Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Review Article
Overnutrition in the early postnatal period influences lifetime metabolic risk: Evidence for impact on pancreatic β-cell mass and function
- Pages: 263-274
- First Published: 09 January 2024
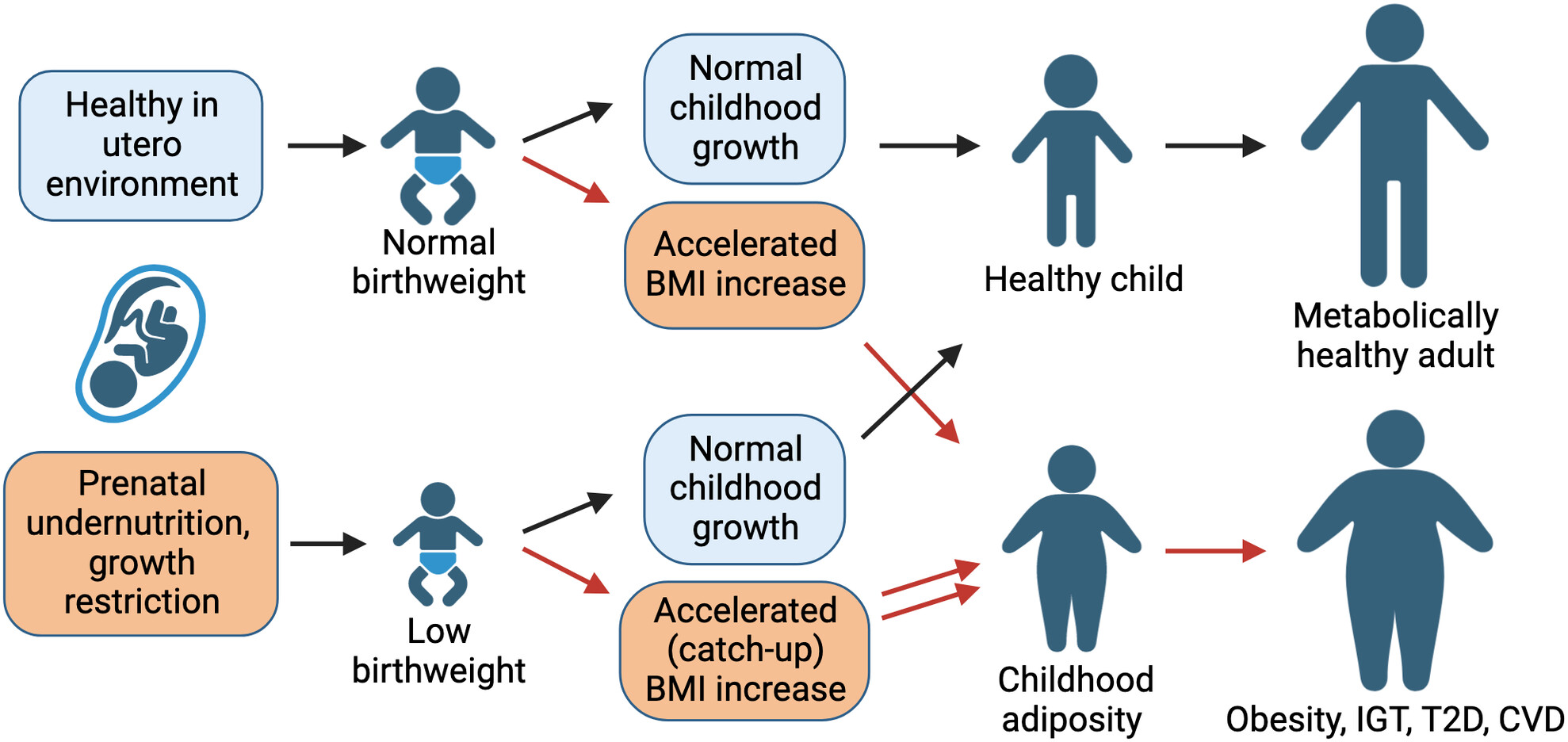
Diabetes causes substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide, as well as high societal cost. Risk of metabolic disease in adulthood increases in people with accelerated childhood growth trajectory. This review explores the metabolic impact of postnatal overnutrition in humans and in rodent models, with specific attention to the connection between accelerated childhood growth and future adiposity, insulin resistance, β-cell mass and β-cell dysfunction.
