Dynamic branch pruning aided low switching fixed complexity sphere decoding for small scale and massive MIMO detection
Corresponding Author
Sourav Chakraborty
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, Howrah, West Bengal, India
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Cooch Behar Government Engineering College, Cooch Behar, West Bengal, India
Correspondence
Sourav Chakraborty, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, Howrah, West Bengal, India.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorNirmalendu Bikas Sinha
Maharaja Nandakumar Mahavidyalaya, Purba Medinipur, West Bengal, India
Search for more papers by this authorMonojit Mitra
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, Howrah, West Bengal, India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sourav Chakraborty
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, Howrah, West Bengal, India
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Cooch Behar Government Engineering College, Cooch Behar, West Bengal, India
Correspondence
Sourav Chakraborty, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, Howrah, West Bengal, India.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorNirmalendu Bikas Sinha
Maharaja Nandakumar Mahavidyalaya, Purba Medinipur, West Bengal, India
Search for more papers by this authorMonojit Mitra
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, Howrah, West Bengal, India
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
In this article, we have proposed a dynamic branch pruning aided low switching fixed complexity sphere decoding (LSFSD) algorithm that can reduce the number of node visits in conventional fixed-complexity sphere decoder (FSD) or imbalanced fixed-complexity sphere decoder (IFSD) detector dynamically based on the channel condition. Further, we propose a low complexity QR-based FSD ordering scheme in the real domain that requires half of the number of real arithmetic operations in the conventional case. As a case study, we have simulated the proposed algorithm for 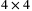 and
and 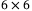 MIMO system with 64-QAM modulation. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can reduce approximately 50% of node visits to achieve a BER of
MIMO system with 64-QAM modulation. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can reduce approximately 50% of node visits to achieve a BER of 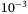 . Additionally, a low complexity solution of the soft bit information generation method is also proposed. The concept is further extended to massive MIMO applications where the number of receiving antenna to transmit antenna ratio is close to one. A smaller node extension parameter is defined for the proposed detector to reduce the complexity in massive MIMO detection. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed detection algorithm has significantly lower computational complexity than other recent state-of-the-art detection algorithms for massive MIMO and large MIMO systems.
. Additionally, a low complexity solution of the soft bit information generation method is also proposed. The concept is further extended to massive MIMO applications where the number of receiving antenna to transmit antenna ratio is close to one. A smaller node extension parameter is defined for the proposed detector to reduce the complexity in massive MIMO detection. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed detection algorithm has significantly lower computational complexity than other recent state-of-the-art detection algorithms for massive MIMO and large MIMO systems.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
REFERENCES
- 1Foschini GJ, Gans MJ. On limits of wireless communications in a fading environment when using multiple antennas. Wirel Pers Commun. 1998; 6(3): 311-335. doi:10.1023/A:1008889222784
10.1023/A:1008889222784 Google Scholar
- 2Alamouti SM. A simple transmit diversity technique for wireless communications. IEEE J Select Areas Commun. 1998; 16(8): 1451-1458. doi:10.1109/49.730453
- 3Paulraj AJ, Gore DA, Nabar RU, Bolcskei H. An overview of MIMO communications-A key to gigabit wireless. Proc IEEE. 2004; 92(2): 198-218. doi:10.1109/JPROC.2003.821915
- 4Shlezinger N, Alexandropoulos GC, Imani MF, Eldar YC, Smith DR. Dynamic metasurface antennas for 6G extreme massive MIMO communications. IEEE Wirel Commun. 2021; 28(2): 106-113. doi:10.1109/MWC.001.2000267
- 5Larsson EG, Edfors O, Tufvesson F, Marzetta TL. Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems. IEEE Commun Mag. 2014; 52(2): 186-195. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2014.6736761
- 6Ngo HQ, Larsson EG, Marzetta TL. Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Trans Commun. 2013; 61(4): 1436-1449. doi:10.1109/TCOMM.2013.020413.110848
- 7Rusek F, Persson D, Lau BK, et al. Scaling Up MIMO: opportunities and challenges with very large arrays. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2013; 30(1): 40-60. doi:10.1109/MSP.2011.2178495
- 8Burg A, Borgmann M, Wenk M, Zellweger M, Fichtner W, Bolcskei H. VLSI implementation of MIMO detection using the sphere decoding algorithm. IEEE J Solid State Circuits. 2005; 40(7): 1566-1577. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2005.847505
- 9Wolniansky PW, Foschini GJ, Golden GD, Valenzuela RA. V-BLAST: an architecture for realizing very high data rates over the rich-scattering wireless channel. Proceedings of the 1998 URSI International Symposium on Signals, Systems, and Electronics. Conference Proceedings (Cat. No. 98EX167); Pisa, Italy. 1998:295-300. 10.1109/ISSSE.1998.738086
- 10Mohammadkarimi M, Mehrabi M, Ardakani M, Jing Y. Deep learning-based sphere decoding. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. 2019; 18(9): 4368-4378. doi:10.1109/TWC.2019.2924220
- 11Askri A, Othman GR. DNN assisted sphere decoder. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT); Paris, France. 2019:1172-1176.
