Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
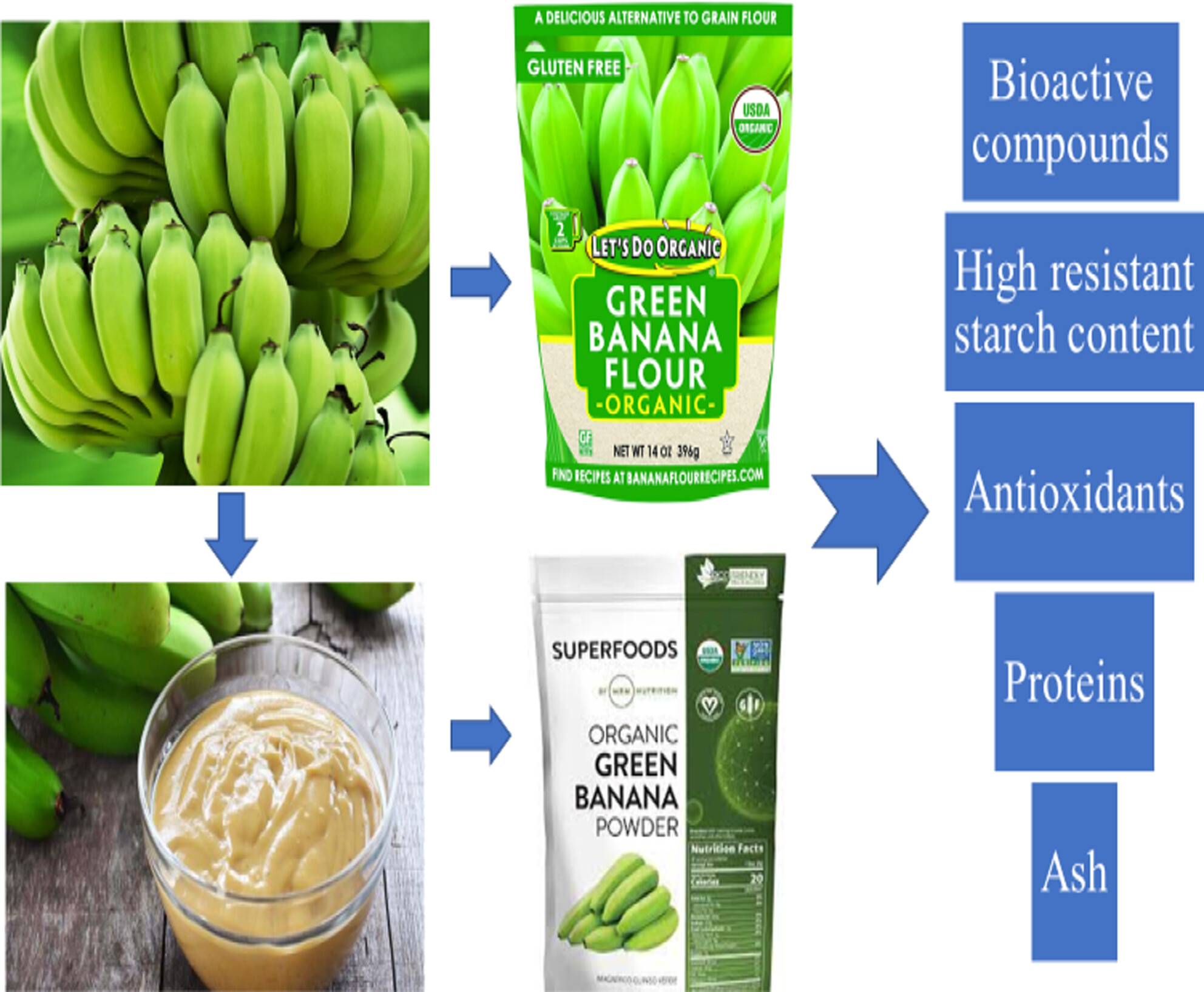
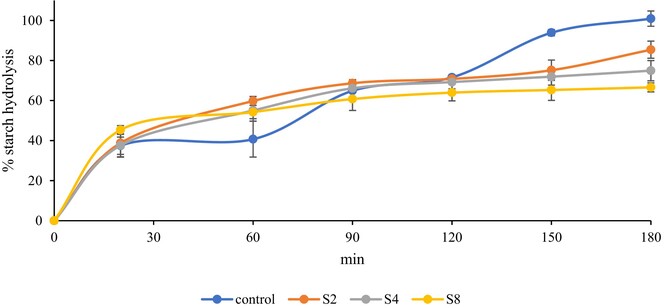
Green banana resistant starch: A promising potential as functional ingredient against certain maladies
- Pages: 3787-3805
- First Published: 06 May 2024
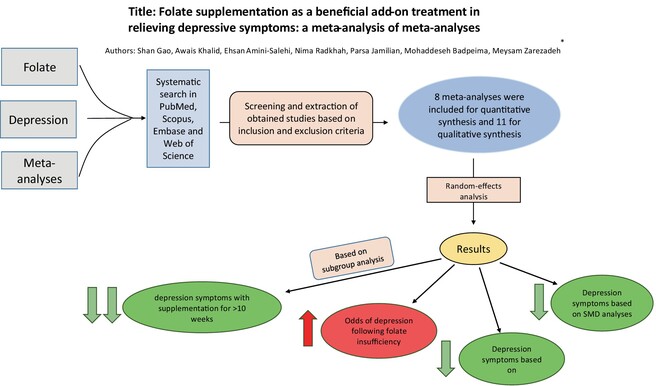
Folate supplementation as a beneficial add-on treatment in relieving depressive symptoms: A meta-analysis of meta-analyses
- Pages: 3806-3818
- First Published: 08 March 2024
The protective role of carnosine against type 2 diabetes-induced cognitive impairment
- Pages: 3819-3833
- First Published: 12 March 2024
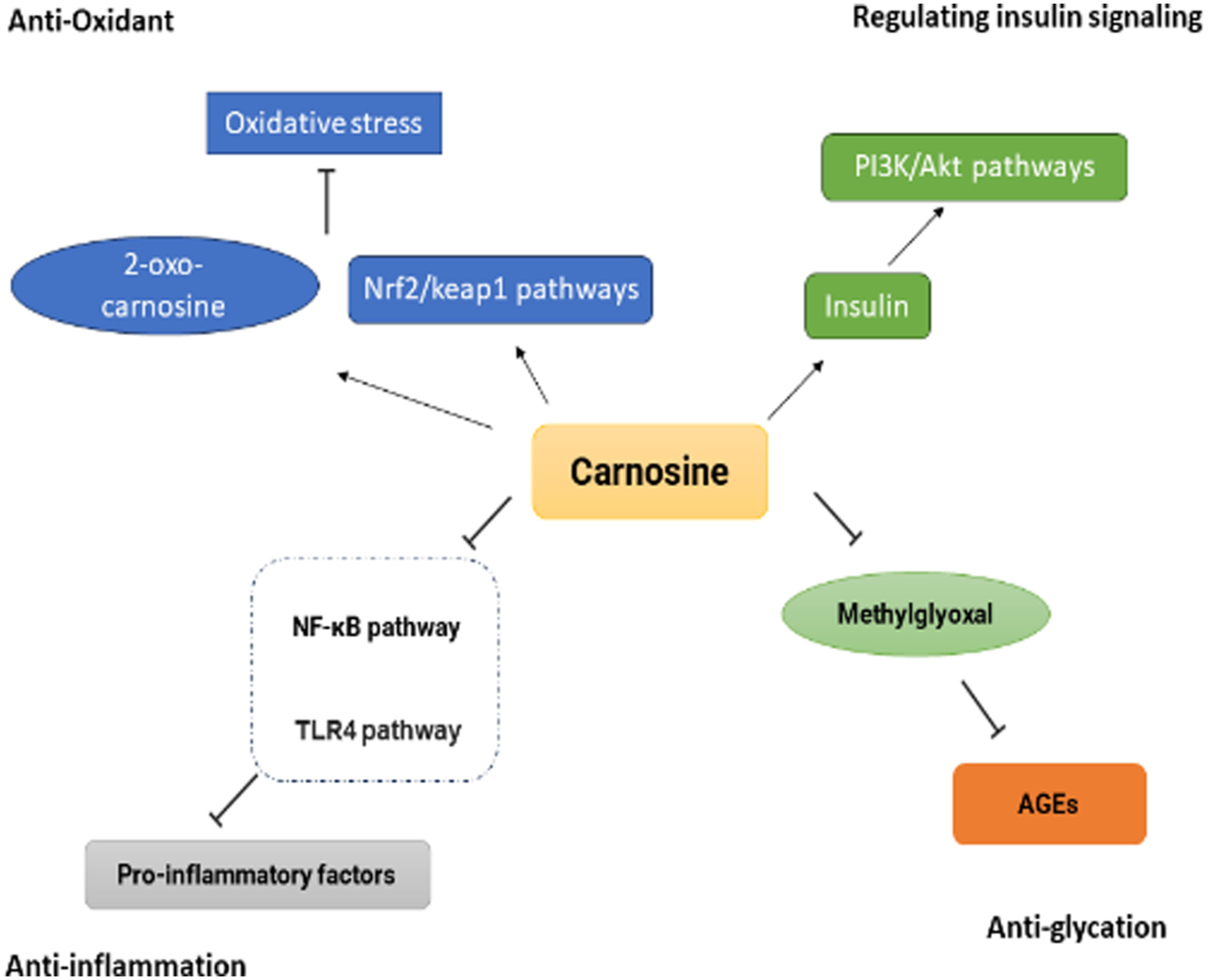
Carnosine has potential as a promising oral formulation of multi-protective therapy for the prevention or treatment of diabetes and neurodegenerative diseases. Specifically, through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-glycation properties, carnosine alleviated cognitive dysfunction, mediated insulin resistance, delayed oxidative damage, downregulated inflammatory cytokines, and inhibited the formation of AGEs.
Garden cress seeds: a review on nutritional composition, therapeutic potential, and industrial utilization
- Pages: 3834-3848
- First Published: 20 March 2024
Garden cress is a highly nutritious plant that contains a significant amount of both macro- and micronutrients. Its seeds contain good quality protein and essential fatty acids, while the leaves comprise minerals such as calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc. In addition to its nutritional value, garden cress is also an important medicinal plant, containing various phytochemicals with anticarcinogenic, antihypertensive, laxative, antidiabetic, and antioxidant properties. Research studies have confirmed that garden cress is safe for consumption without any side effects on the body.
A comprehensive review: Impact of oleogel application on food texture and sensory properties
- Pages: 3849-3862
- First Published: 13 April 2024
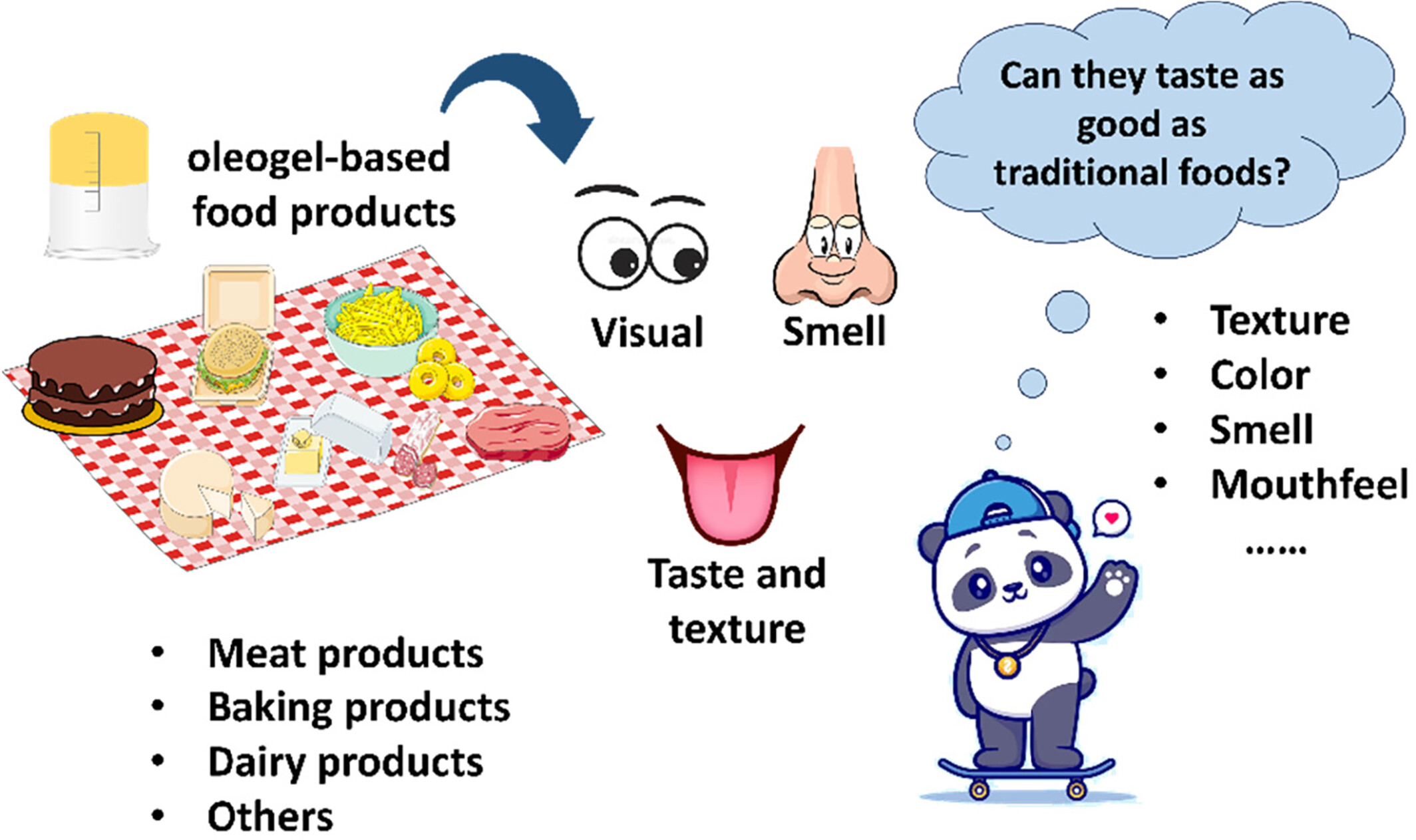
This review highlights the application of oleogels in food innovation, focusing on their ability to improve nutritional value and impact texture and sensory properties. It covers the oleogel application across various food products, their formulation challenges, and the need for further research to optimize their use and consumer acceptance.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Effect on blood lipids and body composition of a high-fat (MUFA) and high-fiber diet: A case–control study
- Pages: 3863-3871
- First Published: 26 April 2024
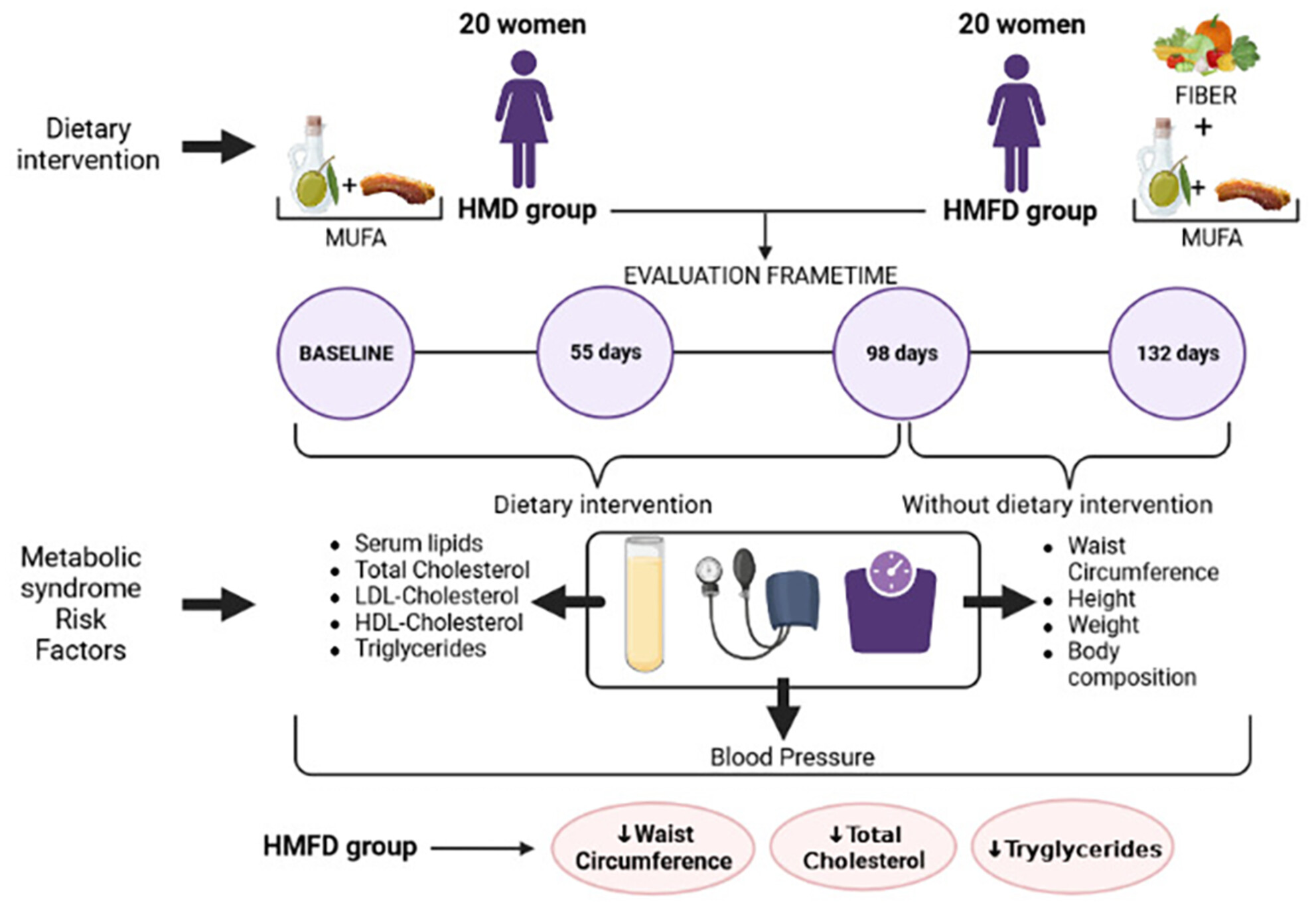
A case–control study demonstrates that high mono-unsaturated fatty acid fiber diet from a weekly consumption of processed meat deeply fried in extra-virgin olive oil in combination with vegetables logged in a Mediterranean diet can improve MetS risk factors in healthy overweight women compared to high mono-unsaturated fatty acid diet.
Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils in different populations of Coriandrum sativum L. (coriander) from Iran and Iraq
- Pages: 3872-3882
- First Published: 20 February 2024
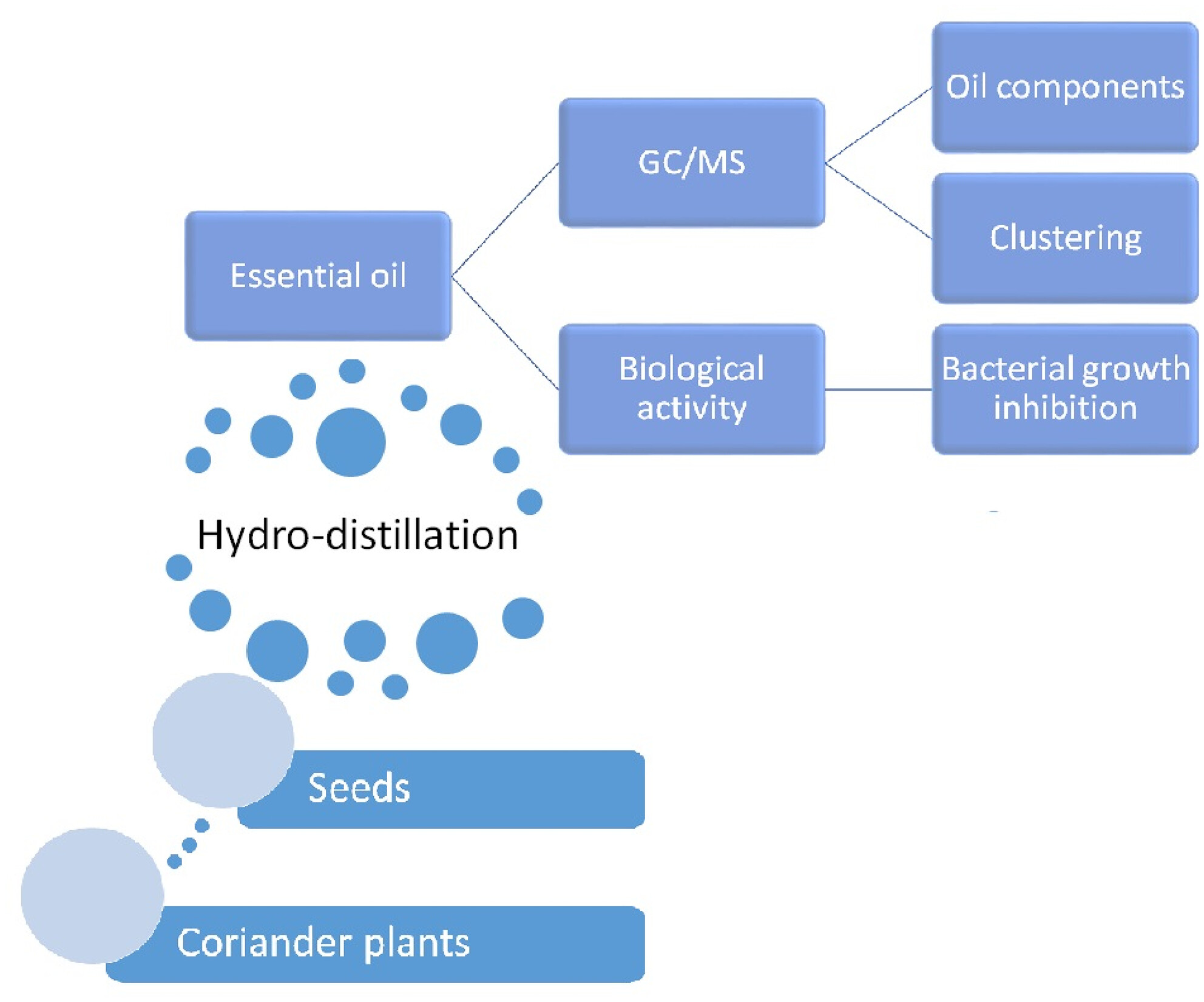
In this study, the seed essential oil composition and its antibacterial activities were evaluated in nine Iranian and Iraqi coriander populations. Results indicated that the oxygenated monoterpenes constituted a great proportion of the oils, with linalool as the major compound, followed by α-pinene, γ-terpinene, and geranyl acetate as other main compounds.
