Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
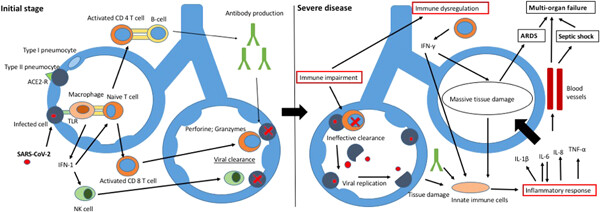
Age-related differences in the immune response could contribute to determine the spectrum of severity of COVID-19
- Pages: 331-339
- First Published: 10 February 2021
Current research status of HLA in immune-related diseases
- Pages: 340-350
- First Published: 03 March 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
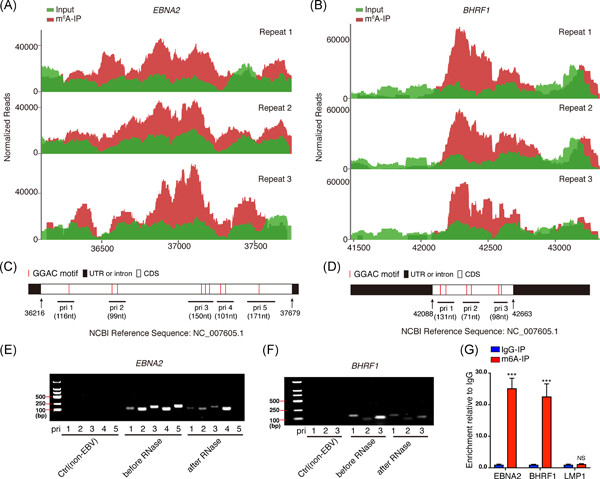
RNA m6A methylation regulates virus–host interaction and EBNA2 expression during Epstein–Barr virus infection
- Pages: 351-362
- First Published: 12 January 2021
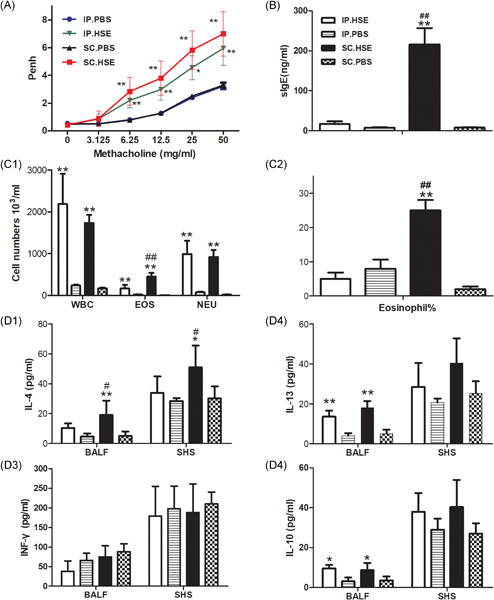
Ruxolitinib inhibits poly(I:C) and type 2 cytokines-induced CCL5 production in bronchial epithelial cells: A potential therapeutic agent for severe eosinophilic asthma
- Pages: 363-373
- First Published: 03 February 2021
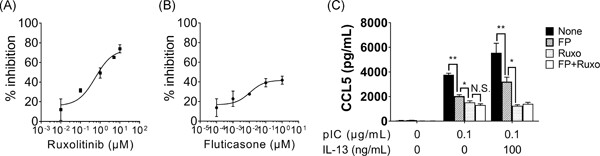
First, we focused on whether treatment with a virus-associated ligand and type-2 cytokine can synergistically stimulate CCL5 production in bronchial epithelial cells, in which we confirmed the synergistic effect. Second, we evaluated the mechanisms underlying the synergistical CCL5 production and found that the JAK1 is a novel therapeutic target for severe eosinophilic asthma. Finally, we have demonstrated that ruxolitinib is a potential therapeutic agent for severe corticosteroid-resistant asthma with airway eosinophilia and persistent Th2-type inflammation.
