Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
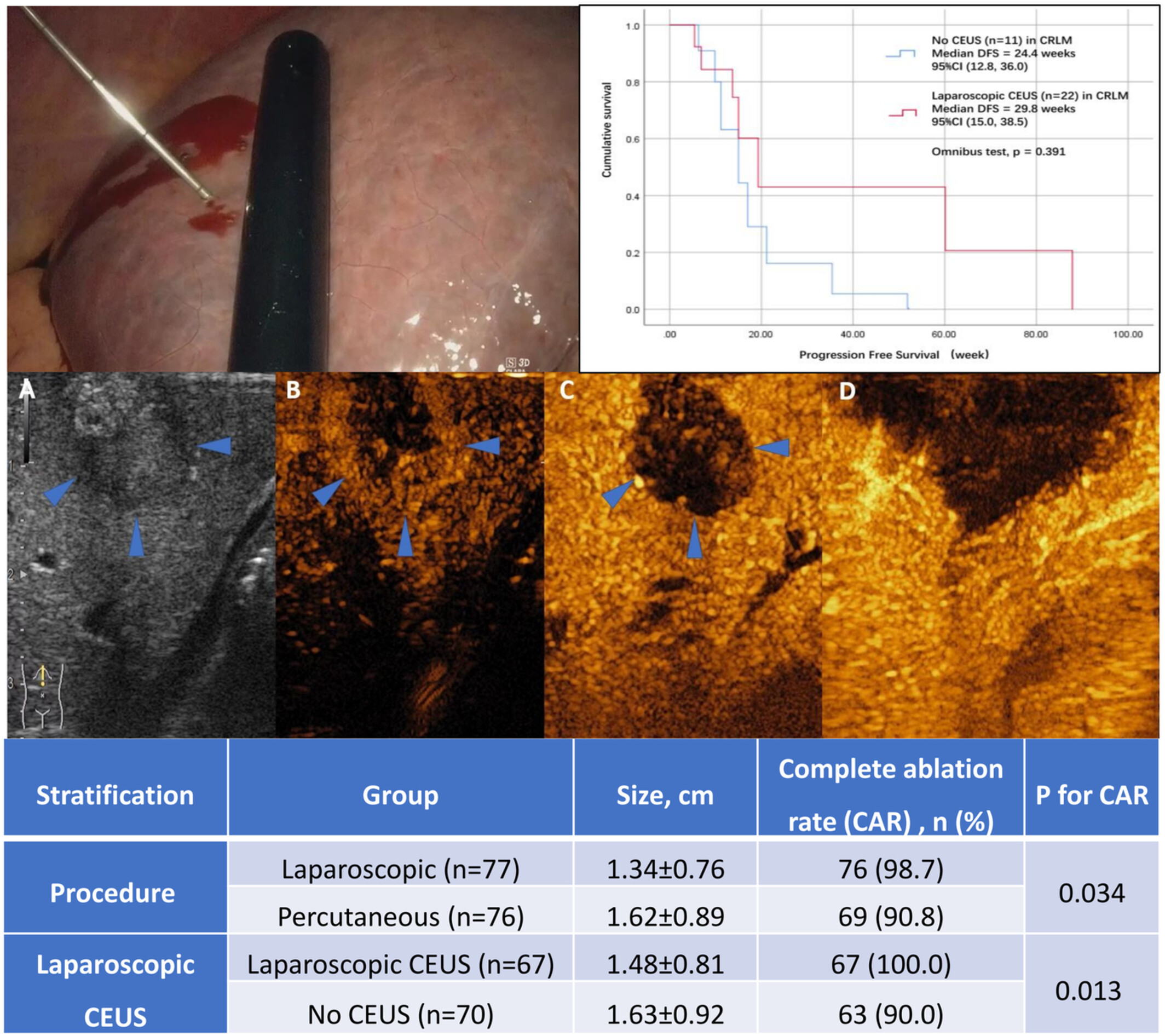
Role of Sonazoid enhanced ultrasound assistant laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation in treating liver malignancy—A single-center retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 9075-9084
- First Published: 06 March 2023
Prognostic nomogram for multiple myeloma early relapse after autologous stem cell transplant in the novel agent era
- Pages: 9085-9096
- First Published: 06 April 2023
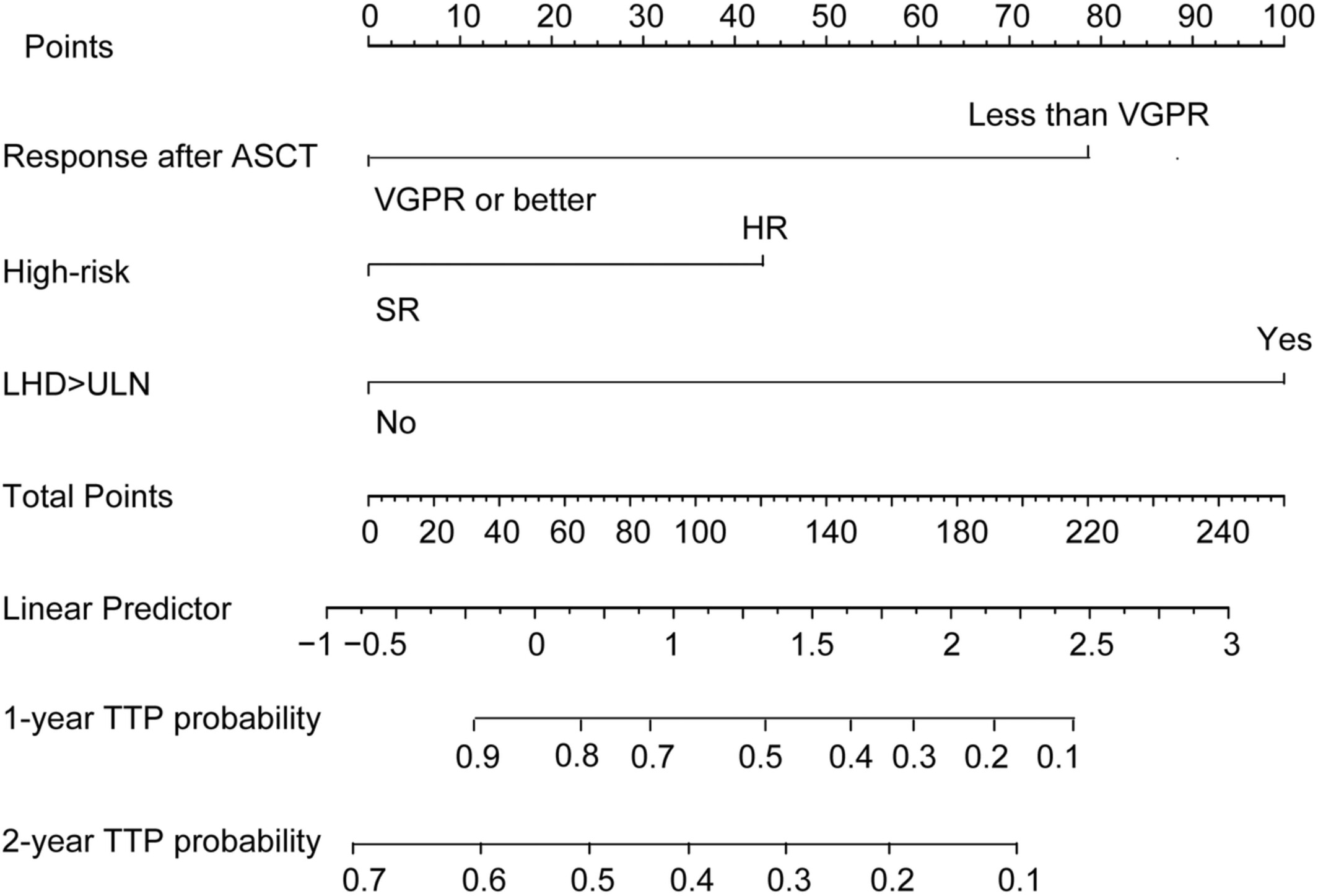
Early relapse post-ASCT in MM makes patients suffer adverse outcomes, which is so far unpredictable. This study retrospectively enrolled data of transplant-eligible MM patients from multicenters in China and established a predictive nomogram for ER. The C-index demonstrates good predictive accuracy for survival and the calibration curve for the probability of survival showed good agreement between the prediction by the nomogram and actual observations, which could be used to modify the post-ASCT strategy for those patients.
Comparison of the prognosis of symptomatic cerebral infarction and pulmonary embolism in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 9097-9105
- First Published: 27 January 2023
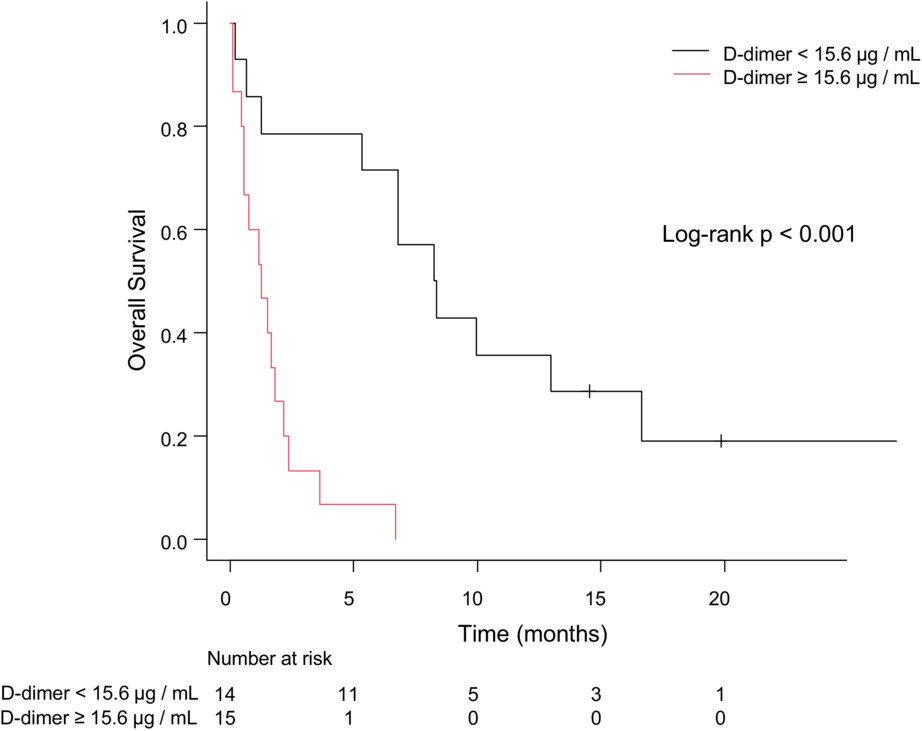
We retrospectively analyzed the prognosis and predictors of survival in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer who developed symptomatic thromboembolism. In this study, the prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction tended to be poorer than that of patients with pulmonary embolism. In addition, we showed that D-dimer levels were a promising prognostic predictor in patients who developed cerebral infarction.
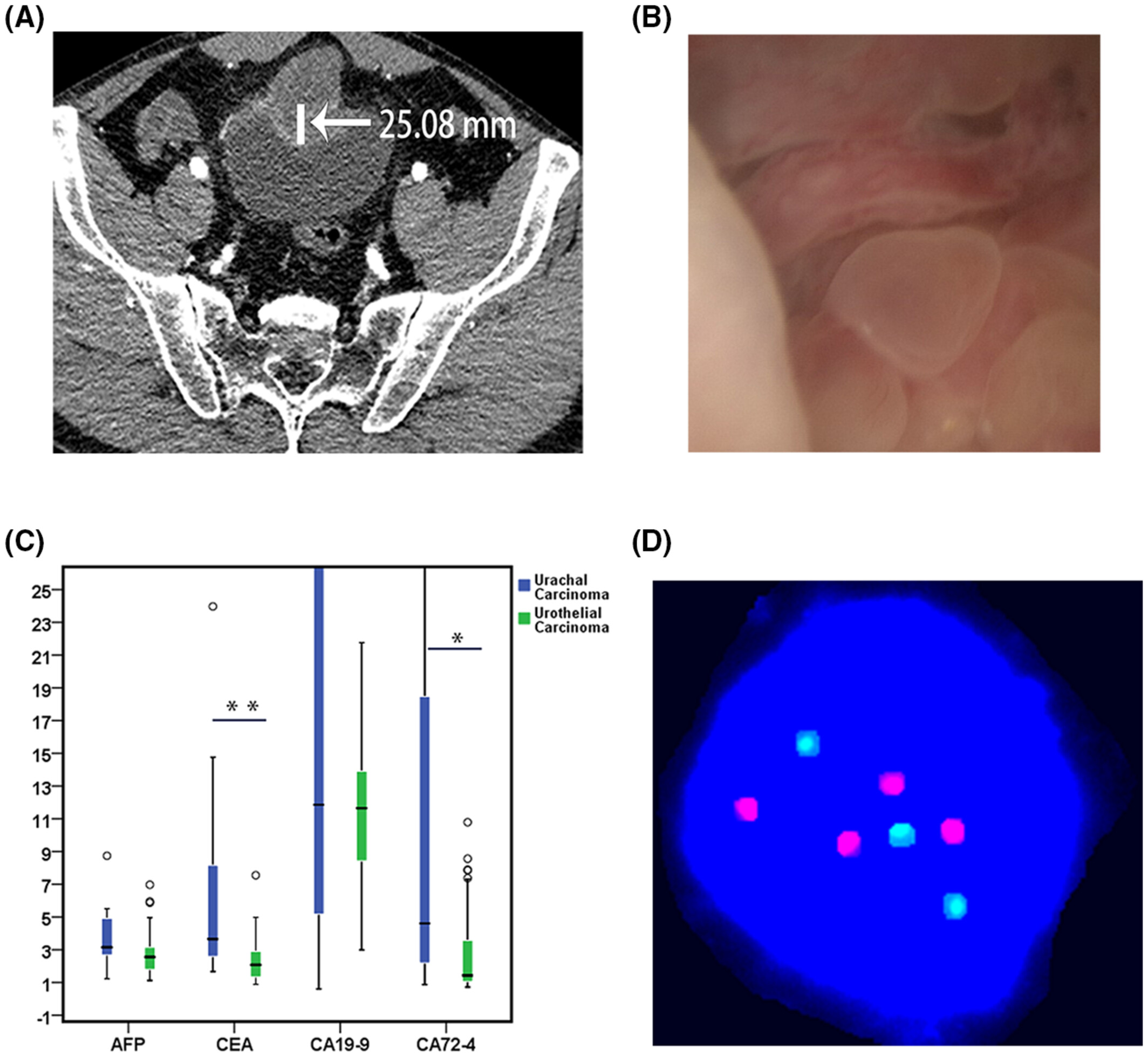
Preoperative accuracy of diagnostic evaluation of urachal carcinoma
- Pages: 9106-9115
- First Published: 03 February 2023
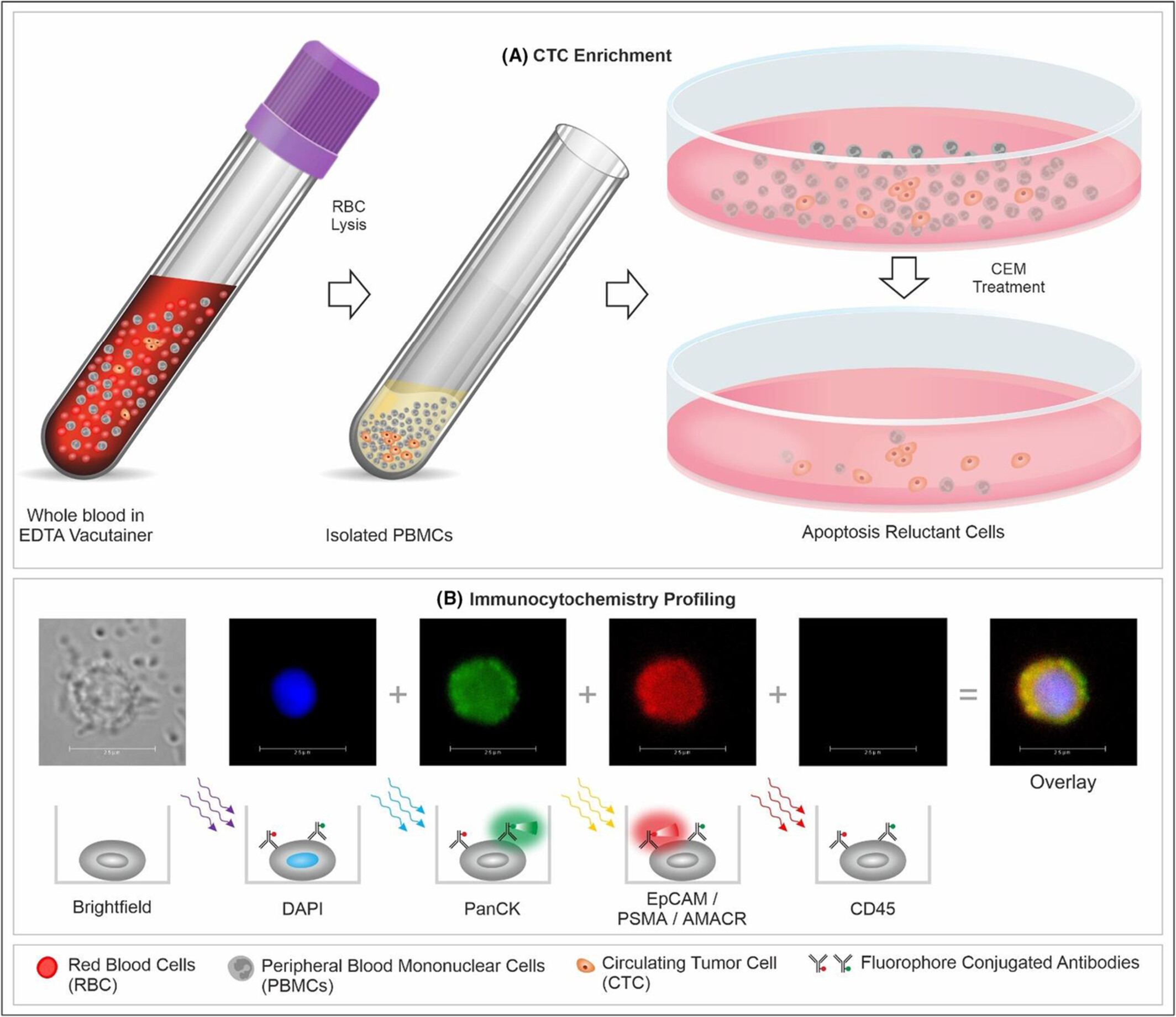
Accurate prostate cancer detection based on enrichment and characterization of prostate cancer specific circulating tumor cells
- Pages: 9116-9127
- First Published: 30 January 2023
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
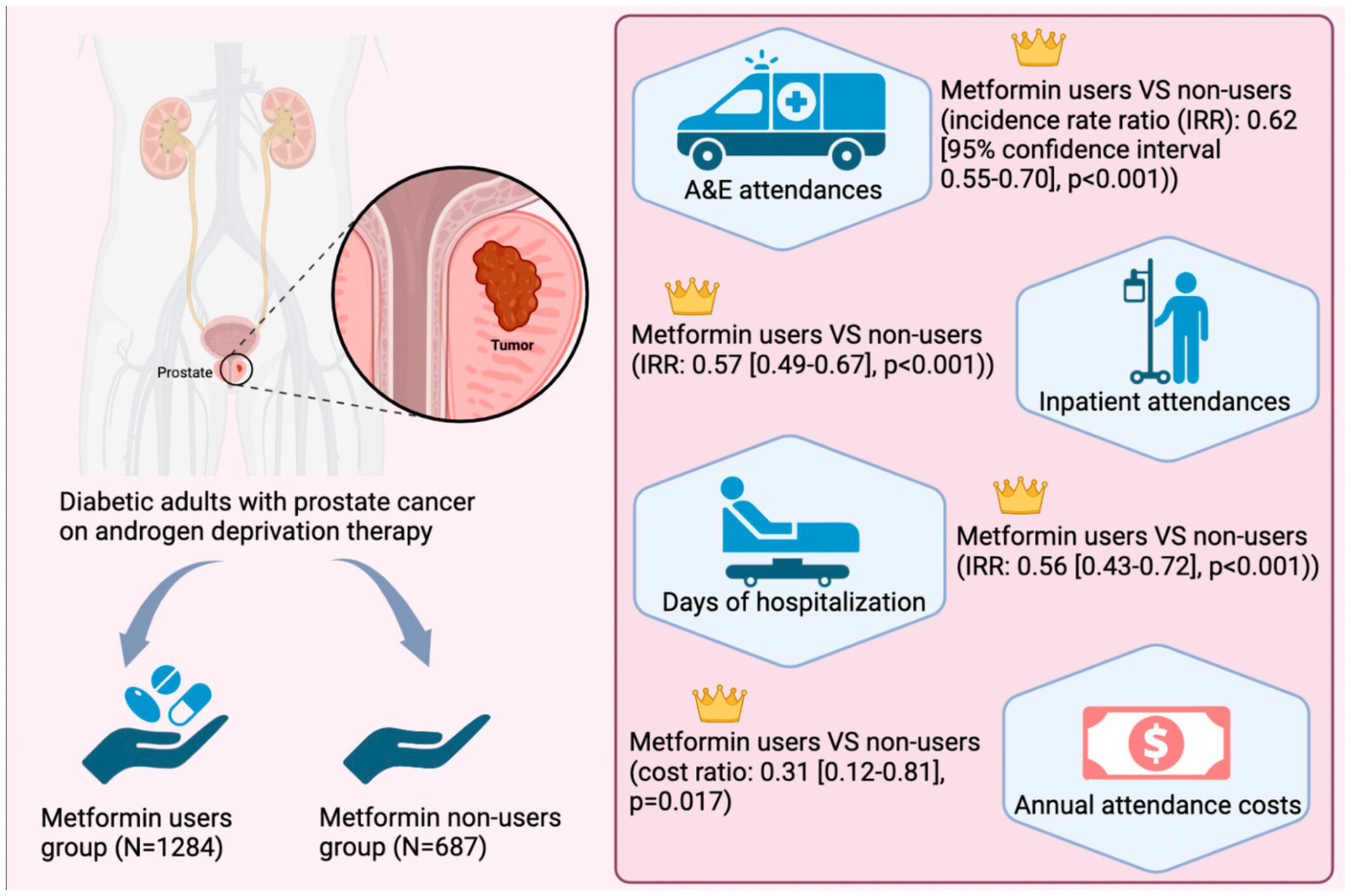
Metformin use and hospital attendance-related resources utilization among diabetic patients with prostate cancer on androgen deprivation therapy: A population-based cohort study
- Pages: 9128-9132
- First Published: 03 February 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
Standard versus low-dose nab-paclitaxel in previously treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized phase II trial (JMTO LC14-01)
- Pages: 9133-9143
- First Published: 21 February 2023
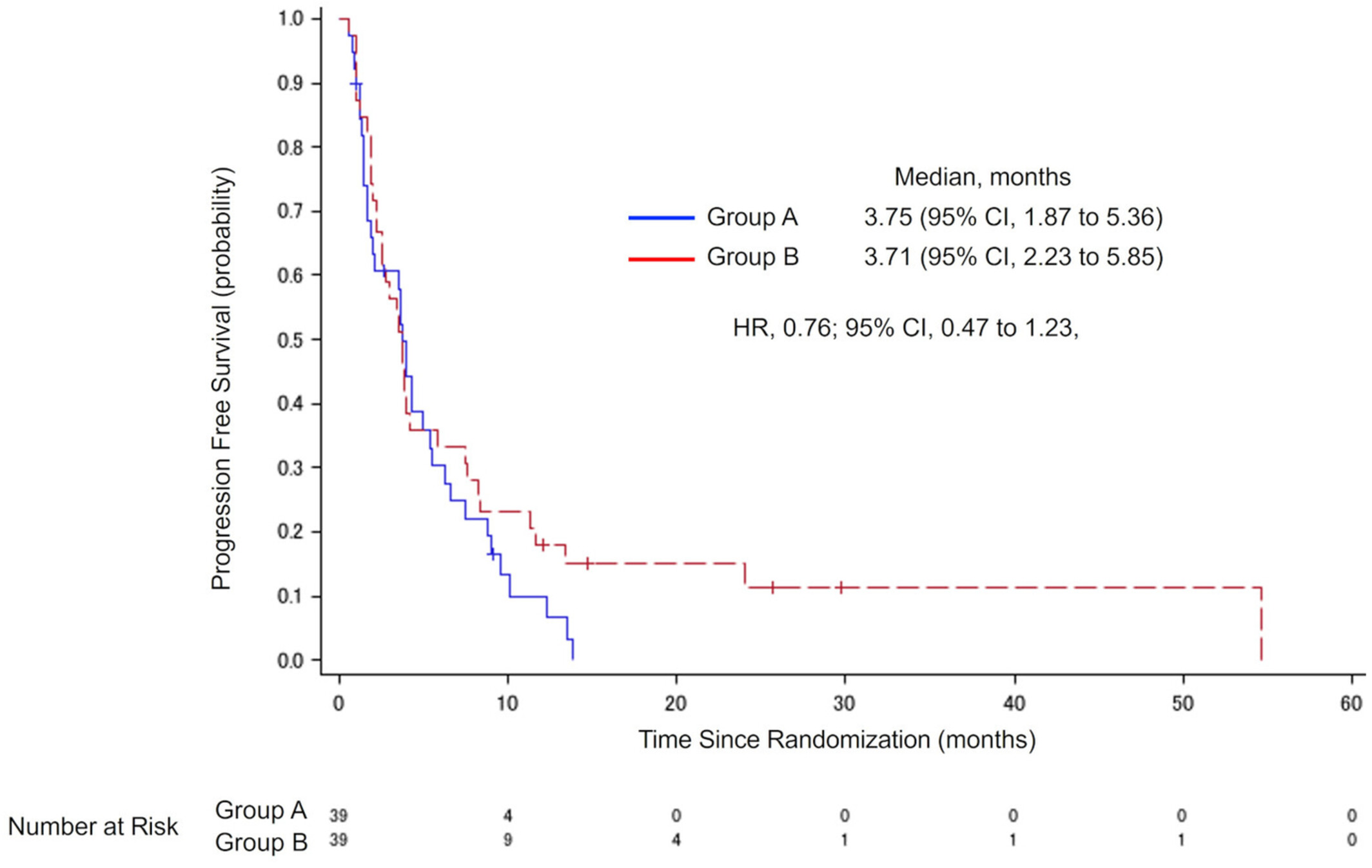
In this phase 2 randomized clinical trial to examine activity and safety, and to determine optimum dose of nab-PTX in patients with previously treated stage IIIB/IV or postoperative relapsed NSCLC, both 100 and 70 mg/m2 of nab-PTX monotherapy were active in patients with previously treated advanced NSCLC. Since the 70 mg/m2 dose has a better safety profile and numerically favored median overall survival, 70 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15 every 4 weeks would be the optimal dose and schedule for nab-PTX during treatment of NSCLC.
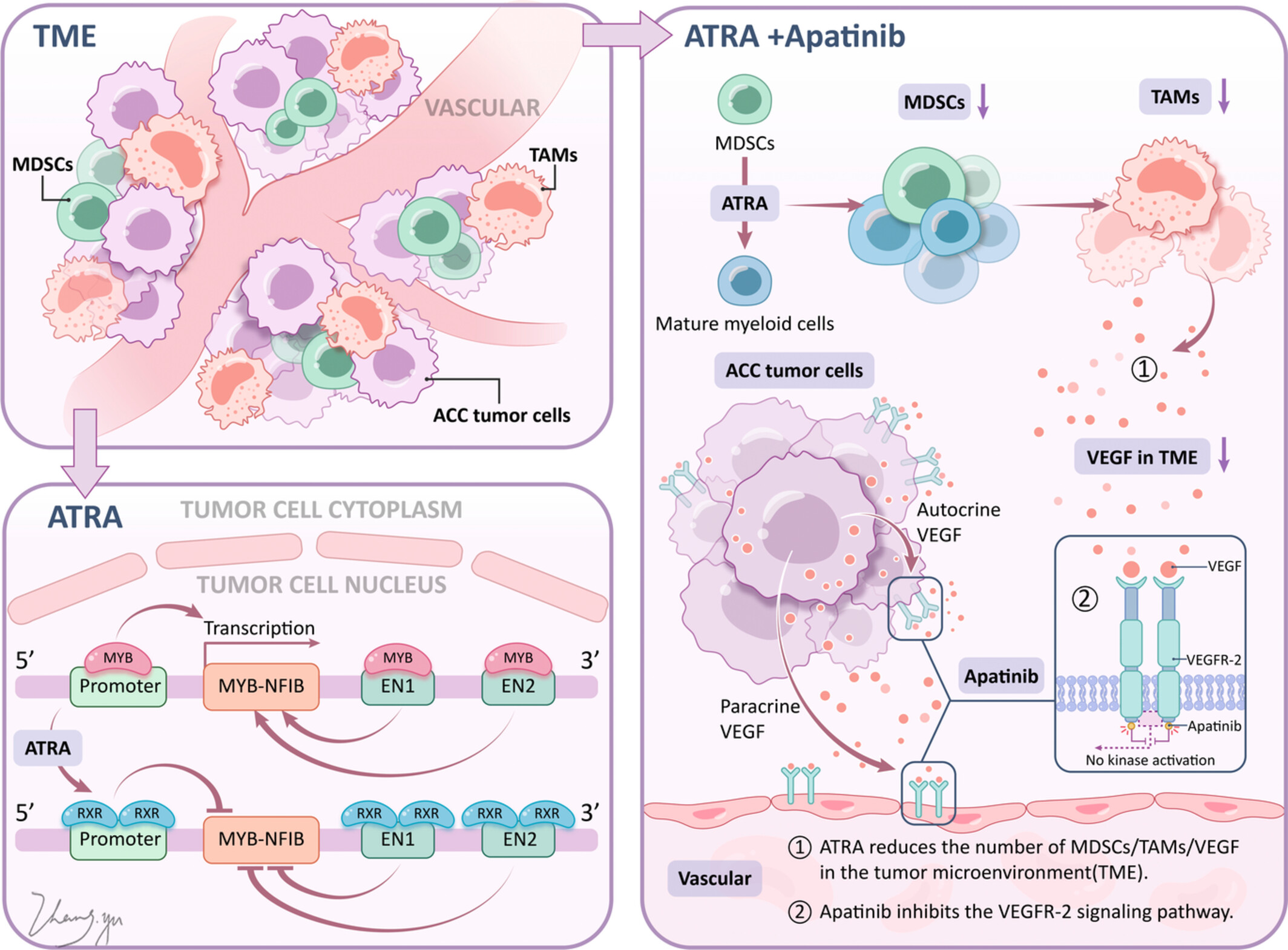
Combined all-trans retinoic acid with low-dose apatinib in treatment of recurrent/metastatic head and neck adenoid cystic carcinoma: A single-center, secondary analysis of a phase II study
- Pages: 9144-9155
- First Published: 03 February 2023
RNA sequencing of myeloid sarcoma, shed light on myeloid sarcoma stratification
- Pages: 9156-9166
- First Published: 14 March 2023
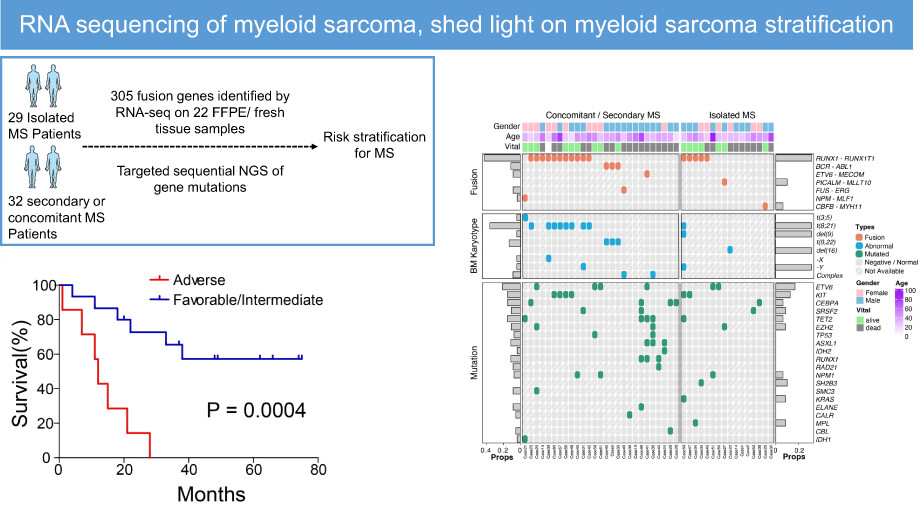
We analyzed the clinical and genetic features of 61 MS cases. We performed genetic abnormalities based risk stratification based on gene mutations and fusion genes identified by RNA-seq on FFPE. Our study suggested that RNA-seq on FFPE could be as markers for MS risk stratification since fresh samples are usually unavailable.
