Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARY
Pleomorphicskin eruptions in a COVID-19 affected patient: Case report and review of the literature
- Pages: 617-621
- First Published: 04 May 2021
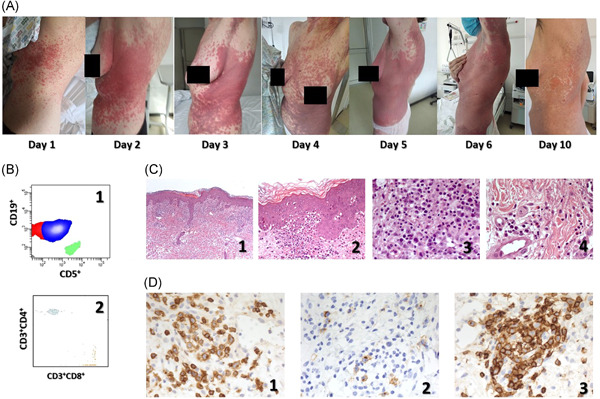
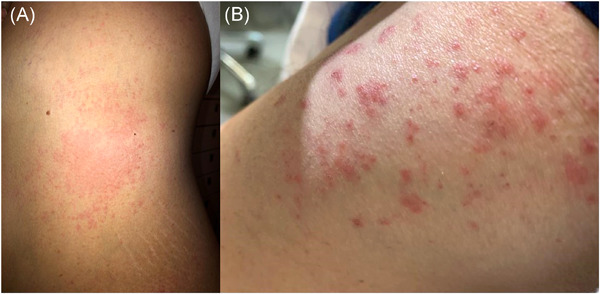
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19), during its course, may involve several organs, including the skin with a petechial skin rash, urticaria and erythematous rash, or varicella-like eruption, representing an additional effect of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, as commonly observed in other viral diseases. Considering that symptomatic patients with COVID-19 generally undergo multidrug treatments, the occurrence of a possible adverse drug reaction presenting with cutaneous manifestations should be contemplated. Pleomorphic skin eruptions occurred in a 59-year-old Caucasian woman, affected by a stable form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, treated with a combination of hydroxychloroquine sulfate, darunavir, ritonavir, sarilumb, omeprazole, ceftriaxone, high-flow oxygen therapy devices, filgrastim (Zarzio®) as a single injection, and enoxaparin. The patient stopped all treatment but oxygen and enoxaparin and received a high-dose Desametasone with complete remission of dermatological impairment in 10 days. It is very important to differentially diagnose COVID-19 disease-related cutaneous manifestations, where is justified to continue the multi-drug antiviral treatment, from those caused by an adverse drug reaction, where it would be necessary to identify the possible culprit drug and to start appropriate antiallergic treatment.
Skin rashes after SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: which relationship, if any?
- Pages: 622-623
- First Published: 19 June 2021
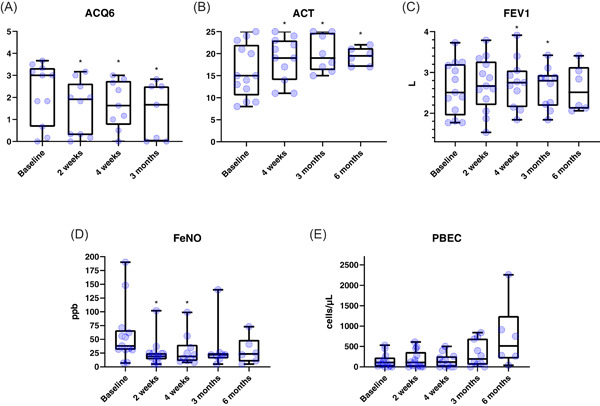
Dupilumab rapidly improves asthma control in predominantly anti-IL5/IL5R pretreated Austrian real-life severe asthmatics
- Pages: 624-627
- First Published: 07 May 2021
The first non-radiographic axial spondyloarthrits with COVID-19
- Pages: 628-631
- First Published: 12 May 2021
COVID-19 infection in CVID patients: What we know so far
- Pages: 632-634
- First Published: 12 May 2021
REVIEW ARTICLES
Nasal nitric oxide testing for allergic rhinitis patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 635-648
- First Published: 05 May 2021
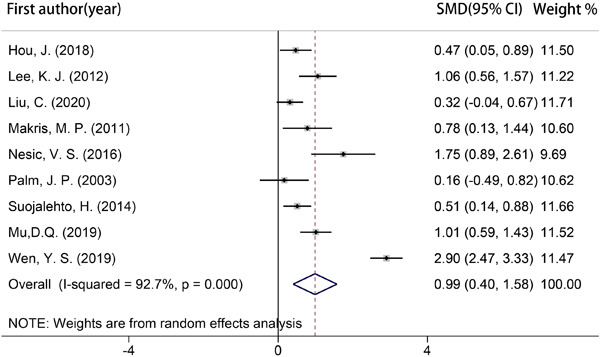
Graphical abstract
The meta analysis shows that nasal nitric oxide (nNO) in allergic rhinitis (AR) is significantly higher than healthy people and nonallergic rhinitis. However sinusitis, nasal polysis and marked ostial obstruction should be taken into consideration before nNO is applied to detect AR.
