Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine
Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Clinical, biochemical, and genetic characterization of acute hepatic porphyrias in a cohort of Argentine patients
- First Published: 25 March 2021
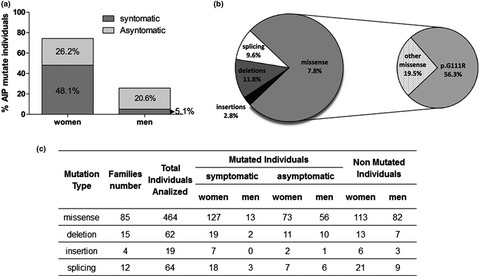
In this paper we review same results obtained from the AIP and VP families studied at biochemical and molecular level at the CIPYP in Argentina.Taking into account the relationship between the porphyric attack and oxidative stress, we also decided to study oxidative stress parameters and homocysteine levels in AHP patients and controls, to identify a marker of neurological dysfunction.
Identification of rare heterozygous linkage R965C-R1309H mutations in the pore-forming region of SCN5A gene associated with complex arrhythmia
- First Published: 25 March 2021
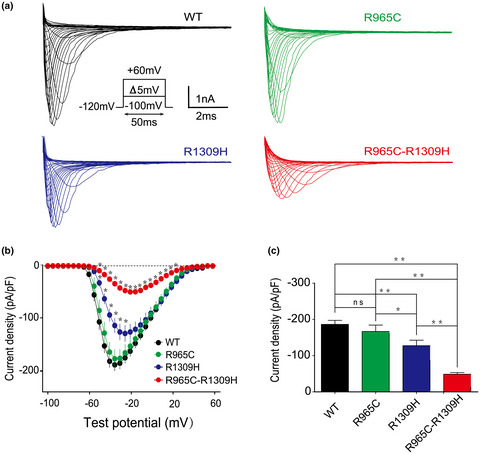
The rare hereditary disease with complex arrhythmia syndrome resulted from the heterozygous linkage SCN5A R965C-R1309H mutation, detected by targeted capture sequencing. The linkage mutation SCN5A R965C-R1309H led to a more dramatic reduction in the current density of sodium channel, more depolarisation-shifted activation and more hyperpolarisation-shifted inactivation than either single mutation, R965C or R1309H, indicating synergistic effects on the pore-gating properties of sodium channels, as detected by whole-cell recordings.
Molecular basis of various forms of maple syrup urine disease in Chilean patients
- First Published: 06 May 2021
This manuscript describes a cross-sectional study of 18 MSUD patients carried out using PCR and DNA sequencing. Four novel pathogenic mutations were identified: one in BCKDHA (p.Thr338Ile), two in BCKDHB (p.Gly336Ser e p.Pro240Thr), and one in DBT (p.Gly406Asp). Four additional pathogenic mutations found in this study have been described previously. There were no correlations between the genotype and phenotype of the patients.
The investigation of genetic and clinical features in patients with hereditary spastic paraplegia in central-Southern China
- First Published: 27 February 2021
We investigated the genetic and clinical features in five families with HSP from central-southern China using targeted exome-sequencing technology. We identified a known mutation (p.Pro435Leu) in SPAST in a family with autosomal dominant HSP (AD-HSP) and four novel variants in three independent HSP families and a sporadic case. These identified four novel variants include a nonsense variant (p.Val1979Ter) in SPG11, two variants (p.Ser475Phe and c.1002 + 2 T > G) in B4GALNT1, and a splicing site variants in SPAST (c.1245 + 5G>A). Minigene analysis of the splicing variant (c.1245 + 5G>A) in SPAST revealed that the mutation resulted in mRNAs with a loss of exon 9
Genetic testing results of children suspected to have Stickler syndrome type collagenopathy after ocular examination
- First Published: 05 May 2021
Clinical and genetic analysis of classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patient caused by synonymous mutation in COL5A2
- First Published: 08 April 2021
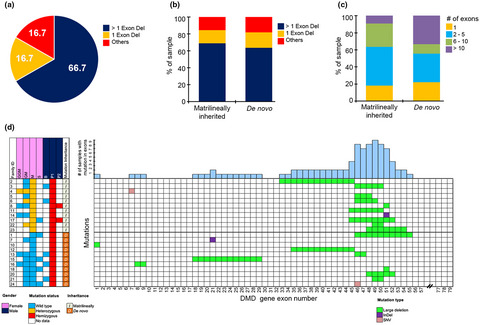
Matrilineal analysis of mutations in the DMD gene in a multigenerational South Indian cohort using DMD gene panel sequencing
- First Published: 07 May 2021
Objective differential diagnosis of Noonan and Williams–Beuren syndromes in diverse populations using quantitative facial phenotyping
- First Published: 27 March 2021

Although distinctive facial features have been reported between Noonan and Williams–Beuren syndromes, studies have found a variable incidence of those characteristics in populations with diverse ancestry. We sought to identify and quantify facial features discriminative of these two syndromes in population with diverse ancestry using facial analysis. We provide for the first time quantitative reference facial metrics in diverse populations that can be used both at the clinic and for training purposes.