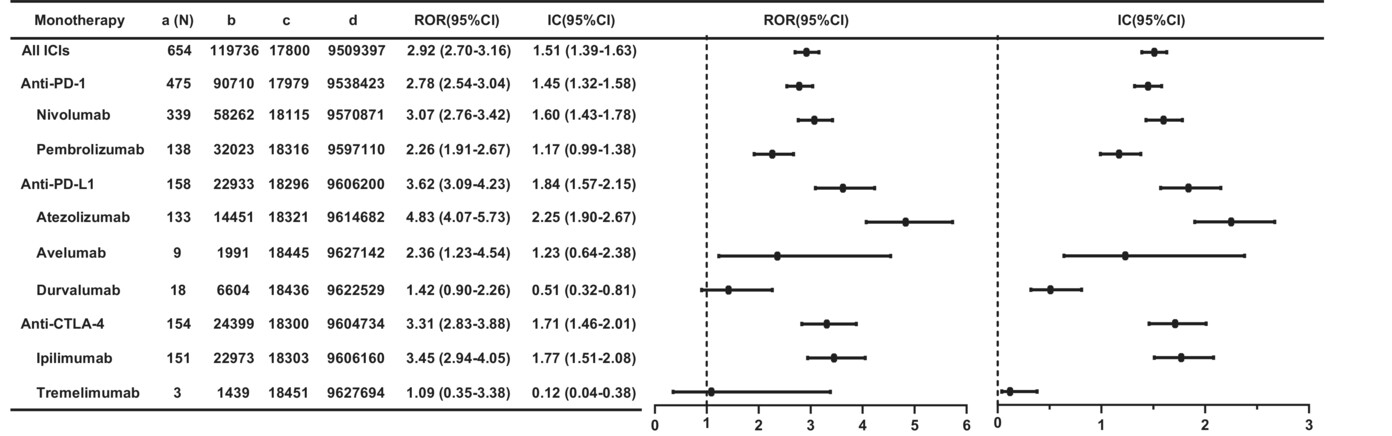
Hepatic failure associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: An analysis of the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System database
- Pages: 9167-9174
- First Published: 03 February 2023
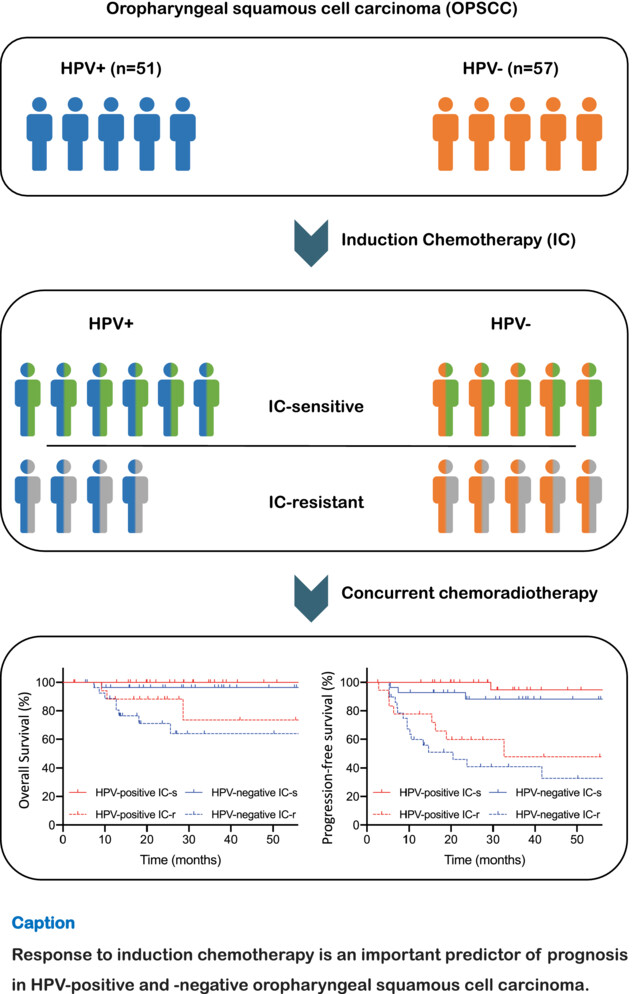
Response to induction chemotherapy predicts survival outcomes in oropharyngeal cancer
- Pages: 9175-9185
- First Published: 27 January 2023
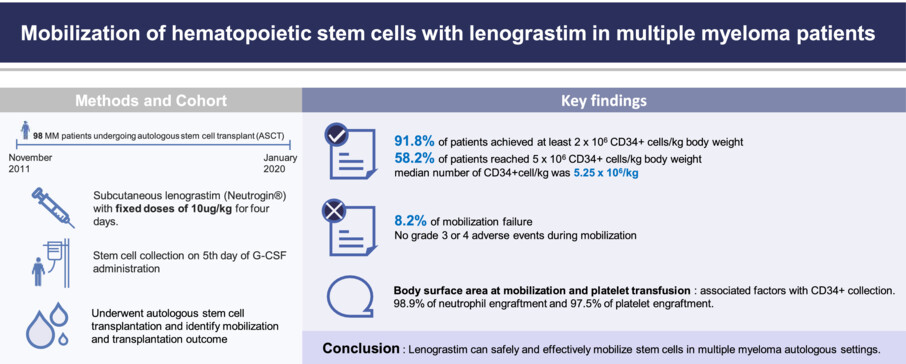
Mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells with lenograstim in multiple myeloma patients: Prospective multicenter observational study (KMM122)
- Pages: 9186-9193
- First Published: 23 March 2023
Assessment of survival outcomes among lung cancer patients at the National and Referral Hospital in Kenya
- Pages: 9194-9201
- First Published: 27 January 2023
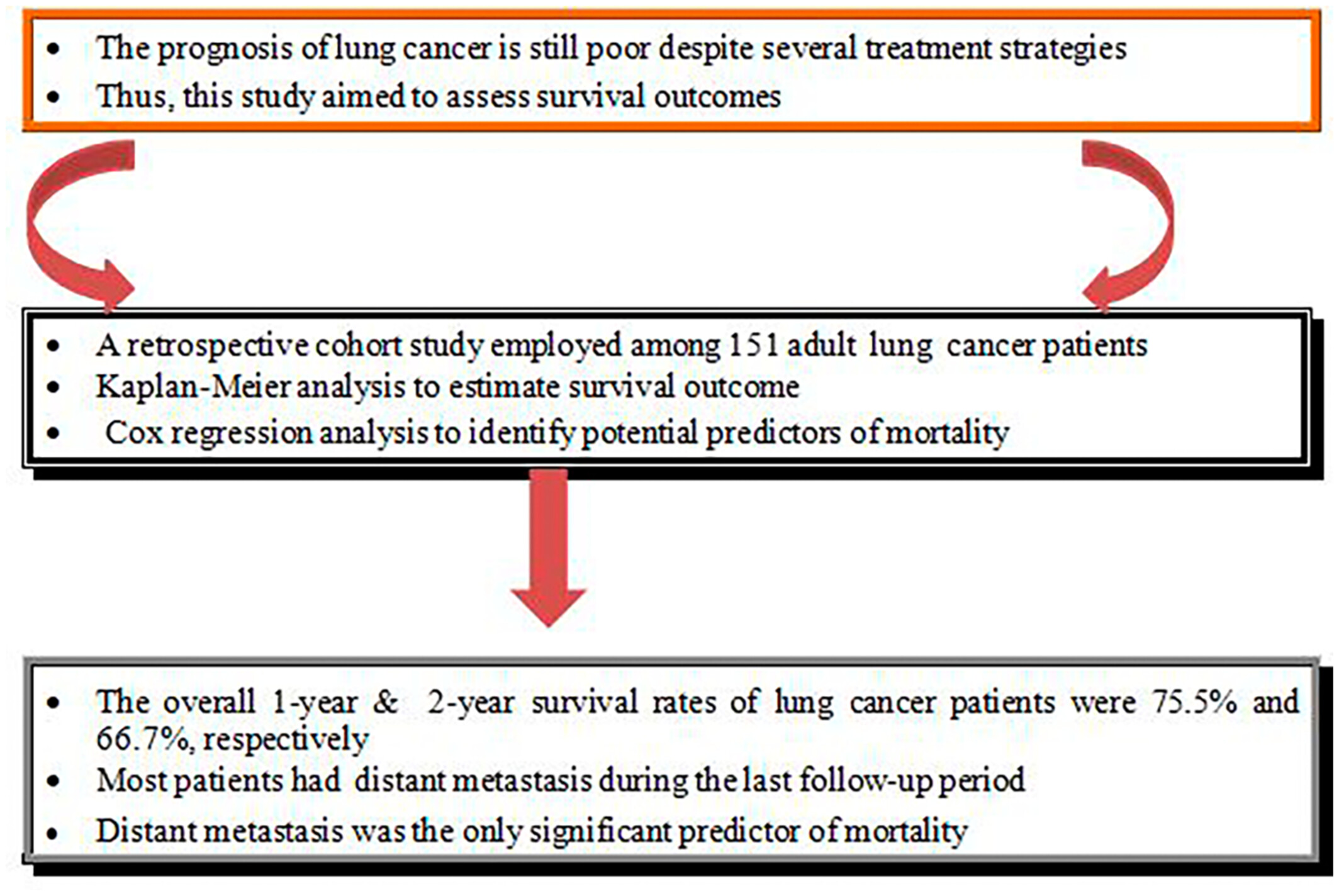
The prognosis of lung cancer is still poor despite several treatment strategies. A retrospective cohort studywas employed among 151 adult lung cancer patients to assess survival outcomes. The study revealed 75.5% one-year and 66.7% two-year survival rates, with most patients having distant metastasis in the follow-up period.
Effectiveness and safety of lenvatinib plus anti-programmed death-1 antibodies in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A real-world cohort study
- Pages: 9202-9212
- First Published: 15 February 2023
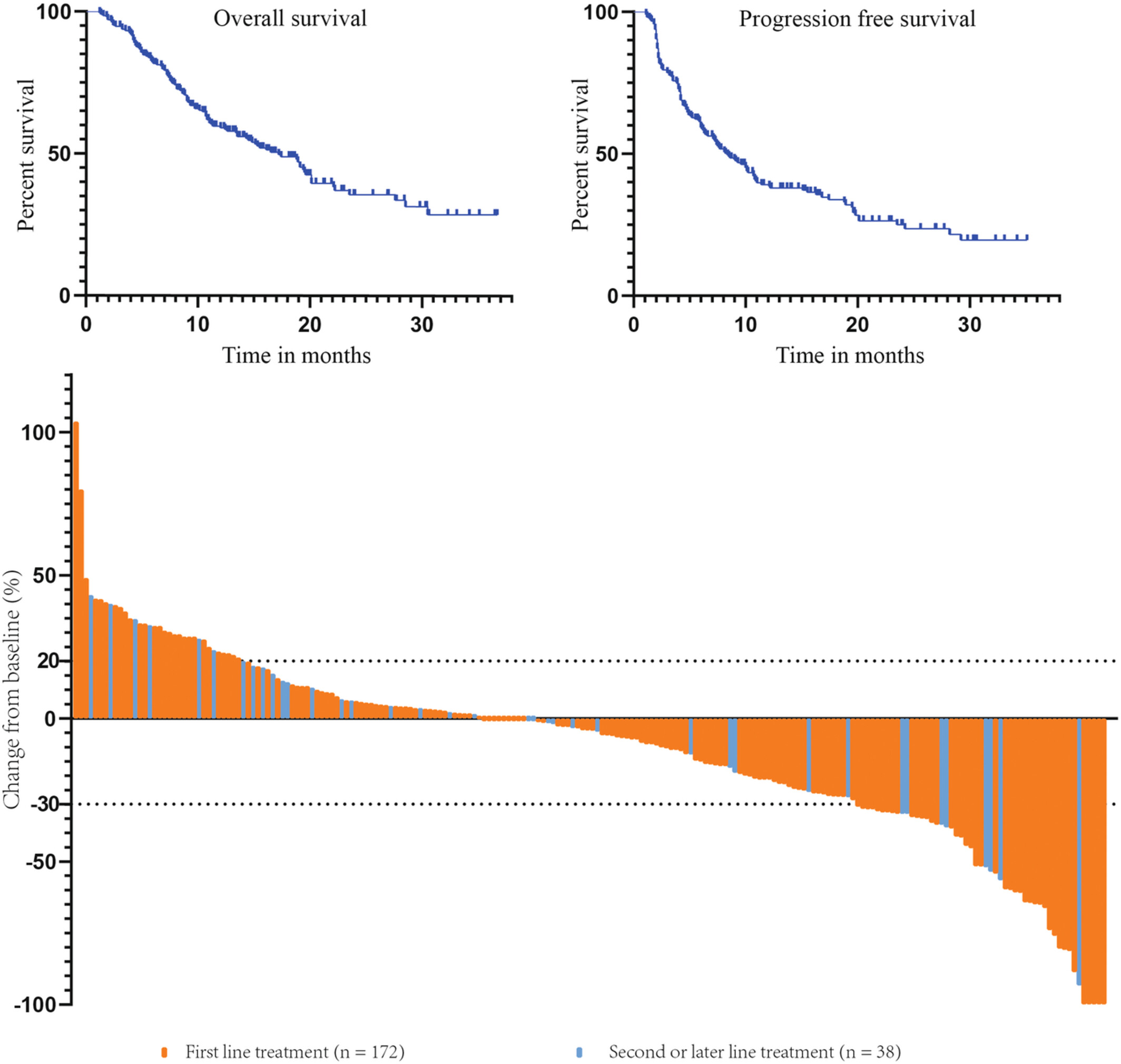
The present study evaluated a real-life cohort of 210 patients with unresectable or advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who received treatment with lenvatinib plus anti-programmed death-1 antibodies between October 2018 and March 2022. The results are encouraging, with median overall survival of 17.2 months and objective response rate of 28.1%.
Repeat hepatic resection combined with intraoperative radiofrequency ablation versus repeat hepatic resection alone for recurrent and multiple hepatocellular carcinoma patients meeting the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Pages: 9213-9227
- First Published: 01 February 2023
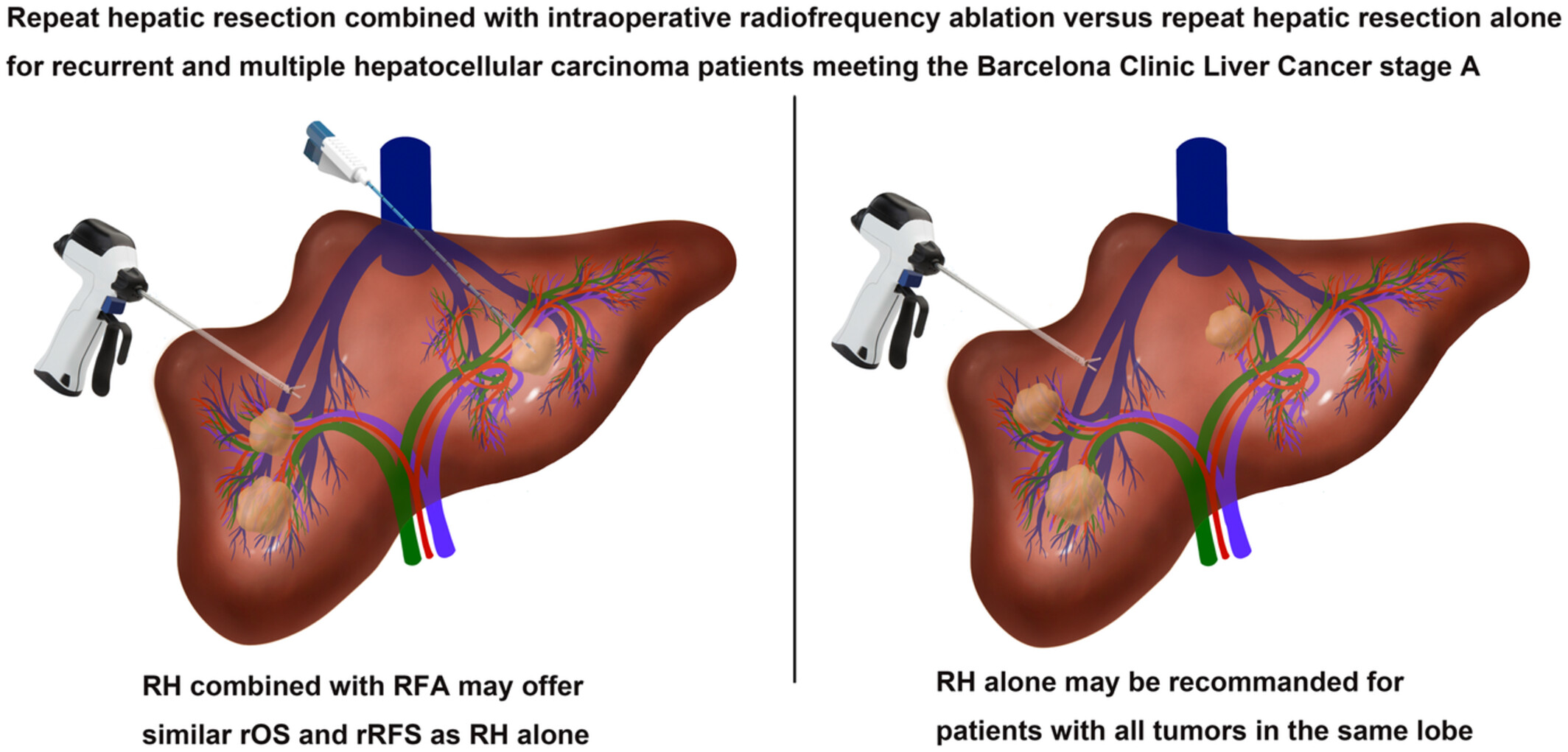
This figure represents our research of comparing the survival outcomes for multifocal recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma patients meeting the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage A who underwent repeat hepatectomy alone or repeat hepatectomy combined with intraoperative radiofrequency. The results may propose some new valuable suggestions and treatment decision-making.
Procalcitonin as a biomarker for predicting bacterial infection in chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy recipients
- Pages: 9228-9235
- First Published: 08 February 2023
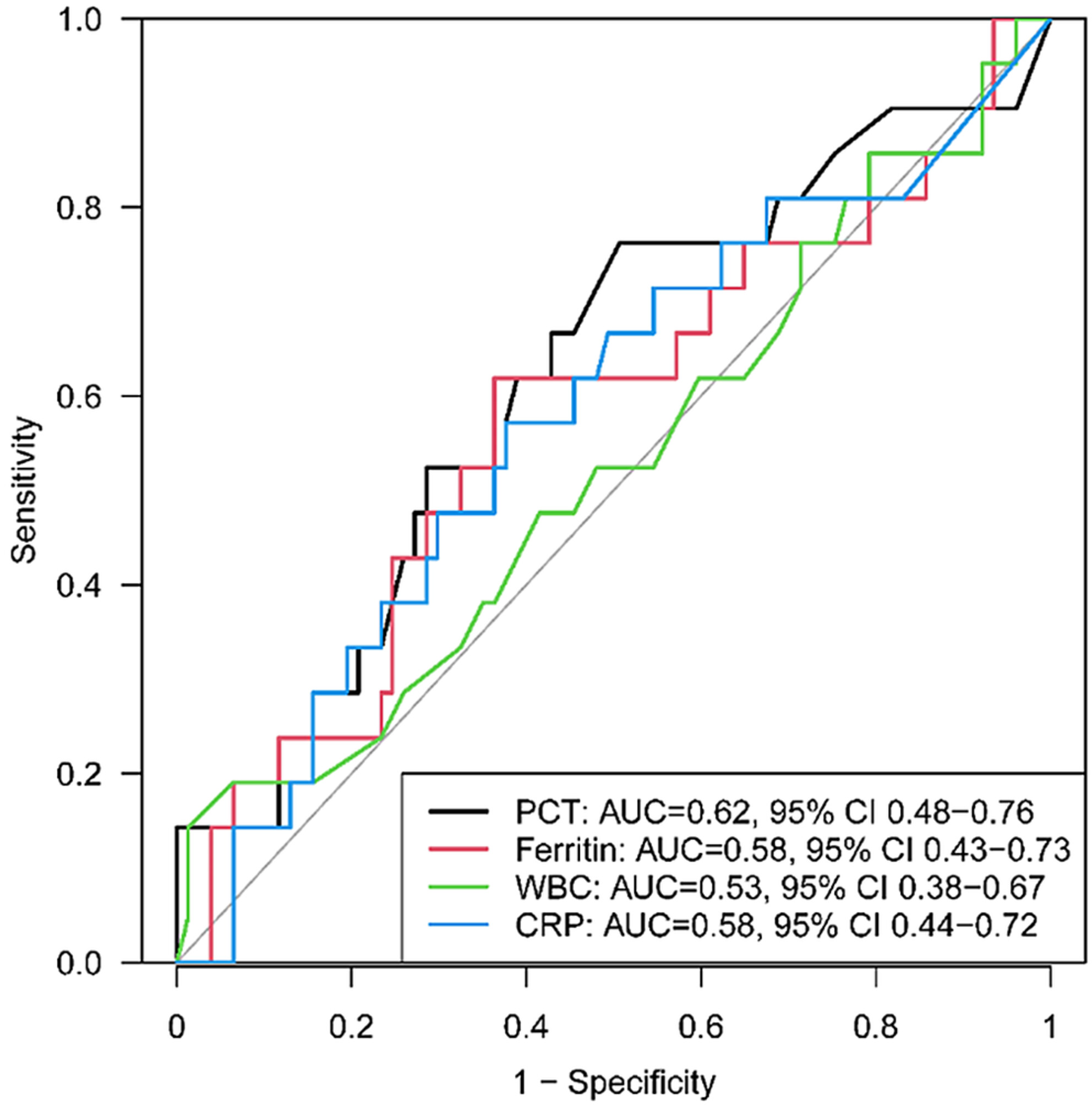
A serum procalcitonin concentration >0.4 ng/mL was significantly associated with confirmed bacterial infection in patients after receiving chimeric antigen T-cell therapy. Procalcitonin may be a useful marker for differentiating bacterial infection from cytokine release syndrome in chimeric antigen T-cell therapy recipients.
Incidence and risk factors for second malignancies among patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Pages: 9236-9246
- First Published: 02 February 2023
Cortisol response in children with cancer and fever during chemotherapy: A prospective, observational study using random serum cortisol levels
- Pages: 9247-9259
- First Published: 03 February 2023
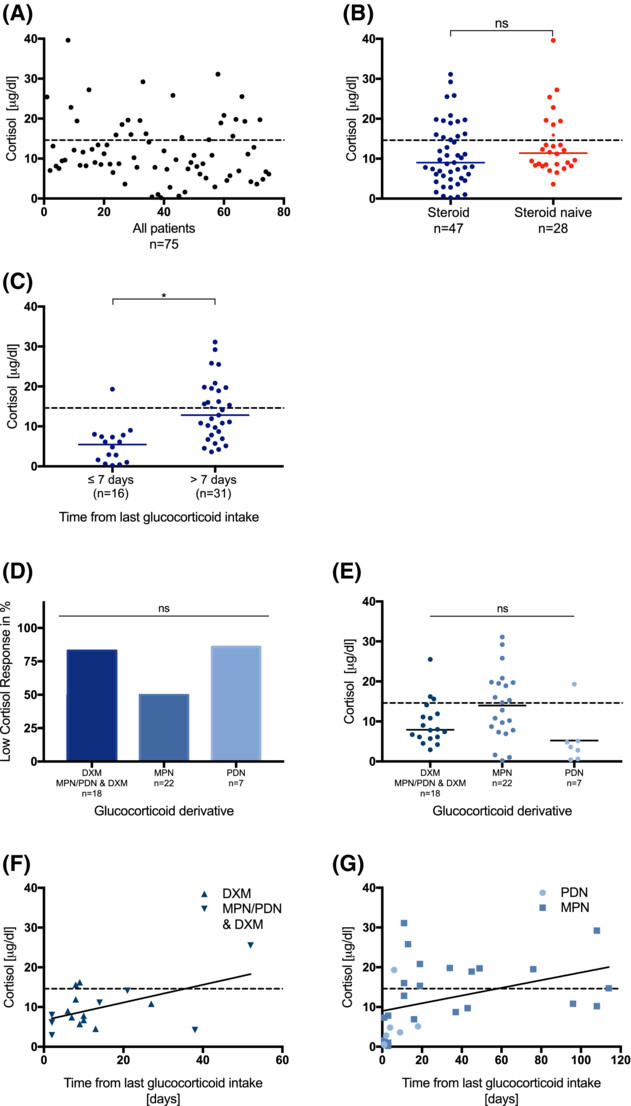
The adrenal gland's response to stress is impaired in most pediatric cancer patients receiving chemotherapy, whether or not they are taking steroids. Intake of dexamethasone and posaconazole and a time period of ≤7 days from the last glucocorticoid intake were additional risk factors for an impaired adrenal response.
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting survival in patients with malignant myofibroblastic tumor
- Pages: 9260-9271
- First Published: 23 March 2023
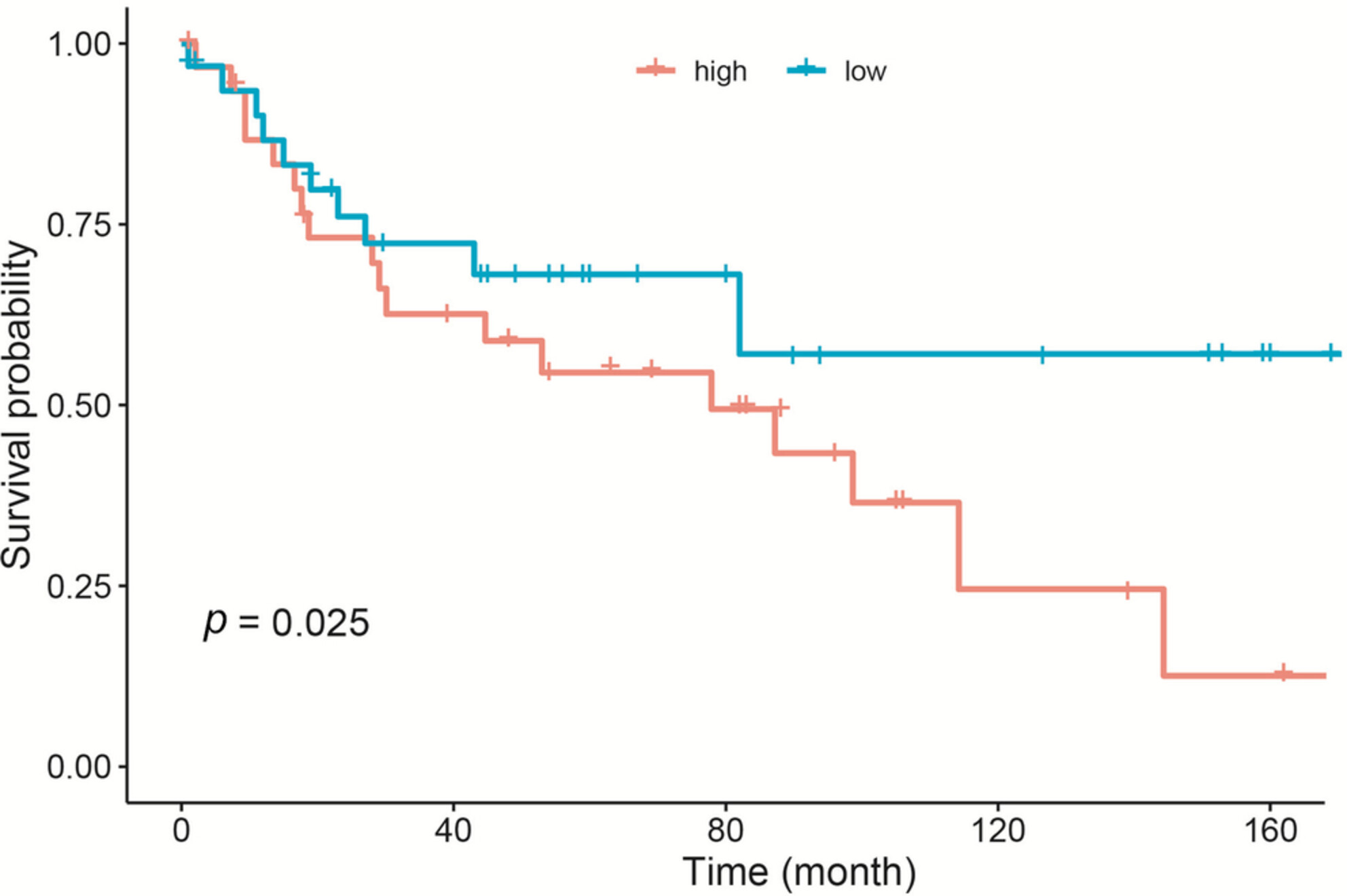
In the present study, age, grade, tumor size, positive lymph node, N stage, M stage, and chemotherapy were identified as prognostic parameters for survival in patients with malignant myofibroblastic tumors. These factors were included in the construction of the nomogram. Evaluation of its predictive performance implied the superior sensitivity and specificity of the model and the higher accuracy of the outcomes than the AJCC system. The established nomogram may assist patients in consultation and help physicians make appropriate clinical decisions.
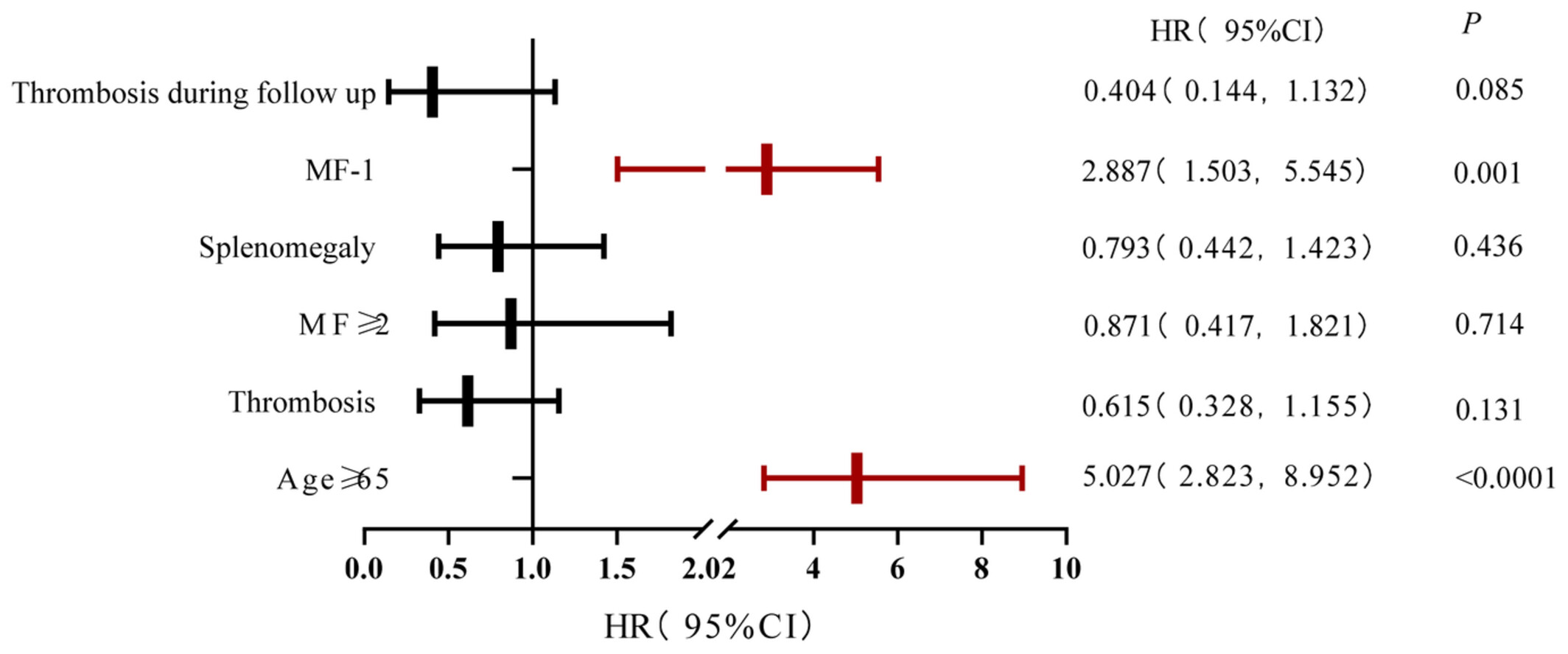
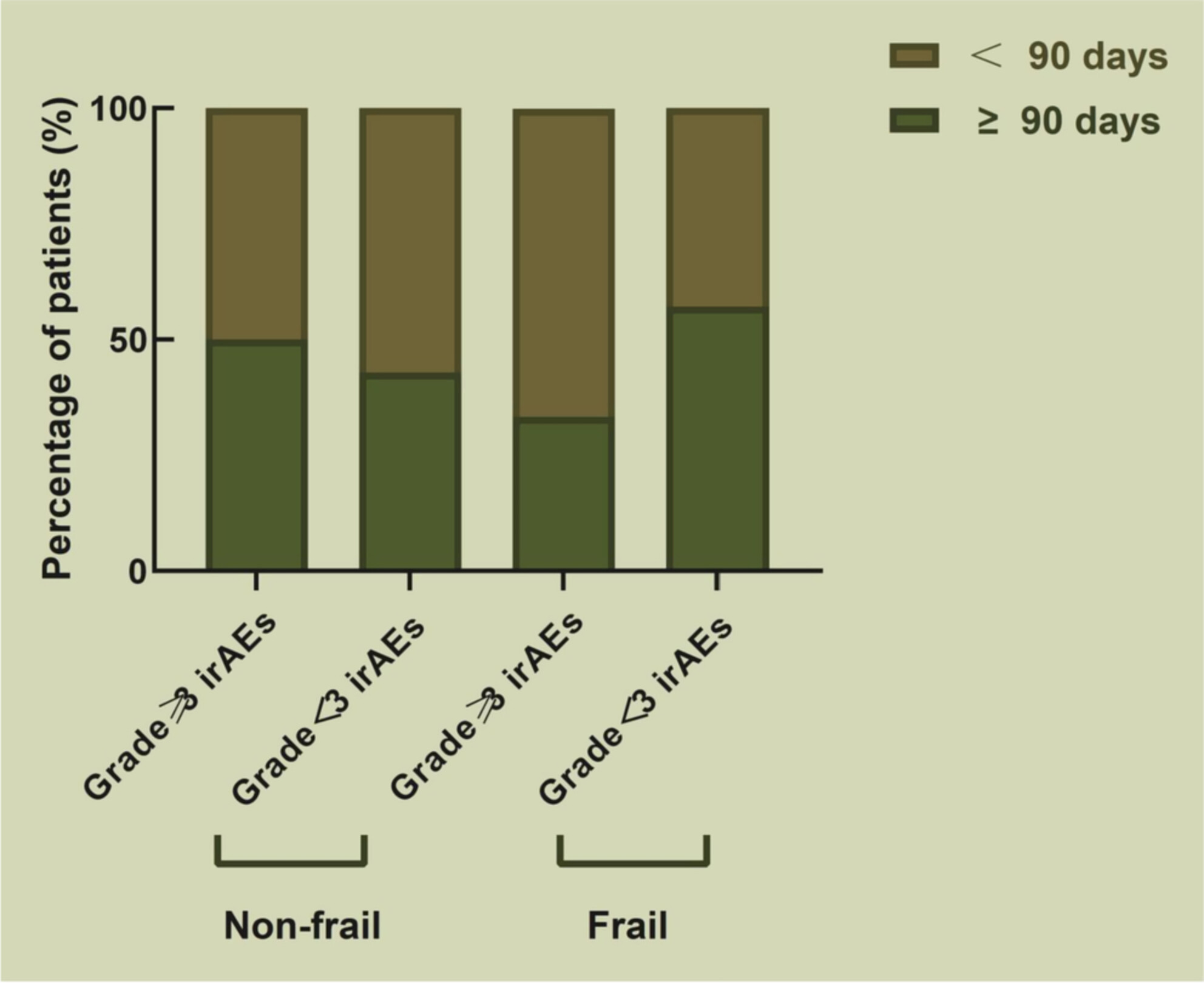
Association between PD-1 inhibitor-related adverse events and frailty assessed by frailty index in lung cancer patients
- Pages: 9272-9281
- First Published: 02 February 2023
The predictive value of PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 9282-9292
- First Published: 25 March 2023
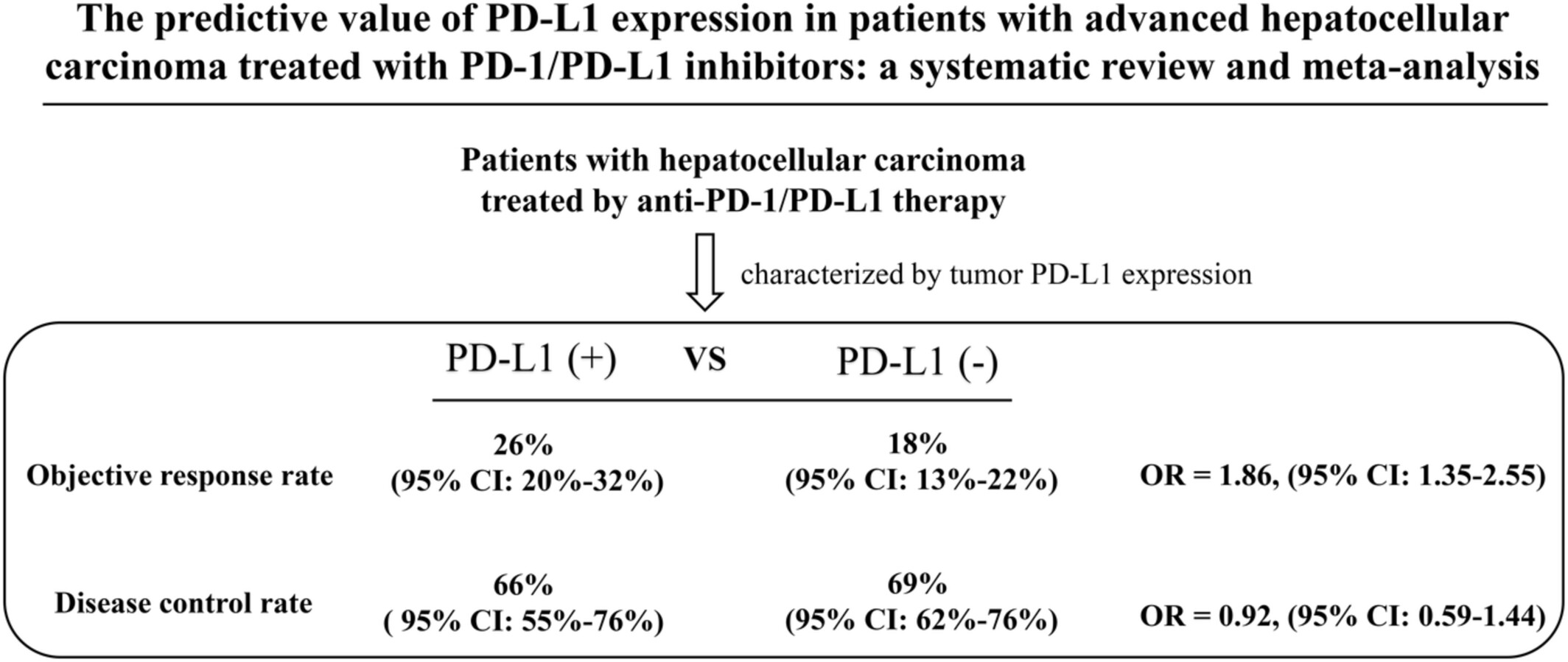
Not all patients with advanced HCC can benefit from anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy, biomarkers for selecting patients for treatment are urgently needed. Tumor PD-L1 expression was significantly associated with improved ORR in HCC patients. The ORR and DCR in patients with positive PD-L1 expression were 26% and 66%, versus 18% and 69% in patients with negative PD-L1 expression.
Characteristics and outcomes of gallbladder cancer patients at the Tata Medical Center, Kolkata 2017–2019
- Pages: 9293-9302
- First Published: 13 February 2023
The curative approach for gallbladder cancer (GBC) is radical cholecystectomy with adjuvant chemotherapy. GBC has non-specific symptoms, so screening/early detection is not possible. We report that 90% of GBC patients presented with late-stage inoperable disease. Patients with late-stage disease who received chemotherapy had significantly better survival over those who did not (p < 0.0001). Our real-world data suggests that GBC is a chemosensitive disease. Clinical trials in low-middle income countries to reposition available therapies are urgently required.