The complex role of AIM2 in autoimmune diseases and cancers
- Pages: 649-665
- First Published: 20 May 2021
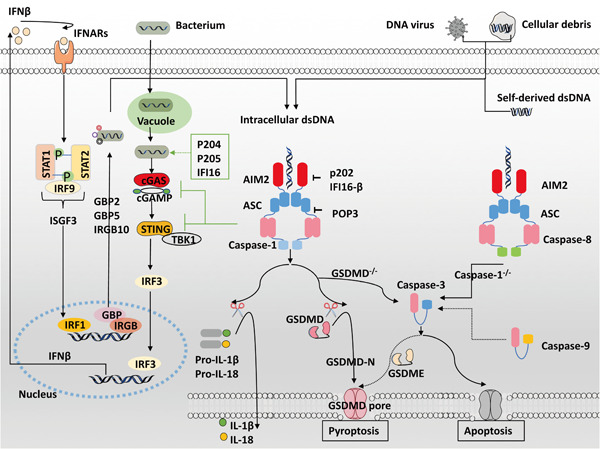
Herein, we provide an overview of the emerging research progress on the function and regulatory pathway of absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) in innate and adaptive immune cells, as well as tumor cells, and discuss its pathogenic role in autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, primary Sjogren's syndrome, and cancers, such as melanomas, non-small-cell lung cancer, colon cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, renal carcinoma, and so on, hopefully providing potential therapeutic and diagnostic strategies for clinical use.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
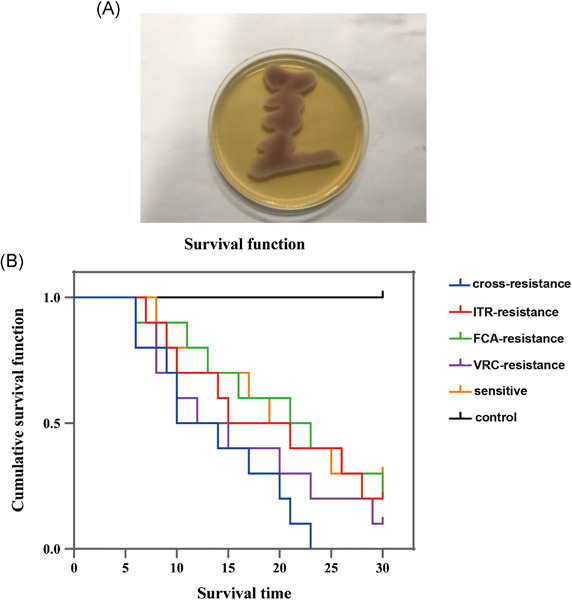
The effects of secreted aspartyl proteinase inhibitor ritonavir on azoles-resistant strains of Candida albicans as well as regulatory role of SAP2 and ERG11
- Pages: 667-680
- First Published: 05 May 2021
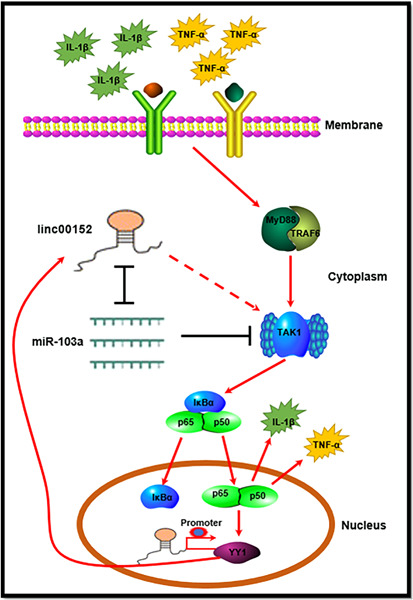
LncRNA linc00152/NF-κB feedback loop promotes fibroblast-like synovial cells inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis via regulating miR-103a/TAK1 axis and YY1 expression
- Pages: 681-693
- First Published: 01 June 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCHS
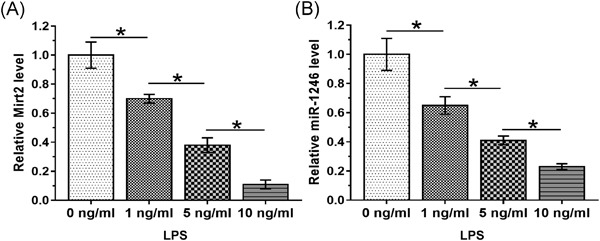
lncRNA Mirt2 upregulates miR-1246 through methylation to suppress LPS-induced lung cell apoptosis
- Pages: 695-701
- First Published: 04 May 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
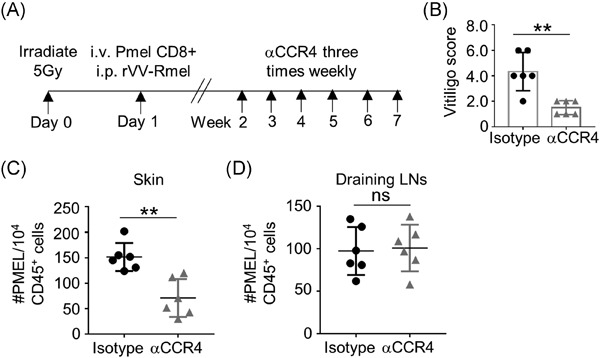
CCL17-CCR4 axis contributes to the onset of vitiligo in mice
- Pages: 702-709
- First Published: 02 June 2021
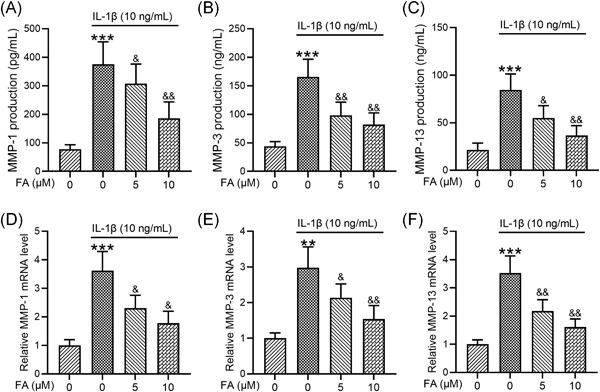
Ferulic acid suppresses interleukin-1β-induced degeneration of chondrocytes isolated from patients with osteoarthritis through the SIRT1/AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway
- Pages: 710-720
- First Published: 02 June 2021
Donor Treg expansion by liposomal α-galactosylceramide modulates Tfh cells and prevents sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease
- Pages: 721-733
- First Published: 04 May 2021

This study showed that multiple administrations of liposomal α-Galactosylceramide (α-GC) modulated both host- and donor-derived invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell homeostasis and induced an early expansion of donor Tregs. This was followed by the decreased levels of CXCL13 in plasma and follicular helper T cells in lymph nodes, which inhibited germinal center formation, resulting in the efficient prevention of sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)."
