Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
SURVEY ARTICLES
Federated learning and next generation wireless communications: A survey on bidirectional relationship
- First Published: 12 February 2022
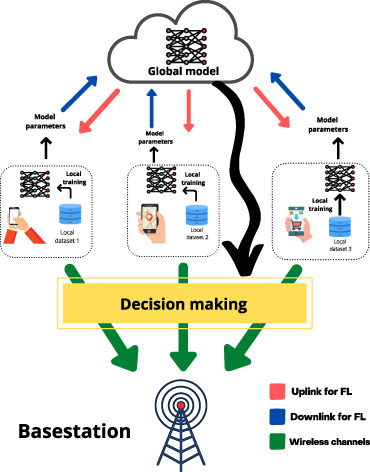
Federated learning (FL) is an emerging distributed learning paradigm and it also finds its applications for the next generation communication systems. Moreover, the performance of the FL depends on the underlying wireless channels, thus establishes a “bidirectional” relationship between the FL and the wireless systems. In this survey article, we provide a comprehensive discussion that highlights this important “bidirectional” relationship between the two scientific fields.
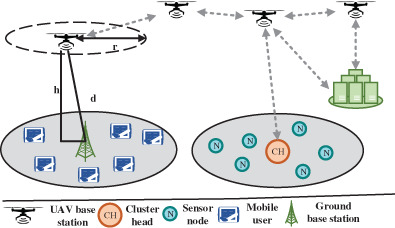
Resource optimization in UAV-assisted wireless networks—A comprehensive survey
- First Published: 07 February 2022
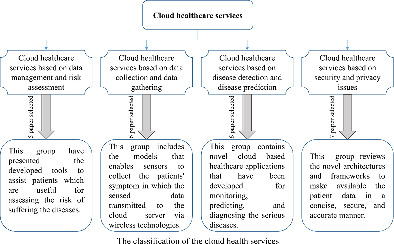
Cloud healthcare services: A comprehensive and systematic literature review
- First Published: 14 March 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Decentralized prediction and reputation approach in vehicular networks
- First Published: 10 February 2022
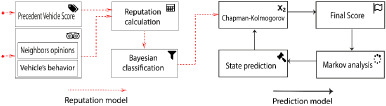
We propose a decentralized prediction and reputation approach. This approach categorizes each vehicle into four possible states. In our approach, the vehicle can predict the future state of other nodes in the vehicular network. In addition, vehicles can decide to interact with reliable vehicles and can detect malicious vehicles.
Similarity-based clustering and data aggregation with independent component analysis in wireless sensor networks
- First Published: 13 February 2022
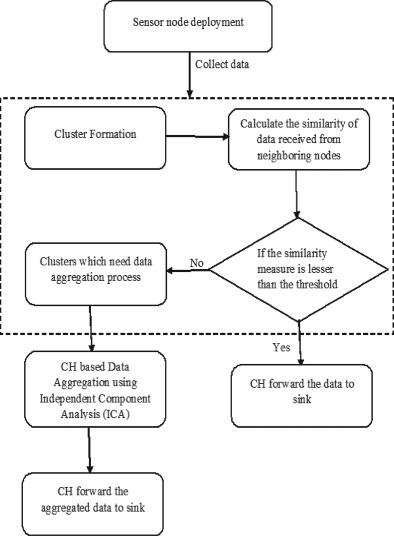
Here, proposes an enhanced clustering and data aggregation scheme, in which the clusters are formed by finding the correlation of data from the sensor nodes. Neighboring sensor nodes data similarity can be evaluated in terms of correlation value after the deployment of nodes. By assuming the cluster heads are predetermined, the data correlation of CH with each of its neighbor node (based on transmission radius) is calculated. After cluster formation with its neighbor nodes, average correlation value of each cluster can be calculated. After cluster formation with its neighbor nodes, average correlation value of each cluster can be calculated. It is possible to set a suitable threshold value for correlation. If the average correlation metric of a cluster is greater than the threshold value, that cluster is marked as higher similarity cluster, which needs data aggregation. If correlation metric is less than threshold, those clusters are marked as dissimilar and data aggregation is not compulsory for these clusters. Dissimilar data clusters transfer data to cluster head and lastly send to the sink. In the context of higher similarity cluster, a cluster based data aggregation scheme with independent component analysis (ICA) is performed. The CH is responsible for aggregating the data. ICA is one of the effective and computationally efficient data reduction methods. Aggregated data from higher similarity clusters are sending to base station. So it is possible to reduce the computation and energy utilization because of less number of aggregation processes and less number of data transmissions. The figure shows the flow diagram of proposed method. The work is mainly divided into two modules: Data aggregation using ICA and clustering based on data similarity.
