Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Cardiac biomarkers, cardiac injury, and comorbidities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1071-1100
- First Published: 18 August 2021
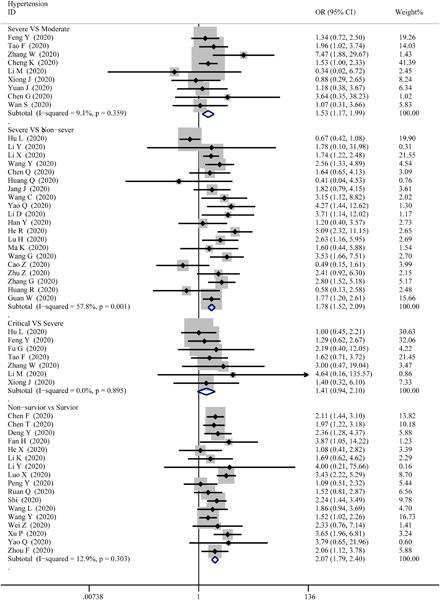
We use a meta-analysis to explore the correlation between cardiac-related comorbidities, cardiac biomarkers, acute myocardial injury, and severity level, outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Most of the findings clearly indicate that hypertension, cardiovascular disease, acute cardiac injury, and related laboratory indicators are associated with the severity of COVID-19. What is now needed are cross-national prospectively designed observational or clinical trials that will help improve the certainty of the available evidence and treatment decision for patients.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Upcoming treatments for morphea
- Pages: 1101-1145
- First Published: 17 July 2021
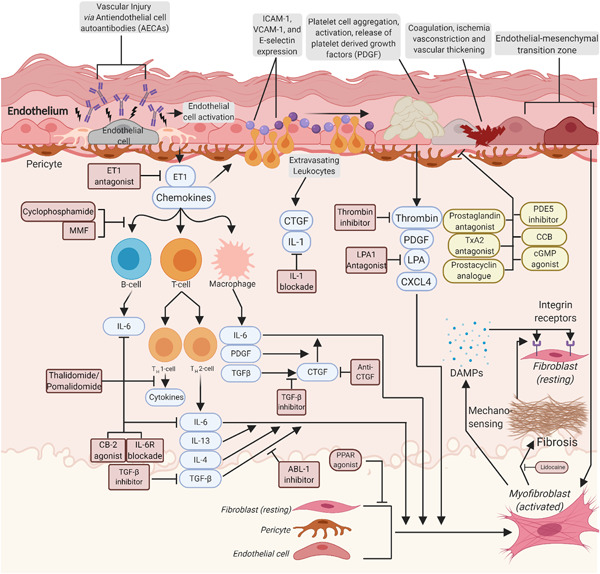
Morphea is a rare connective tissue disease with variable clinical presentations, all of which are characterized by inflammatory fibrosis. No cure for morphea exists, but advances in our understanding of the mediators and cellular pathways underlying fibrosis have revealed potential therapeutic targets. Here, we review the upcoming treatments for morphea and other related inflammatory fibrosing disorders, focusing on anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and senolytics approaches.
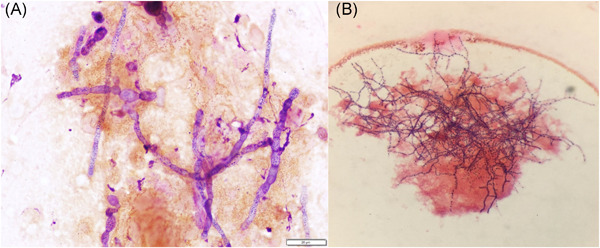
Cladophialophora bantiana and Nocardia farcinica infection simultaneously occurring in a kidney transplant recipient: Case report and literature review
- Pages: 1146-1152
- First Published: 15 June 2021
Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in atopy
- Pages: 1153-1159
- First Published: 03 August 2021
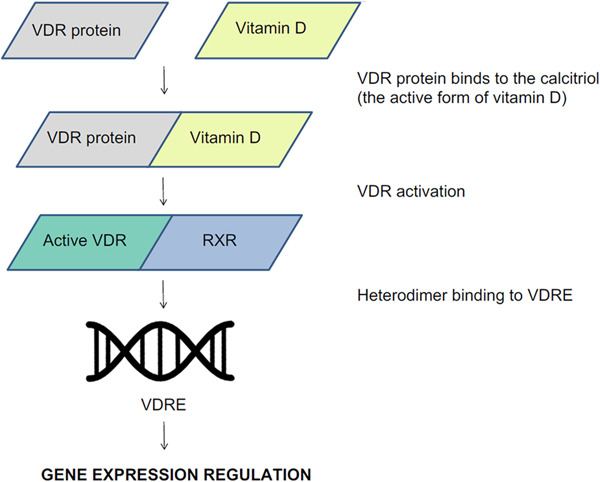
Some evidence suggests that vitamin D is linked with increased risk and more severe forms of allergic diseases. Therefore, this review article aimed to evaluate the role of vitamin D level and vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) polymorphisms in atopy. We found that vitamin D levels in atopy are extensively studied by many research groups, however, vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and their link with vitamin D levels lack comprehensive data. Even though, more evidence shows a positive impact on the risk and outcomes of allergic diseases, especially atopic dermatitis and asthma.
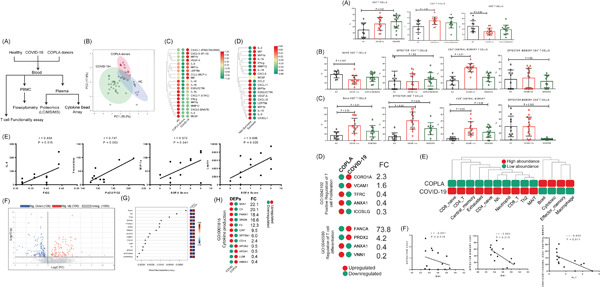
The clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in HIV-positive patients: A systematic review of current evidence
- Pages: 1160-1185
- First Published: 29 July 2021
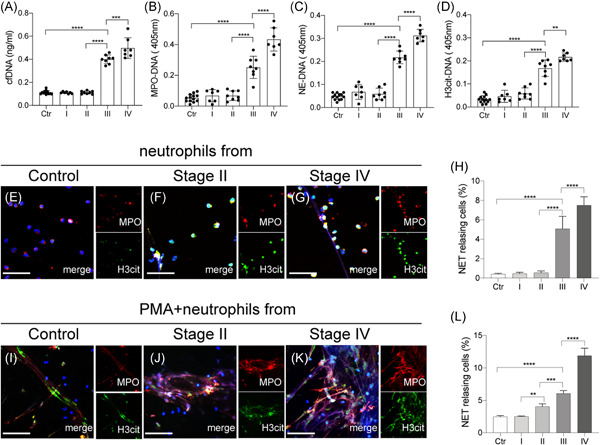
Role of neutrophils in acute viral infection
- Pages: 1186-1196
- First Published: 02 September 2021
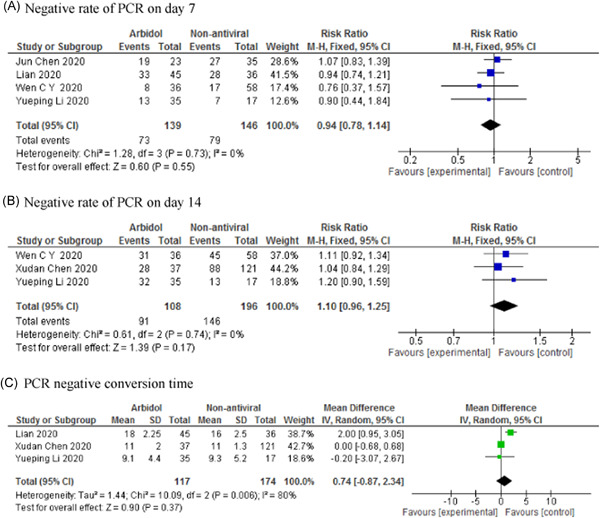
Efficacy and safety of arbidol (umifenovir) in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1197-1208
- First Published: 04 August 2021
microRNAs in human brucellosis: A promising therapeutic approach and biomarker for diagnosis and treatment
- Pages: 1209-1218
- First Published: 27 August 2021
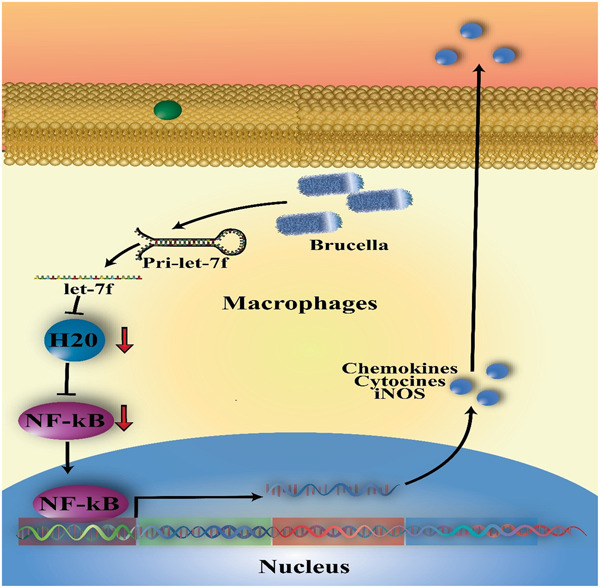
Many molecular and cellular pathways contribute to brucellosis that microRNAs have a significant role in the immunopathogenesis of this infection. In this regard, these molecules apply for their roles by modulating various events like inflammatory reactions and immune defense. Recently, much insight into the significant role of microRNAs in immune protection in human brucellosis was found. In this study, we tried to review the immune defense and immunopathogenesis of Brucella infection and highlight the current knowledge of the microRNAs in infected cells by Brucella pathogens.