IL-13 modulates ∆Np63 levels causing altered expression of barrier- and inflammation-related molecules in human keratinocytes: A possible explanation for chronicity of atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 734-745
- First Published: 01 April 2021
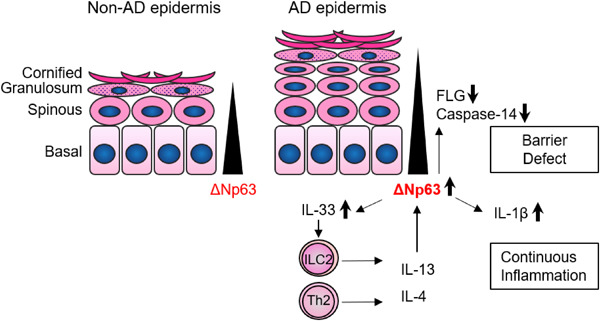
IL-13 exposure inhibits keratinocyte differentiation by interrupting ΔNp63 downregulation. Decreased filaggrin and caspase-14 expression further disturb epidermal barrier integrity, whereas increased IL-1β and IL-33 enhance inflammation. This IL-13–ΔNp63 axis may constitute a vicious cycle, partly explaining the chronicity of atopic dermatitis.
Titanium dioxide nanotubes promote M2 polarization by inhibiting macrophage glycolysis and ultimately accelerate endothelialization
- Pages: 746-757
- First Published: 09 April 2021
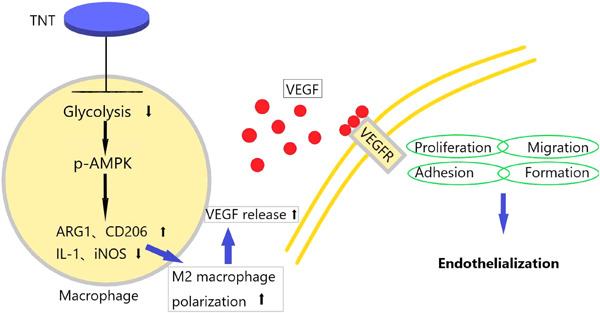
Biofunctionalization titanium with nanotube could inhibit macrophage glycolysis, reduce inflammatory factor release and promote M2 polarization by activating the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway. And endothelialization was accelerated in vitro. Our result demonstrated that titanium nanotube could act as a potential approach to biofunctionlize titanium-based prosthetic valves for endothelialization
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is not pathogenic in lupus nephritis
- Pages: 758-770
- First Published: 07 May 2021
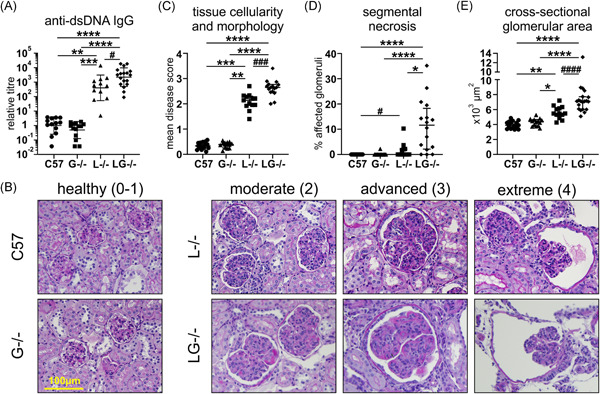
Graphical abstract
Lupus nephritis is perpetuated by unrestrained inflammation, potentially driven by the hematopoietic growth factor granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). Lupus-prone Lyn-deficient mice lacking G-CSF were not protected from the development of autoimmunity and, in fact, exhibited exacerbated indices of kidney pathology. Furthermore, G-CSF levels in human serum were not elevated in systemic lupus erythematosus patients or in correlation with renal disease, overall indicating that G-CSF is not a major pathogenic factor in lupus nephritis.