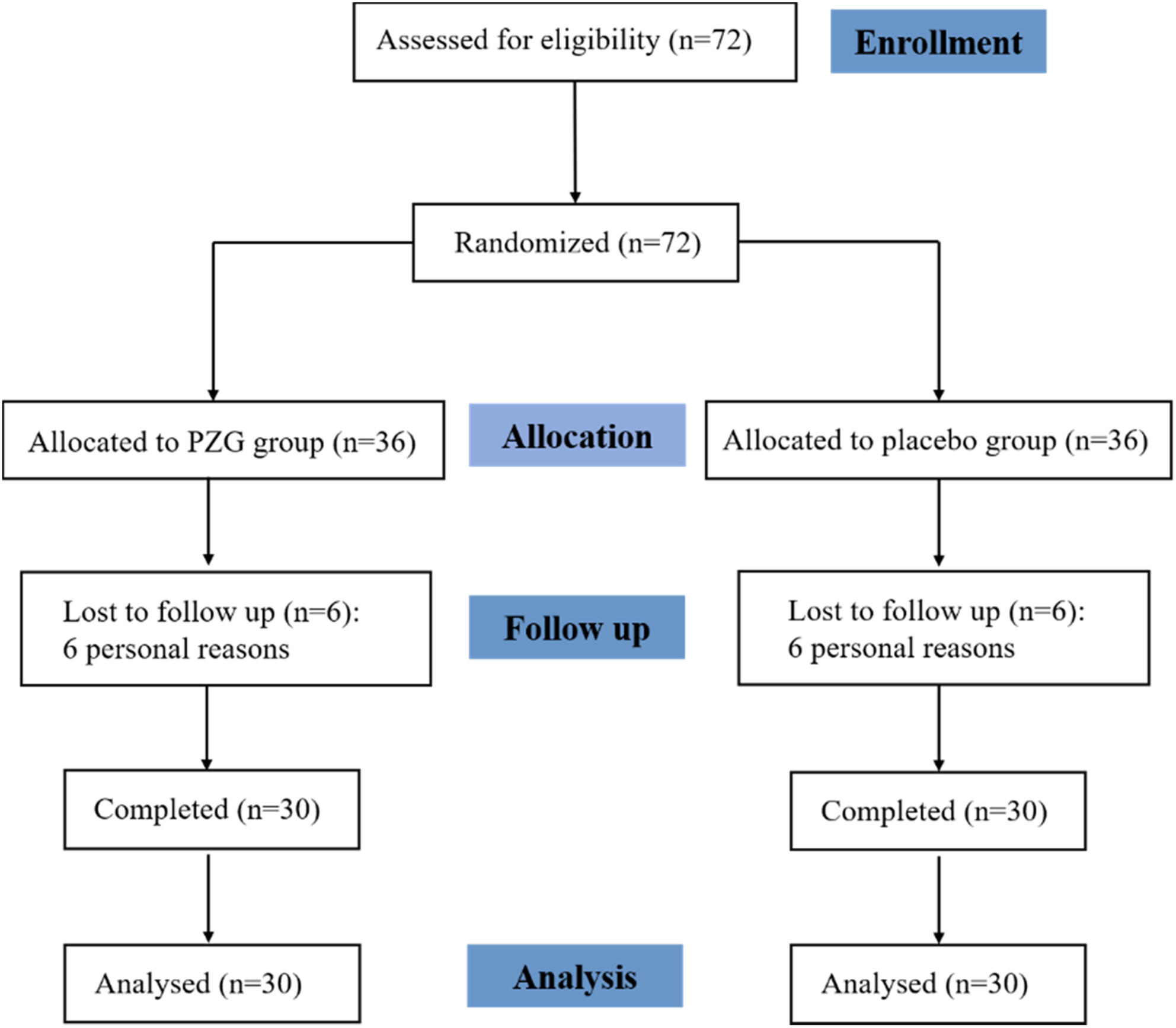
Effects of a combination of Poria Cocos, Ziziphus spinose, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on sleep quality and skin health: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial
- Pages: 3883-3892
- First Published: 22 February 2024
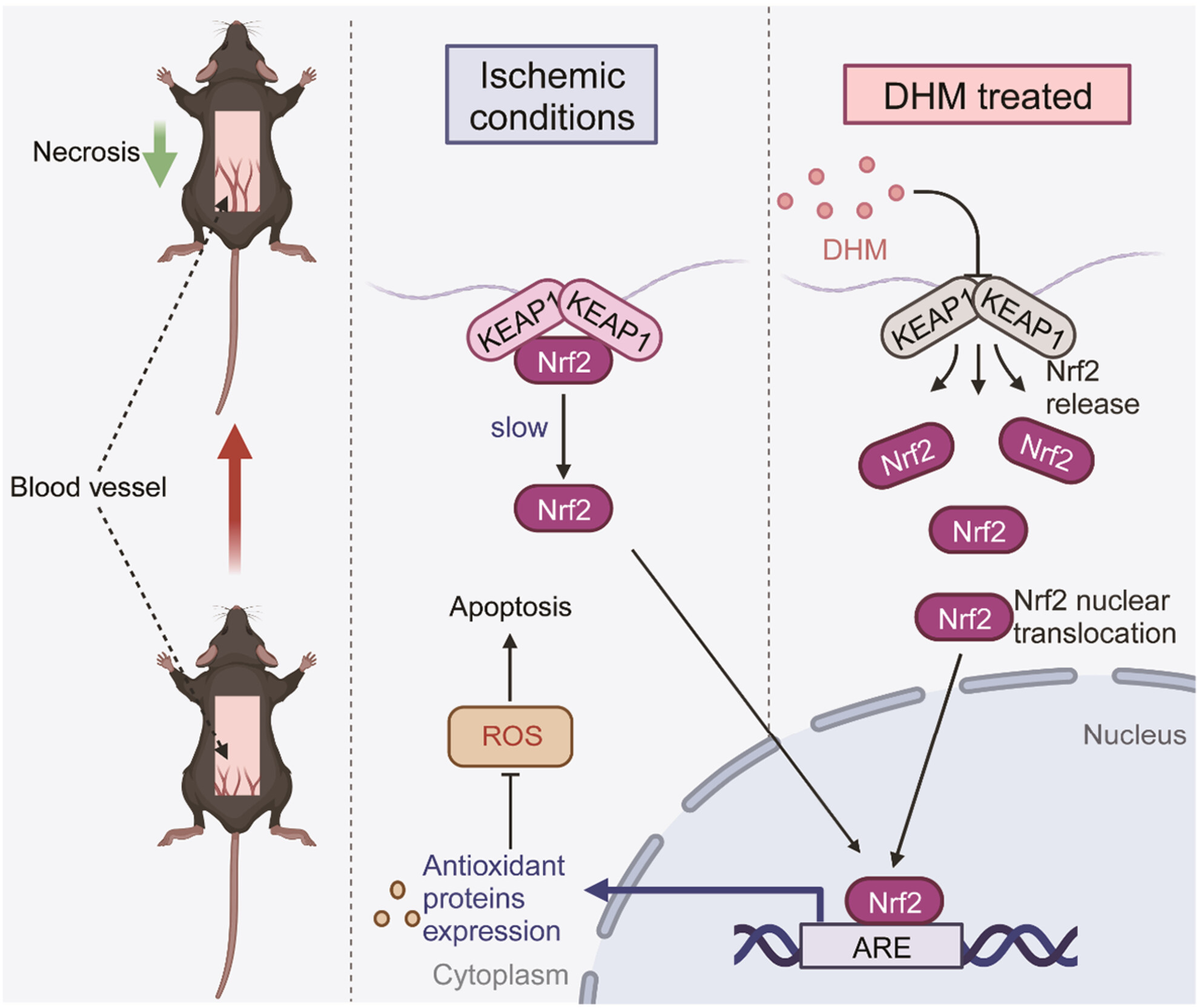
Dihydromyricetin regulates KEAP1-Nrf2 pathways to enhance the survival of ischemic flap
- Pages: 3893-3909
- First Published: 20 February 2024
Wholegrain triticale sourdough: Effects of triticale:Wheat flour ratio and hydration level on bread quality
- Pages: 3910-3919
- First Published: 24 March 2024
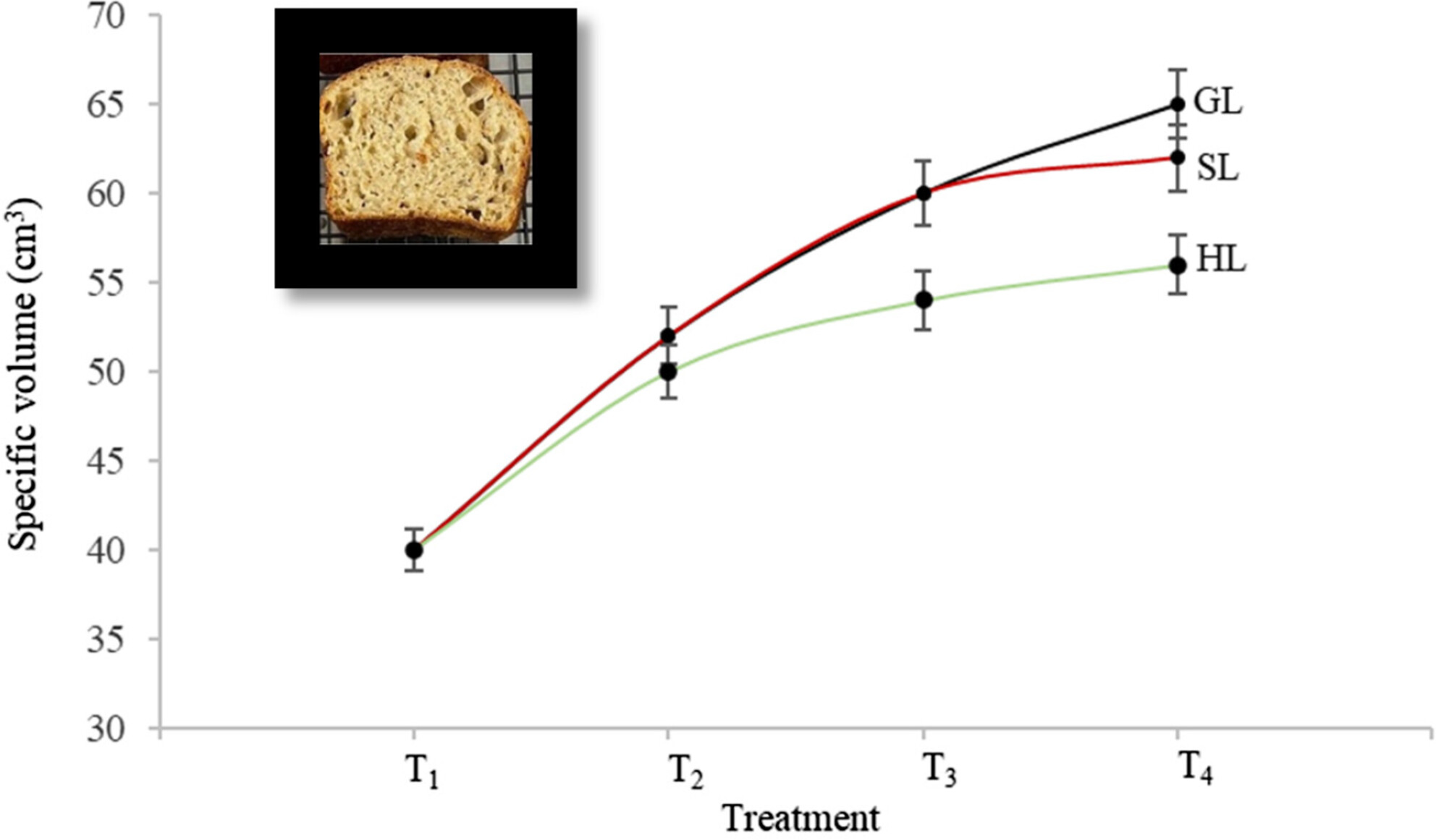
Triticale grain is highly nutritious and should be tested in an expanded range of foods. In this study, the effect of partial substitution of wholemeal wheat flour with wholegrain triticale flour, as well as the effect of varying dough water content, on quality parameters of sourdough bread was tested. The replacement of wholemeal wheat flour with 60% wholegrain triticale cv. Goanna flour and the addition of 100 g water/100 g flour in the dough preparation gave the highest quality sourdough bread based on specific volume, texture, and color.
An approach to manufacturing well-being milk chocolate in partial replacement of lecithin by the functional plant-based combination
- Pages: 3920-3934
- First Published: 10 March 2024
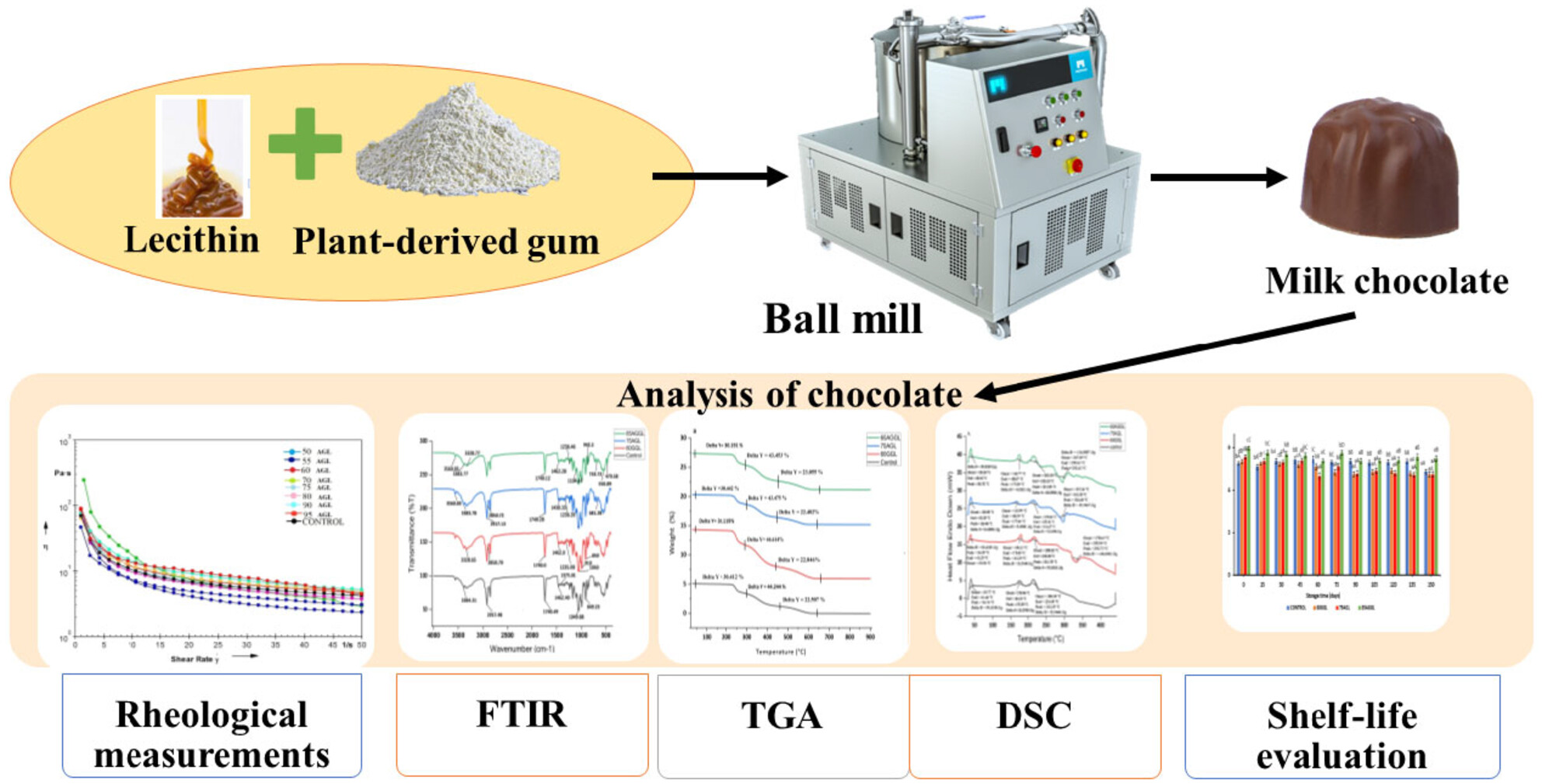
In this study, guar and arabic gum were utilized as lecithin replacements in the formulation of milk chocolate and their effect on the quality was determined. Herein, different concentrations of guar and arabic gum (25%–75%) and their combination (25%–75%) were used to replace the lecithin. Sensory evaluation revealed a comparable score of gum-added milk chocolate in comparison to control samples in terms of taste, texture, color, and overall acceptance. Thus, plant exudate gums could be an excellent alternative to lecithin in milk chocolate, which can enhance the textural properties and shelf life.
Gum tragacanth, a novel edible coating, maintains biochemical quality, antioxidant capacity, and storage life in bell pepper fruits
- Pages: 3935-3948
- First Published: 27 February 2024

This study investigated the impact of varying levels of gum tragacanth (GT) coating on the quality of stored sweet pepper fruits over 28 days. Results indicated that GT concentrations up to 1% positively influenced fruit quality, while 2% concentrations had negative effects on marketability and overall quality. Fruits coated with 1% GT exhibited lower weight loss, more firmness, and higher levels of phenols, ascorbic acid, titratable acidity, SOD, CAT, POD activities, and antioxidant capacity compared to other treatments.
Lactating mothers' perceptions and sensory acceptability of a provitamin A carotenoid–iron-rich composite dish prepared from iron-biofortified common bean and orange-fleshed sweet potato in rural western Uganda
- Pages: 3949-3963
- First Published: 08 March 2024
A provitamin A carotenoid–iron-rich composite dish prepared from iron-biofortified common bean and orange-fleshed sweet potato is acceptable among lactating mothers in rural Uganda. A figure that best represents the scope of the paper. The image supplied should fit within the dimensions of 50 mm x 60 mm, and be fully legible at this size.
Oily fish reduces the risk of acne by lowering fasting insulin levels: A Mendelian randomization study
- Pages: 3964-3972
- First Published: 06 March 2024
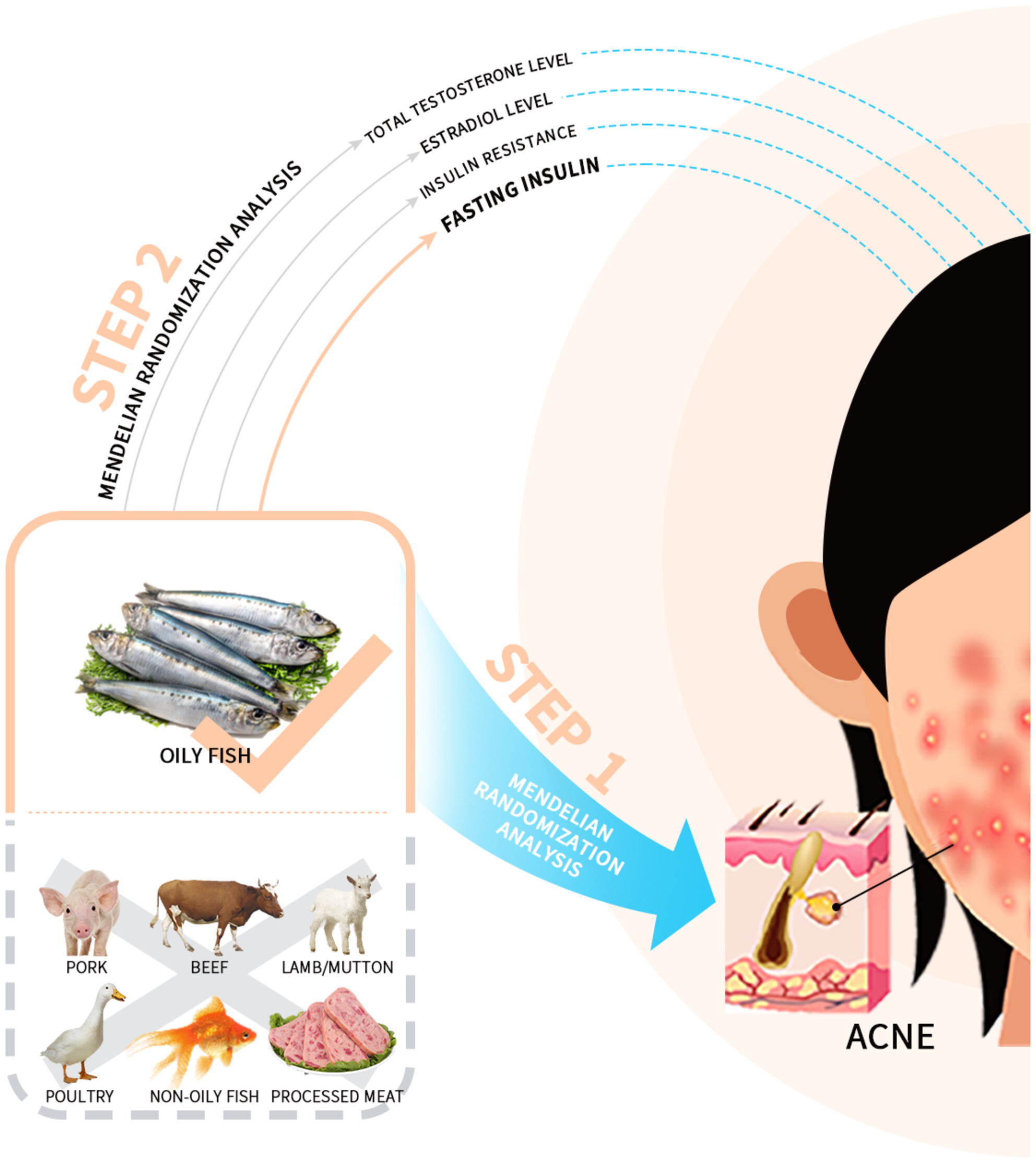
We have adopted Mendelian randomization (MR) to investigate the causal relationship between different types of meat intake (processed meat, poultry, beef, non-oily fish, oily fish, pork, and lamb/mutton) and acne. We found that the intake of oily fish reduces the risk of acne by lowering fasting insulin levels.
