Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine
Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Cover
- First Published: 08 May 2024
The cover image is based on the Clinical Report Novel hemizygous single-nucleotide duplication in RPGR in a patient with retinal dystrophy and sensorineural hearing loss by Ryan J. German et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.2404
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
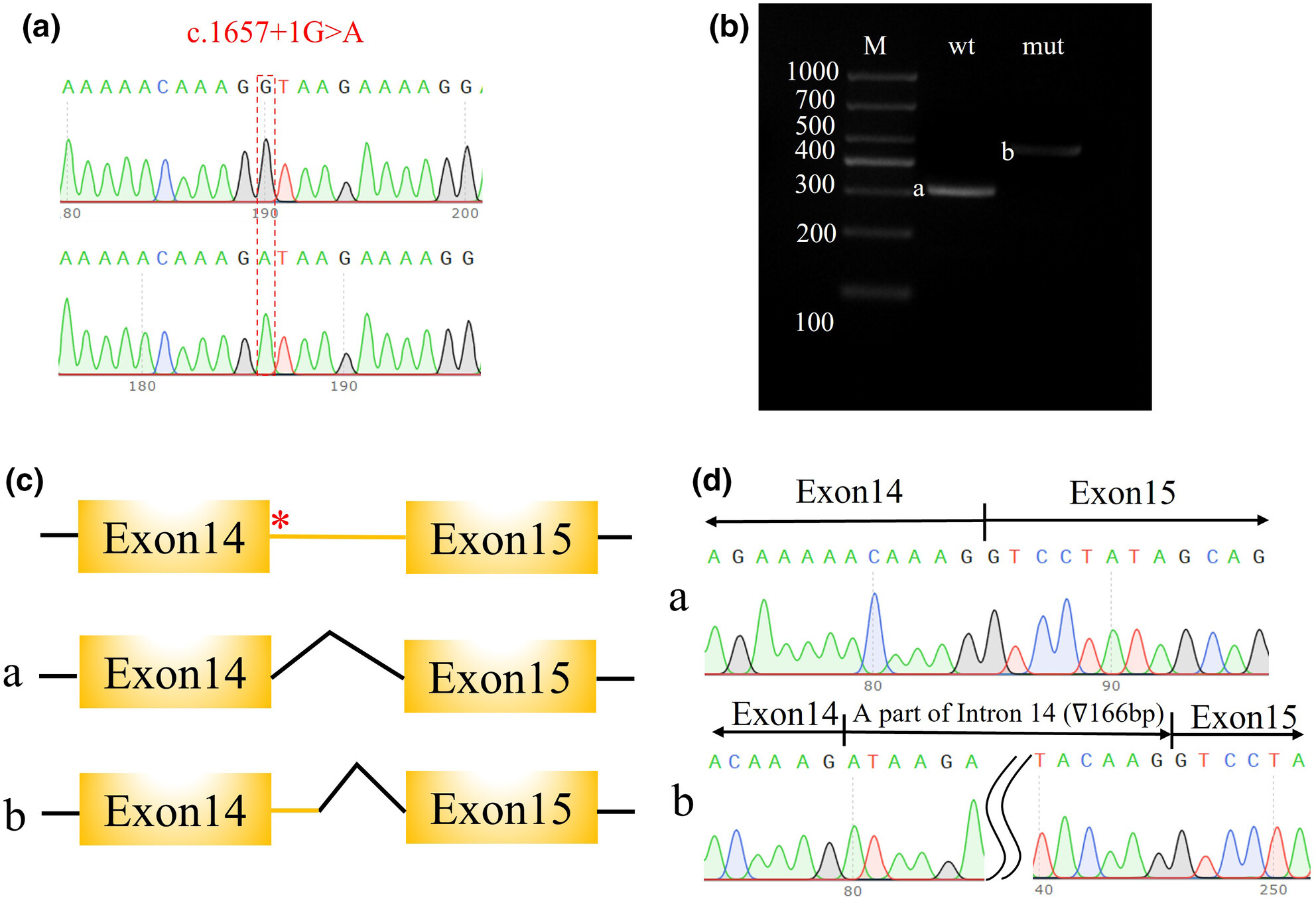
A novel intronic variant causing aberrant splicing identified in two deaf Chinese siblings with enlarged vestibular aqueducts
- First Published: 13 February 2024
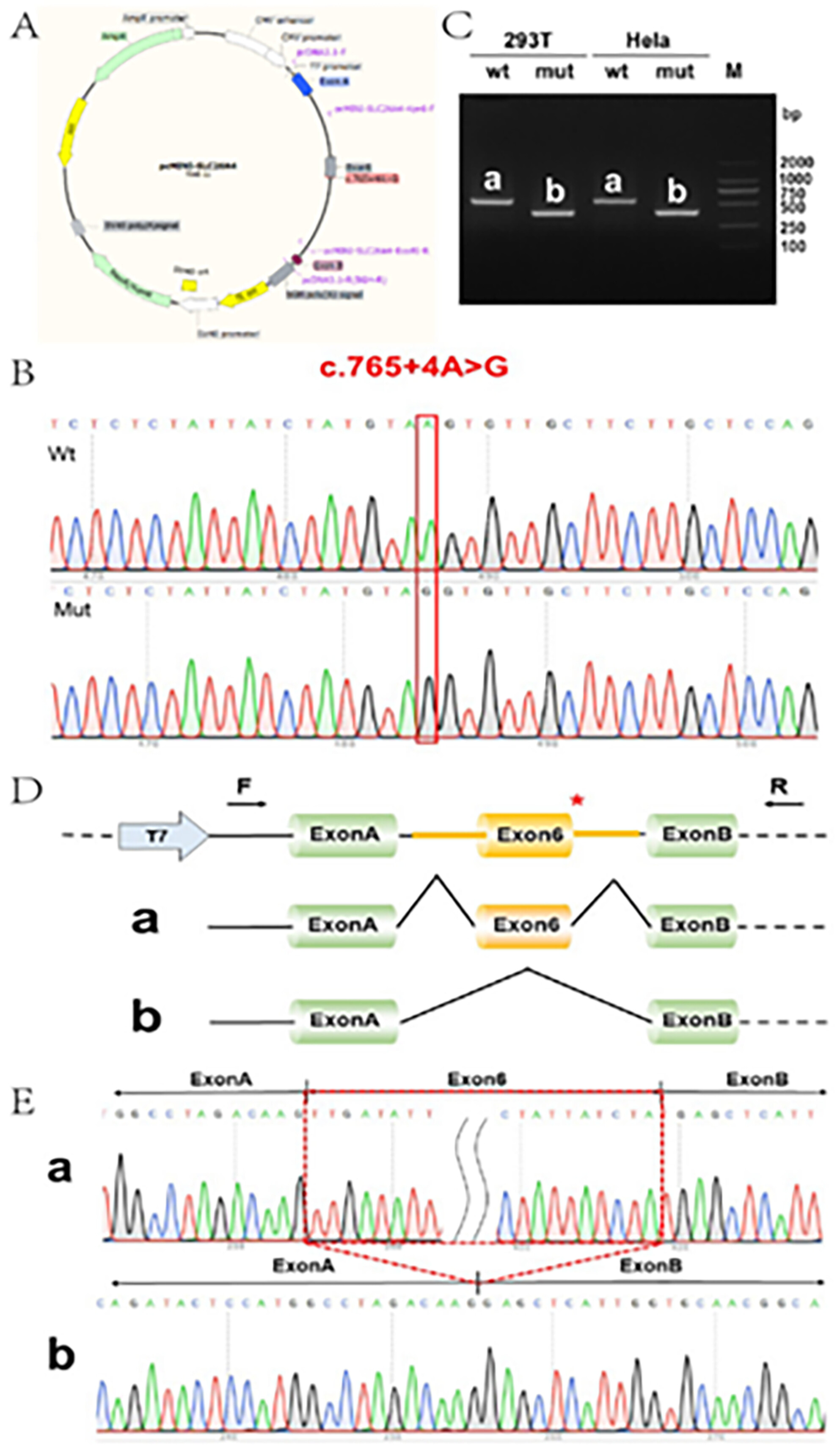
pc-MINI vector detection results. (A) Construction of the pcMINI-SLC26A4-wt/mut vector harboring exon6 and flanking intronic sequences from WT or Mut types (c.765+4A>G) of the SCL26A4 gene. (B) Minigene construction sequencing map, Wt on top and Mut on bottom; (C) RT-PCR products were separated by electrophoresis of the pcMINI-SLC26A4-wt/mut vector in HeLa and c293T cells. (D) The different splicing products for wild-type (a, 554 bps) and variant type (b, 389 bps) are shown on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis and represented graphically, lane b was smaller than the lane a, and the migration was faster. (E) Corresponding sequencing results of shear bands. Red * indicates the mutation position.