A novel mutation in NF1 gene of patient with Neurofibromatosis type 1: A case report and functional study
- First Published: 25 March 2021
A Chinese patient bearing with a novel NF1 mutation is involved in this study. The present complaint of this patient is bone phenotype including short stature and scoliosis. Functional studies confirm that this novel mutant could active Ras/Erk signaling and perhaps further inhibit the development of osteoblasts (OBLs), which provide a potential molecular mechanism to explain the bone maldevelopment of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1.
Mitochondrial DNA insert into CD40 ligand gene-associated X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome
- First Published: 24 March 2021
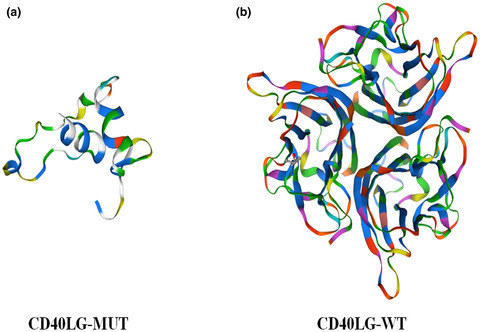
A new mutation of the CD40 ligand gene (CD40LG) that encodes the CD40 ligand (CD40L) molecule was detected in a 20-month-old boy harbouring an X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome (X-HIGM) combined with immunodeficiency syndrome. Inactivation of the CD40LG gene resulted from the insertion of mitochondrial DNA copies into exon 1, which in turn led to a total deficiency of CD40L expression of T lymphocytes.
Prenatal ultrasound findings in Koolen-de Vries foetuses: Central nervous system anomalies are frequent markers of this syndrome
- First Published: 18 March 2021
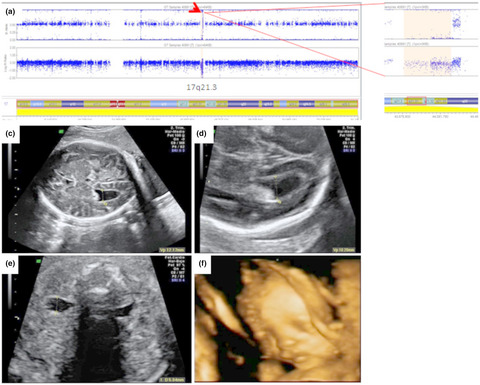
Prenatal CNS anomalies (mainly ventriculomegaly) at third trimester, should be considered a prenatal ultrasound marker of this syndrome. This kind of malformations raise the possibility of an underlying genetic condition including 17q21.31 microdeletion. Thus CMA should be taken into consideration when offering prenatal genetic counselling.
Whole-exome sequencing analysis in 10 families of sporadic microtia with thoracic deformities
- First Published: 03 April 2021
Atypical focal segmental glomerulosclerosis associated with a new PODXL nonsense variant
- First Published: 29 March 2021
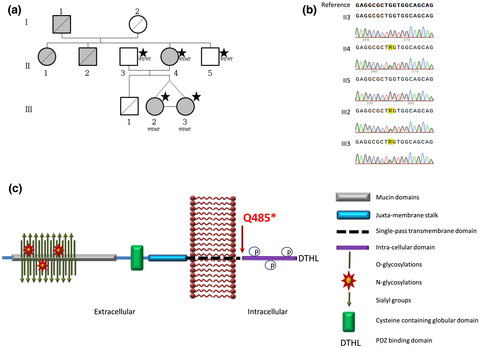
This study describes the association of a genetic Podocalyxin (PODXL) variant with a familial glomerular nephropathy characterized by focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis features. This finding expands the phenotypic spectrum associated to PODXL variants and highlights the importance to screen the PODXL gene for deleterious variants in similar disease forms.