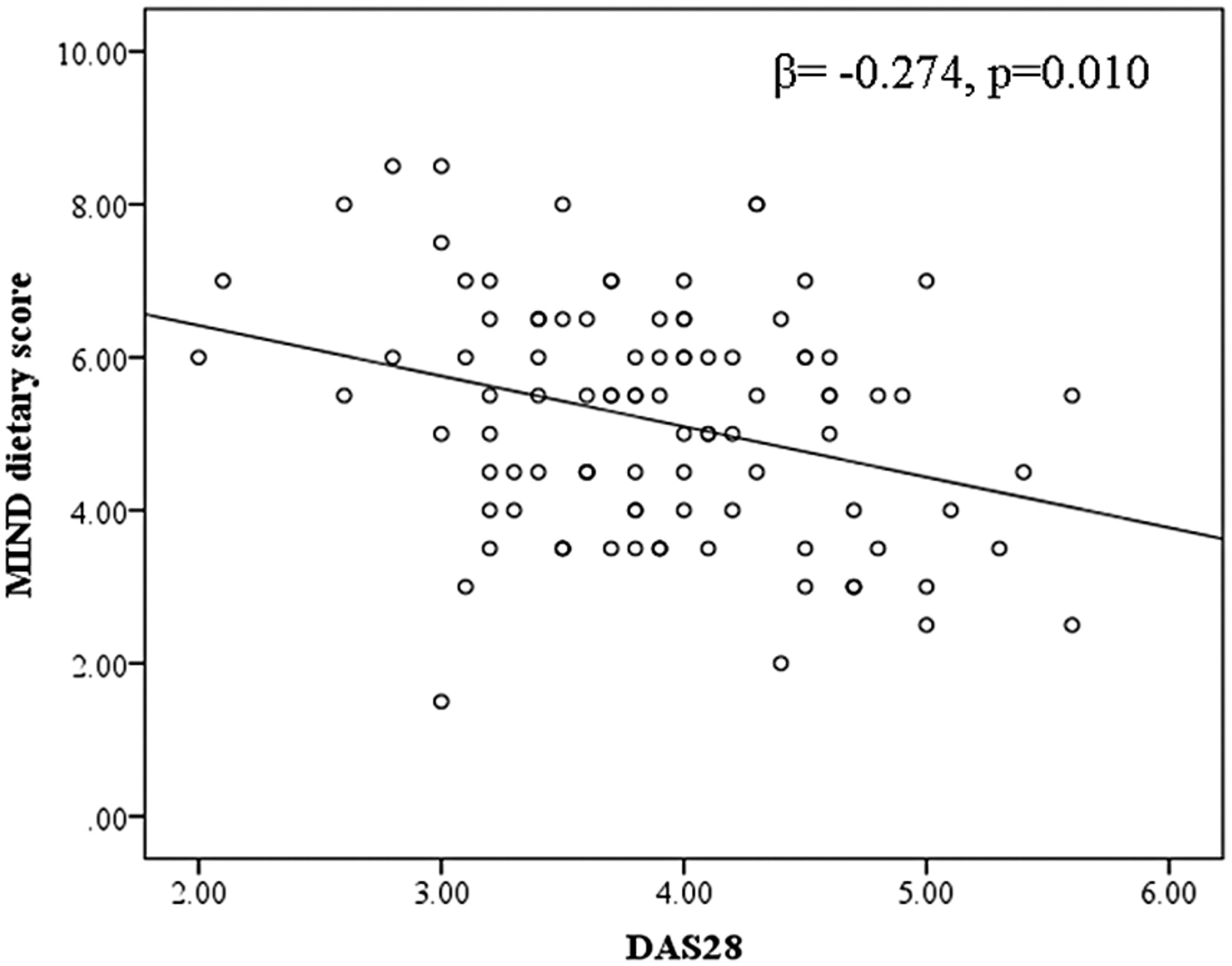
Association between Mediterranean-dietary approaches to stop hypertension intervention for neurodegenerative delay diet and biomarkers of oxidative stress, metabolic factors, disease severity, and odds of disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients
- Pages: 3973-3981
- First Published: 12 March 2024
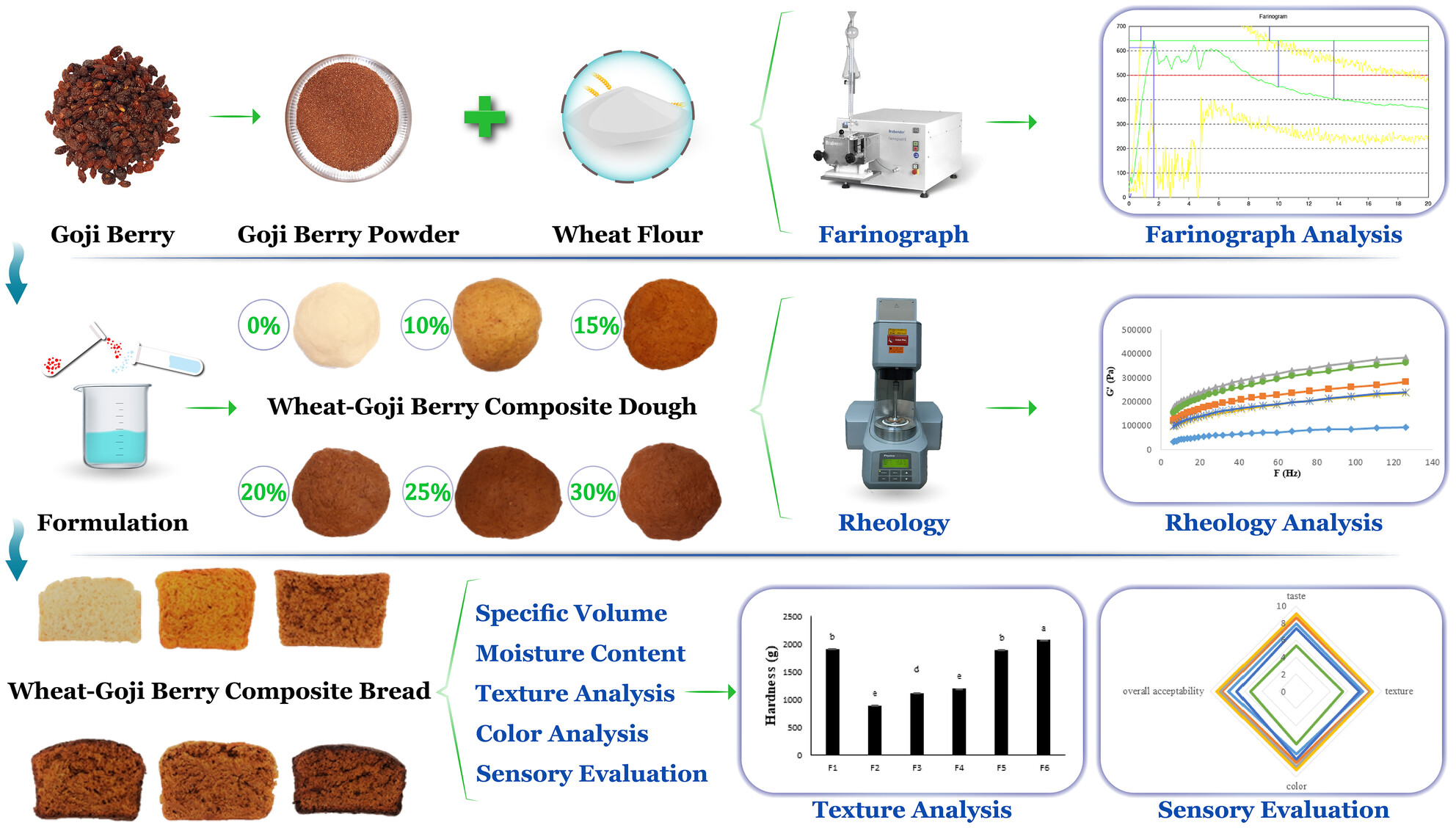
Effect of goji berry incorporation on the texture, physicochemical, and sensory properties of wheat bread
- Pages: 3982-3992
- First Published: 28 February 2024
Effect of the combined intervention of low-FODMAPs diet and probiotics on IBS symptoms in Western China: A randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 3993-4004
- First Published: 29 February 2024
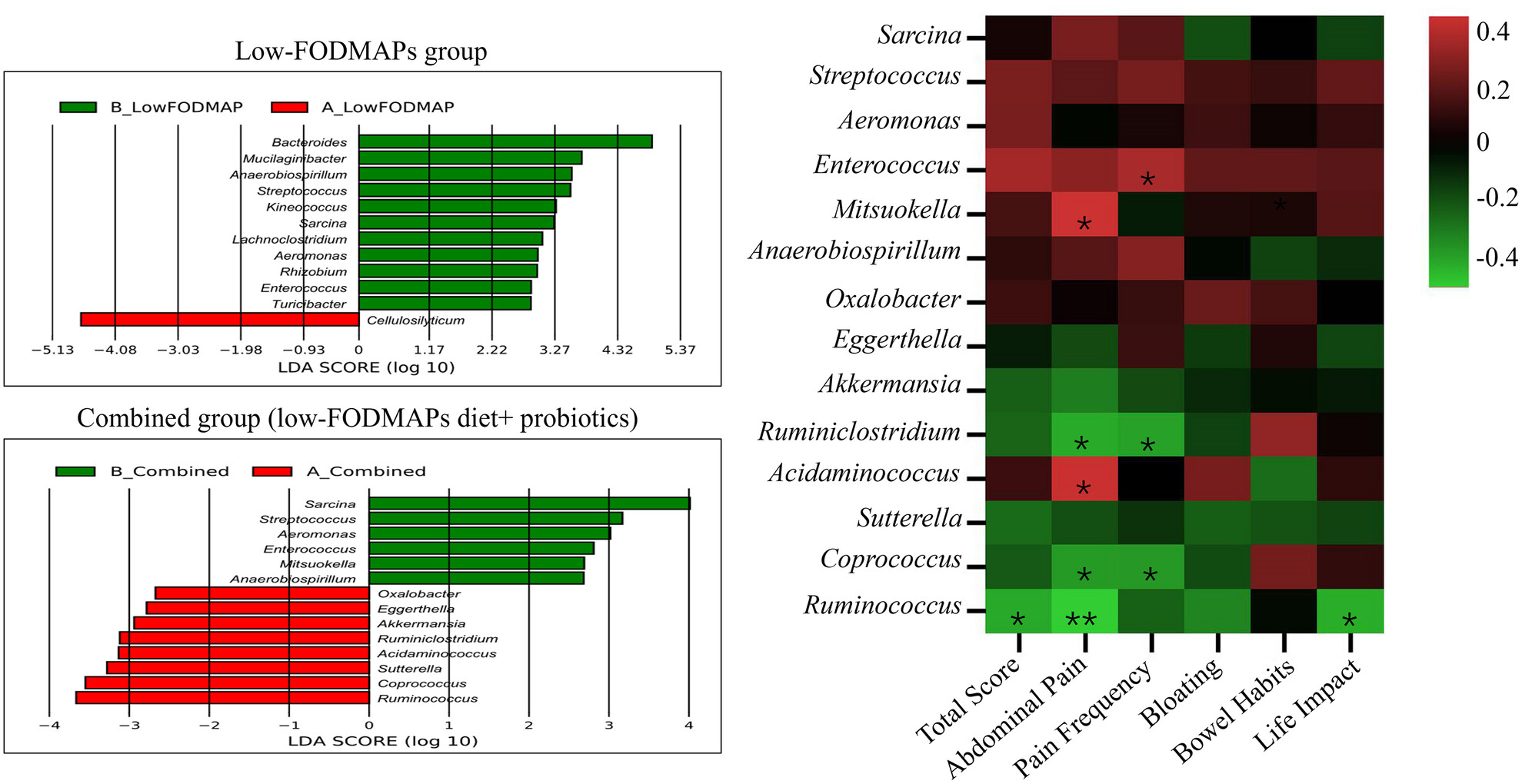
Low-FODMAPs diet and low-FODMAPs diet combined with probiotics could significantly relieve the symptoms of IBS patients. The addition of probiotics increased the abundance of several gut microbiota, including Ruminococcus, Coprococcus, Acidaminococcus et al. Pearson correlation analysis confirmed that alterations of the microbiota induced by probiotics were significantly associated with the improvements in IBS symptoms.
Investigating potato flour processing methods and ratios for noodle production
- Pages: 4005-4018
- First Published: 05 March 2024
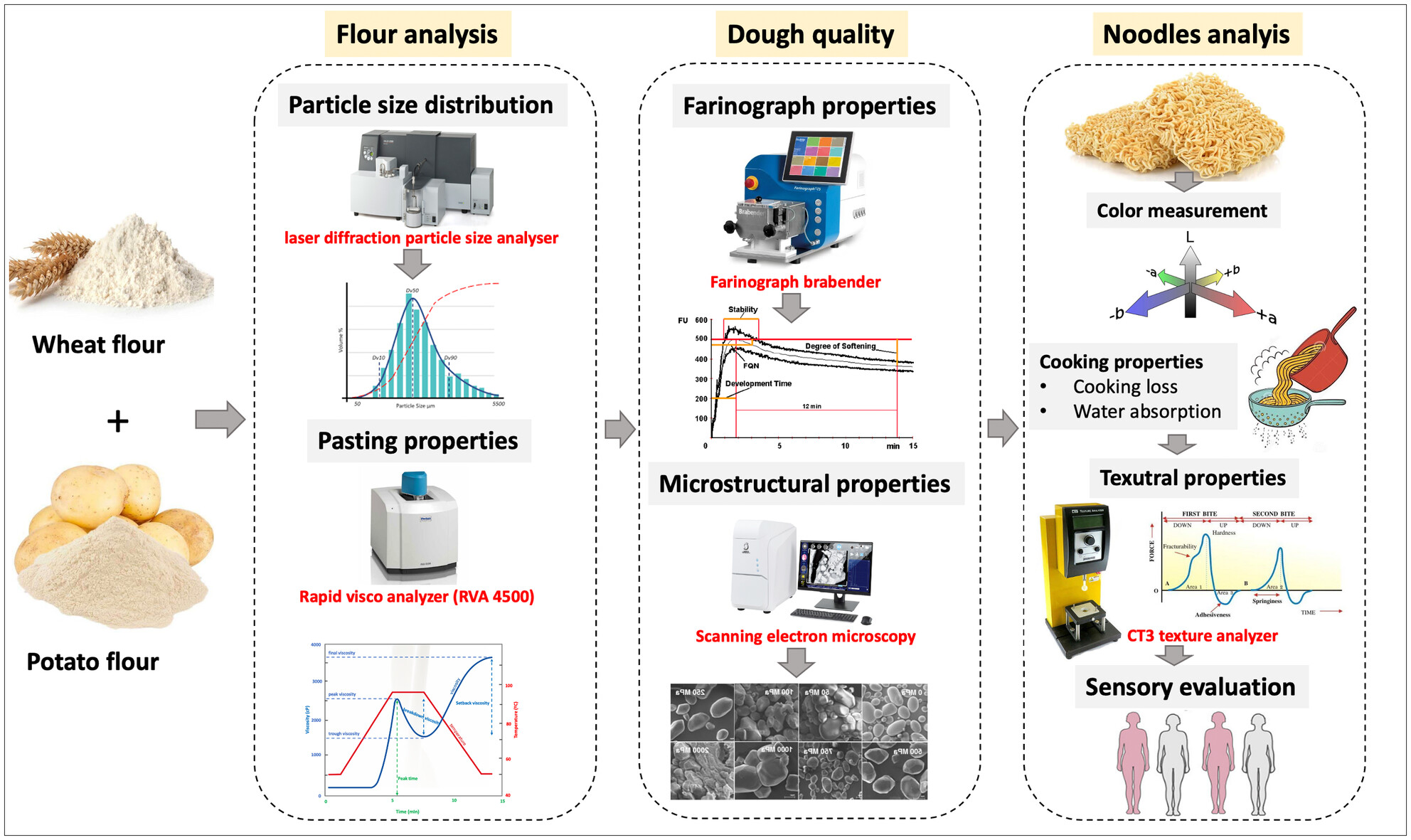
This study investigated the effects of substituting wheat flour with potato flour produced using different processing methods. The results revealed that replacing wheat flour with freeze-dried potato flour improved the blended flour's particle size, pasting properties, and overall liking scores for noodles. In contrast, using low-temperature blanching and oven-dried potato flour led to adverse effects on texture and cooking loss, suggesting that freeze-dried potato flour is a more favorable option for optimizing noodle processing.
Effect of partial mutton meat substitution with Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) flour on physicochemical properties, lipid oxidation, and sensory acceptability of low-fat patties
- Pages: 4019-4037
- First Published: 04 March 2024
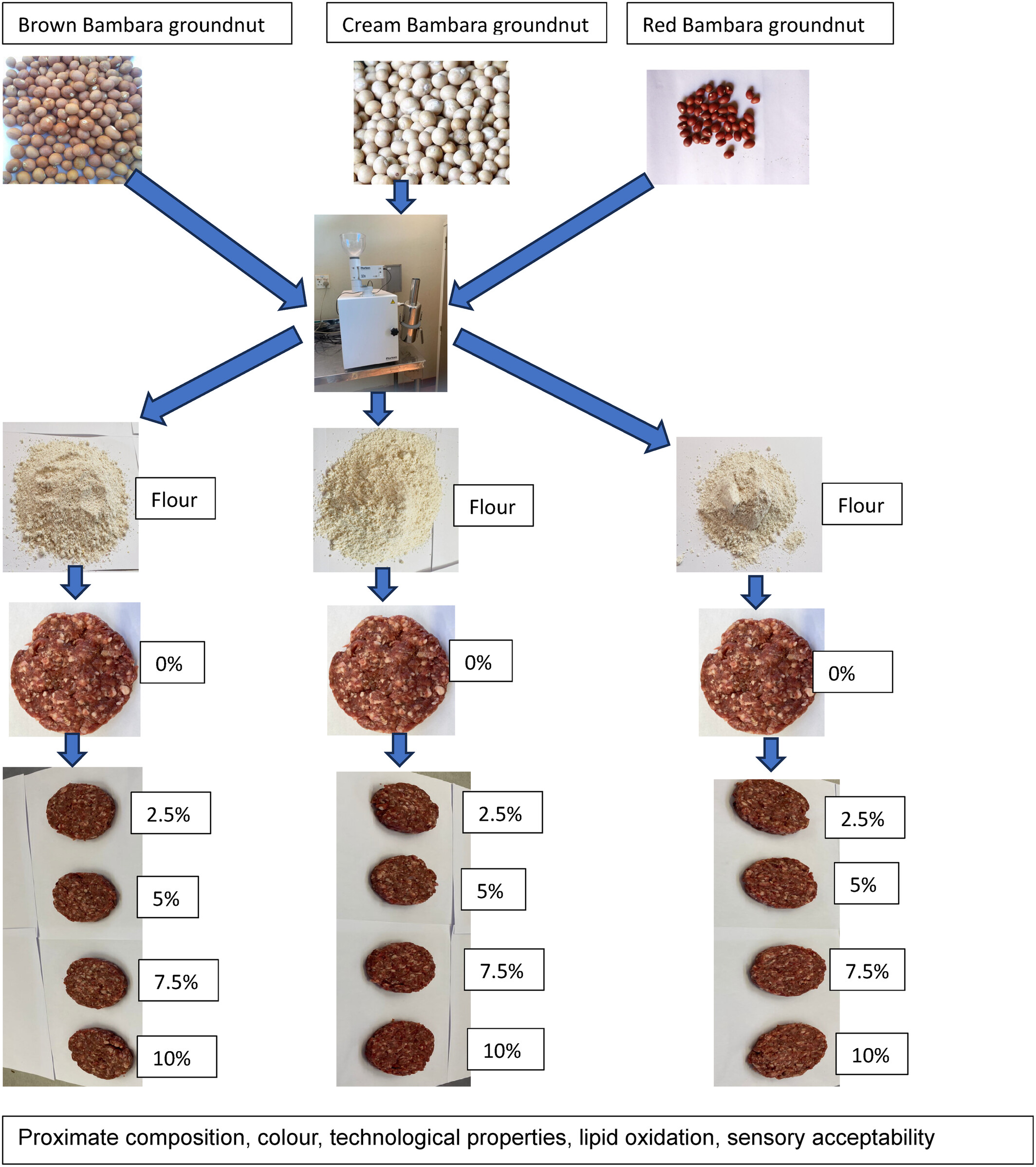
Physicochemical properties, lipid oxidation, and sensory acceptability of low-fat mutton patties substituted with Bambara groundnut flour were determined. The increase in the percentage substitution of BGN flours significantly increased the fiber, ash, and carbohydrate contents of the formulated mutton patties. The cooking yield of the formulated patties significantly increased with the increase in the percentage substitution of BGN flours. The hardness and resilience of formulated patties significantly increased.
Optimization of an ultrasound-assisted extraction method to obtain gallic acid-rich extracts from mango seed kernels
- Pages: 4038-4048
- First Published: 12 April 2024
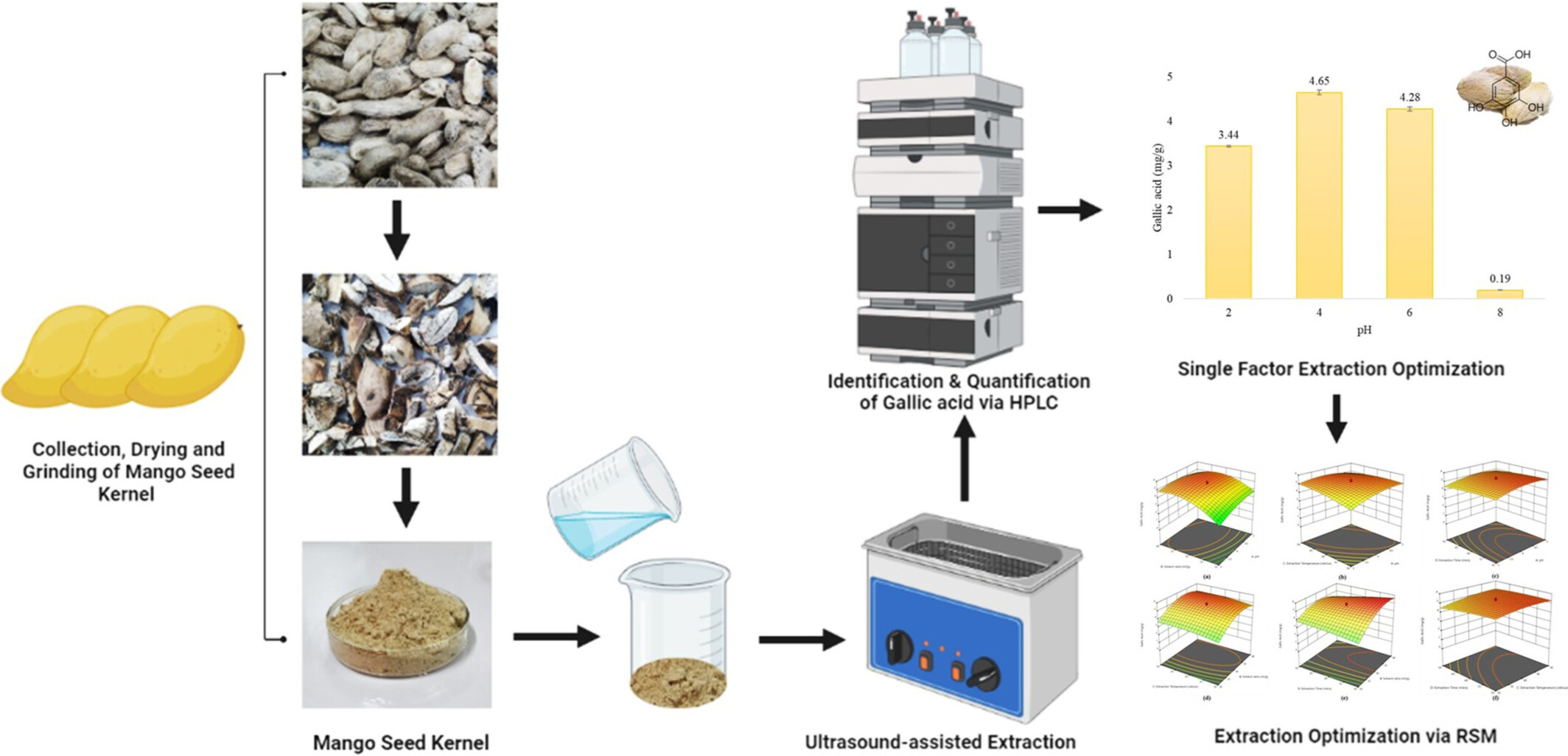

This study aimed to adopt a green extraction approach to extract this valuable compound via ultrasound-assisted extraction without using organic solvents but only water to obtain hazard-free extracts, and the cost of extraction can be minimal. pH (2–8), solvent ratio (20–60 mL/g), temperature (30–60°C) and time (30–60 min) of extraction were the independent variables used for extraction optimization. A central composite design using response surface methodology was used to determine the optimum condition to obtain the maximum yield of gallic acid from mango seed kernel. As a result, the optimized yield was 5.76 ± 0.41 mg/g, comparably equal to and/or better than the other solvent extraction systems.
1H-NMR-based metabolomics reveals the preventive effect of Enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharides on diabetes in Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- Pages: 4049-4062
- First Published: 05 March 2024
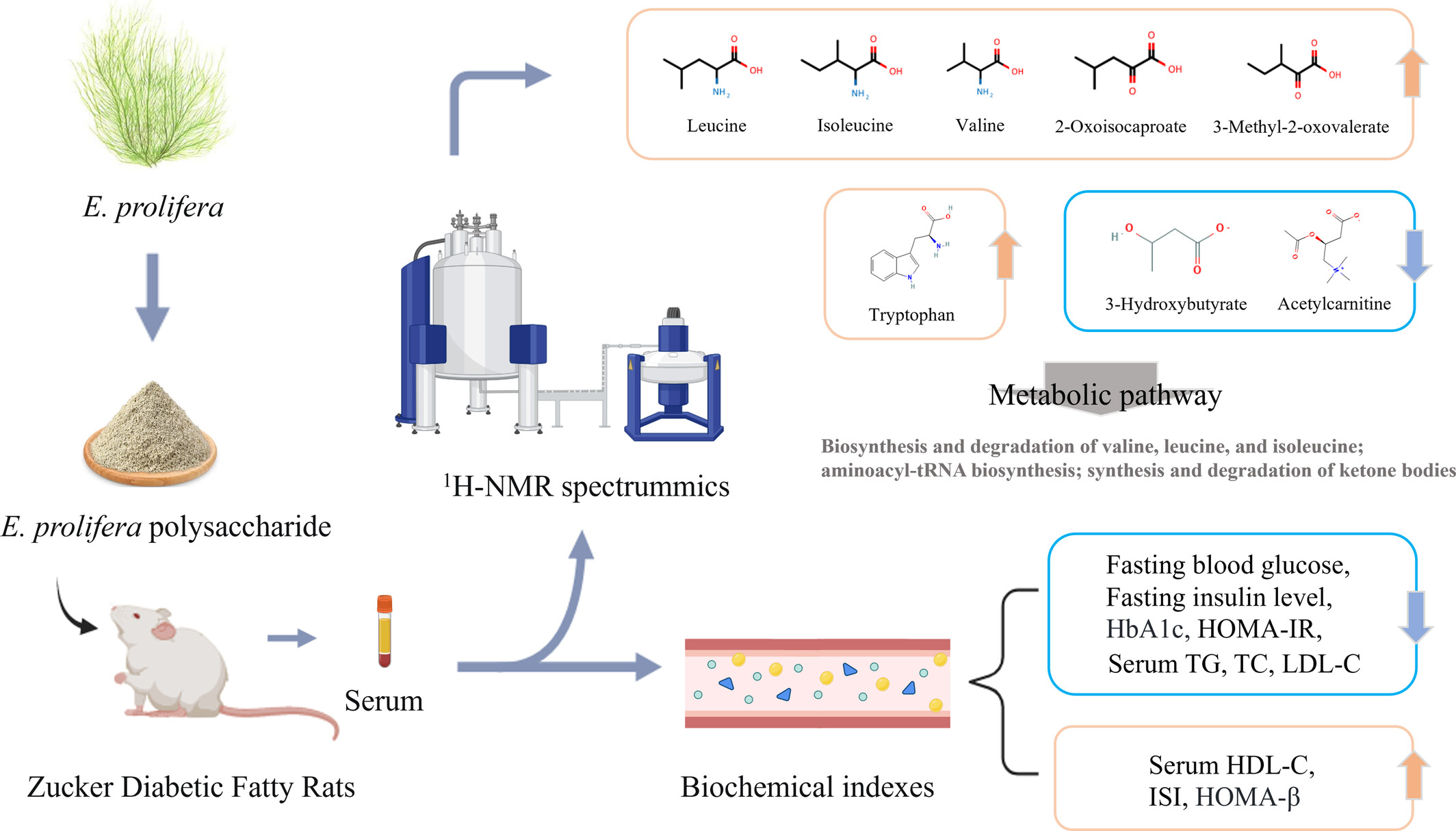
This study aimed to investigate the ameliorative effects of Enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharide (EP) on Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats and elucidate its potential mechanism using 1H-NMR-based metabolomics. We found that EP has potential as a therapeutic agent for preventing glycemic abnormalities and improving insulin resistance, thereby suggesting its utility in the treatment of diabetes.
