Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Risk of Serious Infections in Patients Treated With Biologic or Targeted-synthetic Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Qatar
- First Published: 14 April 2025
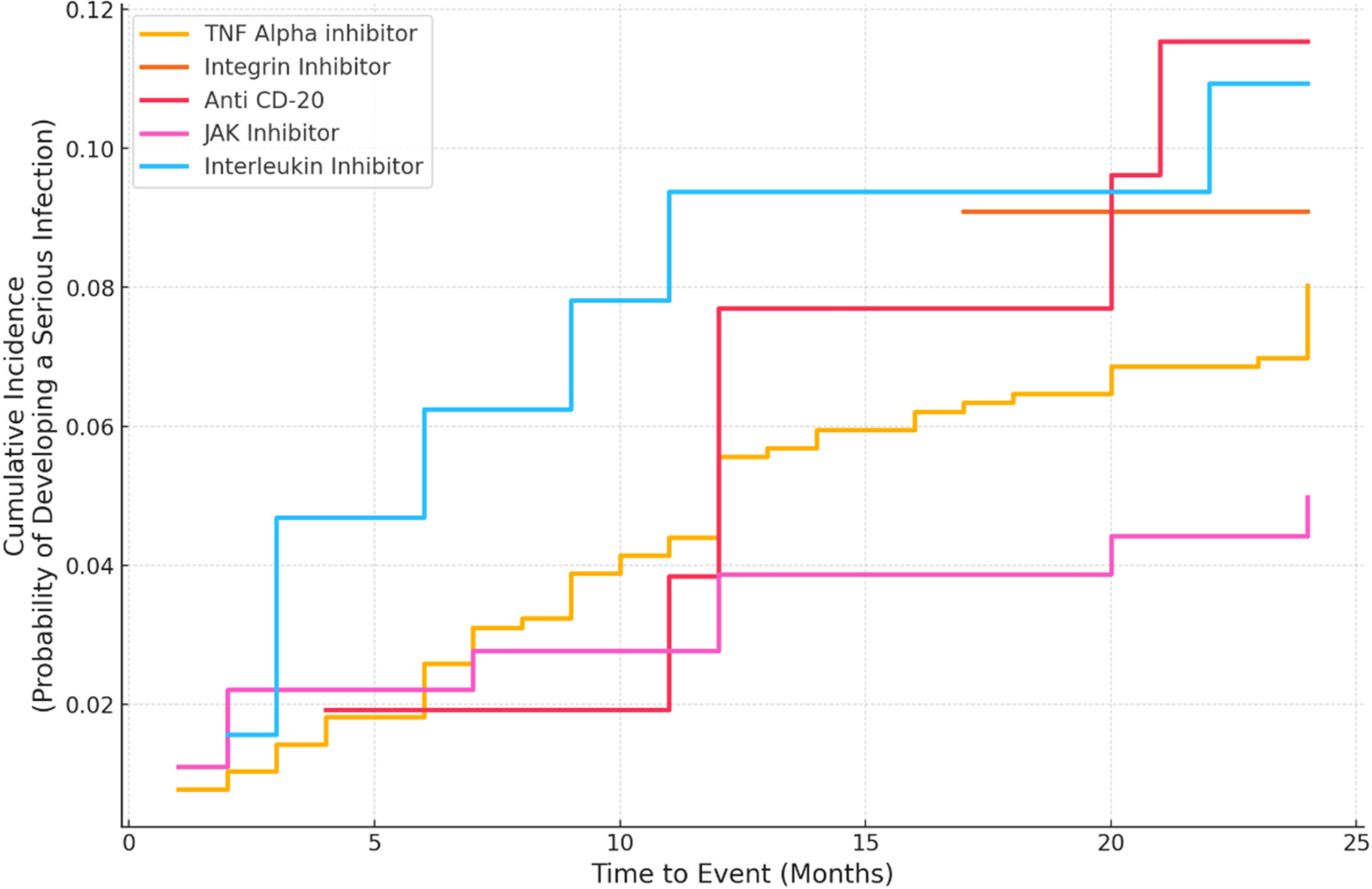
This study investigates the risk of serious infections (SIs) in patients treated with biologic or targeted-synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) in Qatar. Out of 1092 patients, 86 (7.9%) experienced SIs, with adalimumab and infliximab associated with higher SI rates. Our findings highlight the necessity for vigilant monitoring and tailored management strategies to mitigate infection risks in patients on b/tsDMARD therapy.
Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Indicates That Pggt1b Deficiency Promotes Cytokine Secretion in Resiquimod-Stimulated Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages via the NF-κB Pathway
- First Published: 07 April 2025
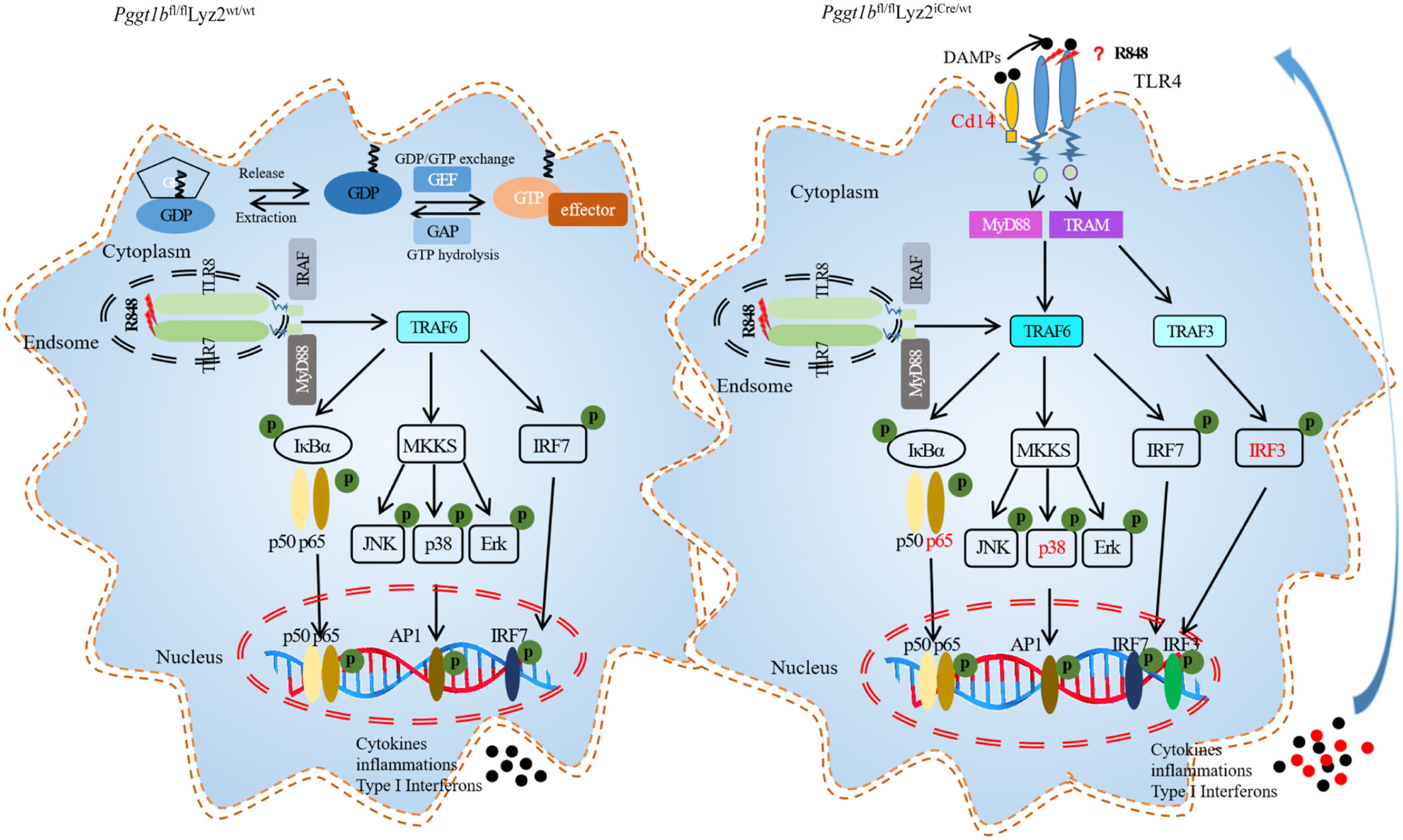
In Pggt1b-deficient macrophages, TLR4 may be in a highly activated state and can be activated by R848 or DAMPS, which strongly correlated with increased cytokine production, interferon-γ production, augmented amide binding and transferase activity, and the activation of NF-κB and/or Nlrp3 inflammasome pathways.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Current Advancements in Serum Protein Biomarkers for Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocyte Remodeling and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- First Published: 07 April 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
