Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLE
Disparities in Seasonal Influenza Vaccination in Europe
- First Published: 08 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
APOBEC3C-Mediated NF-κB Activation Promotes Malignant Progression of Gliomas
- First Published: 24 July 2025
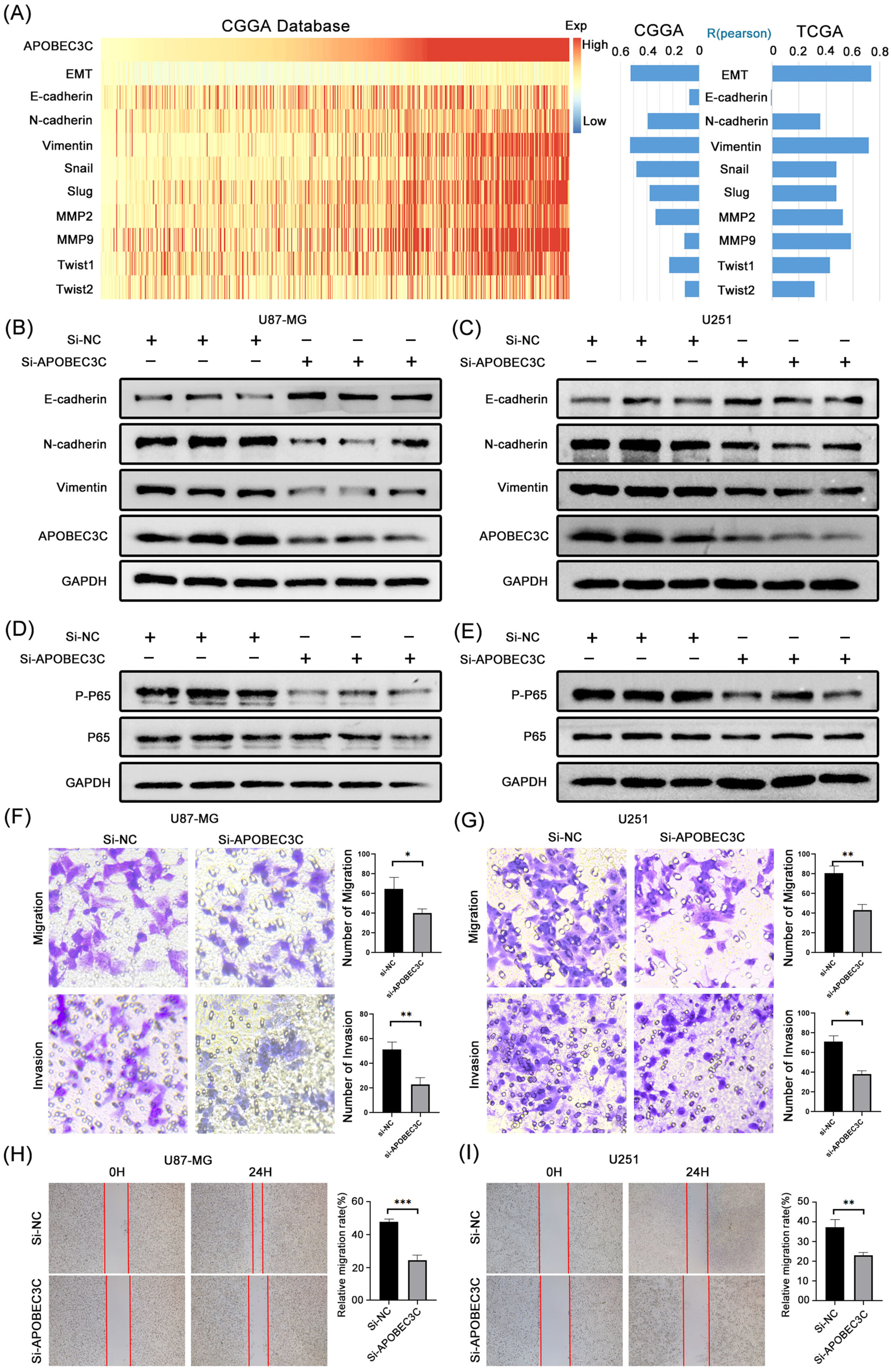
The results of this study suggest that high expression of APOBEC3C is associated with poor prognosis in glioma and may affect immune regulation. Knocking down APOBEC3C can inhibit the invasion and migration abilities of glioma cells. In addition, APOBEC3C can regulate the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is expected to be a target for improving immunotherapy in glioma patients.
Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Protein Biomarkers From Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients
- First Published: 08 July 2025
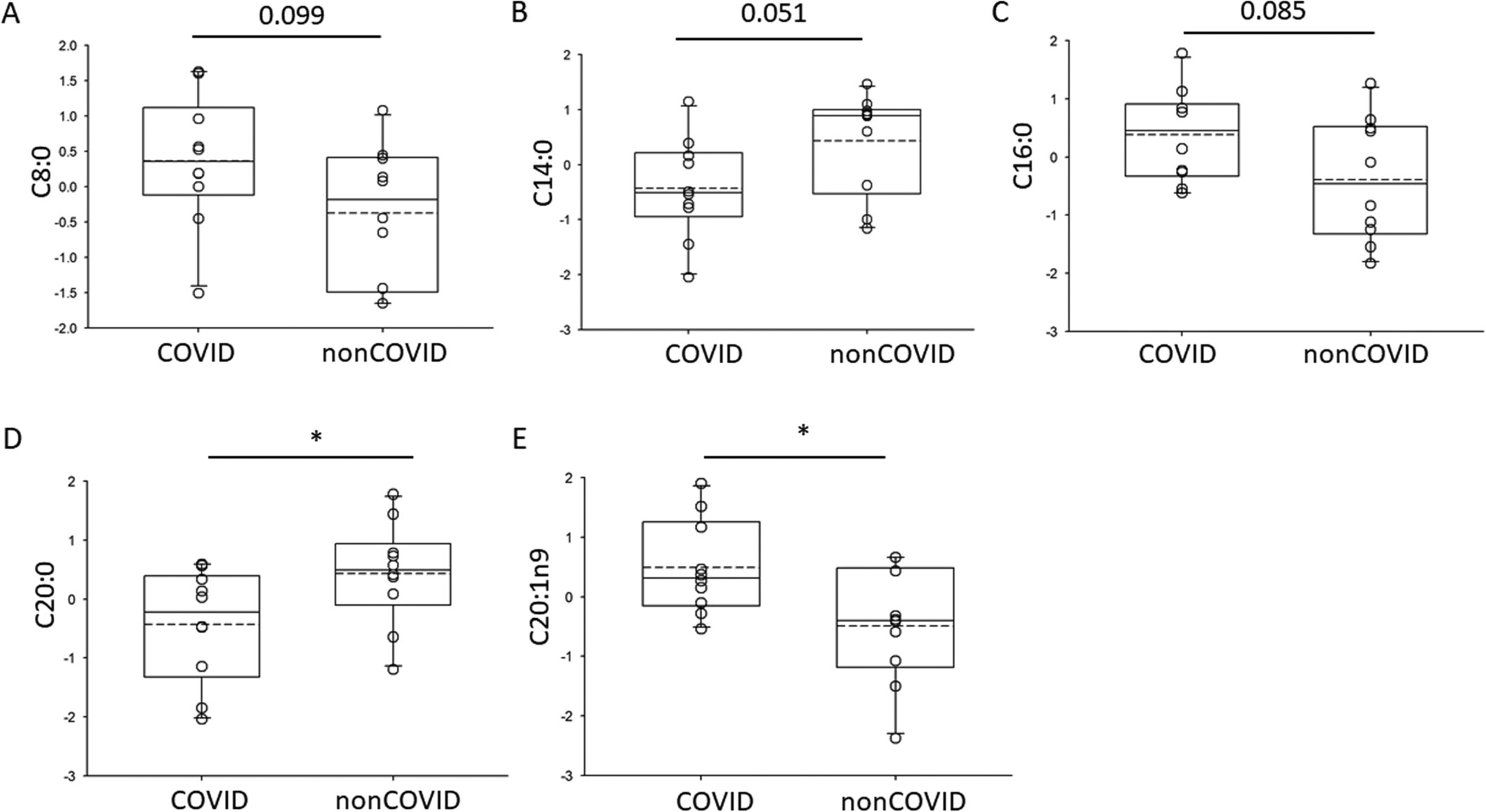
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic created the need to identify new biomarkers and drug targets. In this study, we aimed to establish a unique signature profile of specific fatty acids, cytokines, and chemokines present in the plasma after COVID-19 viral infection to serve as novel biomarkers that can be used to determine the severity of infection, disease prognosis, and consideration for therapeutic options.
