Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
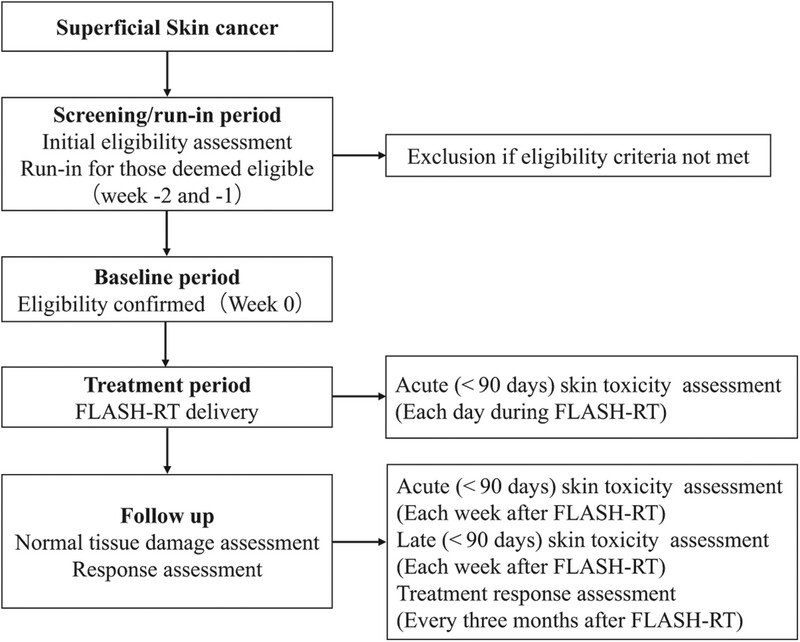
A safety study of ultra-high dose rate FLASH radiotherapy in the treatment of superficial skin tumors: study protocol of a phase I trial (ChiCTR2400080935)
- Pages: 72-76
- First Published: 05 April 2025
Fast estimation of patient-specific organ doses from abdomen and head CT examinations without segmenting internal organs using machine learning models
- Pages: 77-86
- First Published: 29 May 2025
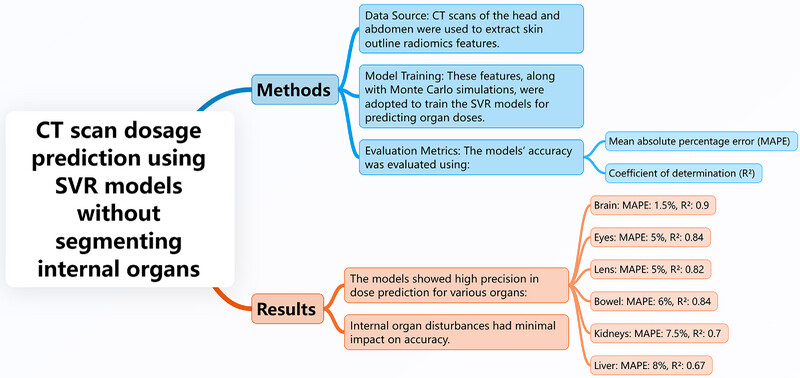
A new method using support vector regression (SVR) models predicts organ doses from CT scans based on skin radiomics, eliminating the need for organ segmentation. High accuracy was achieved for brain, eyes, lens, bowel, kidneys, and liver doses, improving clinical efficiency and accessibility in dose prediction.
Optimized fiducial marker placement using B-spline surface modeling and graph theory for Cyberknife stereotactic body radiotherapy for superficial tumors
- Pages: 87-95
- First Published: 19 June 2025
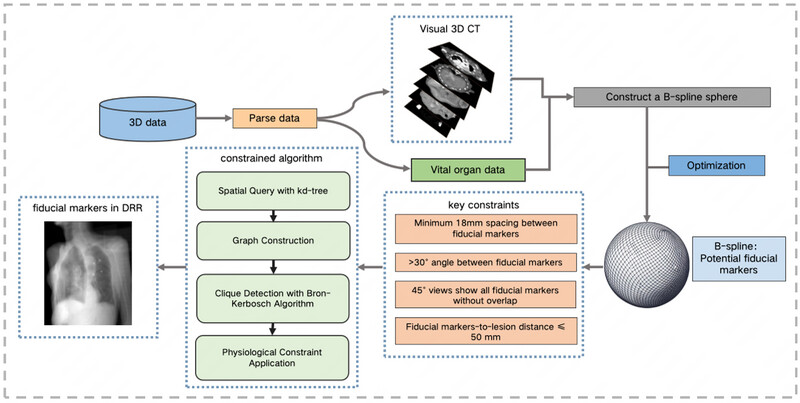
This study introduces a Fiducial marker placement planning algorithm, specifically for superficial tumors that are located 20-50 mm beneath the epidermis. The algorithm proposes numerous potential implantation sites by constructing and optimizing a B-spline surface. The time complexity of the algorithm proposed in this study is O(mlogm+m2+3(n/3)), significantly faster than the brute-force O(n3) approach. Experimental outcomes show that our algorithm can efficiently plan Fiducial marker placements, simplifying the planning process and providing valuable technical support for CyberKnife treatments.