Mini Review
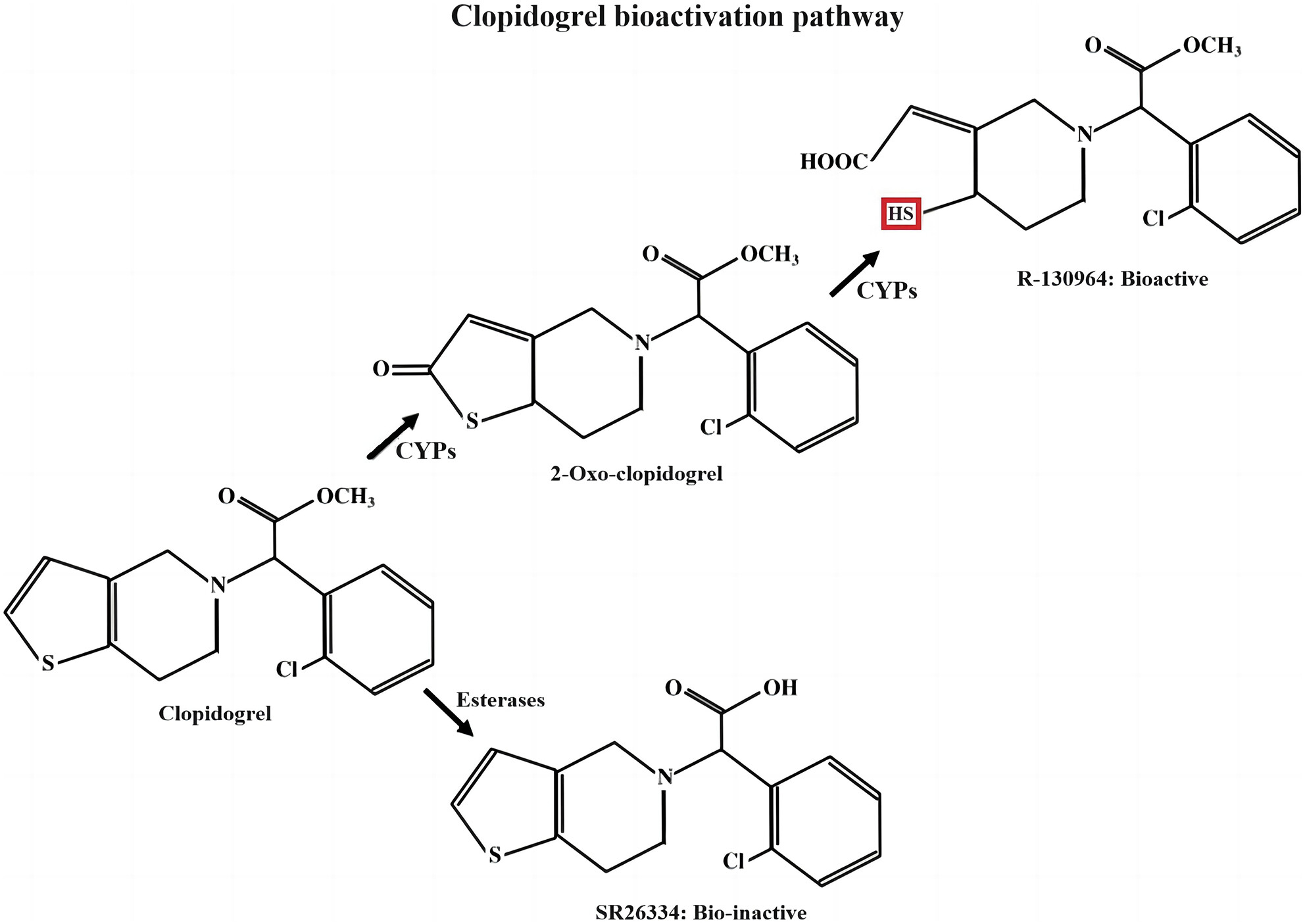
Recurrent hypoglycemia induced by clopidogrel: A case report and mini review
- Pages: 275-281
- First Published: 08 December 2023
Commentary
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor systems in the hypothalamus and the brainstem regulate feeding and weight through distinct pathways
- Pages: 282-284
- First Published: 23 December 2023
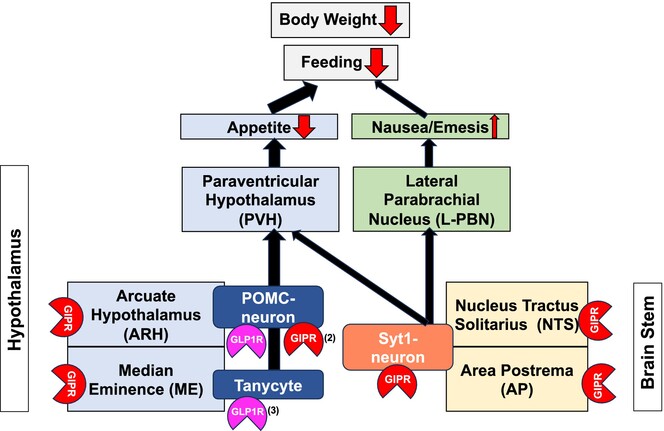
This report showed the role of brain stem glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) neurons in receiving GIPR agonist (GIPRA) to drive the neural circuit to reduce feeding and bodyweight. In this commentary, distinct and possible cooperative roles of the hypothalamic and brainstem pathways will also be discussed.