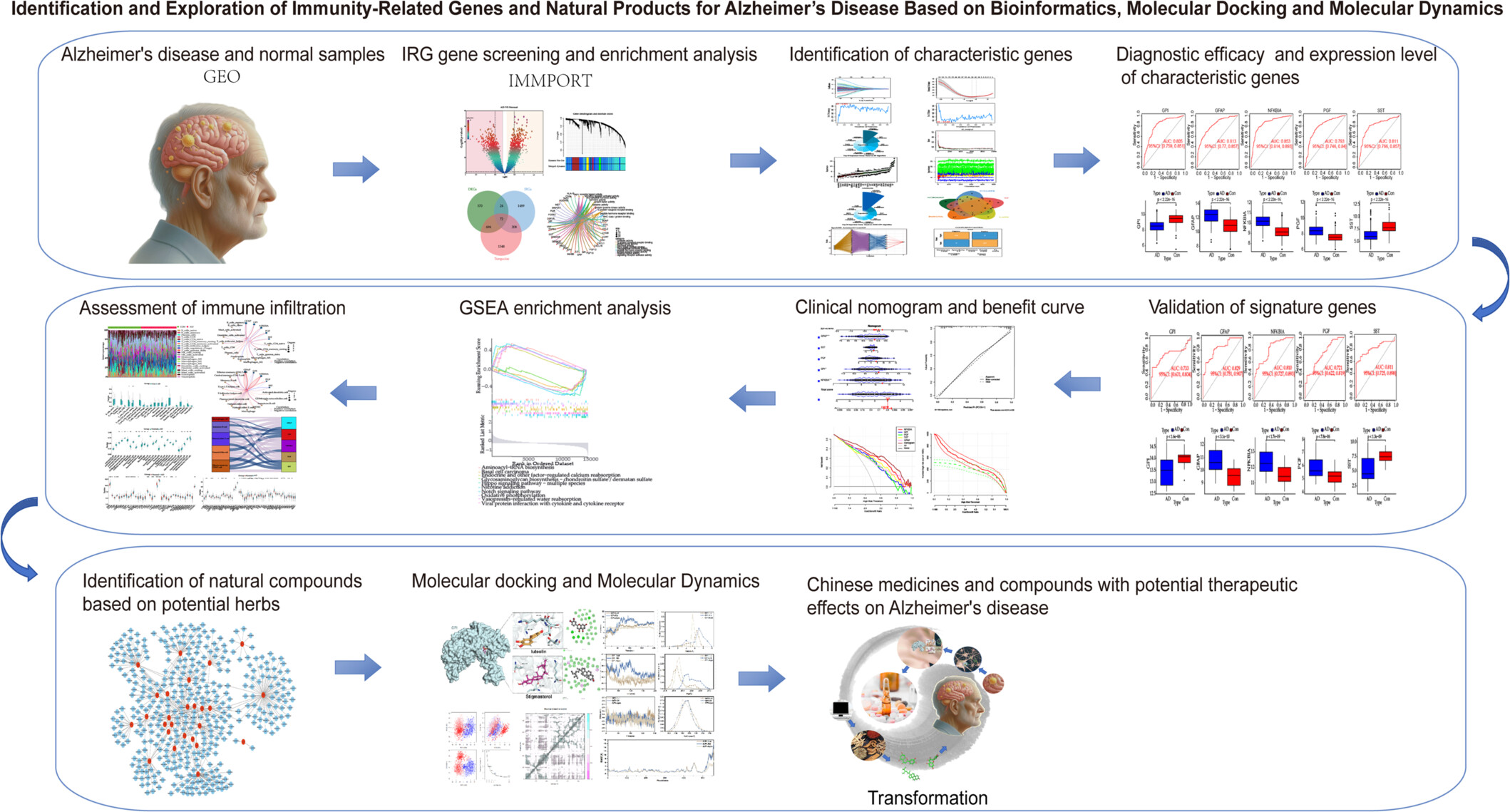
Identification and Exploration of Immunity-Related Genes and Natural Products for Alzheimer's Disease Based on Bioinformatics, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics
- First Published: 07 April 2025
Machine Learning-Based Immuno-Inflammatory Index Integrating Clinical Characteristics for Predicting Coronary Artery Plaque Rupture
- First Published: 07 April 2025
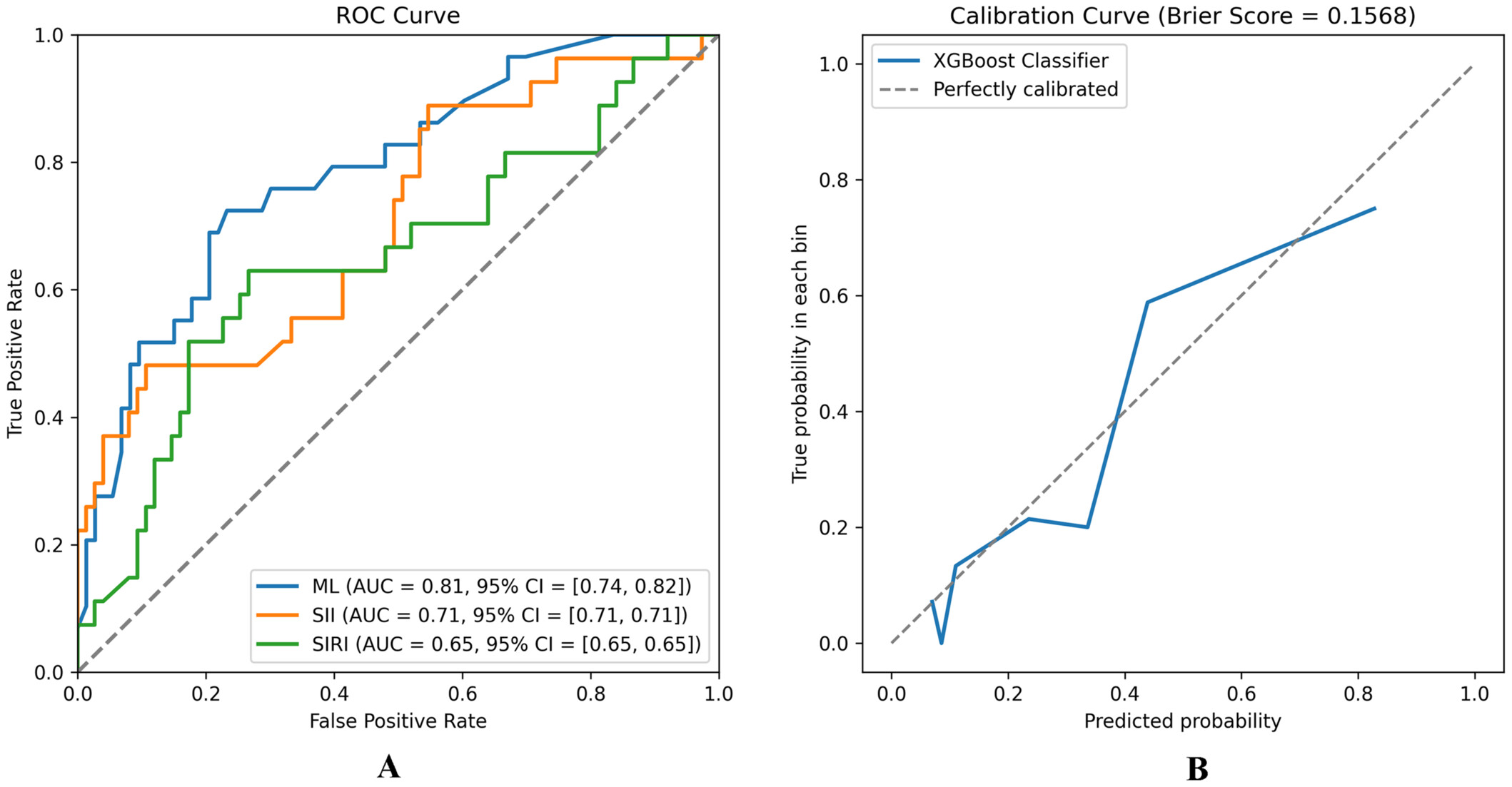
We developed and validated a novel machine learning model that integrates multidimensional features, including SII and SIRI, to predict the occurrence of PR. Our study highlights the potential of ML in predicting PR occurrence, offering promise in assisting physicians to identify high-risk patients promptly.