The effect of low serum calcium level on the severity and mortality of Covid patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1219-1228
- First Published: 17 September 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Agreements and controversies of national guidelines for bronchiolitis: Results from an Italian survey
- Pages: 1229-1236
- First Published: 22 October 2021
The influence of extracellular tissue on neutrophil function and its possible linkage to inflammatory diseases
- Pages: 1237-1251
- First Published: 11 June 2021
Our study compares the impact of different extracellular matrices on neutrophil function. By examining cells with live-cell imaging in an in vitro model, we showed that type III collagen inhibits neutrophil migration and boosts neutrophil reactive oxygen species production. Furthermore, we found NETosis to be retarded in fibrin and myeloperoxidase release to be delayed in agarose. Our findings contribute to a better understanding of neutrophil regulatory activity in tissues and may provide a better understanding of neutrophils' important role in the development and maintenance of inflammatory phenomena in tissues
Relationship of transitional regulatory B and regulatory T cells and immunosuppressive drug doses in stable renal transplant recipients
- Pages: 1252-1271
- First Published: 08 June 2021
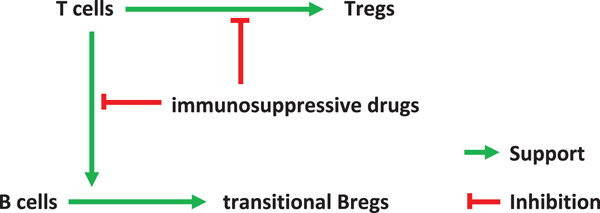
Regulatory B cells (Bregs) might be insensitive to high doses of posttransplant immunosuppressive drugs. The delayed Breg decrease posttransplant might be caused by impaired T cell support mediated by immunosuppressive drugs. Circulating regulatory T cells (Tregs) show an inverse relationship to transitional Bregs in the present study, suggesting that they do not induce each other
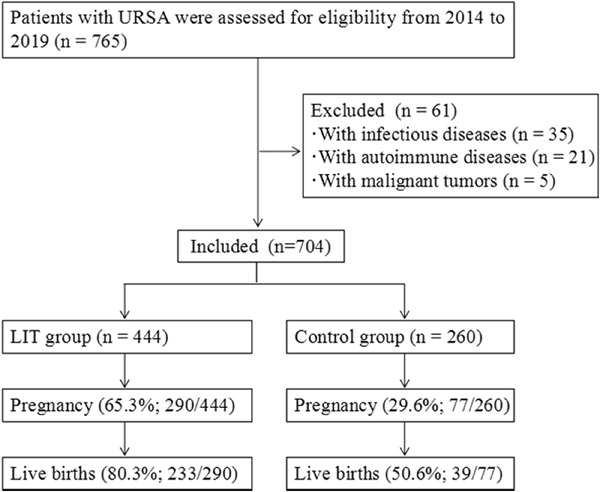
Clinical effect of lymphocyte immunotherapy on patients with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- Pages: 1272-1278
- First Published: 08 June 2021
Sustained expression of inflammatory monocytes and activated T cells in COVID-19 patients and recovered convalescent plasma donors
- Pages: 1279-1290
- First Published: 06 August 2021
CircZNF124 regulates cell proliferation, leucine uptake, migration and invasion by miR-199b-5p/SLC7A5 pathway in endometrial cancer
- Pages: 1291-1305
- First Published: 19 June 2021
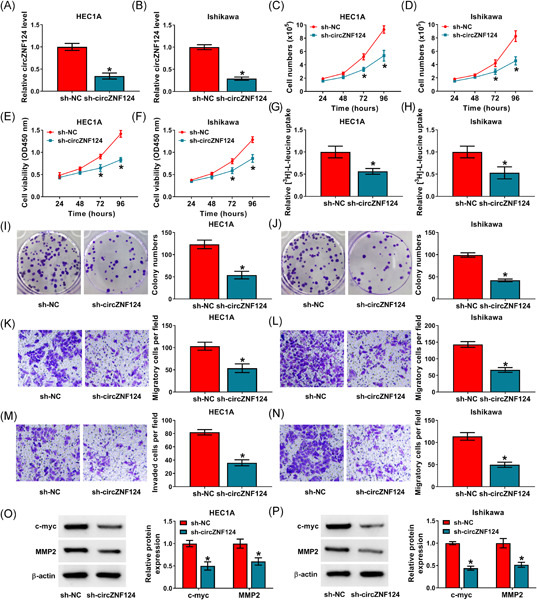
CircZNF124 expression was related to severity of EC and lymph node metastasis. CircZNF124 silencing inhibited EC tumorigenesis by hindering leucine uptake through miR-199b-5p/SLC7A5 axis. This study demonstrates that circZNF124 can be employed as a diagnosis biomarker and circZNF124 inhibitors may be used as an anticancer drug for EC.
Based on bioinformatics analysis lncrna SNHG5 modulates the function of vascular smooth muscle cells through mir-205-5p/SMAD4 in abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Pages: 1306-1320
- First Published: 29 June 2021
The findings of this study show that downregulation of SNHG5 increases expression levels of mir-205-5p and inhibits SMAD4 expression, thus affecting the function of vascular smooth muscle in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Therefore, SNHG5 is an important factor in pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysm and thus is potential therapeutic target for abdominal aortic aneurysm.
A novel anti-inflammatory treatment for bradykinin-induced sore throat or pharyngitis
- Pages: 1321-1335
- First Published: 21 June 2021
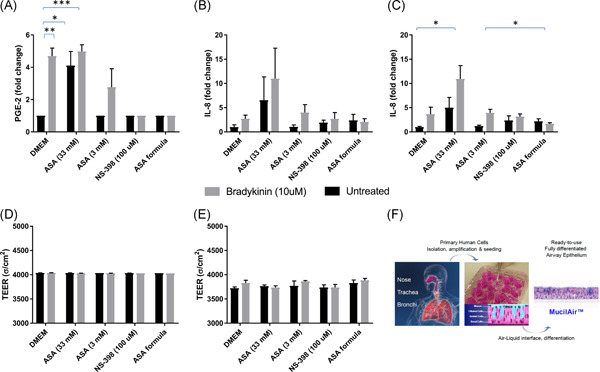
In studying pharyngitis using organotypic human respiratory tissue stimulated with bradykinin, there was an increase in prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) in response to bradykinin. Acetyl salicylic acid (ASA), a non-specific COX inhibitor, was able to mitigate a bradykinin-induced increase in PGE2, but exacerbated inflammation at high concentrations. A novel treatment for sore throat, that contains a low dose of aspirin and other anti-inflammatory ingredients is described.