Update
Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
- Pages: 285-287
- First Published: 21 November 2023
Articles
Basic Science and Research
METTL3/YTHDF2 m6A axis mediates the progression of diabetic nephropathy through epigenetically suppressing PINK1 and mitophagy
- Pages: 288-299
- First Published: 28 November 2023
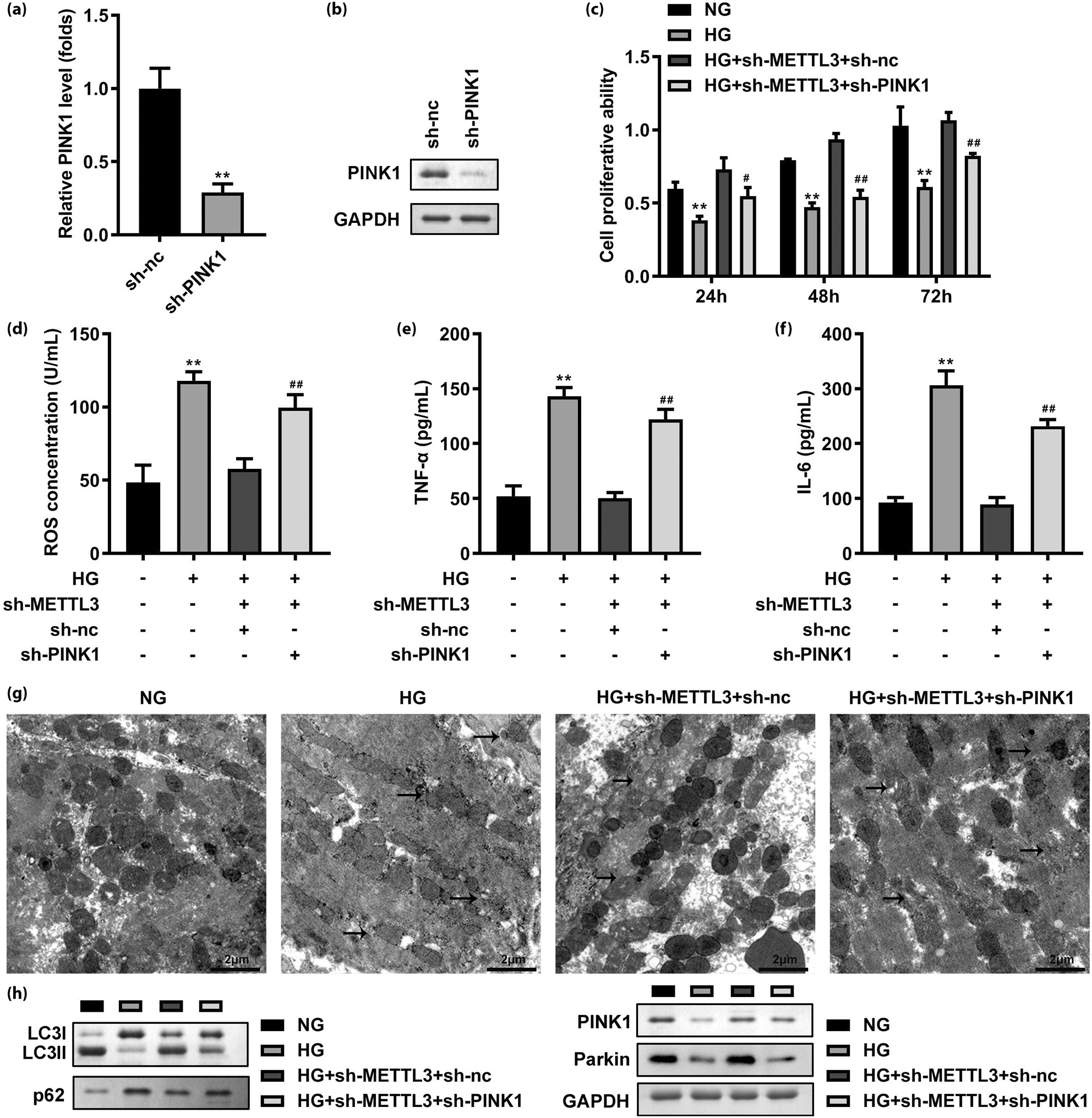
METTL3 mediates the progression of diabetic nephropathy through regulating the apoptosis and mitophagy of renal tubular epithelial cells. Mechanistically, METTL3 regulates the m6A modification and expression of PINK1 dependent on YTHDF2. We hope these findings could provide novel targets for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy disease.