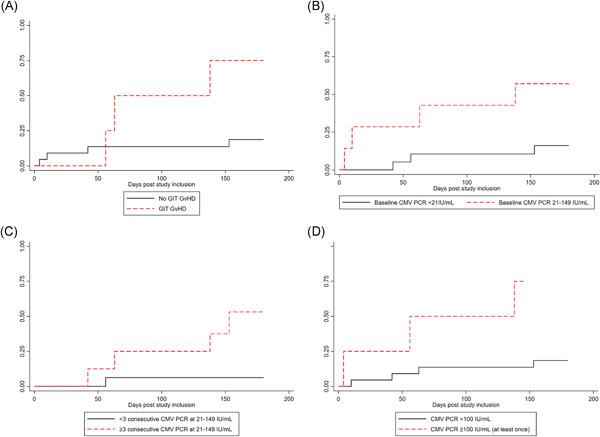
Predictors of breakthrough clinically significant cytomegalovirus infection during letermovir prophylaxis in high-risk hematopoietic cell transplant recipients
- Pages: 771-776
- First Published: 05 May 2021
Inhibitory effect of HTLV-1 infection on the production of B-cell activating factors in established follicular dendritic cell-like cells
- Pages: 777-791
- First Published: 04 May 2021
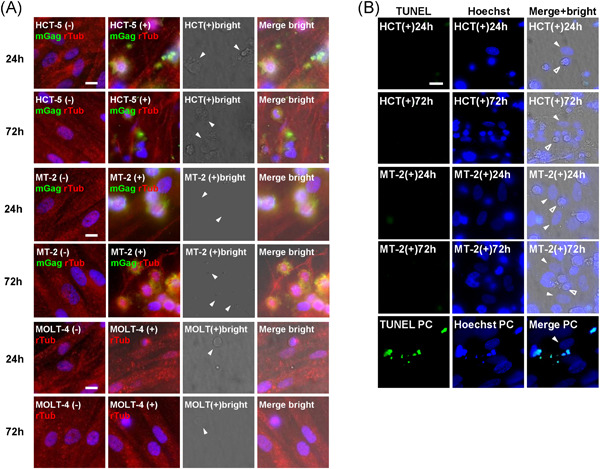
Graphical abstract
Expression of B-cell activating factor (BAFF) was upregulated by addition of interferons. Although BAFF expression was inhibited by addition of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infected cell line, HCT-5 and MT-2, the level was not inhibited by addition of control cell line, MOLT-4.
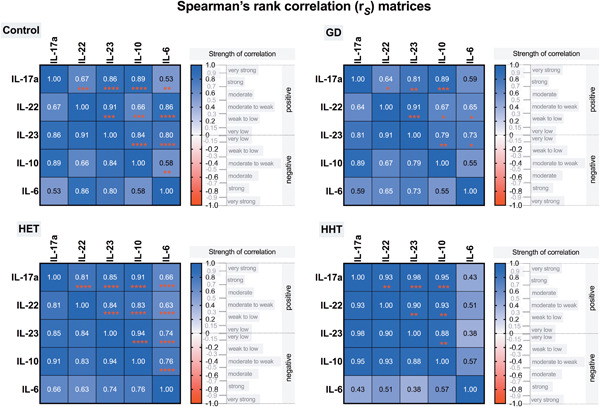
Plasma levels of Th17-associated cytokines and selenium status in autoimmune thyroid diseases
- Pages: 792-803
- First Published: 04 May 2021
The PI3K pathway as a therapeutic intervention point in inflammatory bowel disease
- Pages: 804-818
- First Published: 04 May 2021
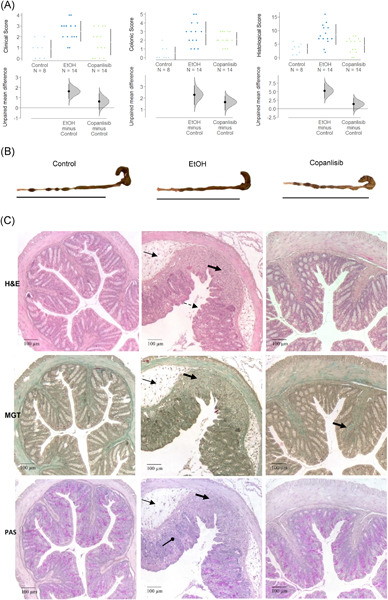
Graphical abstract
In response to an inflammatory assault T cells favor glycolysis to ensure swit energy supply required for proliferation, migration and secretion of cytokines, chemokines and growth factors. Therefore, targetinginflammation has come into focus of interest as a therapeutical intervention point in chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. The phosphoinositide-3-kinases inhibitor copanlisib inhibits glycolysis and suppresses inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis.
Genomic analysis of host gene responses to cerebral Plasmodium falciparum malaria
- Pages: 819-826
- First Published: 04 May 2021
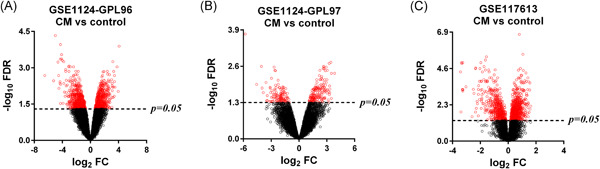
Graphical abstract
The present study used an innovative genomic analysis strategy to explored gene coexpression networks associated with cerebral malaria (CM) pathogenesis and identified several key host genes. The findings will be of interest to host–parasite interaction study and would be of assistance to further investigate CM pathology.
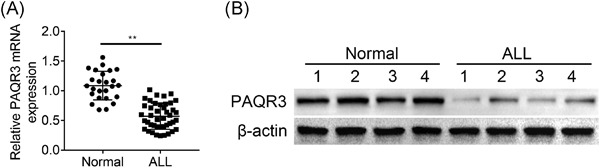
PAQR3 inhibits proliferation and aggravates ferroptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia through modulation Nrf2 stability
- Pages: 827-839
- First Published: 06 May 2021
Expression of OPN3 in acral lentiginous melanoma and its associated with clinicohistopathologic features and prognosis
- Pages: 840-850
- First Published: 06 May 2021
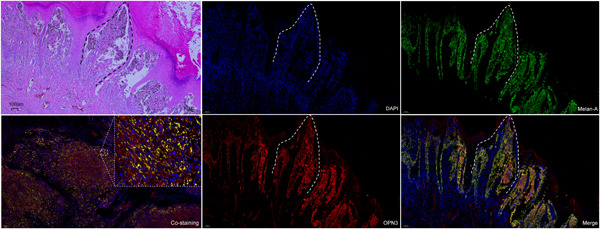
Graphical abstract
Acral lentiginous melanoma has a poor prognosis due to delayed diagnosis aggressive biological behavior. However, its molecule features associated with prognosis remains largely unknown. We have detected the expression characteristic of OPN3 in ALMs, and demonstrated that high OPN3 is a negative prognostic indicator.