Stepwise shortening of agalsidase beta infusion duration in Fabry disease: Clinical experience with infusion rate escalation protocol
- First Published: 23 March 2021
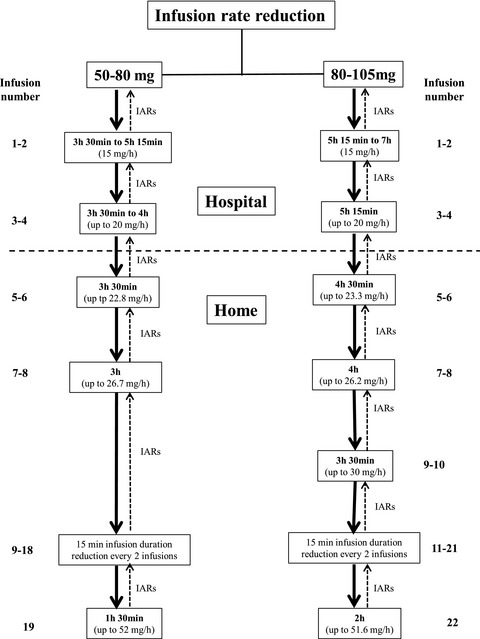
Although enzyme replacement therapy with agalsidase beta resulted in a variety of clinical benefits, life-long biweekly intravenous infusion may impact on patients’ quality of life because regular infusions are time-consuming. In this study, we reported our experience with a stepwise infusion rate escalation protocol developed in our center in a cohort of 53 Fabry patients (both already receiving and treatment-naΪve), and explored factors predictive for the infusion rate increase tolerability. We showed that our infusion rate escalation protocol is safe and could improve patient compliance, satisfaction and quality of life.
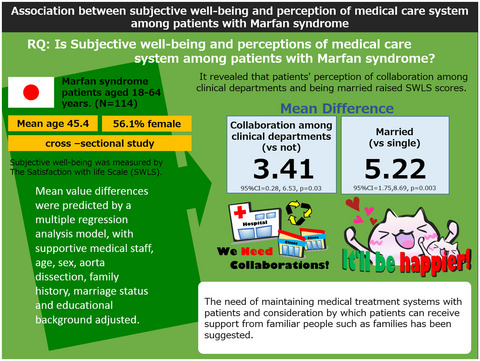
Association between subjective well-being and perception of medical care system among patients with Marfan syndrome: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 05 May 2021
Next-generation sequence-based preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disease resulting from maternal mosaicism
- First Published: 04 May 2021
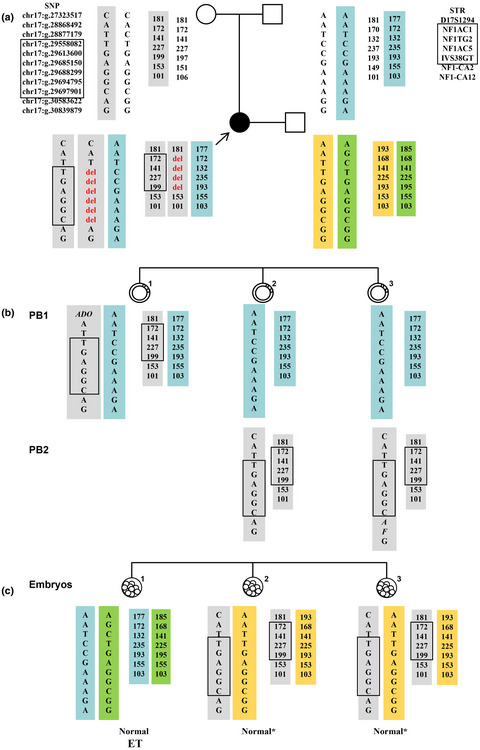
NGS-based PGT is an effective strategy for the detection of monogenic diseases resulting from mosaicism. Furthermore, NGS-based PGT combined with PB genetic analysis can improve the accuracy of PGT for monogenic diseases due to maternal mosaicism. This approach will assist clinicians to undertake a more objective assessment of disease recurrence risk for mosaic individuals and obtain an accurate diagnosis of the genotype of embryos for reproductive interventions.