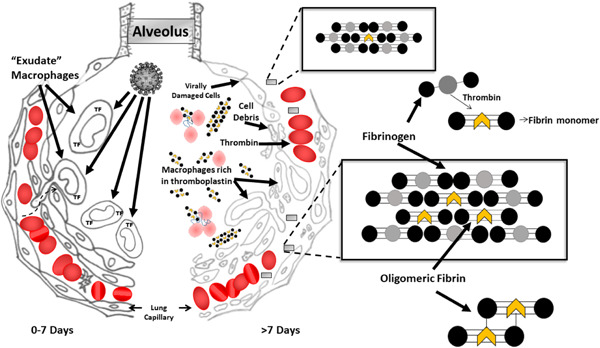
A macrophage attack culminating in microthromboses characterizes COVID 19 pneumonia
- Pages: 1336-1342
- First Published: 07 July 2021
Characterization of the blood and neutrophil-specific microbiomes and exploration of potential bacterial biomarkers for sepsis in surgical patients
- Pages: 1343-1357
- First Published: 20 July 2021
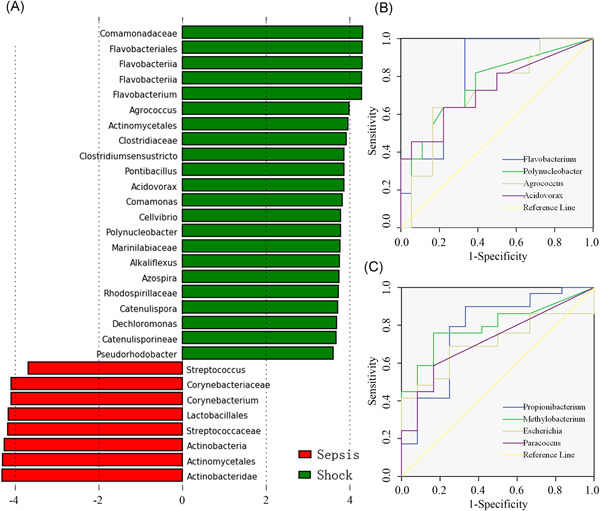
(1) This study characterized for the first time the compositional features of the blood and neutrophli-specific microbiomes in surgical patients and associated the microbiome alterations with the progression of postoperative sepsis. (2) Several certain bacterial genera in blood microbiome could have potential as microbial markers for early detection of sepsis. (3) The functional abnormality of neutrophils might play potentially intrinsic effectors in remodeling blood microbiome toward a disease-provoking state in sepsis.
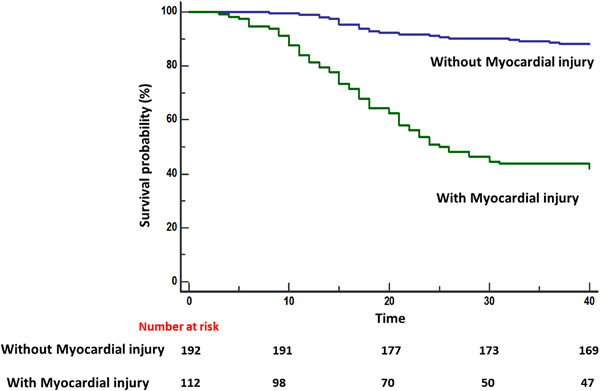
The prognostic value of myocardial injury in COVID-19 patients and associated characteristics
- Pages: 1358-1369
- First Published: 09 July 2021
Alcohol consumption induces murine osteoporosis by downregulation of natural killer T-like cell activity
- Pages: 1370-1382
- First Published: 02 July 2021
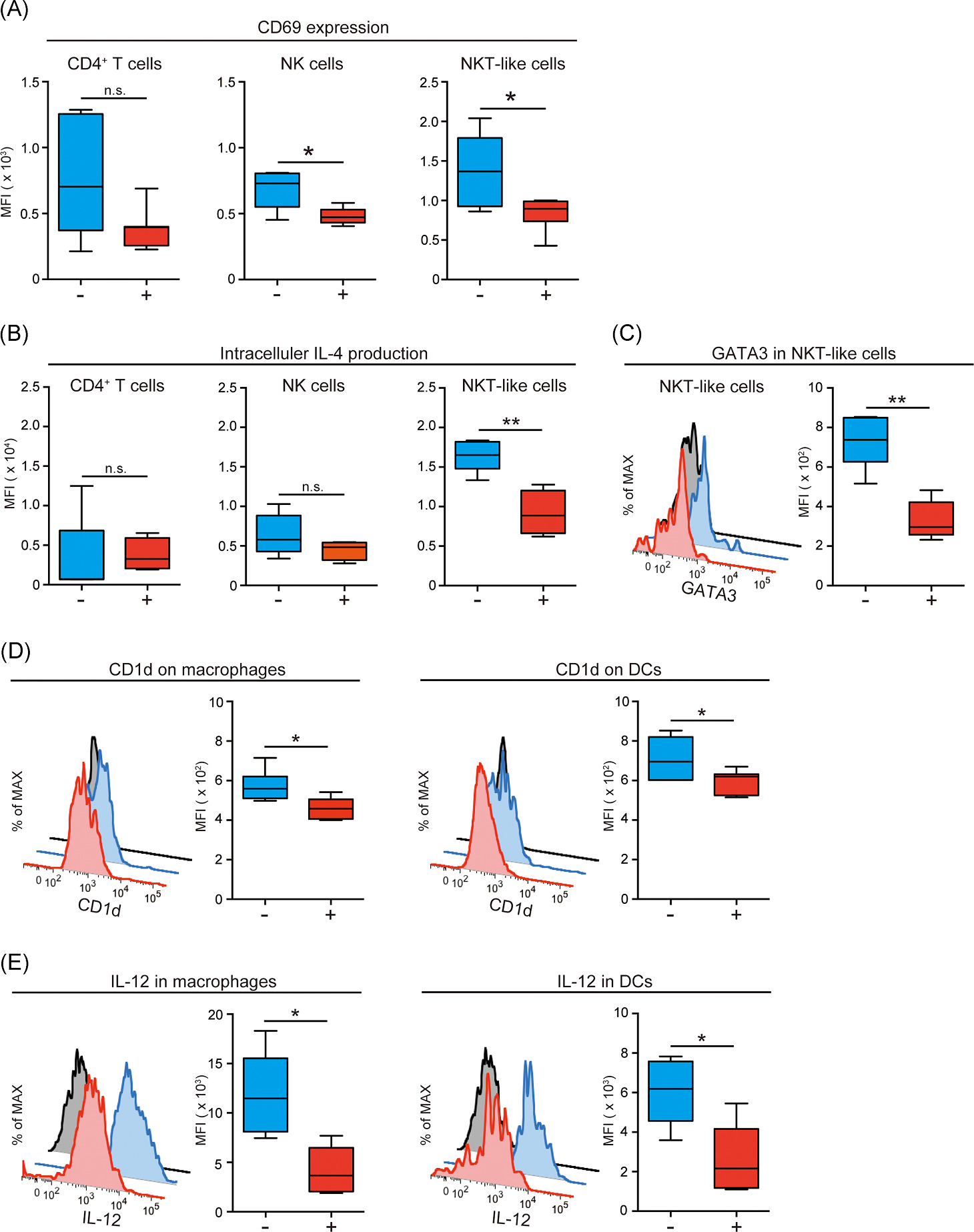
We analyzed alcohol-induced osteoporosis model mice, focusing on immune cells in bone. We mainly obtained three findings: (1) IL-4-highly producing NKT-like cells were more abundant in bone, (2) oral alcohol consumption suppressed IL-4 production from the NKT-like cells, and (3) a glycolipid antigen OCH improved alcohol-induced osteoporosis by restoring IL-4 production.