Parameters associated with diagnosis of COVID-19 in emergency department
- Pages: 851-861
- First Published: 07 May 2021
Associations between maternal and environmental exposures on atopic disease in the offspring of mothers with asthma
- Pages: 862-870
- First Published: 19 June 2021
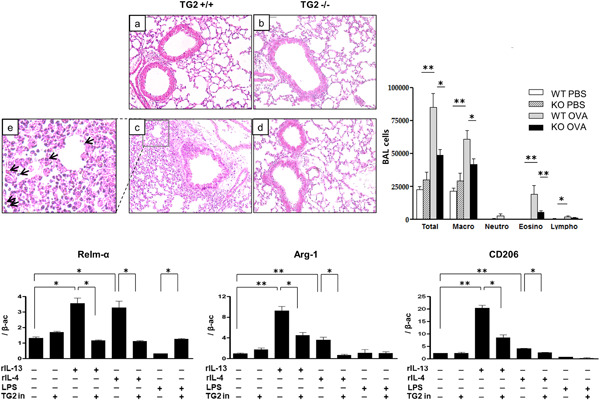
Tranglutaminase 2 contributes to the asthmatic inflammation by modulating activation of alveolar macrophages
- Pages: 871-882
- First Published: 04 May 2021
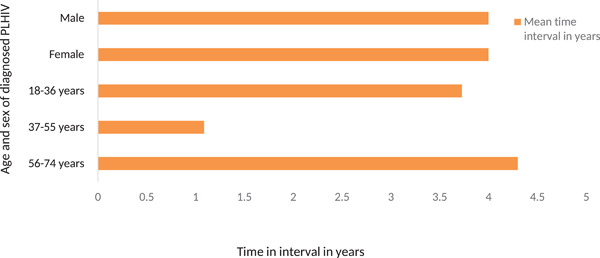
Baseline CD4 count and the time interval between the initial HIV infection and diagnosis among PLHIV in Bhutan
- Pages: 883-890
- First Published: 04 May 2021
CCL17-expressing dendritic cells in the intestine are preferentially infected by Salmonella but CCL17 plays a redundant role in systemic dissemination
- Pages: 891-904
- First Published: 04 May 2021
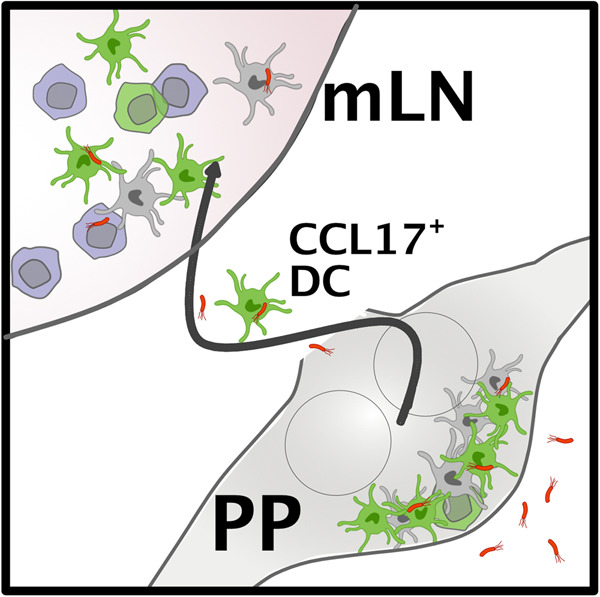
Oral infection with Salmonella enhances the frequency of dendritic cells expressing the pro-inflammatory chemokine CCL17, promoting dendritic cell–T cell interaction. In Peyer's patches, CCL17-expressing cells colocalize with Salmonella and Salmonella-containing cells in mesenteric lymph nodes are preferentially CCL17-positive. While CCL17-expressing cells participate in the early dissemination of Salmonella, CCL17 itself appears to play a redundant role in this process.