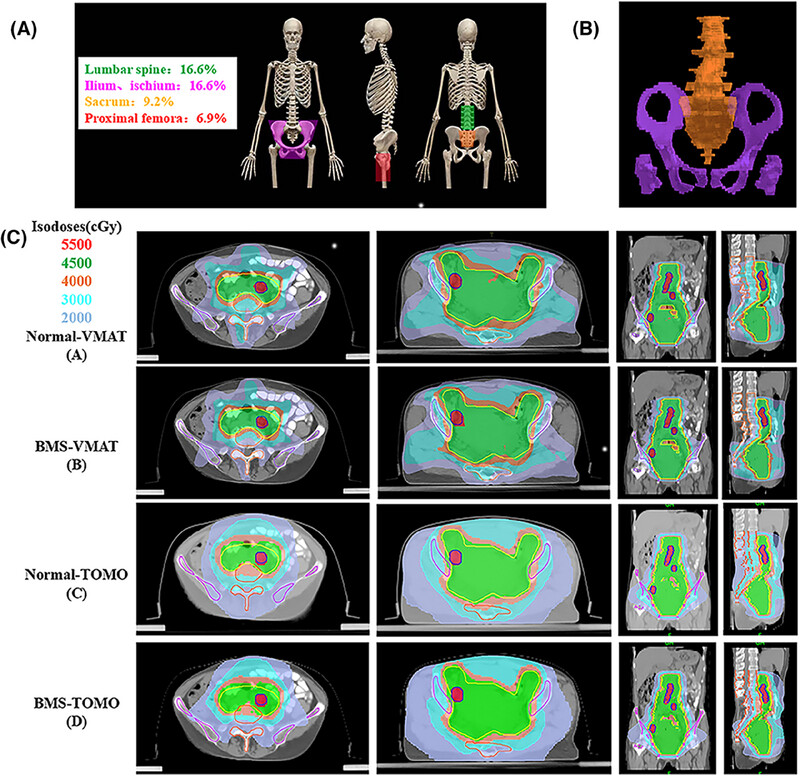
Dosimetric and hematological toxicity analyses of bone marrow-sparing intensity-modulated radiation therapy for patients with cervical cancer treated with extended-field radiation therapy
- Pages: 96-107
- First Published: 12 June 2025
Deep learning-based dose prediction for low-energy electron beam superficial radiotherapy
- Pages: 108-119
- First Published: 26 May 2025
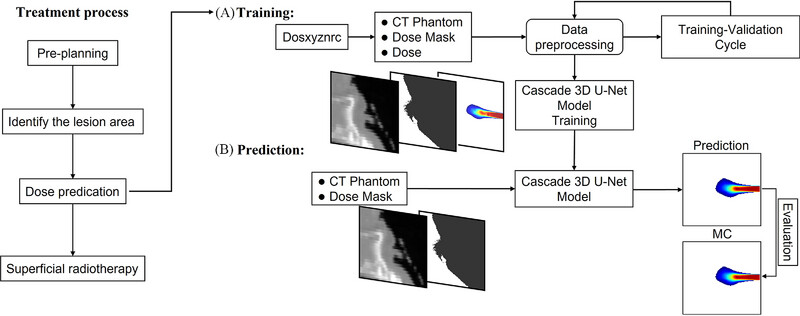
This study integrates Monte Carlo (MC) simulations with a cascaded 3D-UNet (C3D) deep learning model to achieve rapid and accurate dose predictions for low-energy electron radiotherapy. Utilizing CT phantoms of six body sites, the model demonstrates high prediction accuracy with a Gamma pass rate exceeding 92% within 1%/1mm tolerance and a computational speed approximately 140,000 times faster than traditional MC simulations. This approach enhances the efficiency and precision of treatment planning, addressing the challenges of surface contour variations in superficial electron beam therapy.