Handoff optimization for joint base station association and power control in uplink non-orthogonal multiple access small cell networks
- First Published: 13 February 2022
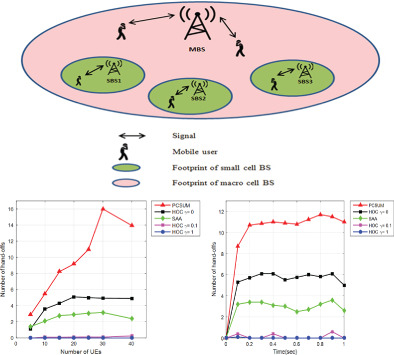
This article investigates the handoff optimization in a uplink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA)-based small cell networks (SCNs) with successive interference cancellation that takes both the base Station (BS) association and power control into consideration. The formulated problem is solved by adopting the coalition formation game theory, in which the coalition value function is designed by considering the handoff number of each BS in every time frame, transmit power of all MUs and the number of associated MUs to each BS.
Altitude and density optimization over UAV-enabled massive IoT wireless communications
- First Published: 16 February 2022
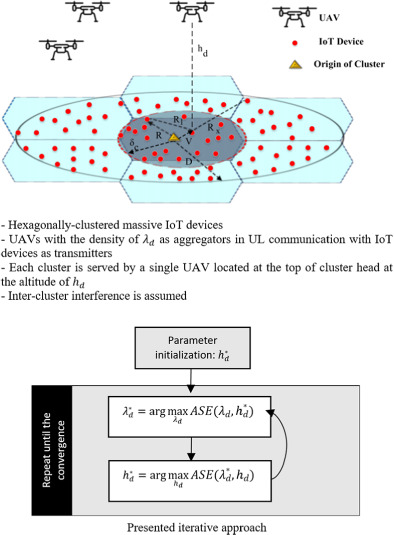
In this article, we propose a novel framework to maximize the area spectral efficiency, 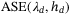 , by finding the optimal parameters
, by finding the optimal parameters 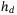 and
and 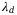 . As such, two propositions are proved to show that ASE has at least one local maximum w.r.t
. As such, two propositions are proved to show that ASE has at least one local maximum w.r.t 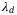 , at a given
, at a given 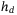 , and w.r.t
, and w.r.t 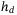 , at a given
, at a given 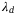 . We present an iterative approach for obtaining the optimal parameters. We achieve comparable results w.r.t the exhaustive search method, and outperform the single-parameter optimization approach.
. We present an iterative approach for obtaining the optimal parameters. We achieve comparable results w.r.t the exhaustive search method, and outperform the single-parameter optimization approach.
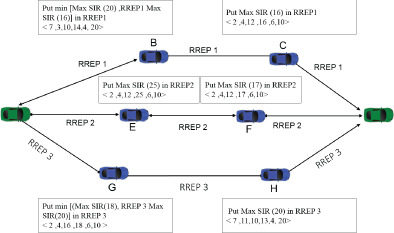
A cross-layered scheme for multichannel and reactive routing in vehicular ad hoc networks
- First Published: 14 February 2022
Auction based cost-efficient resource allocation by utilizing blockchain in fog computing
- First Published: 24 February 2022
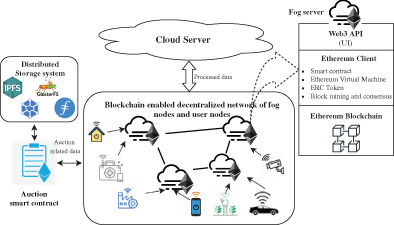
Introduction of fog computing extends the cloud services nearer to the edge of the network. An efficient resource management scheme is required to proficiently handle fog resources. The profit-driven nature of both the fog service providers and user nodes increases the possibility of malicious activity while resource trading for their advantages or to privilege a bunch of devices. In this article, we designed a trusted and fair incentive mechanism that encourages buyers and sellers to trade by leveraging the benefits of blockchain and smart contracts. Especially, a combinatorial double auction employed market model is proposed which satisfies different economical properties such as individual rationality, budget balance, and truthfulness.