Comparison of treatment strategies for resectable locally advanced primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung
- Pages: 9303-9312
- First Published: 15 February 2023
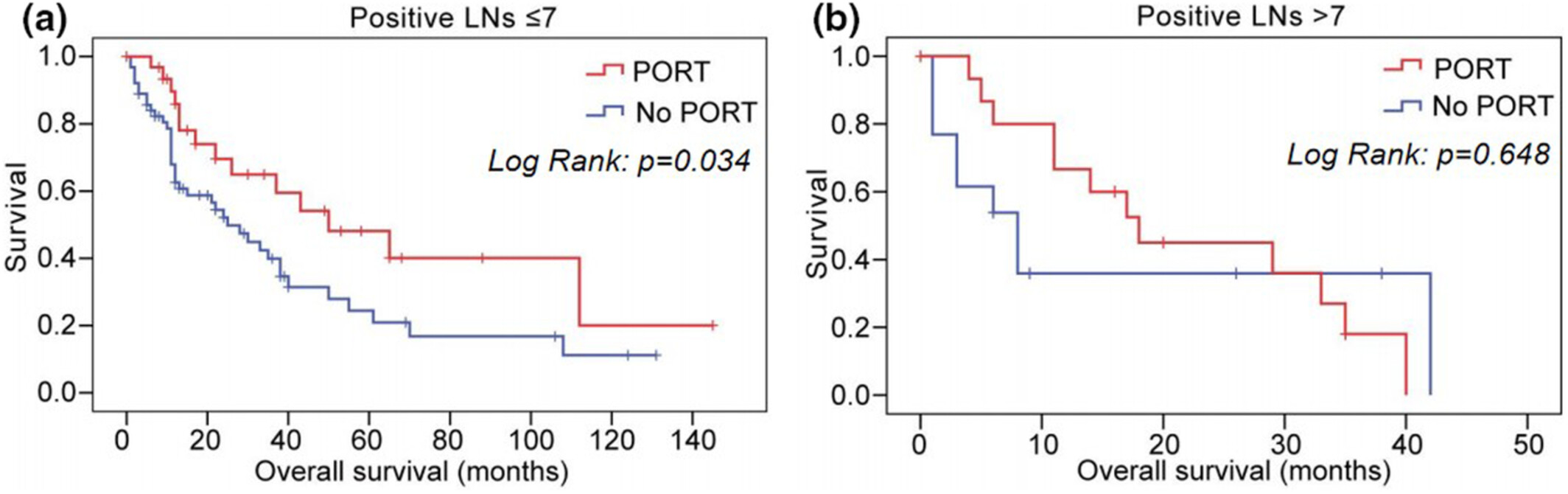
Stage III-N2 lung pure mucinous adenocarcinoma (PMA) tended to appear more in lower lobes, with higher differentiation degree, earlier T stage, and more positive lymph nodes(LNs) than other adenocarcinoma. The prognosis of resectable III-N2 PMAs was worse than other adenocarcinoma. Patients with ≤7 positive LNs benefited from PORT and those with >7 positive LNs benefited from chemotherapy.
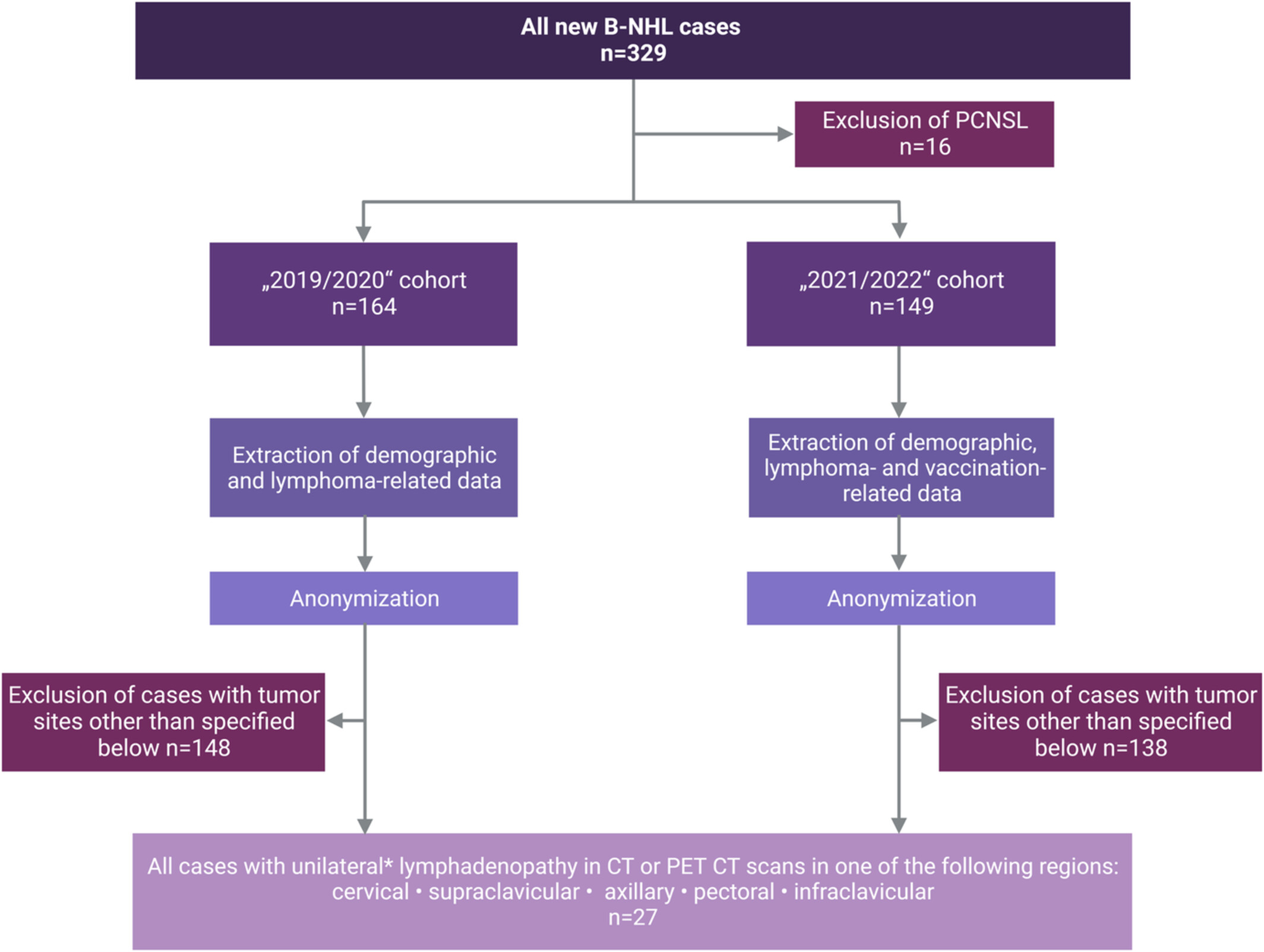
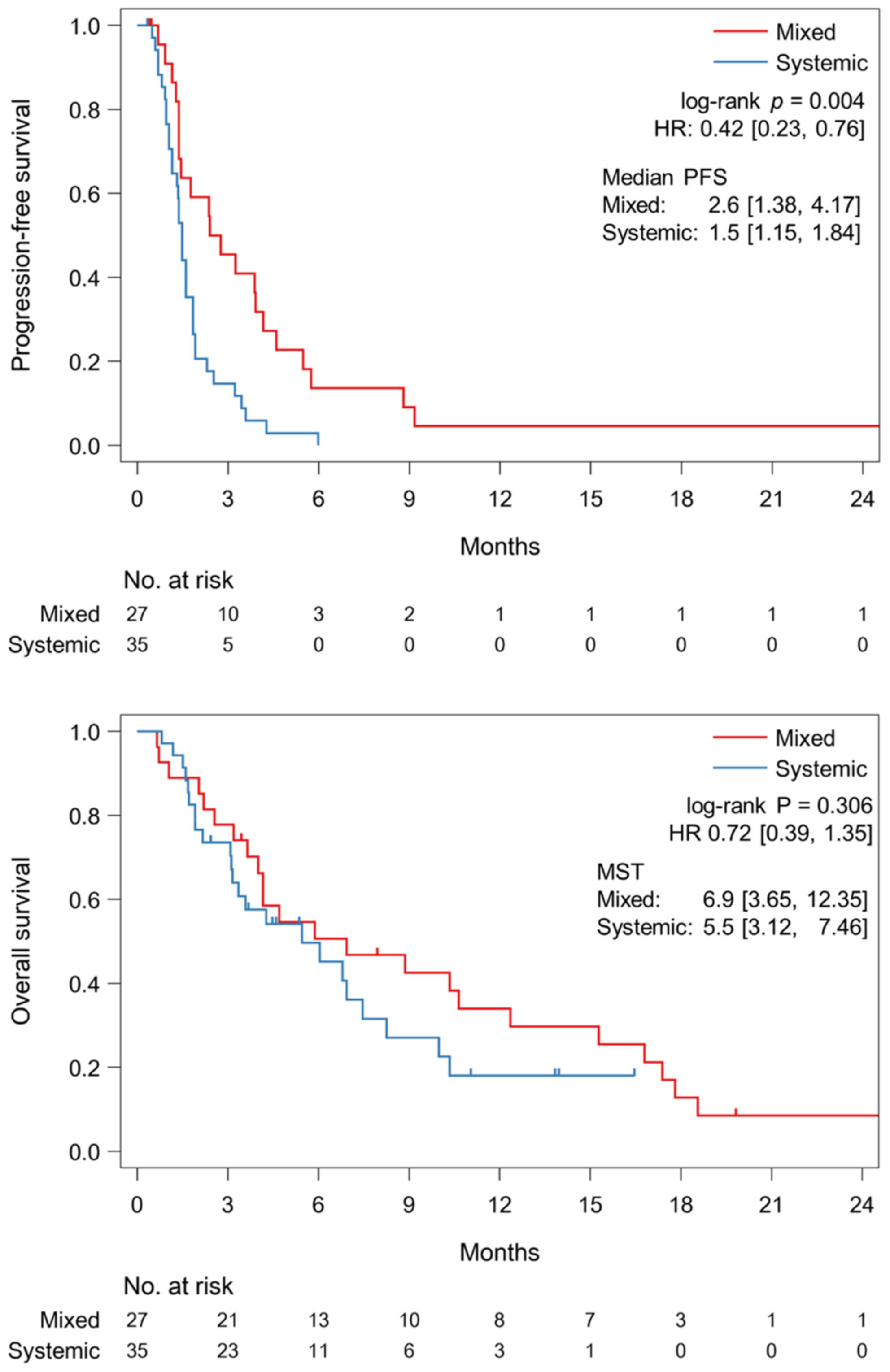
No association of malignant B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas with ipsilateral SARS-CoV-2 vaccination
- Pages: 9313-9321
- First Published: 12 February 2023
Progression patterns and site-specific responses in advanced gastric cancer patients treated with nivolumab
- Pages: 9322-9331
- First Published: 15 February 2023
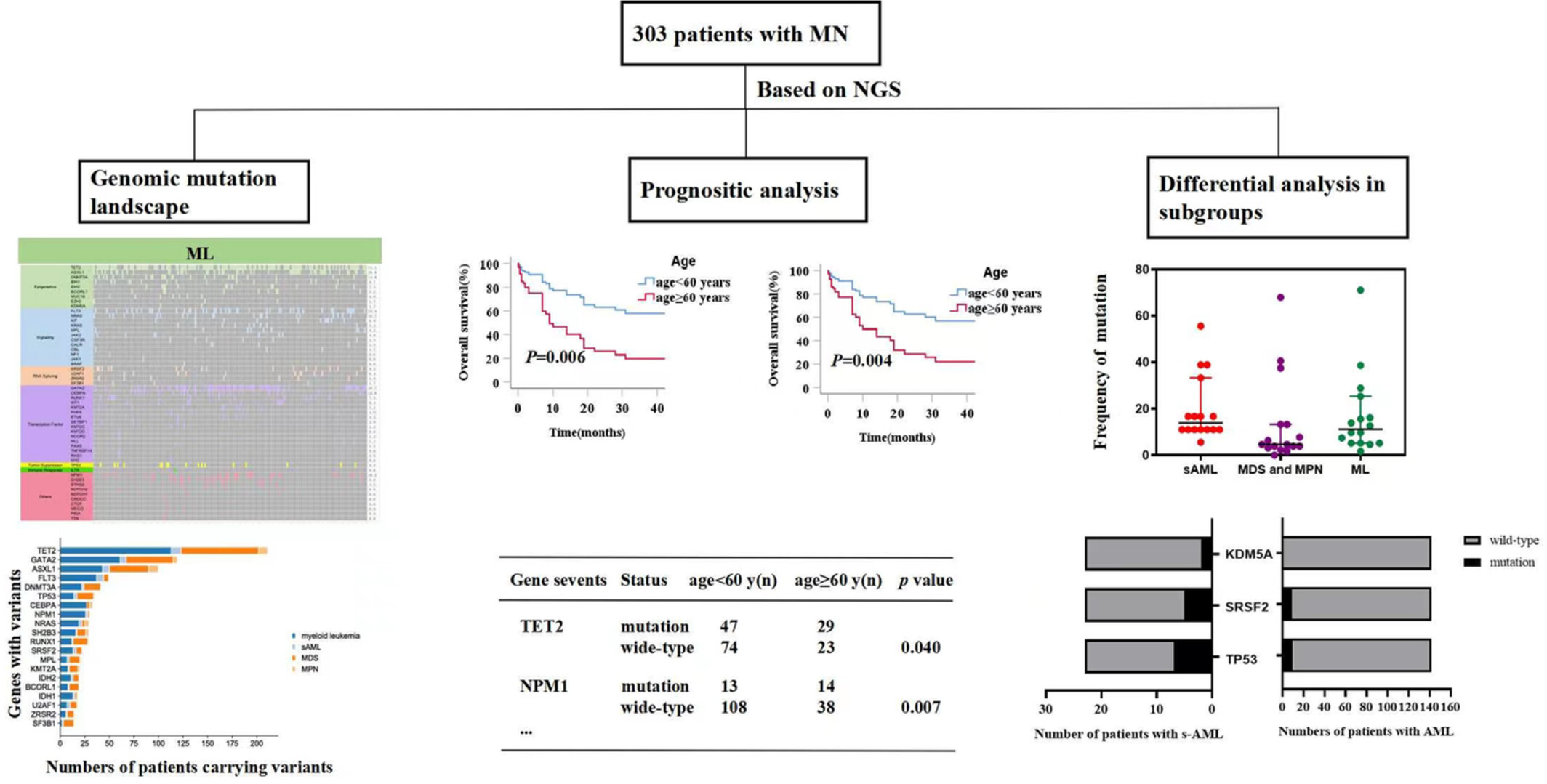
Gene mutation analysis using next-generation sequencing and its clinical significance in patients with myeloid neoplasm: A multi-center study from China
- Pages: 9332-9350
- First Published: 17 February 2023
Cryotherapy for partial gland ablation of prostate cancer: Oncologic and safety outcomes
- Pages: 9351-9362
- First Published: 12 February 2023
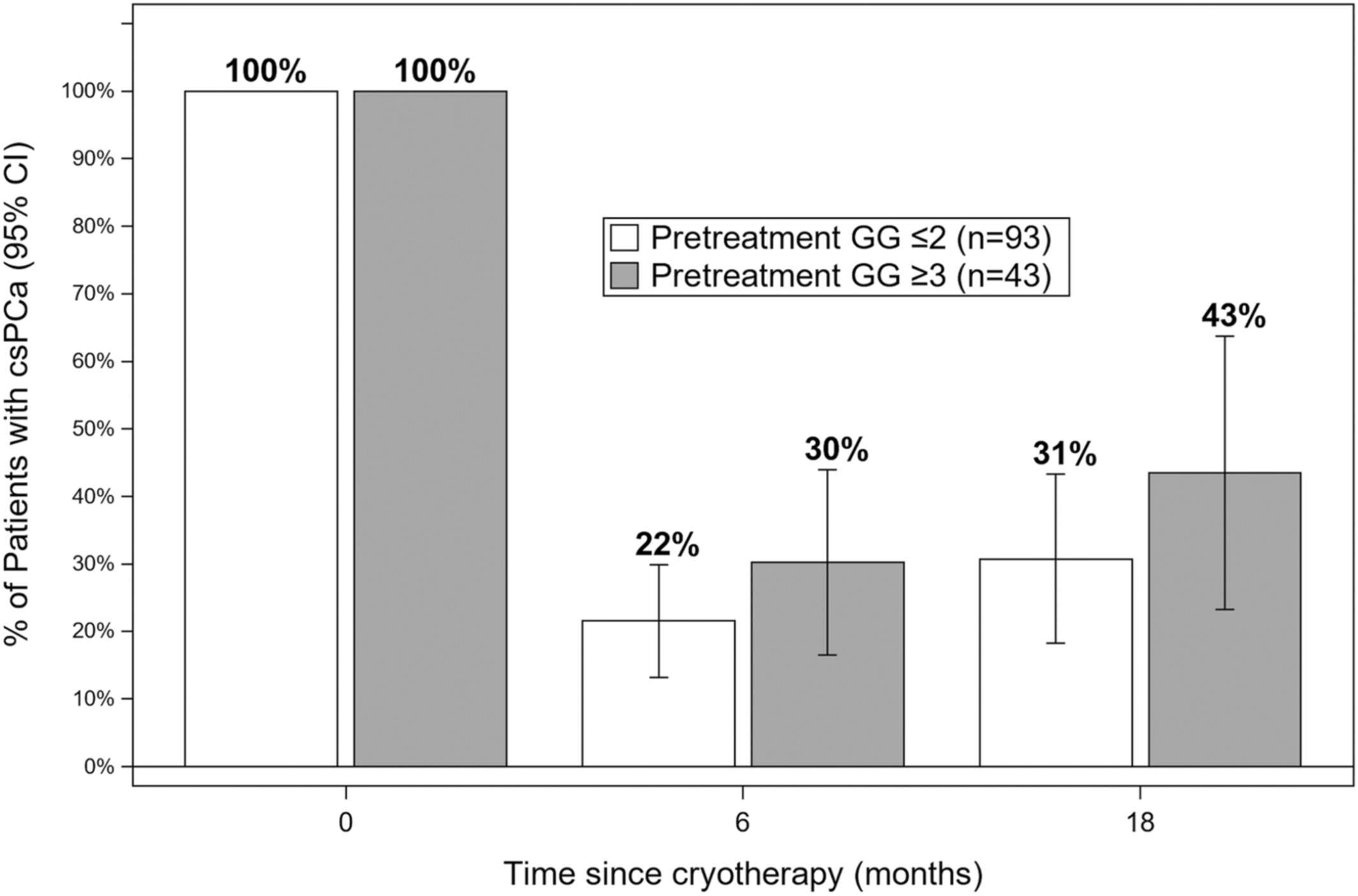
In the near to intermediate term, partial gland ablation with focal cryotherapy was found to be a moderately effective and relatively safe treatment for men with intermediate risk prostate cancer. We also found that treatment success, that is, eradication of the cancer, is best determined by MRI-guided biopsy, rather than by PSA levels or MRI findings.
Prognostic analysis of three forms of Ki-67 in patients with breast cancer with non-pathological complete response before and after neoadjuvant systemic treatment
- Pages: 9363-9372
- First Published: 16 February 2023
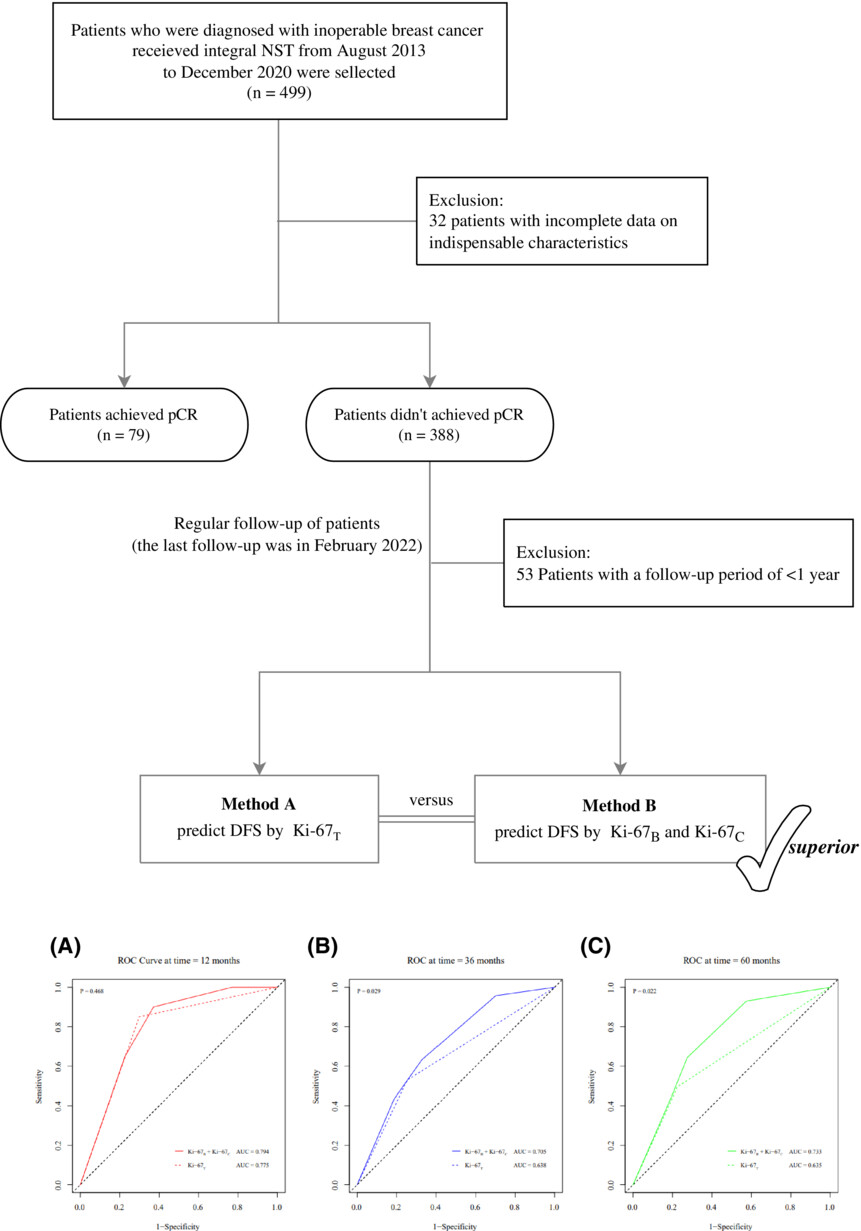
Patients who do not achieve a pathological complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant systemic treatment (NST) have a significantly worse prognosis. This study aimed to explore the most useful form or combination of Ki-67 including the baseline Ki-67 at biopsy before NST (Ki-67B), the percentage change in Ki-67 before and after NST (Ki-67C), and the terminal index of Ki-67 after surgery (Ki-67T), that can provide prognostic information to non-pCR patients. We retrospectively reviewed 499 patients, and 388 patients did not achieve pCR. The forecasting model combining Ki-67B and Ki-67C showed a significantly higher area under the curve (AUC) at years 3 and 5 than Ki-67T (p = 0.029 and p = 0.022, respectively). The combination of Ki-67B and Ki-67C is superior to Ki-67T for predicting DFS, especially at longer follow-ups.
Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 as a potential biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated neurotoxicity
- Pages: 9373-9383
- First Published: 16 February 2023
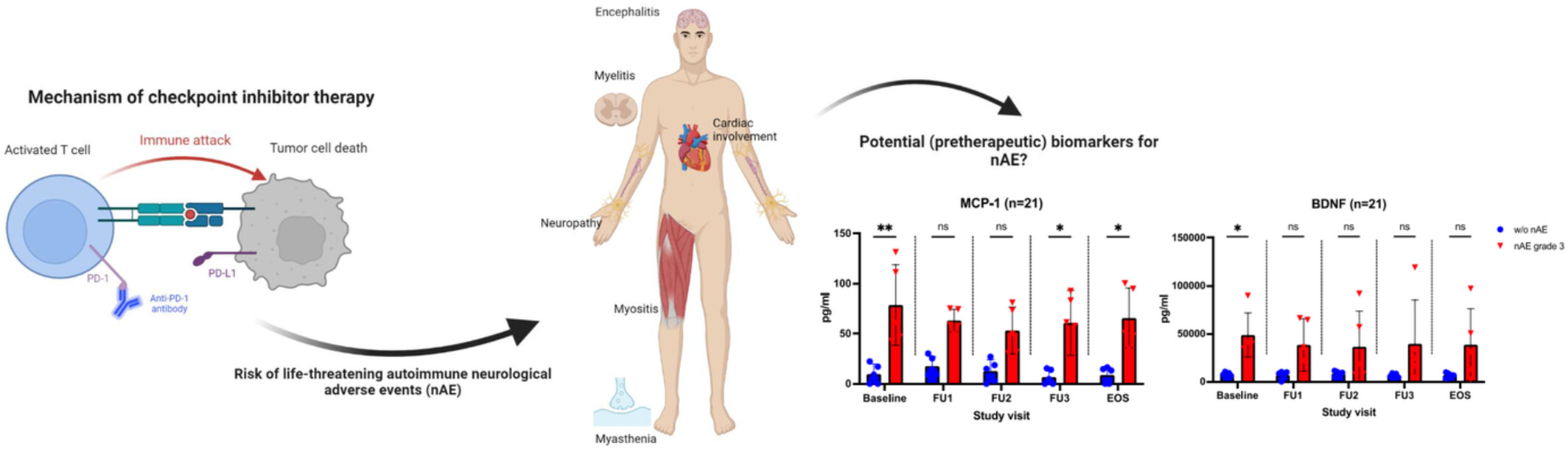
Oncological patients can benefit substantially from treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, there is a growing awareness of immune-related adverse events, especially neurological adverse events (nAE). MCP-1 and BDNF are potentially the first clinical-class nAE predictors for patients under immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
Peripheral lymphocytes and lactate dehydrogenase correlate with response and survival in head and neck cancers treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
- Pages: 9384-9391
- First Published: 21 February 2023
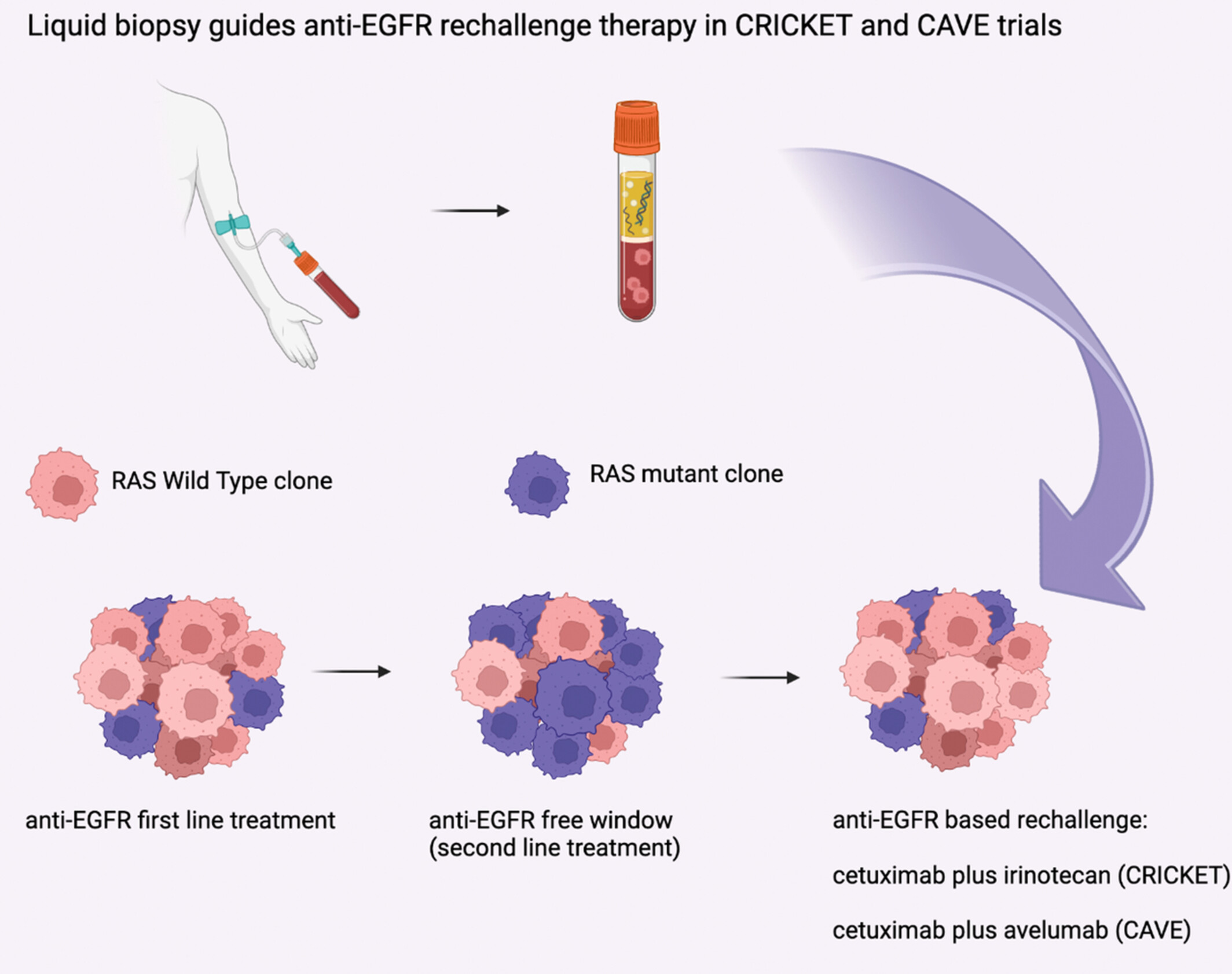
Cetuximab as third-line rechallenge plus either irinotecan or avelumab is an effective treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer patients with baseline plasma RAS/BRAF wild-type circulating tumor DNA: Individual patient data pooled analysis of CRICKET and CAVE trials
- Pages: 9392-9400
- First Published: 07 March 2023
Lymphovascular or perineural invasion is associated with lymph node metastasis and survival outcomes in patients with gastric cancer
- Pages: 9401-9408
- First Published: 23 March 2023
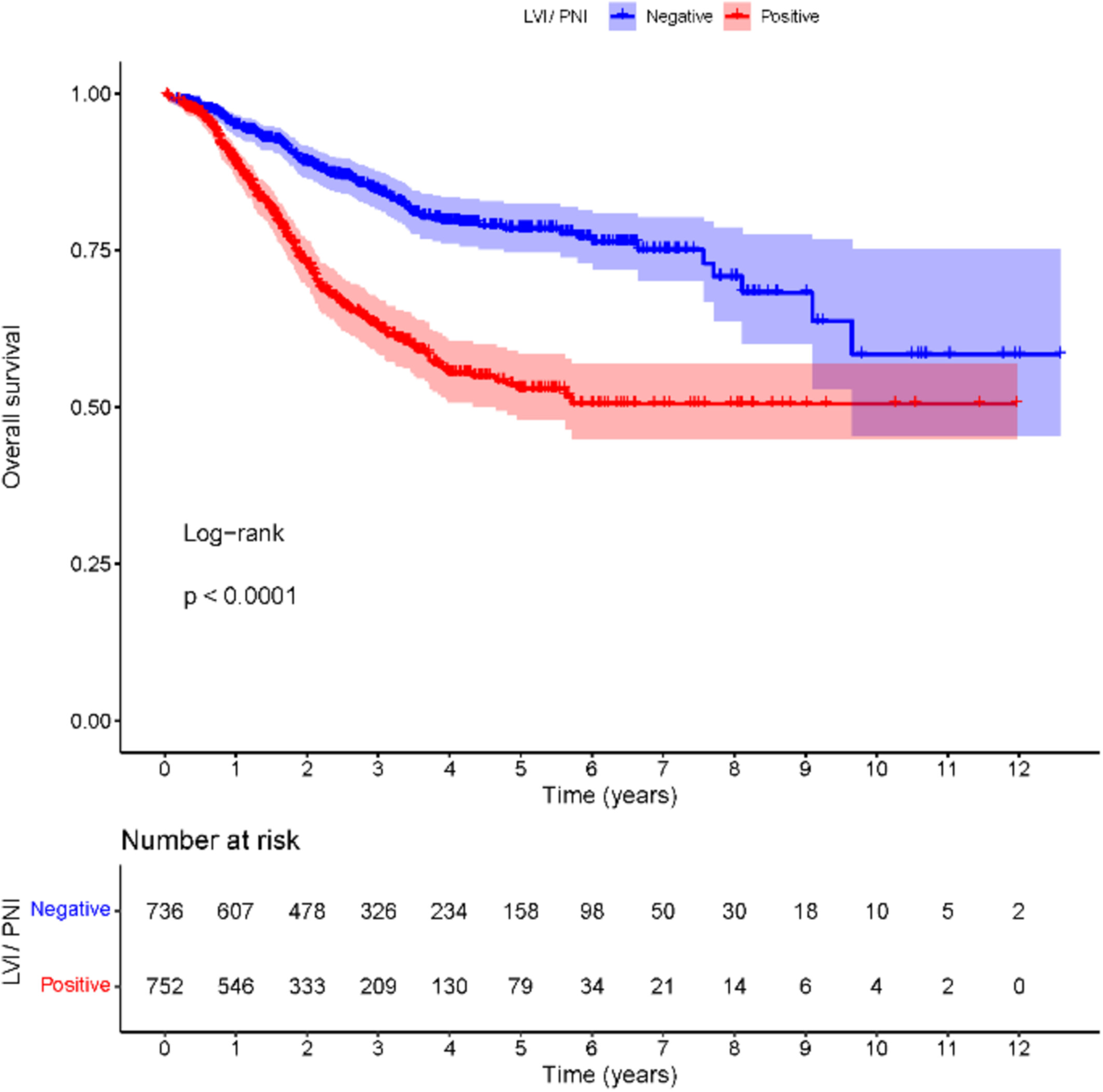
Gastric cancer has a high incidence of LVI/PNI, which was closely associated with disease progression. LVI/PNI could serve as an independent risk factor for lymph node metastasis and the prognosis of patients with curative resected gastric cancer. These findings will be helpful in predicting survival outcomes more accurately and establishing individualized treatment plans.
Long-term follow-up results of pediatric and adolescent patients with localized Ewing sarcoma treated based on stratified modalities
- Pages: 9409-9419
- First Published: 21 February 2023
Prognostication refinement in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia stratified by FLT3-ITD status with different induction doses of cytarabine
- Pages: 9420-9433
- First Published: 21 February 2023
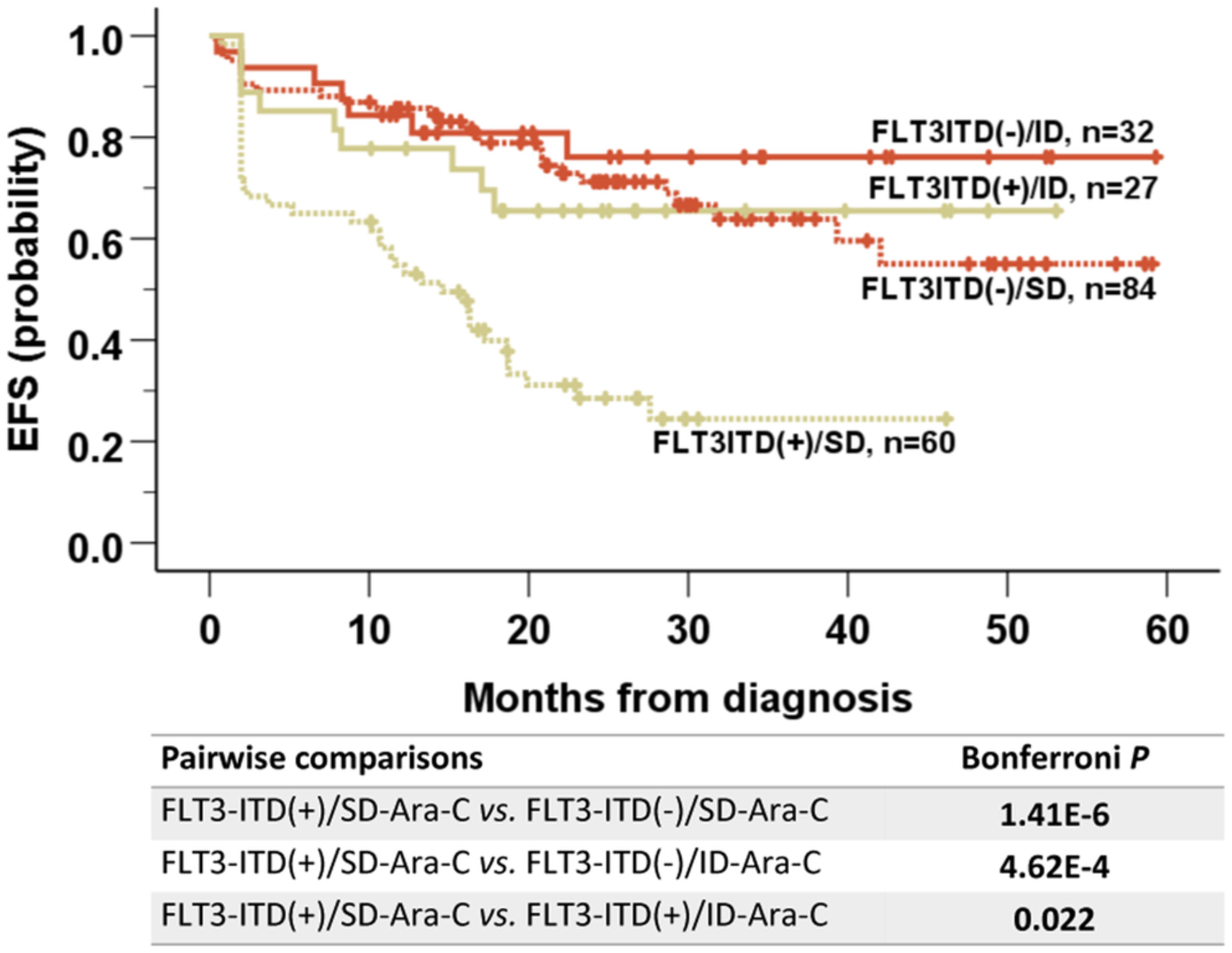
NPM1mut/FLT3-ITD(−)/TET2(+) is identified as an unfavorable prognostic subset in NPM1mut/FLT3-ITD(−) patients. Induction containing intermediate-dose cytosine arabinoside improves outcome in NPM1mut/FLT3-ITD(+) patients. Clinicopathologic parameters, including age and white blood cell count, convey an outcome risk modulation for NPM1mut/FLT3-ITD(−), as does CD34 for NPM1mut/FLT3-ITD(+).