Active Compounds, Targets, and Mechanisms of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge in Treating Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
- First Published: 14 April 2025
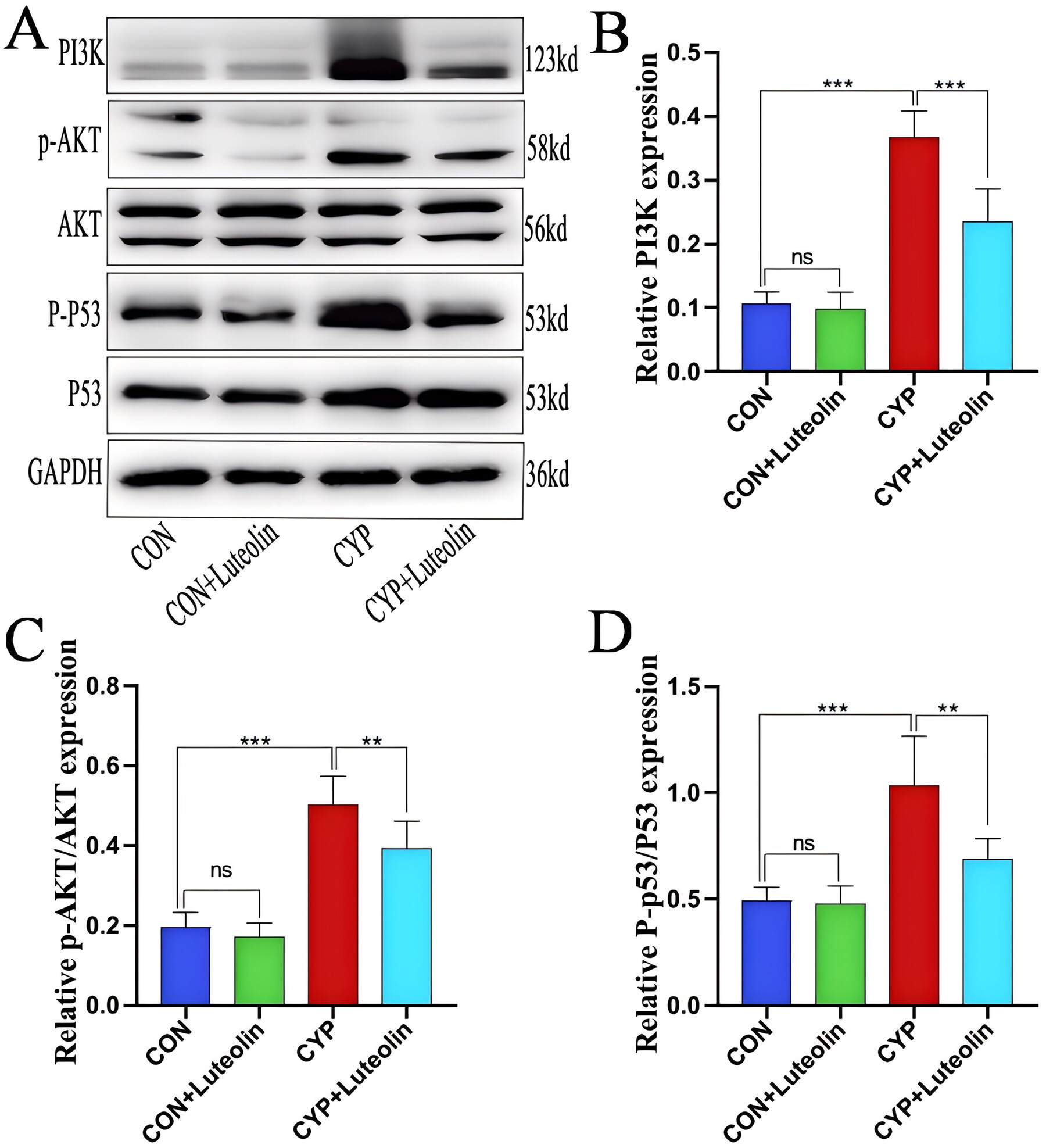
Salvia miltiorrhiza can play the role of treating interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome through multiple targets and multiple components. Luteolin is the most potential active ingredient of S. miltiorrhiza in the treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Luteolin can inhibit oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis through PI3K Akt and p53 signaling pathways to treat interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome.