Patients’ and caregivers’ maximum acceptable risk of death for non-curative gene therapy to treat Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- First Published: 23 March 2021

There are no quantitative data on the risk that parents or adults with Duchenne would accept for a non-curative gene therapy. We used a survey with threshold technique and a hypothetical treatment vignette to measure maximum acceptable risk (MAR) for death at four timepoints in the life of the person with Duchenne. We find relatively high tolerance for mortality risk that increases with progression. Patients and caregivers overall showed a willingness to accept risk and uncertainty in exchange for the hypothetical benefit profile presented.
Characterization of a novel COL10A1 variant associated with Schmid-type metaphyseal chondrodysplasia and a literature review
- First Published: 25 March 2021
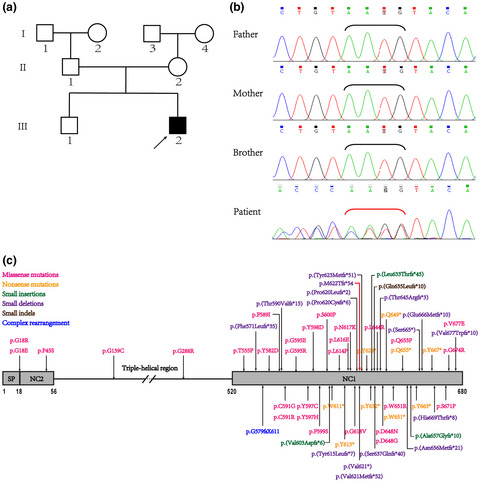
This study characterized a novel COL10A1 variant (c.1863_1866delAATG, p.M622 Tfs*54) associated with Schmid type metaphyseal chondrodysplasia in a two-year-old Chinese patient. The novel variant was predicted to impair the trimerization of collagen X (α1) and combination with molecules in the matrix by in silico analysis. The NC1 domain of COL10A1 was a key region underlying SMCD, patients with NC1 mutations tend to present severer manifestations at earlier age.
CLINICAL REPORTS
Novel frameshift mutation in PURA gene causes severe encephalopathy of unclear cause
- First Published: 22 March 2021
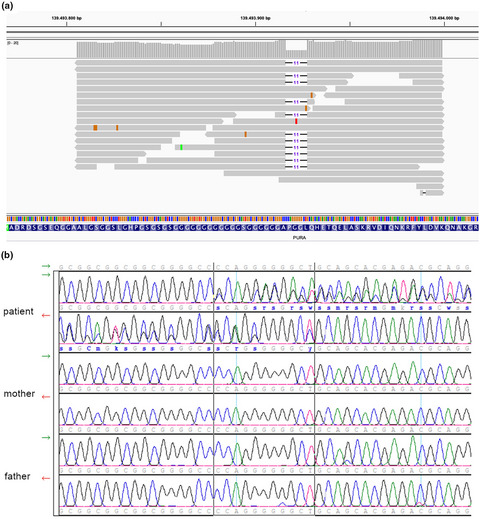
Rare diseases present several difficulties for patients, from the delay in the diagnosis to the lack of treatments. Next generation sequencing techniques have improved the search for diagnosis in several such pathologies. Here, we present the case of an undiagnosed six years old boy with severe encephalopathy of unclear cause, whose etiological diagnosis was achieved by whole genome sequencing.
A novel essential splice site variant in SPTB in a large hereditary spherocytosis family
- First Published: 04 May 2021
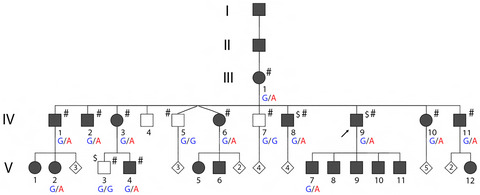
We studied a large family with 22 individuals affected with autosomal dominant hereditary spherocytosis (HS). Genome-wide linkage and whole-genome sequencing analyses revealed a heterozygous G>A transition in the 14q23 locus, at position +1 of the intron 8 donor splice site of the spectrin beta, erythrocytic (SPTB) gene.