Consumer insights into the at-home liking of commercial beers: Integrating nonvolatile and volatile flavor chemometrics
- Pages: 4063-4075
- First Published: 07 March 2024
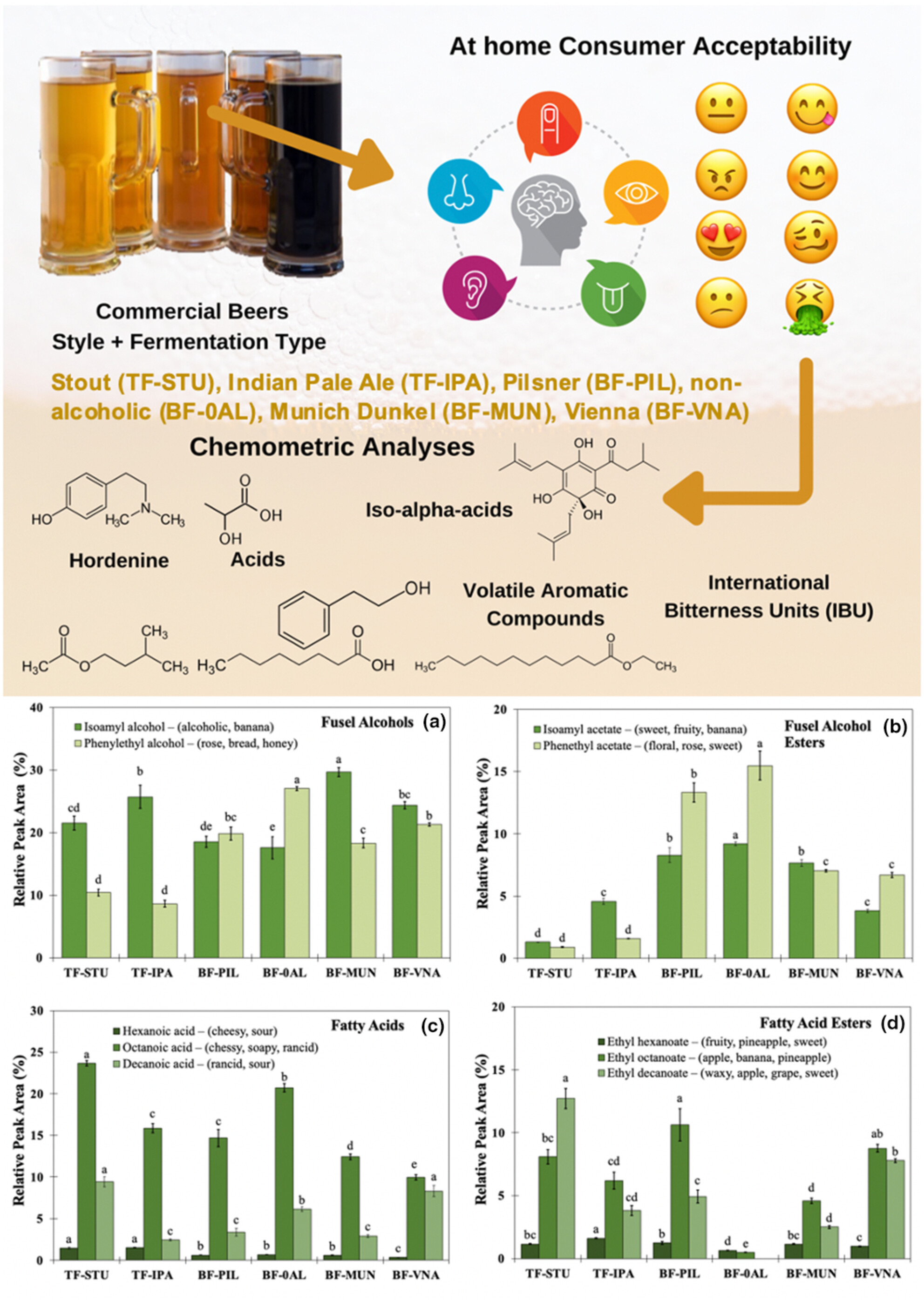
Most liked beers (Pilsners and Munich Dunkel) contained higher fusel alcohol esters linked to fruity aromatic notes. Consumers penalized top fermentation beers characterized by higher concentrations of bitter molecules and hordenine. Light-colored and medium-height foam were the highest scored sensory visual attributes.
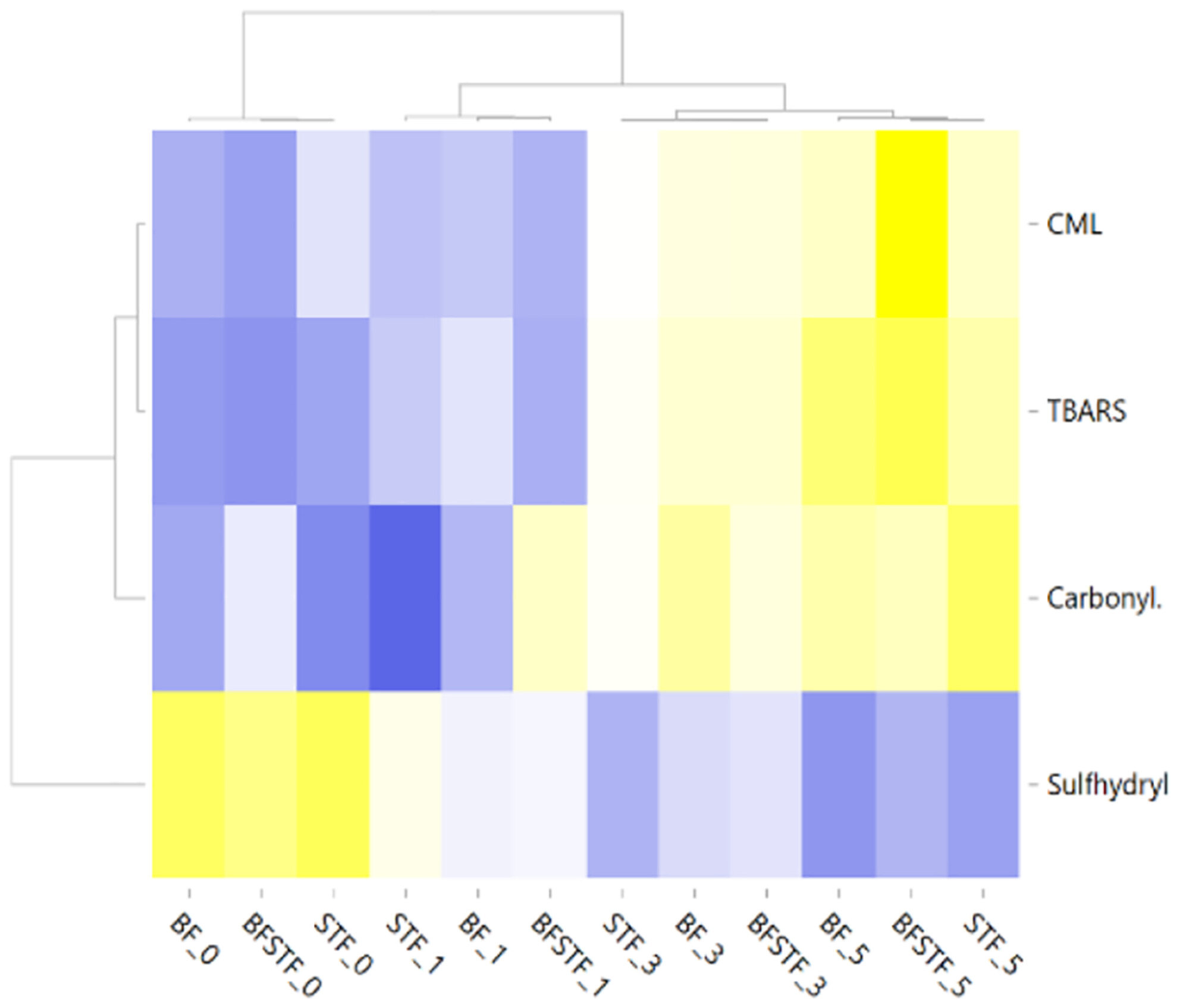
The effects of using sheep tail fat and cooking time on carboxymethyl-lysine formation and some quality characteristics of heat-treated sucuk
- Pages: 4076-4085
- First Published: 07 March 2024
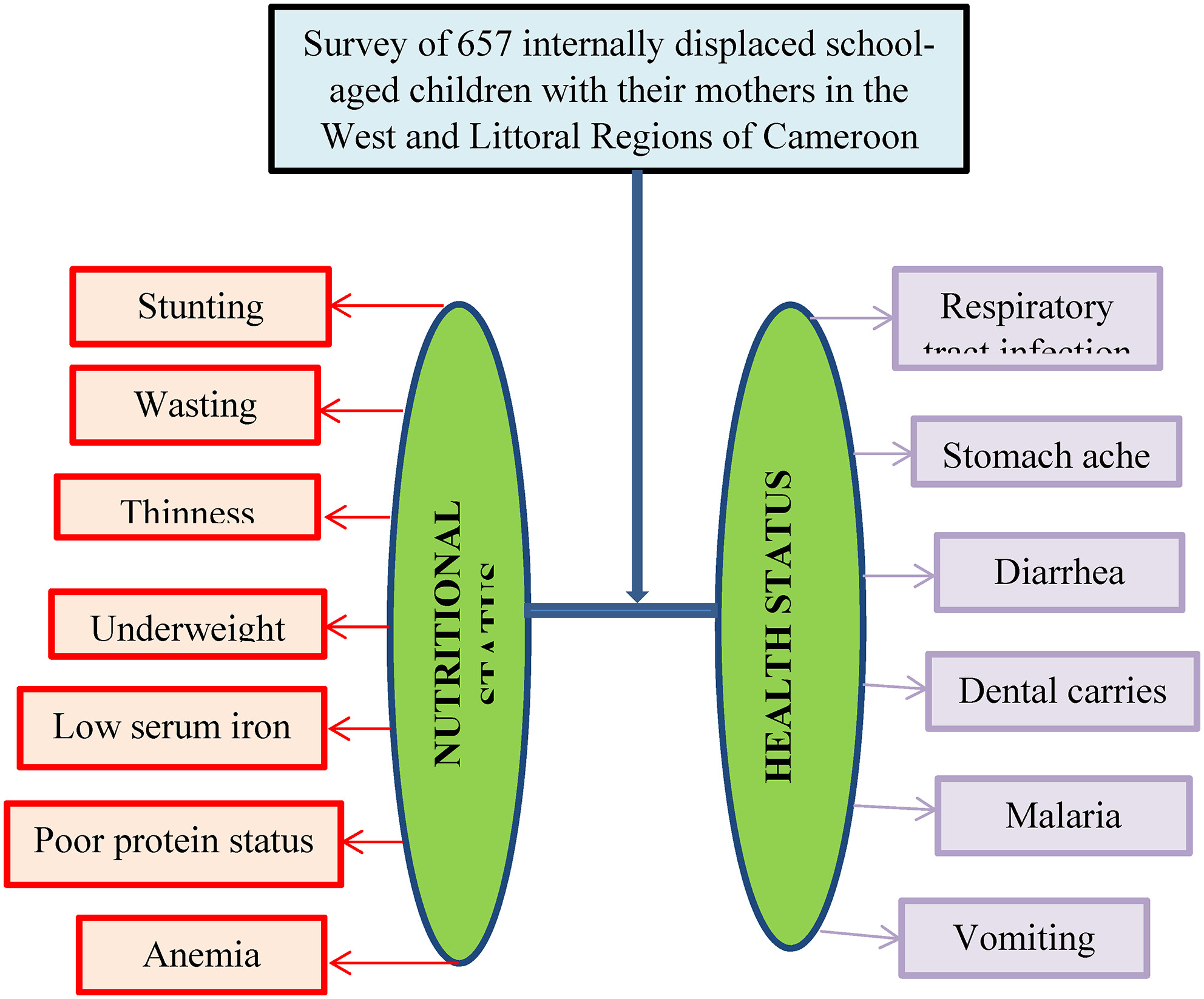
An assessment of the nutritional status of internally displaced school children in the West and Littoral Regions of Cameroon
- Pages: 4086-4099
- First Published: 21 April 2024
Evaluation of rhizomania infection on sugar beet quality in multi-year field assessment
- Pages: 4100-4109
- First Published: 05 April 2024
Linking the relationship between dietary folic acid intake and risk of osteoporosis among middle-aged and older people: A nationwide population-based study
- Pages: 4110-4121
- First Published: 05 March 2024
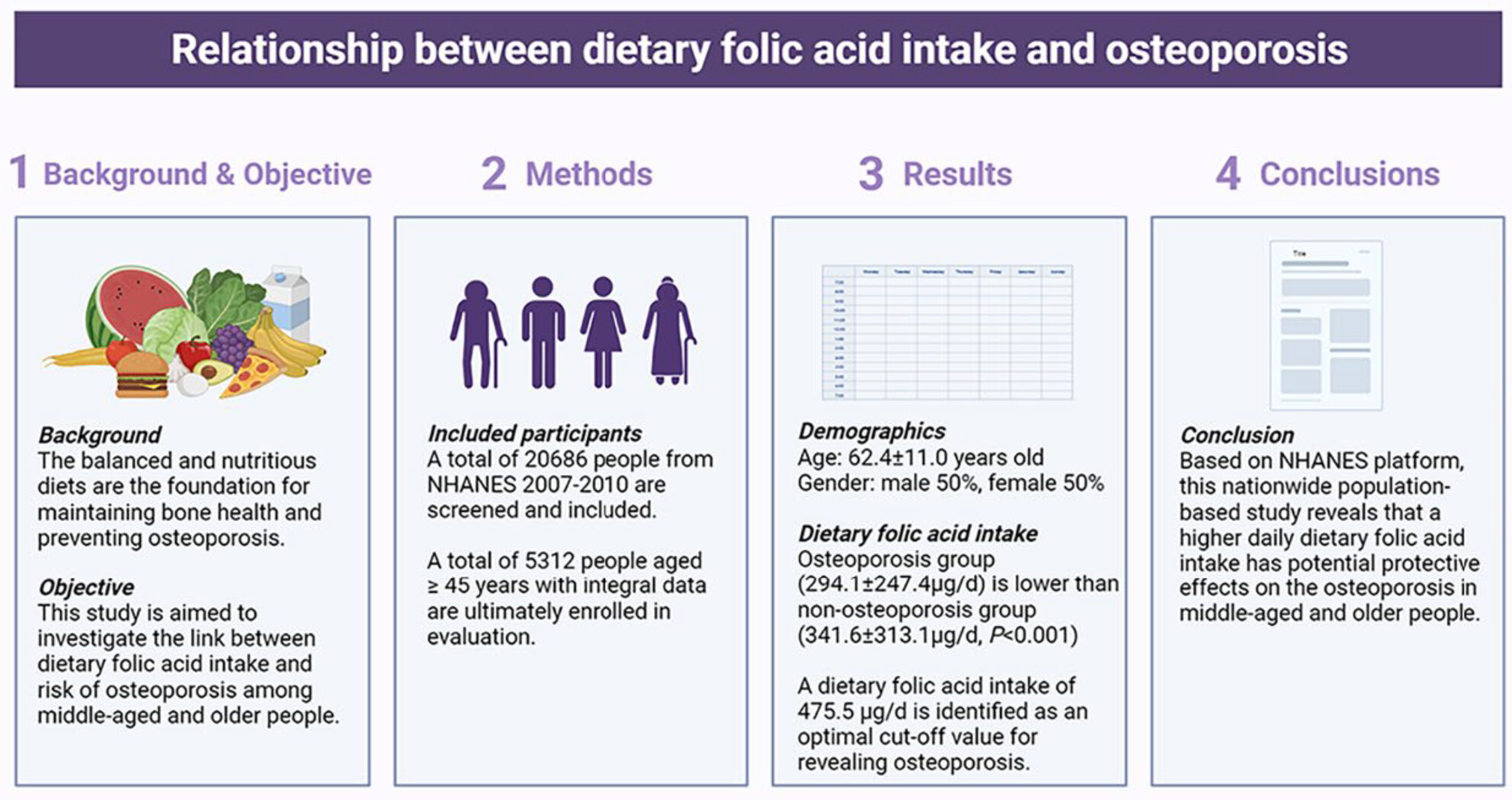
This study is aimed at investigating the link between dietary folic acid intake and the risk of osteoporosis among middle-aged and older people, and a total of 20,686 people from the National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2010 were screened and included. The results indicate that a higher daily dietary folic acid intake has potential protective effects on osteoporosis in middle-aged and older people.
Escherichia coli isolates from vegetable farms in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Antimicrobial susceptibility profile and associated resistance genetic markers
- Pages: 4122-4132
- First Published: 10 March 2024
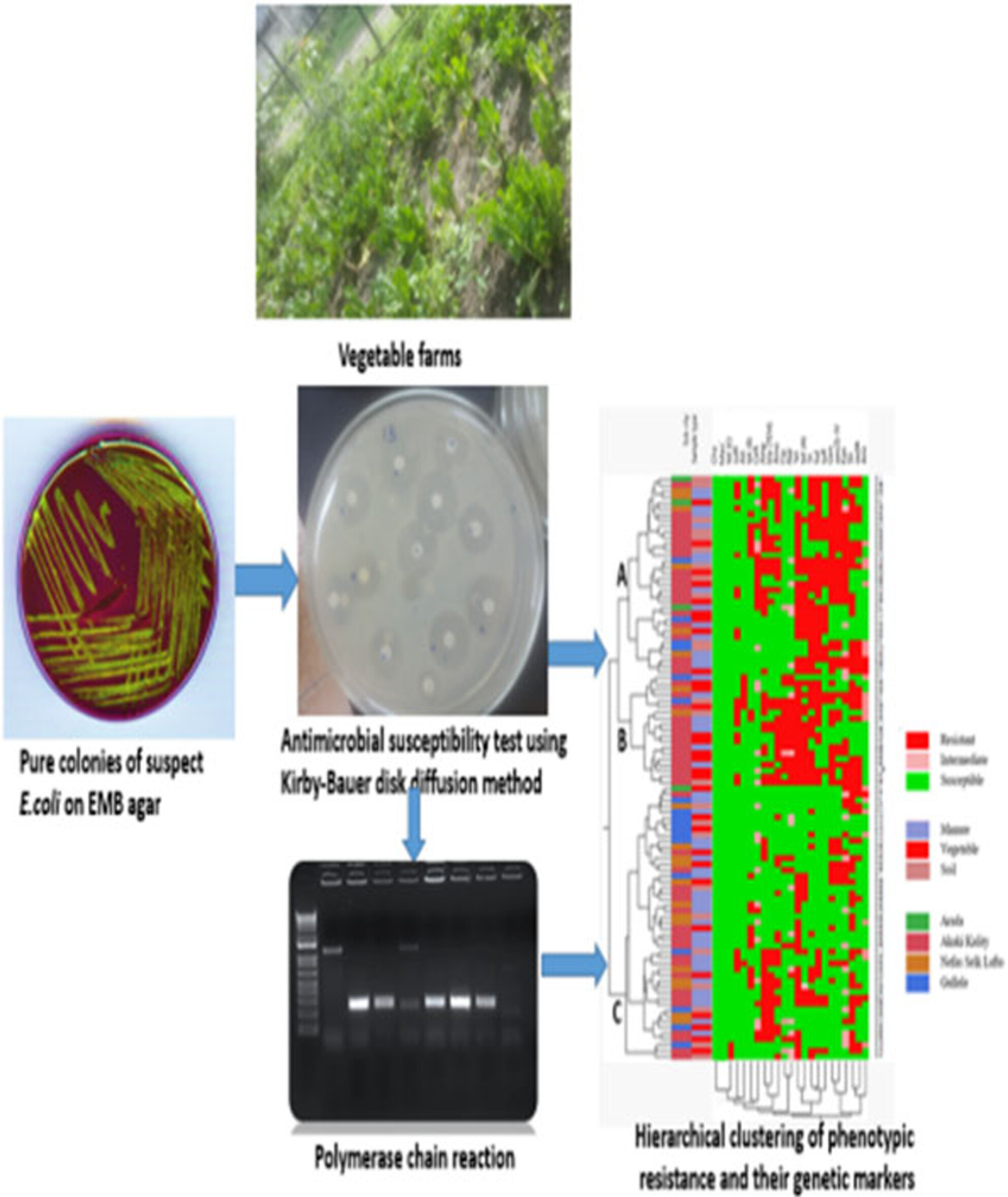
This study investigated the prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli among vegetable farms in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The prevalence of E. coli was 32.3% in manure, 23.6% in soil, and 19.8% in vegetables. Multidrug resistance was detected in 61% of the E. coli isolates, with the highest resistance to tetracycline (72%), streptomycin (63%), and sulfamethoxazole+ trimethoprim (56%). aac(3)-IV (76.9%), bla TEM (65.4%), aadA (60.3%), tet(A) (58.3%), and sulI (51.7%) were the commonly detected antimicrobial resistance genetic markers.
Perceived nutrition needs of people experiencing disadvantage in utilizing support services: An Australian case study
- Pages: 4133-4142
- First Published: 06 March 2024

Individuals experiencing socio-economic disadvantage face higher rates of food insecurity and diet-related health disparities. Addressing these issues requires identifying barriers and devising strategies that encompass individual and systemic factors and prioritizing client-informed, cost-effective, and sustainable models for improving nutrition access and health equity.
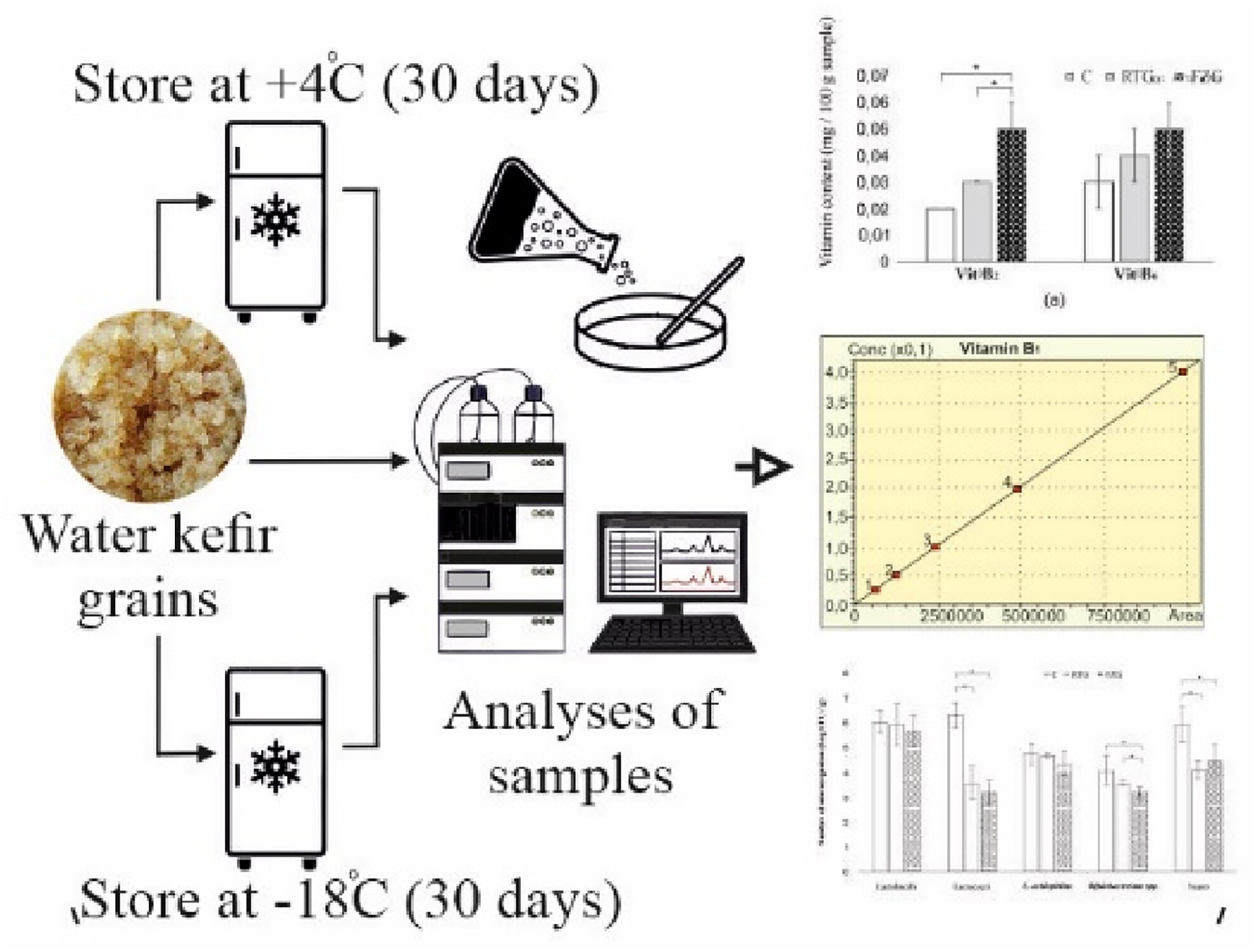
Microbial viability and nutritional content of water kefir grains under different storage conditions
- Pages: 4143-4150
- First Published: 05 March 2024
The levels of essential nutrients and nonessential metals in different varieties of teff produced in Hidabu Abote Woreda, Oromia, Ethiopia
- Pages: 4151-4159
- First Published: 04 March 2024
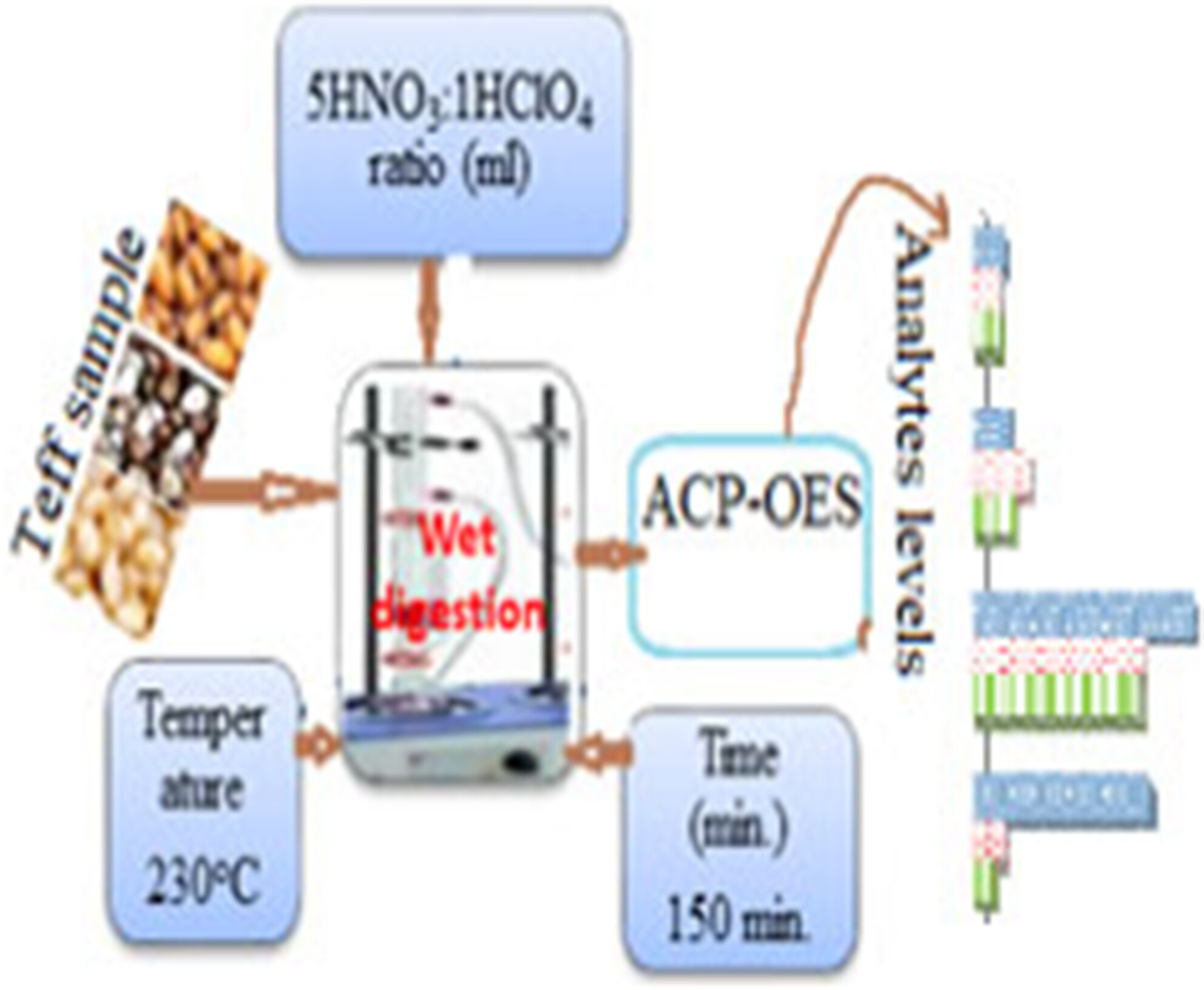
Optimizing the regent volume and ratio, temperature, and digestion duration led to the development of wet digestion sample preparation. Based on this, the optimal condition for sample preparation was found to be regents (a combination of 5-mL HNO3 and 1-mL HClO4) at 230°C for 150 min. Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) was used to analyze teff samples for 17 analytes (both essential and nonessential) once the established method had been validated.