Neutrophil extracellular traps induce a hypercoagulable state in glioma
- Pages: 1383-1393
- First Published: 19 July 2021
ORMDL3 overexpression facilitates FcεRI-mediated transcription of proinflammatory cytokines and thapsigargin-mediated PERK phosphorylation in RBL-2H3 cells
- Pages: 1394-1405
- First Published: 19 July 2021
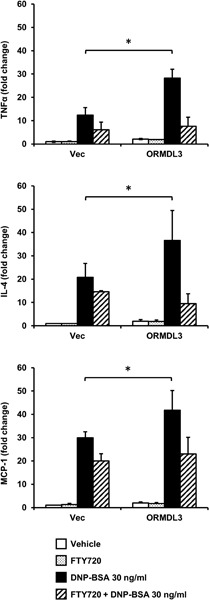
The messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of TNF-α, IL-4, and MCP-1 were significantly upregulated after engagement of FcεRI in orosomucoid-like 3 (ORMDL3) overexpressing cells. FTY720 significantly reduced cytokine mRNA expression in ORMDL3-overexpressing cells and inhibited the expression to a level that was comparable with that observed in vector-transfected cells.
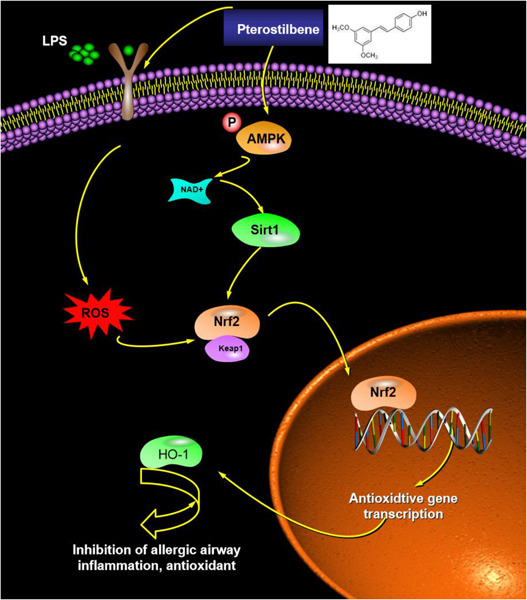
Pterostilbene suppresses oxidative stress and allergic airway inflammation through AMPK/Sirt1 and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways
- Pages: 1406-1417
- First Published: 02 August 2021
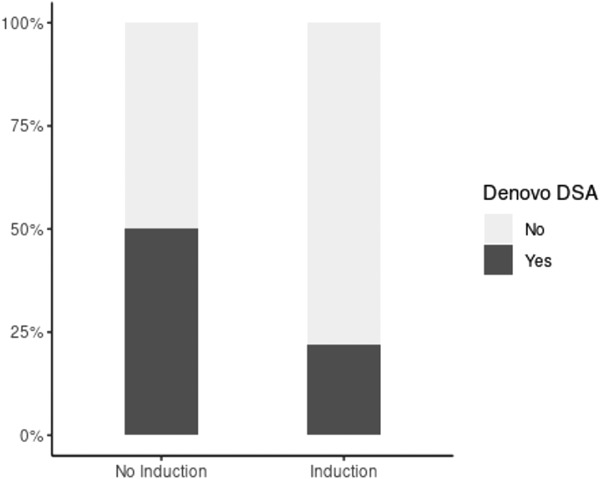
Antithymocyte globulin is associated with a lower incidence of de novo donor-specific antibody detection in lung transplant recipients: A single-center experience
- Pages: 1418-1427
- First Published: 26 July 2021
The infection characteristics and autophagy defect of dermal macrophages in STZ-induced diabetic rats skin wound Staphylococcus aureus infection model
- Pages: 1428-1438
- First Published: 14 October 2021
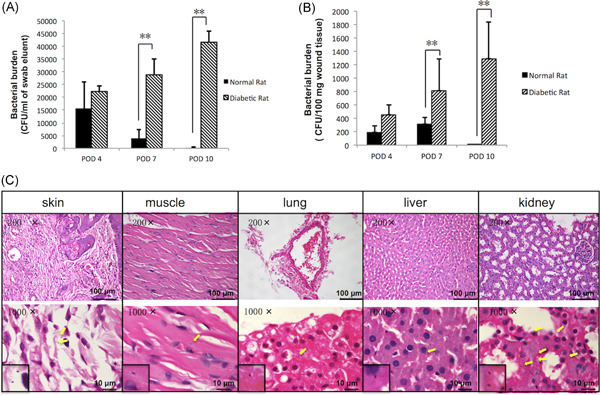
Infections in diabetic rats appeared more severe and more invasive with weakened pathogen clearance ability of the host immune system, which coincided with the suppressed autophagic flux in dermal macrophages, featured by a significant increase in endogenous LC3II/I and in p62. Our results provided convincing evidence that autophagy of macrophages was dysfunctional in diabetes, especially after being infected by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), which weakens the intracellular killing of S. aureus, potentially worsen the infections, and accelerates the infection spread in the diabetic rat model.
Alkaloid leonurine exerts anti-inflammatory effects via modulating MST1 expression in trophoblast cells
- Pages: 1439-1446
- First Published: 28 July 2021
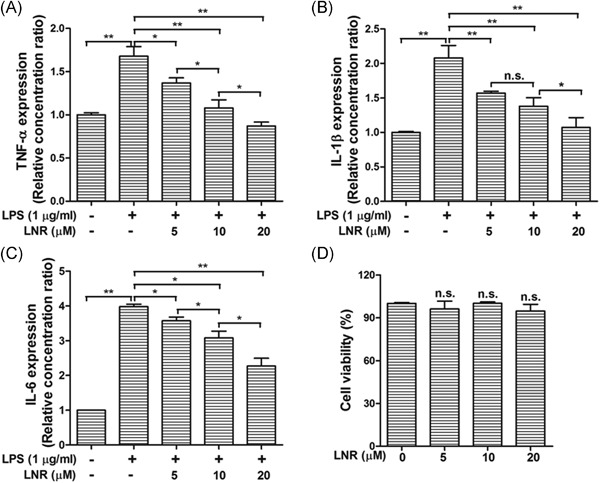
Leonurine (LNR) exhibited anti-inflammatory effects and suppressed the NF-κB signaling by inhibiting LPS-induced inflammation in trophoblast cells. LNR played its anti-inflammation effects on human and mouse trophoblast cells by upregulating MST1 in the NF-κB signal pathway. LNR, leonurine; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; NF-κB, nuclear factor kB.