Cordyceps cicadae polysaccharides attenuate diabetic nephropathy via the miR-30a-3p/TRIM16 axis
- Pages: 300-314
- First Published: 27 December 2023
Clinical Science and Care
Association between area under the C-peptide curve during an oral glucose tolerance test and diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes patients
- Pages: 315-325
- First Published: 22 November 2023

The indexes related to the area under the C-peptide curve for six time periods during an oral glucose tolerance test and C-peptide release test might be independent predictors of the incidence of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. The area under the C-peptide curve has the added advantage of being a cheap and convenient risk assessment over traditional ophthalmic screening.
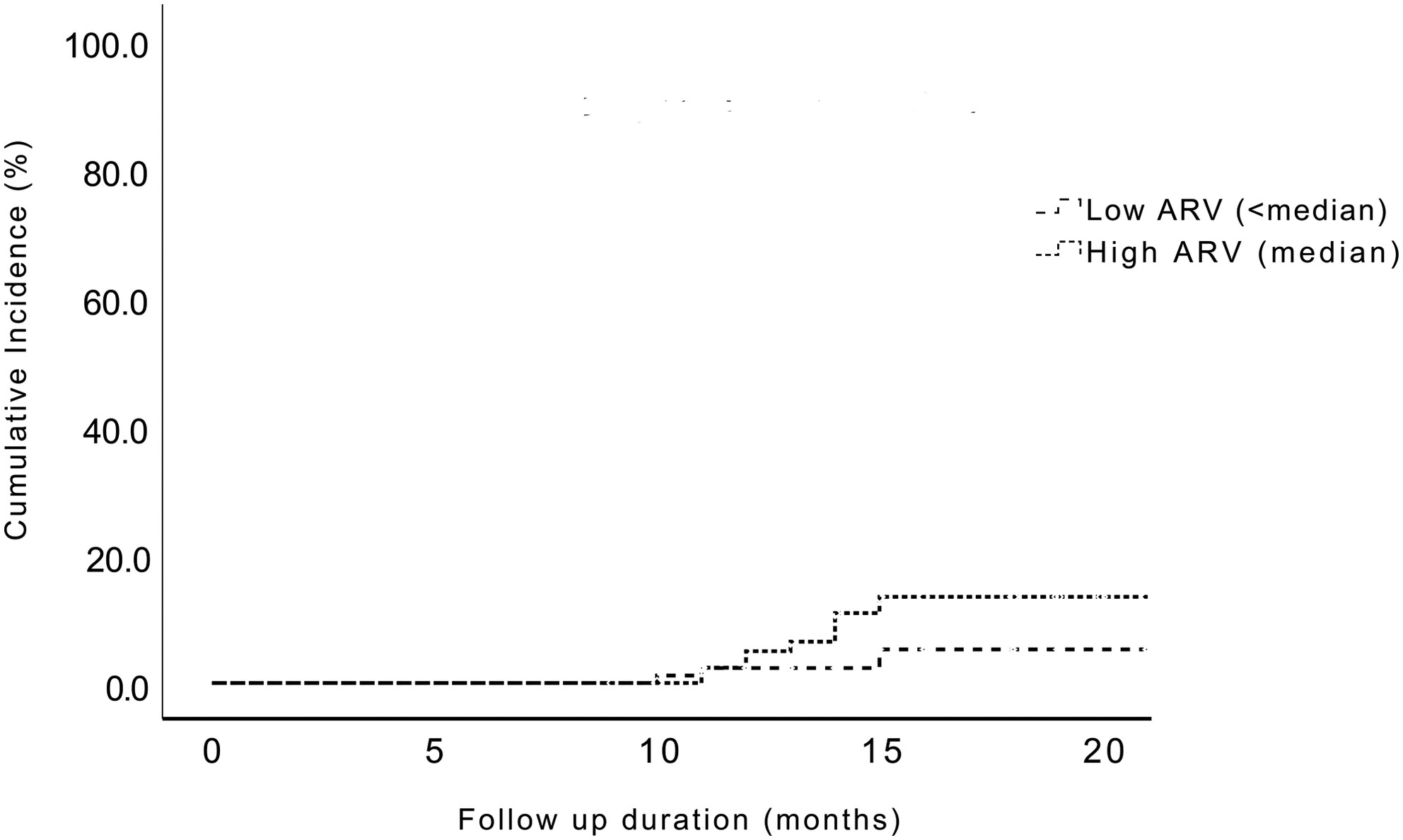
Prognostic value of longitudinal HbA1c variability in predicting the development of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort observational study
- Pages: 326-335
- First Published: 03 January 2024