Effectiveness and Safety of Simnotrelvir/Ritonavir and Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir in the Treatment of Moderate to Severe COVID-19
- First Published: 14 April 2025
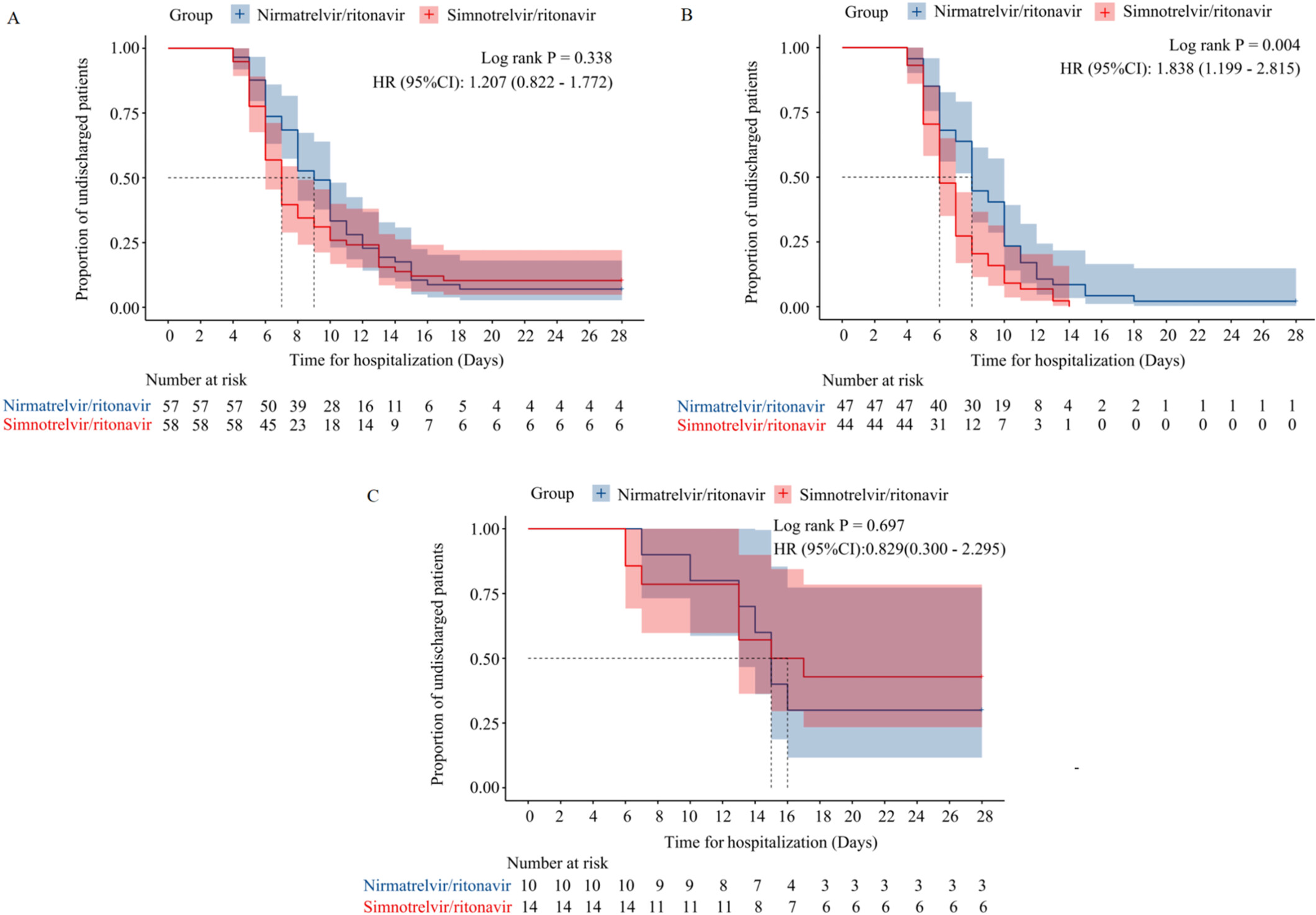
This is the first study comparing the effectiveness of simnotrelvir/ritonavir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in treating moderate and severe COVID-19 patients. Patients who received simnotrelvir/ritonavir exhibited shorter hospitalization. Disease progression, viral clearance times, and symptom resolution time were similar between the two groups.
Impact of COVID-19 on Renal Transplant Recipients in a National Transplant Center