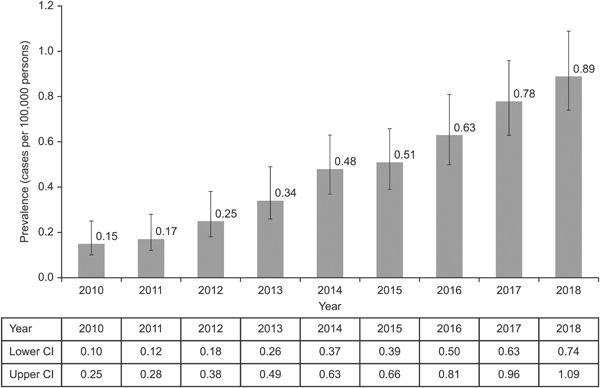
The increasing incidence and prevalence of hypereosinophilic syndrome in the United Kingdom
- Pages: 1447-1451
- First Published: 22 July 2021
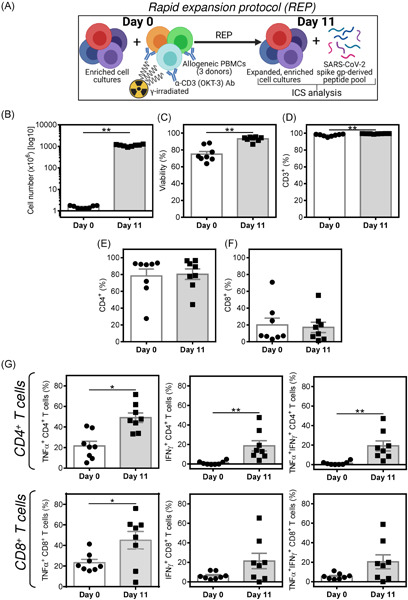
SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein-reactive T cells can be readily expanded from COVID-19 vaccinated donors
- Pages: 1452-1467
- First Published: 27 July 2021
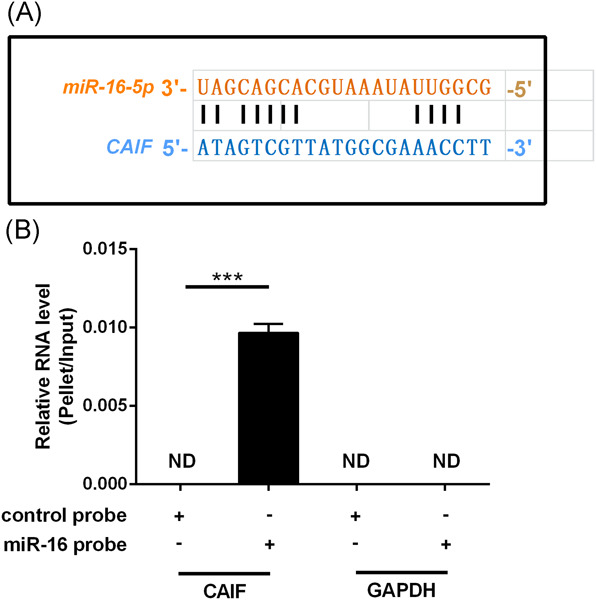
LncRNA CAIF suppresses LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes through regulating miR-16 demethylation
- Pages: 1468-1478
- First Published: 21 September 2021
Long-term B cell depletion associates with regeneration of kidney function
- Pages: 1479-1488
- First Published: 29 July 2021
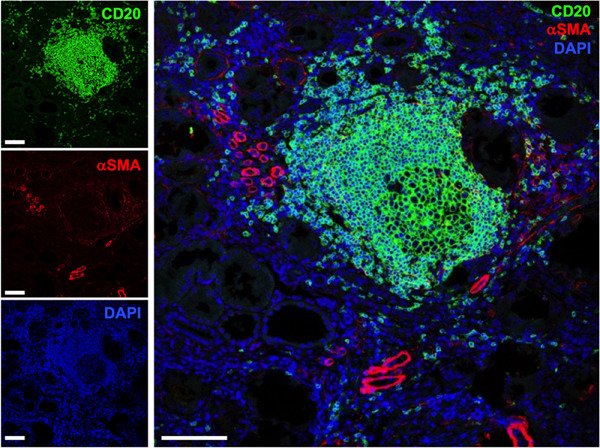
B cell aggregates are recognized in a growing number of kidney diseases of diverse etiologies. We tested the effect of long-term B cell depletion on renal function. Our data show long-term improvement in two independent patient cohorts. This is consistent with the hypothesis that B cell-directed intervention may be successful in chronic renal inflammation of diverse etiologies.
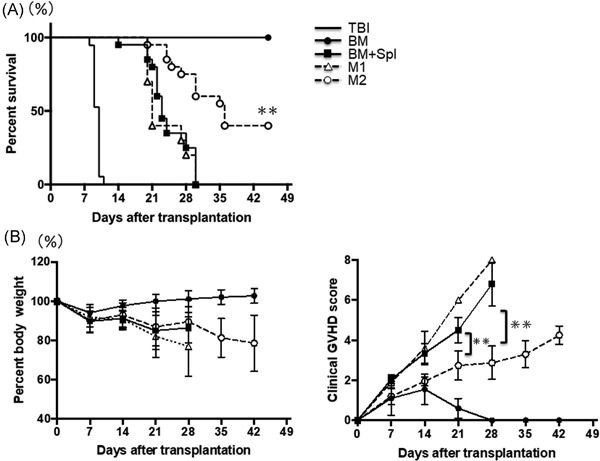
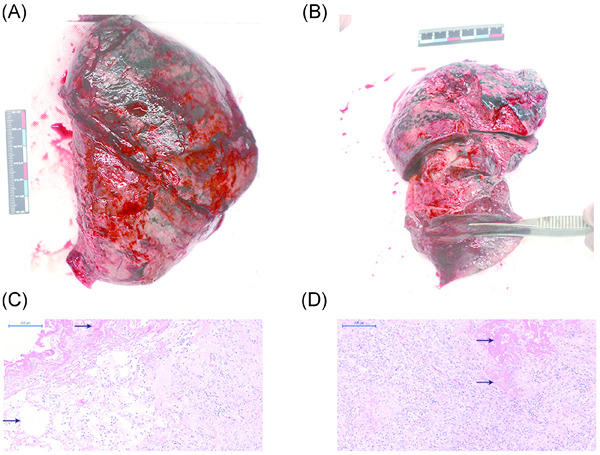
Donor-derived M2 macrophages attenuate GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Pages: 1489-1499
- First Published: 19 August 2021
First lung transplant in Wuhan for a critical and elderly COVID-19 patient
- Pages: 1500-1507
- First Published: 01 September 2021
Impact of low-level pretransplant donor-specific antibodies on outcomes after kidney transplantation
- Pages: 1508-1519
- First Published: 18 August 2021
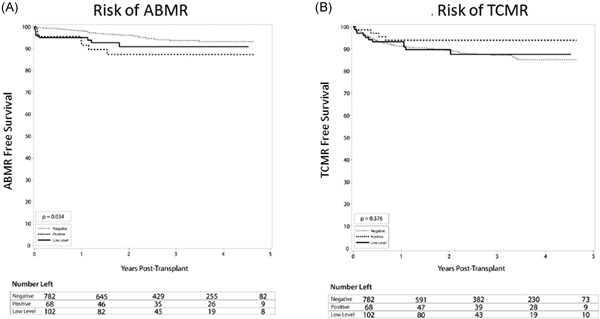
The presence of pretransplant donor-specific antibody (DSA) represents a significant barrier to kidney transplantation for highly sensitized patients as they are less likely to undergo transplants compared with their nonsensitized counterparts. The goal of this study was to compare outcomes among patients of varying immunologic risk, based on the level of pre-transplant DSA. The positive DSA group had the highest rate of antibody-mediated rejection (10.3%), followed by low-level DSA (7.8%) and the negative DSA group (4.5%) (p = .034). Also, the rate of BK viremia was highest in the positive DSA group (39.7%), followed by the low-level group (30.4%) and the negative DSA group (25.6%), (p = .025).
The study on the function and cell source of interleukin-6 in interstitial cystitis/bladder painful syndrome rat model
- Pages: 1520-1528
- First Published: 18 August 2021
Machine learning gene expression predicting model for ustekinumab response in patients with Crohn's disease
- Pages: 1529-1540
- First Published: 01 September 2021
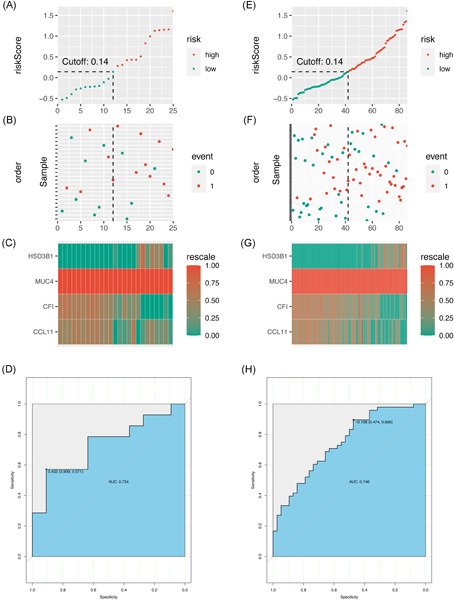
In the present study, we used bioinformatics analysis to obtain the gene expression profiles from the Gene Expression Omnibus to build a model for UST response prediction. As a result, the gene expression profiling was revealed, and a multivariate logistic regression equation that comprises four genes (HSD3B1, MUC4, CF1, and CCL11) for UST response prediction was successfully built and evaluated. This study is the first to build a machine learning gene expression prediction model for UST response in patients with CD and provides valuable data sources for further basic and clinical studies in the future.