REVIEW
Deep learning (DL)-based advancements in prostate cancer imaging: Artificial intelligence (AI)-based segmentation of 68Ga-PSMSA PET for tumor volume assessment
- Pages: 120-132
- First Published: 03 May 2025
This review highlights the use of 68Ga-PSMA PET in prostate cancer (PC) for tumor volume quantification, crucial for staging, treatment planning, and prognosis. Traditional manual segmentation methods are time-consuming and variable, while AI-based segmentation techniques, particularly deep learning models like convolutional neural networks, offer automated, accurate, and efficient solutions. AI-based segmentation improves reproducibility and processing times, aiding personalized medicine. However, challenges such as standardized protocols, extensive validation, and clinical integration need addressing for its widespread adoption in 68Ga-PSMA PET for PC, enhancing patient care.
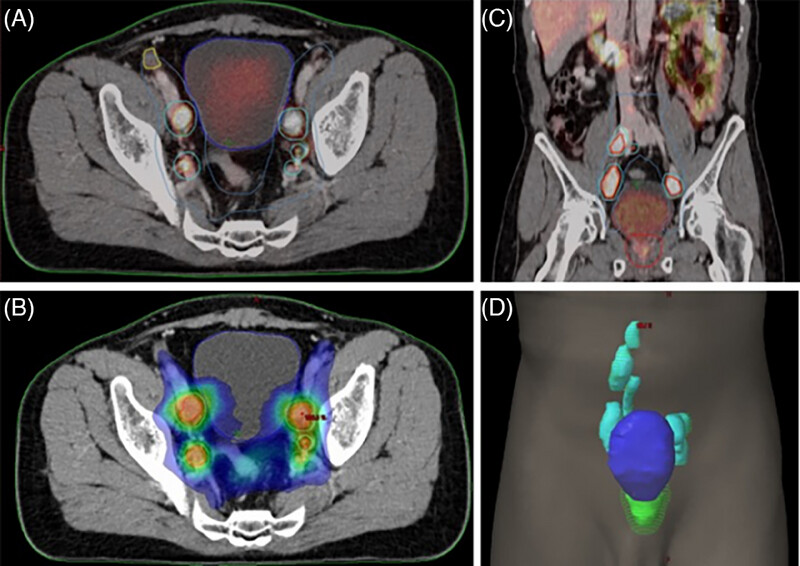
Application of high-dose-rate endorectal brachytherapy in the treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer
- Pages: 133-142
- First Published: 30 March 2025

This image compares the studies included in this article with the meta-analysis from the Cochrane Library, indicating that the incorporation of brachytherapy in neoadjuvant treatment for rectal cancer can achieve better pathological response rates. Additionally, the use of brachytherapy can reduce the local recurrence rate in patients. However, there are no significant differences in long-term survival and distant metastasis.
PERSPECTIVE
Radiotherapy after Neoadjuvant Immunochemotherapy in Unresectable Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Novel Therapeutic Approach?
- Pages: 143-144
- First Published: 30 April 2025
CASE REPORT
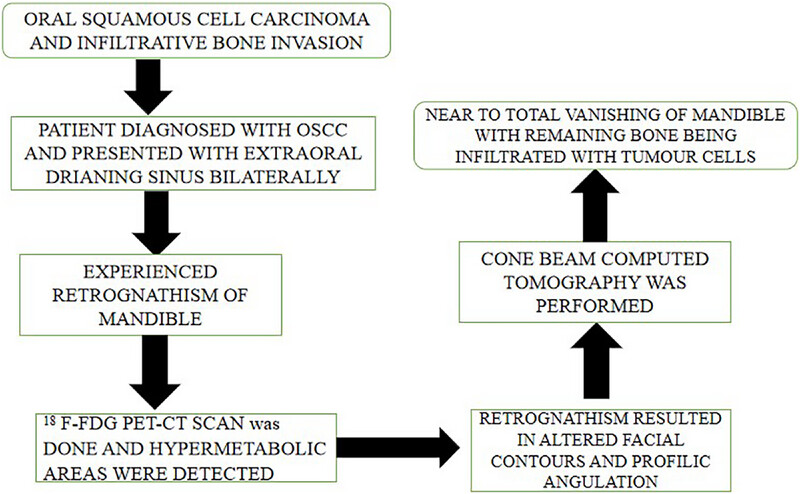
Massive Infiltrative Osteolysis of the Mandible in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report with a Review of the Literature
- Pages: 145-151
- First Published: 30 April 2025