Machine learning for power control in device-to-device communications with full-duplex relays using ITLinQ spectrum sharing scheme
- First Published: 22 February 2022
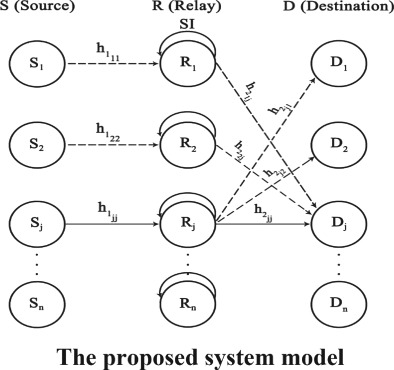
A machine learning (ML) technique with the full-duplex relay-information theoretic links scheduling spectrum sharing method in device-to-device communications is employed. Transmission powers of transmitters and corresponding relays are determined with a power control (PC) mechanism employing genetic algorithm (GA). The objective functions are maximizing the average sum rate, energy efficiency, and addressing two objectives simultaneously. Due to the ML approaches has more flexibility and lower computational complexity in comparison to the traditional optimization methods, we use ML to determine the transmission powers of transmitters and their corresponding relay pairs. The proposed neural network considers the channel coefficients as inputs and optimal power for transmitters and relays as outputs. The simulation results show that the PC mechanism with ML approach has almost the same performance as GA, while the calculation time and system complexity are reduced.
Energy and spectral efficient resource allocation in 5G HetNet using optimized deep bi-BRLSTM model
- First Published: 07 March 2022

In this research, an energy and spectrum efficient optimized resource allocation model is developed. The joint contribution of the maximization of energy efficiency (EE) and spectral efficiency (SE) with its constraints is formulated as a multiobjective optimization problem. The resource allocation (RA) issue in the network is handled by the hybrid deep bidirectional battle royale long short term memory (Deep bi-BRLSTM) model. Fuzzy based energy efficient adaptive atom search optimizer (FEEAAS) is instigated to optimize the trade-off of EE and SE consecutively also it improves the overall throughput.
Cooperative vehicles-assisted task offloading in vehicular networks
- First Published: 22 February 2022
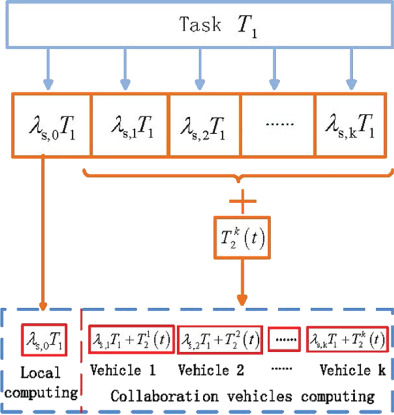
In this paper, we utilize parallel computing of multivehicle cooperation, to provide low-delay computation services without exceeding the energy constraint. Furthermore, a cooperative vehicles assisted task offloading strategy based on double deep Q-network (DDQN) is proposed to obtain the optimal task offloading ratio after selecting cooperative vehicles. Simulation results indicate that our proposed strategy can effectively decrease the total system delay.
HP-SPC algorithm with dynamic partially connected structure for mmWave MIMO systems
- First Published: 28 February 2022
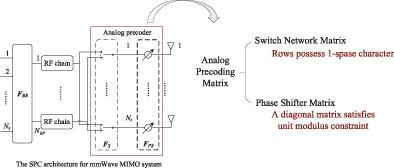
We introduce a hybrid precoding algorithm to improve the spectral efficiency and reduce the computational complexity of switch network-based dynamic partially connected for millimeter wave multiple-input multiple-output system. Invoking compressed sensing, the proposed algorithm alternately optimizes the precoding matrices and enjoys satisfactory computational complexity.