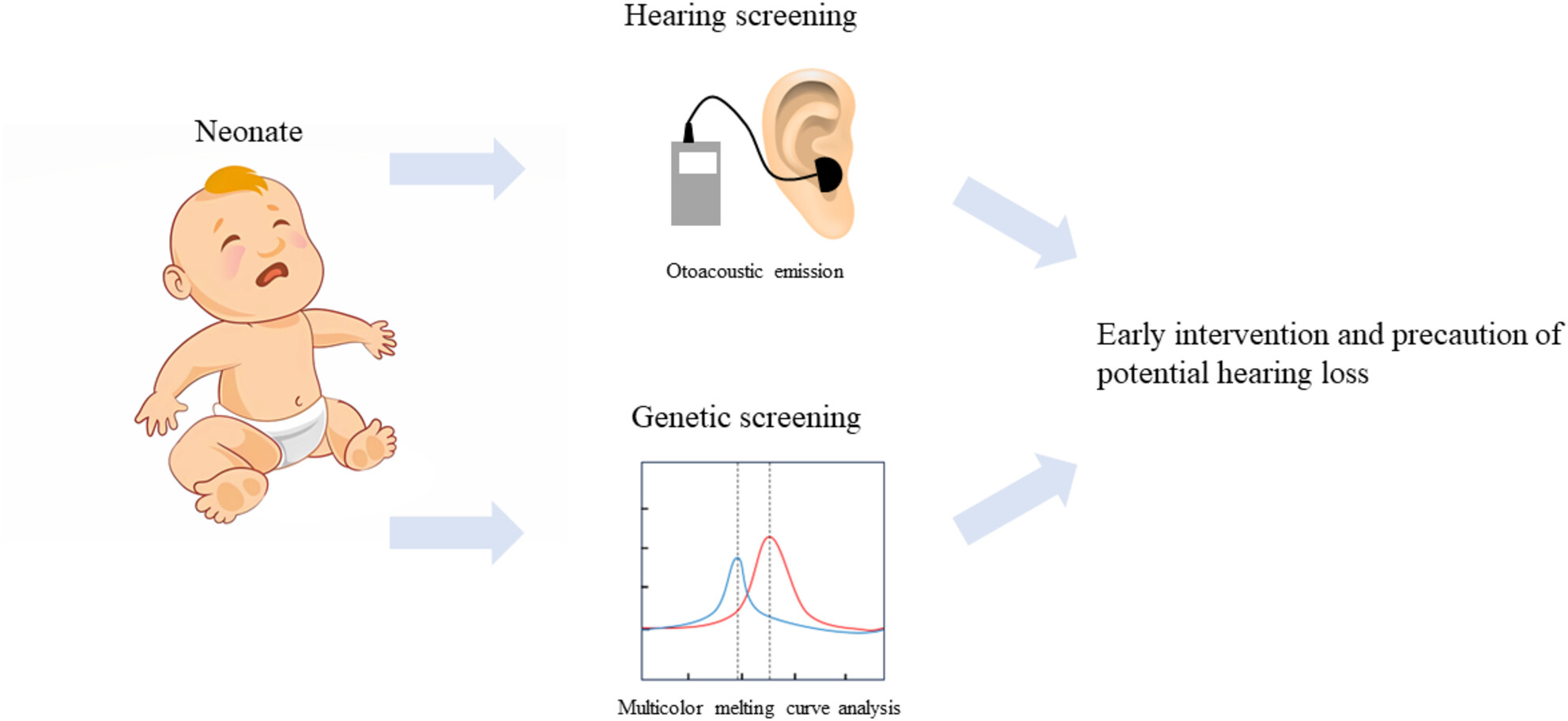
Multicolor melting curve analysis discloses high carrier frequency of hearing loss-associated variants among neonates in Jiangsu province
- First Published: 06 February 2024
Associations of genetic variants within TYK2 with pulmonary tuberculosis among Chinese population
- First Published: 09 February 2024
TYK2 modified TB risk.
Real-world data of Brazilian adults with X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) treated with burosumab and comparison with other worldwide cohorts
- First Published: 09 February 2024
The first Chinese intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 57 patient with two novel MBOAT7 variants
- First Published: 05 February 2024
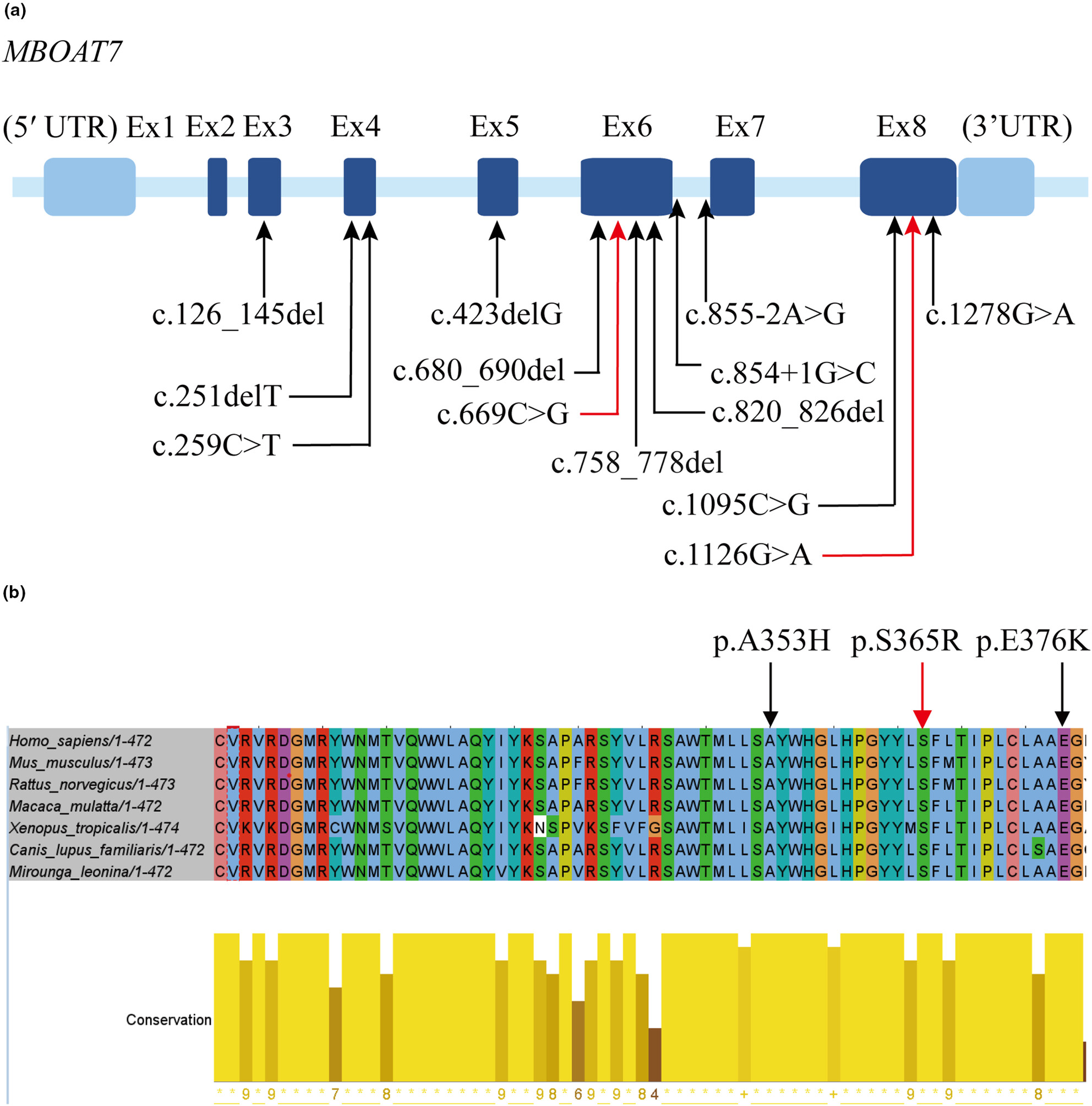
We here report a Chinese patient with Intellectual Developmental Disorder (IDD), autosomal recessive 57. Two previously unreported mutations in MBOAT7, c.669C>G (p.(Y223*)) and c.1095C>G (p.(S365R)) were identified by trio whole-exome sequencing. The patient we reported here is the first Han Chinese IDD patient known to be related to MBOAT7 mutation. In addition, this patient is the first case that carried compound heterozygous variants in the MBOAT7 gene, which expands the complexity of this disorder.