- First Published: 18 April 2025
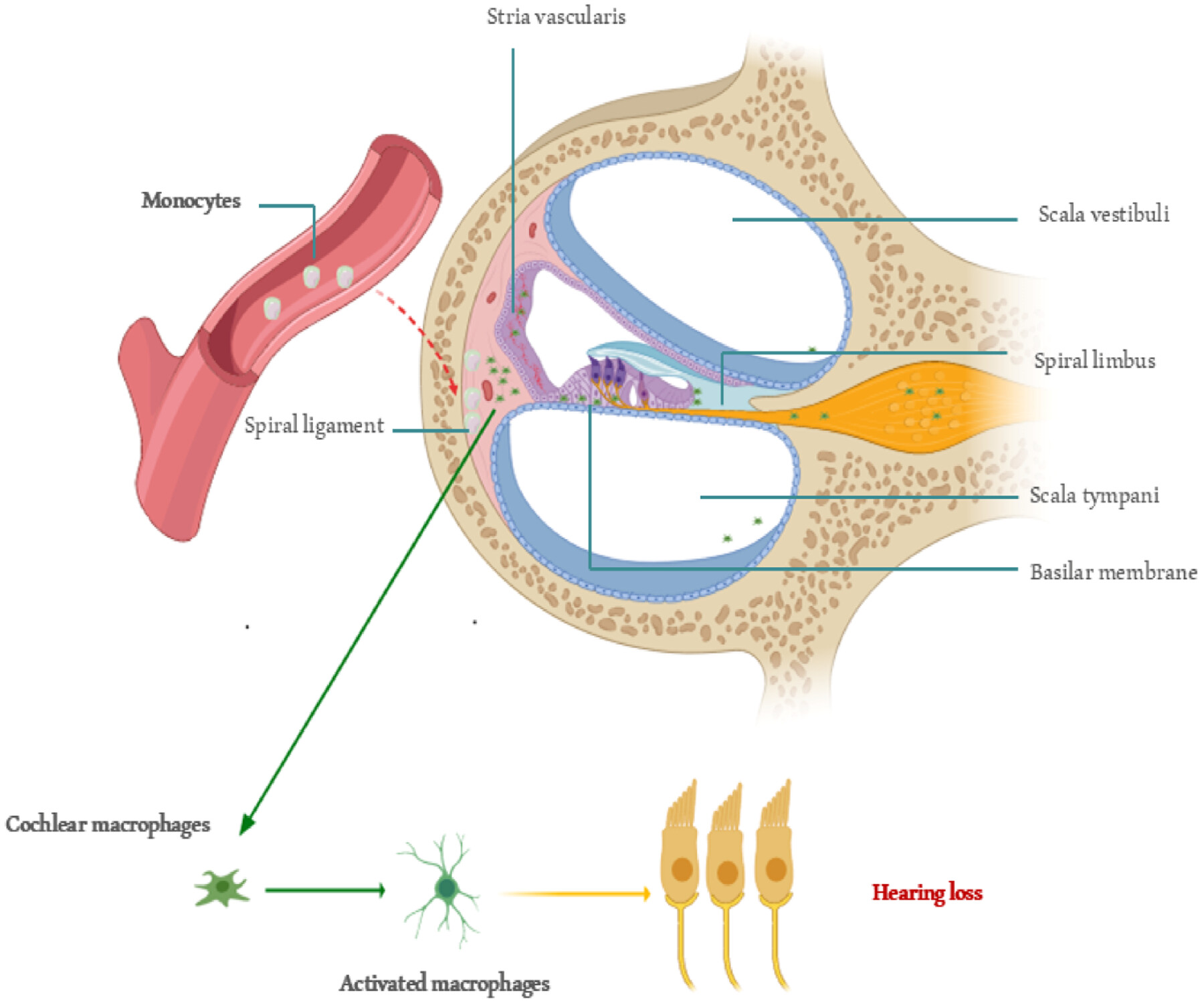
Chronic Inflammation and Hearing Loss: Key Biomarkers and Subgroup Differences by Gender and BMI in a National Cohort
- First Published: 09 April 2025
Altered Circulating Cytokine Profile Among mRNA-Vaccinated Young Adults: A Year-Long Follow-Up Study
- First Published: 09 April 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
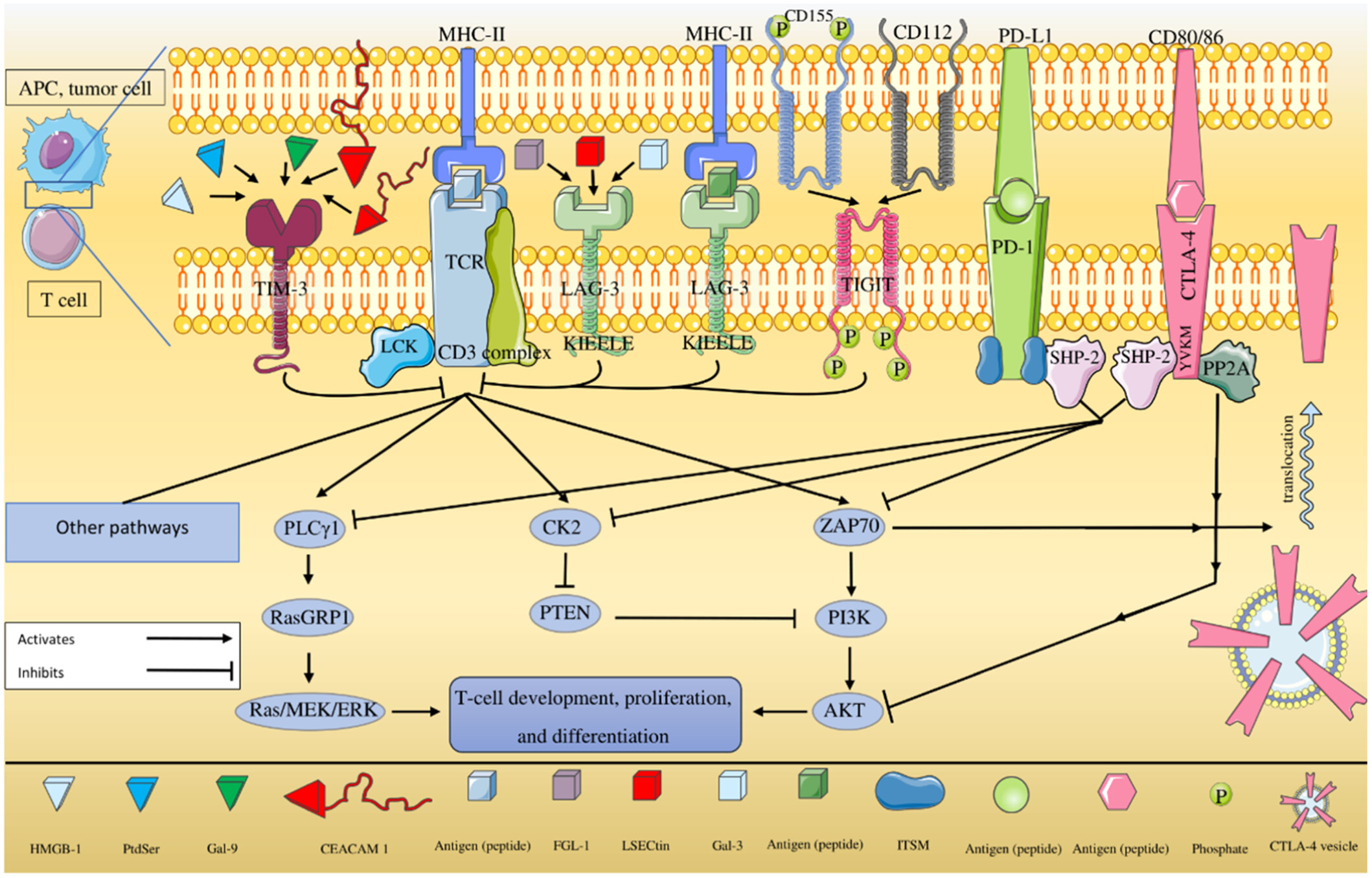
Immune Checkpoint Molecules: A Review on Pathways and Immunotherapy Implications
- First Published: 17 April 2025
CORRECTION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