Effect of hemoglobin A1c management levels on coronary physiology evaluated by quantitative flow ratio in patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention
- Pages: 336-345
- First Published: 27 November 2023
This retrospective study investigated the relationship between the different levels of hemoglobin A1c and coronary physiology, focus on the effect of hemoglobin A1c on coronary physiology and short-term poor prognosis in patients with coronary heart disease combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Body composition and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Pages: 346-354
- First Published: 27 November 2023
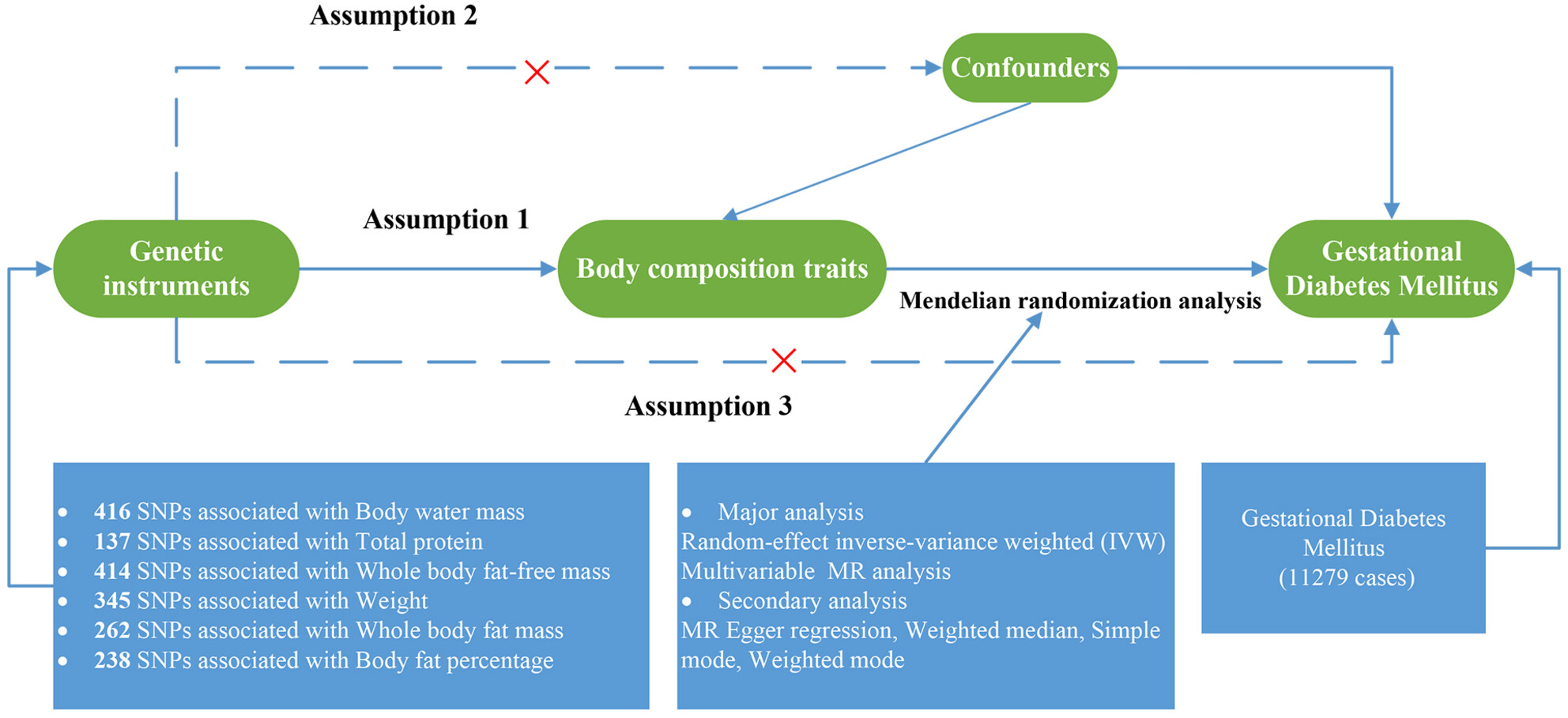
The potential causal relationship between body composition traits and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) reminds clinical doctors and nurses to pay attention to the early screening of pregnant women in order to reduce the risk of GDM and other complications. Additionally, further studies are imperative to establish a causal connection between body composition traits and GDM.