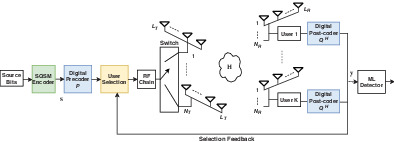
Multiuser steered signed quadrature spatial modulation for millimeter-wave massive multiple-input multiple-output with hybrid beamforming
- First Published: 27 February 2022
A new method of hybrid optimization of small cell range development and density for energy efficient ultra-dense networks
- First Published: 16 March 2022
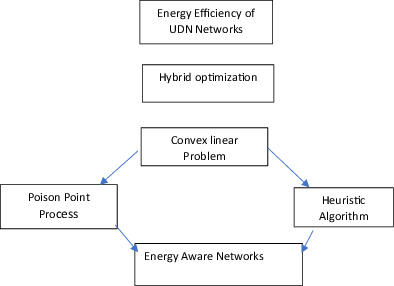
This figure represents the graphical abstract of the proposed work. Energy efficiency of the UDN networks are achieved by using hybrid optimization technique. The problem is formulated as convex linear problem. The closed form as a factor has been considered as a factor of the density of SBSs. After this the Poisson point process and heuristic algorithms are finally formulated and analyzed to achieve energy aware networks.
Performance analysis of non-orthogonal multiple access assisted cooperative maritime communication system over two-wave with diffuse power fading
- First Published: 17 March 2022
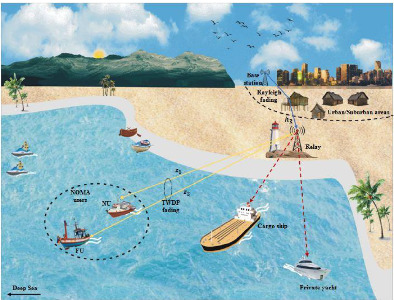
This article proposes the exact and asymptotic closed-form expressions of NOMA users' average symbol error probability (ASEP) for dual-hop cooperative DF maritime communication systems over TWDP fading using Appell's and Lauricella's hypergeometric functions for various modulations sets, that is, BPSK-BPSK and QPSK-BPSK. The outage probability of the aforementioned system is also investigated utilizing performance metrics such as distance, path loss exponent, and Rician factor.
Evaluation of cooperative spectrum sensing with filtered bank multi carrier utilized for detecting in cognitive radio network
- First Published: 15 March 2022
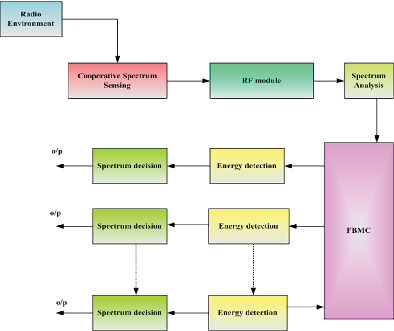
This article proposes cooperative spectrum sensing (CSS) with filtered bank multi carrier (FBMC) in cognitive radio network (CRN) for mitigating the interference with proficient bandwidth utilization. Here, five primary users (PU) and one secondary user (SU) are considered. The secondary user only occupies the slot in the absence of primary user.
Continuous lightweight authentication according group priority and key agreement for Internet of Things
- First Published: 08 March 2022

- Proposing a lightweight mutual authentication protocol between sensors and servers in the IoT. The sensor nodes were placed in groups. Each node is using static and continuous authentications.
- Using only hash and XOR operators in authentication so that our scheme has low computational costs and can be used in sensors with limited resources.
- Reducing the communications cost, resisting against security attacks, privacy-preserving, providing forward secrecy, and allowing key agreement.
- Using BAN logic and AVISPA tool to verify for security.