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
Efficacy of gemcitabine in combination with nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel in the treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer: A retrospective single institution review
- Pages: 9434-9438
- First Published: 21 February 2023
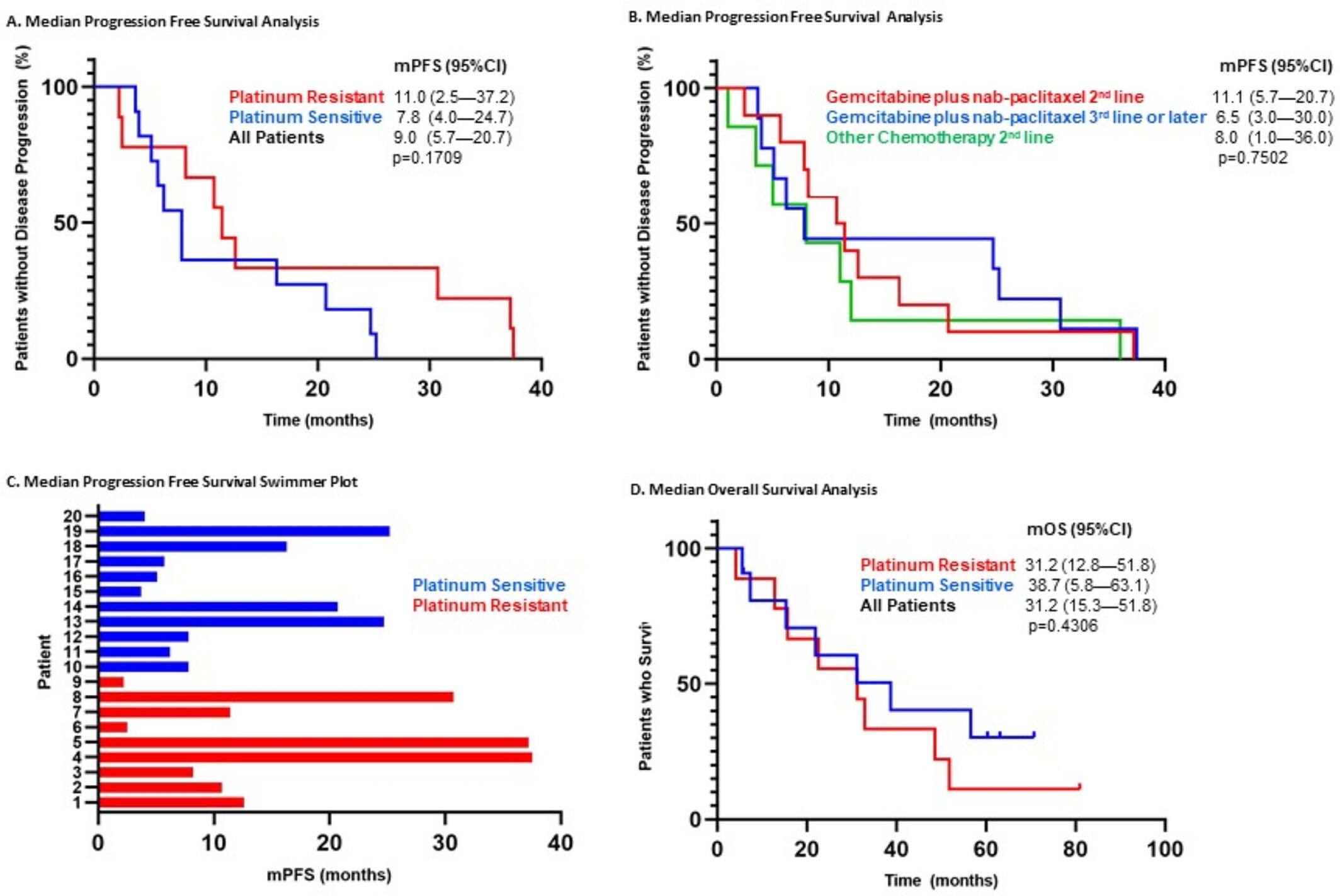
In this retrospective review, 20 patients were treated with gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel and the median PFS was 9 months (95% CI, 5.7–20.7). Overall, 17 of the 20 patients (85%) achieved a clinical benefit (complete response 5%, partial response 55%, or stable disease at 3 months 25%). For platinum-sensitive disease and platinum-resistant disease, the median OS were 38.7 months (95% CI, 5.8–63.1) and 31.2 months (95% CI, 12.8–51.8), respectively (p = 0.4306). This regimen is a viable and well tolerated option for patients who are intolerant to paclitaxel or carboplatin because of allergic reactions.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
A controlling nutritional status score is an independent predictor for patients with newly diagnosed nasal-type extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma based on asparaginase-containing regimens
- Pages: 9439-9448
- First Published: 03 March 2023
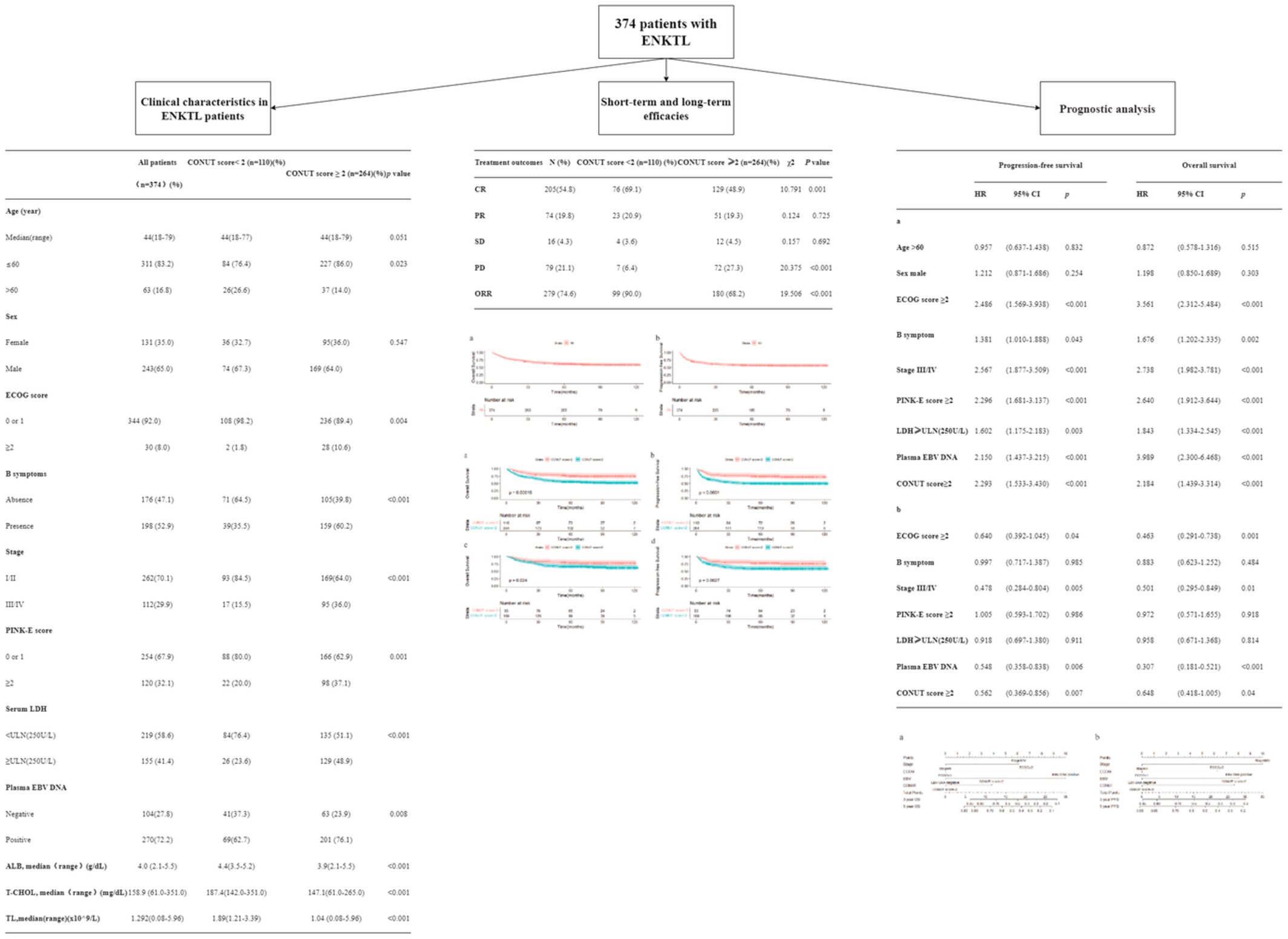
The controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score is a prognostic marker for survival in patients with nasal-type extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Patients with CONUT scores <2 had higher complete response and overall response rates, as well as better overall and progression-free survival rates. A CONUT score ≥2 was identified as an independent poor prognostic factor for both overall survival and progression-free survival and could be used to stratify risk in low-risk patients.
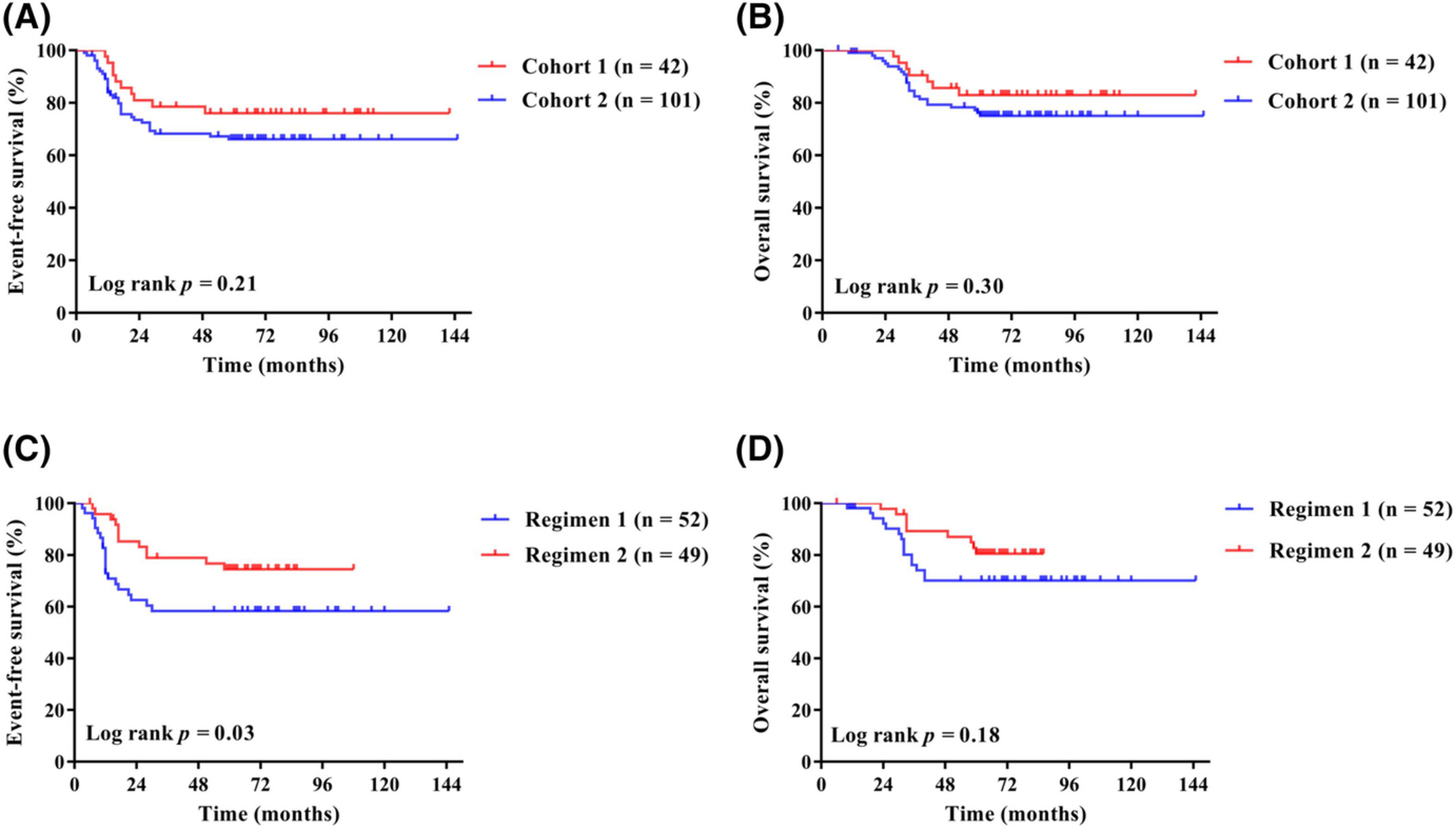
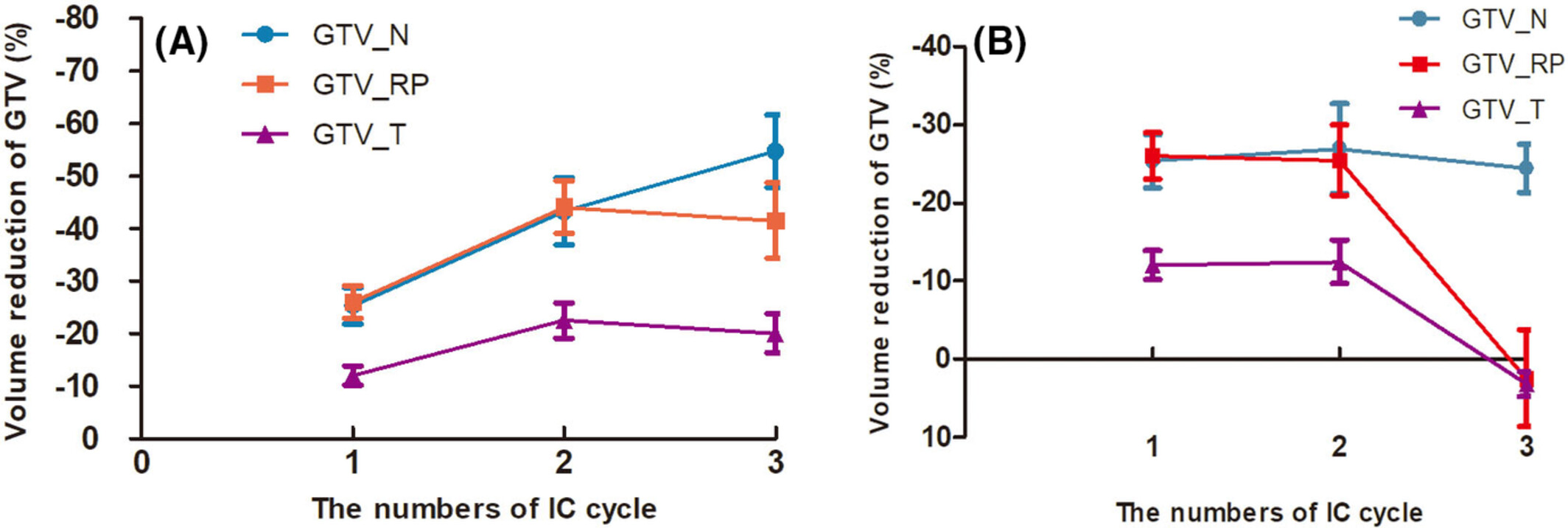
Optimizing induction chemotherapy regimens for radiotherapy in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Pages: 9449-9457
- First Published: 05 March 2023
Comparison of the clinical efficacies of two L-asparaginase-based chemotherapy regimens for newly diagnosed nasal-type extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 9458-9470
- First Published: 31 March 2023

In this retrospective analysis of 267 newly diagnosed nasal-type extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma patients, LVDP (L-asparaginase, etoposide, dexamethasone and cisplatin) and GLIDE (gemcitabine, L-asparaginase, ifosfamide, dexamethasone and etoposide) chemotherapy regimens showed similar short-term and long-term efficacies, with 85.5% ORR and 62.2% CR rates, and 64.3% PFS and 68.5% OS rates at a median 71-month follow-up. However, LVDP was associated with milder treatment-related toxicities compared to GLIDE, even after adjusting for confounders via PSM. These findings suggest that LVDP could be a preferable option for patients with nasal-type extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma.
A retrospective analysis of the prognosis of Japanese patients with sarcoma brain metastasis
- Pages: 9471-9481
- First Published: 22 February 2023
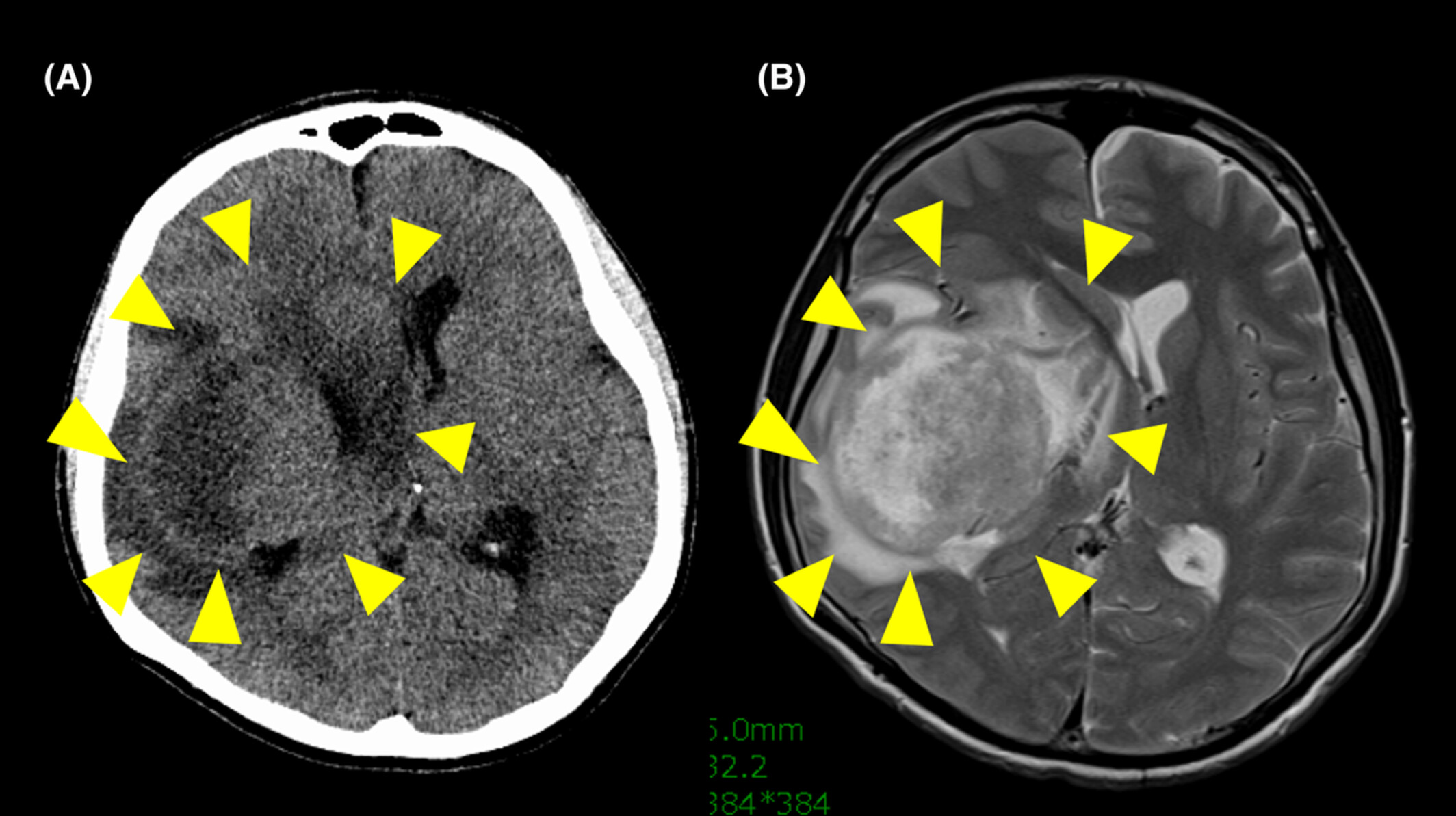
We retrieved Japanese sarcoma patients with brain metastasis (BM) in a single institution and analyzed the prognostic factors for BM. We have identified several prognostic factors for brain metastases. We believed that our data is useful for understanding the prognosis and treatment strategy for BM of sarcoma.
The predictive value of lymphocyte to monocyte ratio for overall survival in cholangiocarcinoma patients with hepatic resection
- Pages: 9482-9495
- First Published: 24 February 2023
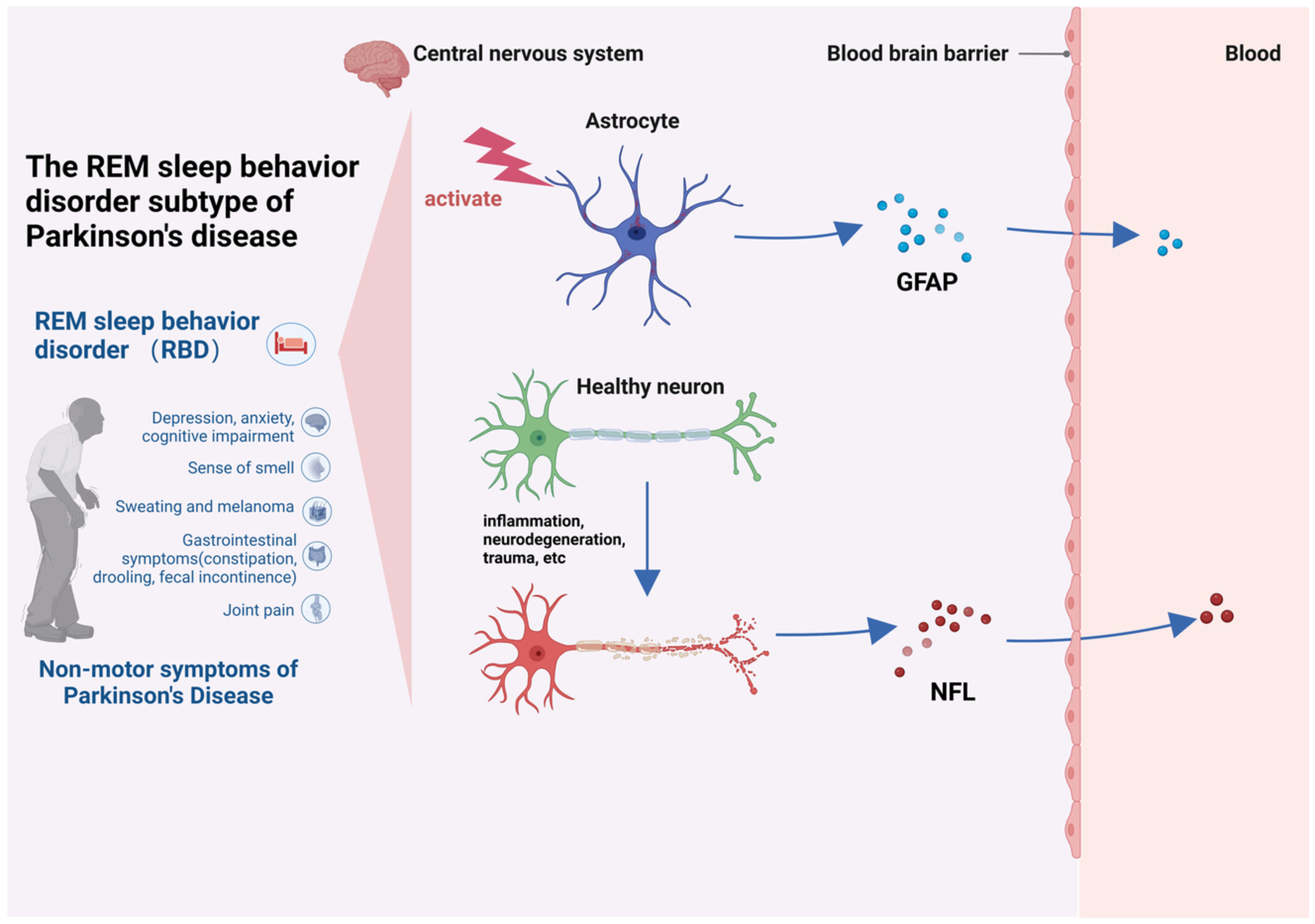
1.By retrospectively analyzing the clinical data of 145 CCA patients with hepatic resection, we determined the optimal LMR cutoff value according to the receiver operating characteristic (ROC).
2.We found there was a longer OS in CCA patients of the high LMR group than the low LMR group.
3.Preoperative LMR was a vital prognostic factor to predict the prognosis of CCA patients with hepatic resection and provided additional prognostic value beyond standard clinicopathological parameters.
Prior irinotecan exposure does not preclude benefit to liposomal irinotecan in patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 9496-9505
- First Published: 19 March 2023
Effect of percutaneous stenting strategy of unresectable malignant hilar biliary obstruction by three-dimensional reconstruction volumetry
- Pages: 9506-9516
- First Published: 20 February 2023
Real-world clinical outcomes of the combination of anti-PD-1 antibody, trastuzumab, and chemotherapy for HER2-positive gastric/gastroesophageal junction cancer
- Pages: 9517-9526
- First Published: 13 March 2023
Construction of the prognostic model for small-cell lung cancer based on inflammatory markers: A real-world study of 612 cases with eastern cooperative oncology group performance score 0–1
- Pages: 9527-9540
- First Published: 04 April 2023
We explored the relationship between pre-treatment inflammatory markers and other clinical characteristics and the survival of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients who received first-line platinum-based treatment. The nomograms for predicting progression-free survival and overall survival had good predictability and stability. This research may provide clues and guides for individual treatment of SCLC patients.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
Association between immune checkpoint inhibitors and myocardial infarction in Asians: A population-based self-controlled case series
- Pages: 9541-9546
- First Published: 21 February 2023
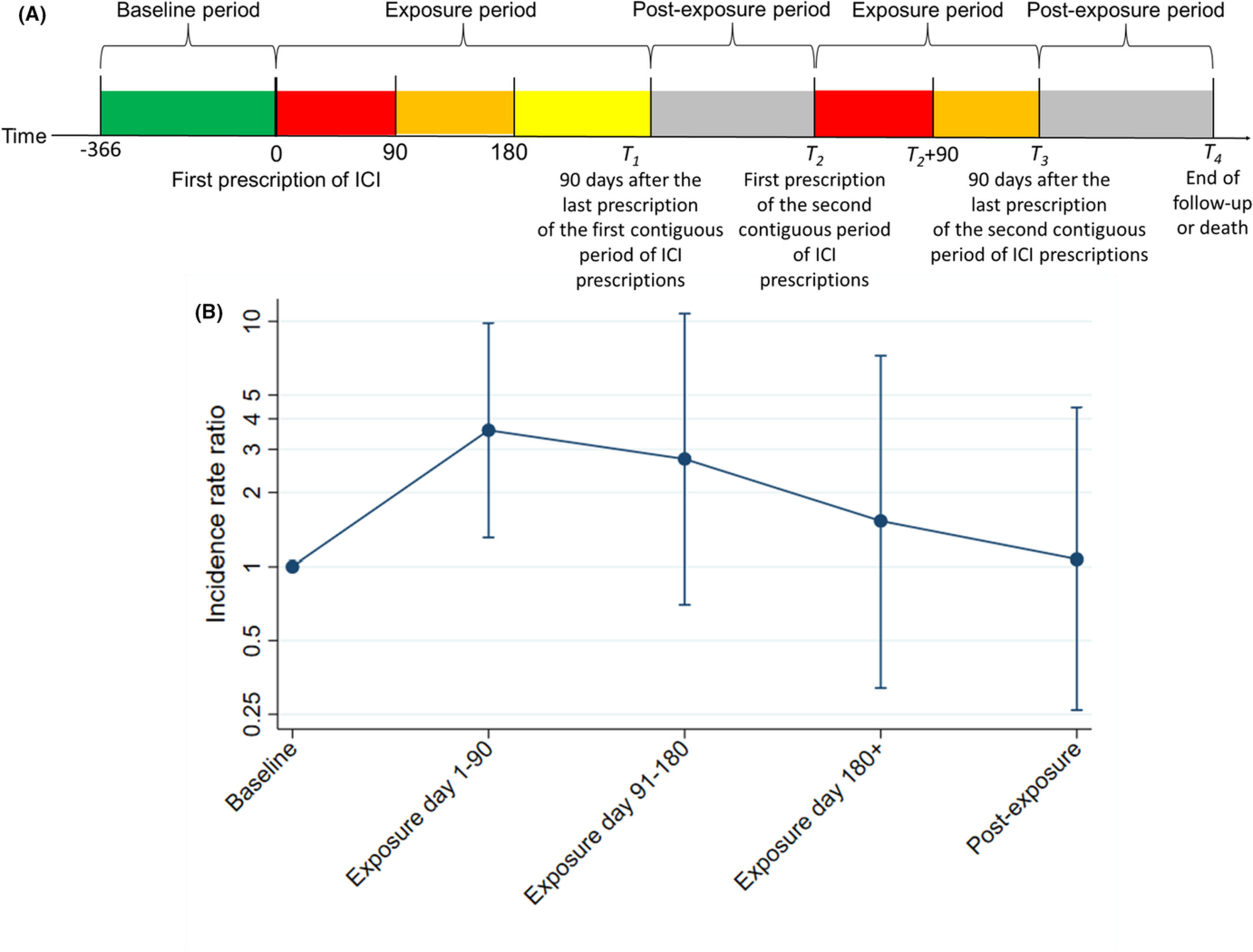
Using prospectively collected population-based data, this self-controlled case series investigated the link between immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) use and myocardial infarction (MI) in Chinese patients. Compared to the year prior to ICI use, MI incidence increased significantly in the first 90 days of exposure, but not in later exposure periods nor post-exposure.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
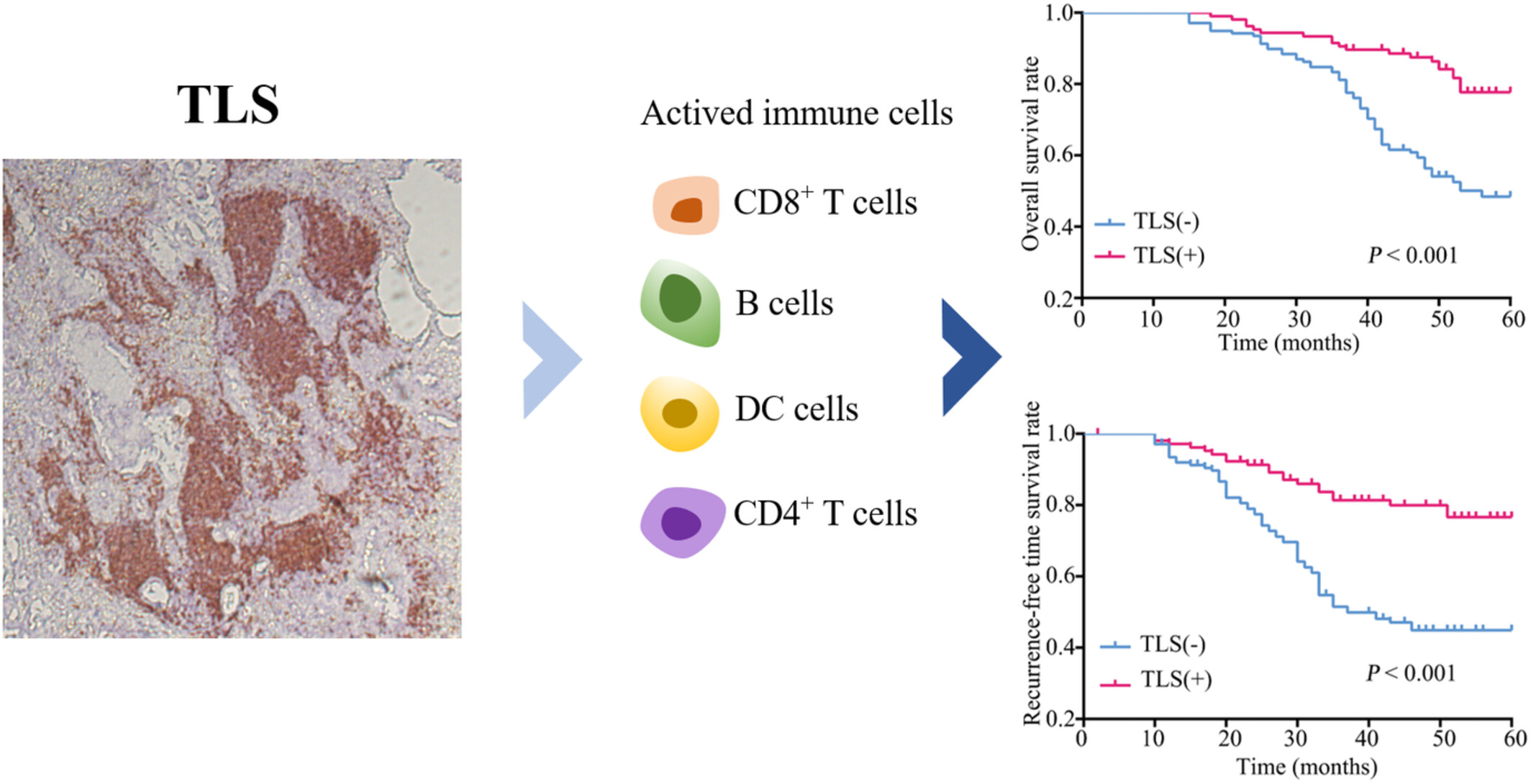
Clinical implications and molecular features of tertiary lymphoid structures in stage I lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 9547-9558
- First Published: 06 March 2023
Five-year survival post hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases in a real-world Chinese cohort: Recurrence patterns and prediction for potential cure
- Pages: 9559-9569
- First Published: 27 February 2023

With the advances in treatment for colorectal liver metastases (CRLM), accurately predicting recurrence-free survival post hepatectomy has become increasingly important. This study retrospectively analyzed patients with CRLM who underwent surgery with actual follow-up over 5 years; we found that approximately one quarter of patients got a potential cure chance without recurrence. Patients with RAS wild-type, preoperative CEA <10 ng/mL, and liver metastases ≤3 were shown to have a higher chance of cure rate after hepatic resection for CRLM.