Systemic immune responses in patients with early localized or early disseminated Borrelia afzelii lyme borreliosis
- Pages: 375-387
- First Published: 31 December 2020
Serum proteome-wide identified ATP citrate lyase as a novel informative diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in pediatric sepsis: A pilot study
- Pages: 389-397
- First Published: 30 December 2020
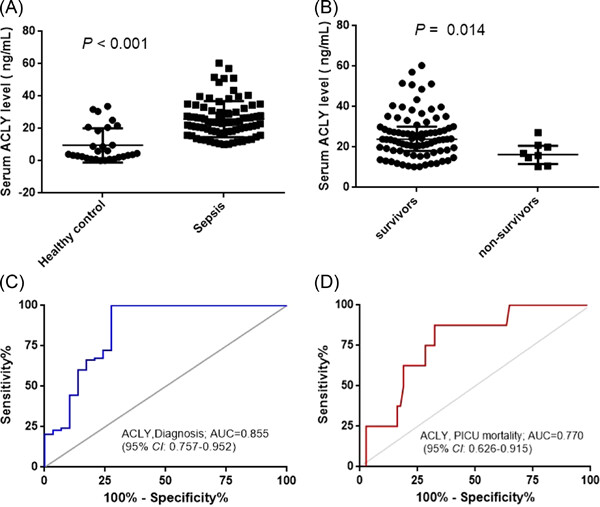
ACLY is firstly identified in sera of patients with sepsis. Serum ACLY level is an additional diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in pediatric patients with sepsis.The relationship between serum ACLY and IL-18 and underlying mechanisms involved in pathophysiology of sepsis need further study in the future.
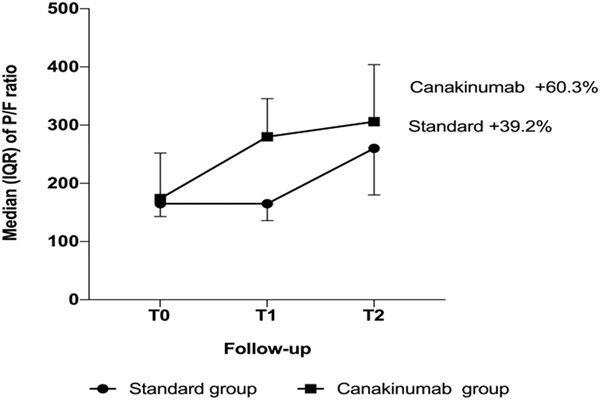
Efficacy of canakinumab in mild or severe COVID-19 pneumonia
- Pages: 399-405
- First Published: 19 January 2021
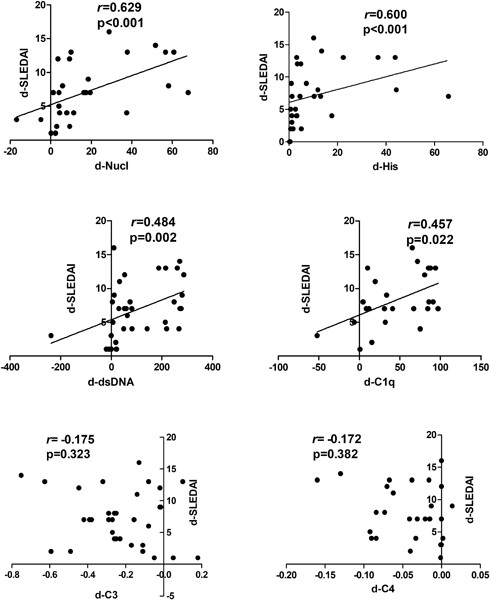
Anti-dsDNA, anti-nucleosome, anti-C1q, and anti-histone antibodies as markers of active lupus nephritis and systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity
- Pages: 407-418
- First Published: 20 January 2021
Disease-duration based comparison of subsets of immune cells in SARS CoV-2 infected patients presenting with mild or severe symptoms identifies prognostic markers for severity
- Pages: 419-434
- First Published: 16 January 2021
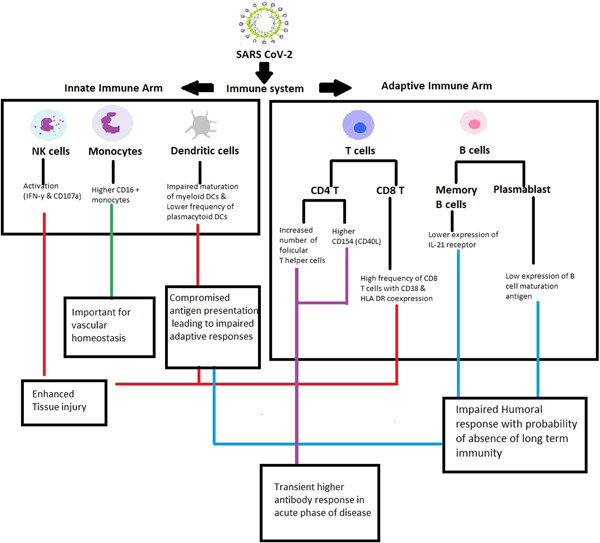
Understanding pathogenesis of severity in current SARS-CoV2 pandemic is of prime importance. Another concern is the recent observations (including ours) of early, higher neutralizing antibody titers in severe disease. India is reporting >80,000/day for several weeks now. Identification of prognostic markers for severity may help identifying “extra-care-needed” patients. As a first step, this