Curcumin mitigates acrylamide-induced ovarian antioxidant disruption and apoptosis in female Balb/c mice: A comprehensive study on gene and protein expressions
- Pages: 4160-4172
- First Published: 07 March 2024
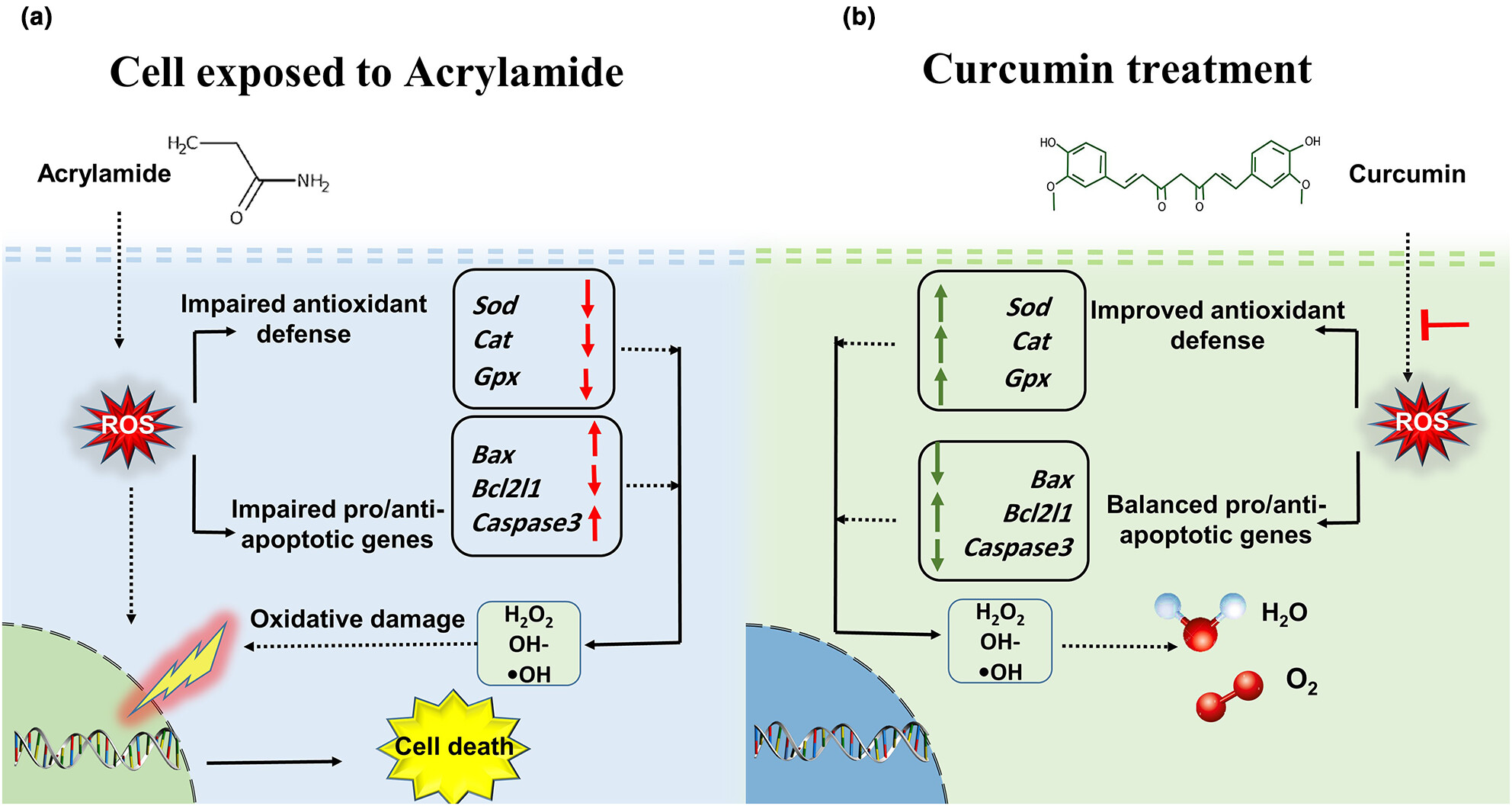
The issue of whether and how acrylamide intake affects human health and fertility status, has recently attracted considerable attention. The purpose of this study was to determine whether curcumin treatment, as a potential antioxidant, impacts ACR-induced alterations in the first-line antioxidant defense and apoptosis in the mouse ovarian tissues.
The impact of chitooligosaccharides with a certain degree of polymerization on diabetic nephropathic mice and high glucose-damaged HK-2 cells
- Pages: 4173-4184
- First Published: 22 March 2024
Association of caffeine consumption with all-cause and cause-specific mortality in adult Americans with hypertension
- Pages: 4185-4195
- First Published: 08 March 2024
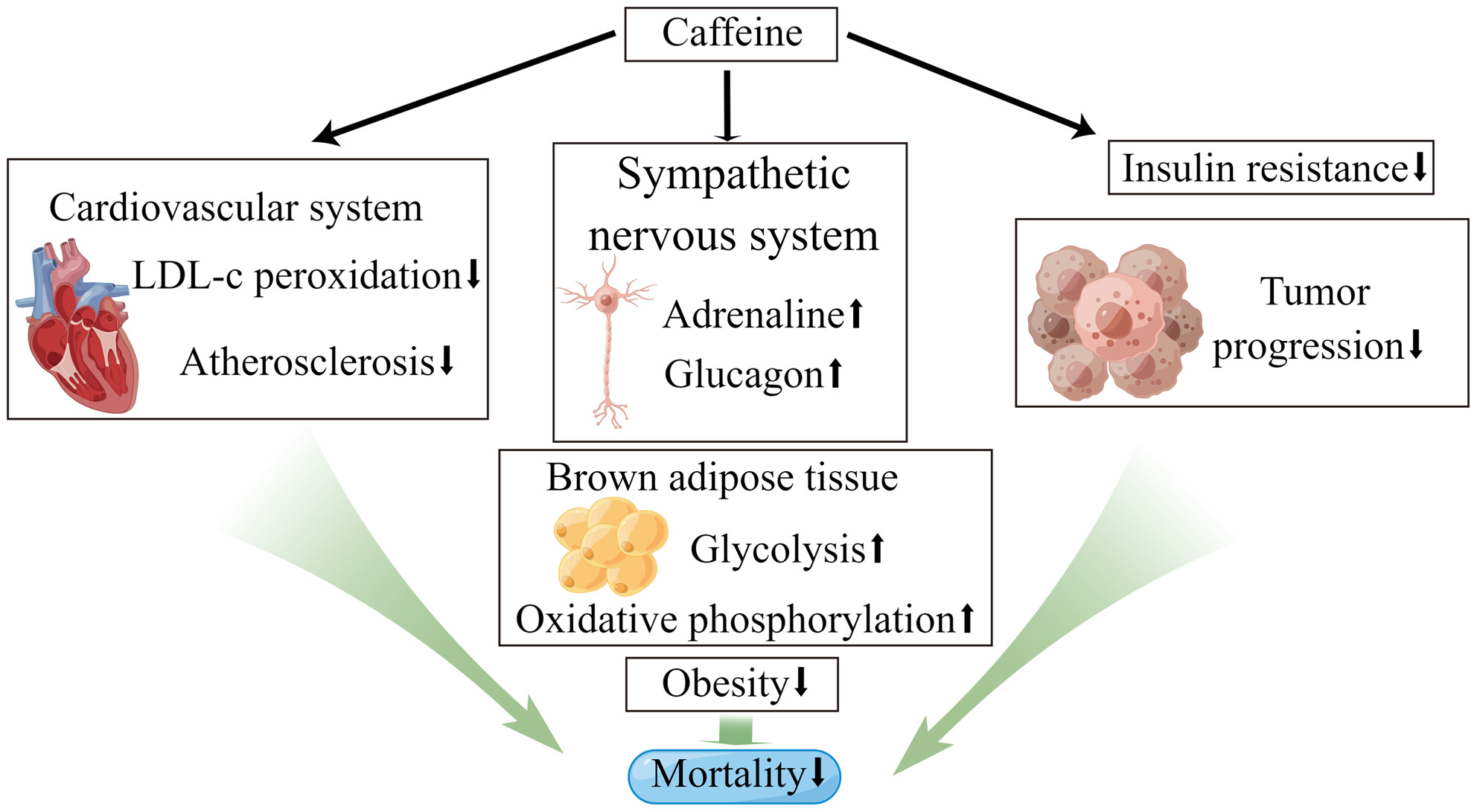
The long-term relationship between caffeine consumption and mortality in hypertensive patients has rarely been studied. Our findings indicate a nonlinear association between average caffeine consumption and all-cause mortality, suggesting that hypertensive patients may benefit from moderate caffeine intake.
Edible bird's nest alleviates pneumonia caused by tobacco smoke inhalation through the TNFR1/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Pages: 4196-4210
- First Published: 01 April 2024
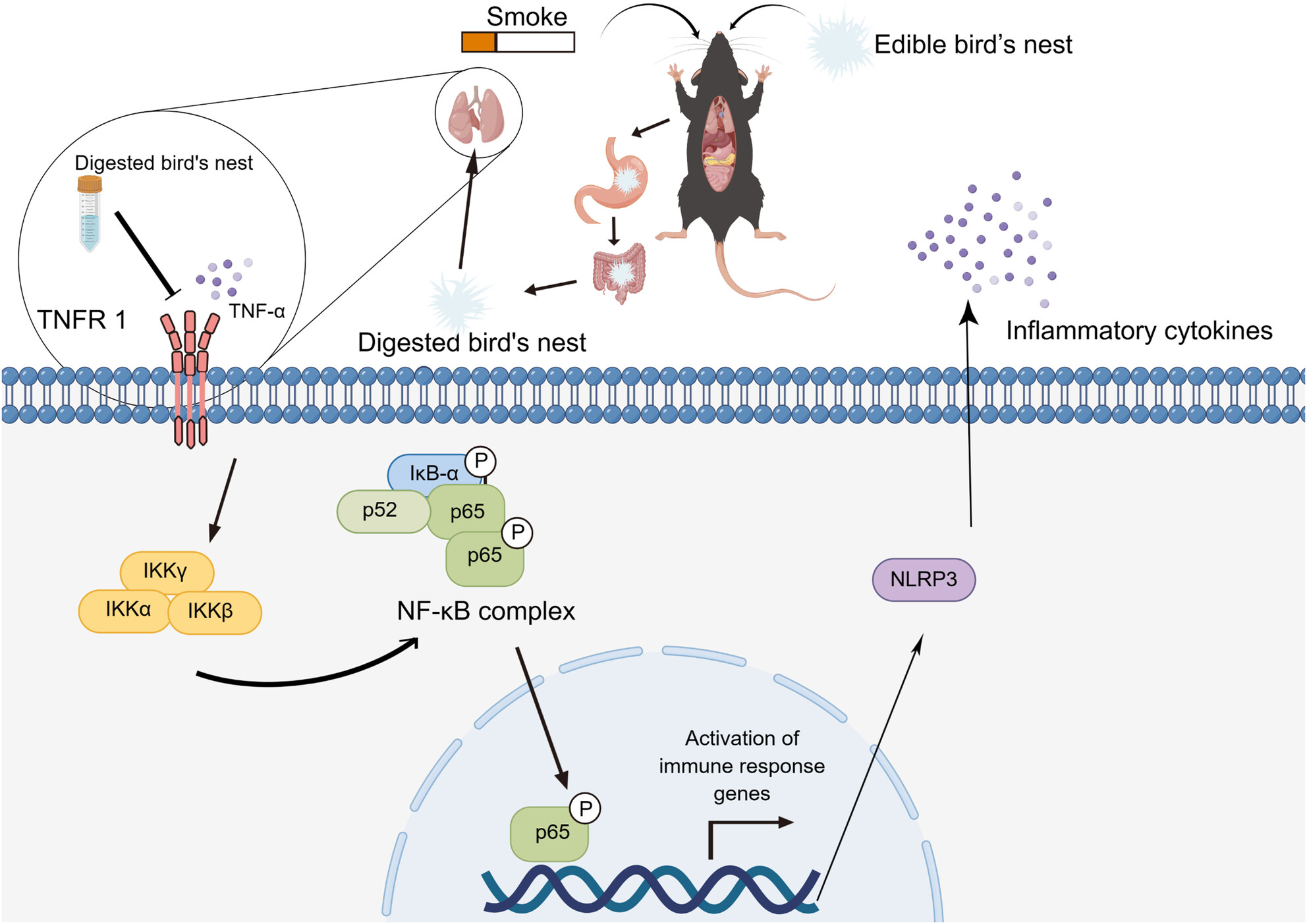
Edible bird's nest (EBN) promotes epithelial cell proliferation and viability, which reduces alveolar epithelial damage and lower levels of inflammation in the lungs and body. Edible bird's nest can effectively inhibit the expression of NOD-like receptor pyrin 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, thereby effectively controlling the smoke-induced pulmonary inflammatory response. Edible bird's nest reduces the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by inhibiting the activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway during inflammatory injury.
Performance of spray-dried Ziziphus jujuba extract using insoluble fraction of Persian gum–sodium alginate and whey protein: Microstructural and physicochemical attributes of micro- and nano-capsules
- Pages: 4211-4222
- First Published: 18 April 2024
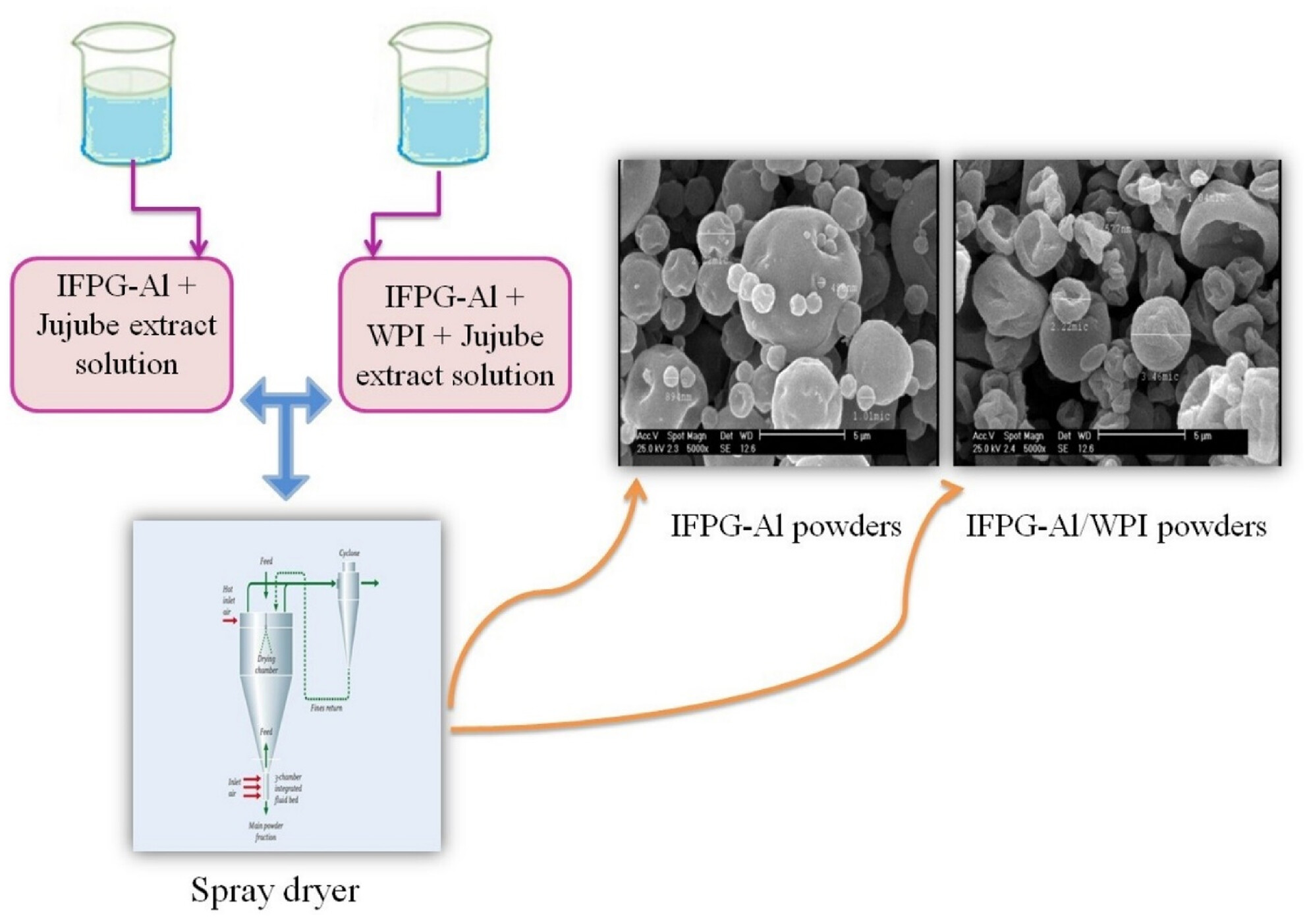
The encapsulation efficiency of Ziziphus jujuba extract in IFPG-alginate/WPI powders was more (74.84%). Incorporation of WPI to IFPG-alginate led to lower yield, higher solubility, and better protection of TPC. IFPG-alginate capsules had more spherical particles with larger particle sizes than IFPG-alginate/WPI.