A multi-controller placement method for software defined network based on improved firefly algorithm
- First Published: 07 March 2022
Performance enhancement for differential energy signal detection of ambient backscatter communications
- First Published: 17 March 2022
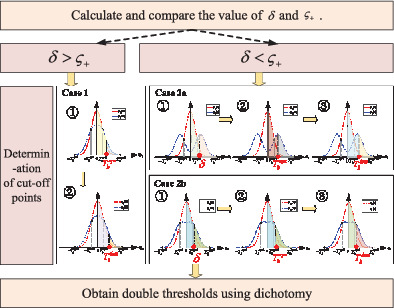
In this article, we propose an enhanced signal detection scheme for the receiver of ambient backscatter communications adopting differential energy detection. We discovered that the universal approximate threshold in classic detection will not provide accurate results in universal scenarios, thus double-threshold detection is proposed, integrating with differential energy detection and maximum likelihood method. Results show that the detector with double thresholds will offer performance improvement in diverse scenarios, especially when the system is in a poor channel status environment.
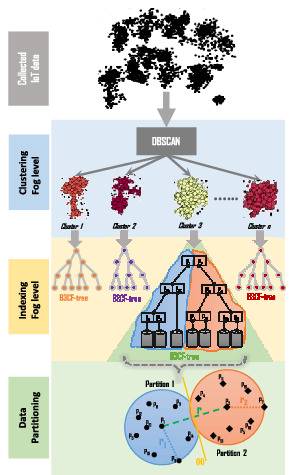
Clustering and parallel indexing of big IoT data in the fog-cloud computing level
- First Published: 07 March 2022
Learning-based deep neural network inference task offloading in multi-device and multi-server collaborative edge computing
- First Published: 10 March 2022
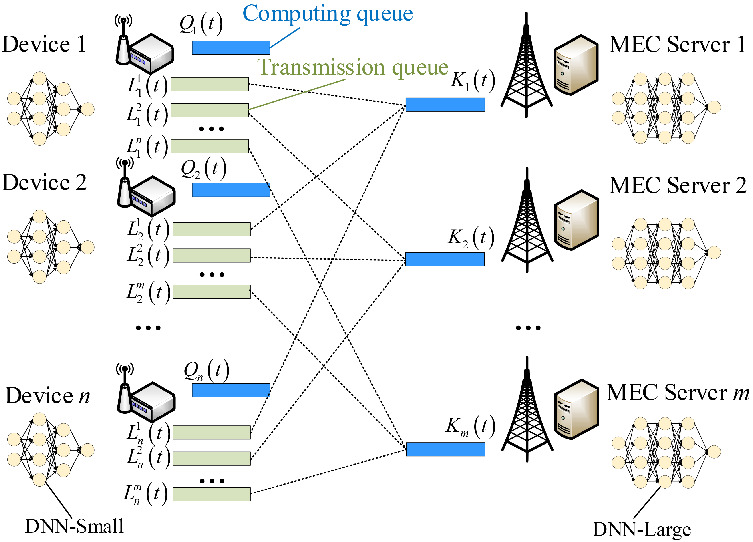
In this article, the DNN inference task offloading problem in queue-based multi-device and multi-server collaborative edge computing is investigated. A deep reinforcement learning based task offloading algorithm, named LSTM-TD3, is proposed to minimize the average inference delay and maximizes average inference accuracy.
Design and analysis of 28 GHz CMOS low power LNA with 6.4 dB gain variability for 5G applications
- First Published: 10 March 2022
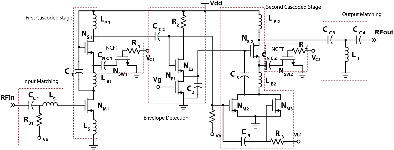
A 28 GHz two stage variable gain low noise amplifier (LNA) is proposed with envelope detection technique for power reduction (21.62%) and tunable negative feedback capacitor for gain variation in 40 nm CMOS technology. A 6.22 GHz of bandwidth is achieved with the tunable gain from 20.3 dB to 26.7 dB.