Association of Y chromosome AZF region microdeletions with recurrent miscarriage in Iranian couples: A case–control study
- First Published: 06 February 2024
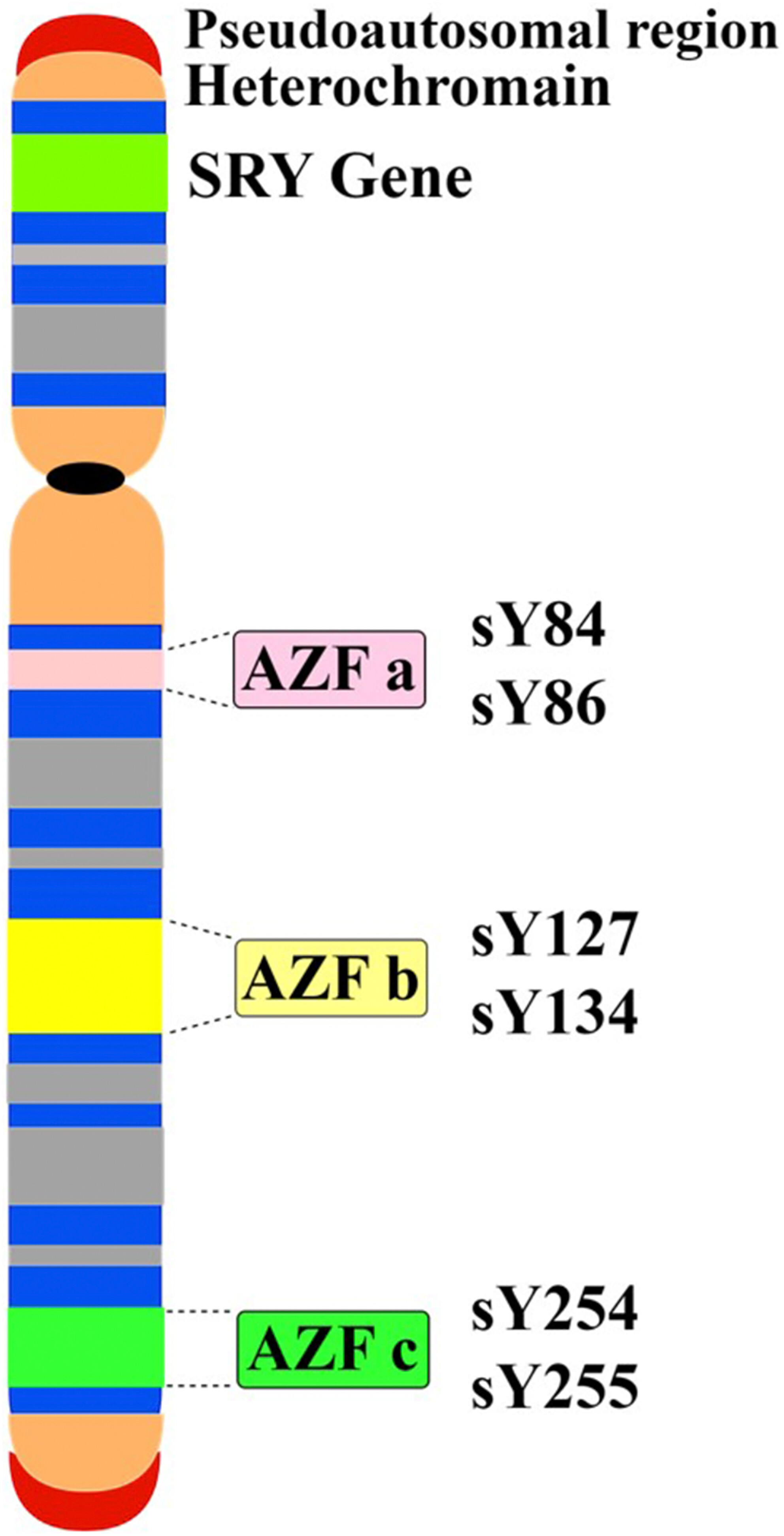
Male partners of women with RPL showed poorer semen quality and altered hormonal profile. Multiplex-PCR revealed microdeletions in AZFb (sY134), significantly more prevalent in RPL-men (16.7%) versus controls (p < 0.001). Y chromosome microdeletions provide valuable biomarkers, complementing semen and hormone analyses for identifying male factor contributions in couples with idiopathic RPL.