- 12El-Khamy M, Medra M, ElKamchouchi HM. Reduced complexity list sphere decoding for MIMO systems. Dig Signal Process. 2014; 25: 84-92. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2013.10.023
- 13Barbero LG, Thompson JS. Fixing the complexity of the sphere decoder for MIMO detection. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. 2008; 7(6): 2131-2142. doi:10.1109/TWC.2008.060378
- 14Zhan G, Nilsson P. Algorithm and implementation of the K-best sphere decoding for MIMO detection. IEEE J Select Areas Commun. 2006; 24(3): 491-503. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2005.862402
- 15Wenk M, Zellweger M, Burg A, Felber N, Fichtner W. K-best MIMO detection VLSI architectures achieving up to 424 Mbps. Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems; Kos, Greece. Vol. 4; 2006:1154. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2006.1692794
- 16Bello IA, Halak B, El-Hajjar M, Zwolinski M. VLSI implementation of a fully-pipelined K-Best MIMO detector with successive interference cancellation. Circuits Syst Signal Process. 2019; 38: 4739-4761. doi:10.1007/s00034-019-01079-0
- 17Joshi P, Joshi S, Jain V, Joshi S. A novel segregated K-best detection algorithm for low complexity near optimal MIMO receivers. AEU-Int J Electron C. 2017; 75: 130-139. doi:10.1016/j.aeue.2017.03.020
- 18Mao X, Cheng Y, Ma L, Xiang H. Step reduced K-best sphere decoding. Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall); Quebec City, QC, Canada. 2012:1-4. doi: 10.1109/VTCFall.2012.6398910
- 19Liu T-H, Wang S-L, Lin Y-J, Hwang Y-T, Chen C-E, Chu Y-S. Fixed-complexity tree search schemes for detecting generalized spatially modulated signals: algorithms and hardware architectures. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap. 2021; 68(2): 904-917. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2020.3040375
- 20Liu L, Lofgren J, Nilsson P. Area-efficient configurable high-throughput signal detector supporting multiple MIMO modes. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap. 2012; 59(9): 2085-2096. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2012.2185297
- 21Ro J-H, Yu S-J, You Y-H, Hong SK, Song H-K. An adaptive QR-based energy efficient signal detection scheme in MIMO-OFDM systems. Comput Commun. 2020; 149: 225-231. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2019.10.017
- 22Chakraborty S, Sinha NB, Mitra M. Performance evaluation of fixed point FSD using 1's complement based approximation. Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Innovative Mechanisms for Industry Applications (ICIMIA); Bangalore, India. 2020:190-194. doi: 10.1109/ICIMIA48430.2020.9074960
- 23Chakraborty S, Sinha NB, Mitra M. Low complexity MIMO detection using complement and LSB set approximation. Proceedings of the 2021 8th International Conference on Smart Computing and Communications (ICSCC); Kochi, Kerala, India. 2021:134-139. doi: 10.1109/ICSCC51209.2021.9528259
- 24Chandrakasan AP, Sheng S, Brodersen RW. Low-power CMOS digital design. IEEE J Solid State Circuits. 1992; 27(4): 473–484.
- 25Albreem MA, Juntti M, Shahabuddin S. Massive MIMO detection techniques: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor. 2019; 21(4): 3109-3132. doi:10.1109/COMST.2019.2935810
- 26Zheng K, Zhao L, Mei J, Shao B, Xiang W, Hanzo L. Survey of large-scale MIMO systems. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor. 2015; 17(3): 1738-1760. doi:10.1109/COMST.2015.2425294
- 27Shahabuddin S, Hautala I, Juntti M, Studer C. ADMM-based infinity-norm detection for massive MIMO: algorithm and VLSI architecture. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr (VLSI) Syst. 2021; 29(4): 747-759. doi:10.1109/TVLSI.2021.3056946
- 28Srinidhi N, Datta T, Chockalingam A, Rajan BS. Layered Tabu search algorithm for large-MIMO detection and a lower bound on ML performance. IEEE Trans Commun. 2011; 59(11): 2955-2963.