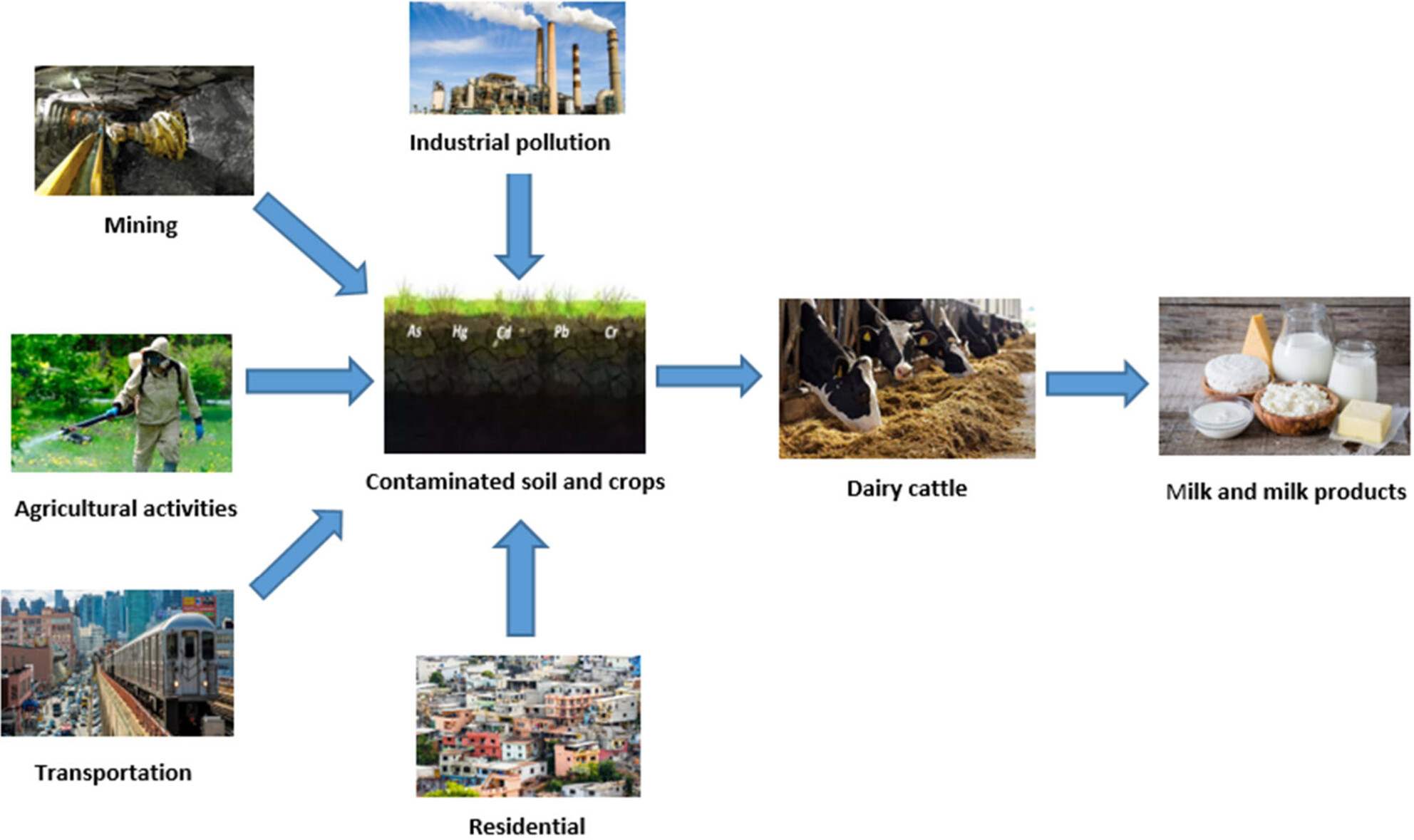
Influence of geographical location on the distribution of heavy metals in dairy cattle feeds sourced from two South African provinces
- Pages: 4223-4232
- First Published: 07 March 2024
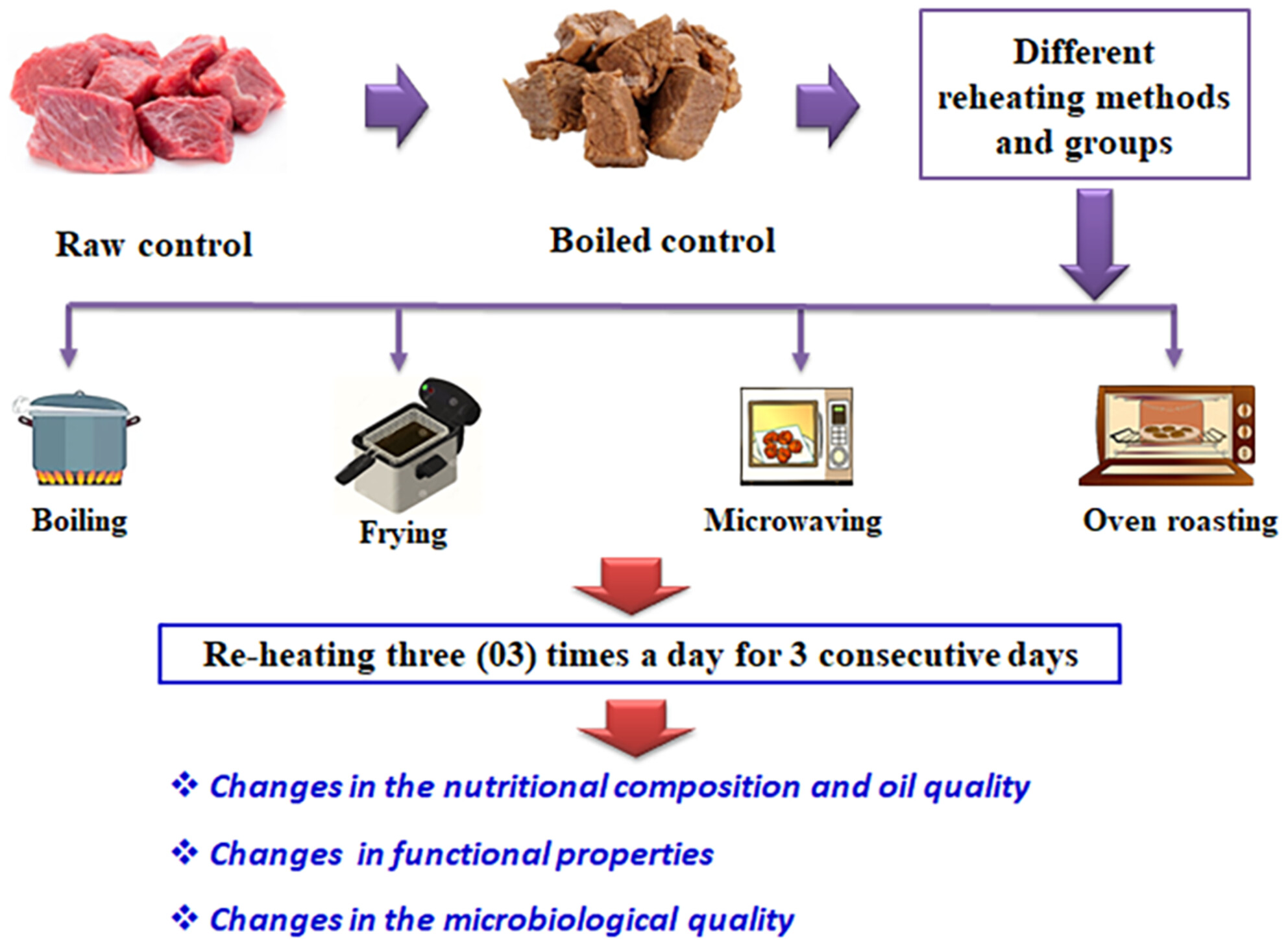
Effect of different reheating processes and conditions on the nutritional, functional, and microbiological properties of cow meat
- Pages: 4233-4247
- First Published: 18 March 2024
Improving dietary citric acid production by the wild-type Aspergillus niger ASP26 strain isolated from date by-product
- Pages: 4248-4258
- First Published: 08 April 2024
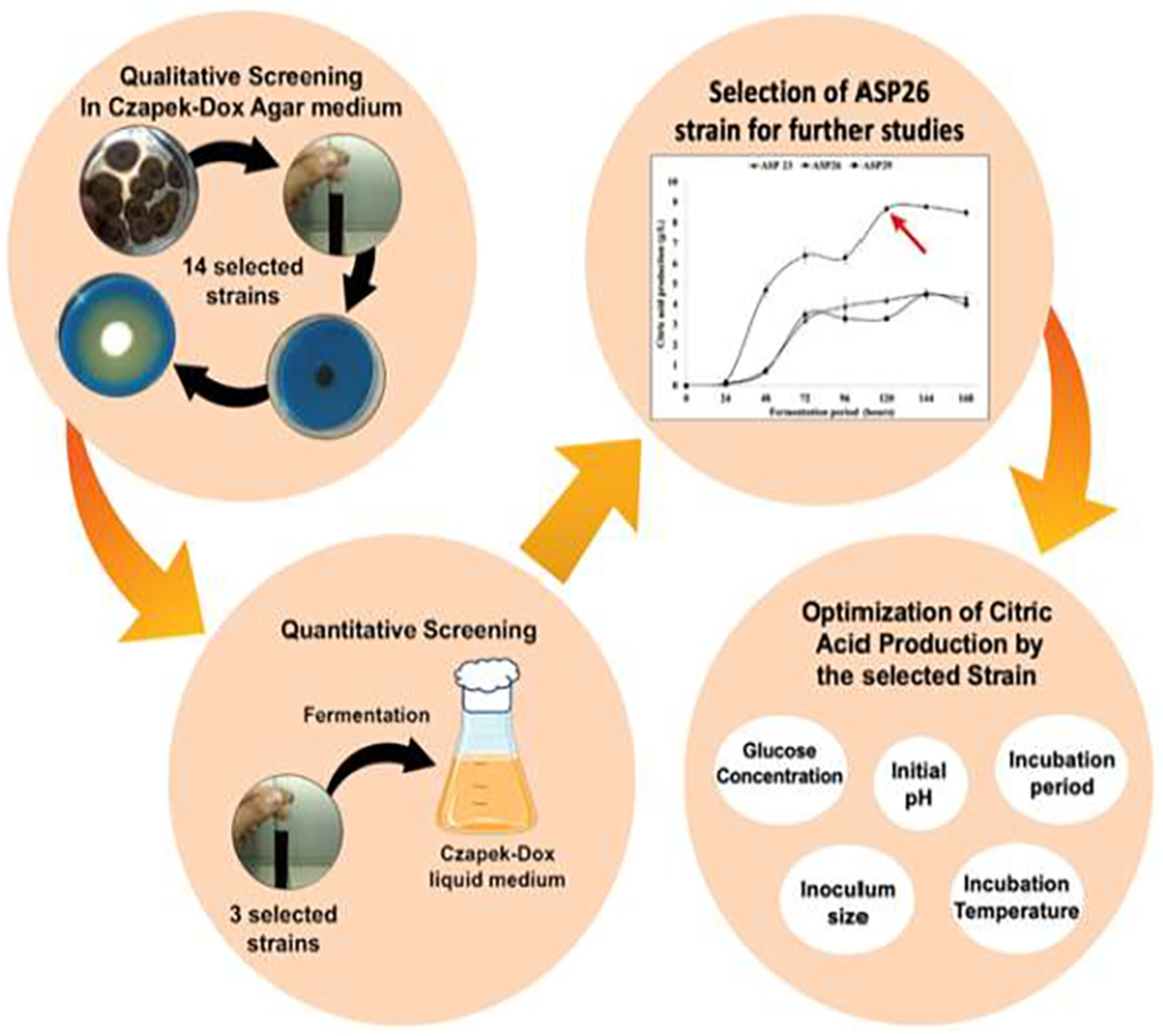
Initially, fungi capable of producing citric acid were isolated and identified based on their characteristics and enzymatic activity. These isolates were then screened for CA production using a modified Czapek-Dox medium. The study revealed significant effects of pH, carbon sources, inoculum size, and fermentation duration on CA production.
Bitter melon extract mitigates heterocyclic aromatic amine formation in chicken thigh meat
- Pages: 4259-4268
- First Published: 07 March 2024
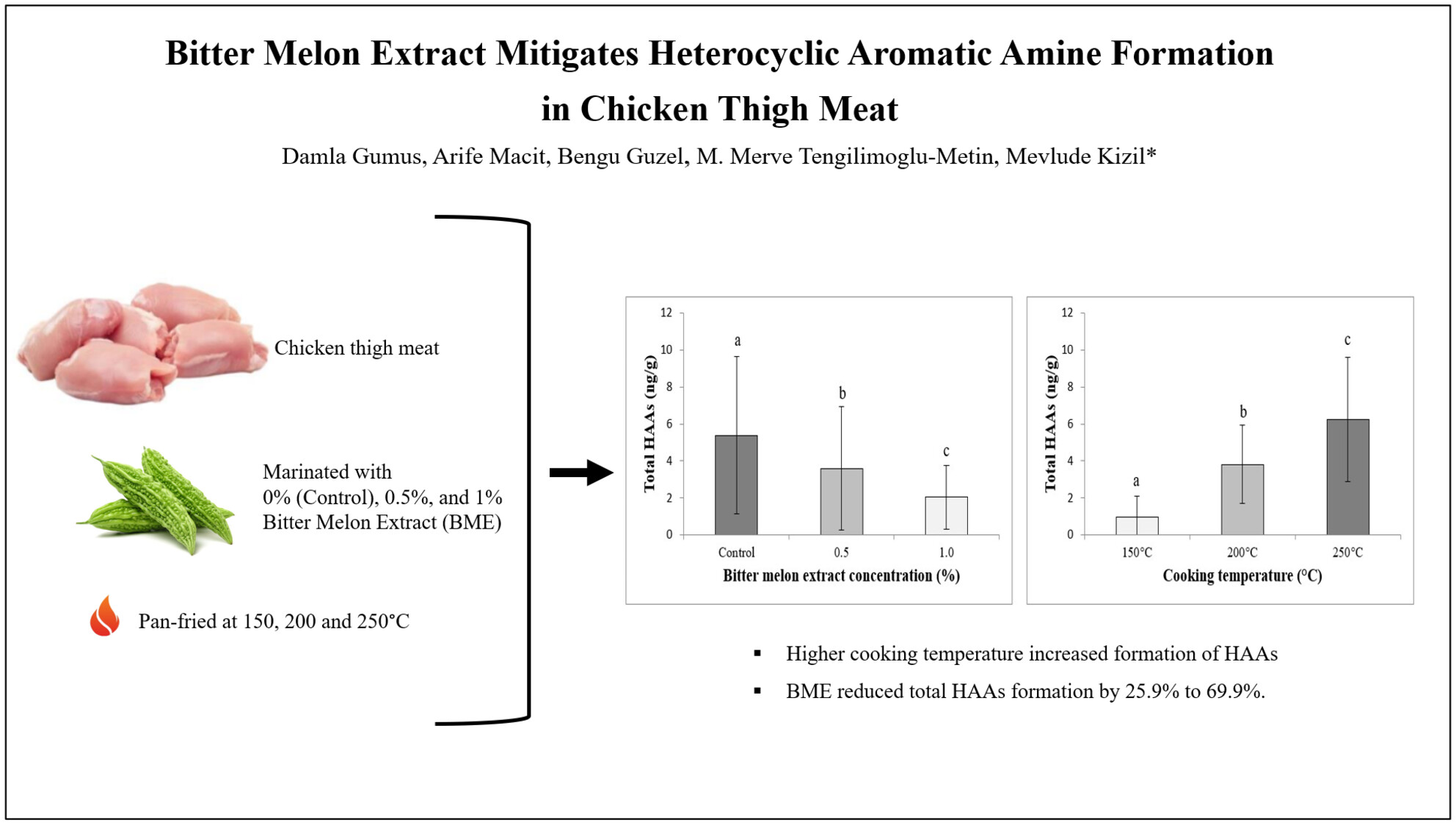
The impact of bitter melon extract (BME) on heterocyclic aromatic amine (HAA) formation in chicken thigh meat during pan-frying at various temperatures has been investigated. Higher cooking temperatures led to increased total HAA levels, while marination with BME significantly mitigated HAA formation, demonstrating reductions ranging from 25.9% to 69.9%.
The effect of nano/microparticles of bee pollen on the shelf life of high-fat cooked sausage during refrigerated storage
- Pages: 4269-4283
- First Published: 07 March 2024
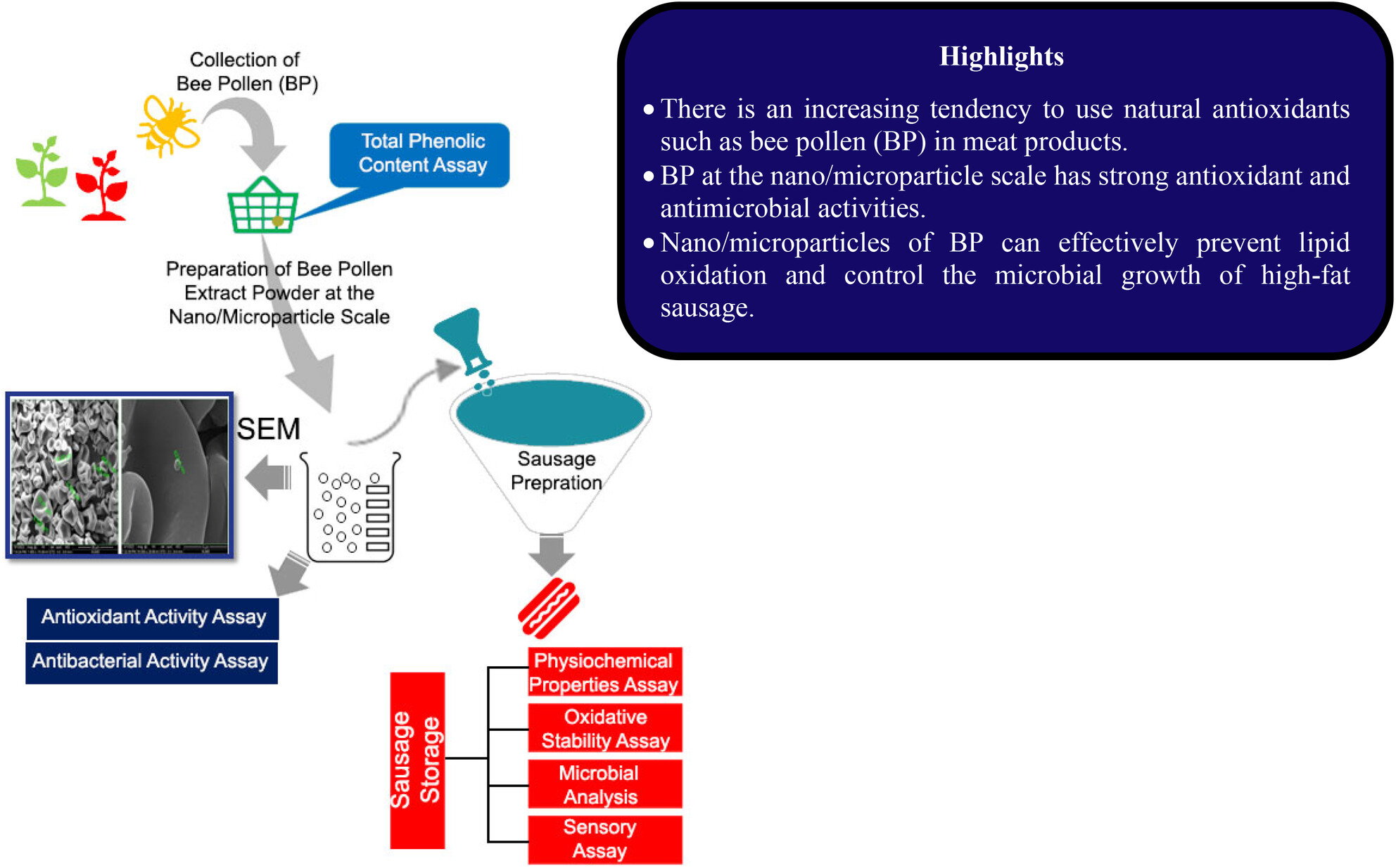
There is an increasing tendency to use natural antioxidants such as bee pollen (BP) in meat products. BP at the nano/microparticle scale has strong antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Nano/microparticles of BP can effectively prevent lipid oxidation and control the microbial growth of high-fat sausage.
Enhancing nutritional and functional properties of rice starch by modification with Matcha extract
- Pages: 4284-4291
- First Published: 08 March 2024
Impact of low-oxalate diet on hyperoxaluria among patients suffering from nephrolithiasis
- Pages: 4292-4298
- First Published: 05 April 2024

Consuming high amounts of foods which are rich in oxalate content may lead to the formation of hyperoxaluria among patients suffering from nephrolithiasis. Dietary modification is a vital component in the treatment of hyperoxaluria. Nuts(Almonds), tea, coffee, prunes, chocolate, root vegetables, rhubarb, paneer, navy beans, and spinach are some of the foods highest in oxalate in the diet causing calcium oxalate stones. Low-oxalate diet (LOD) is a one dietary pattern which is associated with lower a risk of hyperoxaluria. This diet offers a lot of low-oxalate fruits and vegetables, herbs and spices, cereals or grains, nuts, and seeds, a moderate amount of low-fat dairy products and little animal protein and also promotes urinary citrate excretion, a key inhibitor of calcium oxalate stones. Those people whose are suffered from hyperoxaluria may also attain benefits from low-oxalate diet because a low-oxalate diet acts as a therapeutic diet and it may help in proper utilizing of oxalate without causing metabolism alteration and remove the excess oxalate from kidney without stone forming.
Preparation and evaluation of functional cocoa-free spread alternatives from different sources
- Pages: 4299-4310
- First Published: 12 April 2024
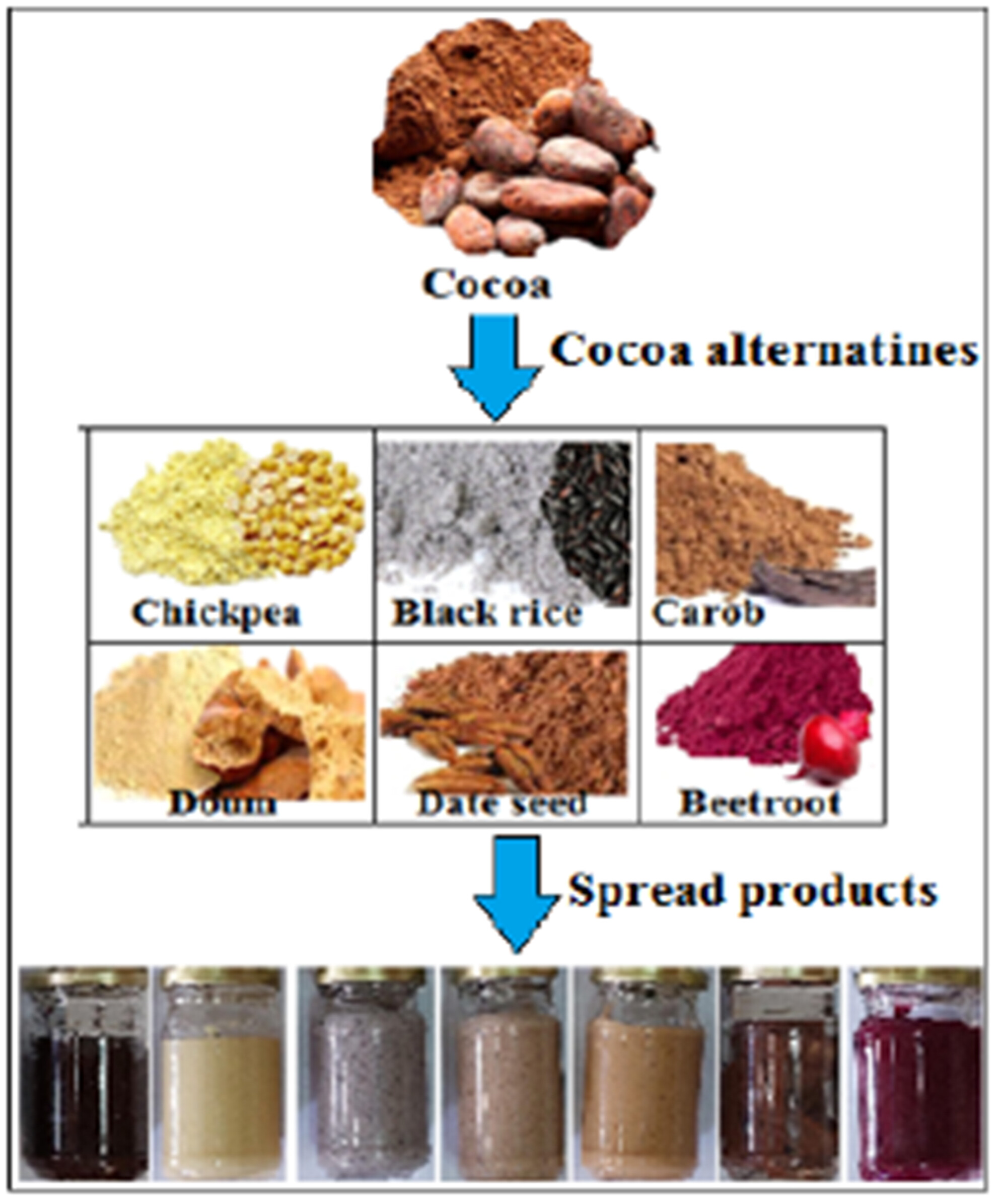
- Functional cocoa-free spread was successfully prepared.
- The potential of powdered hulled chickpea, black rice, carob, doum, date seeds, and beetroot as cocoa alternatives.
- Formulation of novel functional/alternative spreads.
- A variation in the proximate chemical analysis of the produced functional spreads was found.
- The experimental functional cocoa-free products had competitive nutritional compositions.
- Microbial load of spread samples was within the acceptable limits for their shelf life of 9 months.
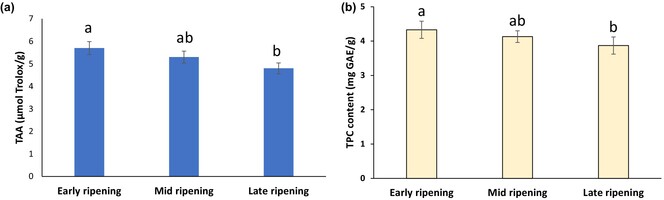
The influence of ripening on the nutrient composition and antioxidant properties of New Zealand damson plums
- Pages: 4311-4320
- First Published: 30 March 2024
A randomized controlled trial of sweet basil leaf powder-enriched cookies for anemia management in adolescent girls
- Pages: 4321-4329
- First Published: 15 March 2024
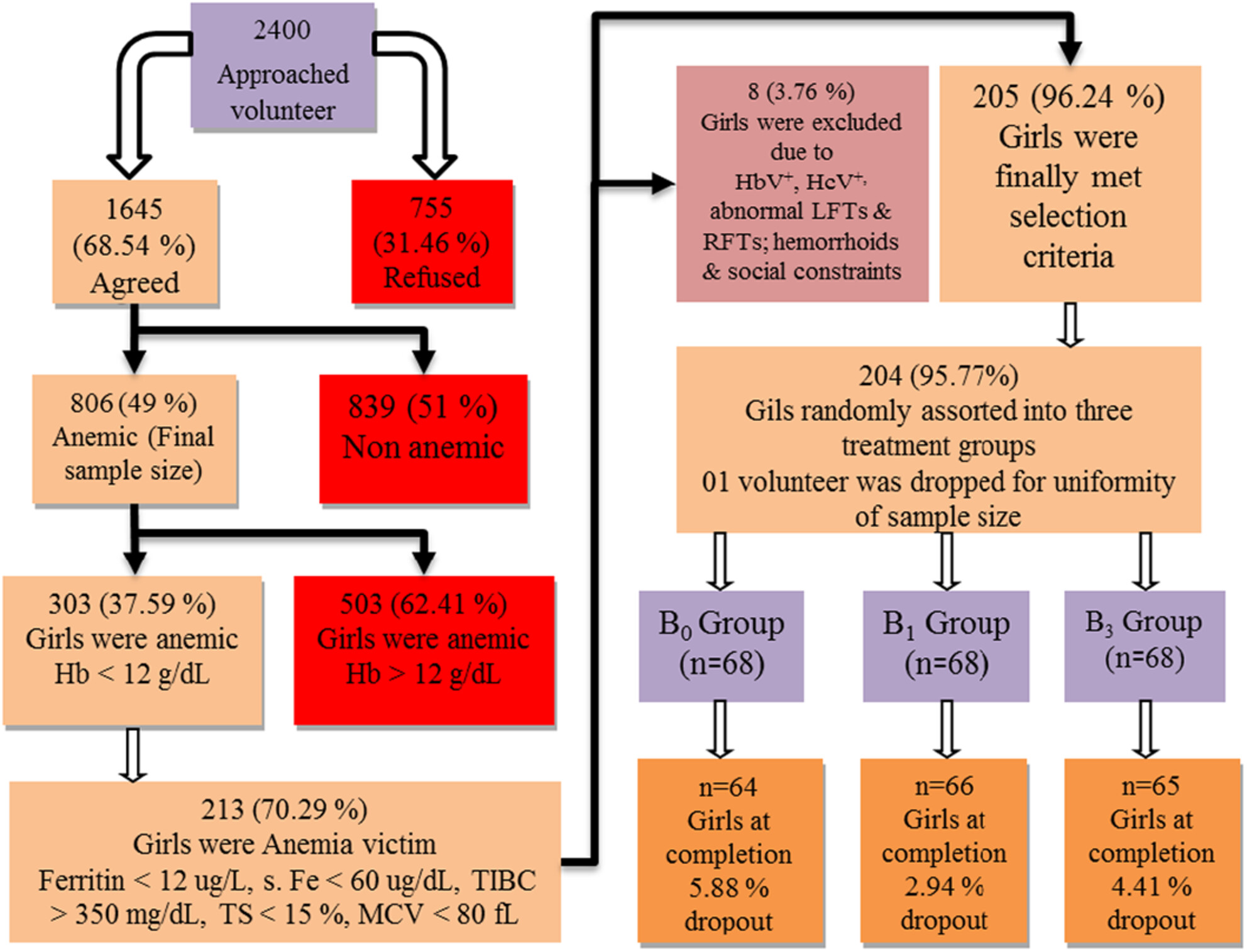
- The effectiveness of sweet basil leaf powder as a natural source of iron for the treatment of anemia in adolescent girls.