REVIEW ARTICLE
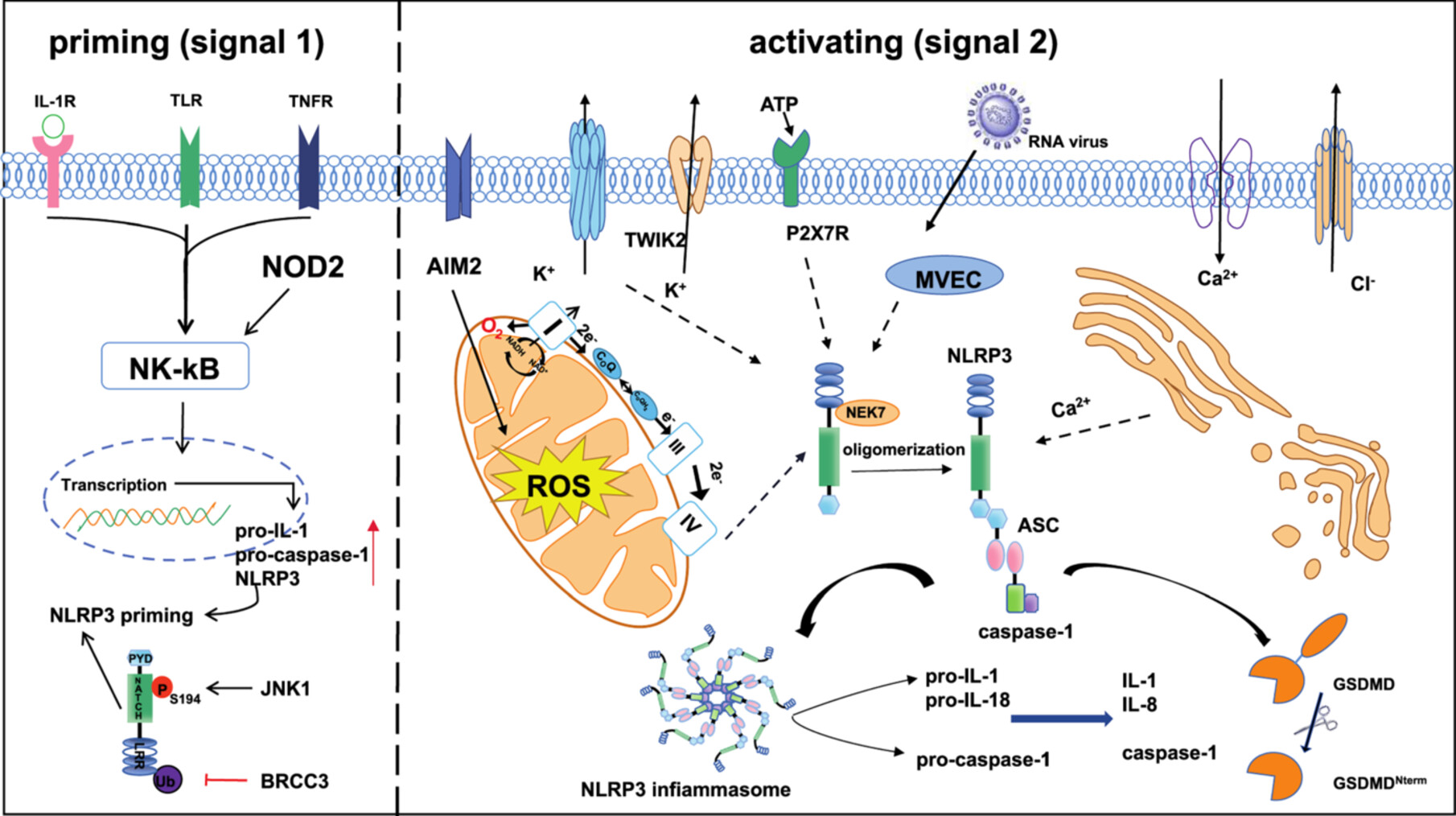
Molecular Mechanism of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Diseases and Tumors
- First Published: 16 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Amphiregulin Promotes Proliferation and Migration of the Damaged Endothelial Cells in Kawasaki Disease Cell Models
- Page: publicationMeta
- First Published: 15 July 2025