Impaired T helper cell responses in human immunodeficiency virus-exposed uninfected newborns
- Pages: 1541-1553
- First Published: 19 August 2021
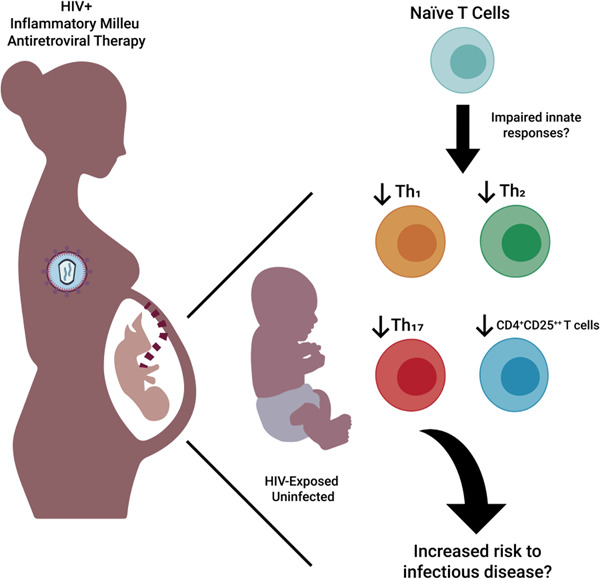
The frequency of differentiated peripheral Th cells in HIV-exposed uninfected (HEU) newborns is reduced compared to control newborns. The consequences of this poorly differentiated pool of Th cells in HEU newborns could contribute to the high susceptibility to infections during the first months of life
Cytomegalovirus mismatch after heart transplantation: Impact of antiviral prophylaxis and intravenous hyperimmune globulin
- Pages: 1554-1562
- First Published: 15 September 2021
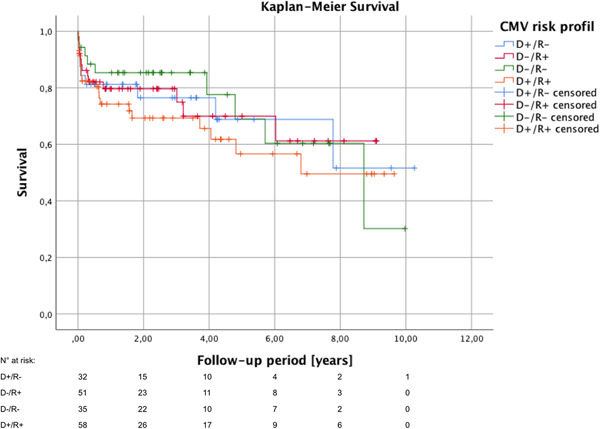
Seropositive recipients carry an important risk for CMV-DNAemia. However, we did not observe differences in perioperative morbidity and mortality regarding CMV matching, which might be related to regularly administer prophylactic virostatics and additional CMV-IVIG for risk constellations. For high-risk constellation, long-term application of CMV-IVIG during the first year after transplant may be beneficial.
Follow-up of renal transplant recipients after acute COVID-19—A prospective cohort single-center study
- Pages: 1563-1572
- First Published: 20 August 2021
Programmed death-ligand 1 expression in swine chronic infections and enhancement of interleukin-2 production via programmed death-1/programmed death-ligand 1 blockade
- Pages: 1573-1583
- First Published: 20 August 2021
Clinical observation of the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in the treatment of patients with advanced solid tumors
- Pages: 1584-1595
- First Published: 18 August 2021
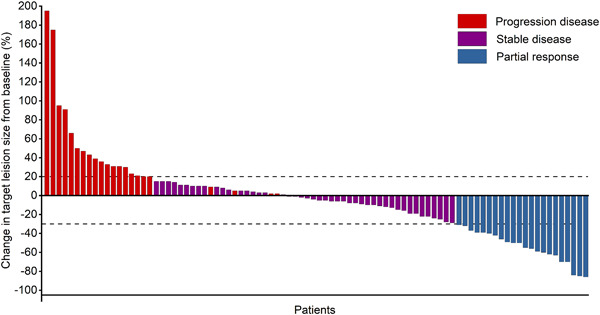
we evaluate the efficacy of programmed death 1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors in patients with advanced solid tumors and explore the effect of clinical characteristics. ECOG status, smoking status, liver metastasis status, and NLR might predict the recurrence between PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors treatment and liver metastasis, lactate dehydrogenase might predict the survival. This finding has great significance and value of the guidance for the application of immunotherapy.
Integrated analysis on the N6-methyladenosine-related long noncoding RNAs prognostic signature, immune checkpoints, and immune cell infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1596-1612
- First Published: 25 August 2021
Extra-articular involvement of rheumatoid arthritis in three seropositive patients in the absence of initial joint involvement
- Pages: 1613-1617
- First Published: 02 September 2021
Highly expressed of SERPINA3 indicated poor prognosis and involved in immune suppression in glioma
- Pages: 1618-1630
- First Published: 27 August 2021
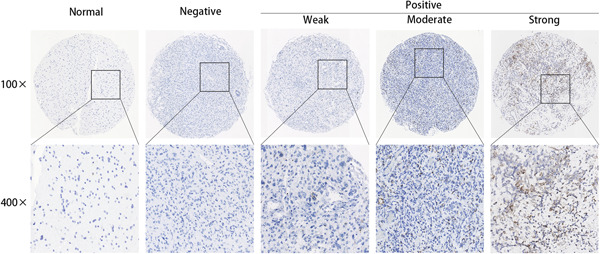
We observed that serpin peptidase inhibitor clade A member 3 (SERPINA3) messenger RNA was overexpressed in glioma tissues and involved in proliferation procession of glioma cells. SERPINA3 participate in promoting immune suppression in glioma TME. SERPINA3 could serve as a novel prognosis biomarker and therapy target in glioma.
NOD/scid IL-2Rγnull mice reconstituted with peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with Crohn's disease reflect the human pathological phenotype
- Pages: 1631-1647
- First Published: 09 September 2021
Ferritin level: A predictor of severity and mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Pages: 1648-1655
- First Published: 26 August 2021
Immunomodulation of endothelial cells induced by macrolide therapy in a model of septic stimulation
- Pages: 1656-1669
- First Published: 12 October 2021

This study reports phenotypic and gene expression changes in septic-stimulated microvascular endothelial cells after exposure to macrolides. Although a significant decrease in cell-surface human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I and HLA-DR expression and in interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene expression was observed, these modifications did not result in altered functional response following endothelial cells' interaction with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) regarding T-lymphocyte viability, cytokine production, or CD4 + -T differentiation.
Study on the contrast of the MHC–peptide interaction of B2/B21 haplotype and MHC-related virus resistance in chickens
- Pages: 1670-1677
- First Published: 02 September 2021
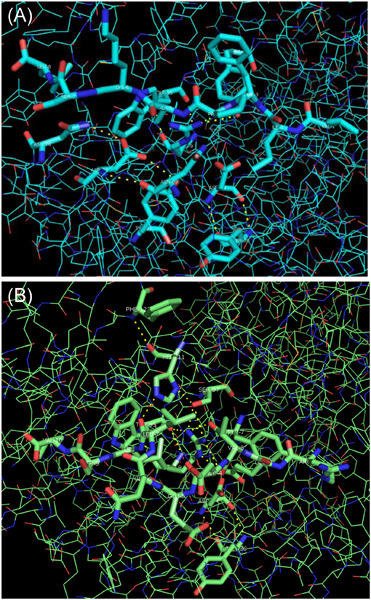
The research is dedicated to the 3D structure of 4cvx from the B2 haplotype and the contrast of the BF-peptide interaction of 4cvx and 3bew from the B21 haplotype. Conclusion of this study: There are usually various kinds of peptides presented by the BF21*2101 molecules of B21 haplotypes, resulting in resistance to pathogenic microorganisms, such as Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) and/or Marek's disease virus (MDV).