flow-cytometry based study was planned to understand (1) differences in immunologic modulations in patients with mild and severe disease (2) if we can identify early events associated with severity (3) prognostic markers for severity (4) association of functionality of immune cells with higher antibody titers in severe disease.
Detection of antigens and anti-Toxocara canis antibodies in children with different asthma severities
- Pages: 435-442
- First Published: 08 February 2021
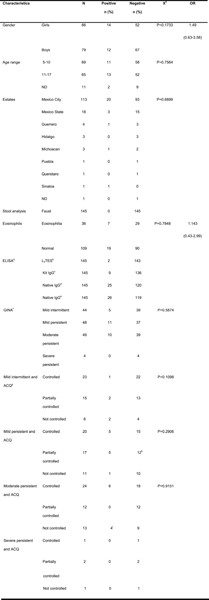
Graphical abstract
We performed two assays aimed to detect antigens from Toxocara third-stage larvae, and to detect anti-T-canis immunoglobulin G in children with asthma, to infer the status of the infection and its impact on the asthma severity. We detected patients with Toxocara antigens (recent infection); antigens and antibodies (active larva migrans) and only antibodies (immunological memory). There was no significant association among asthma severity and detection of antigens or antibodies against T. canis.
Establishment and characterization of murine models of asthma and subcutaneous immunotherapy for Humulus pollen allergy
- Pages: 443-455
- First Published: 12 January 2021
Enhanced airway hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic children and mice with A(H1N1)pdm09 infection
- Pages: 457-465
- First Published: 20 January 2021
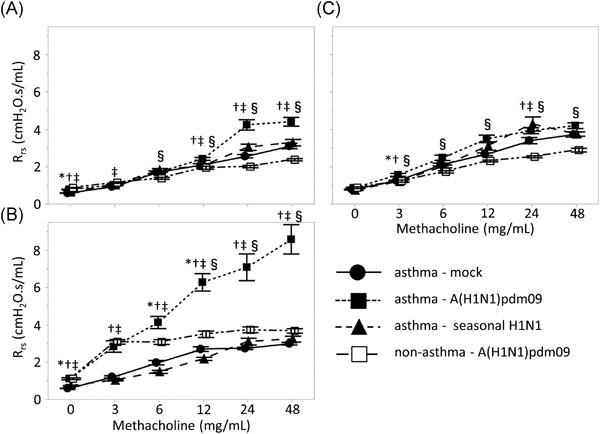
AHR was significantly enhanced in asthmatic mice with A(H1N1)pdm09 infection compared with seasonal influenza infection. AHR and pulmonary inflammation of A(H1N1)pdm09-infected mice showed peak at 7 days post infection and they were improved by 10 days postinfection. Also, AHR in asthmatic children after A(H1N1)pdm09 infection were temporarily increased, and alleviated by 3 months after discharge.