A simple, sensitive, and low-cost FACS assay for detecting antibodies against the native SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
- Pages: 905-917
- First Published: 12 May 2021
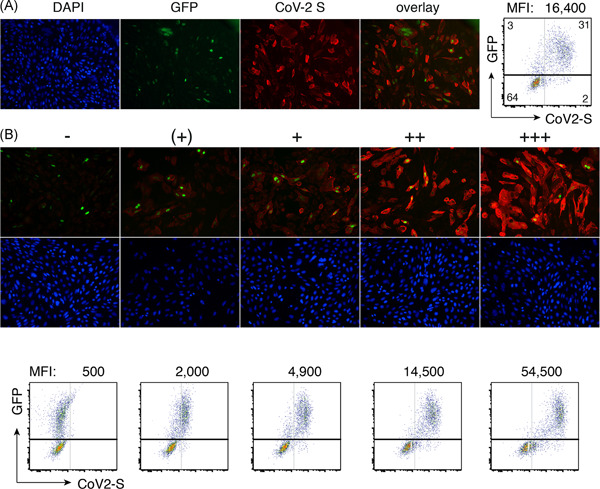
We report a low-cost FACS assay for antibodies against the native severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike protein that does not require recombinant proteins or infectious virus. We demonstrate the utility of the assay by assessing antibody responses of hospitalized patients, health care personnel, and house-holds of coronavirus diasease 2019 + individuals and their co-quarantined room mates in the city state of Hamburg
Early introduction oral immunotherapy for IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy: A follow-up study confirms this approach as safe and appealing to parents
- Pages: 918-922
- First Published: 18 May 2021
Comprehensive analysis of Syk gene methylation in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 923-931
- First Published: 12 May 2021
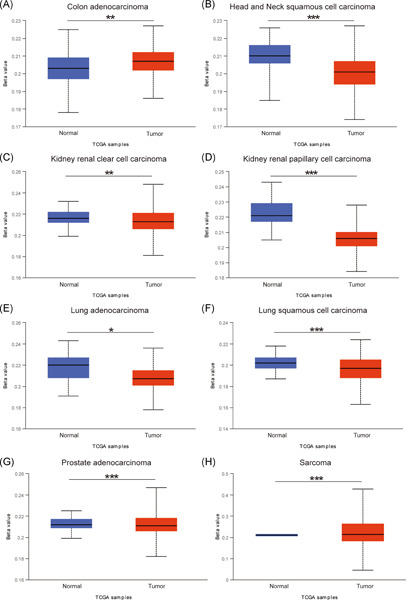
In our study, we aimed to research the correlation of methylation level of Syk and metastasis of colorectal cancer (CRC). We further used Decitabine to restore the expression of Syk in CRC cells. The results revealed that Decitabine could restore the expression of Syk and therefore prohibited the migration and invasion of CRC cells.
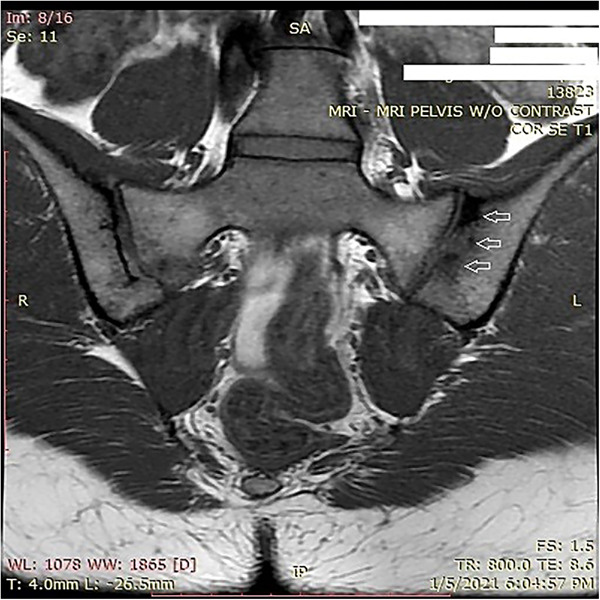
Activation of the cGAS–STING signaling pathway in adenomyosis patients
- Pages: 932-942
- First Published: 19 May 2021
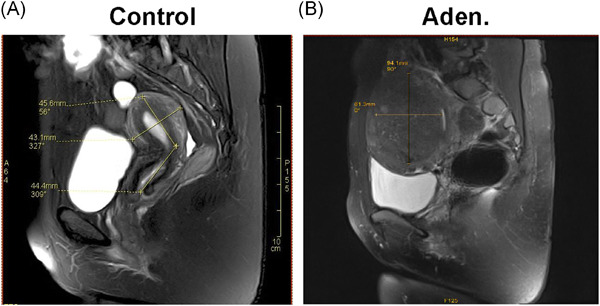
Representative pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) from the control and adenomyosis patients. A. In a control patient (control), the MRI picture shows the normal uterine, with dimensions of a 45.6-mm length and 43.1-mm width crossing the whole uterus. B. In an adenomyosis patient (Aden.), the MRI scan shows typical focal adenomyosis, with a 40.6-mm length and 56.9-mm width of pathological foci located in the uterine junctional zone (indicated with a red star).