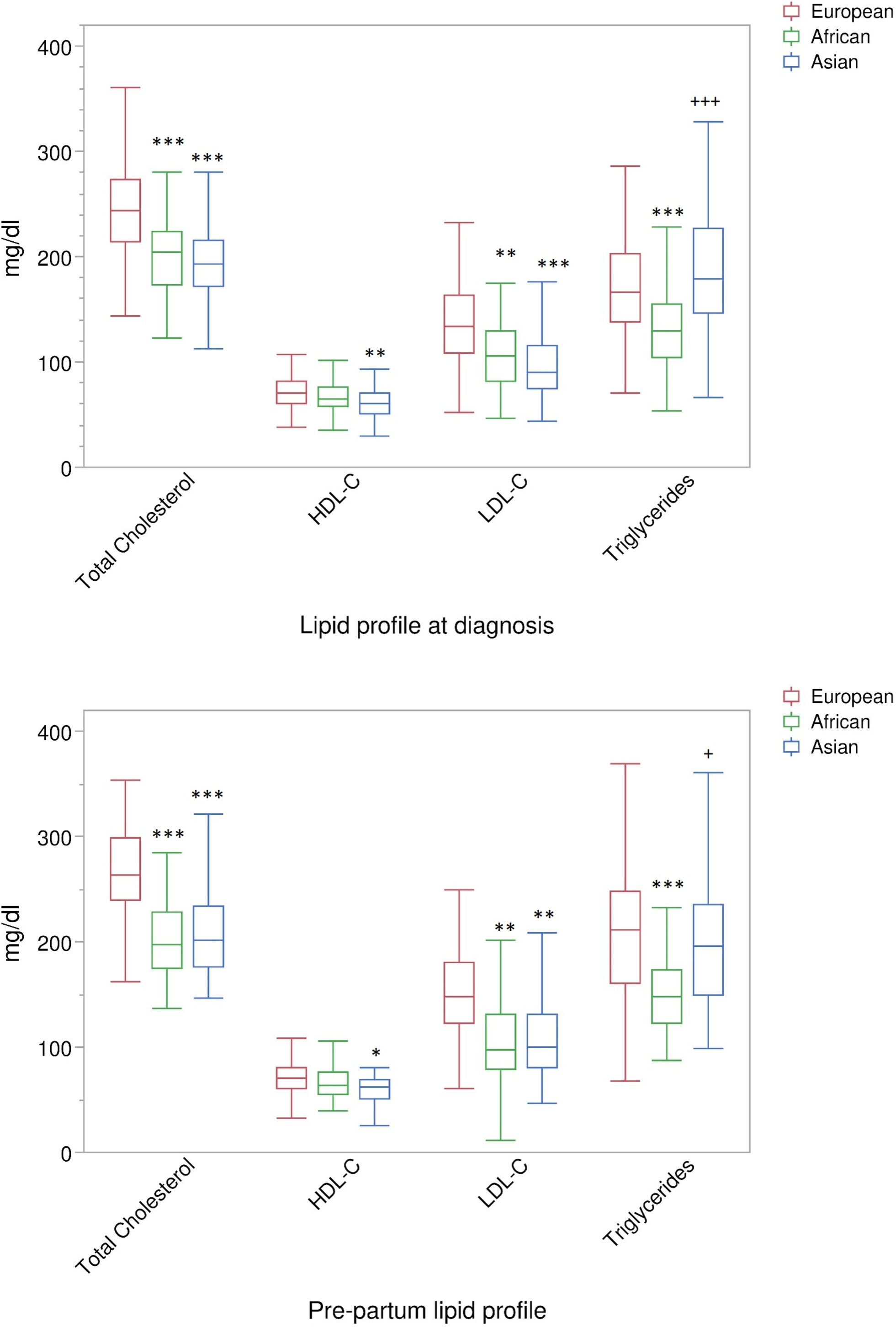
Lipid profile in women of different ethnicity with gestational diabetes: Relationship with fetal growth
- Pages: 355-363
- First Published: 13 December 2023
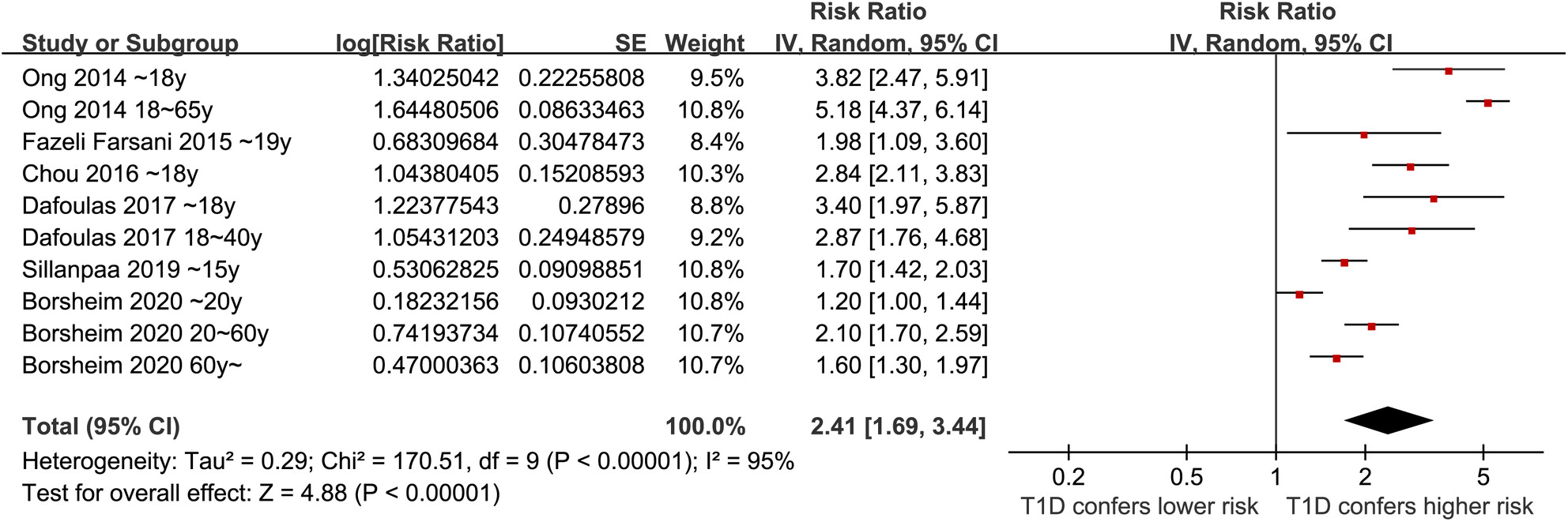
Type 1 diabetes and the risk of epilepsy: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 364-373
- First Published: 18 December 2023
Healthcare resource utilization and healthcare costs in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus initiating sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors vs dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in Japan: A real-world administrative database analysis
- Pages: 374-387
- First Published: 19 December 2023
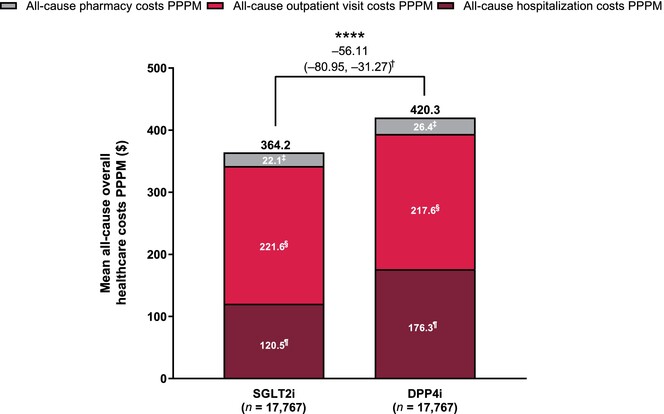