Performance analysis of power-domain non-orthogonal multiple access for full-duplex two-way relaying
- First Published: 11 March 2022

This article investigates the two-way information exchange process by using the power-domain non-orthogonal multiple access strategy. The investigation considers a dual-hop amplify-and-forward based full-duplex bi-directional relay-assisted network in the system model. The transmitters exchange the superimposed signals and utilize the echo-cancellation and successive interference cancellation at the receivers.
User relay-aided energy-efficient resource allocation in heterogeneous cloud radio access network
- First Published: 22 April 2022

This article investigates a resource allocation method to improve energy efficiency in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks using a user relay-aided. A multilayer network consisting of macrocells, femtocells, and D2D communications is used to target BBU and RRH traffic offloading to femtocells. The simulation results show that the suggested technique can effectively decrease energy consumption of BBUs through switching off under-utilized BBUs and offloading the traffic from remote radio heads and macro-cell to FAPs.
Impact of fractional power control on downlink uplink decoupled-based HetNets in varying path loss exponent environment
- First Published: 25 March 2022
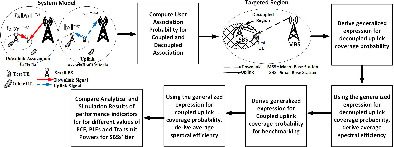
In this paper, we have analyzed the impact of Fractional Power Control on Downlink Uplink Decoupled-based HetNets in varying Path Loss Exponent environment. To the best of our knowledge, such an analysis of DUDe performance using stochastic geometry have not been published before. We have developed a generalized system model and derived generalized expressions for uplink network performance indicators like decoupled uplink coverage probability and average spectral efficiency. Moreover, we have performed a baseline comparison of obtained results with the ones obtained while considering coupled association criteria based on maximum downlink received signal power. We have gauged, compared and observed interesting results regarding DUDe performance under different system model parameters.
Revenue maximization approaches in IaaS clouds: Research challenges and opportunities
- First Published: 22 March 2022
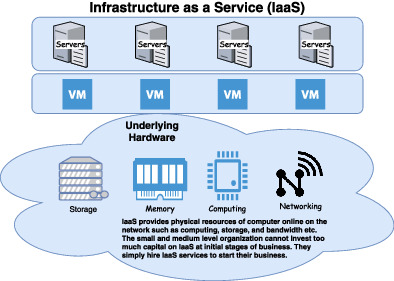
Main revenue factors are categorized as service level agreement and penalty management, resource scalability, customer satisfaction and management, resource utilization and provision, cost and price management, and advertising and auction. These parameters are investigated in detail and new dynamics for researchers in the field of the cloud are discovered.
Visible light communication performance using MIMO-ADO-OFDM system
- First Published: 19 March 2022
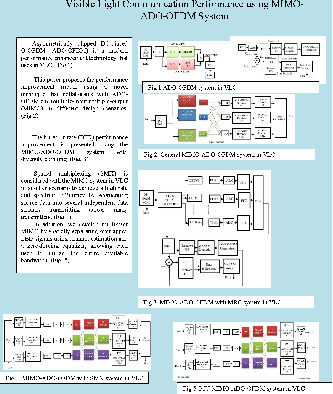
The performance improvement methodology using ADO-OFDM and MIMO in various design scenarios is presented. The BER performance is enhanced for MIMO-ADO-OFDM with maximum ratio combining, and the spectral efficiency is maximized by utilizing spatial multiplexing. Also, multi-user MIMO is developed by adopting ADO-OFDM with zero-forcing interference cancellations, allowing users to consume all available bandwidth.
The offloading algorithm of mobile edge computing considering mobility in the intelligent inspection scenario
- First Published: 26 March 2022
High mobility transmission system under intelligent reflecting surface
- First Published: 26 March 2022
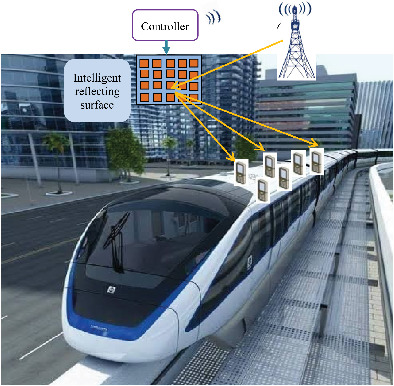
In this paper, a railway communication system with the help of intelligent surface technology is proposed for high mobility scenario. Results demonstrate the significant mobile service enhancement introduced by the intelligent surface in railway communication system and show the effectiveness of our proposed scheme.