A novel heterozygous mutation in PTHLH causing autosomal dominant brachydactyly type E complicated with short stature
- First Published: 05 February 2024
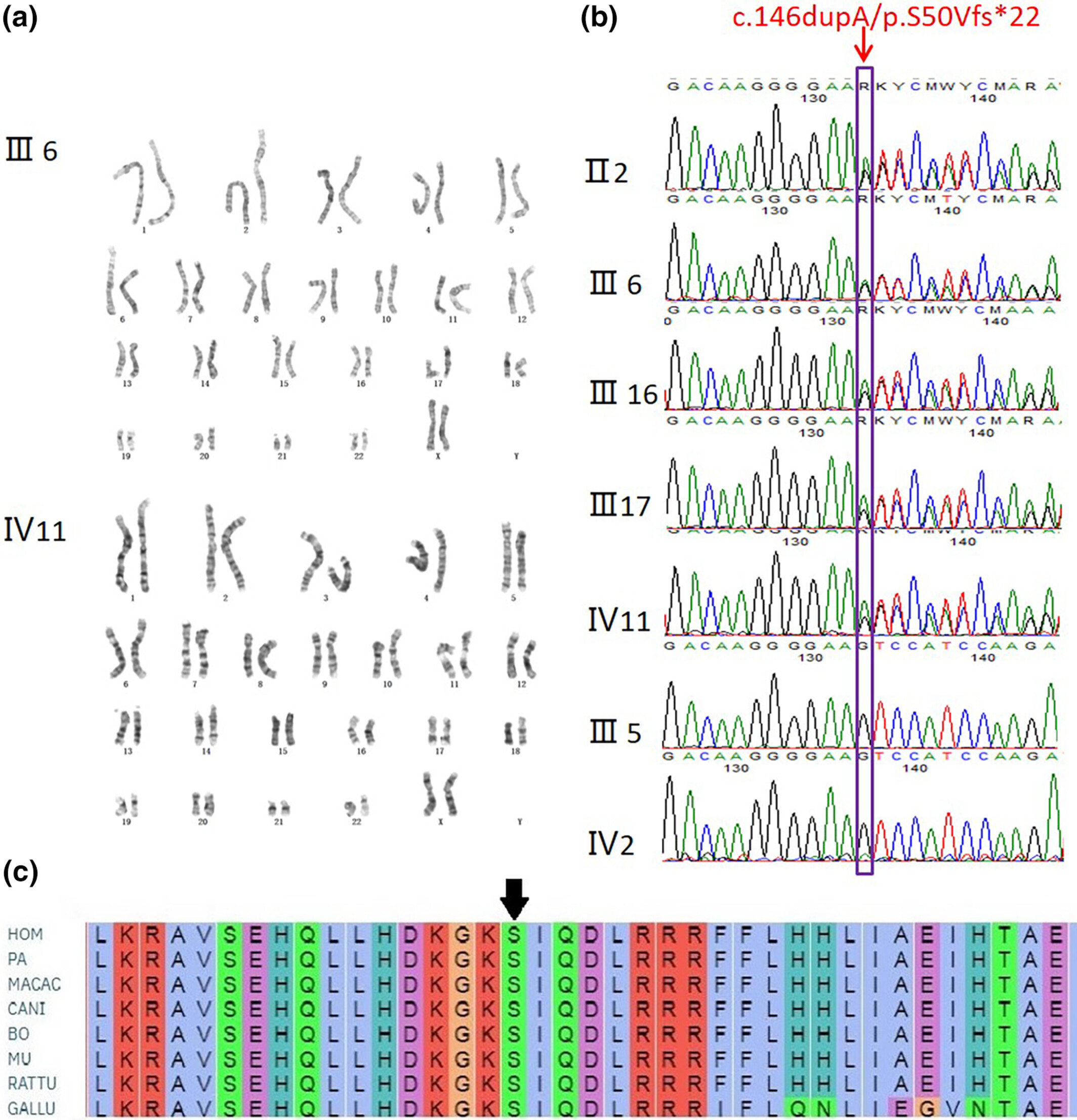
(A) No obvious chromosome aberration was found in the affected individuals. (B) Direct sequencing of PTHLH exons showing heterozygous c.146dupA, p.S50Vfs*22 mutation identified in BDE affected individuals (II2, III6, III16, III17, IV11) but not in normal family members (III5, IV2). (C) Evolutionary conservation of the cluster across multiple species.
Three exonic variants in the COL4A5 gene alter RNA splicing in a minigene assay
- First Published: 23 February 2024
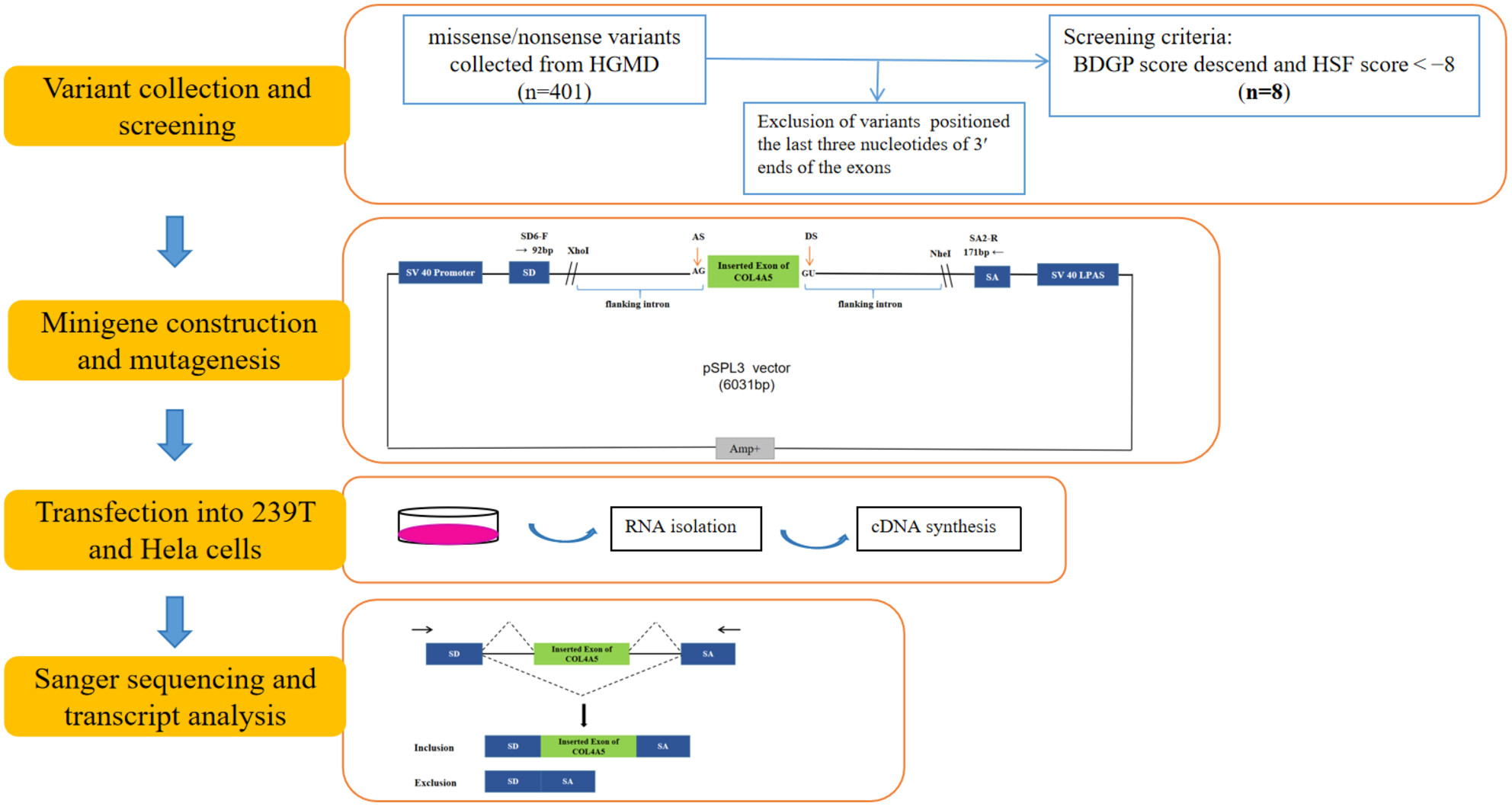
Three exonic variants in the COL4A5 gene alter RNA splicing in a minigene assay. Two missense variants positioned the first nucleotides of the 5′ end of COL4A5 exons and one internal exonic nonsense variant caused aberrant splicing. Emphasized the necessity of assessing the effects of SNVs at the mRNA level.