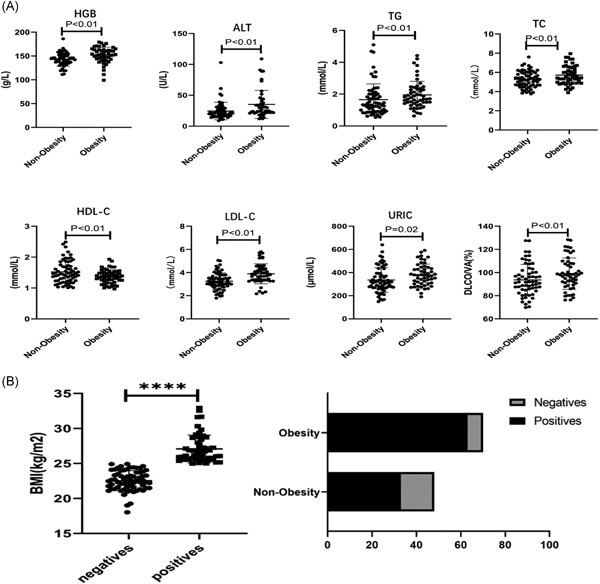
Long-term effects of obesity on COVID-19 patients discharged from hospital
- Pages: 1678-1685
- First Published: 09 September 2021
CCL2 produced by pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is essential for the accumulation and activation of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- Pages: 1686-1695
- First Published: 15 September 2021
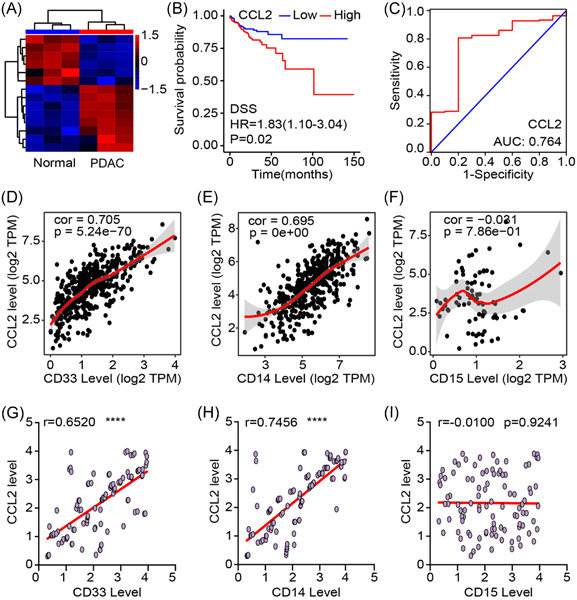
Our data indicate that CCL2 performs a significant role in PDAC progression by recruiting and activating M-MDSCs. Targeting MDSCs is able to improve antitumoral immunological responses providing with potential applicability of immune-based combination therapies against an extensive spectrum of solid tumors. These miscellaneous approaches might prove available for tumor therapeutics against solid carcinomas in which M-MDSCs perform a major role in immune evasion of tumors. These results are promising and need further assessment of the M-MDSCs-targeting combination or vaccination approaches for the whole therapeutic capacity of these tactics in PDAC and other carcinomas
Predominant frequency of HLA-B*27 in patients with ankylosing spondylitis in southeastern China
- Pages: 1696-1701
- First Published: 09 September 2021
SARS-CoV-2 infection shortly after BNT162b2 vaccination results in high anti-spike antibody levels in nursing home residents and staff
- Pages: 1702-1706
- First Published: 09 September 2021
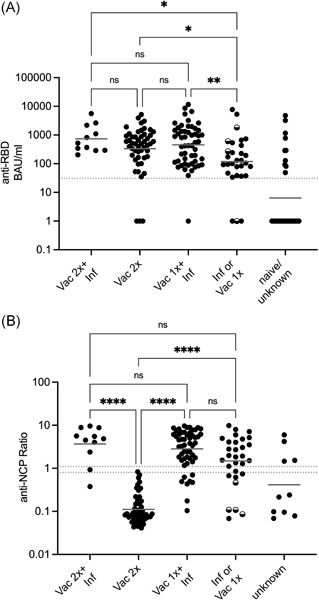
It is unclear how a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection shortly after a first coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine dose affects antibody responses. Here, we show that individuals who got infected as early as 10 days after their first BNT162b2 immunization show antibody levels comparable to fully vaccinated individuals.
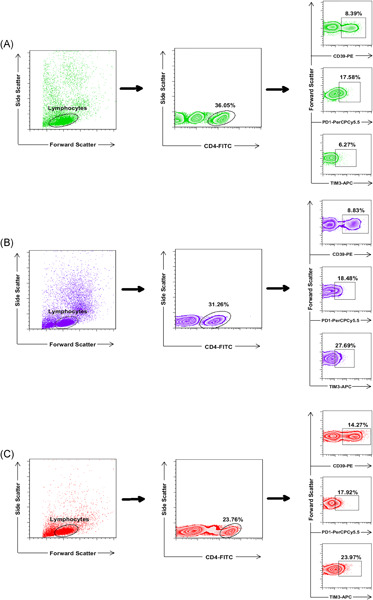
TIM-3 as a potential exhaustion marker in CD4+ T cells of COVID-19 patients
- Pages: 1707-1715
- First Published: 09 September 2021
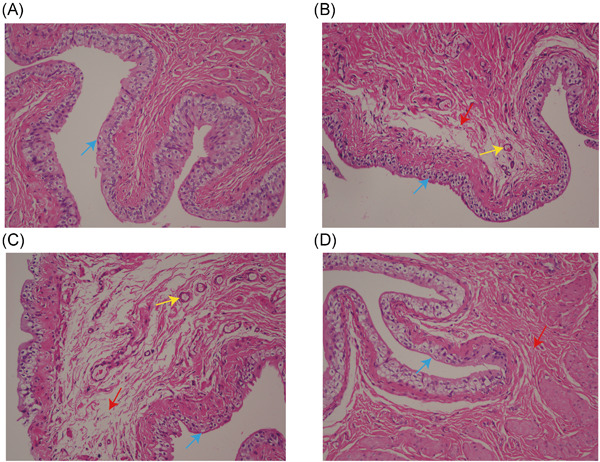
Airway cilia recovery post lung transplantation
- Pages: 1716-1723
- First Published: 21 September 2021
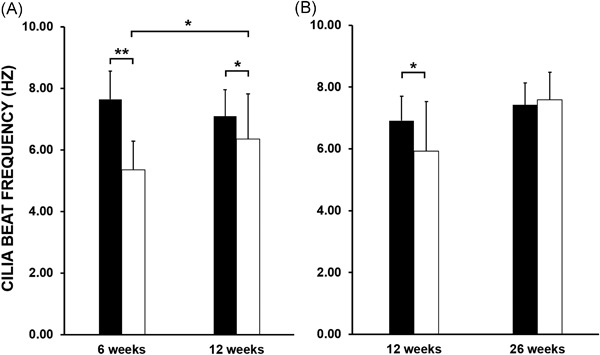
Reduced airway cilia function is evident in the first 12 weeks post lung transplant, with both CBP and CBF returning to levels of function indistinguishable to the patients' upper airway cilia beyond this time. This difference may be a cause for increased risk of airway infection during this period.