Prognosis and complications of patients with primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Development and validation of the systemic inflammation response index-covered score
- Pages: 9570-9582
- First Published: 03 March 2023
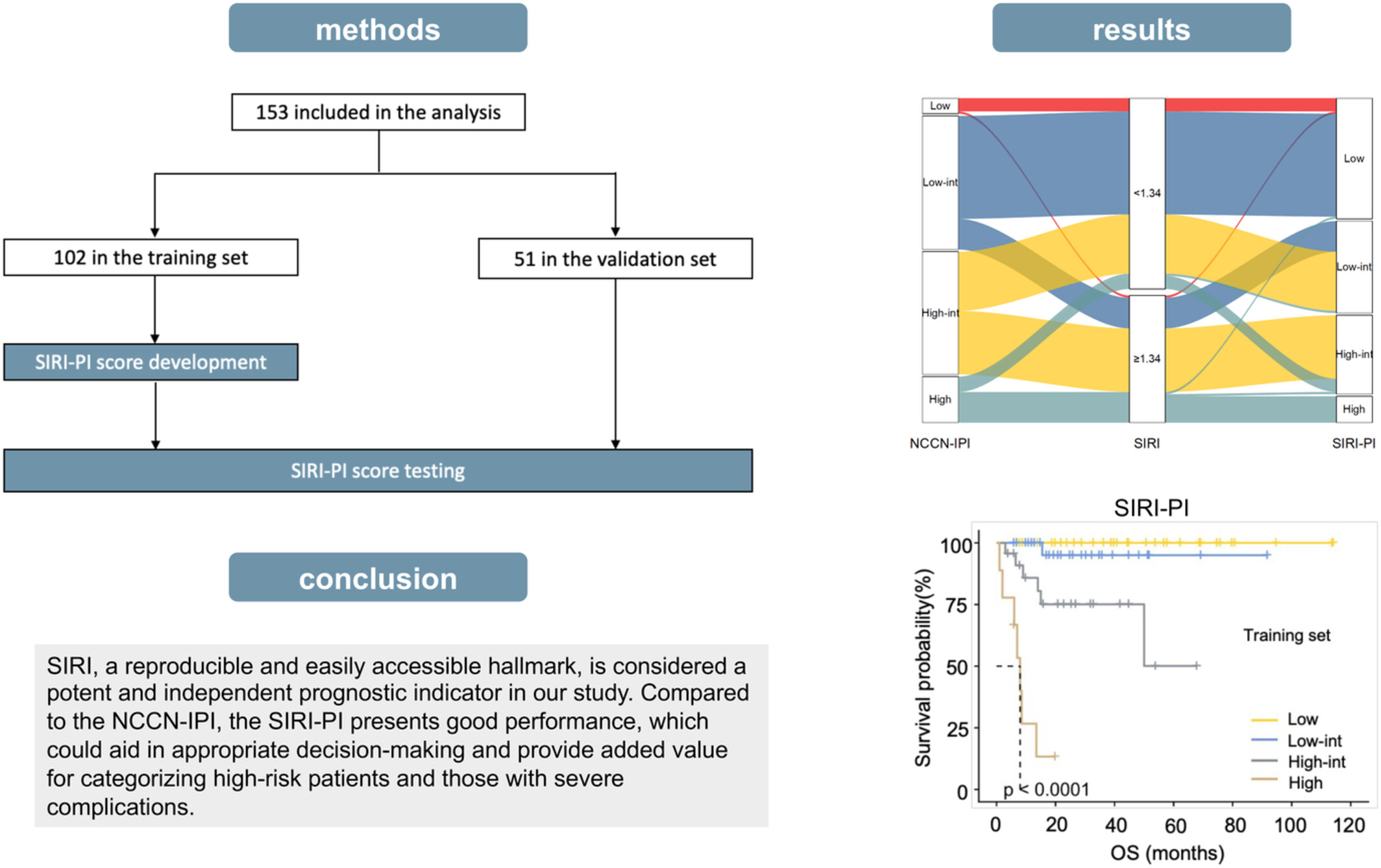
SIRI, a reproducible and easily accessible hallmark, is considered a potent and independent prognostic indicator in our study. Compared to the NCCN-IPI, the SIRI-PI presents good performance, which could aid in appropriate decision-making and provide added value for categorizing high-risk patients and those with severe complications.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
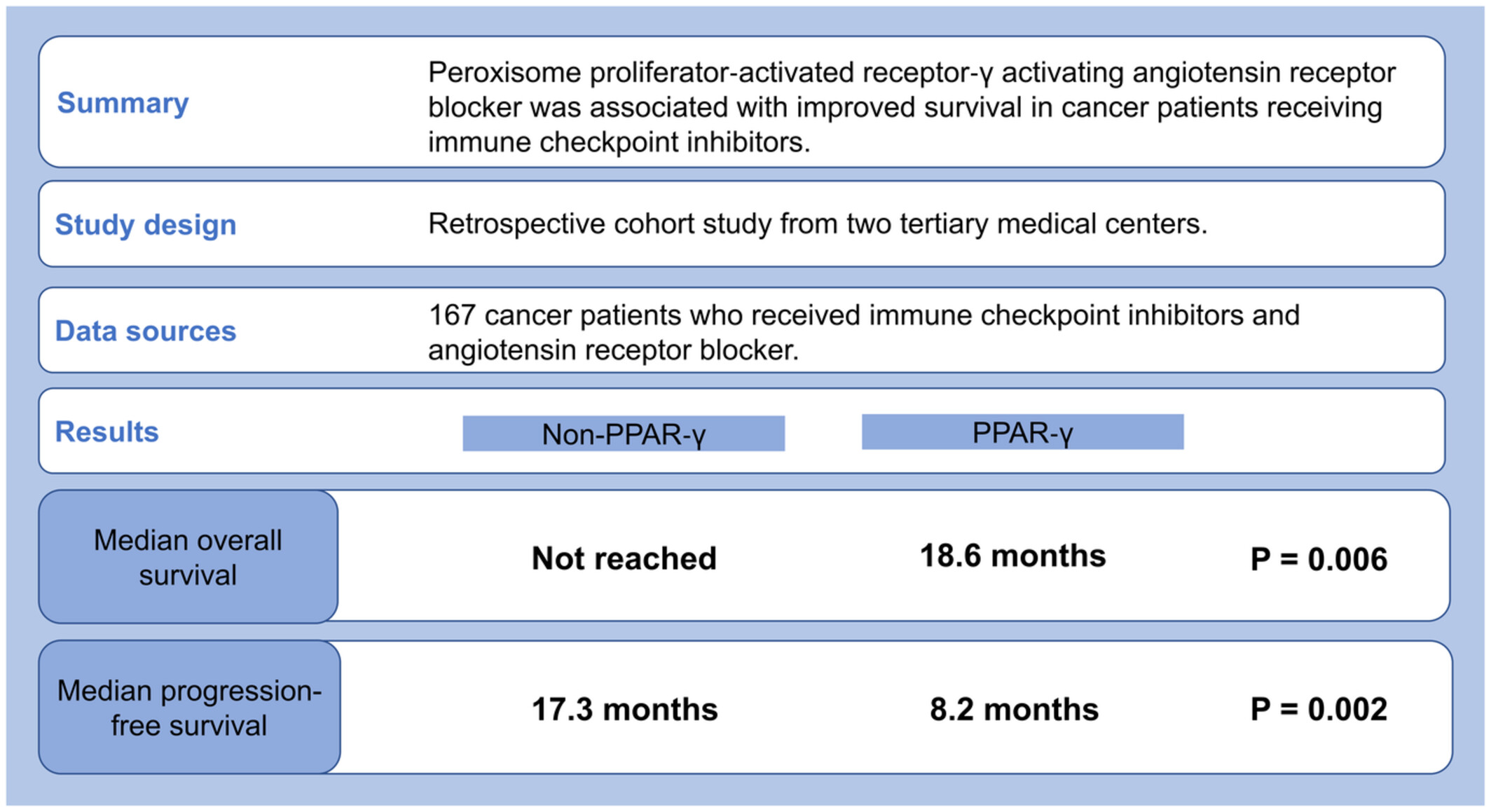
The impact of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activating angiotensin receptor blocker on outcomes of patients receiving immunotherapy
- Pages: 9583-9588
- First Published: 24 February 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Clinical Cancer Research
Establishment and validation of systematic prognostic nomograms in patients over 60 years of age with osteosarcoma: A multicenter external verification study
- Pages: 9589-9603
- First Published: 29 March 2023
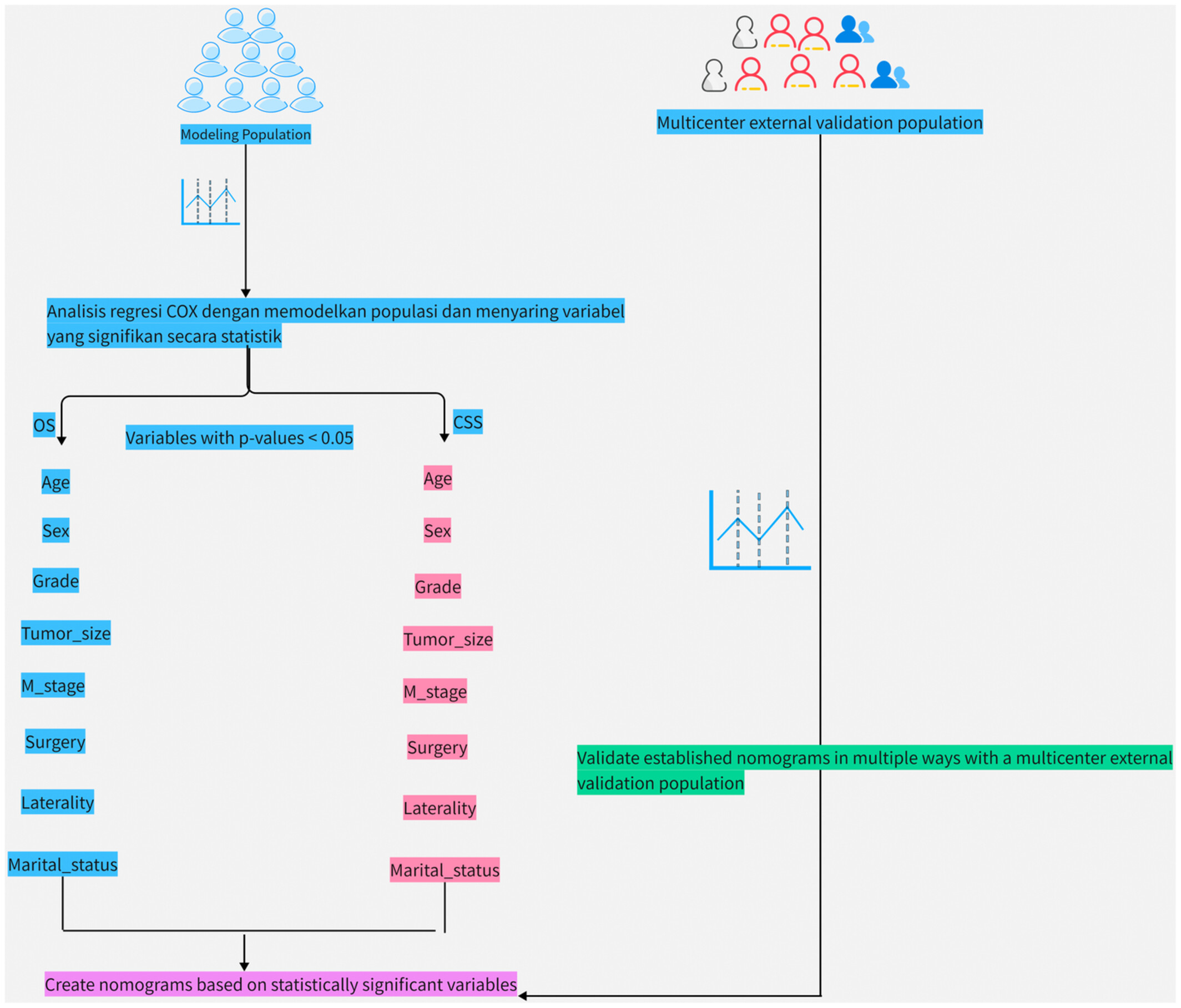
In this study, we used osteosarcoma patients over 60 years of age from the SEER database as the modeling population, identified statistically significant variables by means of multiple regression analyses, and used these variables to build nomograms that can accurately predict the risk of OS & CSS in osteosarcoma patients over 60 years of age. In addition, this study collected data from multiple medical centers as an external validation population to assess the accuracy and precision of the prediction models we have constructed.
The evolving diagnosis and treatment paradigms of multiple myeloma in China: 15 years' experience of 1256 patients in a national medical center
- Pages: 9604-9614
- First Published: 21 February 2023
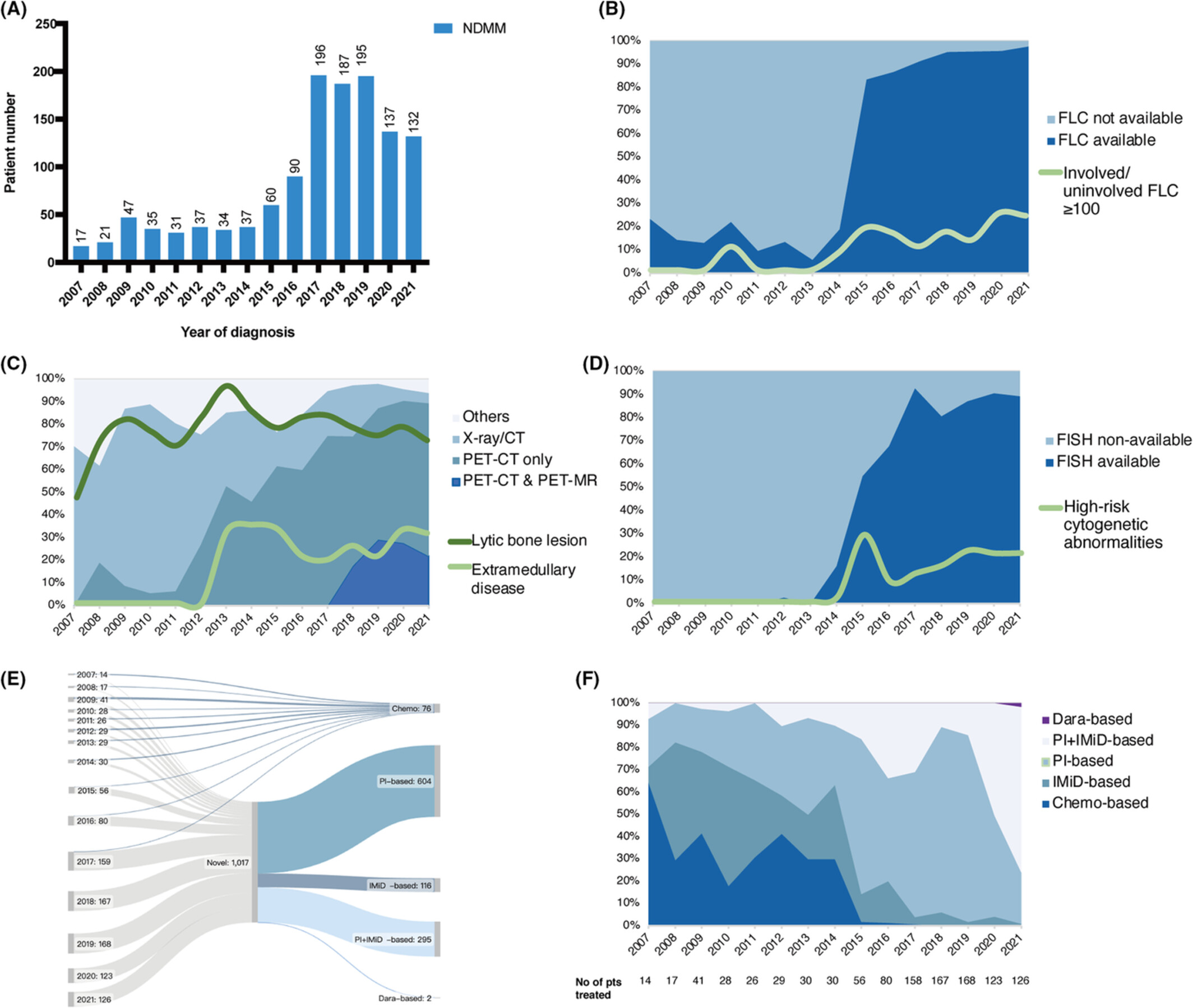
This is the first report illustrating the evolving patterns of multiple myeloma (MM) diagnosis and treatment and a reflection of the dynamic landscape of China's myeloma management. Chinese MM patients evidently benefited from comprehensive baseline evaluation and novel-drug-based (proteasome inhibitors [PIs] and immunomodulatory drugs [IMiDs]) standardized initial treatment.
Prognostic value of cross-lineage expression of the myeloid-associated antigens CD13 and CD33 in adult B-lymphoblastic leukemia: A large real-world study of 1005 patients
- Pages: 9615-9626
- First Published: 23 March 2023
HBcAb positivity increases the risk of postoperative complications after extended hemihepatectomy for hilar cholangiocarcinoma
- Pages: 9627-9636
- First Published: 27 February 2023
The present study aims to evaluate the prevalence of HBcAb positivity in hCCA patients and explore the effect of HBcAb positivity on postoperative complications of hCCA patients after curative resection. Among all the 217 patients, 160 (73.7%) patients were HBcAb positive. Data of 99 HBsAg negative patients who underwent curative resection were analyzed, and the HBcAb positivity markedly increased the risk of postoperative complications and mortality after curative resection for hCCA. Surgeons should pay more attention to HBcAb status in hCCA patients with negative HBsAg, which could help them to select optimal surgical modalities.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Clinical Cancer Research
Immunophenotypic profiles and prognosis for colorectal mucinous adenocarcinomas are dependent on anatomic location
- Pages: 9637-9643
- First Published: 14 March 2023
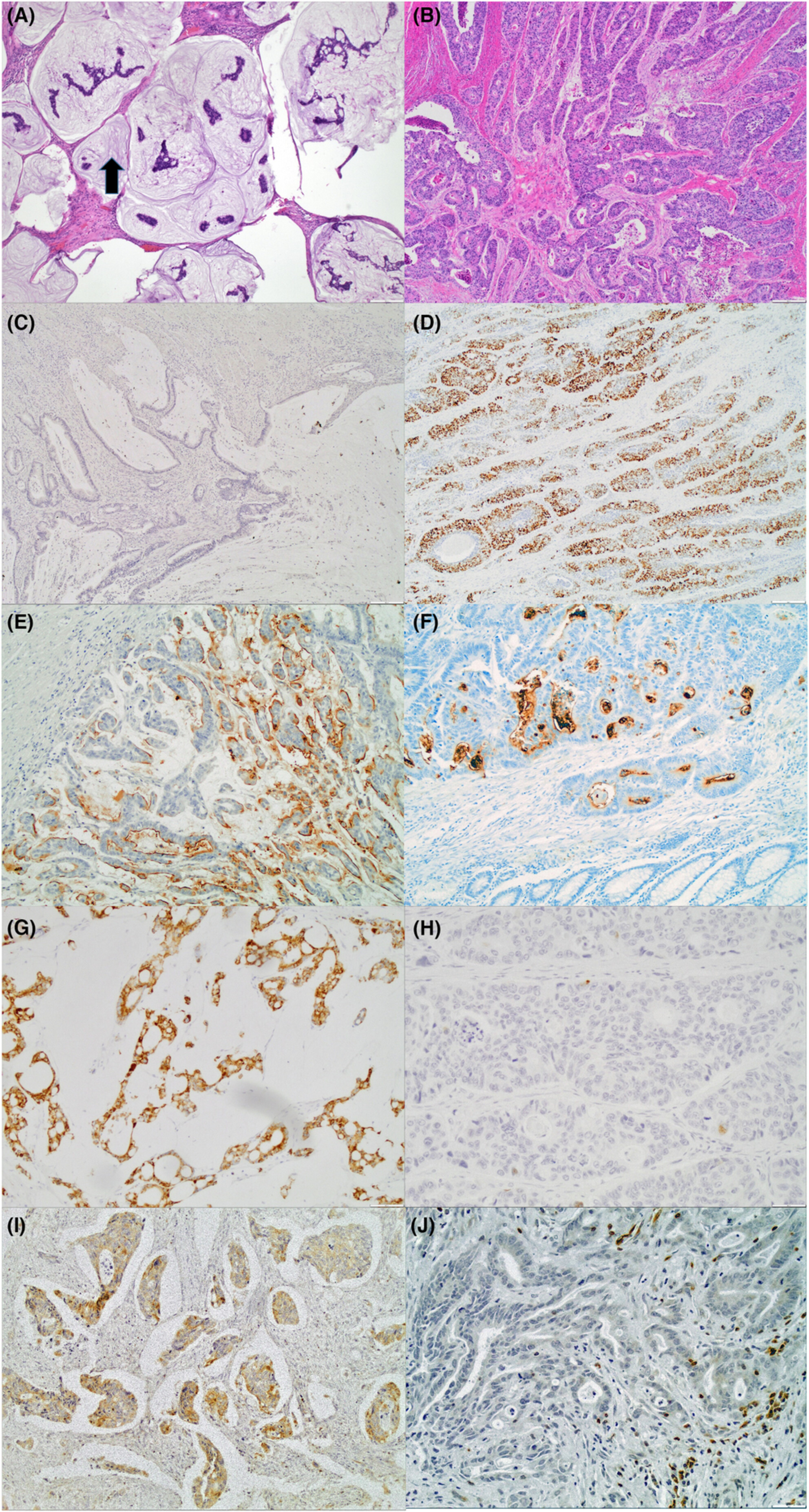
Overall, our study found that mucinous adenocarcinomas (MCAs) were more commonly located in the right colon, high grade, and prevalent in younger patients (<40 years). They exhibited strong expression of MUC2 and Bcl-2 and showed less aberrant p53 nuclear staining. In adjusted multivariate survival models split by tumor location, MCAs of the rectum were associated with poorer outcomes relative to NMCAs (HR 1.85, CI 95% 1.15-2.97). Our results support the concept that patients with MCAs located in the rectum should be considered for rigorous treatment regimens.
Differences in clinical characteristics and prognosis between breast neuroendocrine carcinoma and breast invasive ductal carcinoma: A multicentre population-based study from China
- Pages: 9644-9649
- First Published: 23 March 2023
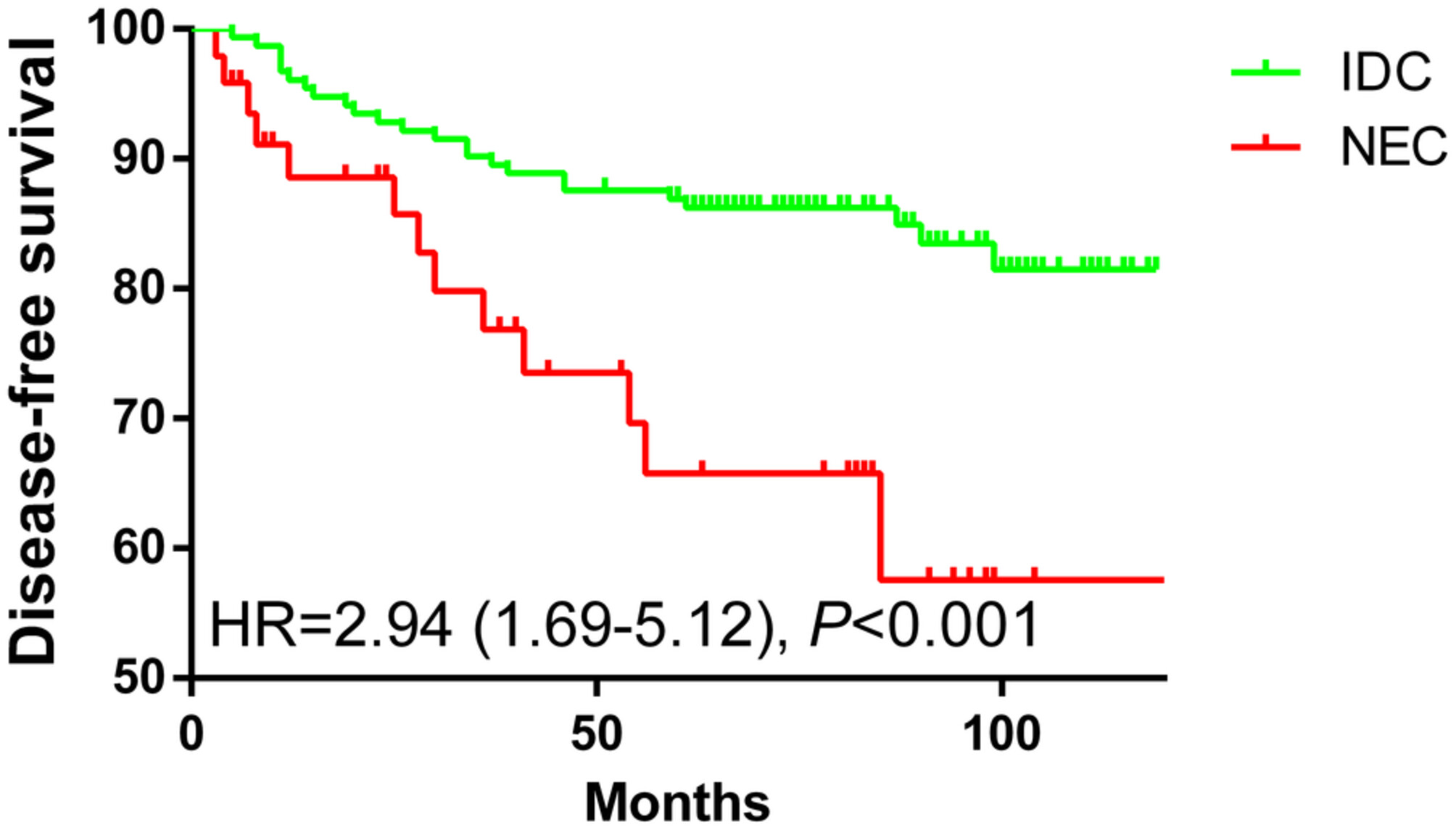
Neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC) of the breast is a very rare pathological type with few studies illustrating the prognosis compared with invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). Our team used propensity score matching to make a 1:3 match between NEC and IDC. Thus, 153 patients with IDC and 51 patients with NEC were analysed. Compared to patients with IDC, patients with NEC had a worse disease-free survival (HR = 2.94, 95% CI: 1.69–5.12, p < 0.001).
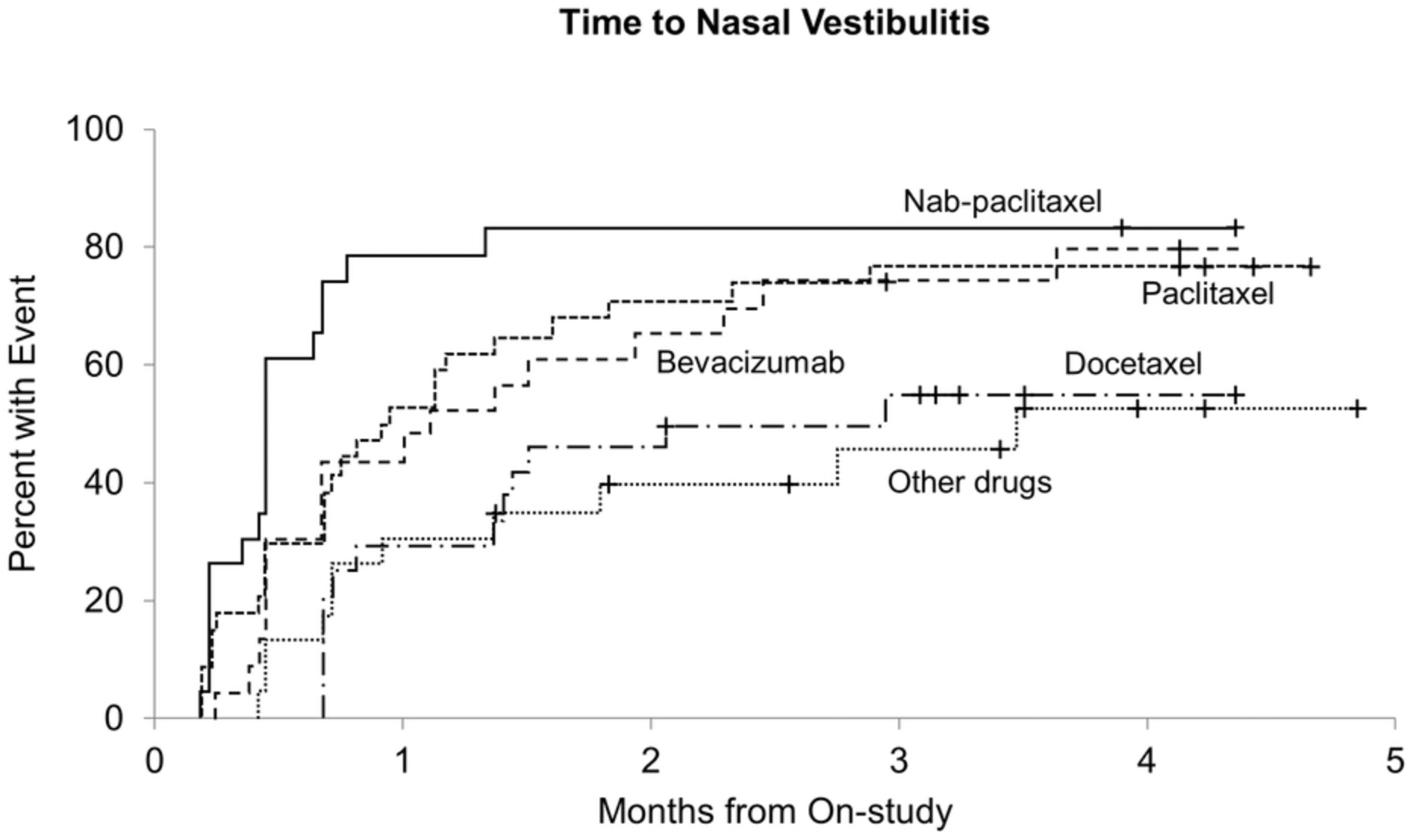
A five arm natural history study of nasal vestibulitis
- Pages: 9650-9654
- First Published: 05 April 2023
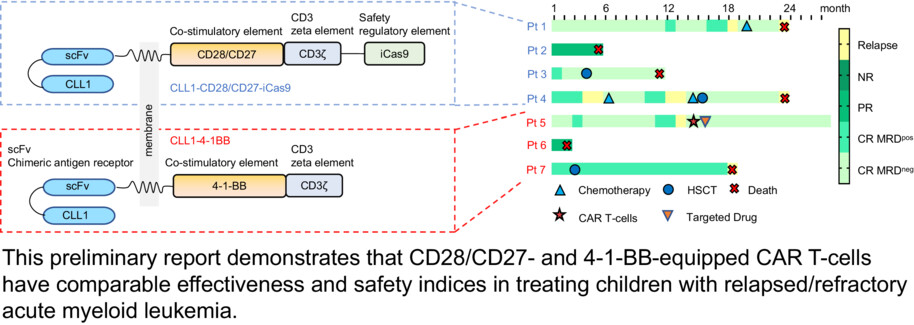
Anti-CLL1-based CAR T-cells with 4-1-BB or CD28/CD27 stimulatory domains in treating childhood refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 9655-9661
- First Published: 09 April 2023
Single-center study on SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients affected by CML: Vaccination status and bosutinib therapy as possible protective factors for hospitalization
- Pages: 9662-9667
- First Published: 11 April 2023
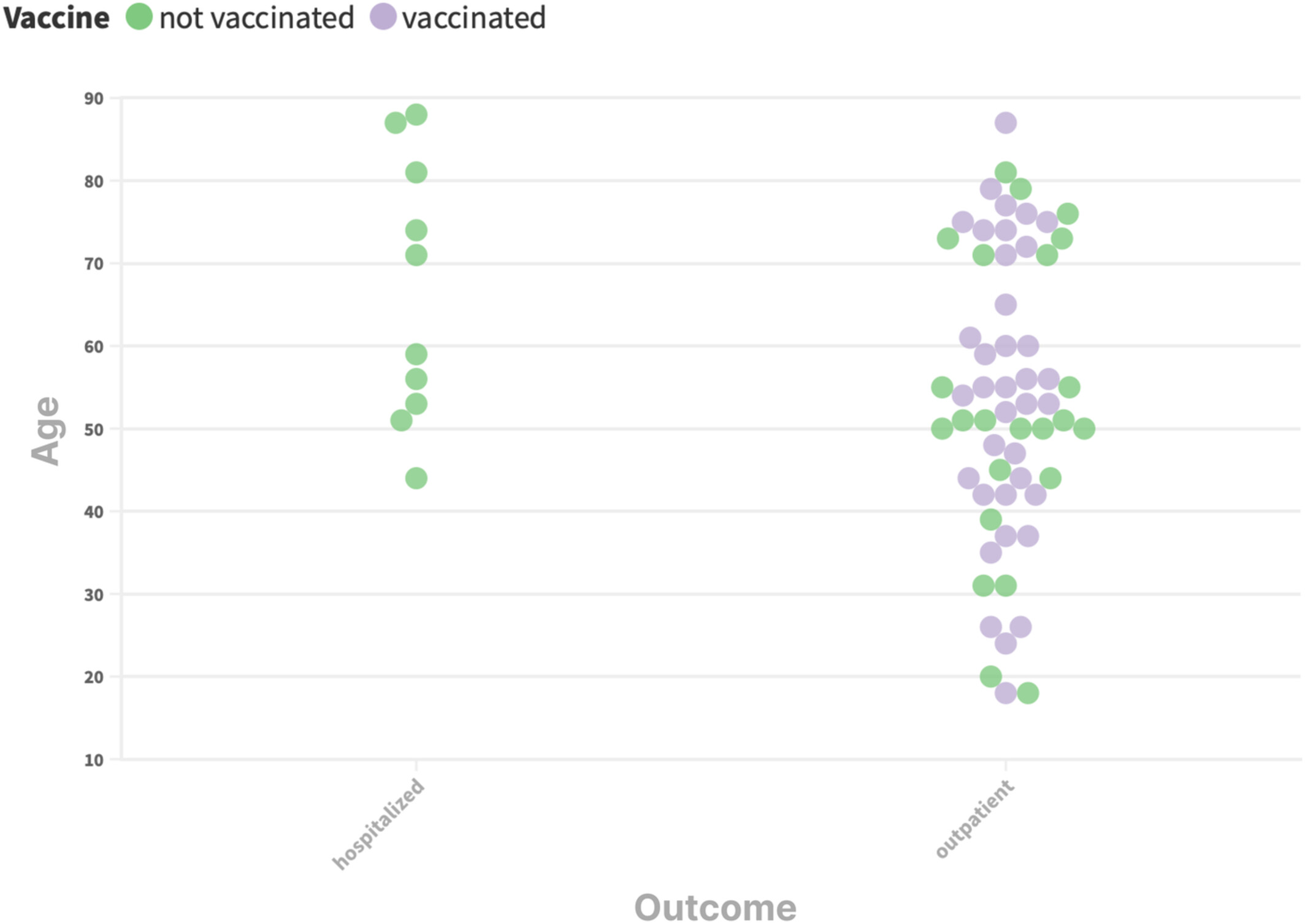
We collected data from 325 consecutive CML patients followed at our institution, of whom 67 tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. We found out that the death rate observed in our serie was not different from that observed in national data. Moreover, the risk of hospitalization was significantly reduced in vaccinated patients or in those taking bosutinib.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Biology
Blue light induces apoptosis and autophagy by promoting ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction in synovial sarcoma
- Pages: 9668-9683
- First Published: 01 February 2023
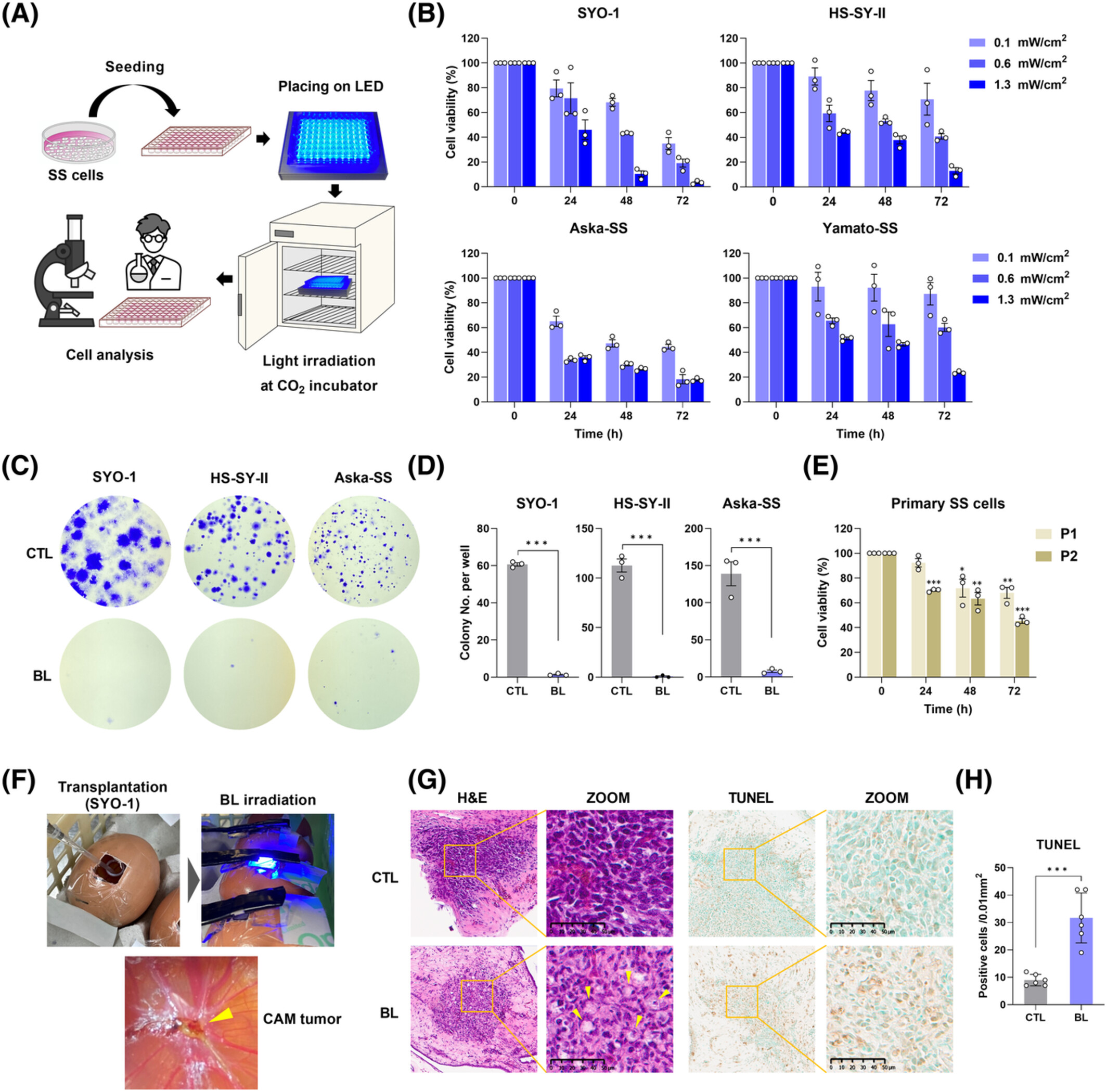
In this study, we investigated the antitumor effect of Blue light (BL) on Synovial sarcoma (SS). Here, we found that BL induced apoptosis via the ROS-mitochondrial signaling pathway, and autophagy was activated in response to the production of ROS, which protected SS cells from apoptosis. Therefore, BL is a promising candidate for the development of an antitumor therapeutic strategy targeting SS.