Clinical details of individuals with Rauch–Steindl syndrome due to NSD2 truncating variants
- First Published: 14 February 2024
Antenatal description of large 4q13.2q21.23 deletion and outcomes
- First Published: 13 February 2024
A homozygous stop codon in HORMAD2 in a patient with recurrent digynic triploid miscarriage
- First Published: 23 February 2024
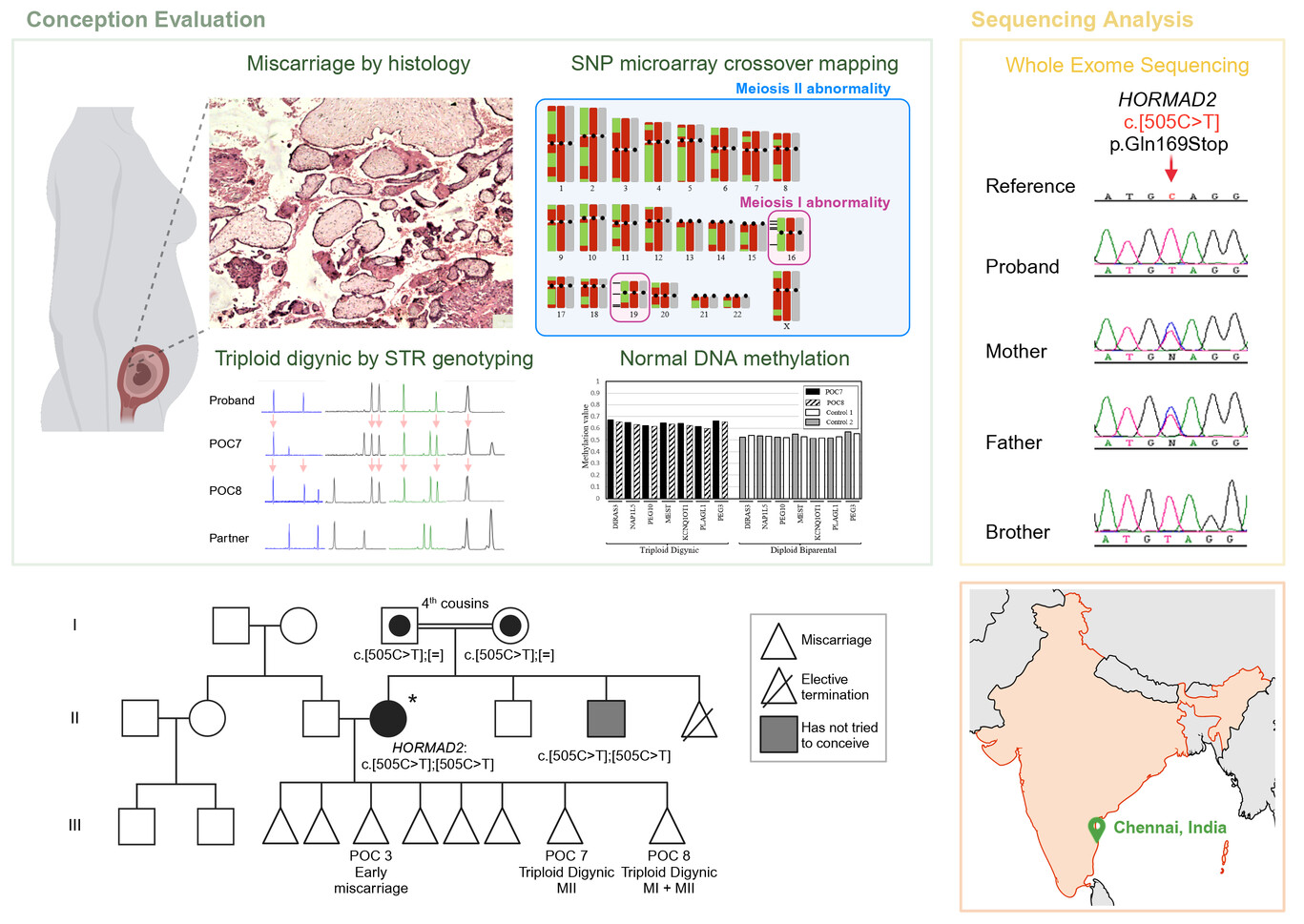
Genotype analysis of two products of conception, from a couple with eight consecutive miscarriages and no live birth, demonstrated their triploid digynic genomes and maternal Meiosis I and II errors. Exome sequencing narrowed down the search for the causative gene to two genes, EIF4ENIF1 and HORMAD2. The presence of meiotic errors are in favor of the causal role of HORMAD2 in the causation of RM. This figure was created with BioRender.com.
A novel gain-of-function STAT3 variant in infantile-onset diabetes associated with multiorgan autoimmunity
- First Published: 26 February 2024
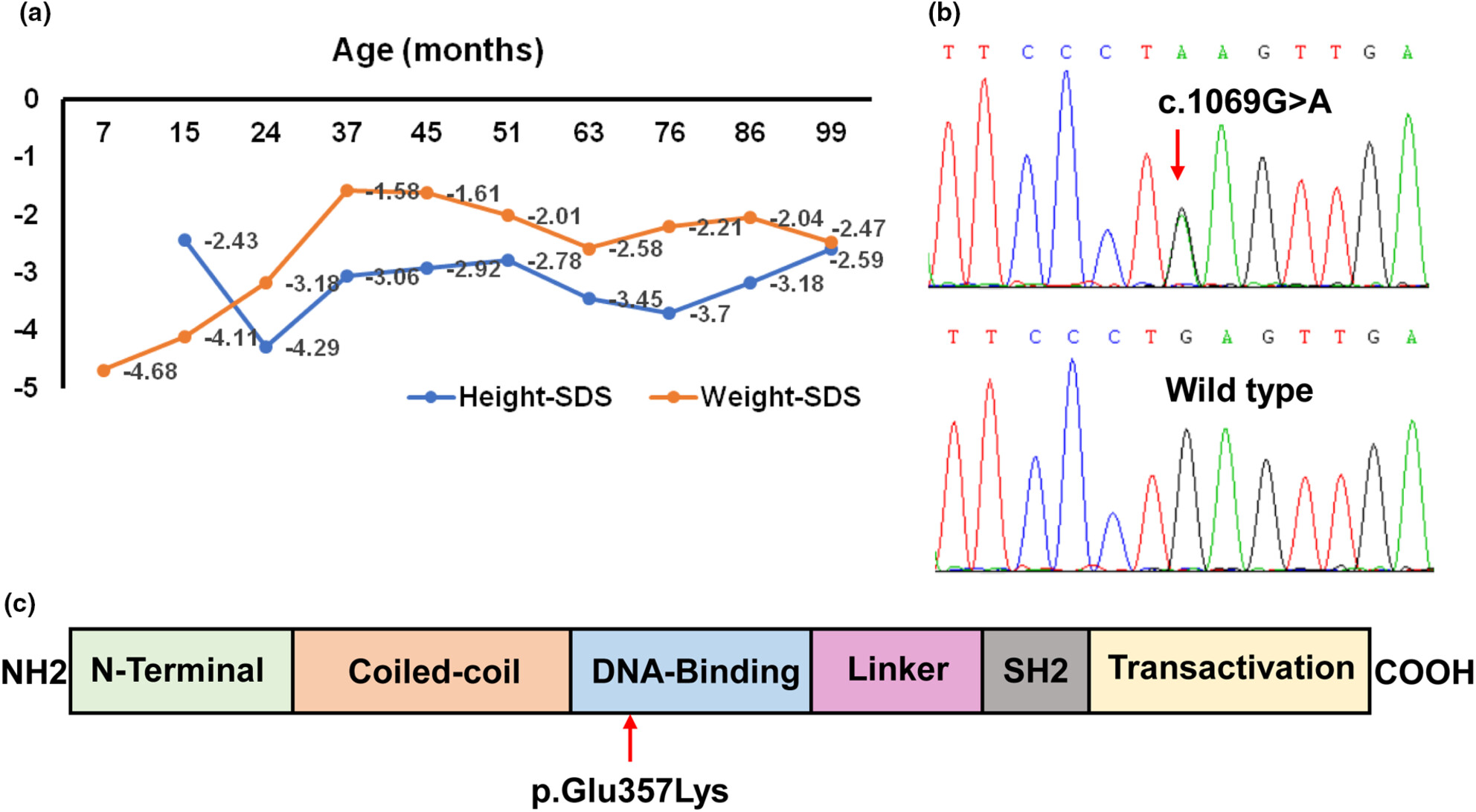
Gain-of-function (GOF) variants of STAT3 cause early-onset multiorgan autoimmunity. In this study, we described a patient with early-onset diabetes, hypothyroidism, enteropathy, and postnatal short stature. Of note, the chronic diarrhea lasted 3 years and resolved spontaneously. We identified a novel STAT3 GOF variant p.E357K. Further functional data showed that the variant caused dysregulation of insulin gene expression through inhibition of the transcription factor ISL1.