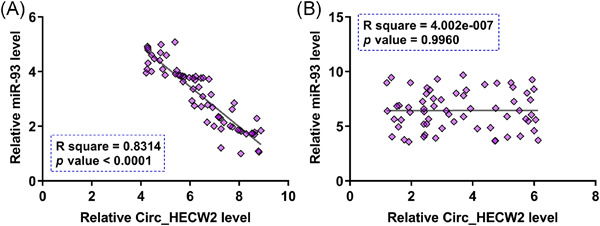
Circ_HECW2 regulates LPS-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes via miR-93 methylation
- Pages: 943-949
- First Published: 02 June 2021
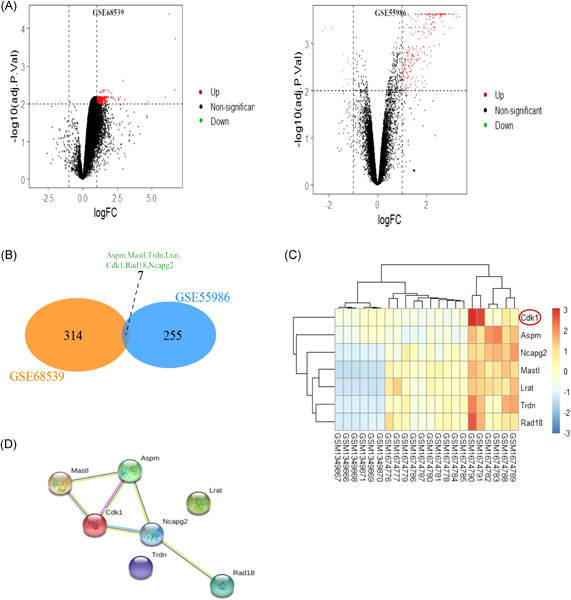
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 shows to be a potential genetic target for chemical cystitis
- Pages: 950-958
- First Published: 03 June 2021
Polydatin has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in LPS-induced macrophages and improves DSS-induced mice colitis
- Pages: 959-970
- First Published: 19 May 2021
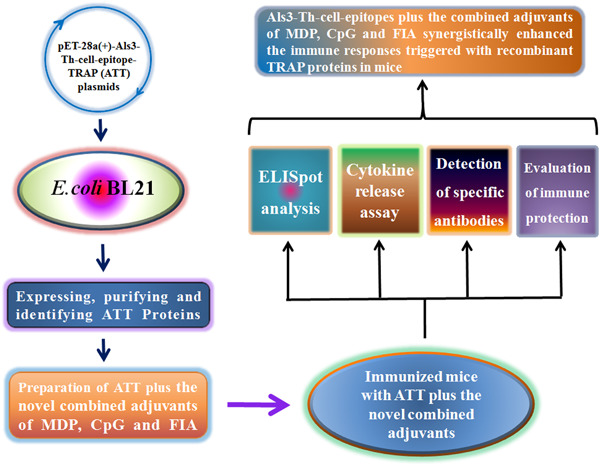
Als3-Th-cell-epitopes plus the novel combined adjuvants of CpG, MDP, and FIA synergistically enhanced the immune response of recombinant TRAP derived from Staphylococcus aureus in mice
- Pages: 971-983
- First Published: 19 May 2021
Tick salivary gland extract induces alpha-gal syndrome in alpha-gal deficient mice
- Pages: 984-990
- First Published: 25 May 2021
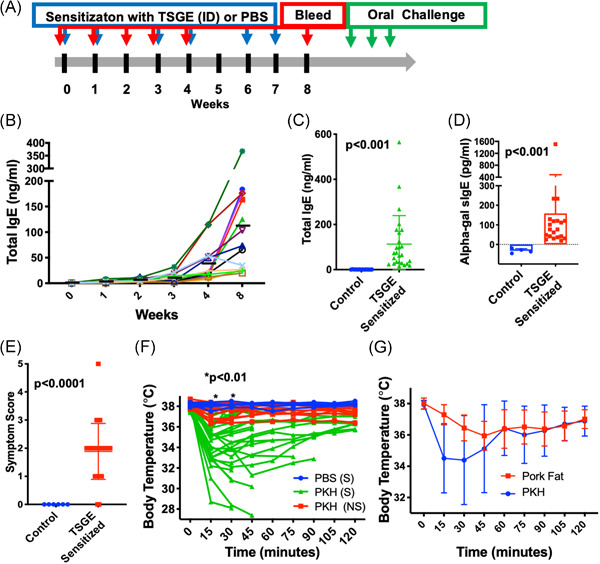
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS) is characterized by delayed hypersensitivity to non-primate mammalian meat in people having specific IgE (sIgE) to the oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose and has been linked to tick bites from Amblyomma americanum (Aa) in the U.S. We demonstrate that intradermal injection of Aa tick salivary gland extract (TSGE) in alpha-gal knockout (AGKO) mice induce alpha-gal sIgE production and mice displayed moderate clinical allergic signs along with a drop in core body temperature as an objective measure of a systemic allergic reaction. Further, this model recapitulates several aspects of red meat allergy seen in the humans and will be used to mechanistically study this novel food allergy and model therapeutic approaches to treat this disease.
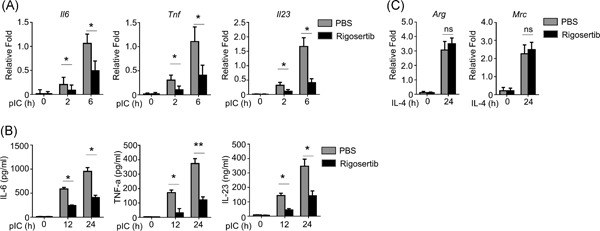
Rigosertib inhibits MEK1–ERK pathway and alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis
- Pages: 991-999
- First Published: 01 June 2021
Association between neutrophils and renal impairment of rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Pages: 1000-1008
- First Published: 25 May 2021
In this present study, neutrophil greater than 7.5 × 109/L may be associated with a high risk of renal impairment in RA. We also found that UA > 360 μmol/L and hemoglobin less than 120 g/L independently associated with a higher risk of renal impairment in RA patients. Although more prospective studies are needed to verify our results, based on the above data, we believe that continuous monitoring of these risk factors in RA patients is necessary and it could be used for early detection and identification of changes in GFR, allowing doctors to treat patients with potential kidney damage promptly.