Dual-targeting therapy against HER3/MET in human colorectal cancers
- Pages: 9684-9696
- First Published: 07 February 2023
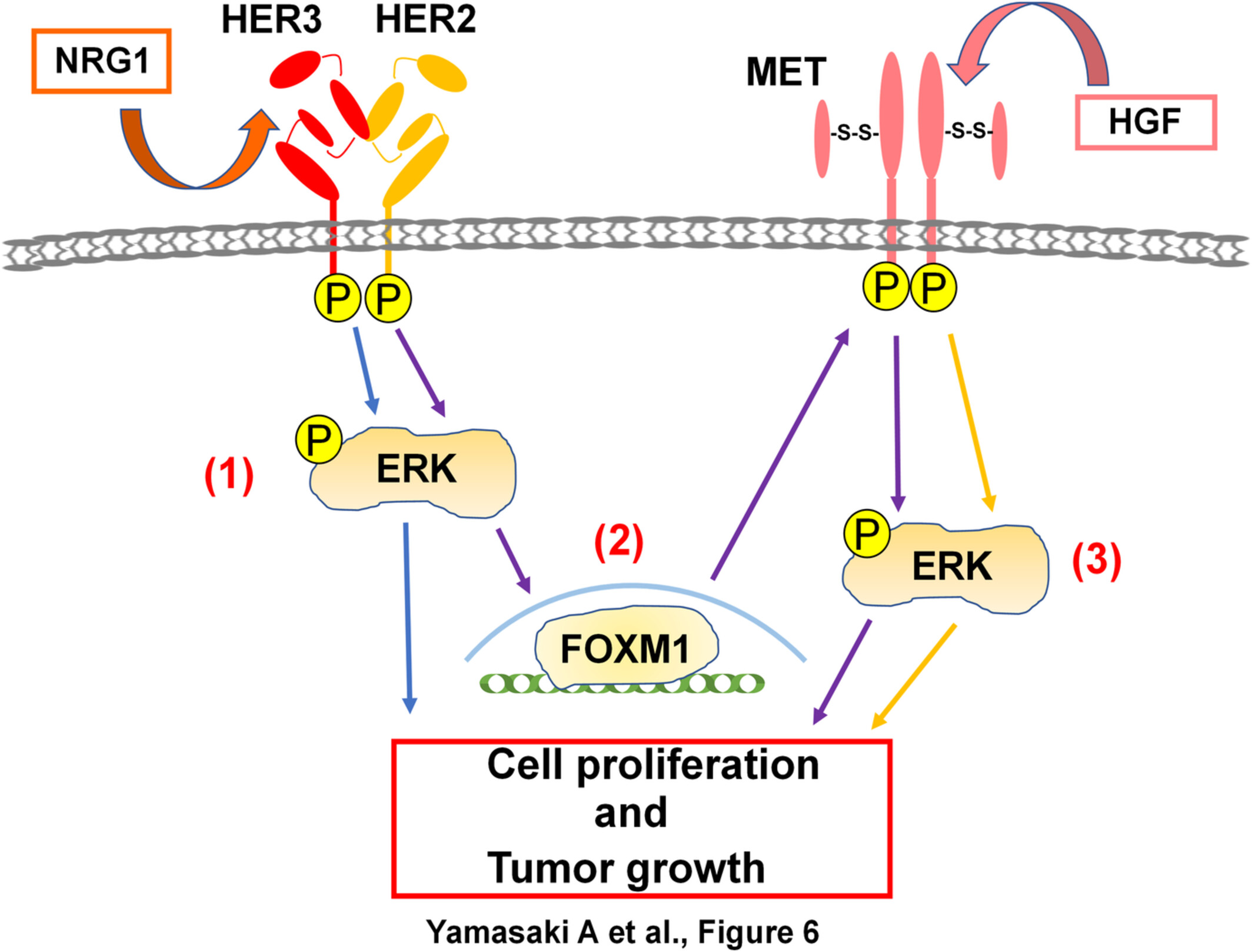
The present study demonstrated that HER3 and MET were not directly associated with each other in CRC but cooperated for the cellular and tumor growth of CRC. In this context, the combination of anti-HER3 (patritumab) and anti-MET (PHA665752) drugs was definitely effective against HER3/MET-high SW1116 CRC cells, indicating the potential of the dual inhibition of HER3 and MET as targeting therapy in human CRC.
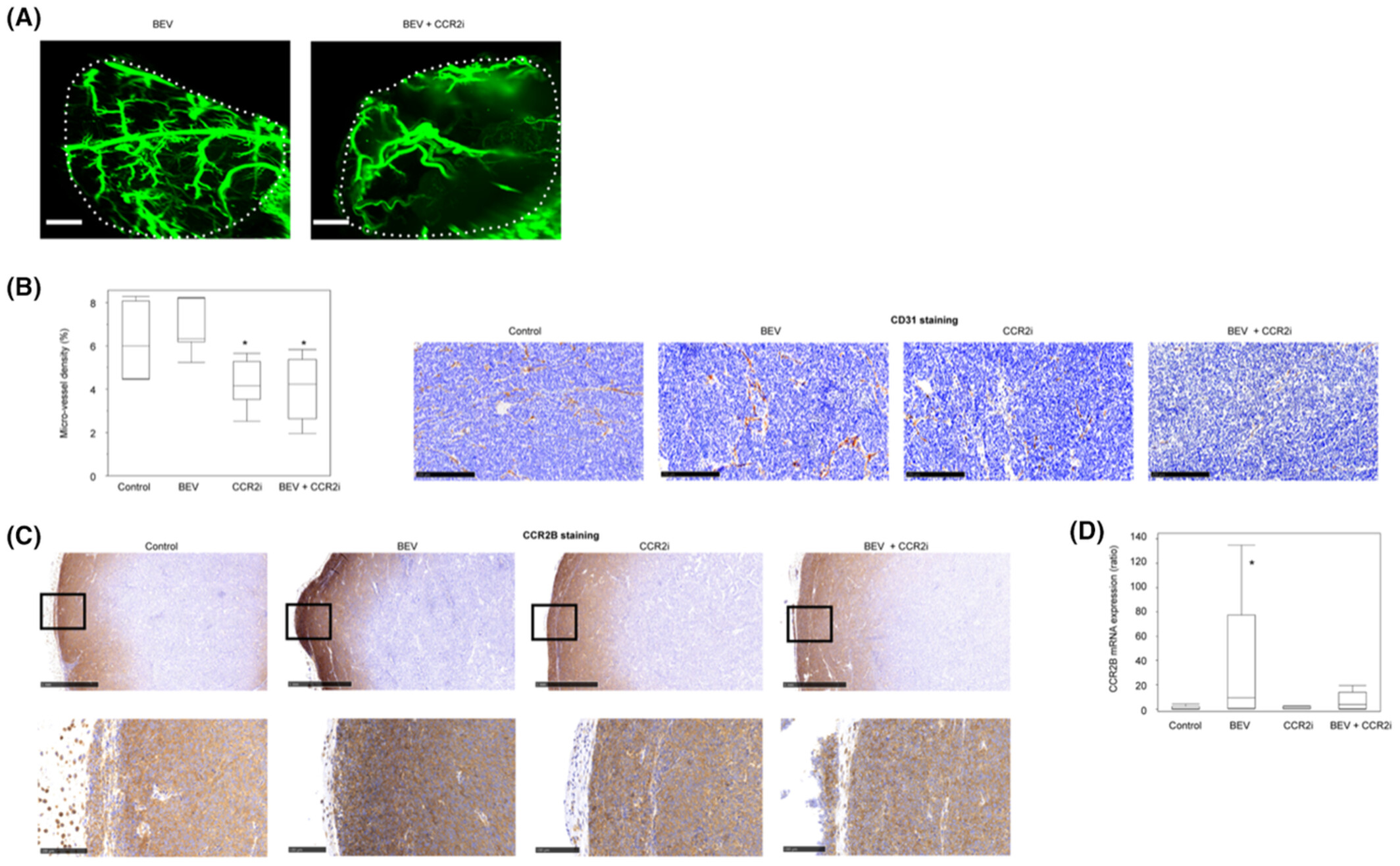
Combination therapy with bevacizumab and a CCR2 inhibitor for human ovarian cancer: An in vivo validation study
- Pages: 9697-9708
- First Published: 22 February 2023
Hypoxia-induced oxidative stress promotes therapy resistance via upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 in multiple myeloma
- Pages: 9709-9722
- First Published: 12 February 2023
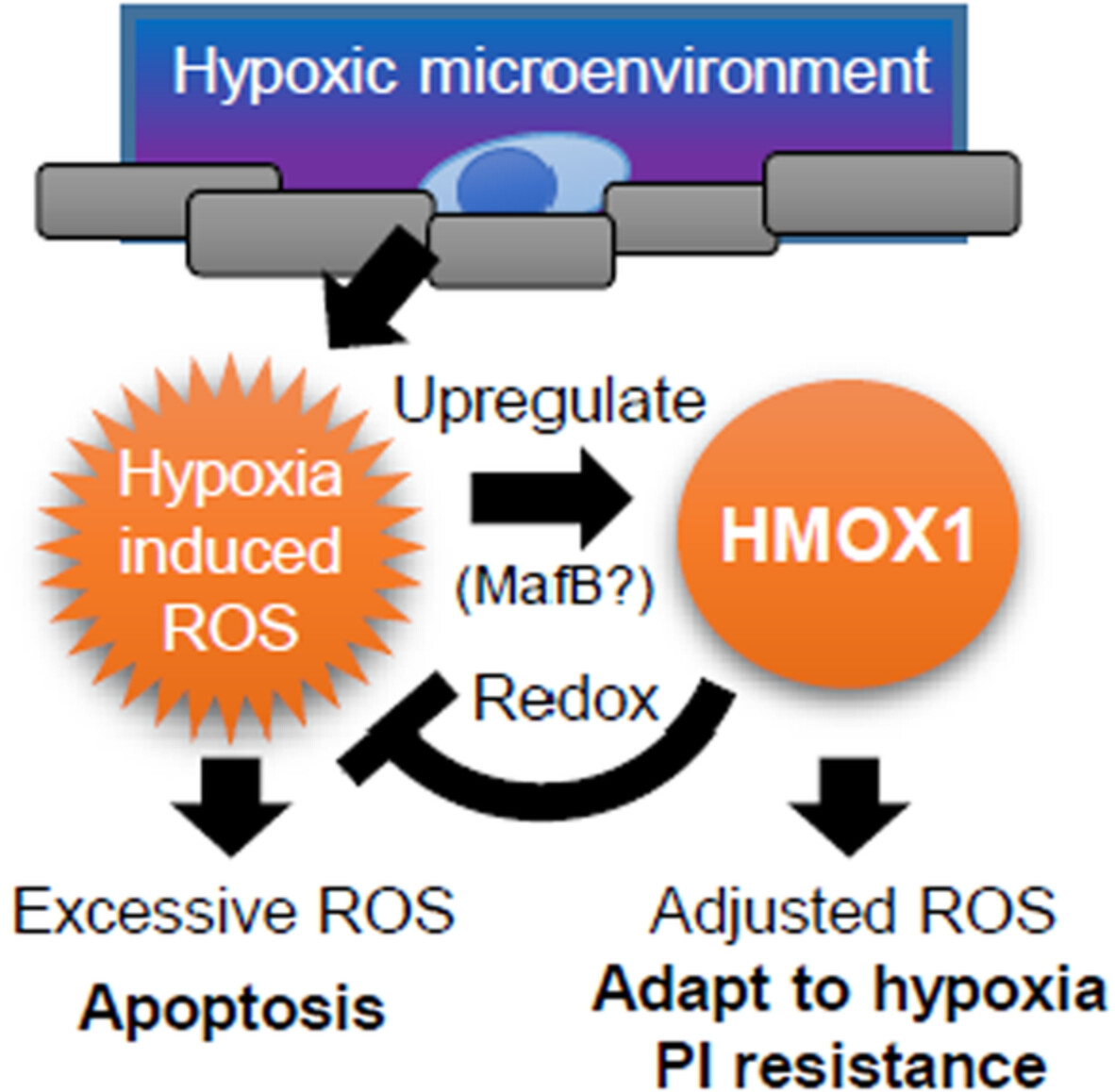
By examining in detail the function of genes that are highly expressed in side population (SP) cells exposed to hypoxia, we clarified the contribution of the hypoxia-ROS-HMOX1 axis to proteasome inhibitor resistance in hypoxic environments. This axis might also be involved in hypoxia-induced MafB expression.
Hypoxia-induced YAP activation and focal adhesion turnover to promote cell migration in mesenchymal TNBC cells
- Pages: 9723-9737
- First Published: 09 February 2023
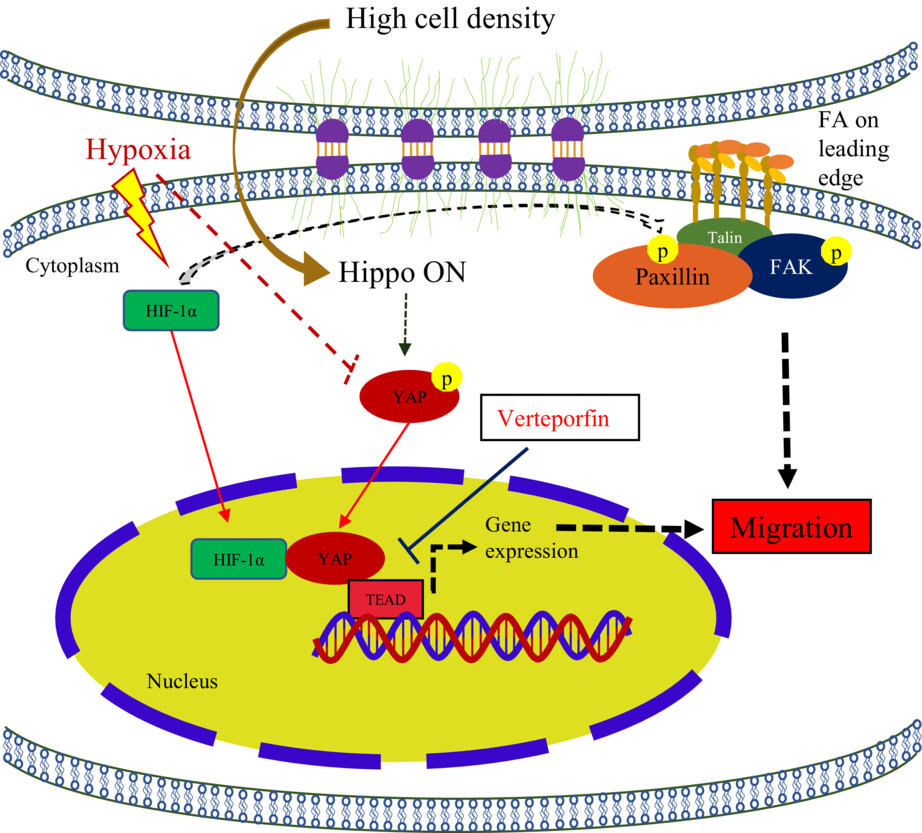
Identifying YAP as a key mediator of hypoxia-induced mesenchymal TNBC cell migration based on the following evidence. (1) Hypoxia triggers YAP nuclear translocation at high cell density in mesenchymal TNBC; (2) Hypoxia only promotes mesenchymal TNBC cell migration, and YAP plays a crucial role in cell migration under hypoxia; and (3) Hypoxia promotes focal adhesions activation to support mesenchymal TNBC cell migration and YAP is also required for focal adhesions activation.
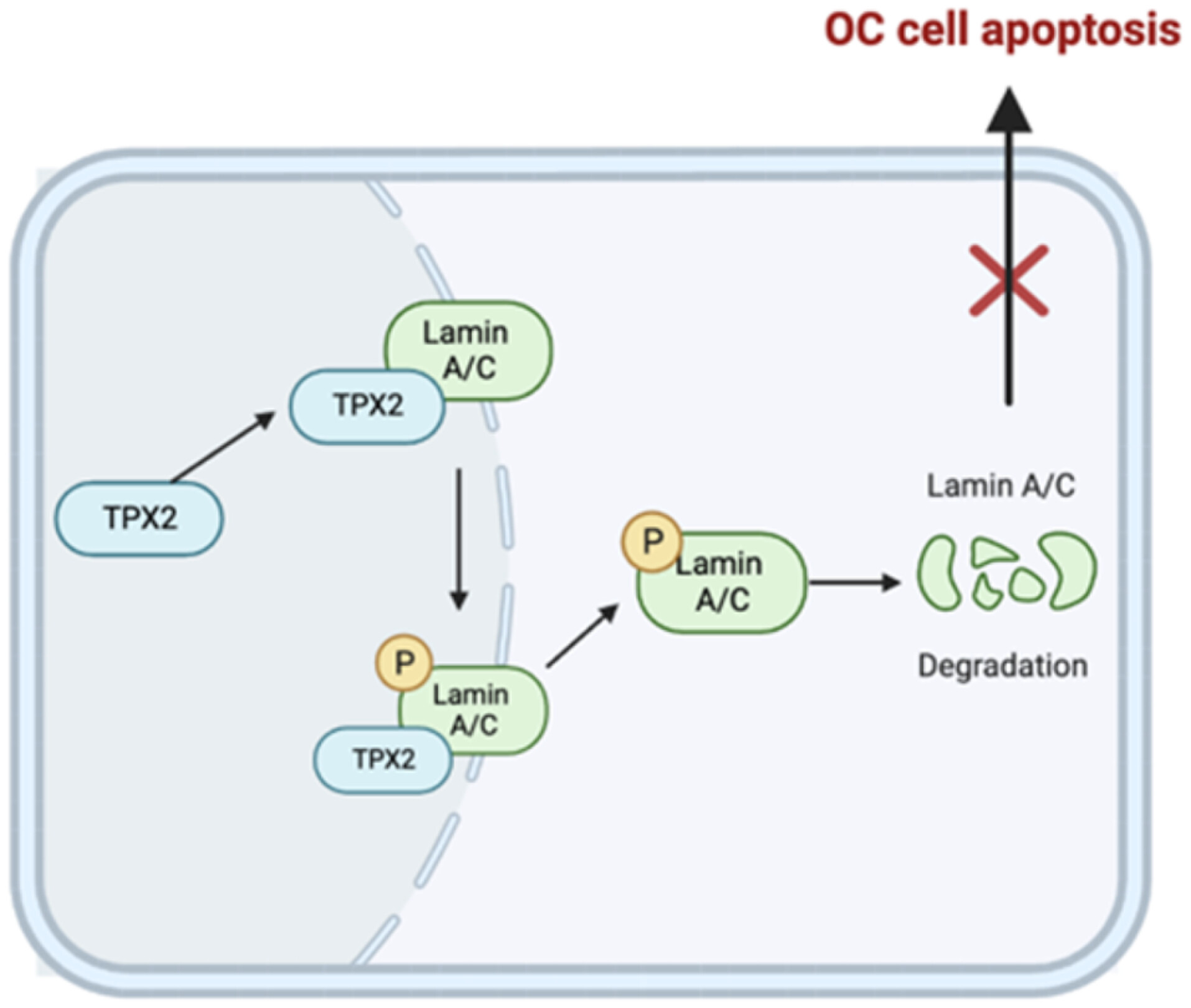
TPX2 promotes ovarian tumorigenesis by interacting with Lamin A/C and affecting its stability
- Pages: 9738-9748
- First Published: 15 February 2023
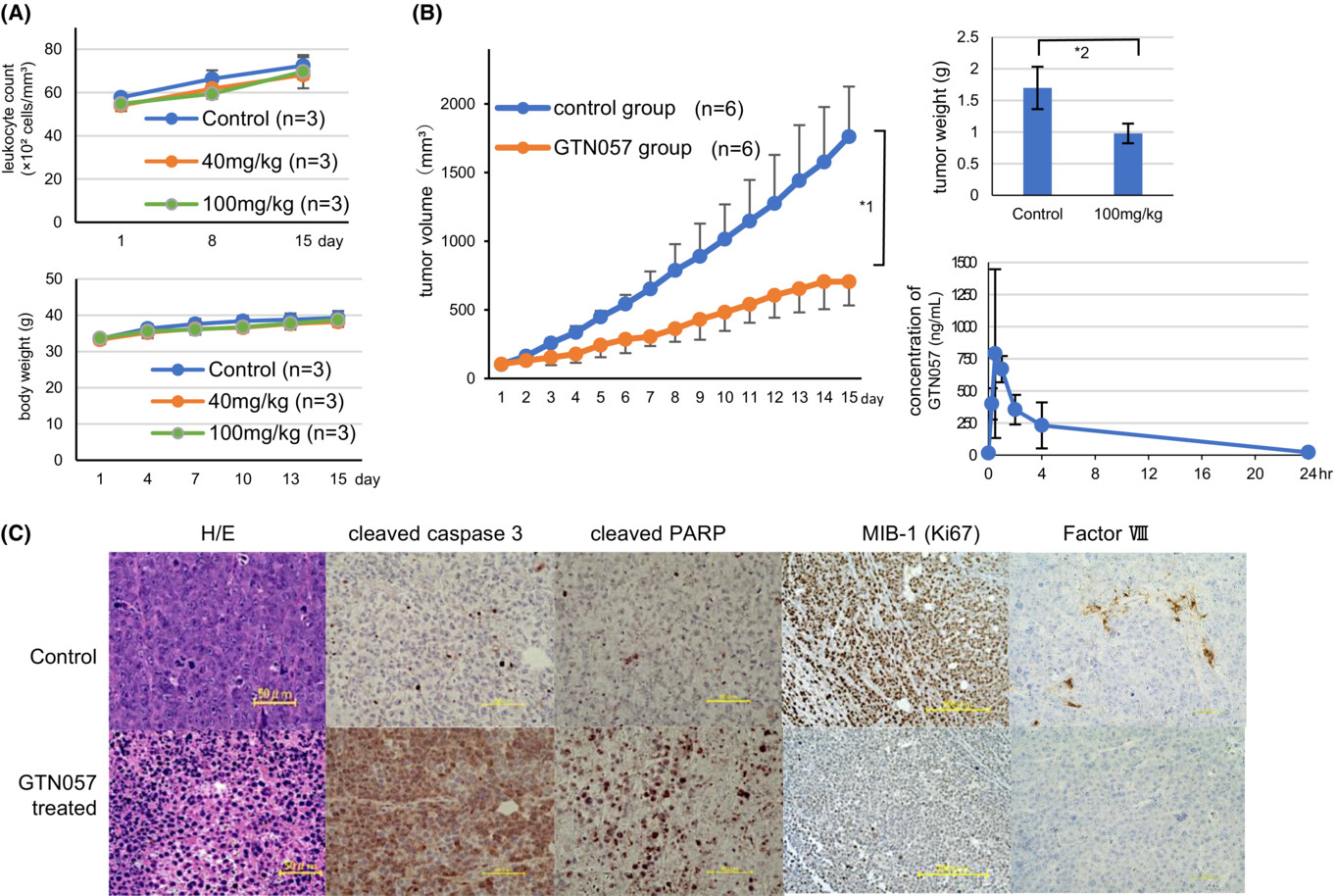
GTN057, a komaroviquinone derivative, induced myeloma cells' death in vivo and inhibited c-MET tyrosine kinase
- Pages: 9749-9759
- First Published: 24 February 2023
Angiogenic inhibitor pre-administration improves the therapeutic effects of immunotherapy
- Pages: 9760-9773
- First Published: 19 February 2023
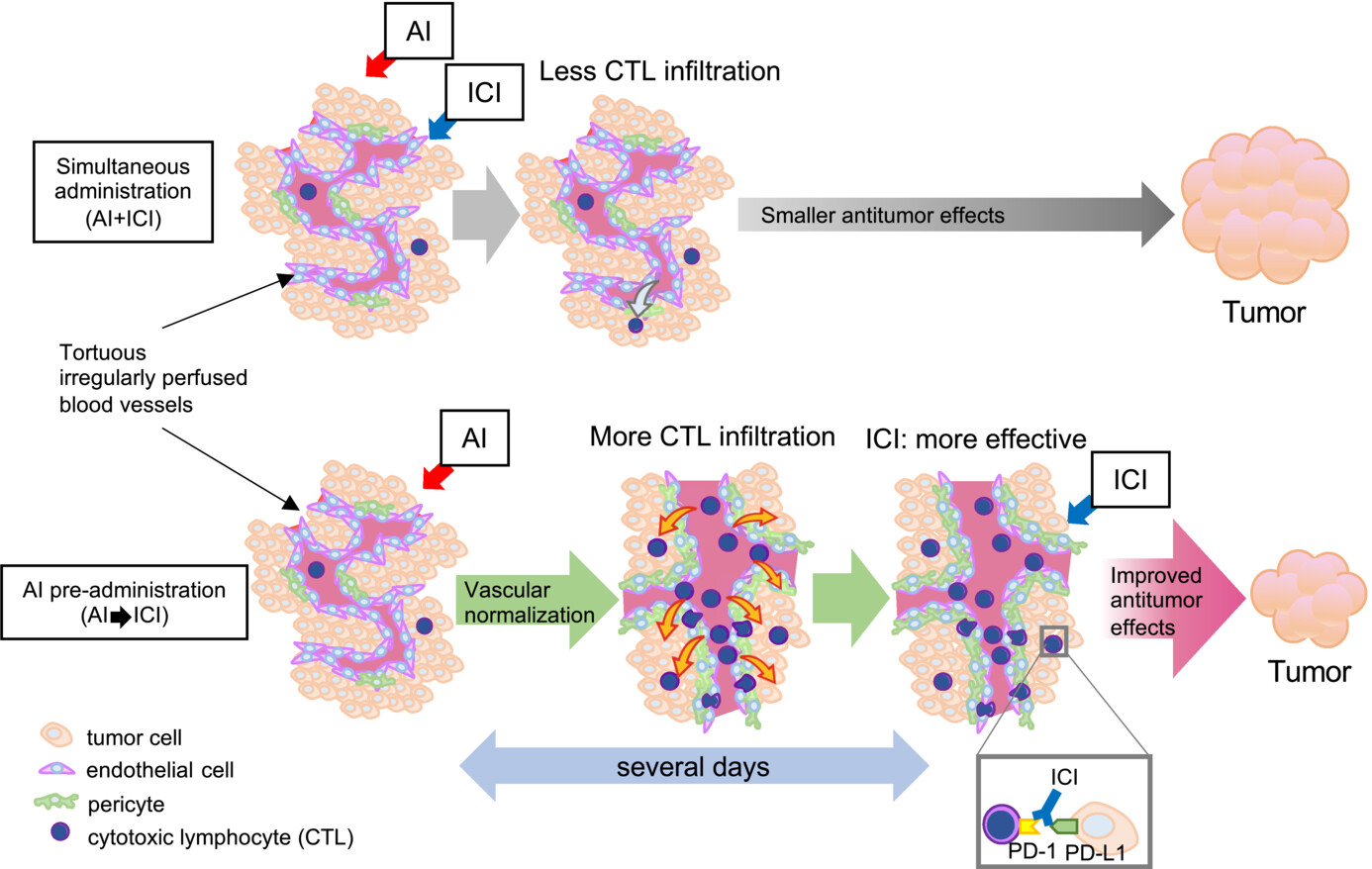
A pre-angiogenesis inhibitor strategy improves immune checkpoint inhibitor effects by improving CD8 infiltration and drug delivery.The current clinical protocol of administering AI and ICI on the same day results in ICI acting when vascular normalization is insufficient to mobilize CTL in the tumor tissue. In contrast, the anti-tumor effect is enhanced when AI is administered several days before ICI, as ICI is given after vascular normalization and the number of immune cells infiltrating into the tissue has increased.