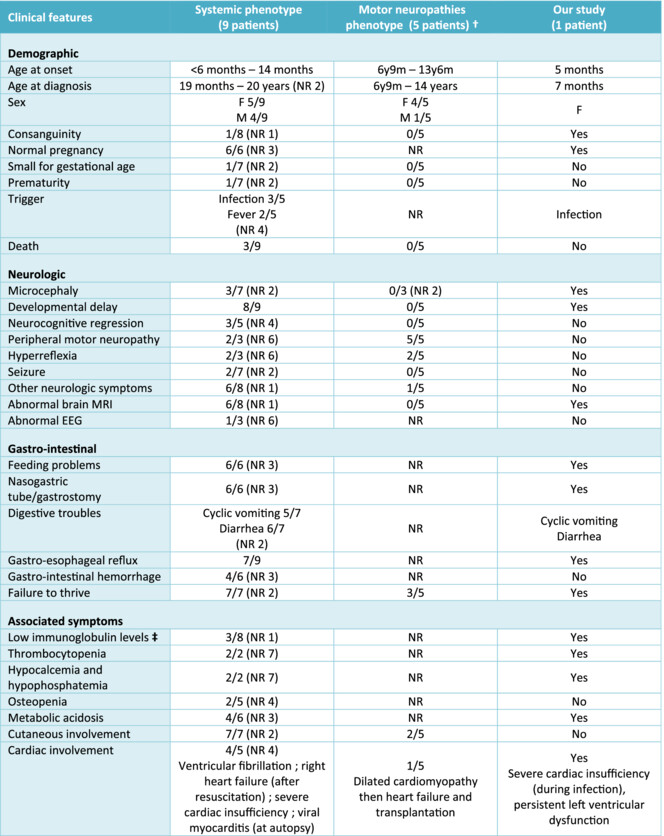
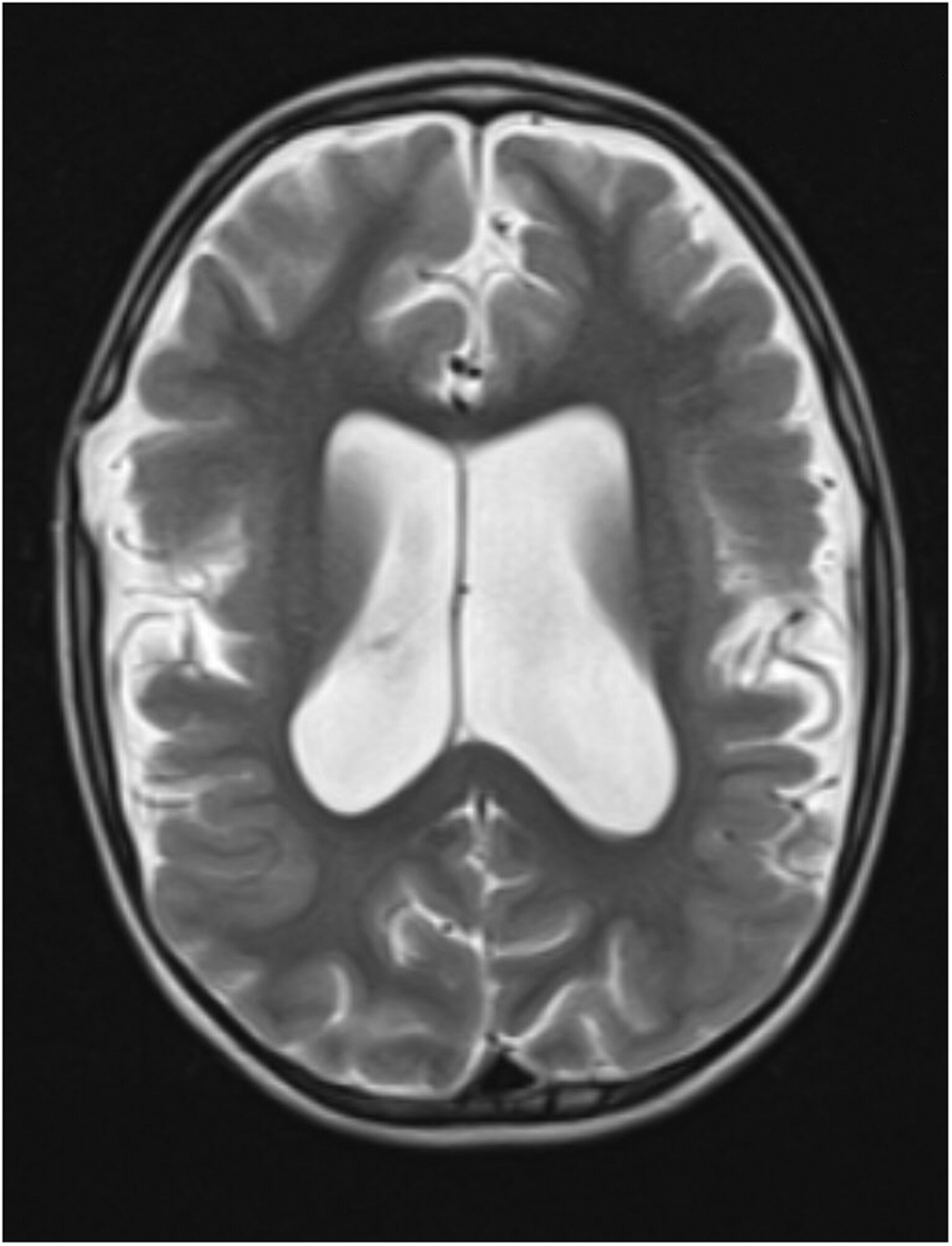
Novel variants in TNRC6B cause global developmental delay with speech and behavioral abnormalities, short stature, low body weight, café-au-lait spots, and metabolic abnormality
- First Published: 26 February 2024
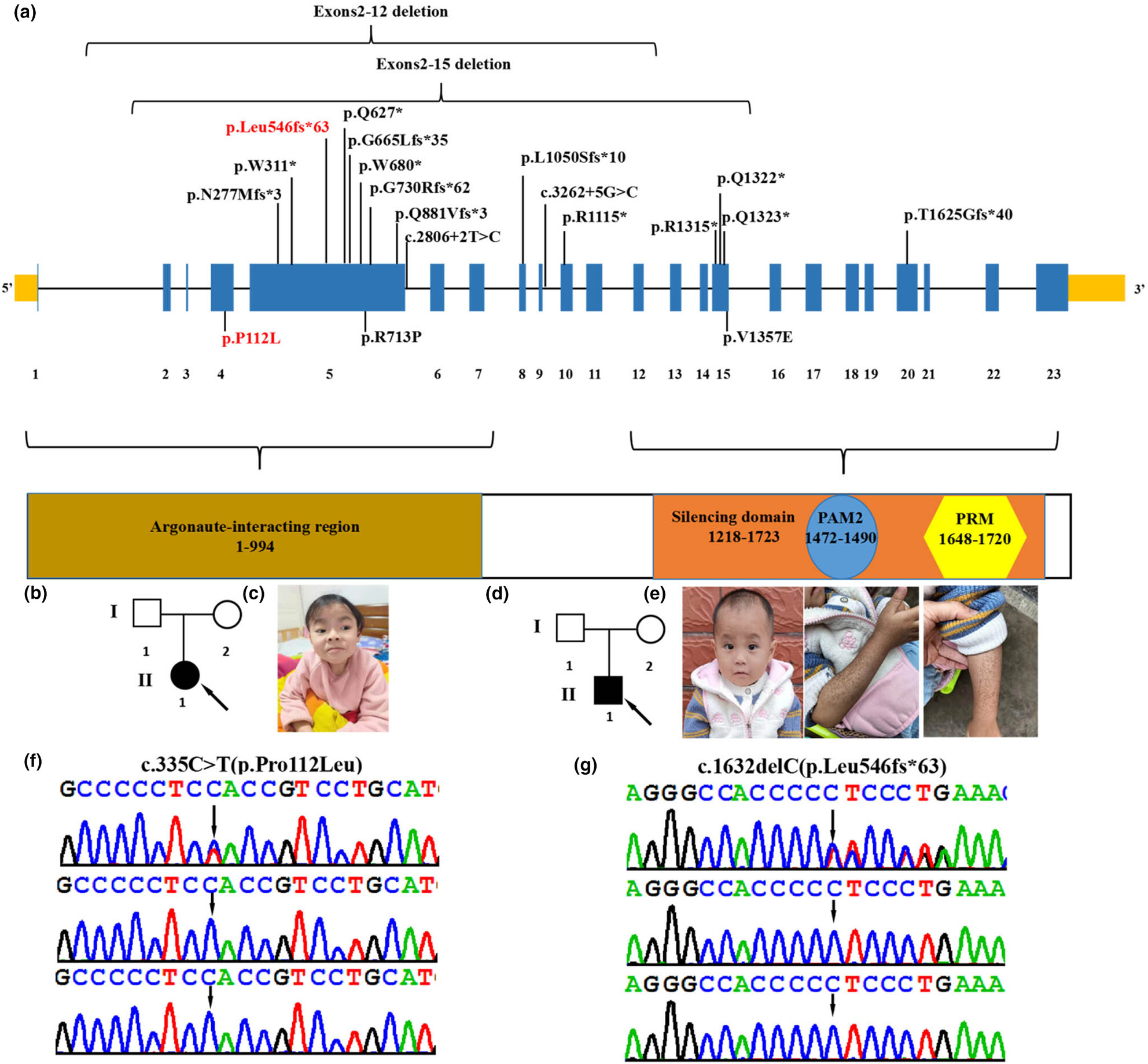
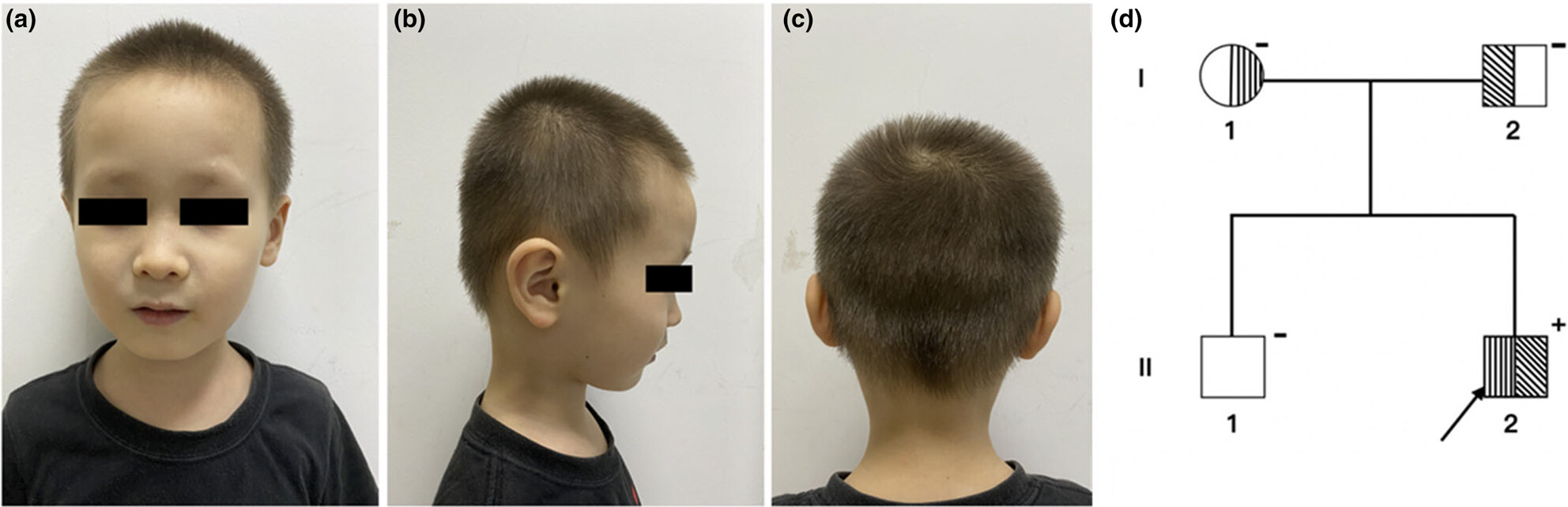
In this article, we investigate the pathogenesis of two unrelated Chinese children who exhibited developmental delay/intellectual disability, delayed speech, attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder, behavioral abnormalities, short stature, low body weight, café-au-lait spots, metabolic abnormalities, and facial dysmorphism including coarse facial features, sparse hair, frontal bossing, hypertelorism, amblyopia, strabismus, and downslanted palpebral fissures. Two novel de novo likely pathogenic or pathogenic TNRC6B variants c.335C>T (p.Pro112Leu) and c.1632delC (p.Leu546fs*63) were found in these patients. This study expands the genetic and phenotype spectrum of TNRC6B deficiency syndrome.
CLINICAL REPORTS
Oculocutaneous albinism type 4: Novel compound heterozygous mutations in the SLC45A2 gene in a Chinese case
- First Published: 09 February 2024
In this study, we present a case with less pigmented hair and fairer than normal skin. Strabismus, hyperopia, astigmatism and the absence of iris pigment were found in his both eyes. Whole exome sequencing was performed in all samples, and Sanger sequencing was then used to verify the mutations. Compound heterozygous variants, c.1304C>A (p.S435Y) and c.301C>G (p.R101G) in SLC45A2 gene, were detected proband. We emphasize that this compound heterozygous mutation case of OCA4 was the first report from China.
A new case of sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter defect occurring as a life-threatening condition responsive to early vitamin supplementation and literature review
- First Published: 06 February 2024
We highlight the life-threatening presentation of SMVT deficiency. Increased and isolated excretion of urinary 3-hydroxyisovaleric acid may suggest, in the absence of markedly reduced biotinidase activity, a SMVT deficiency. Prompt supplementation with high doses of biotin and pantothenic acid should be initiated while awaiting results of SLC5A6 sequencing as this condition may be life-threatening and a high dose of these water-soluble vitamins seems harmless.