Dynamic branch pruning aided low switching fixed complexity sphere decoding for small scale and massive MIMO detection
- First Published: 29 March 2022
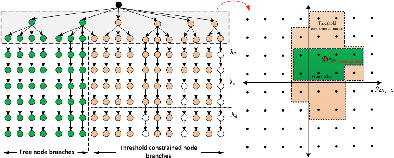
This article proposes a low complexity detection technique suitable for small scale and massive MIMO applications. In addition, a low complexity preprocessing technique is also developed. Finally, an efficient symbol ordering and soft symbol generation method is developed to reduce computational overhead.
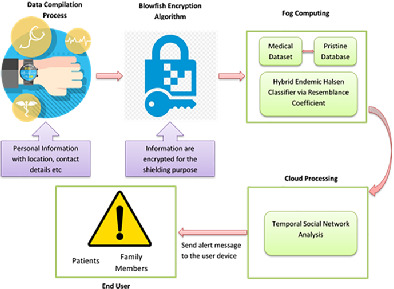
Health monitoring jeopardy prophylaxis model based on machine learning in fog computing
- First Published: 18 April 2022
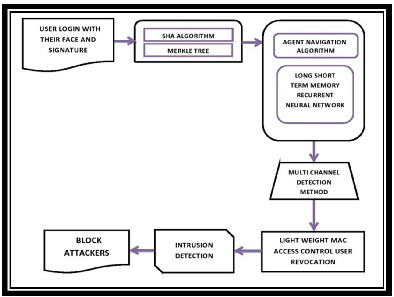
Multi-channel attack detection based on lightweight message authentication code access control using Internet of Things design
- First Published: 08 June 2022
Roadside units plane optimization scheme in software-defined vehicular networks
- First Published: 01 April 2022
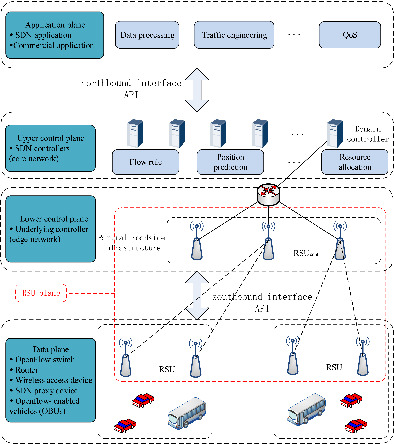
The main contributions of this paper are as follows: (1) Some studies use a part of the roadside units (RSUs) in the RSU plane as the underlying controllers to assist network management in reducing the vehicle communication delay in the edge network. Given the lack of in-depth research on how the RSU plane works, the roles and tasks of the domain controller and the RSU controllers in processing the flow rule request sent by the on board units (OBUs) are clearly explained, and the flow setup delay is also clearly defined. (2) Formulate an optimization objective model of the RSU plane in software-defined vehicular networks. Based on the high mobility of the vehicle network, the increase of flow setup delay caused by RSU node remapping is reduced by reducing the state fluctuation of the RSU plane. (3) By adding a traffic flow trajectory prediction module for the domain controller, issue the flow rules in advance to the underlying RSU controller covering the arrival position of the vehicle, to further reduce the flow setup delay.
Joint spectrum sensing and resource allocation against byzantine attack in overlay cognitive radio networks
- First Published: 09 May 2022
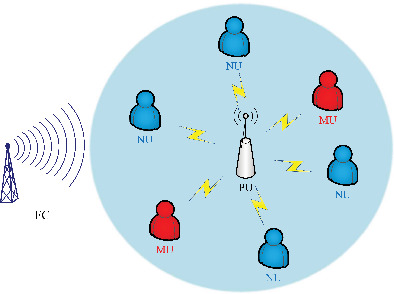
This paper proposes a joint spectrum sensing and resource allocation scheme for overlay CRNs. Based on the overlay CRN model and hard combining, we propose a selective majority algorithm to exploit the malicious behavior based on Byzantine identification, which can maintain excellent performance in various attack scenarios. In addition, our proposed spectrum resource allocation scheme further deters Byzantine attack, forming a complete closed-loop for Byzantine defense scheme.