EGCG Regulates the Effect of HDAC6 on Oxidative Stress of Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts Induced by Lipopolysaccharide
- First Published: 27 April 2025
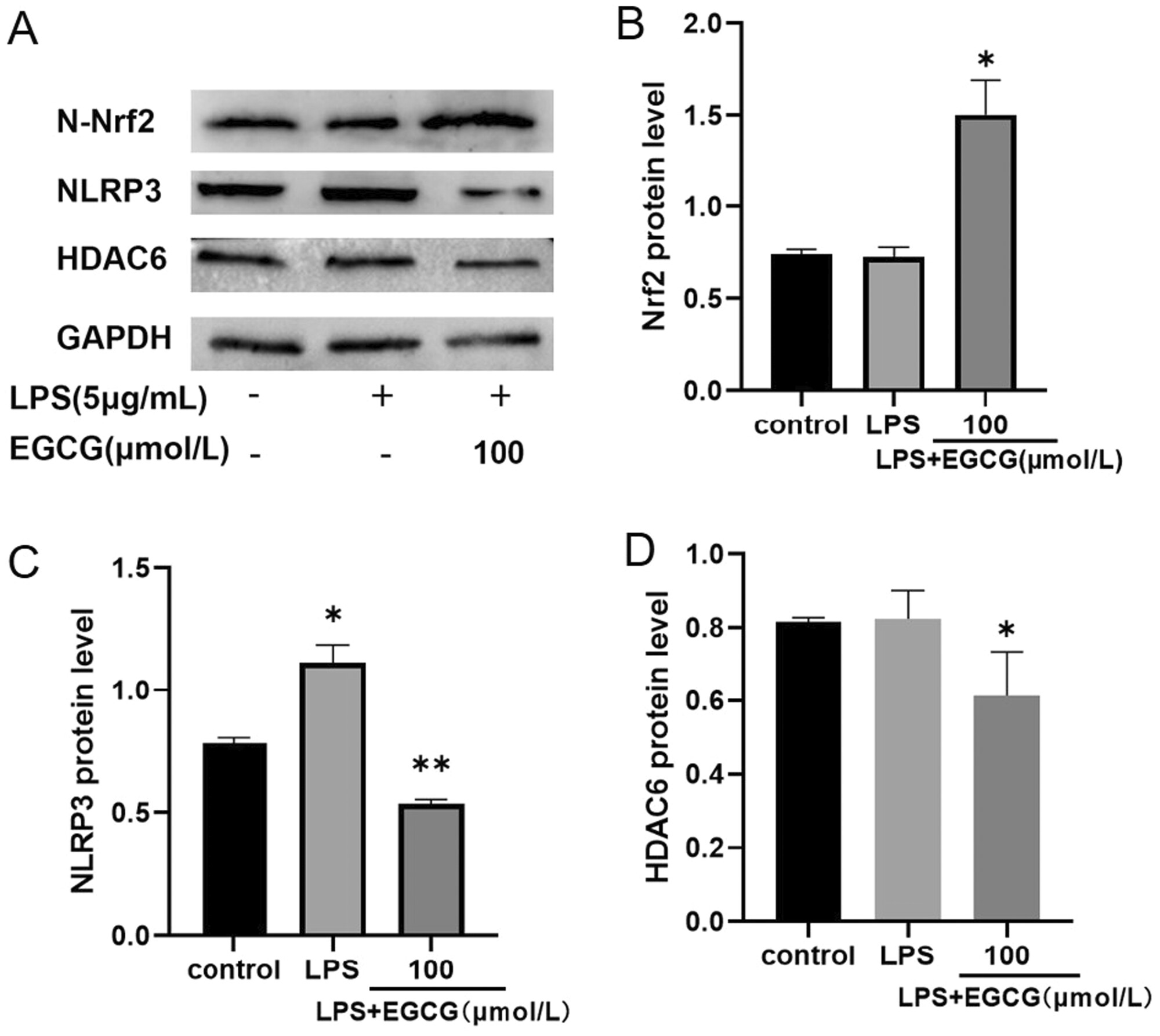
(1) At concentrations of less than 100 μmol/L, EGCG can promote cell proliferation and significantly inhibit the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β. (2) EGCG can activate the Nrf2 pathway and inhibit ROS production. (3) EGCG inhibited the expression of HDAC6 and promoted the expression of p62 and Hsp70, indicating that the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of EGCG are closely related to HDAC6.