Hemizygous splicing variant in CNKSR2 results in X-linked intellectual developmental disorder
- First Published: 09 February 2024
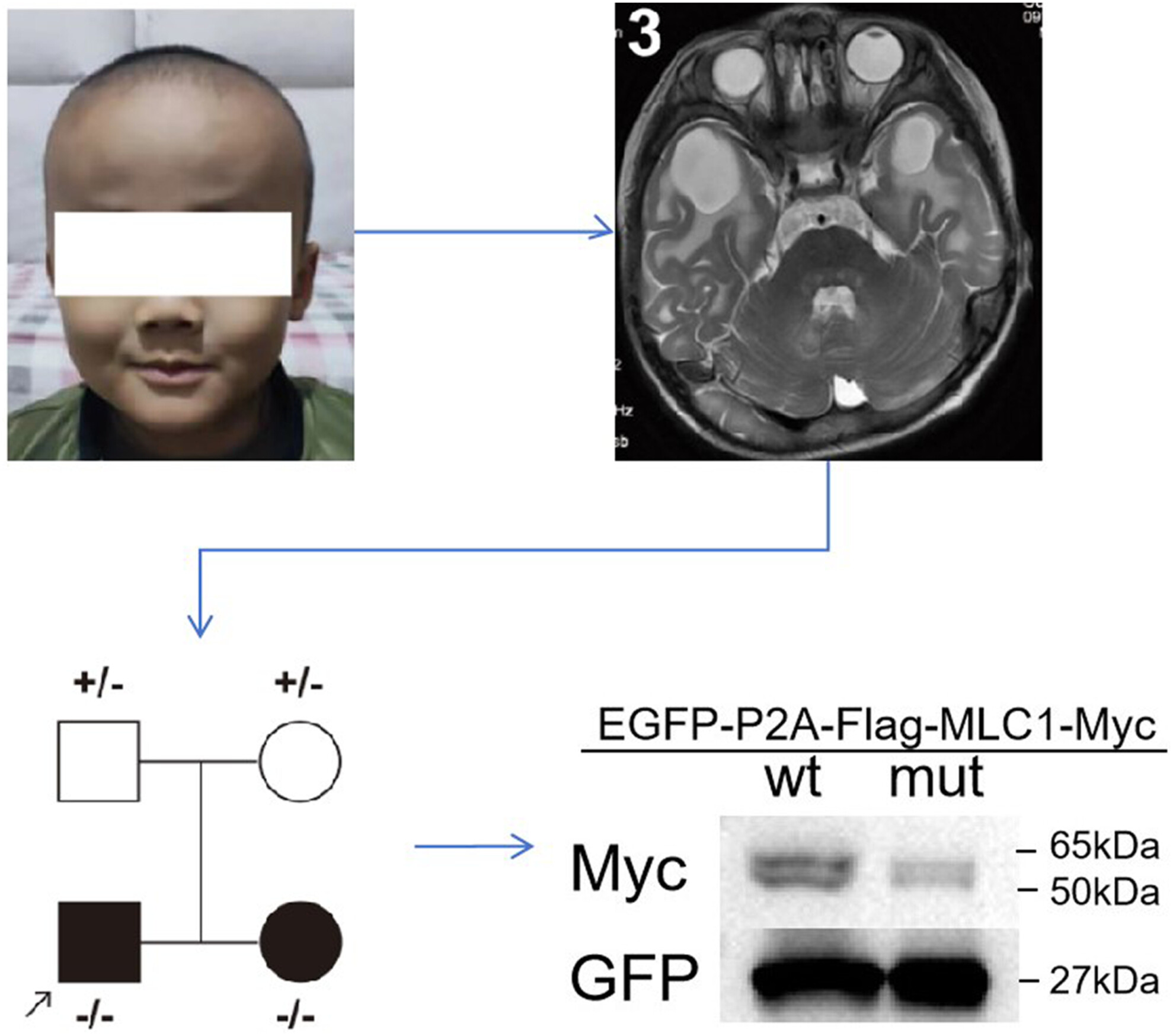
Homozygous variant of MLC1 results in megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts
- First Published: 09 February 2024
Novel hemizygous single-nucleotide duplication in RPGR in a patient with retinal dystrophy and sensorineural hearing loss
- First Published: 26 February 2024

Comprehensive genetic testing is a powerful tool for diagnosis in medically underserved populations. After other smaller genetic tests were nondiagnostic, provision of whole exome sequencing through the Texome Project uncovered a novel likely pathogenic variant in RPGR that explains some of the patient phenotypes.
Type 1 early infantile epileptic encephalopathy: A case report and literature review
- First Published: 23 February 2024
Variants in Aristaless-related homeobox (ARX) gene lead to a variety of phenotypes with intellectual disability being a steady feature. Other features can include severe epilepsy, spasticity, movement disorders, hydranencephaly, and ambiguous genitalia in males. Ohtahara syndrome or Type 1 early infantile epileptic encephalopathy is a severe early-onset epileptic encephalopathy with arrest of psychomotor development caused by hemizygous mutations in the ARX gene, which encodes a transcription factor in fundamental brain developmental processes. We presented a case report of 2-year-old boy, which indicates symptoms of Ohtahara syndrome.
RETRACTION
Retracted: MtDNA polymorphism analyses in the Chinese Mongolian group: Efficiency evaluation and further matrilineal genetic structure exploration
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Population genetics of 24 Y-STR loci in Chinese Han population from Jilin Province, Northeast China
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: An innovative panel containing a set of insertion/deletion loci for individual identification and its forensic efficiency evaluations in Chinese Hui ethnic minority
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Genetic polymorphism and phylogenetic analyses of 21 non-CODIS STR loci in a Chinese Han population from Shanghai
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Forensic characteristics and genetic affinity analyses of Xinjiang Mongolian group using a novel six fluorescent dye-labeled typing system including 41 Y-STRs and 3 Y-InDels
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Genetic diversity and phylogenetic structure of four Tibeto-Burman-speaking populations in Tibetan-Yi corridor revealed by insertion/deletion polymorphisms
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Population genetic data from 23 autosomal STR loci of Huaxia Platinum system in the Jining Han population
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Comprehensive genetic structure analysis of Han population from Dalian City revealed by 20 Y-STRs
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Haplotype diversity and phylogenetic characteristics for Guanzhong Han population from Northwest China via 38 Y-STRs using Yfiler™ Platinum Amplification System
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Population genetic analysis of Shaanxi male Han Chinese population reveals genetic differentiation and homogenization of East Asians
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Forensic features and genetic background exploration of a new 47-autosomal InDel panel in five representative Han populations residing in Northern China
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Haplotypic diversity and population genetic study of a population in Kashi region by 27 Y-chromosomal short tandem repeat loci
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Evaluation of a six-dye multiplex composed of 27 markers for forensic analysis and databasing
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Forensic characteristics and phylogenetic analyses of one branch of Tai-Kadai language-speaking Hainan Hlai (Ha Hlai) via 23 autosomal STRs included in the Huaxia™ Platinum System
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Genetic diversity, forensic feature, and phylogenetic analysis of Guizhou Tujia population via 19 X-STRs
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Forensic applications and genetic characterization of Liaoning Han opulation revealed by extended set of autosomal STRs
- First Published: 14 February 2024
Retraction: Genetic structure and forensic characterization of 36 Y-chromosomal STR loci in Tibeto-Burman- speaking Yi population
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Retraction: Concordance and characterization of massively parallel sequencing at 58 STRs in a Tibetan population
- First Published: 12 February 2024