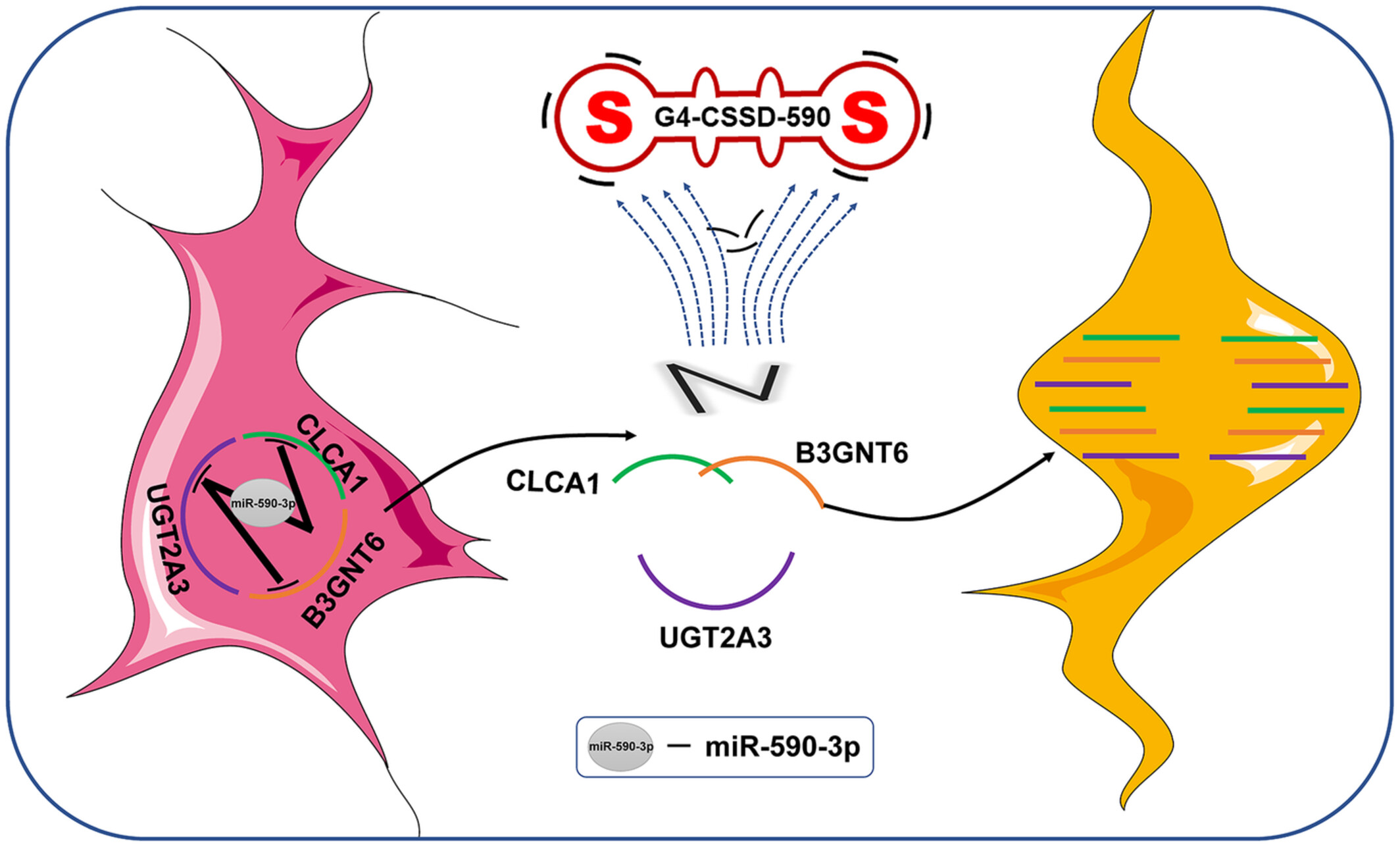
G-quadruplex-enhanced circular single-stranded DNA (G4-CSSD) adsorption of miRNA to inhibit colon cancer progression
- Pages: 9774-9787
- First Published: 28 February 2023
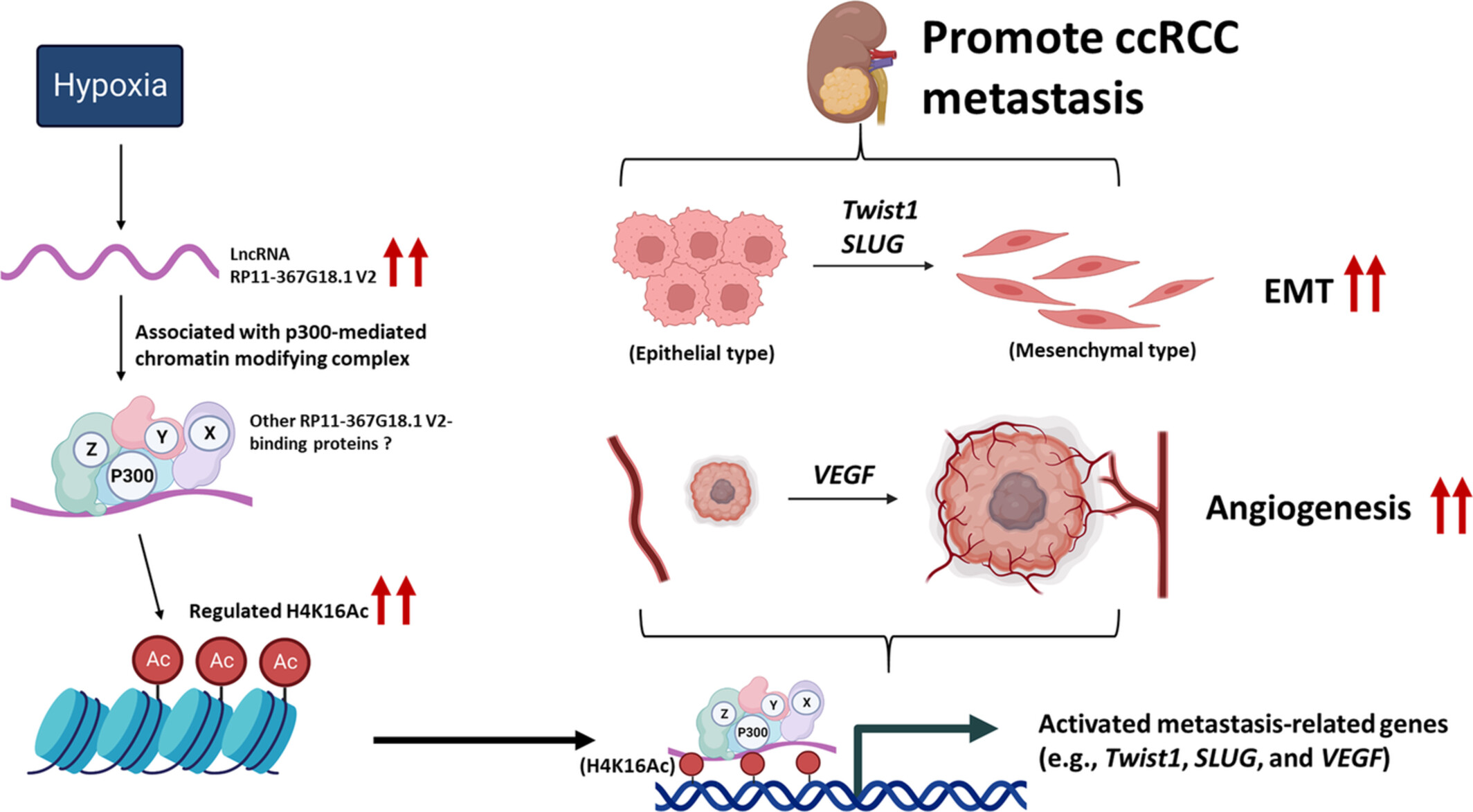
RP11-367G18.1 V2 enhances clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression via induction of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Pages: 9788-9801
- First Published: 27 February 2023
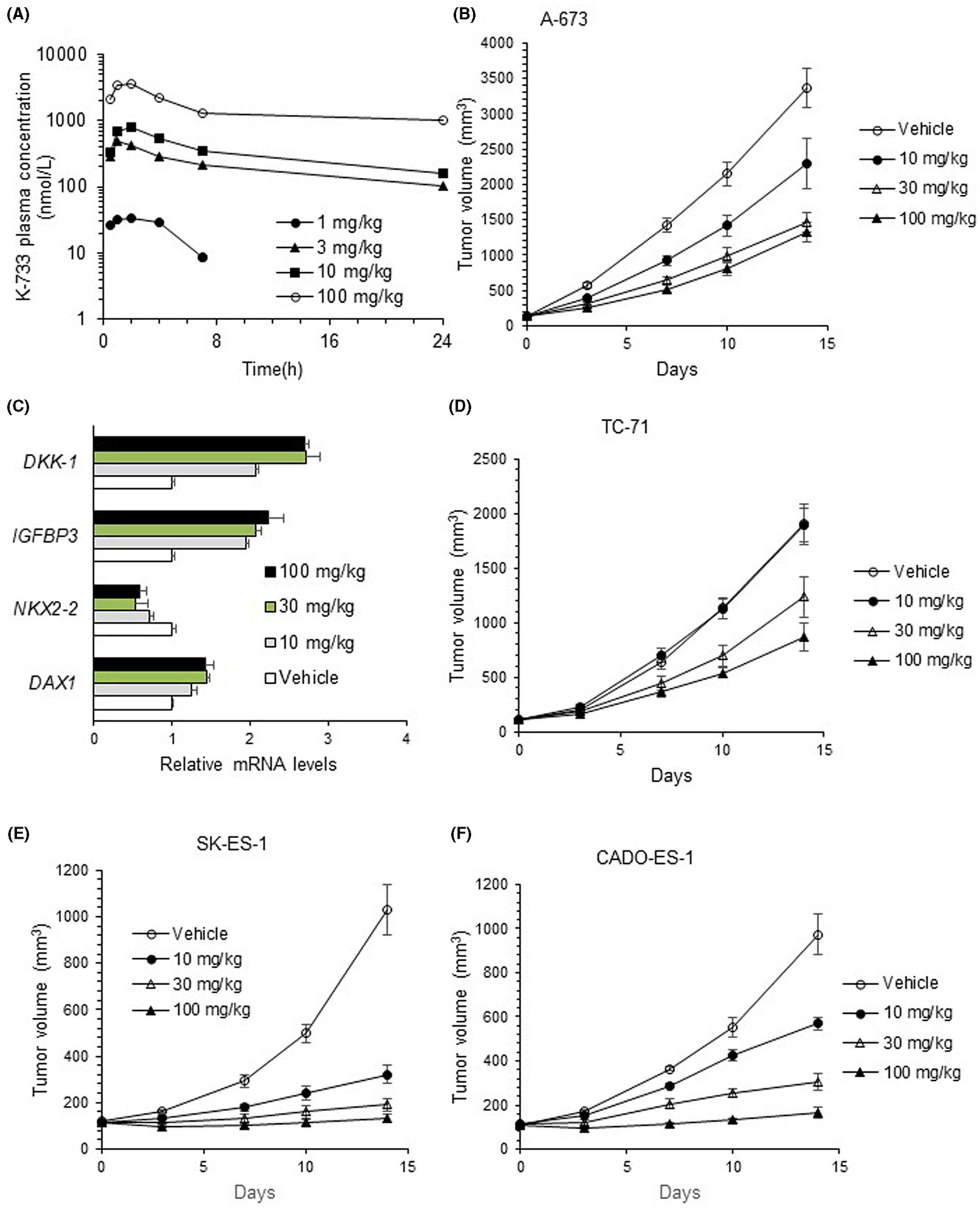
Screening for DAX1/EWS-FLI1 functional inhibitors identified dihydroorotate dehydrogenase as a therapeutic target for Ewing's sarcoma
- Pages: 9802-9814
- First Published: 24 February 2023
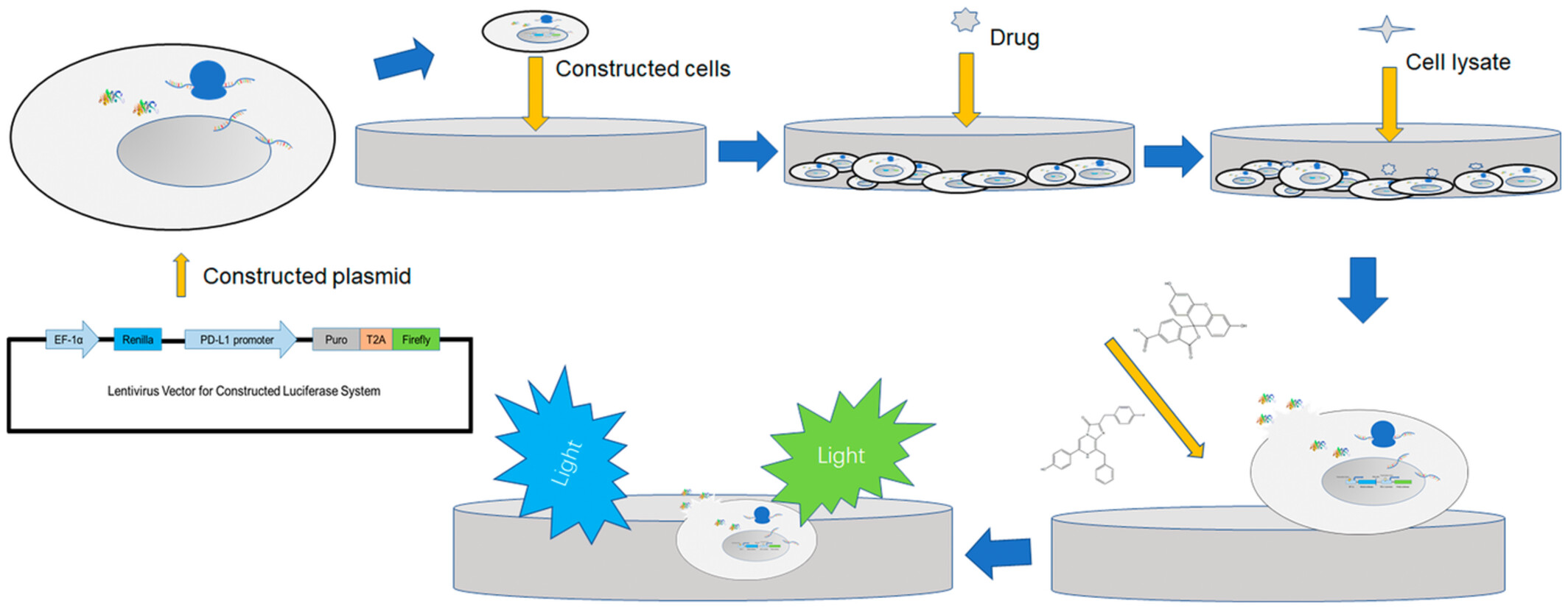
The screening of compounds regulating PD-L1 transcriptional activity in a cell functional high-throughput manner
- Pages: 9815-9825
- First Published: 25 March 2023
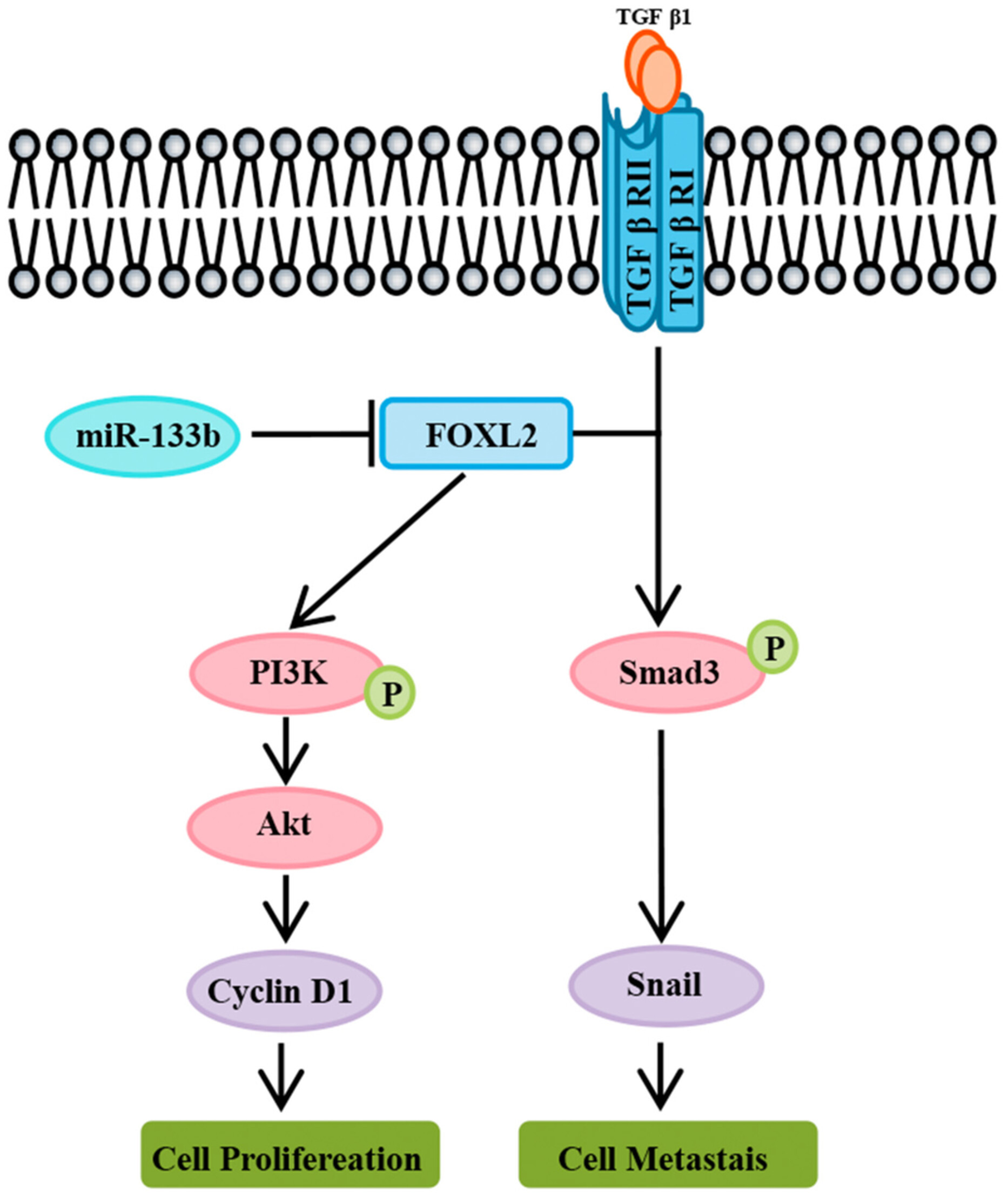
Forkhead box L2 is a target of miR-133b and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 9826-9842
- First Published: 27 February 2023
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Cancer Biology
AIRE illuminates the feature of medullary thymic epithelial cells in thymic carcinoma
- Pages: 9843-9848
- First Published: 13 March 2023
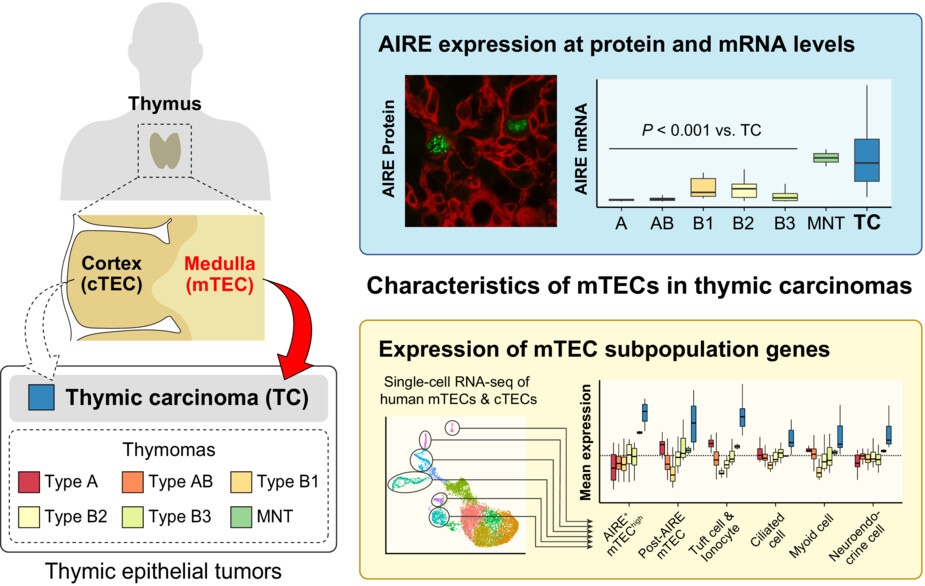
Thymic epithelial tumors originating from thymic epithelial cells (TECs) are classified into six types of thymomas (Type A, AB, B1-B3 thymomas, and micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma [MNT]) and thymic carcinoma (TC). Despite the clear distinction between cortical (cTECs) and medullary TECs (mTECs) in physiology, the cell of origin of each TET has remained enigmatic. In the current study, we confirmed the expression of AIRE, an mTEC-specific transcriptional regulator, in most TCs at both protein and mRNA levels. Furthermore, our bioinformatics approach has revealed that TCs hold molecular characteristics of multiple mTEC subpopulations, suggesting their cell of origin as mTECs.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Prevention
Developing a comorbidity score in cancer patients using healthcare utilization databases during the COVID-19 pandemic: An experience from Italy
- Pages: 9849-9856
- First Published: 20 December 2022
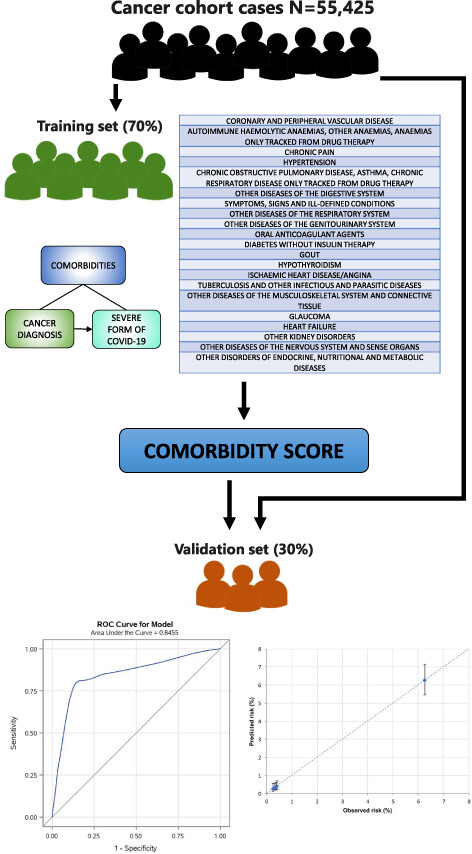
Developement and validation of a COVID-19 comordity score for cancer patients. The total cancer patient cohort was split into training (70%) and validation (30%) sets. In the training set, comorbidities associated with the risk of developing a severe/fatal form of COVID-19 were identified and the score weights were estimated. The score performances were then assesed in the validation set, by areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and calibration plots.
Role, race, and place: Prostate cancer disparities in Patients' and Partners' health outcomes and psychosocial factors
- Pages: 9857-9867
- First Published: 07 February 2023
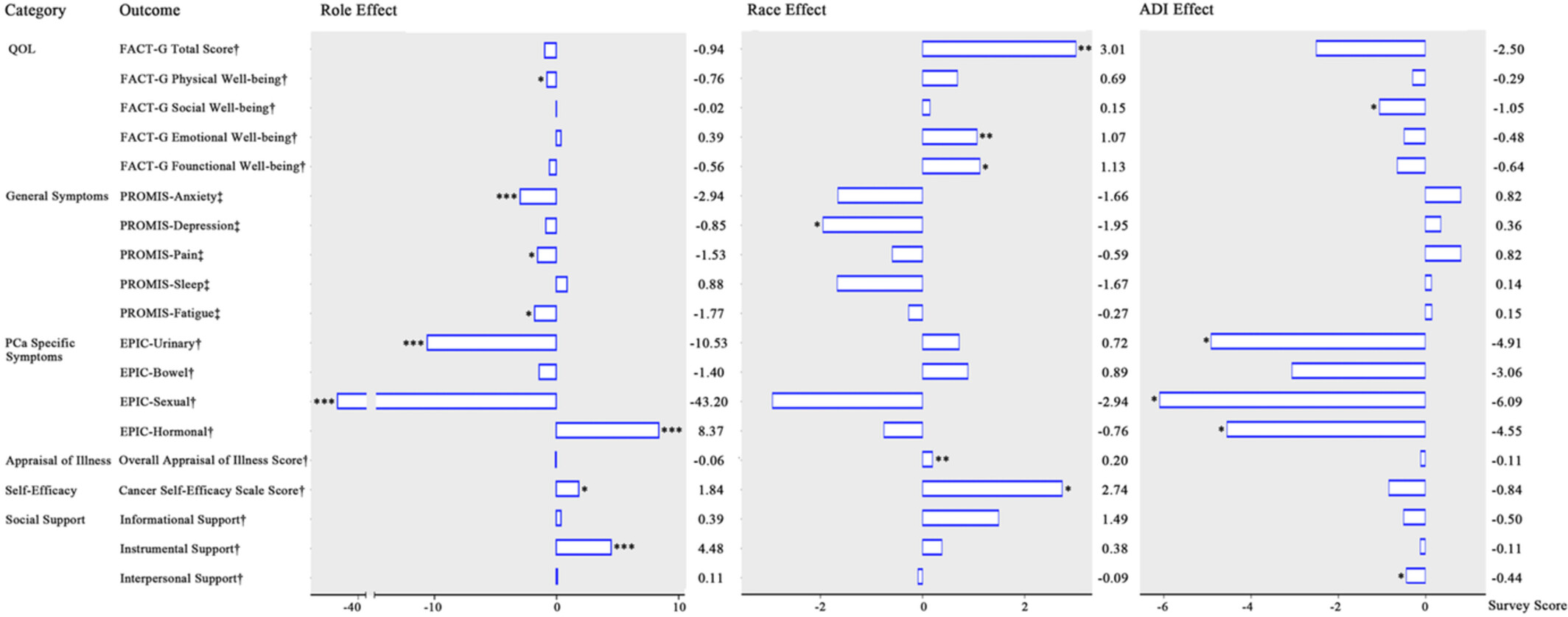
This study used a multilevel approach to examine the effects of role, race, and ADI on health outcomes and psychosocial factors among patients with PCa and their partners, controlling for various demographic and cancer-related covariates. Our work contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of PCa disparities than previous research focusing on individual- and/or family-level factors (e.g., race and role). In addition to personal- and family-focused strategies, supportive care programs should be tailored at multiple levels and provide adequate support to address neighborhood resource disparities, and ultimately, to reduce PCa disparities for patients and their partners and improve their health outcomes.
Socioeconomic determinants are associated with the utilization and outcomes of active surveillance or watchful waiting in favorable-risk prostate cancer
- Pages: 9868-9878
- First Published: 02 February 2023

In this population-based, cross-sectional study, the utilization rates of conservative management were significantly higher in low socioeconomic status (SES), unmarried and urban patients diagnosed with low-risk prostate cancer. Unmarried status and low SES were associated with worse overall survival among patients undertaking active surveillance/watchful waiting. The utilization of conservative management was affected by socioeconomic factors, which might serve as a barrier of treatment decision-making and targeted a population in need of social support.
Awareness of ovarian cancer symptoms and risk factors in a young ethnically diverse British population
- Pages: 9879-9892
- First Published: 07 February 2023
Awareness of ovarian cancer symptoms is low. Participants incorrectly associate ovarian cancer as a disease of pre-menopausal women as well as confusing it with cervical cancer. Ovarian cancer awareness campaigns should include common misconceptions identified in this research.
Do young adults with cancer receive information about treatment-related impact on sex life? Results from a population-based study
- Pages: 9893-9901
- First Published: 07 February 2023
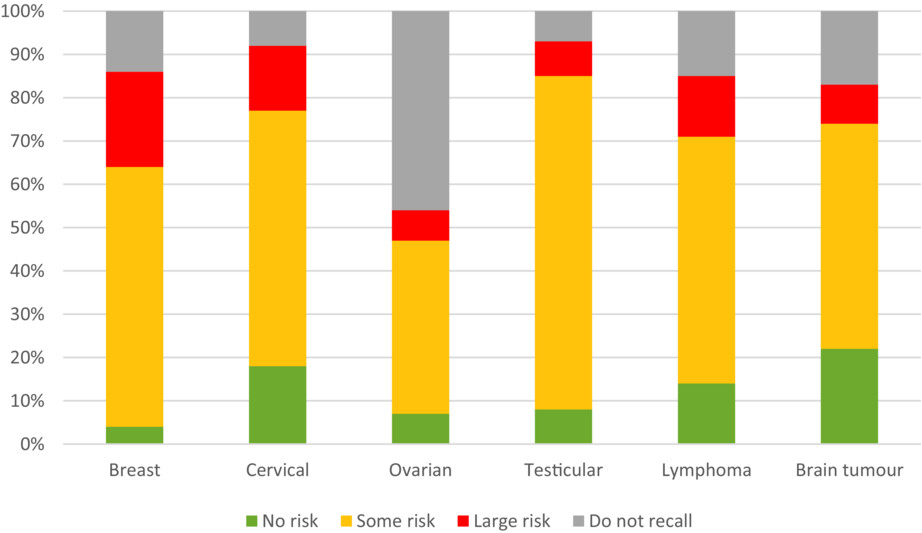
Young women with cancer report having received information about potential treatment-related impact on sex life to a lesser extent than men, and there is also a variation across cancer types. The majority of recipents recalled being informed that there was "some risk" of sex life being affected, see figure below. Routines clarifying when to discuss these issues are recommended to improve sexual health communication with young patients in cancer care.
Trends in oncological imaging during the COVID-19 pandemic through the vaccination era
- Pages: 9902-9911
- First Published: 12 February 2023
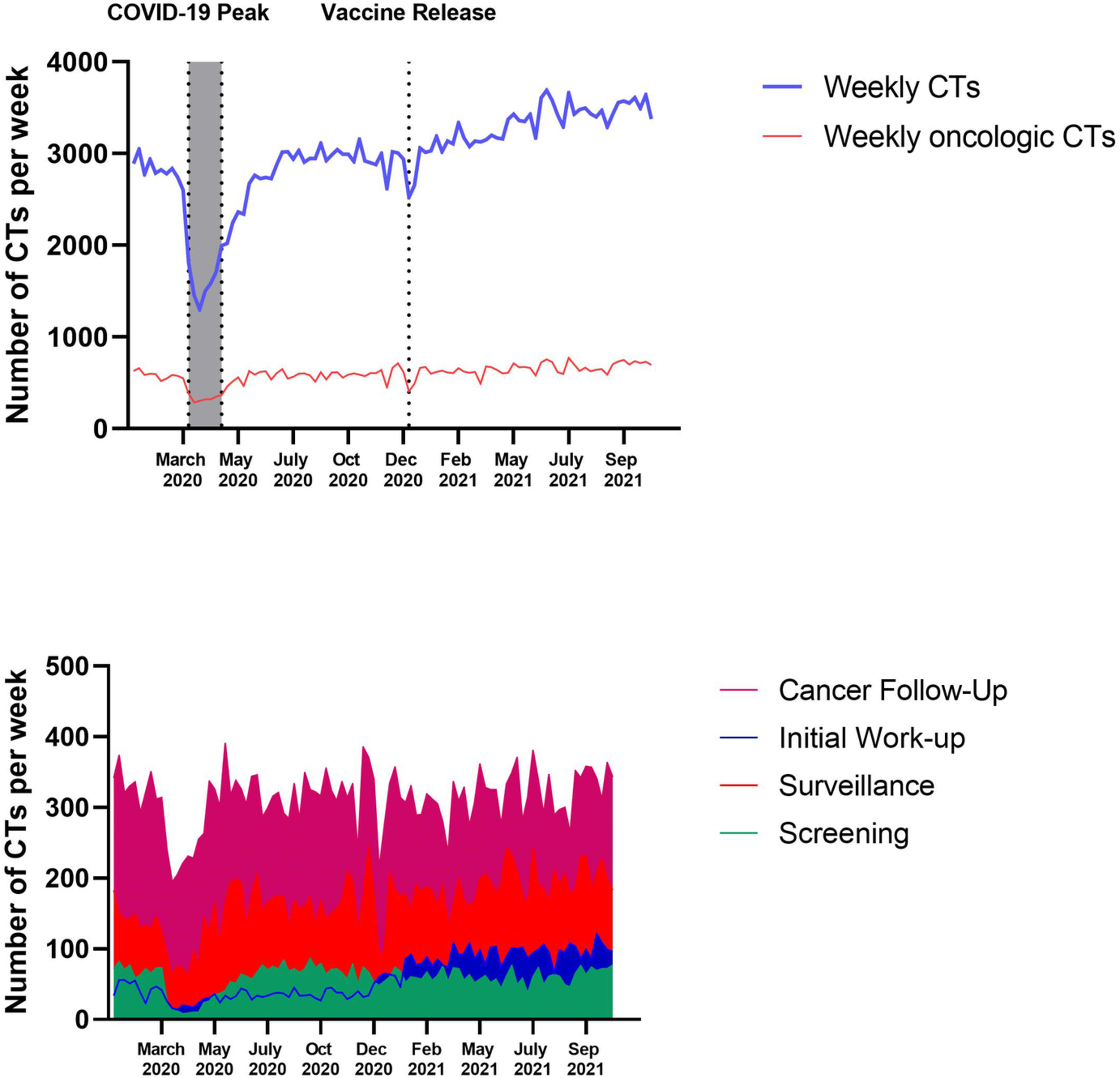
The pandemic continues to impact cancer care. We observe significant declines in cancer screening CTs through the end of 2021. Concurrently, we observe a 2x increase in initial cancer workup CTs and a 2.4x increase in active cancer CTs in the ED during a time period following the introduction of vaccinations (20th December 2020-30th October 2021), suggesting a boom of new cancers and more cancer exams associated with emergency level acute care.
Trends in gastric cancer mortality 1990–2019 in 36 countries worldwide, with predictions to 2025, and incidence, overall and by subtype
- Pages: 9912-9925
- First Published: 23 February 2023
Pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma: A population level analysis of epidemiological trends and prognosis
- Pages: 9926-9936
- First Published: 27 February 2023

The incidence and IB mortality of PASC have been steadily increasing in recent years, manifesting that the preventive and treatment measures of PASC are not ideal. Therefore, we must identify the significance of this condition as soon as possible and commit greater attention and resources to it. This can help us further understand PASC and develop more targeted and standardized preventive and therapeutic measures.
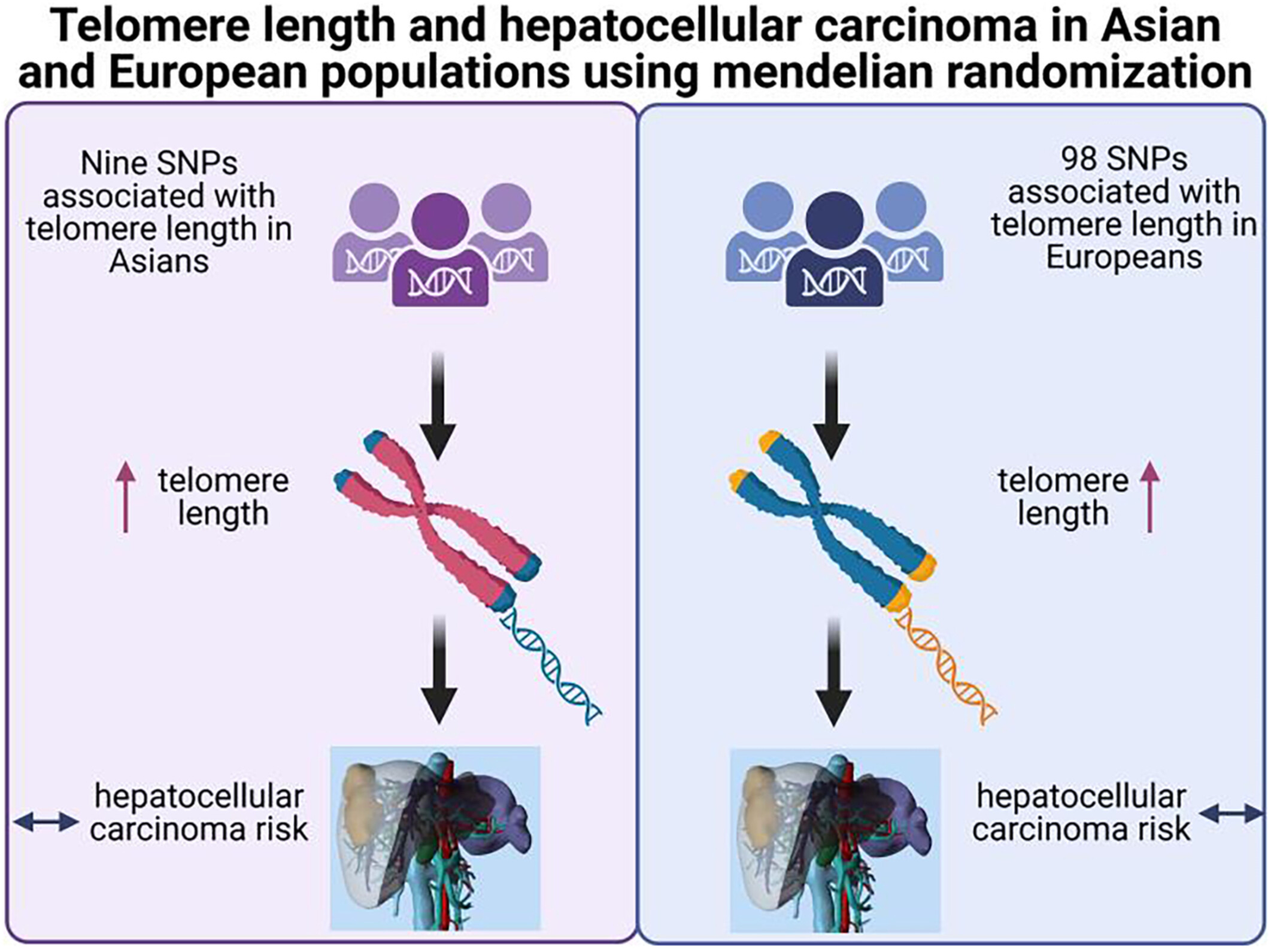
Association between telomere length and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A Mendelian randomization study
- Pages: 9937-9944
- First Published: 07 March 2023
Psychosocial factors impacting barriers and motivators to cancer genetic testing
- Pages: 9945-9955
- First Published: 19 February 2023
Many factors influence an individual's barriers and motivators to getting cancer genetic testing including age, sex, having children, time since cancer diagnosis, cancer type, and mental health. Depression showed the largest impact: those with higher depression scores were significantly more likely to endorse more barriers to testing.
A prospective study of psychological distress among patients with advanced cancer and their caregivers
- Pages: 9956-9965
- First Published: 19 March 2023
Understanding hope at diagnosis: A study among Guatemalan parents of children with cancer
- Pages: 9966-9975
- First Published: 27 February 2023
Race and socioeconomic status interact with HPV to influence survival disparities in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 9976-9987
- First Published: 27 February 2023
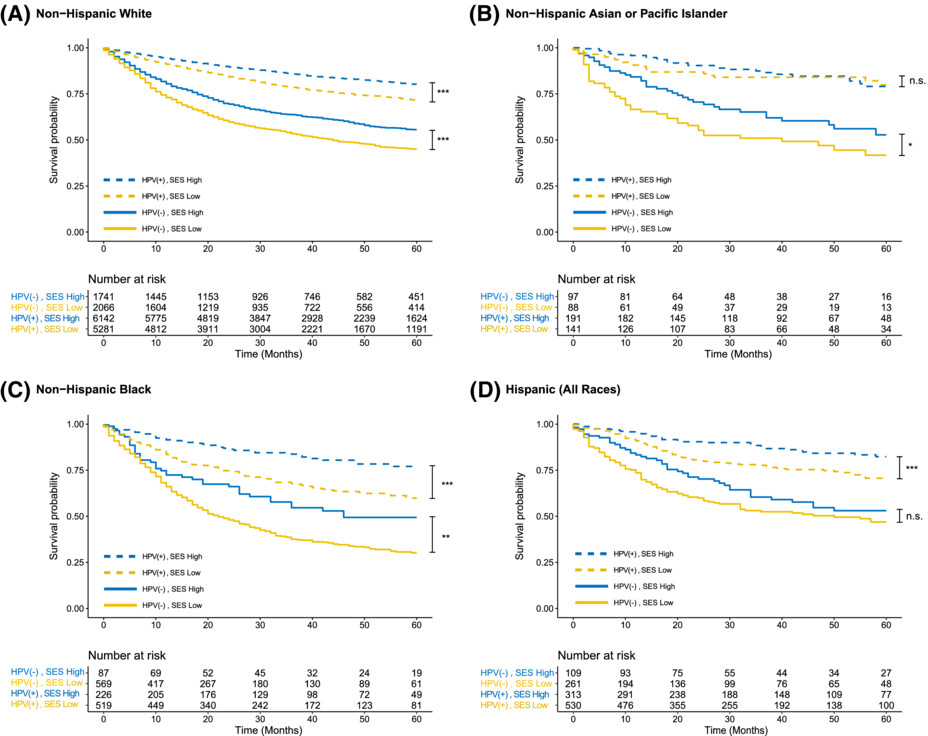
The epidemic of HPV-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) has remarkably changed the landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with the potential to improve outcomes and decrease treatment morbidity uniformly across demographic groups. This study evaluated the combined influence of race and socioeconomic status (SES) on OPSCC survival stratified by HPV status. Survival disparities between patients of high and low SES census tracts and Black and White race remained despite the increase in HPV-related disease. Black patients with OPSCC had lower survival than patients of other races regardless of HPV status. High SES was protective of the adverse effects of race, although there remains a disparity in outcomes among Black and non-Black patients, even in high SES populations.
