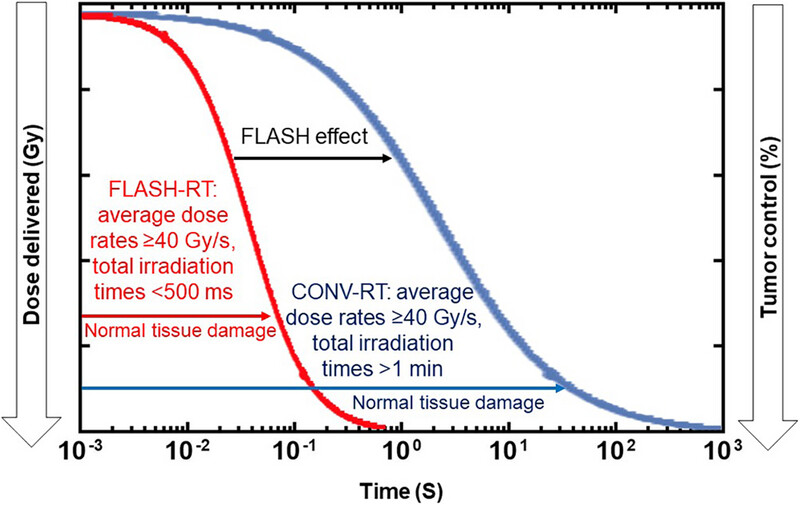
• FLASH-RT as a novel irradiation technique shows a protective effect on normal tissues while maintaining comparable tumor killing effect as CONV-RT, also known as the FLASH effect.
• We develop a consensus statement on the exploration of clinical translation of FLASH-RT, and provide insights for the further application of this technology in clinical practice.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Deep learning with attention modules and residual transformations improves hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) differentiation using multiphase CT
- Pages: 13-22
- First Published: 22 March 2025
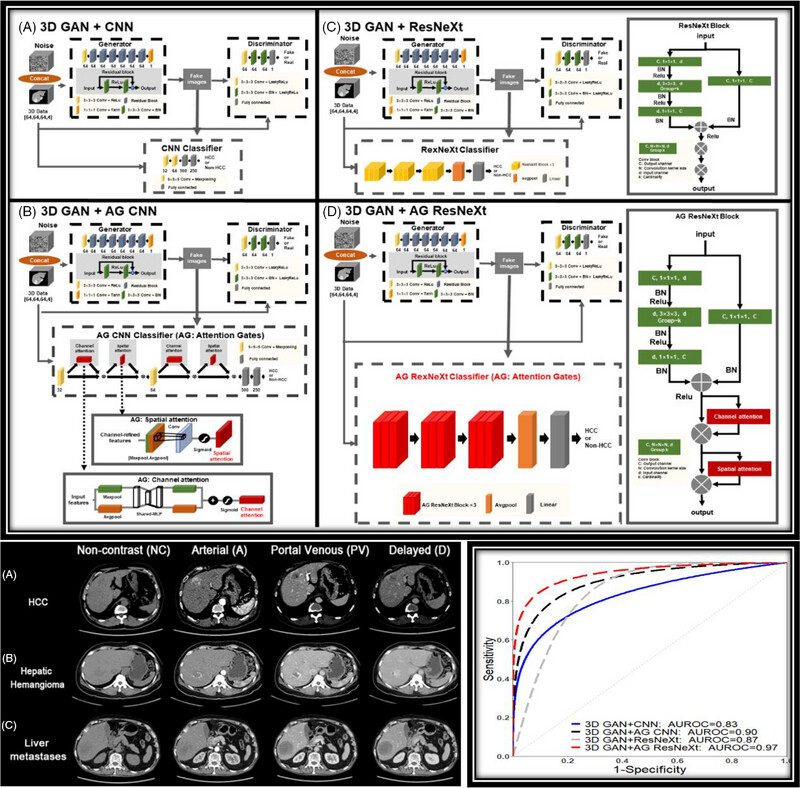
The proposed deep learning model with attentions and residual transformations (Top Figure (d) 3D GAN+AG ResNeXt) is applied to multi-phase CTs for HCC differentiation (Bottom Left). ROC curves (Bottom Right) showed the 3D deep GAN model with attentions and residual transformations (RED) had better performance.