Proteomic profiling of saliva reveals association of complement system with primary Sjögren's syndrome
- Pages: 1724-1739
- First Published: 13 September 2021
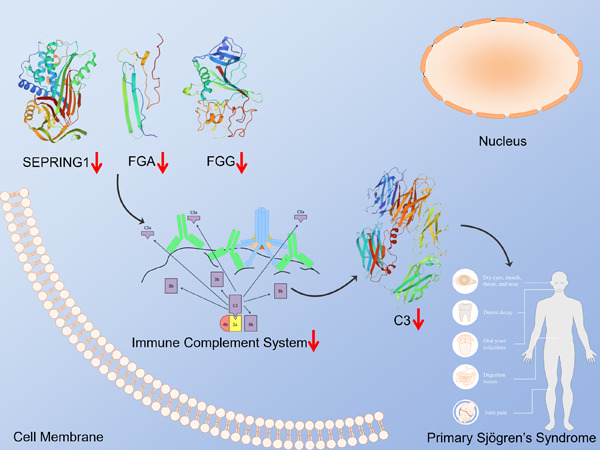
To summarize our findings, Serpin family G member 1 (SERPING1), C3, fibrinogen alpha (FGA), fibrinogen gamma (FGG), and complement factor H (CFH) were significantly decreased in the saliva of ESS model mice and may therefore be potential diagnostic biomarkers of pSS. The role of these proteins in pSS and other autoimmune diseases (especially systemic lupus erythematosus) will have to be verified in experimental and cohort studies before possible applications in clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Development and characterization of a unique anti-IgE mouse monoclonal antibody cross-reactive between human and canine IgE
- Pages: 1740-1748
- First Published: 17 September 2021
Interleukin-6 receptor alpha and CD27 discriminate intratumoral T helper 17 subpopulations with distinct functional properties in a mouse lung cancer model
- Pages: 1749-1758
- First Published: 27 September 2021
Cancer-testis antigen ACRBP expression and serum immunoreactivity in ovarian cancer: Its association with prognosis
- Pages: 1759-1770
- First Published: 16 September 2021
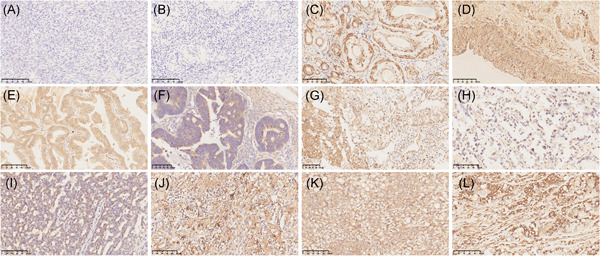
(1) Acrosin binding protein (ACRBP) was a restricted expression cancer-testis antigen in cancers. Its expression was markedly upregulated in ovarian cancer tissues and induced humoral immune response in patients with ovarian cancer. Serological detection of ACRBP had high sensitivity in ovarian cancer. (2) The overexpression of ACRBP was associated with advanced stage of tumor, metastasis, and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. High ACRBP expression was associated with a poor clinical outcome. (3) ACRBP also displayed inherent immunogenicity. Together with its restricted expression pattern and high specificity to cancer cells, ACRBP could be a potential target for prognostic evaluation and tumor-specific antigen-based immunotherapy for patients with ovarian cancer.
A single-center, open-label, randomized cross-over study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of once-daily prolonged-release formulations of tacrolimus in de novo liver transplant recipients
- Pages: 1771-1780
- First Published: 24 September 2021
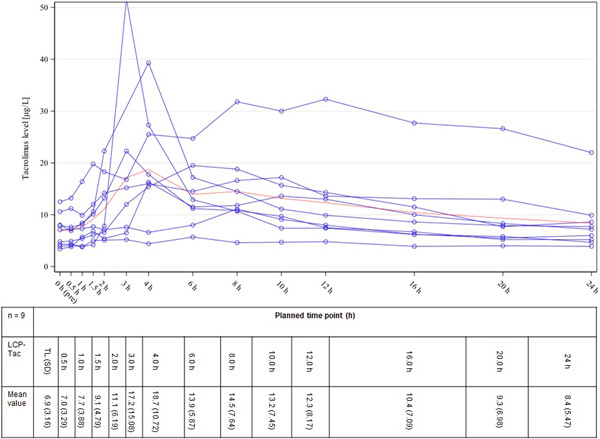
This is a single-center, open-label, randomized cross-over pharmacokinetic (PK) study, designed to compare LCP-Tac with the established once-daily prolonged-release formulation of tacrolimus (PR-Tac) in adult de novo liver transplant recipients. As a result, we have more consistent drug exposure for Envarsus® and, in particular, a lower medication requirement to achieve equivalent trough levels.
SHORT REPORTS
High-resolution HLA genotyping identifies alleles associated with severe COVID-19: A preliminary study from India
- Pages: 1781-1785
- First Published: 21 July 2021
Are hematopoietic cell transplant recipients with Gram-negative bacteremia spending more time outpatient while on intravenous antibiotics? Addressing trends over 10 years at a single center
- Pages: 1786-1794
- First Published: 21 July 2021
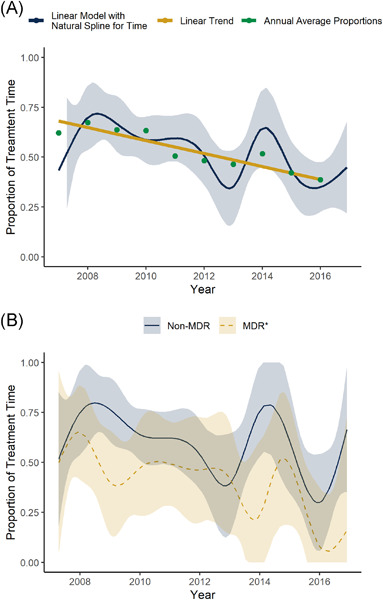
Over a 10-year period, Gram-negative rod bacteremia (GNRB) incidence and the proportion of GNRBs treatment time spent outpatient declined significantly. However, among patients with similar posttransplant complications, no decline in outpatient treatment was observed. This suggests that the decline in outpatient antibiotic days may be linked to increased frequency of posttransplant complications.
The future of tumor vaccines in the post-COVID-19 era—Current challenges
- Pages: 1795-1797
- First Published: 02 September 2021
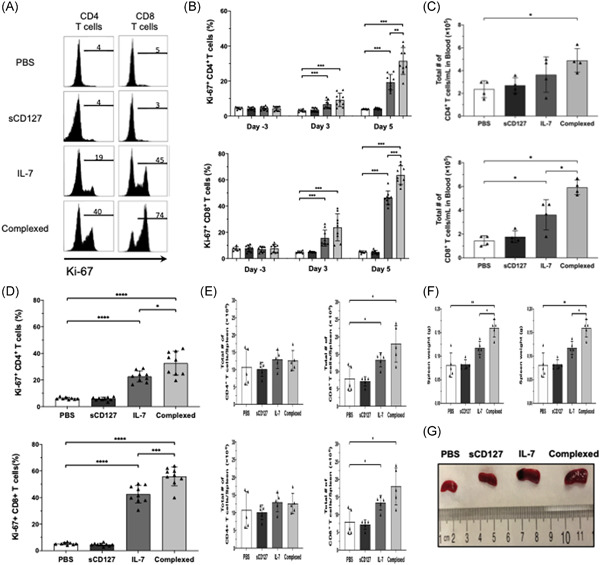
Soluble CD127 potentiates IL-7 activity in vivo in healthy mice
- Pages: 1798-1808
- First Published: 15 September 2021
A single dose of the Biontech/Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine protected elderly residents from severe COVID-19 during a SARS-coronavirus-2 outbreak in a senior citizen home in Germany
- Pages: 1809-1814
- First Published: 16 September 2021
Background: A total of 62/66 residents in a senior citizen home in Bremen, Germany, received the first dose of the Biontech/Pfizer vaccine BNT162b2 on December 27th 2020. After routine SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests showed positive results on January 5th, all residents and staff were tested by RT-PCR.
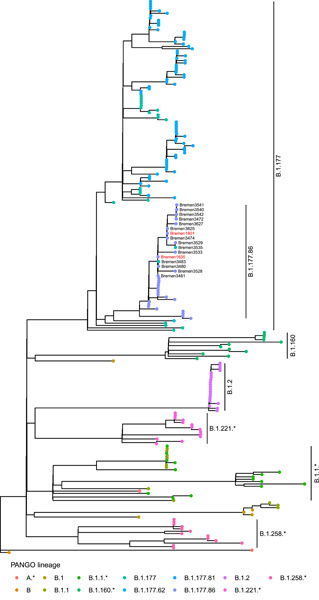
Results: Nine staff members and 23 residents had a positive result. PCR positive staff members reported mild to severe COVID-19 symptoms, one was hospitalized. None of them had been vaccinated. In contrast, the vaccinated residents reported no or only mild symptoms. Sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 genomes of infected individuals revealed a monophyletic origin of the outbreak within the PANGO lineage B.1.177.86.
Conclusions: In summary, our data show that partial vaccination prevented severe COVID-19 among the residents during this local SARS-CoV-2 outbreak, suggesting a high effectiveness of even a single vaccine dose, but also emphasize that asymptomatic individuals might still be carriers/spreaders.
Difference in the plasma level of miR-628-3p in atopic dermatitis patients with/without atopic keratoconjunctivitis
- Pages: 1815-1819
- First Published: 21 September 2021