Endocrinological features of a patient with 14q microdeletion and Dubowitz phenotype
- First Published: 31 March 2021
Severe brain calcification and migraine headache caused by SLC20A2 and PDGFRB heterozygous mutations in a five-year-old Chinese girl
- First Published: 01 April 2021
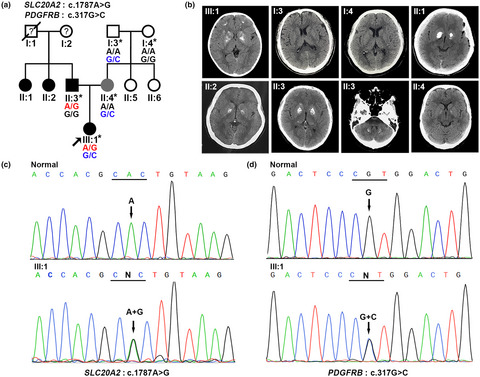
We report a family in which the members have various genetic states and manifestations of PFBC. Notably, the proband carrying the SLC20A2 and PDGFRB heterozygous mutations showed more severe brain calcification and earlier onset age of clinical symptoms than her family members, highlighting digenic influences on the characteristics of PFBC patients.
REVIEW ARTICLES
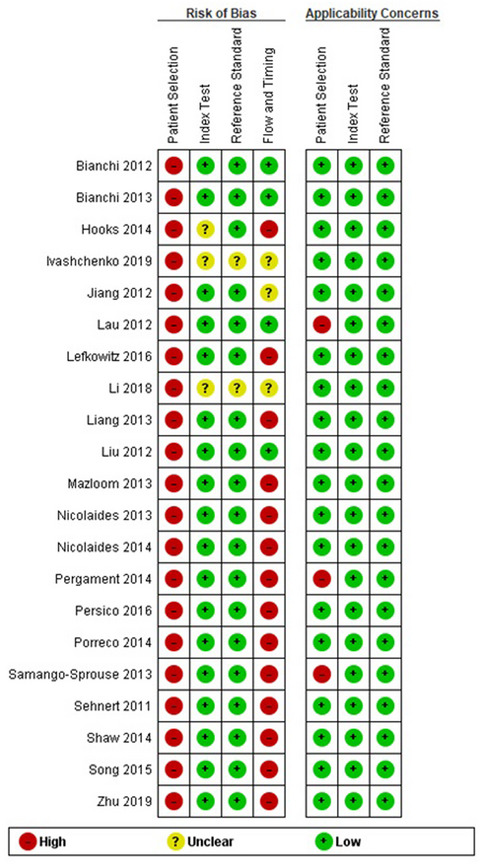
Non-invasive prenatal testing for the prenatal screening of sex chromosome aneuploidies: A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies
- First Published: 23 March 2021
The benefits and challenges of family genetic testing in rare genetic diseases—lessons from Fabry disease
- First Published: 09 April 2021
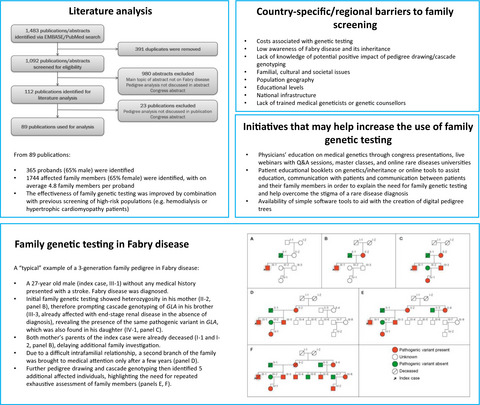
This review article discusses the literature published on family genetic testing for Fabry disease and the experiences of 19 Fabry experts from 15 countries regarding family screening in their countries and the barriers they are facing. Together, this literature overview and combined global experience provides valuable insights to medical geneticists working to improve the diagnosis of rare diseases within their countries and globally.
LETTER TO THE EDITORS
Genetic variants associated with diseases in Afghan population
- First Published: 24 January 2021