- 29Céspedes J, Olmos PM, Sánchez-Fernández M, Perez-Cruz F. Expectation propagation detection for high-order high-dimensional MIMO systems. IEEE Trans Commun. 2014; 62(8): 2840-2849. doi:10.1109/TCOMM.2014.2332349
- 30Yao G, Chen H, Hu J. An improved expectation propagation based detection scheme for MIMO systems. IEEE Trans Commun. 2021; 69(4): 2163-2175. doi:10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3048942
- 31Jeon C, Ghods R, Maleki A, Studer C. Optimality of large MIMO detection via approximate message passing. Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT); Hong Kong, China. 2015:1227-1231. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2015.7282651
- 32Narasimhan TL, Chockalingam A. Channel hardening-exploiting message passing (CHEMP) receiver in large-scale MIMO systems. IEEE J Select Top Signal Process. 2014; 8(5): 847-860. doi:10.1109/JSTSP.2014.2314213
- 33Goldberger J, Leshem A. MIMO detection for high-order QAM based on a Gaussian tree approximation. IEEE Trans Inf Theory. 2011; 57(8): 4973-4982. doi:10.1109/TIT.2011.2159037
- 34Minango J, Almeida C. Low complexity zero forcing detector based on Newton-Schultz iterative algorithm for massive MIMO systems. IEEE Trans Veh Technol. 2018; 67(12): 11759-11766. doi:10.1109/TVT.2018.2874811
- 35Chu X, McAllister J. Software-defined sphere decoding for FPGA-based MIMO detection. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 2012; 60(11): 6017-6026. doi:10.1109/TSP.2012.2210951
- 36Azzam L, Ayanoglu E. Reduced complexity sphere decoding for square QAM via a new lattice representation. Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM 2007 - IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference; Washington, DC, USA. 2007:4242-4246. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2007.807
- 37Lofgren J, Nilsson P. On MIMO K-best sphere detector architecture complexity reductions. Proceedings of the 2008 2nd International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems; Gold Coast, QLD, Australia. 2008:1-9. doi: 10.1109/ICSPCS.2008.4813732
- 38Liu L, Ma X, Ye F, Ren J. Design of highly-parallel, 2.2Gbps throughput signal detector for MIMO systems. Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Communications; Beijing, China. 2008:742-745. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2008.145
- 39Kim T-H. Low-complexity sorted QR decomposition for MIMO systems based on pairwise column symmetrization. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. 2014; 13(3): 1388-1396. doi:10.1109/TWC.2014.011514.130566
- 40Liu L, Löfgren J, Nilsson P, Öwall V. VLSI implementation of a soft-output signal detector for multimode adaptive multiple-input multiple-output systems. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr (VLSI) Syst. 2013; 21(12): 2262-2273. doi:10.1109/TVLSI.2012.2231706
- 41Hochwald BM, ten Brink S. Achieving near-capacity on a multiple-antenna channel. IEEE Trans Commun. 2003; 51(3): 389-399. doi:10.1109/TCOMM.2003.809789
- 42Studer C, Bölcskei H. Soft-input soft-output single tree-search sphere decoding. IEEE Trans Inf Theory. 2010; 56(10): 4827-4842. doi:10.1109/TIT.2010.2059730
- 43Kermoal JP, Schumacher L, Pedersen KI, Mogensen PE, Frederiksen F. A stochastic MIMO radio channel model with experimental validation. IEEE J Select Areas Commun. 2002; 20(6): 1211-1226. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2002.801223
- 44Godana BE, Ekman T. Parametrization based limited feedback design for correlated MIMO channels using new statistical models. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun. 2013; 12(10): 5172-5184. doi:10.1109/TWC.2013.092013.130045
- 45Biguesh M, Gershman AB. Training-based MIMO channel estimation: a study of estimator tradeoffs and optimal training signals. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 2006; 54(3): 884-893. doi:10.1109/TSP.2005.863008