Resource allocation for cellular device-to-device-aided vehicle-to-everything networks with partial channel state information
- First Published: 10 April 2022
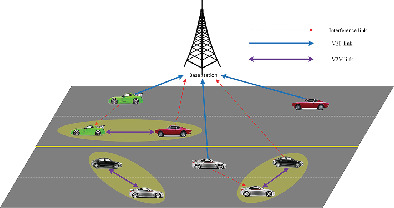
V2X, aided with cellular D2D communication, has a great potential in enhancing the road safety and transportation. However, due to the fast variations of channel state information (CSI) caused by high mobility of vehicles, the accurate CSI is difficult to be obtained in real time. Therefore, we consider a more realistic channel state model that only partial CSI is available and propose the corresponding resource allocation scheme.
Blockchain enabled joint trust (MF-WWO-WO) algorithm for clustered-based energy efficient routing protocol in wireless sensor network
- First Published: 11 April 2022
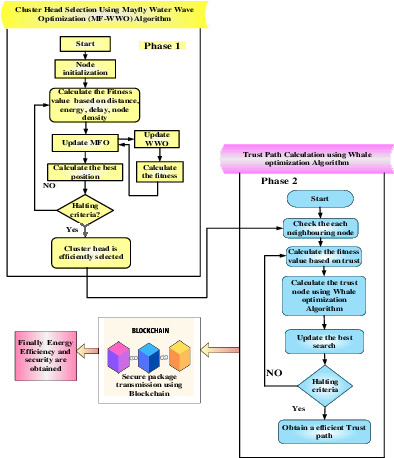
In this manuscript, blockchain enabled joint trust (MF-WWO-WO) algorithm for clustered based energy efficient routing protocol on wireless sensor network is proposed for secure data transmission by finding the optimum CHs under network. Initially, MayflyWater Wave Optimization (MF-WWO) algorithm is used for the selection of CH accurately. After the selection of CH, arrival of malicious node is occurred in the cluster. Hence, multi objective whale optimization algorithm is suggested to find the trust path from the several paths. At last, the optimized selected trust paths are given to the blockchain for communications in the network that is safe and more trustworthy.
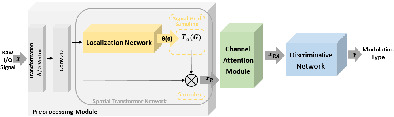
A hybrid attention mechanism for blind automatic modulation classification
- First Published: 05 April 2022
Proportional rate constrained resource allocation in multicarrier nonorthogonal multiple access systems
- First Published: 05 April 2022
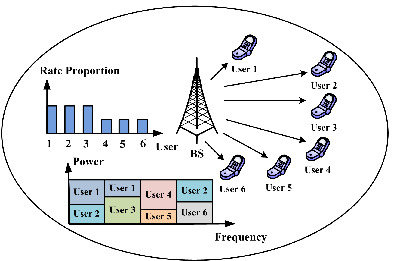
We investigate resource allocation in MC-NOMA systems and formulate an optimization problem to jointly optimize subcarrier and power allocation with proportional rate constraints. By using variable substitution, we convert the original problem into a convex optimization problem and develop joint subcarrier and power allocation algorithms.
Position-sensitivity security transmission with orbital angular momentum directional modulation based on frequency diverse array
- First Published: 19 April 2022

The uniform circular frequency diverse array (FDA) element is excited by the designed signal to generate OAM beams related to the range, elevation and azimuth. OAM beams generated by FDA with the random frequency offset can maintain the helical phase and the intensity pattern characteristics at the desired range and two-dimensional direction information of OAM beam radiation pattern can be modulated into the signal to generate the waveform of the angle-dependent direction modulation. The single antenna can employ the phase compensation and helical phase factor to restore composite dual-mode OAM signal in the desired position.