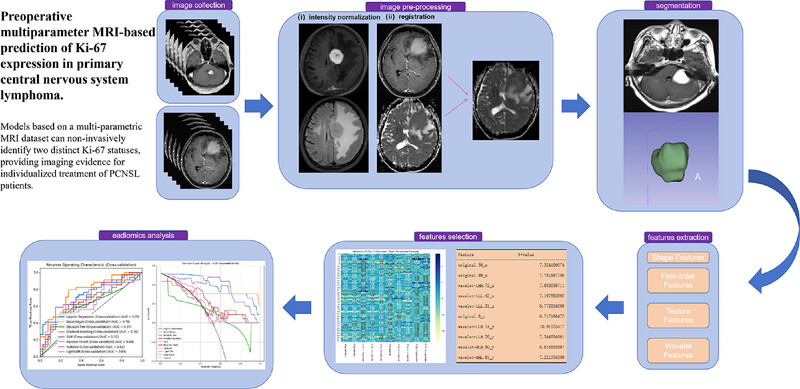
Preoperative multiparameter MRI-based prediction of Ki-67 expression in primary central nervous system lymphoma
- Pages: 23-34
- First Published: 18 March 2025
Measurements of Small Field Output Correction Factors on a RefleXion Treatment Machine
- Pages: 35-42
- First Published: 17 March 2025
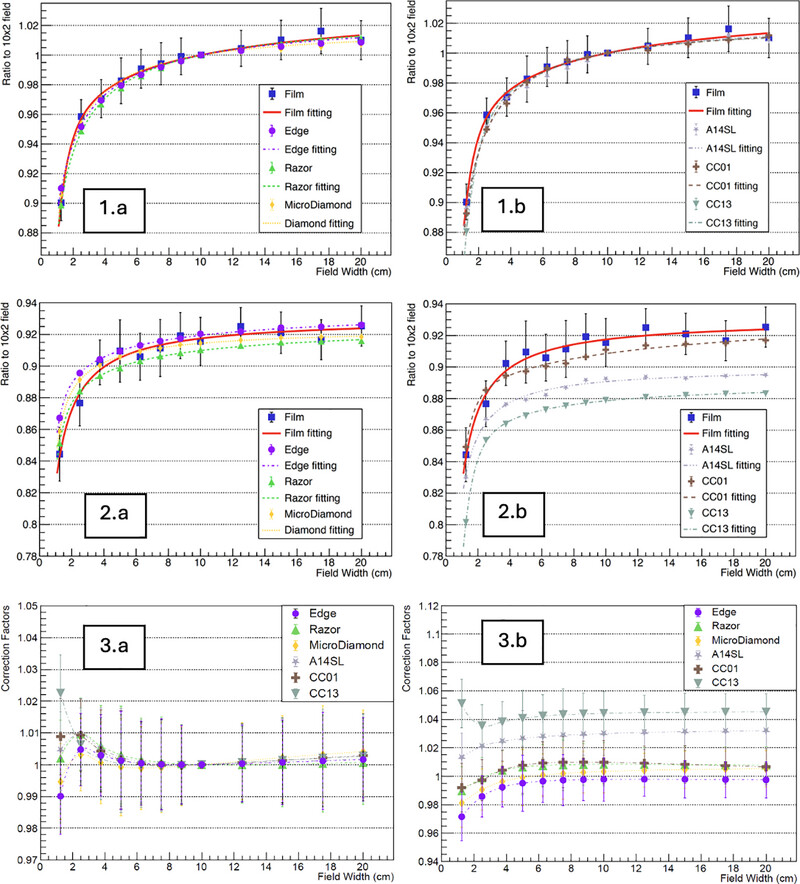
The small field output correction factors of six different detectors were determined for a clinical RefleXion system. Figure 1: Raw data of reference output factors (blue squares) with film dosimetry in the field sizes of 2 cm jaw and corresponding fitted curve (red). Raw data of detector output ratios of Edge (purple dots), Razor (green triangles) and Micro-Diamond (yellow diamonds) detectors and corresponding fitted curves are in 1.a; raw data of detector output ratios of A14SL (gray-purple stars), CC01 (brown crosses) and CC13 (green downwards triangles) data and their fitted curves are in 1.b. Figure 2: Same as Figure 1, but in the fields of 1 cm jaw. Figure 3: Output correction factors of the six detectors in the fields of 2 cm jaw (3.a) and 1 cm jaw (3.b).