- Hematological parameters such as Hb, Hct, TIBC, MCV, MCH, MCHC, serum iron, and serum ferritin were significant (p ≤ .05).
- The study demonstrated that SBLP-fortified cookies can be an effective treatment option for anemia.
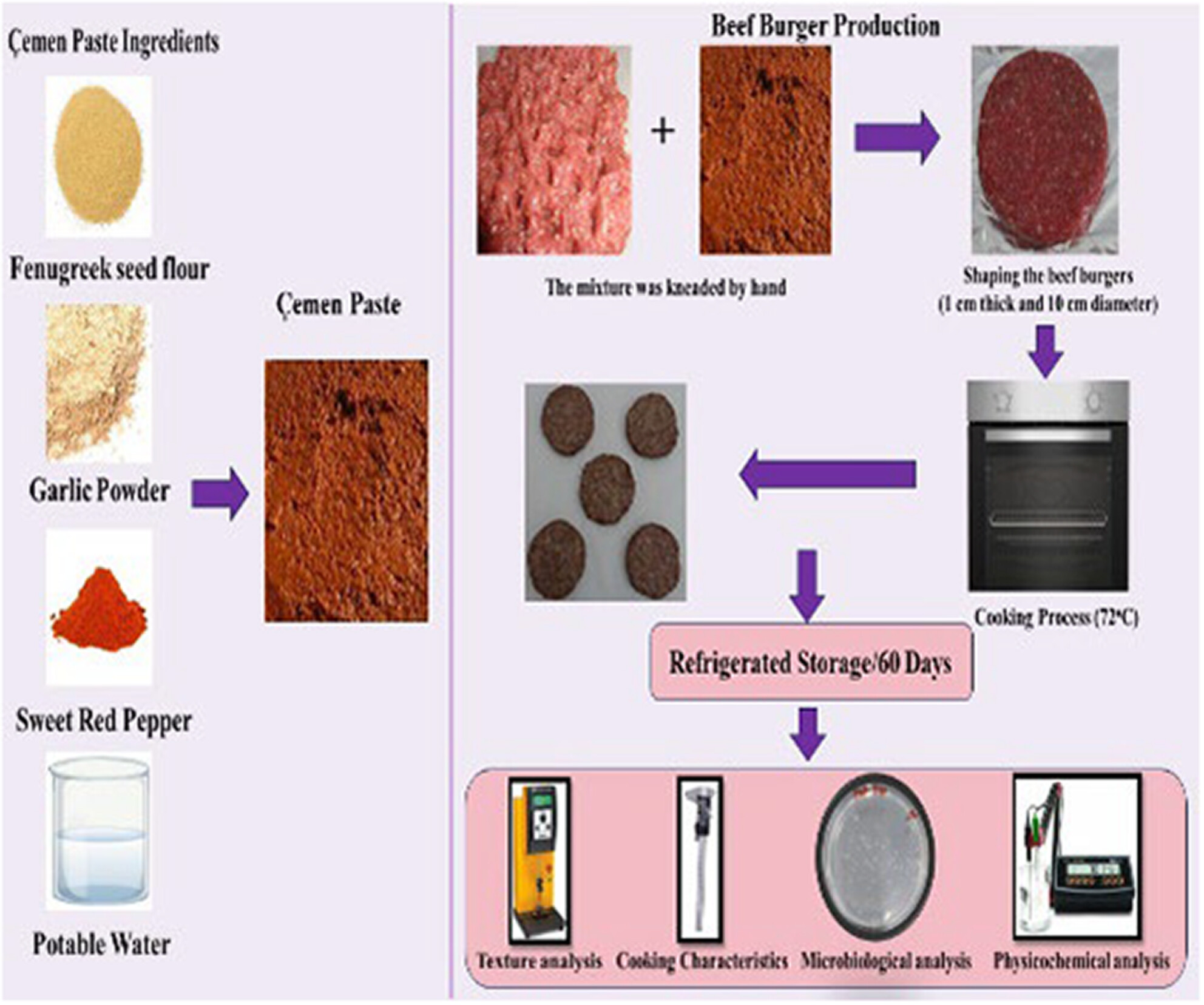
Effects of Çemen pastes prepared in different formulations on physicochemical, microbiological, and textural properties of beef hamburger patties during refrigerated storage
- Pages: 4330-4341
- First Published: 15 March 2024
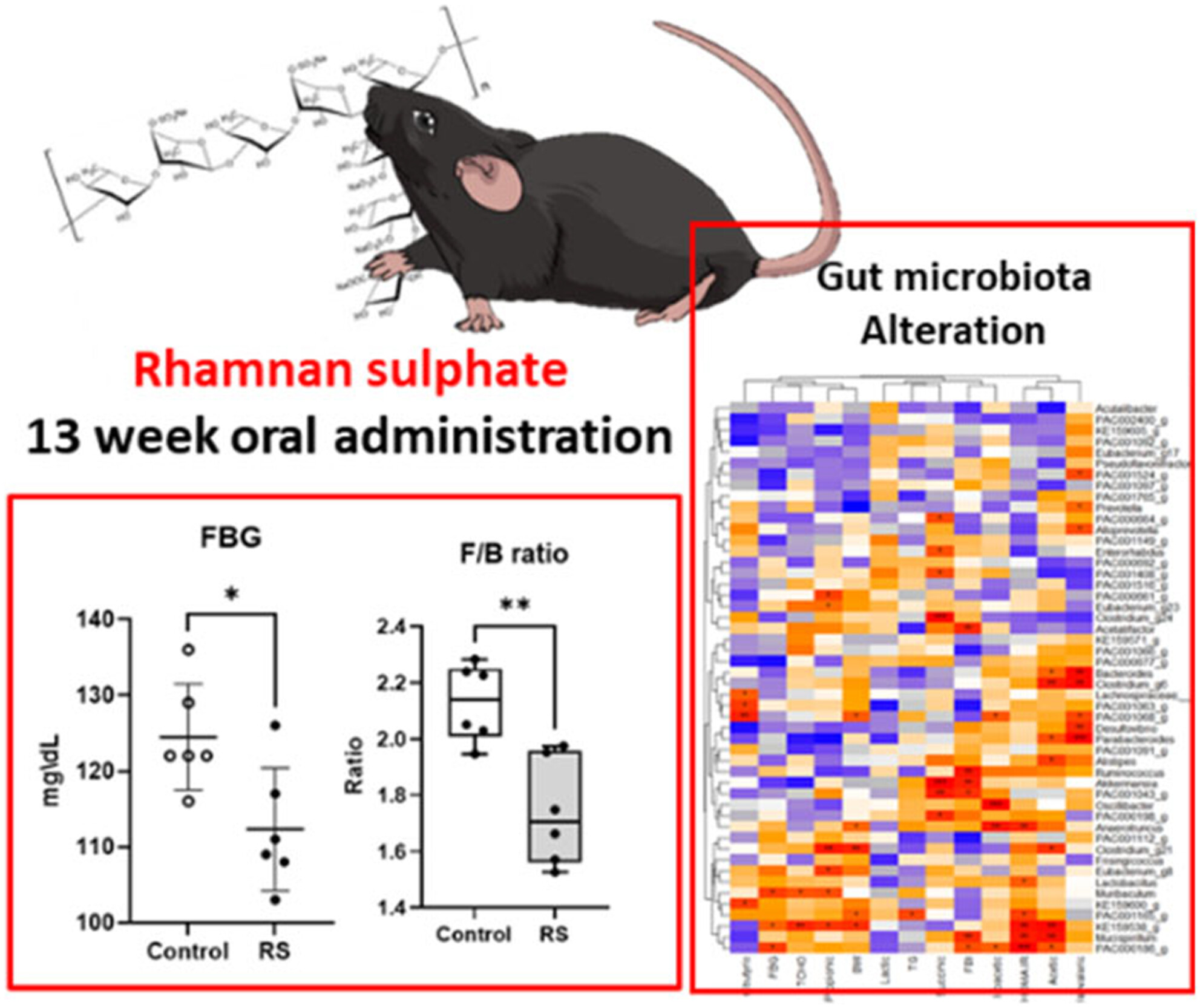
Lipid- and glucose-lowering effects of Rhamnan sulphate from Monostroma nitidum with altered gut microbiota in mice
- Pages: 4342-4352
- First Published: 25 March 2024
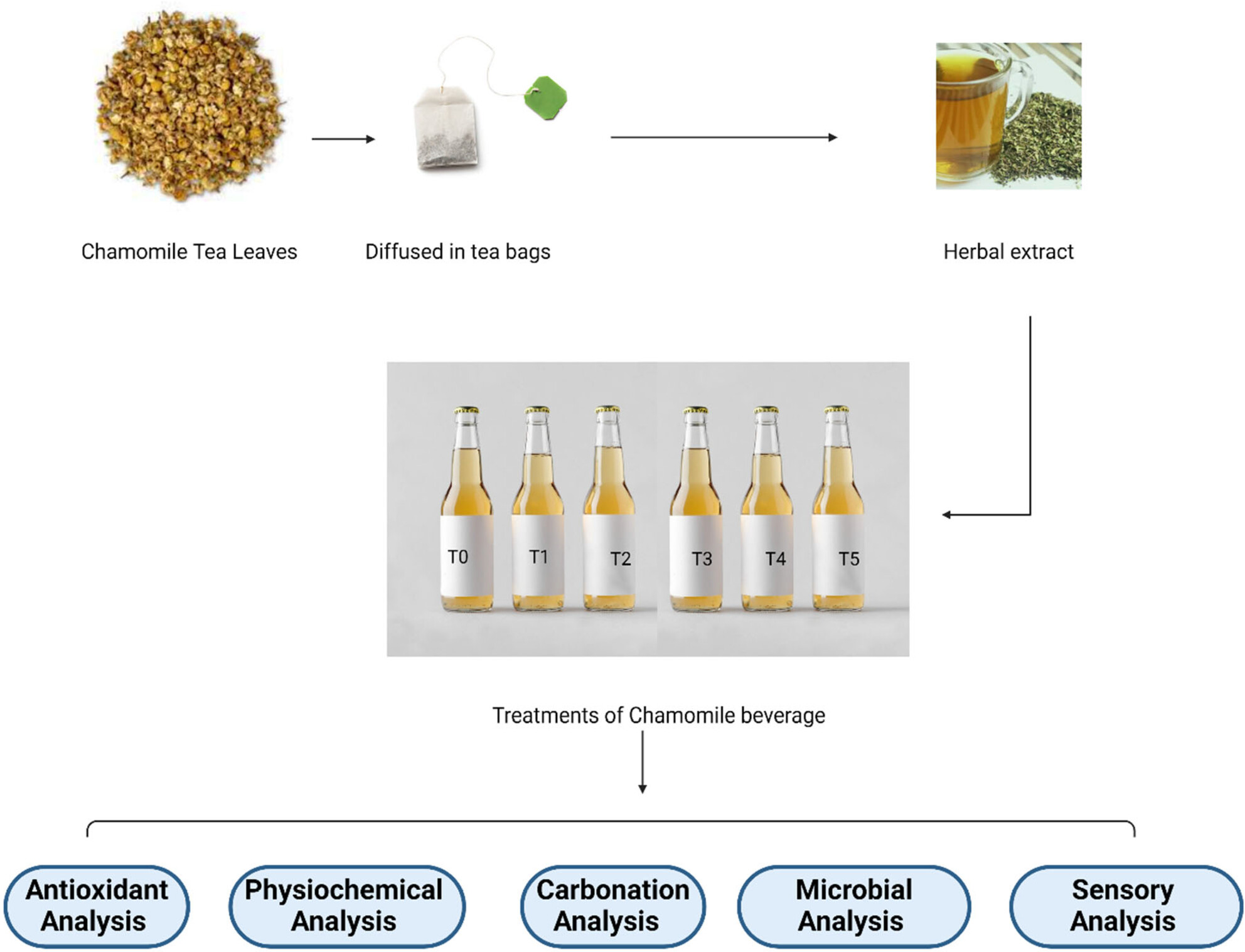
Characterization of carbonated beverage fortified with chamomile herbal extract
- Pages: 4353-4361
- First Published: 15 March 2024
Valorization of various nut residues grown in Turkey: Antioxidant, anticholinesterase, antidiabetic, and cytotoxic activities
- Pages: 4362-4371
- First Published: 27 May 2024
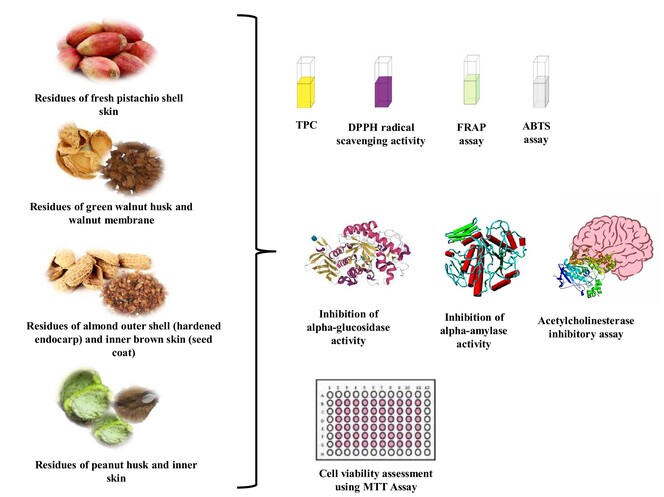
Nut residual types significantly affected the bioactive properties. Extracts obtained from nut residues demonstrated cytotoxic impacts on MIA-PaCa-2 and CaCo-2 cancer cells. Hazelnut residues exhibited inhibitory effects on enzymes, but these were less potent than the standards (galantamine or acarbose).
Evaluation of black grape pomace, a fruit juice by-product, in shalgam juice production: Effect on phenolic compounds, anthocyanins, resveratrol, tannin, and in vitro antioxidant activity
- Pages: 4372-4384
- First Published: 25 March 2024
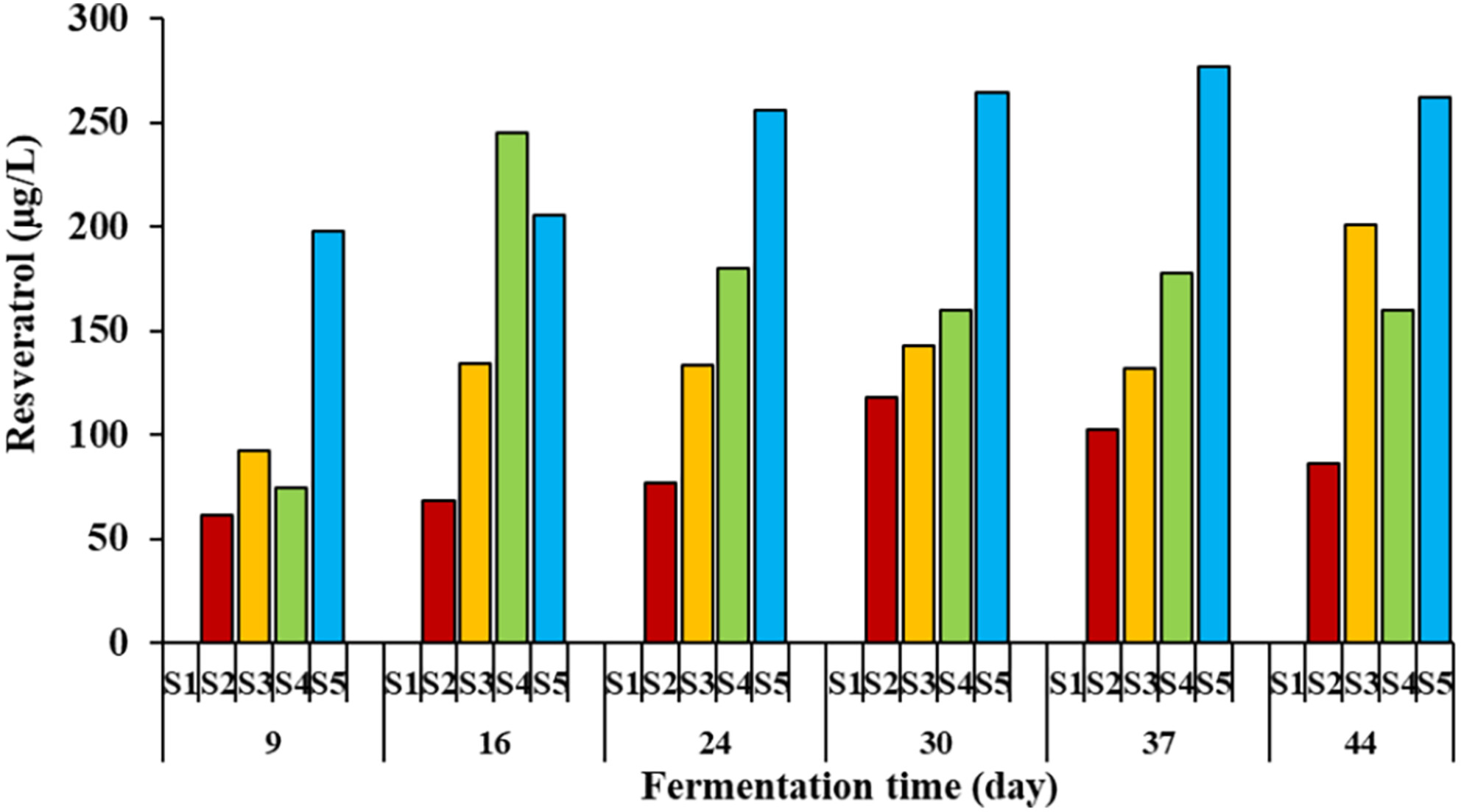
The phenolic diversity of traditional shalgam juice was increased in terms of phenolic compounds, such as delphinidin, cyanidin, petunidin, malvidin, peonidin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin glycosides, and resveratrol and catechin by using black grape pomace. The total phenolic contents and ABTS (2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)) antioxidant activity increased only in the shalgam juices obtained with the black grape pomace throughout the fermentation, except for the 24th day of fermentation. There was a strong relationship between total phenolic content and ABTS antioxidant activity.
Co-encapsulation of Shirazi thyme (Zataria multiflora) essential oil and nisin using caffeic acid grafted chitosan nanogel and the effect of this nanogel as a bio-preservative in Iranian white cheese
- Pages: 4385-4398
- First Published: 15 April 2024
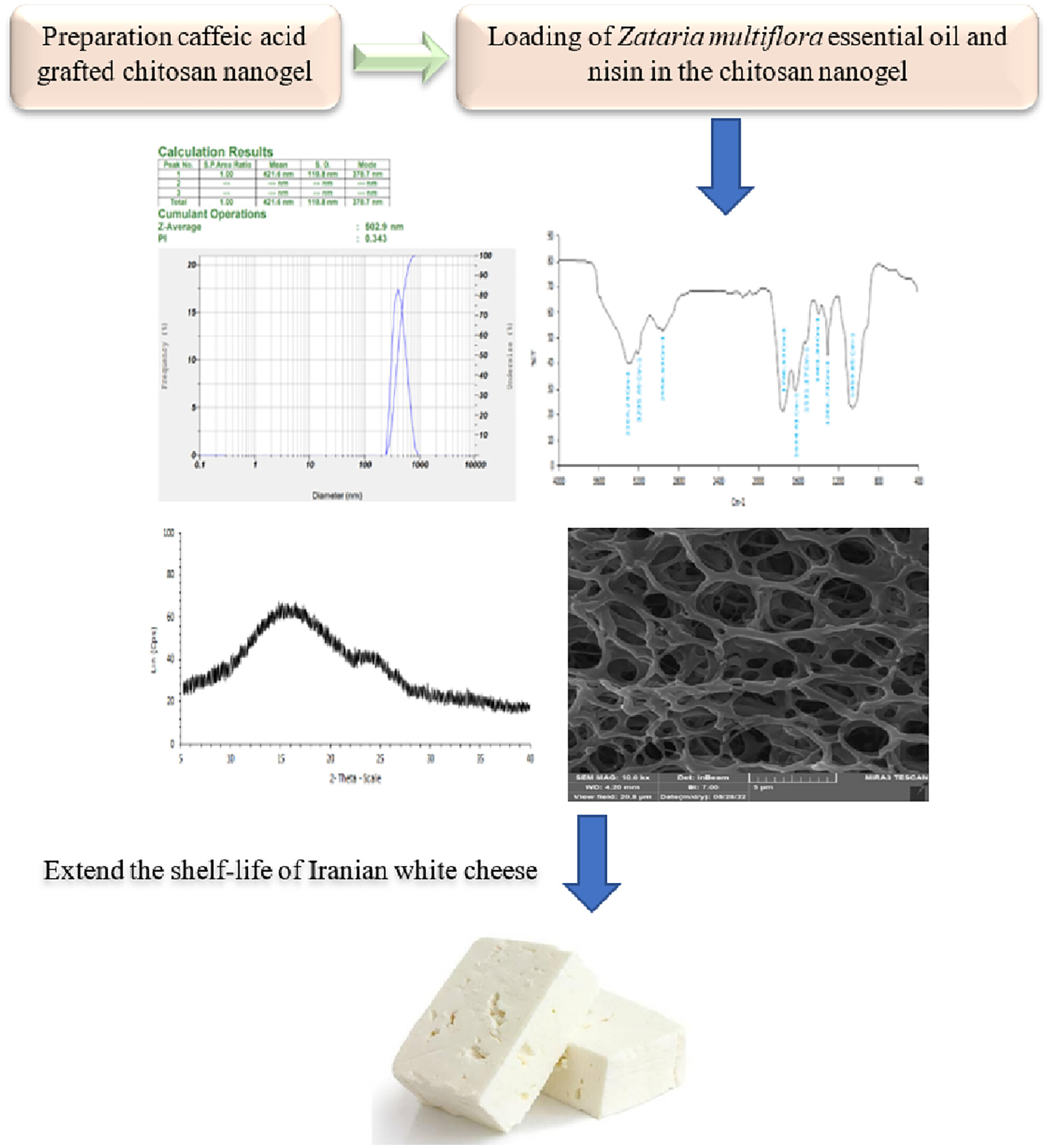
Preparation of caffeic acid grafted chitosan nanogel containing Zataria multiflora essential oil (ZEO) and nisin. Confirming the stability of the optimal chitosan nanogel containing ZEO-nisin. Successful loading of the ZEO and nisin into the chitosan-caffeic acid (CS-CA) nanogel. Chitosan-ZEO-nisin nanogel increasing the shelf-life of Iranian white cheese. The preservative effect of chitosan-ZEO-nisin nanogel was comparable with that of sodium nitrate.