Development of a prognostic index based on immunogenomic landscape analysis in glioma
- Pages: 467-479
- First Published: 27 January 2021
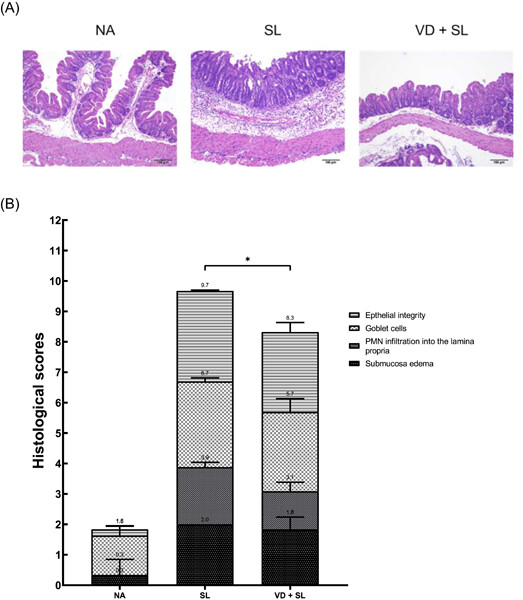
Active vitamin D3 attenuates the severity of Salmonella colitis in mice by orchestrating innate immunity
- Pages: 481-491
- First Published: 08 February 2021
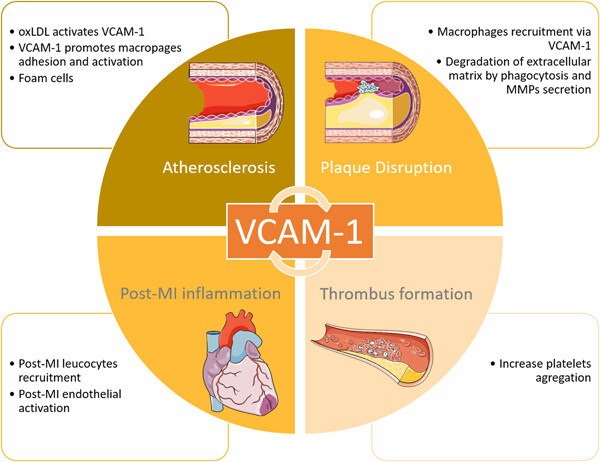
Kinetics and prognostic value of soluble VCAM-1 in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients
- Pages: 493-501
- First Published: 08 February 2021
Oral birch pollen immunotherapy with apples: Results of a phase II clinical pilot study
- Pages: 503-511
- First Published: 23 February 2021
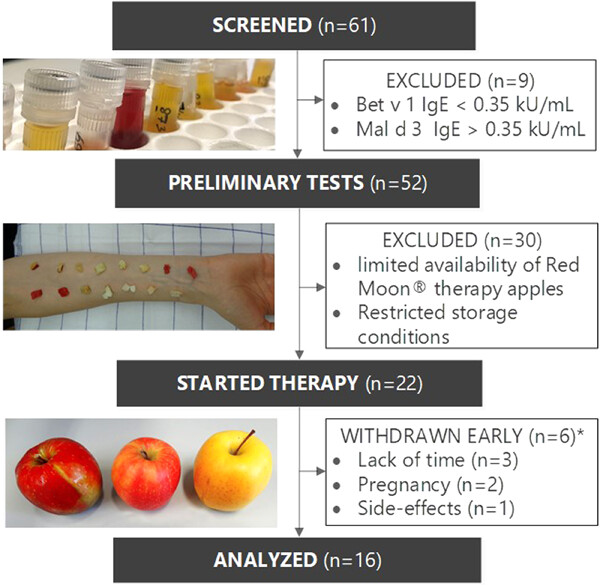
A 70% of patients suffering from birch pollen allergy (BPA) develop a pollen-related food allergy (prFA), especially to apples. This is due to a strong clinically relevant homology between the major allergen in birch Bet v 1 and Mal d 1 in apples. Therefore a pilot trial using fresh apples for allergen-specific immunotherapy to birch pollen was performed. After 8 months of therapy, patients showed increased tolerance to apples and other birch pollen-related food allergens. Moreover, daily rhinoconjunctivitis combined symptom and medication score (CSMS) declined by 34% (p < .001), as did conjunctival reactivity to birch pollen extract by 27% (p < .01), while specific IgG4 to Mal d 1 and Bet v 1 increased (p < .01). In this small pilot trial daily apple consumption improved both birch pollen and related food allergies. If confirmed by a larger controlled trial apples could provide a natural, healthy and cost-saving causal treatment for BPA.