This large retrospective cohort study of type 2 diabetes mellitus conducted in Japan, using an administrative database, showed significantly lower numbers of hospitalizations per person per month (PPPM) and outpatient visits PPPM and shorter length of stay per hospitalization in patients newly treated with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) than those newly treated with a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP4i). All-cause overall healthcare costs PPPM and all-cause hospitalization costs PPPM were also generally lower in patients receiving an SGLT2i than those receiving a DPP4i. The results suggest economic benefits with SGLT2i vs DPP4i in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Case Report
A case of type 2 diabetes mellitus with weight gain and worsening of glycemic management after tezepelumab administration for severe bronchial asthma
- Pages: 388-390
- First Published: 08 December 2023
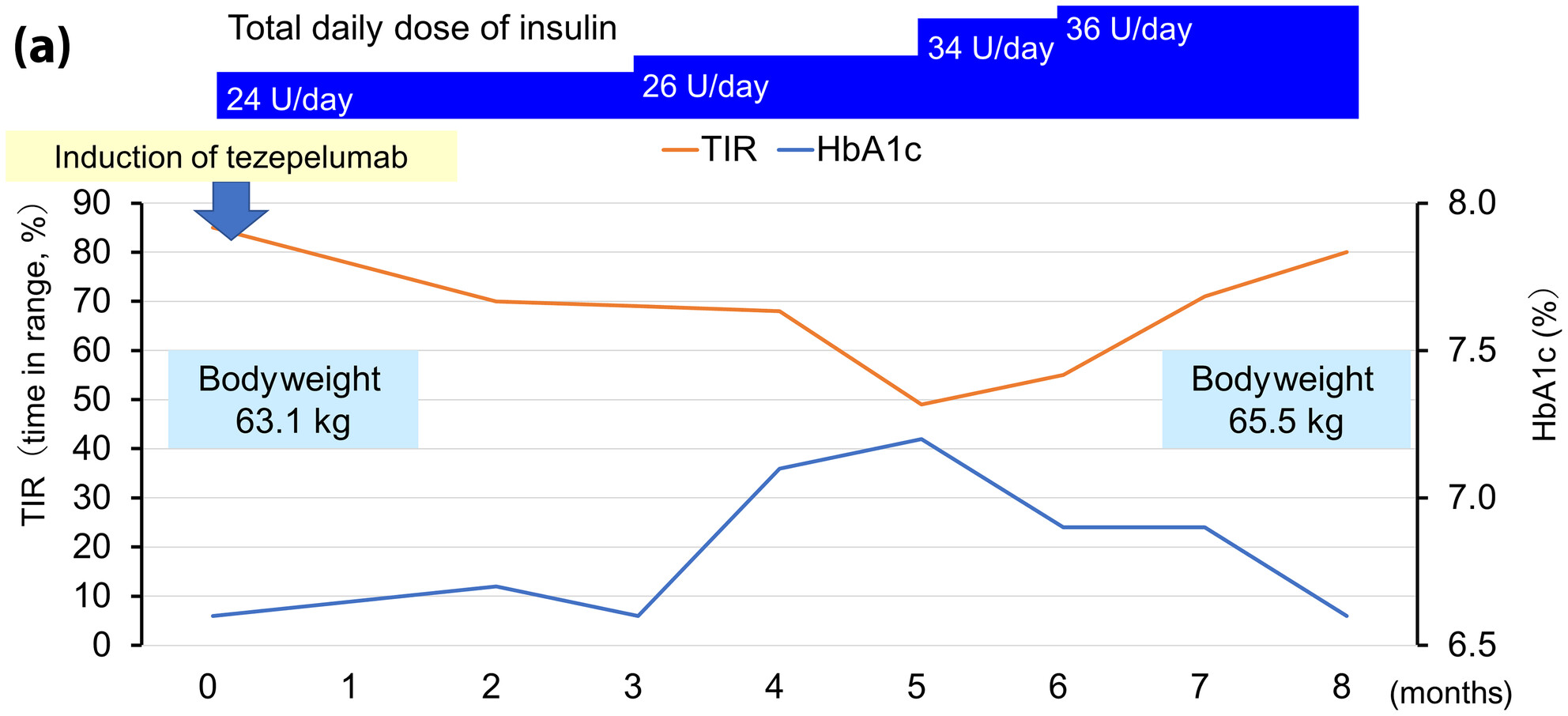
Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by refractory severe asthma were treated with tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin antibody. The requirement of prednisolone due to asthma exacerbation was decreased, but the patient showed worsening of glycemic management, increased insulin requirement and weight gain. When administering tezepelumab to patients with asthma complicating type 2 diabetes, careful follow up regarding glycemic management and weight might be necessary.