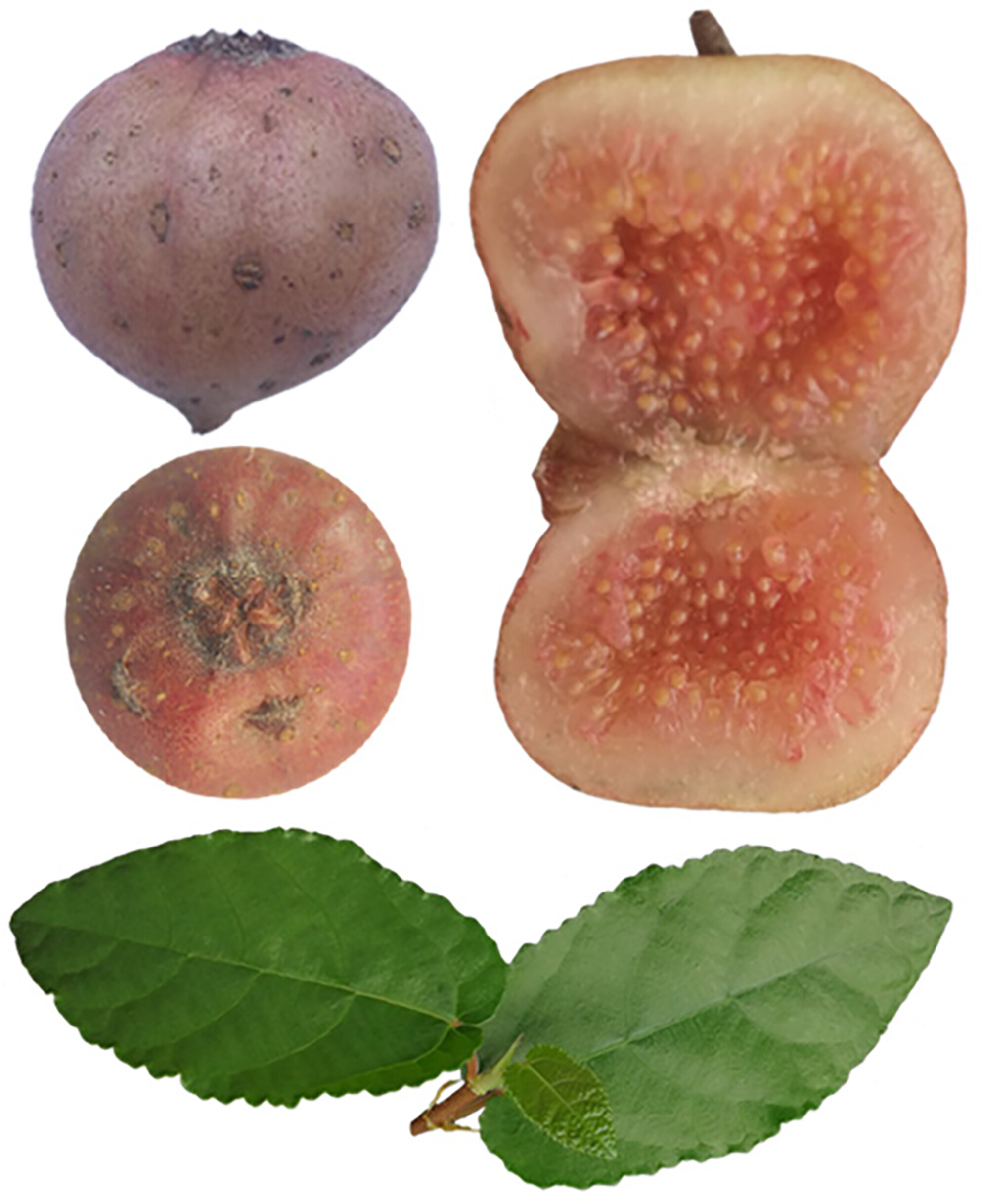
Appearance quality, nutritional value, and aroma components of wild diguo (Ficus tikoua Bur.) fruit collected from southwest China
- Pages: 4399-4407
- First Published: 19 March 2024
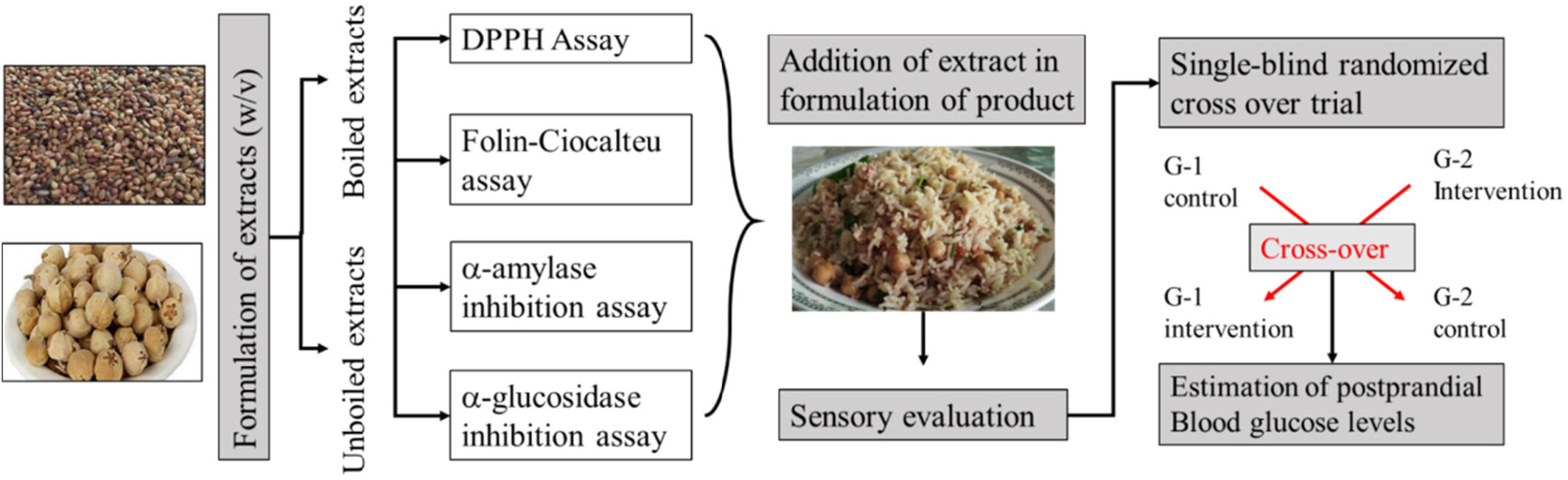
Formulation and assessment of chickpea pulao using fenugreek seeds and Indian rennet to improve blood glycemic levels
- Pages: 4408-4420
- First Published: 18 March 2024
Tree peony seed oil alleviates hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites in high-fat diet mice
- Pages: 4421-4434
- First Published: 04 April 2024
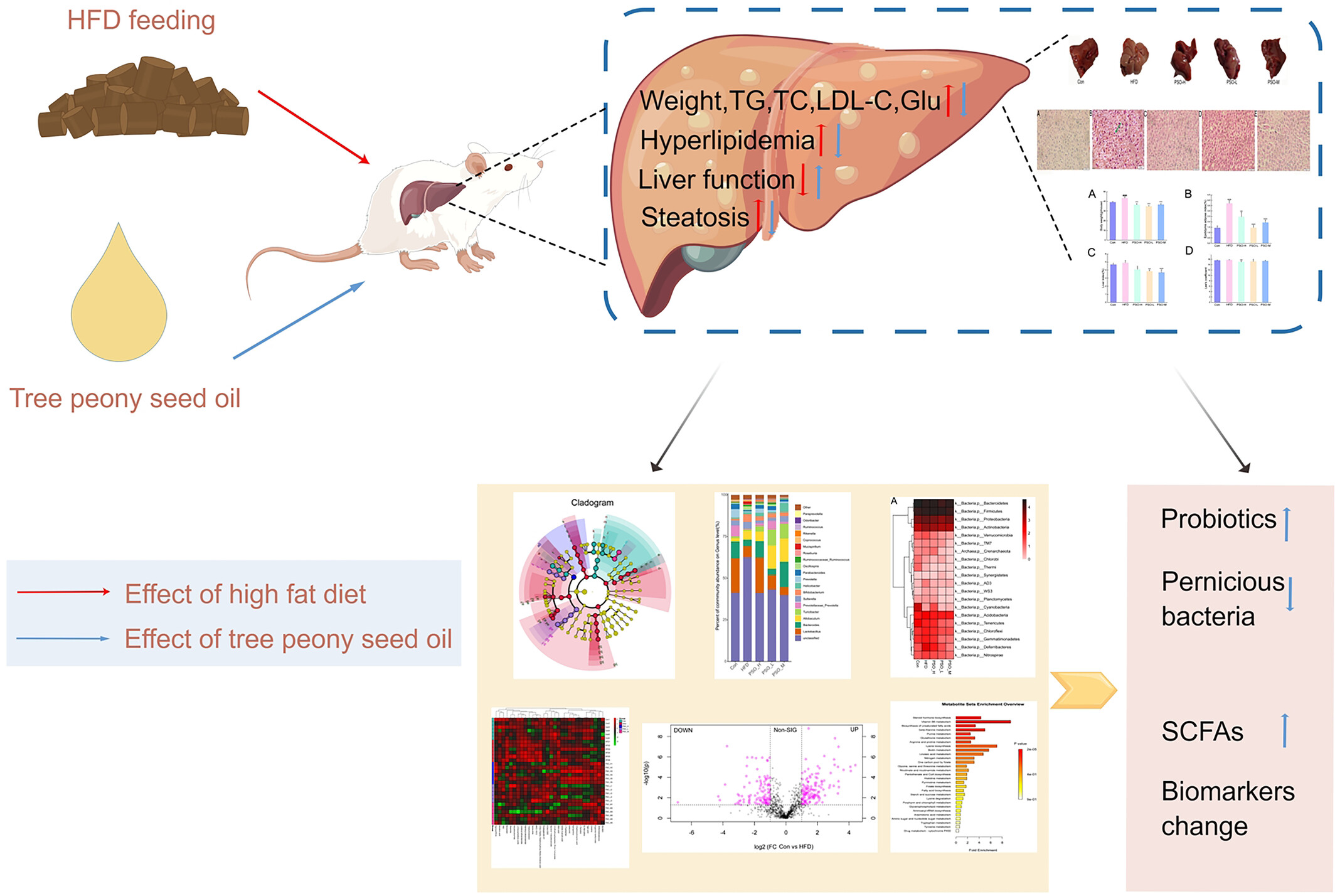
Tree peony seed oil (PSO) has the capacity of regulating gut microbiota and metabolites to decrease the body weights, fat vacuole levels triglyceride, total cholesterol, blood glucose, and low-density lipoprotein. Our findings will allow readers to understand the mechanism of tree peony seed oil improving hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia (By Figdraw).
Construction of a Zygosaccharomyces rouxii strain overexpressing the QOR gene for increased HDMF production
- Pages: 4435-4442
- First Published: 18 March 2024
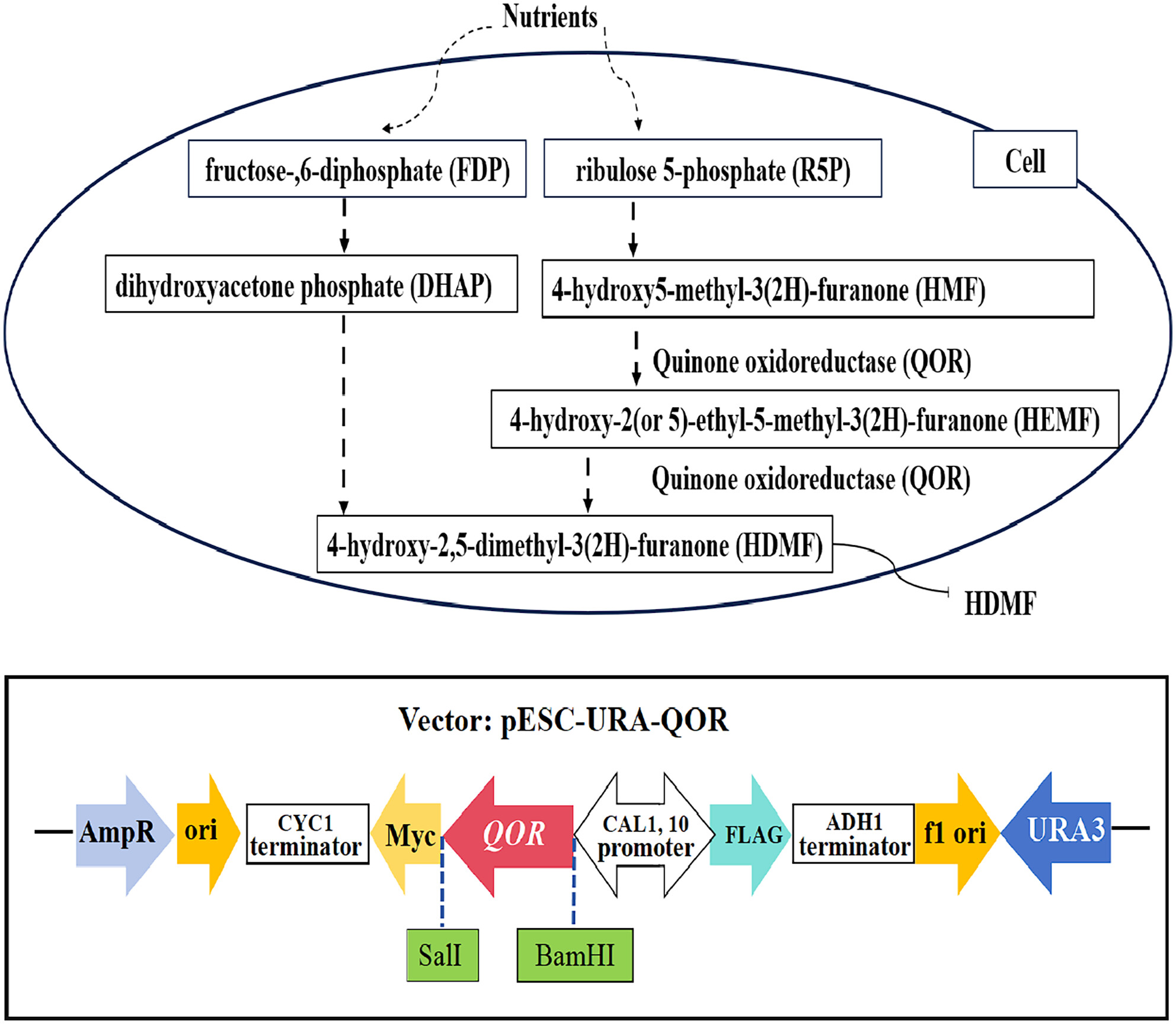
This study proposed a formation pathway from exogenous nutrients to 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (HDMF). During this procedure, quinone oxidoreductase (QOR) is a key enzyme for HDMF production. Therefore, the QOR gene was cloned and overexpressed in Zygosaccharomyces rouxii, and its impact on HDMF production by Z. rouxii was then further analyzed.
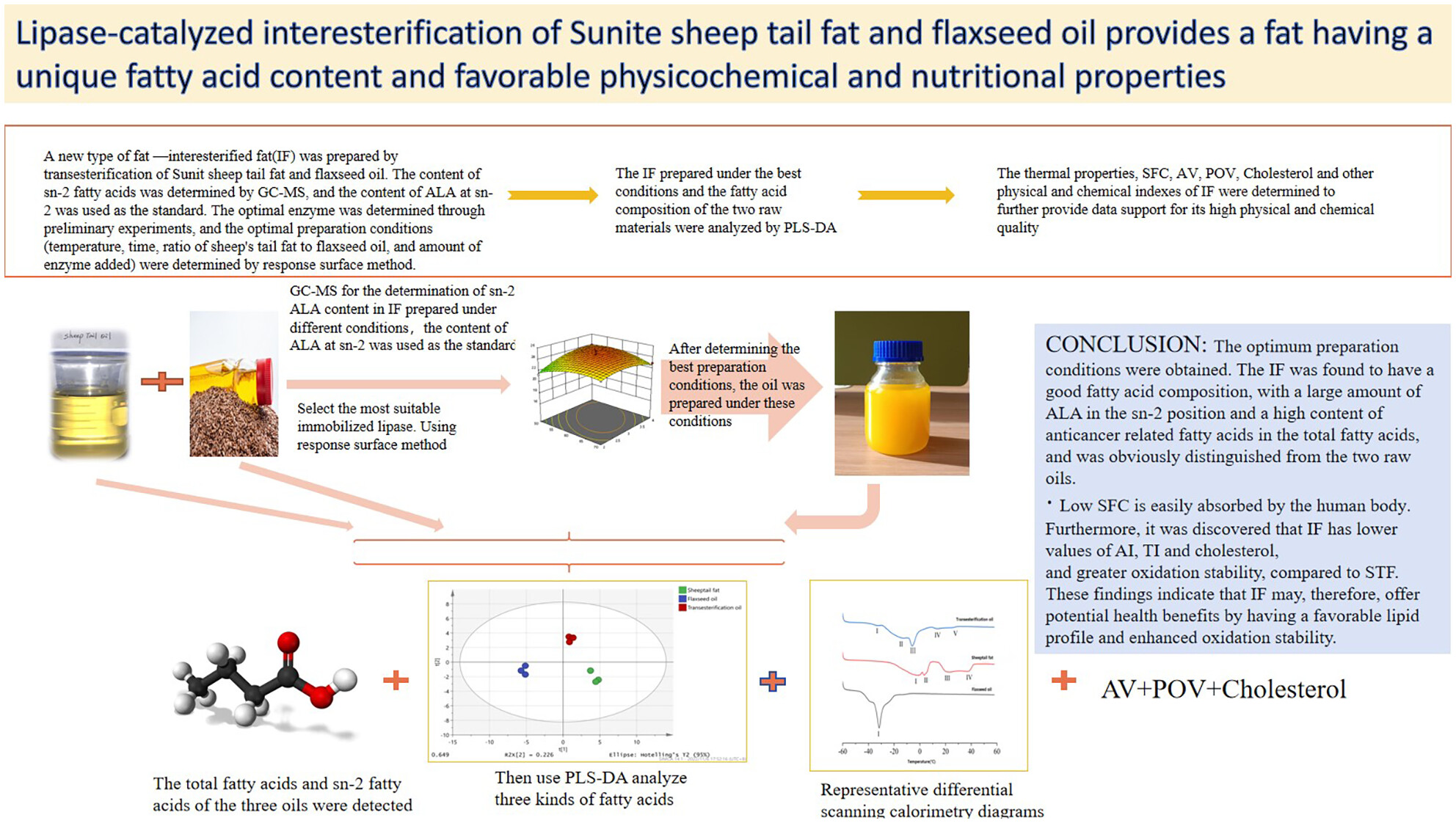
Lipase-catalyzed interesterification of Sunite sheep tail fat and flaxseed oil provides a fat having a unique fatty acid content and favorable physicochemical and nutritional properties
- Pages: 4443-4458
- First Published: 24 March 2024
Peganum harmala L. extract-based Gold (Au) and Silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs): Green synthesis, characterization, and assessment of antibacterial and antifungal properties
- Pages: 4459-4472
- First Published: 19 March 2024
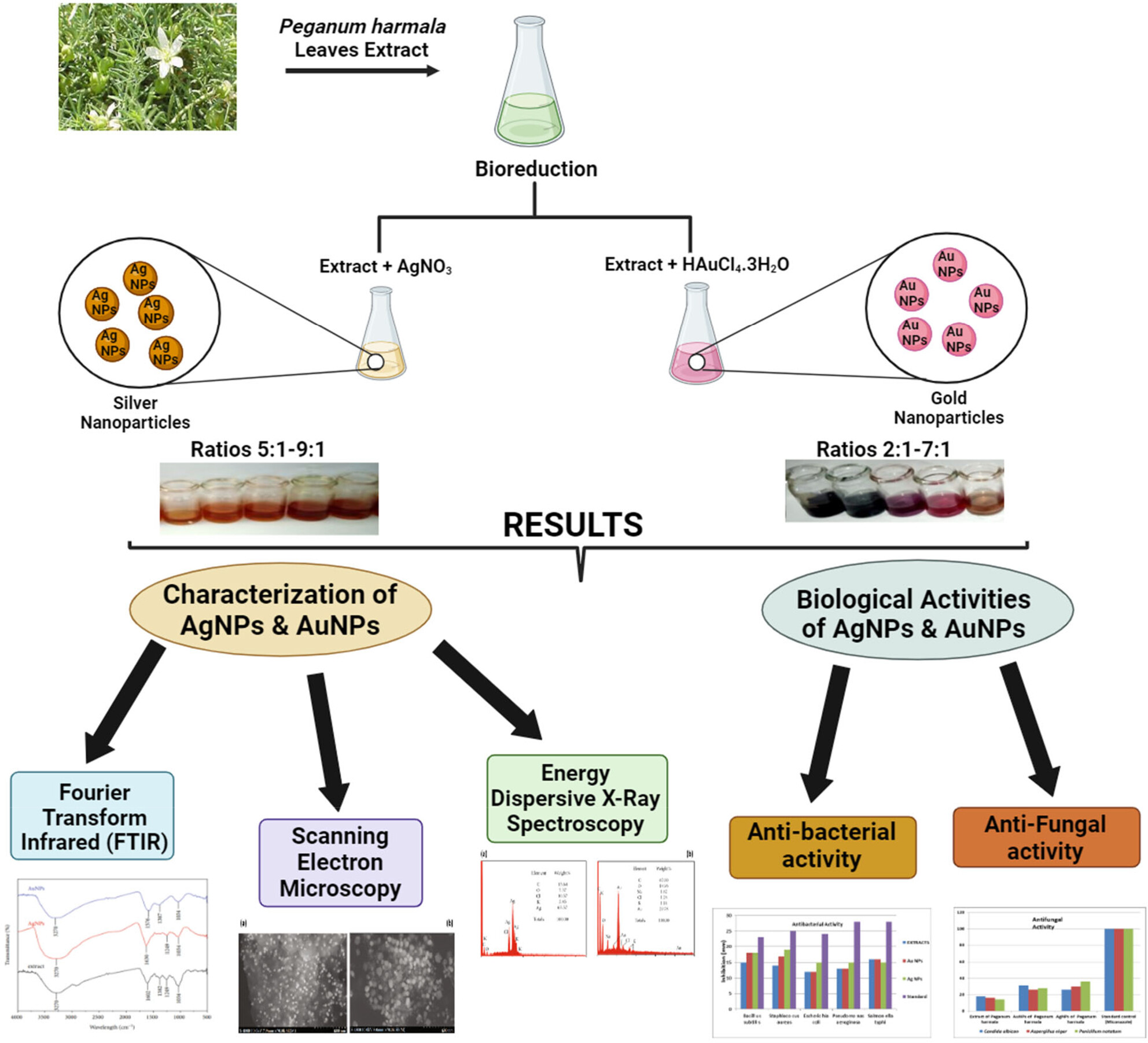
This manuscript highlights the synthesis of Peganum harmala L. Extract-based Gold (Au) and Silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs). These nanoparticles were characterized using UV–visible spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and were later evaluated for their antimicrobial properties. Results revealed that both synthesized nanoparticles possessed significant antibacterial and antifungal properties.
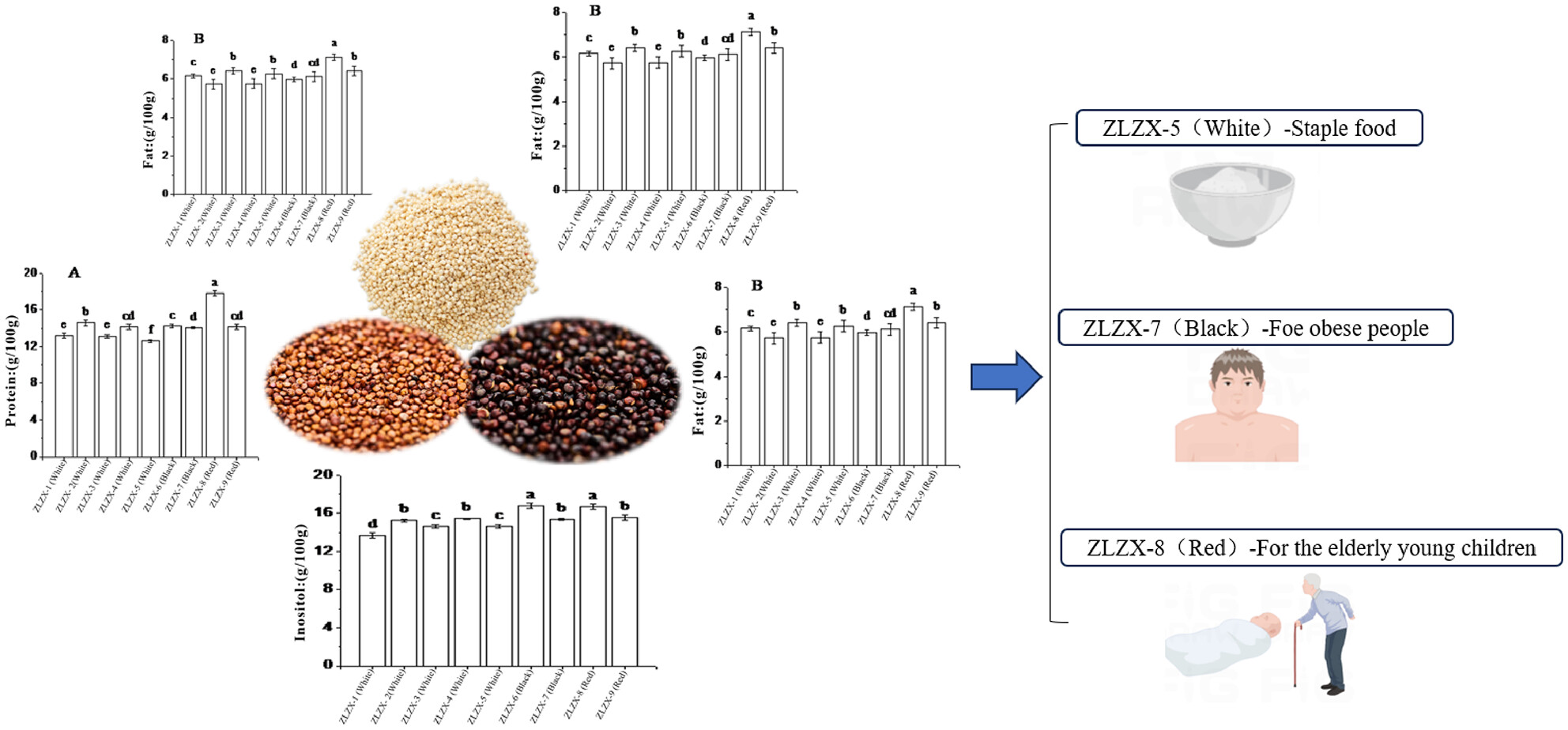
A comparative analysis of the nutrient and phytochemical richness among different varieties of quinoa in China
- Pages: 4473-4485
- First Published: 24 April 2024