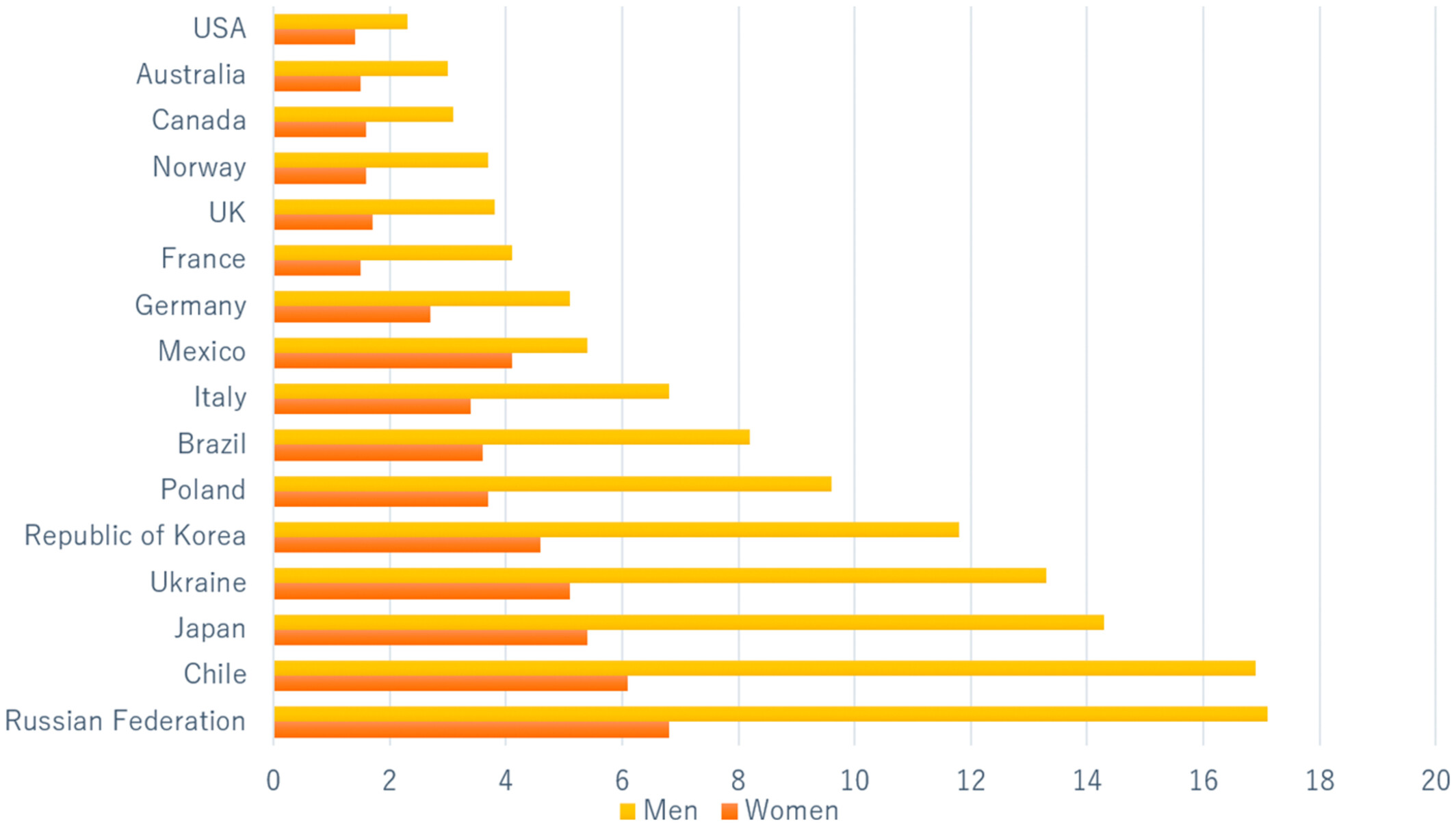
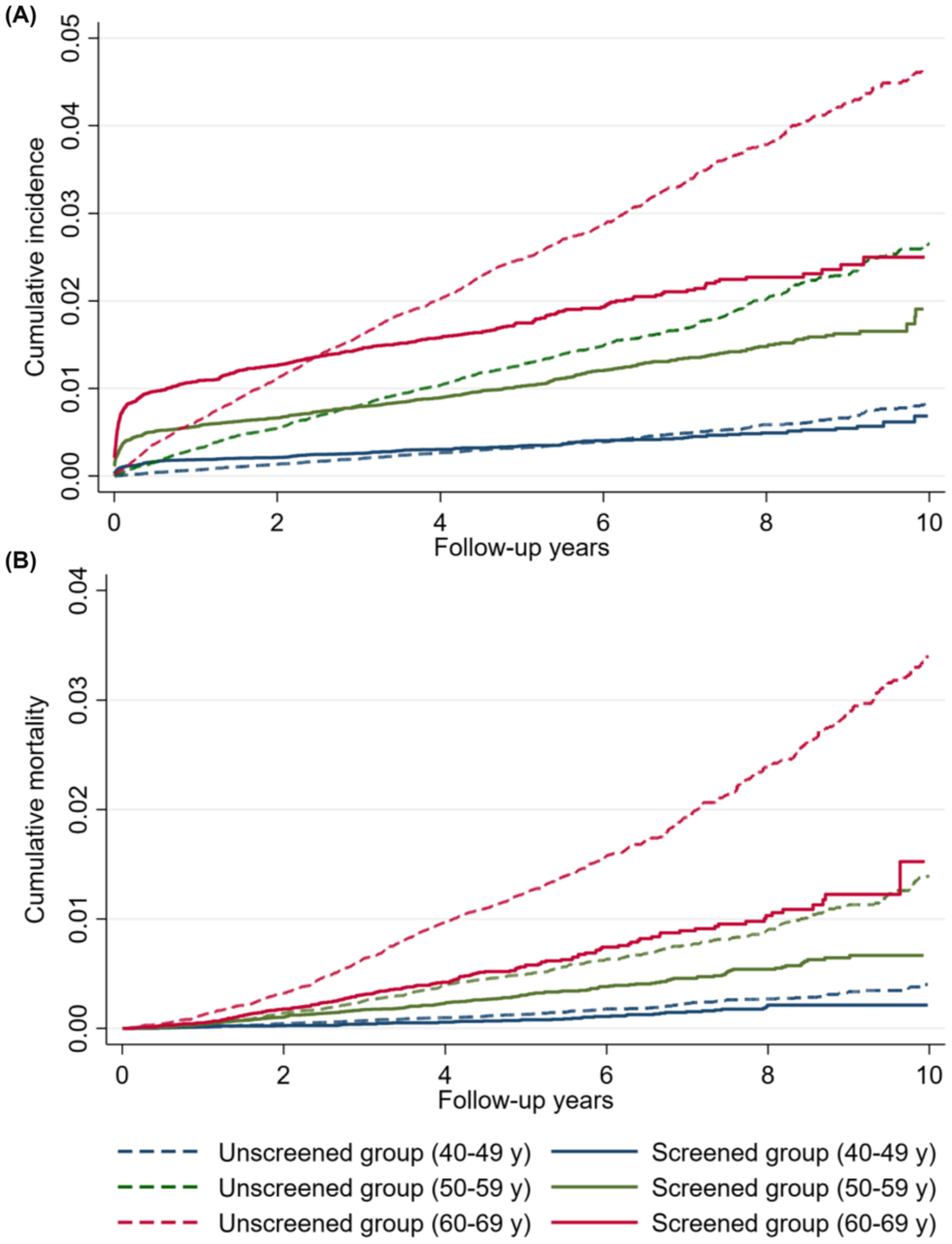
Optimal starting age of endoscopic screening for esophageal cancer in China: A multicenter prospective cohort study
- Pages: 9988-9998
- First Published: 07 April 2023
Investigating the efficiency of lung multi-disciplinary team meetings—A mixed methods study of eight lung multi-disciplinary teams
- Pages: 9999-10007
- First Published: 19 March 2023
There is considerable variation in MDTM structures and processes, influenced by organisational contextual factors. Inefficient referral and diagnostic pathways were highlighted, causing repeat discussions. Developing the diagnostic workforce and facilities to support implementation of diagnostic pathways will improve efficiency.
Association between rapid renal function deterioration and cancer mortality in the elderly: A retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 10008-10019
- First Published: 07 March 2023
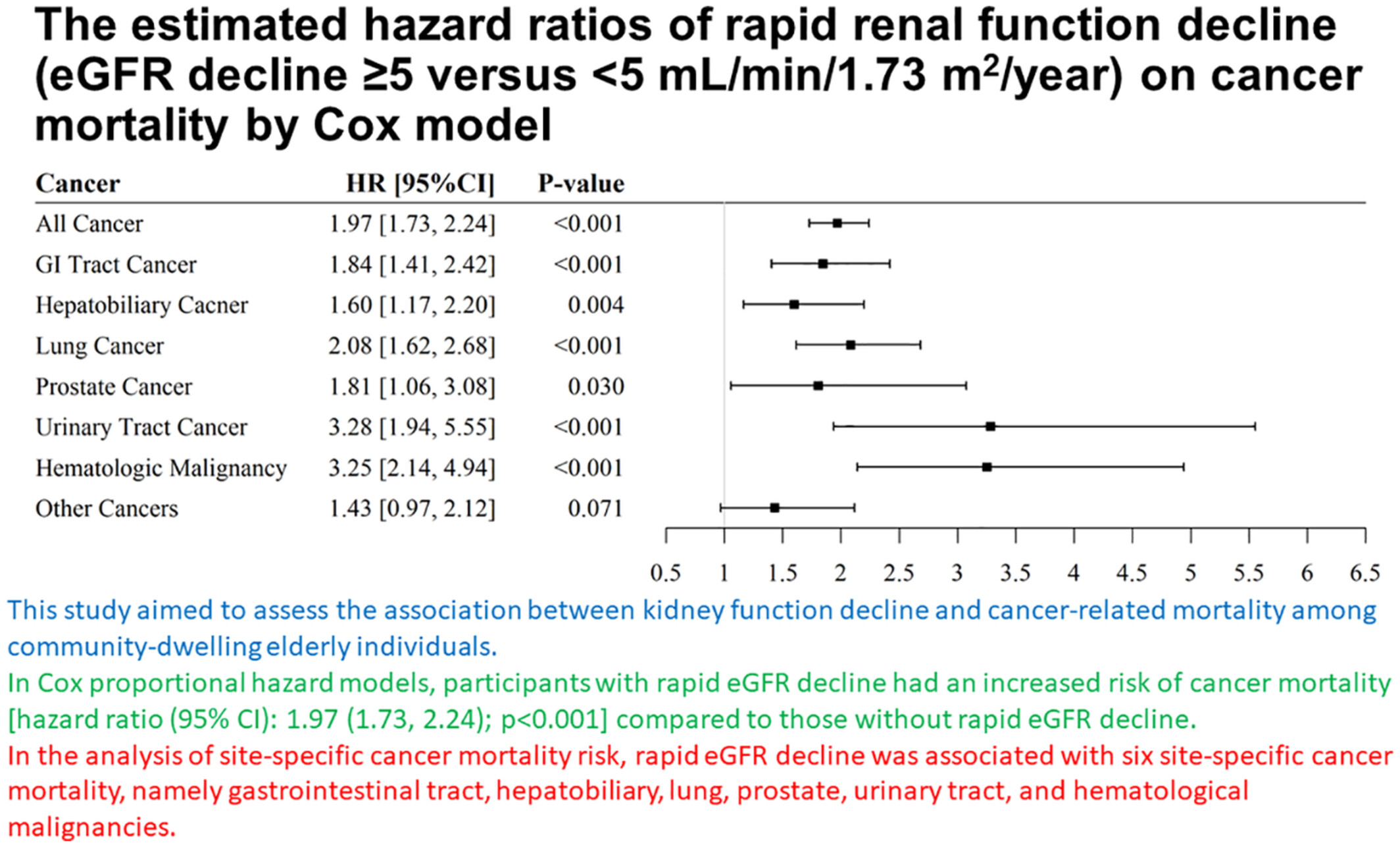
This study aimed to assess the association between kidney function decline and cancer-related mortality among community-dwelling elderly individuals. In Cox proportional hazard models, participants with rapid eGFR decline had an increased risk of cancer mortality compared to those without rapid eGFR decline. In the analysis of site-specific cancer mortality risk, rapid eGFR decline was associated with six site-specific cancer mortality, namely gastrointestinal tract, hepatobiliary, lung, prostate, urinary tract, and hematological malignancies.
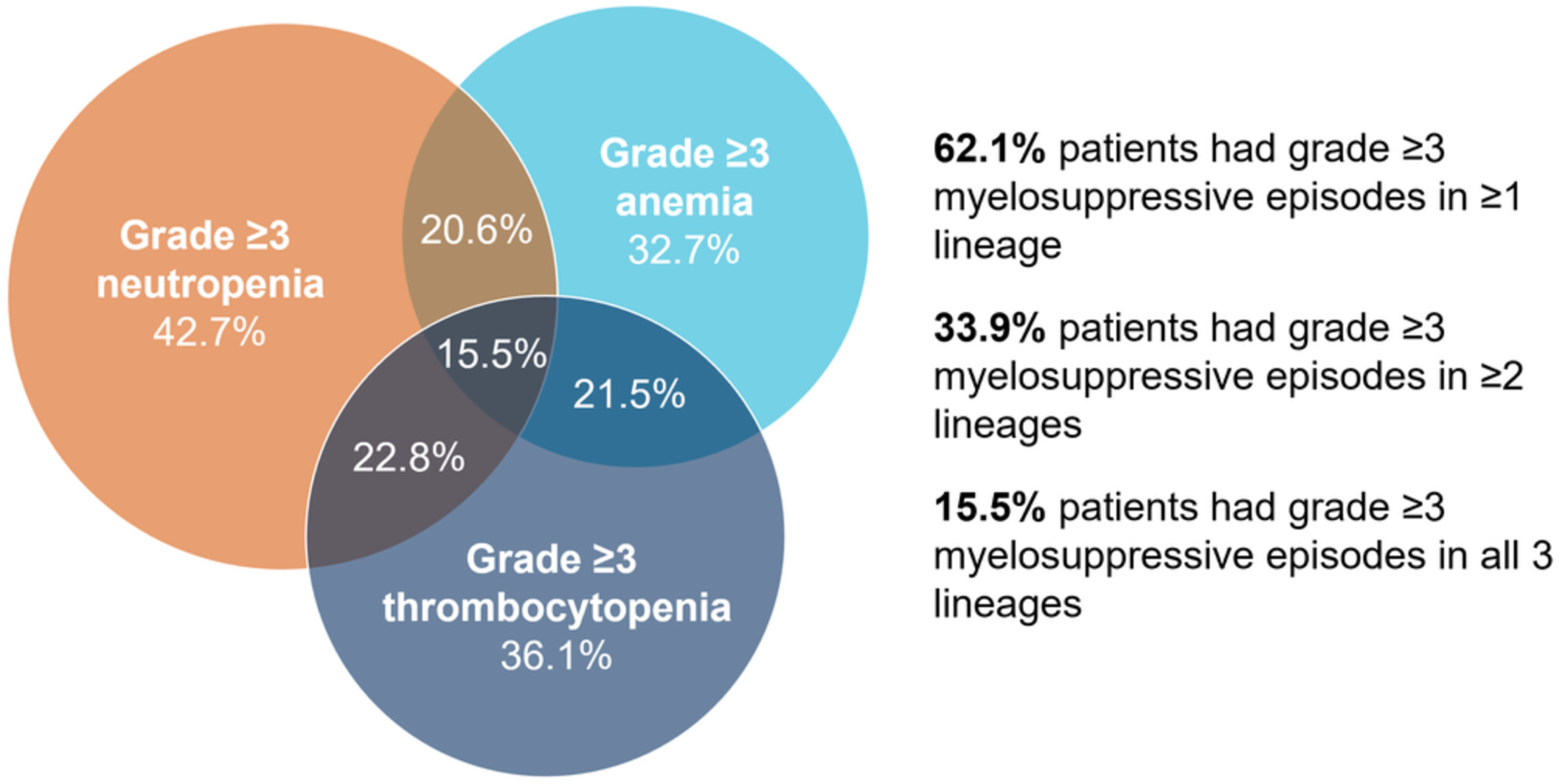
Burden of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression among patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study from community oncology practices
- Pages: 10020-10030
- First Published: 31 March 2023
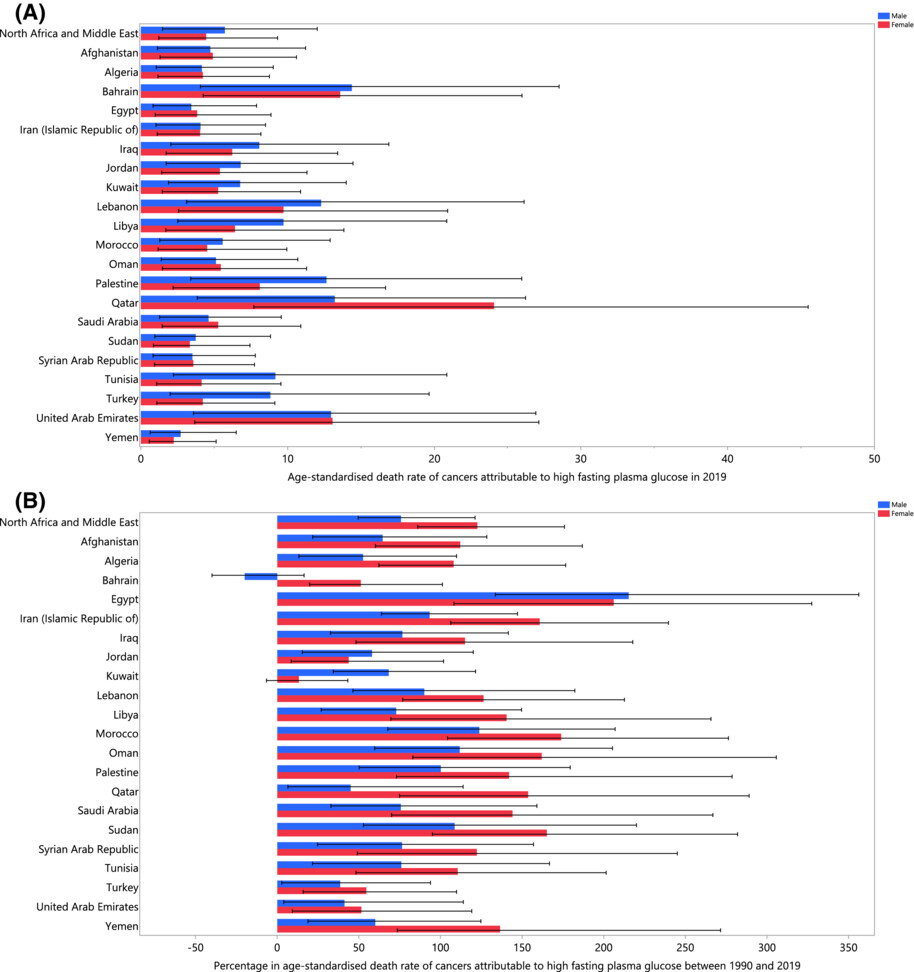
Burden of cancers attributable to high fasting plasma glucose in the Middle East and North Africa region, 1990–2019
- Pages: 10031-10044
- First Published: 23 March 2023
Bioinformatics
Peripheral and tumor-infiltrating immune cells are correlated with patient outcomes in ovarian cancer
- Pages: 10045-10061
- First Published: 16 January 2023
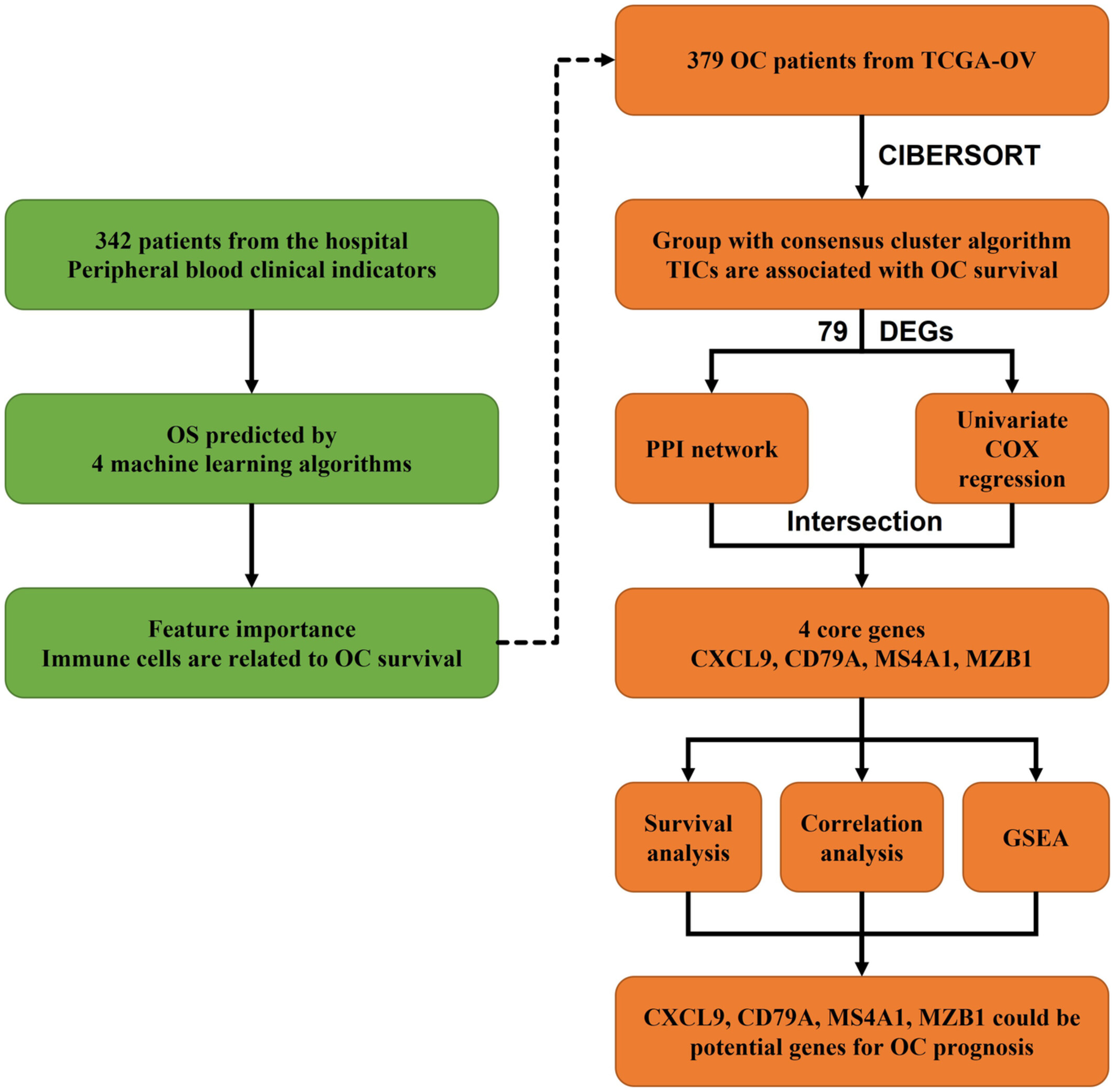
This study combines several machine-learning and bioinformatic analysis methods to explore the correlation of peripheral and tumor-infiltrating immune cells with patient outcomes in ovarian cancer. The results suggest that both peripheral blood markers and TICs can be used as prognostic predictors in patients with ovarian cancer, and CXCL9, CD79A, MS4A1, and MZB1 may be potential therapeutic targets for ovarian cancer immunotherapy.
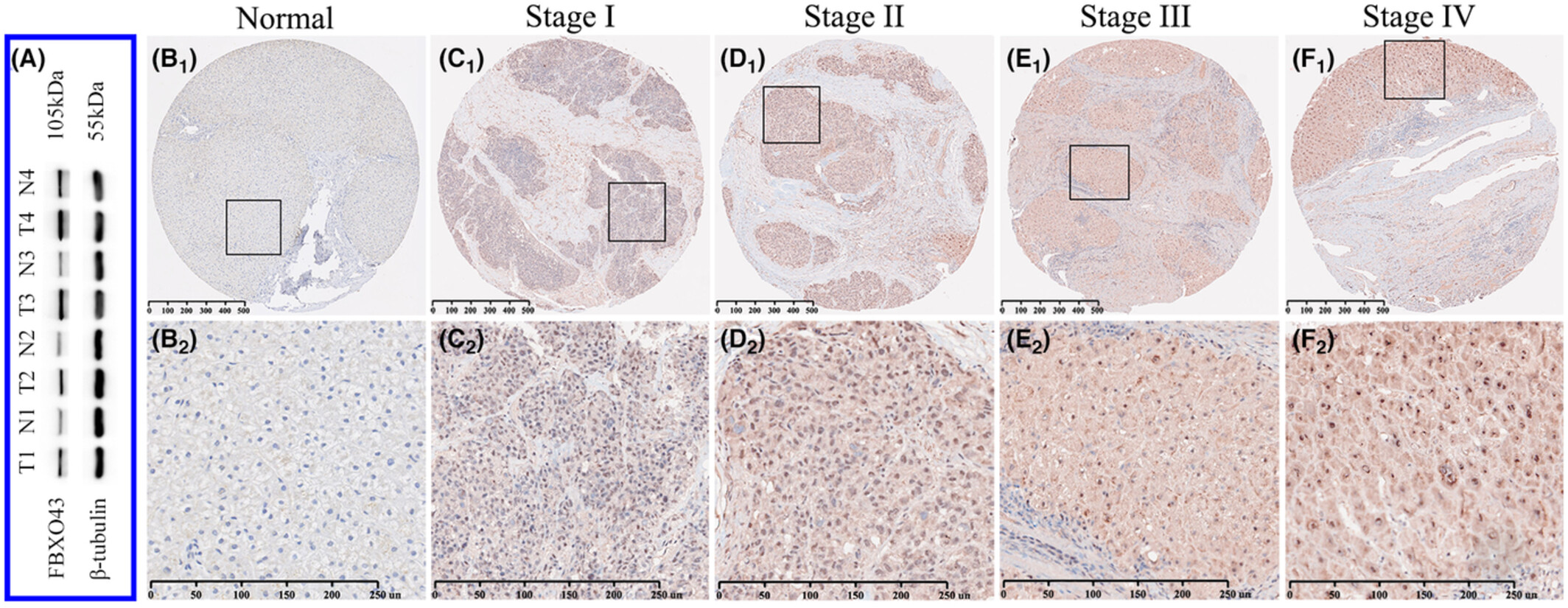
Association between F-box-only protein 43 overexpression and hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis and prognosis
- Pages: 10062-10076
- First Published: 29 January 2023
The effects of altered DNA damage repair genes on mutational processes and immune cell infiltration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 10077-10090
- First Published: 27 January 2023
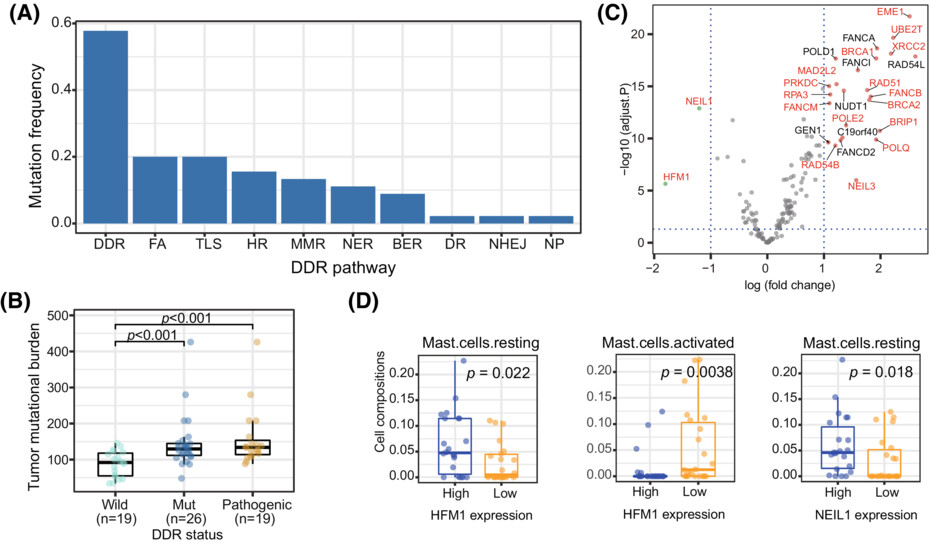
DNA damage repair (DDR) deficiency leads to genomic instability and oncogenesis and is prevalent in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Using whole-exome and transcriptome sequencing data from Taizhou and TCGA, we demonstrated that DDR alterations could impact mutational processes and immune cell infiltration in ESCC. The suppression of HFM1 and NEIL1 could play a crucial role in ESCC progression and may also serve as prognostic markers.
Reduced expression of alanyl aminopeptidase is a robust biomarker of non-familial adenomatous polyposis and non-hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer syndrome early-onset colorectal cancer
- Pages: 10091-10104
- First Published: 07 February 2023

Visualization of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) identified between early-onset colorectal cancer (EOCRC) and late-onset colorectal cancer (LOCRC). (A) DEG heatmap. Genes were sorted in accordance with their fold-change values. The top and bottom rows represent upregulated and downregulated genes in the EOCRC patients, respectively. (B) Pathway terms associated with the DEGs. (C) Gene ontology terms associated with the DEGs.
Development of lactate-related gene signature and prediction of overall survival and chemosensitivity in patients with colorectal cancer
- Pages: 10105-10122
- First Published: 12 February 2023
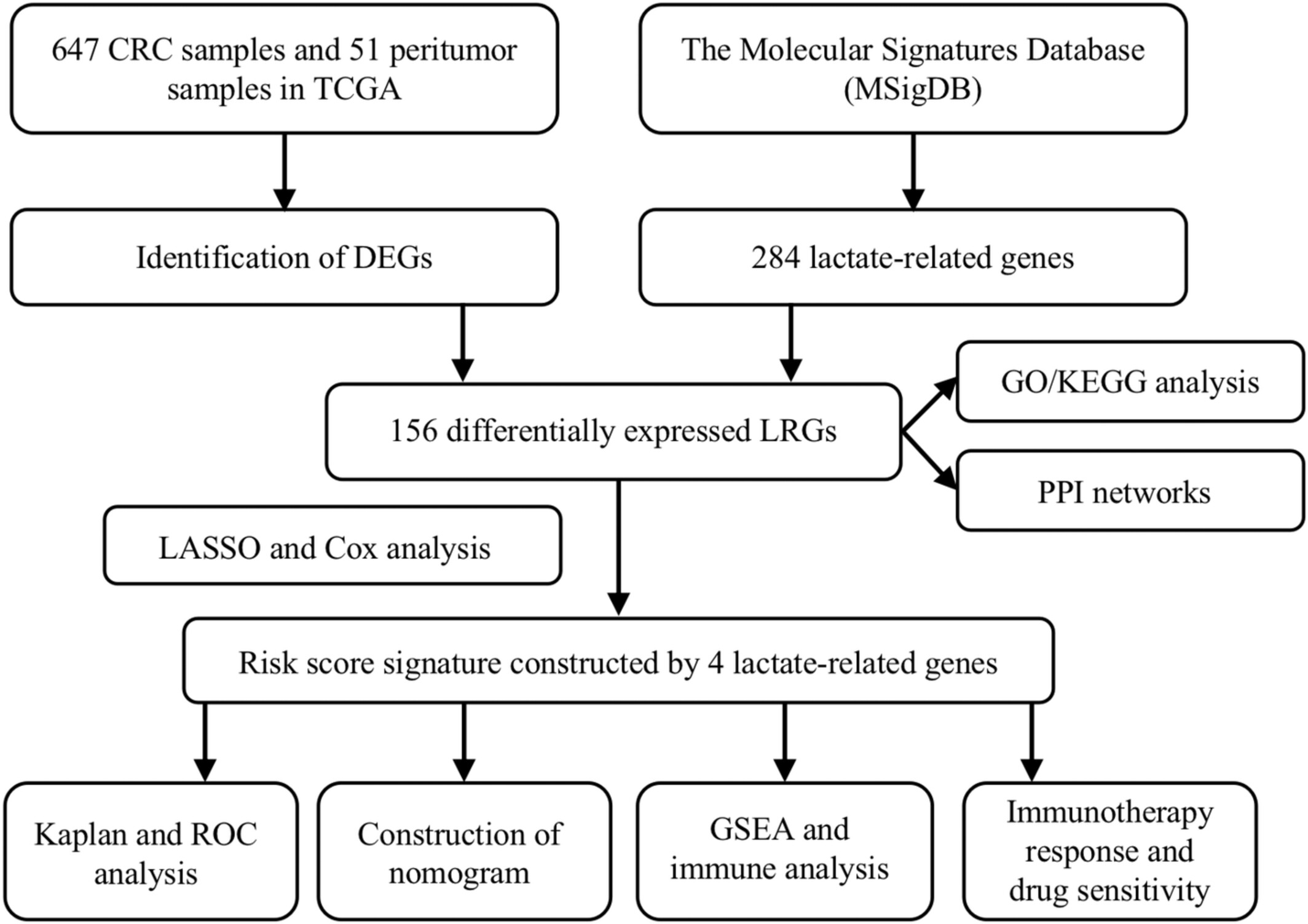
Lactate-related gene signature (LRGS) based on 4 lactate-related genes were developed and validated in CRC patients to predict clinical outcomes and provide individualized treatment recommendations. Patients with higher LRGS showed worse outcomes in different cohorts. Higher LRGS indicate better immunotherapy response, while lower LRGS indicate better sensitivity to targeted drugs.
Identification of a copper metabolism-related gene signature for predicting prognosis and immune response in glioma
- Pages: 10123-10137
- First Published: 01 March 2023
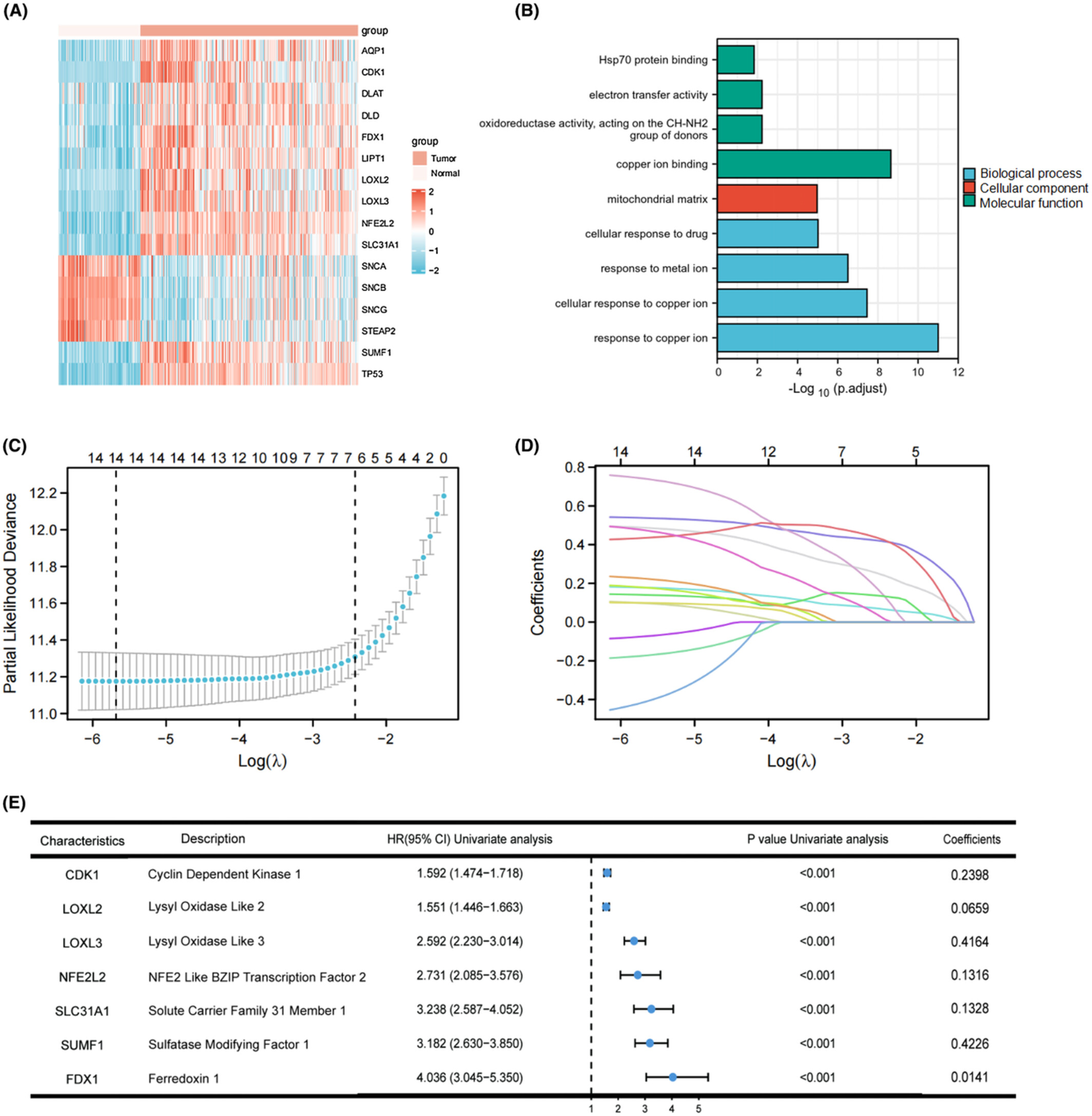
A copper metabolism-related gene signature was identified as a prognostic model for glioma, and the prognostic model has good accuracy in predicting patient outcomes in both TCGA and CGGA cohorts. Besides, the high-risk group had higher levels of immune cell infiltration, immune checkpoint genes expression, and higher tumor mutational burden, suggesting that they might be more likely to benefit from immunotherapy. Our study can provide a reference for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with glioma.
Cell division cycle-associated 8 is a prognostic biomarker related to immune invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 10138-10155
- First Published: 28 February 2023

Functions of CDCA8 in hepatocellular carcinoma. The expression of CDCA8 regulated the expression of tumor related proteins such as P53, PPAR, MYC etc. High level of CDCA8 activating the Notch pathway. Moreover, CDCA8 take part in the cell cycle and related to immune invasion. High level of CDCA8 means bad tumor status and poor survival in patients.
Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis to identify biological and clinical differences in cholangiocarcinoma
- Pages: 10156-10168
- First Published: 20 March 2023