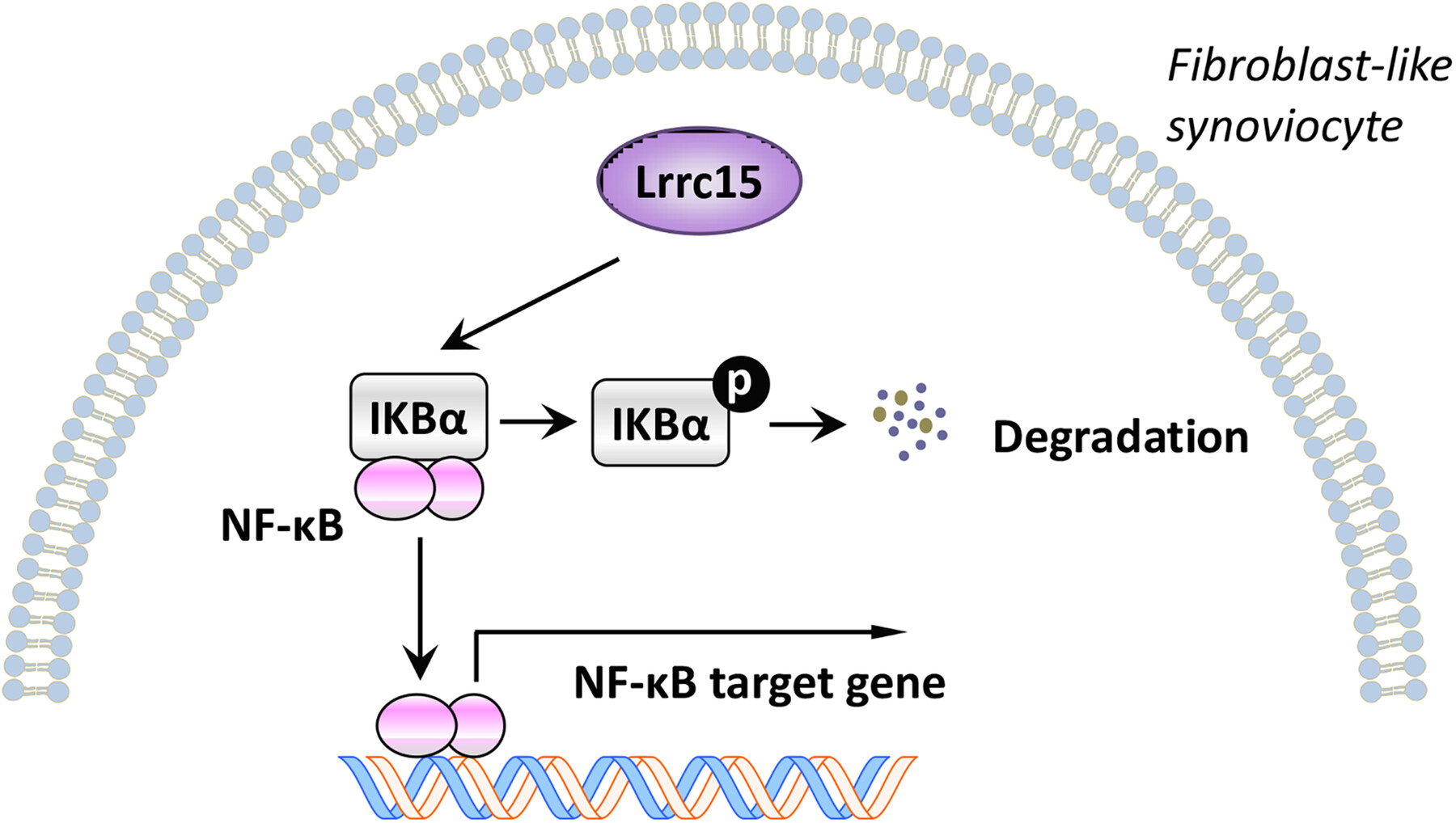
Leucine-Rich Repeat Containing 15 Promotes the Inflammatory Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating NF-κB Pathway
- First Published: 11 July 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Bitter Taste Receptors in Bacterial Infections and Innate Immunity
- First Published: 25 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