Monitoring of hepatitis E virus RNA during treatment for chronic hepatitis E virus infection after renal transplantation
- Pages: 513-520
- First Published: 08 February 2021
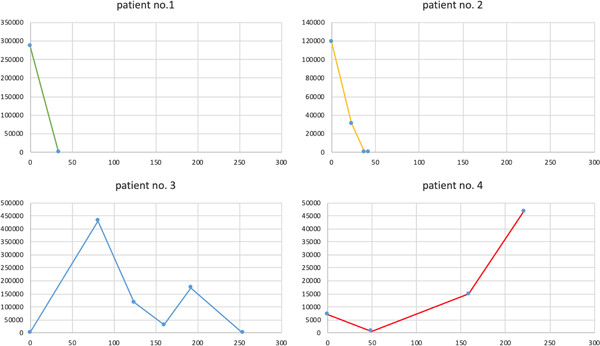
Graphical abstract
In this article, hepatitis E virus (HEV) infections in renal transplant recipients were examined. Serial measurements of HEV-RNA are helpful to determine the optimal duration of ribavirin treatment. We identified previous rituximab treatment to be a risk factor for a prolonged treatment course.
Cathepsin K maintains the compartment of bone marrow T lymphocytes in vivo
- Pages: 521-532
- First Published: 16 February 2021
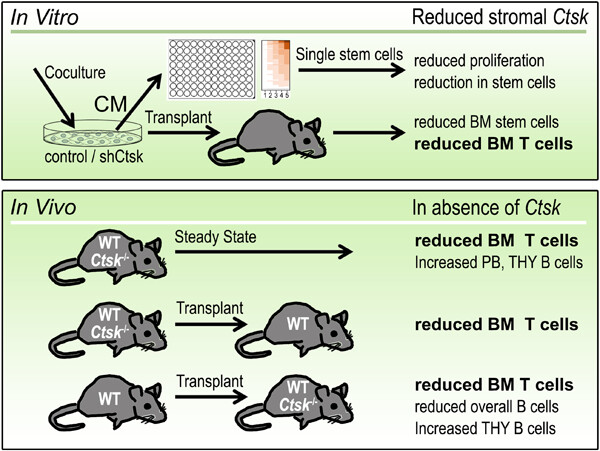
This manuscript describes how stromal cathepsin K regulates stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Transplantation experiments show that the main effect of the loss of the cathepsin K gene in vivo is a deregulated lymphocyte homeostasis, particularly the T lymphocyte subsets in the bone marrow compartment, in both autonomous and nonautonomous manners.