Time-related variation in IgG subclass concentrations in a group of healthy Danish adults
- Pages: 1009-1015
- First Published: 02 June 2021
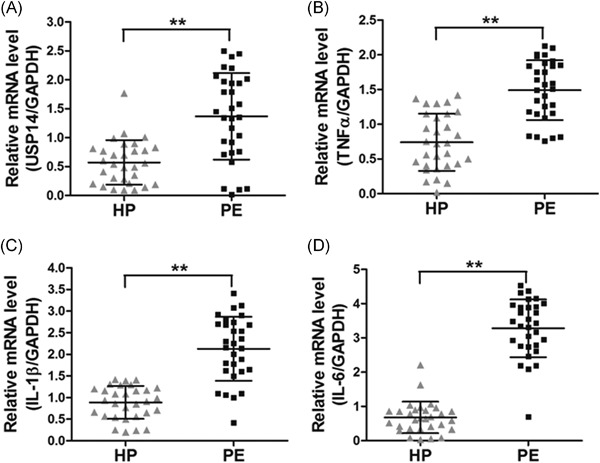
Inhibiting USP14 ameliorates inflammatory responses in trophoblast cells by suppressing MAPK/NF-κB signaling
- Pages: 1016-1024
- First Published: 05 June 2021
Neutrophil extracellular traps induce thrombogenicity in severe carotid stenosis
- Pages: 1025-1036
- First Published: 08 June 2021
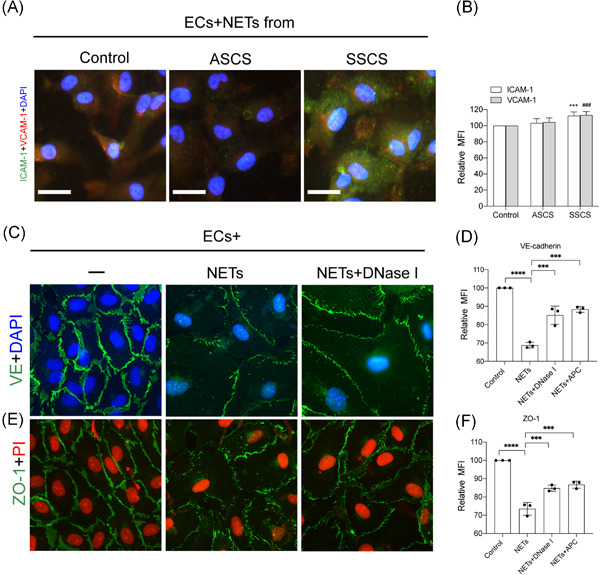
The plasma levels of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are increased in samples from severe carotid stenosis patients. • Platelets (PLT) initiate the formation of NETs in severe carotid stenosis patients. • NETs induce hypercoagulation state in severe carotid stenosis patients and convert endothelial cells (ECs) to procoagulant phenotype.
Long-coronavirus disease among people living with HIV in western India: An observational study
- Pages: 1037-1043
- First Published: 02 June 2021
Identification and validation of immune-related lncRNA prognostic signatures for melanoma
- Pages: 1044-1054
- First Published: 02 June 2021
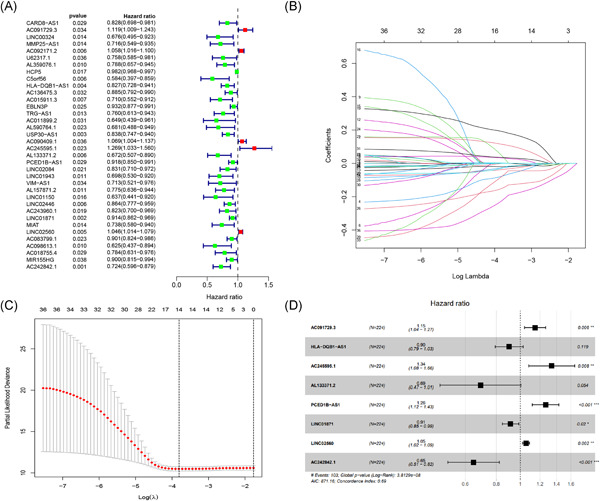
We applied univariate Cox, LASSO, and multivariate Cox regression analysis to identify immune-related lncRNAs with remarkable prognostic potential and constructed a multiple immune-related lncRNAs signature to predict melanoma' prognosis. lncRNA signatures of immune-related offers prognostic markers and potential immunotherapeutic targets for melanoma.
Serum triglyceride levels and related factors as prognostic indicators in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study
- Pages: 1055-1060
- First Published: 08 July 2021
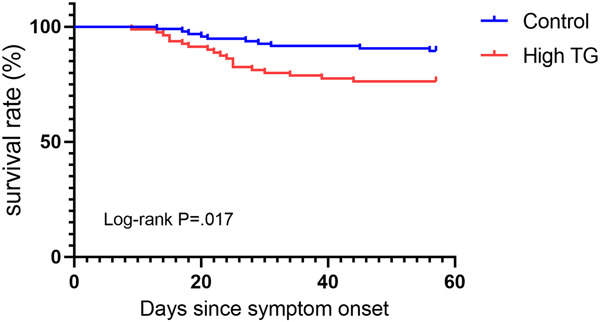
The triglycerides (TG) level in coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients is correlated to serum ferritin and IL-10 levels, which reflects the activation of macrophages. It is suggested that COVID-19 patients be monitored for elevated TG as both a prognostic indicator and potential therapeutic target for COVID-19.
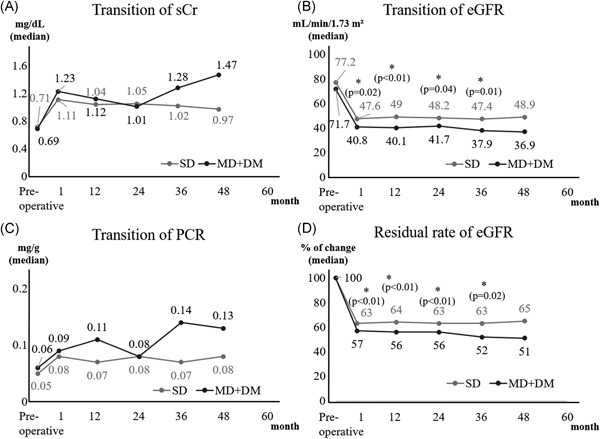
Feasible kidney donation with living marginal donors, including diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 1061-1068
- First Published: 08 June 2021