Multi-sequence MRI-based clinical-radiomics models for the preoperative prediction of microsatellite instability-high status in endometrial cancer
- Pages: 43-53
- First Published: 03 March 2025

Results: Four clinical factors (progesterone receptor, tumor suppressor gene P53, diabetes, carbohydrate antigen 153) and 15 radiomic features (4 extracted from T1-weighted images, 6 from T2-weighted images, and 5 from apparent diffusion coefficient images) were identified as key predictors of microsatellite instability status in endometrial cancer.
Conclusion: This nomogram may aid in identifying endometrial cancer patients who may benefit from immunotherapy.
Hypofractionated radiotherapy (RT) combined with dihydroartemisinin (DHA): No synergistic effect observed in a preliminary animal study
- Pages: 54-60
- First Published: 03 March 2025
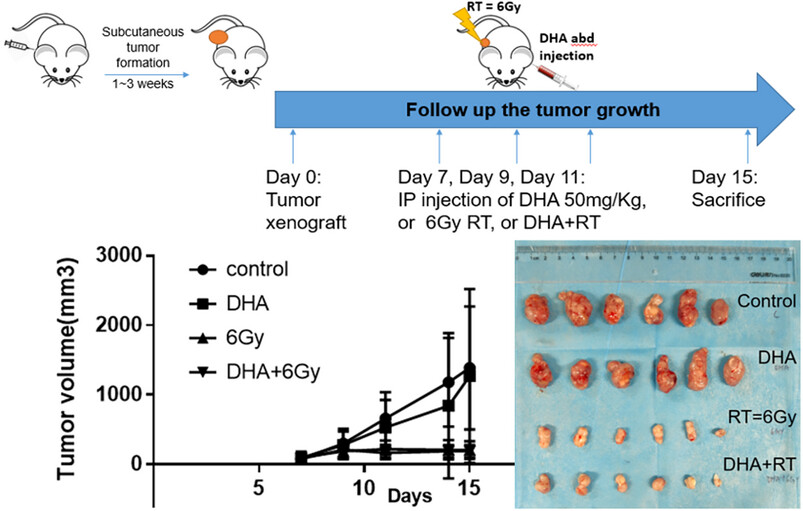
Subcutaneous xenografts were formed after colorectal cancer cells CT26 inoculation in nude mice, followed by a preliminary animal study in four groups: (1) control; (2) dihydroartemisinin (DHA), a potential natural anticancer drug; (3) radiotherapy (RT); (4) DHA+RT (n = 6 per group). Results showed no significant tumor volume reduction in the concurrent DHA+RT group in comparison to the RT alone group. No synergistic effect was observed in adding DHA to RT for the proposed SBRT dose regimen. Tumor progression inhibition was observed in the RT and DHA+RT groups, but was not obvious in the DHA group.
REVIEW
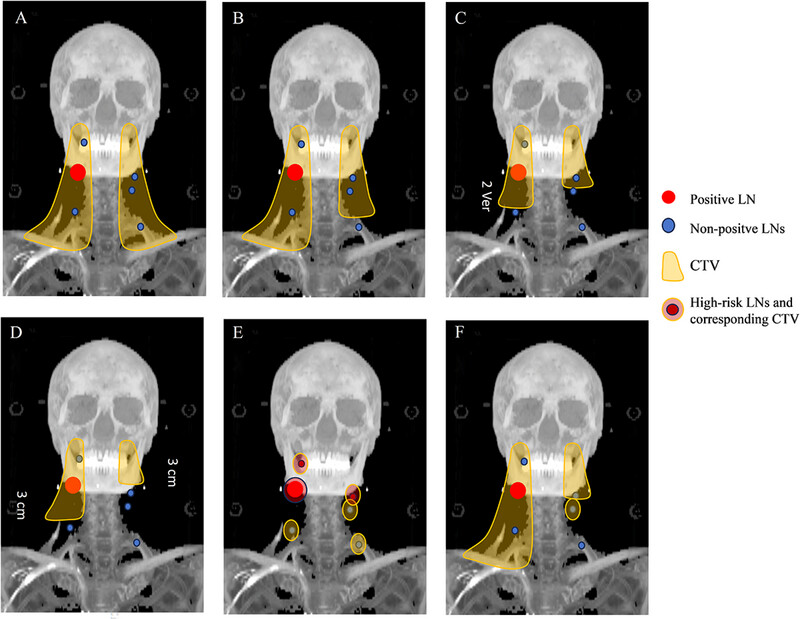
The evolution of prophylactic neck irradiation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Changing concepts and irradiation ranges
- Pages: 61-68
- First Published: 20 March 2025