REVIEW ARTICLE
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
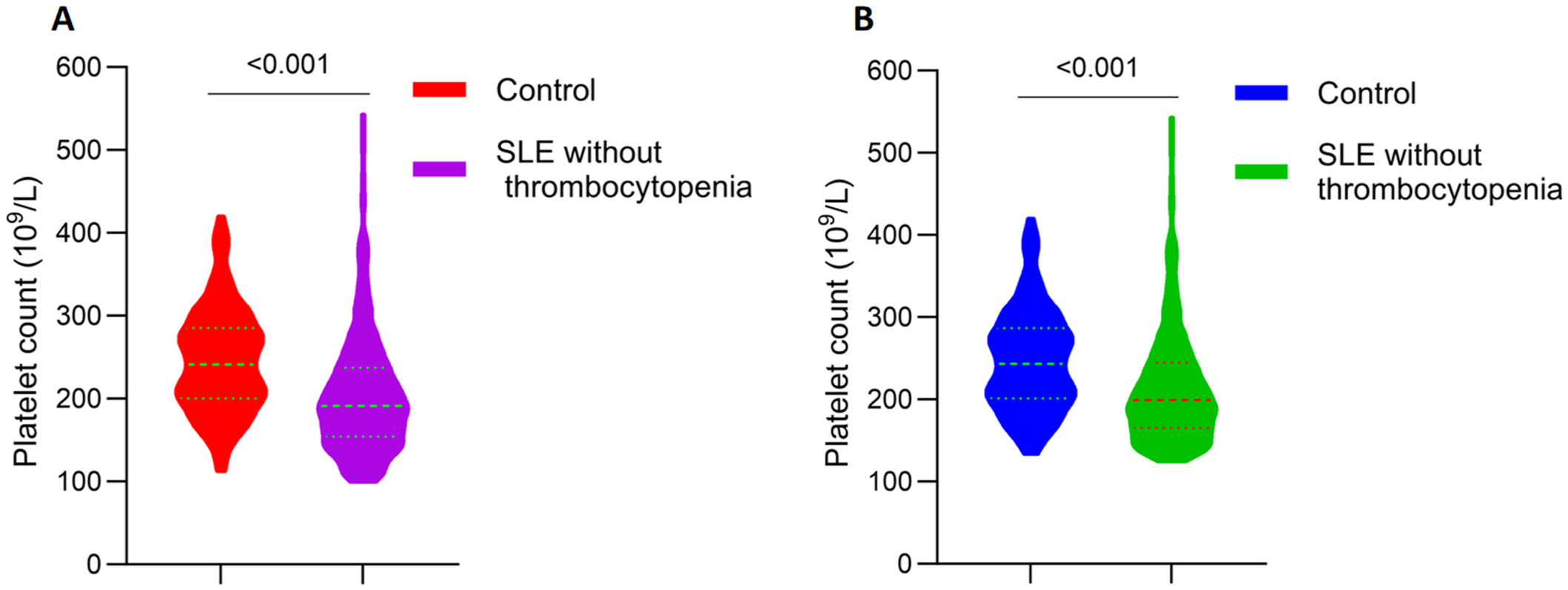
The Relationship of Platelets With the Clinical Manifestations and Serologic Markers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
- First Published: 23 April 2025
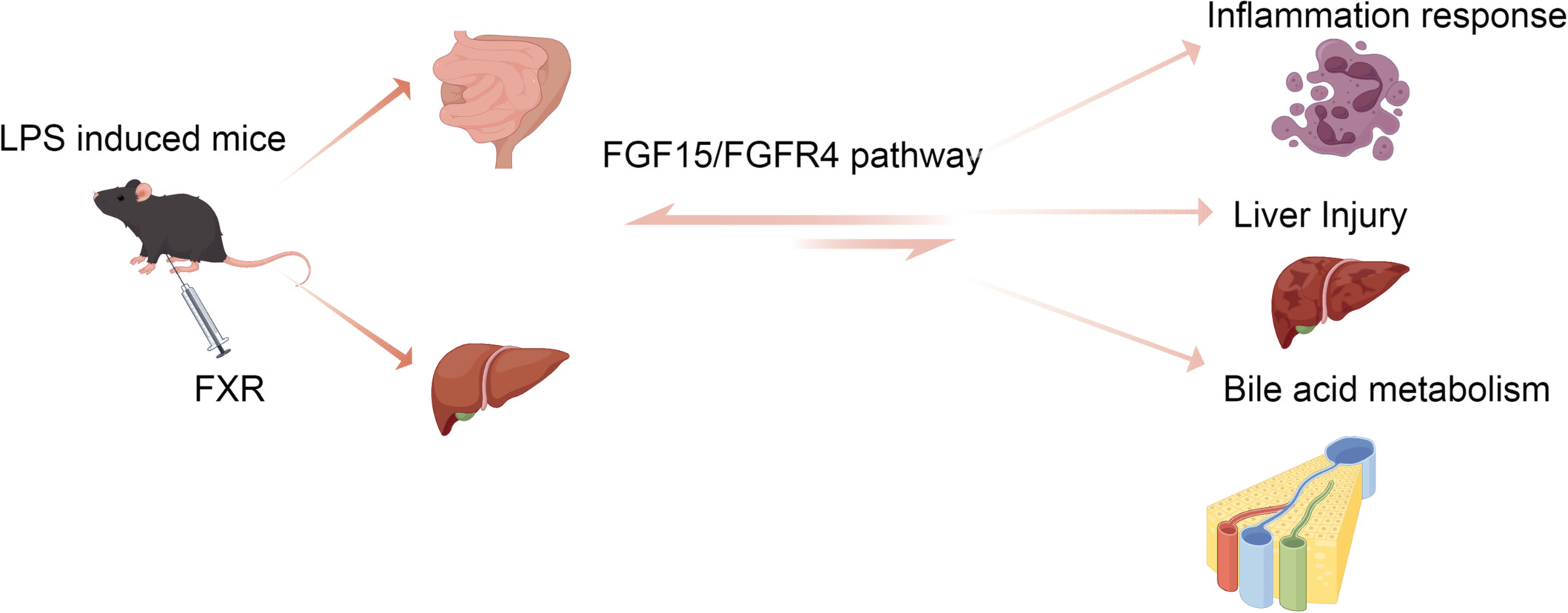
Farnesoid X Receptor Regulated Sepsis-Induced Abnormal Bile Acid Metabolism via the Fibroblast Growth Factor 15/Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 Pathway
- First Published: 07 April 2025
RETRACTION
RETRACTION: MicroRNA-425-3p Inhibits Myocardial Inflammation and Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Mice With Viral Myocarditis Through Targeting TGF-β1
- First Published: 11 April 2025
RETRACTION: Oxaliplatin Activates P53/miR-34a/Survivin Axis in Inhibiting the Progression of Gastric Cancer Cells
- First Published: 11 April 2025
RETRACTION: Expression and Significant Roles of the lncRNA NEAT1/miR-493-5p/Rab27A Axis in Ulcerative Colitis
- First Published: 11 April 2025
RETRACTION: LncRNA TUG1 Relieves Renal Mesangial Cell Injury by Modulating the miR-153-3p/Bcl-2 Axis in Lupus Nephritis
- First Published: 11 April 2025