SLy2-overexpression impairs B-cell development in the bone marrow and the IgG response towards pneumococcal conjugate-vaccine
- Pages: 533-546
- First Published: 16 February 2021
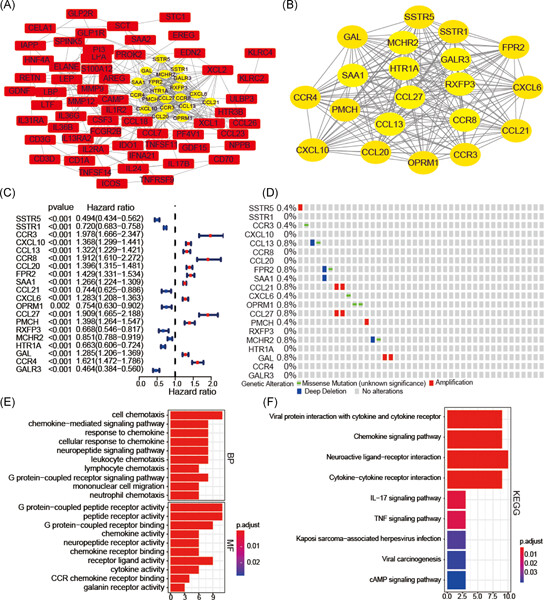
Bioinformatics analysis of the prognosis and biological significance of VCAN in gastric cancer
- Pages: 547-559
- First Published: 25 February 2021
Pediatric asthma control during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 561-568
- First Published: 03 March 2021
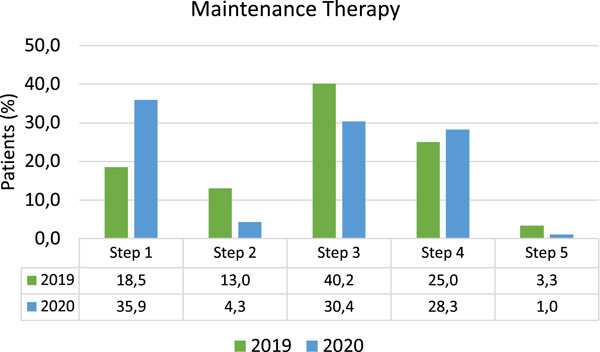
Our research showed a significant impact of the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown in the north-east of Italy on asthmatic children. In particular: (1) The level of asthma control resulted improved during the lockdown period, likely because of the reduced exposure to typical asthma triggers due to the confinement; (2) The maintenance treatment resulted reduced in some patients, likely because of the good level of disease control, and increased in other patients, either because of symptoms or because of fear and anxiety related to the spreading of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A territory-wide study on the factors associated with recurrent asthma exacerbations requiring hospitalization in Hong Kong
- Pages: 569-581
- First Published: 03 March 2021
Immune cytopenias as a continuum in inborn errors of immunity: An in-depth clinical and immunological exploration
- Pages: 583-594
- First Published: 10 April 2021
Construction and validation of a machine learning-based nomogram: A tool to predict the risk of getting severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Pages: 595-607
- First Published: 13 March 2021
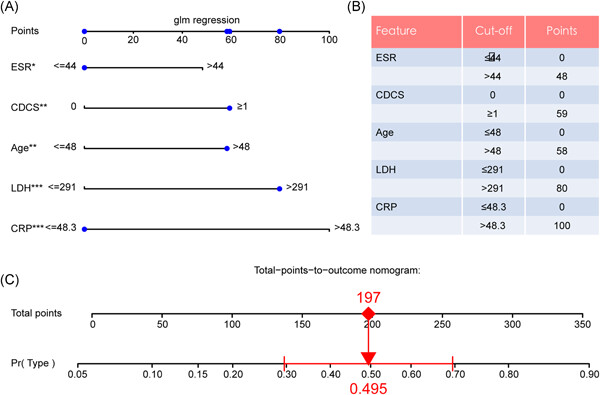
We generated the nomogram for predicting severe COVID-19. (Our predicting model of COVID-19 patients will enable clinicians to predict the potential risk of developing critical illness and optimize medical management.) In the training cohort, the area under curves (AUCs) were 0.822 (95% CI, 0.765–0.875) and the internal validation cohort was 0.762 (95% CI, 0.768–0.844) and validated it in a prospective cohort with the AUCs of 0.705 (95% CI, 0.627–0.778).
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Immunoglobulin G: A useful outcome marker in the follow-up of cystic fibrosis patients?
- Pages: 608-614
- First Published: 30 March 2021