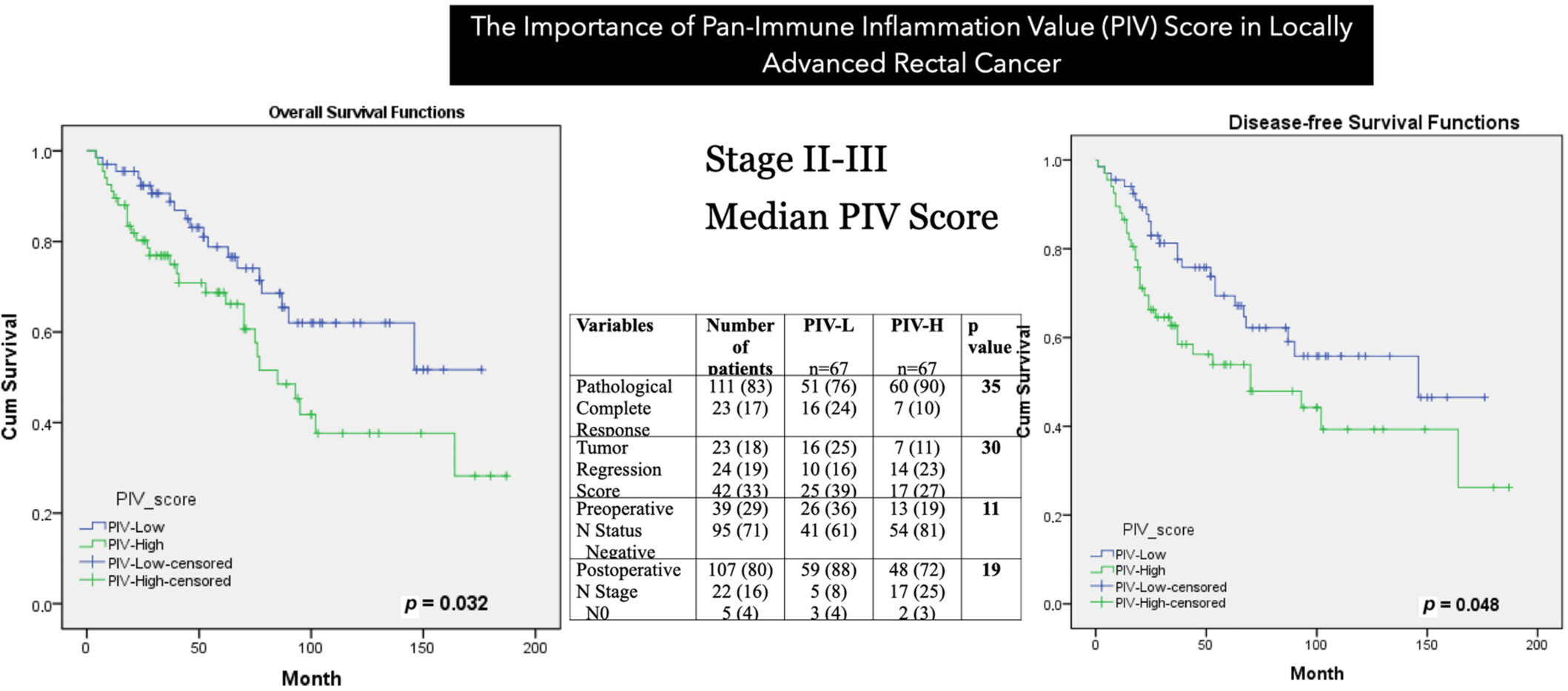
The Importance of Pan-Immune-Inflammation Value Score in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
- First Published: 24 July 2025
Inflammatory Responses Potentiate GAS M Protein Induced Cardiac Damage in an Experimental Model of Rheumatic Heart Disease
- First Published: 11 July 2025
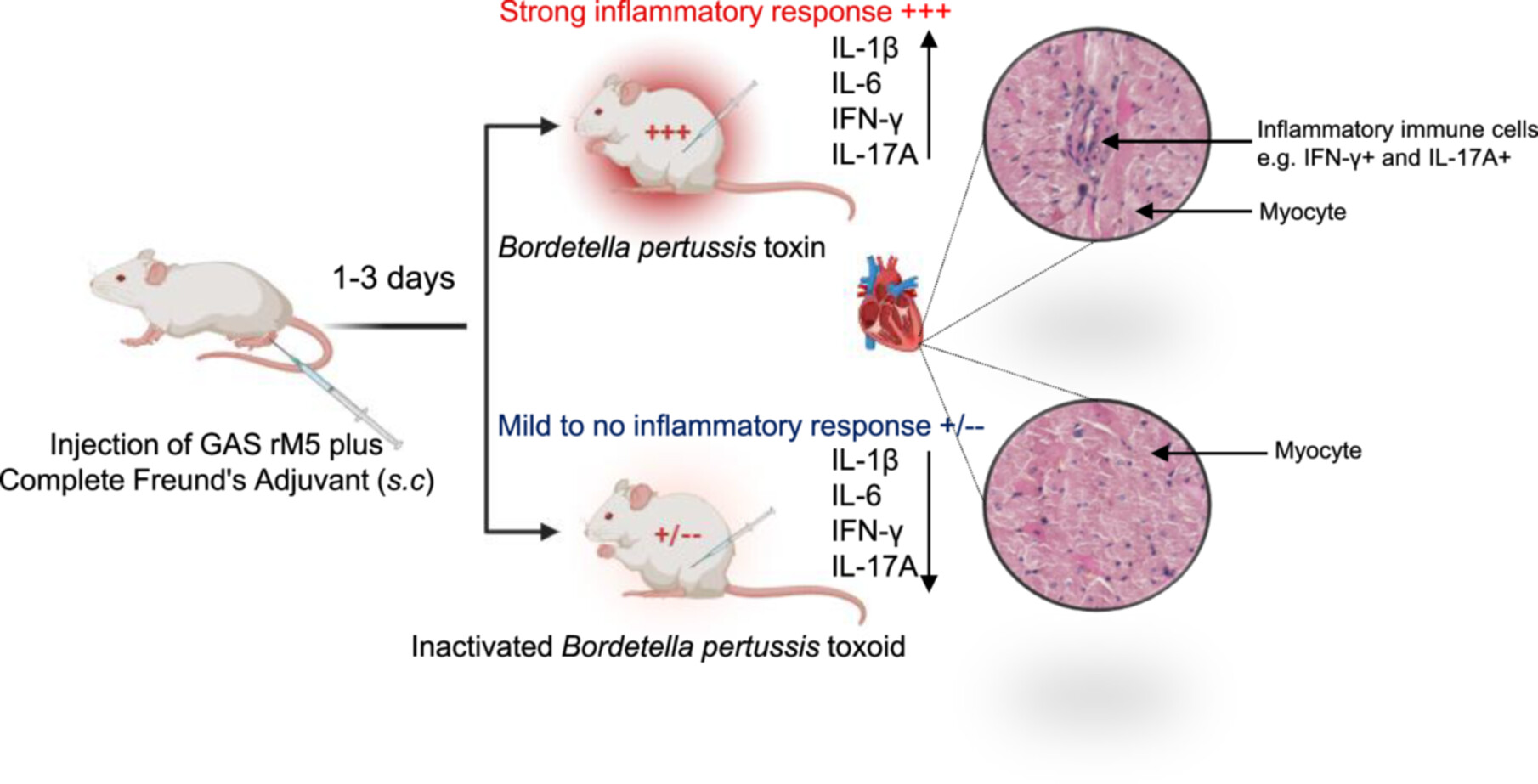
Group A streptococcal M protein elicit antibody and T-cell responses that cross react with cardiac and connective tissue proteins in the Rat Autoimmune Valvulitis (RAV) model of rheumatic heart disease. Bordetella pertussis Toxin induce a robust Th1 response that potentiates the autoimmune process in the RAV model A robust Th1/Th17 response was found to be a major driver of cardiac pathology in the RAV model