Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Review Articles
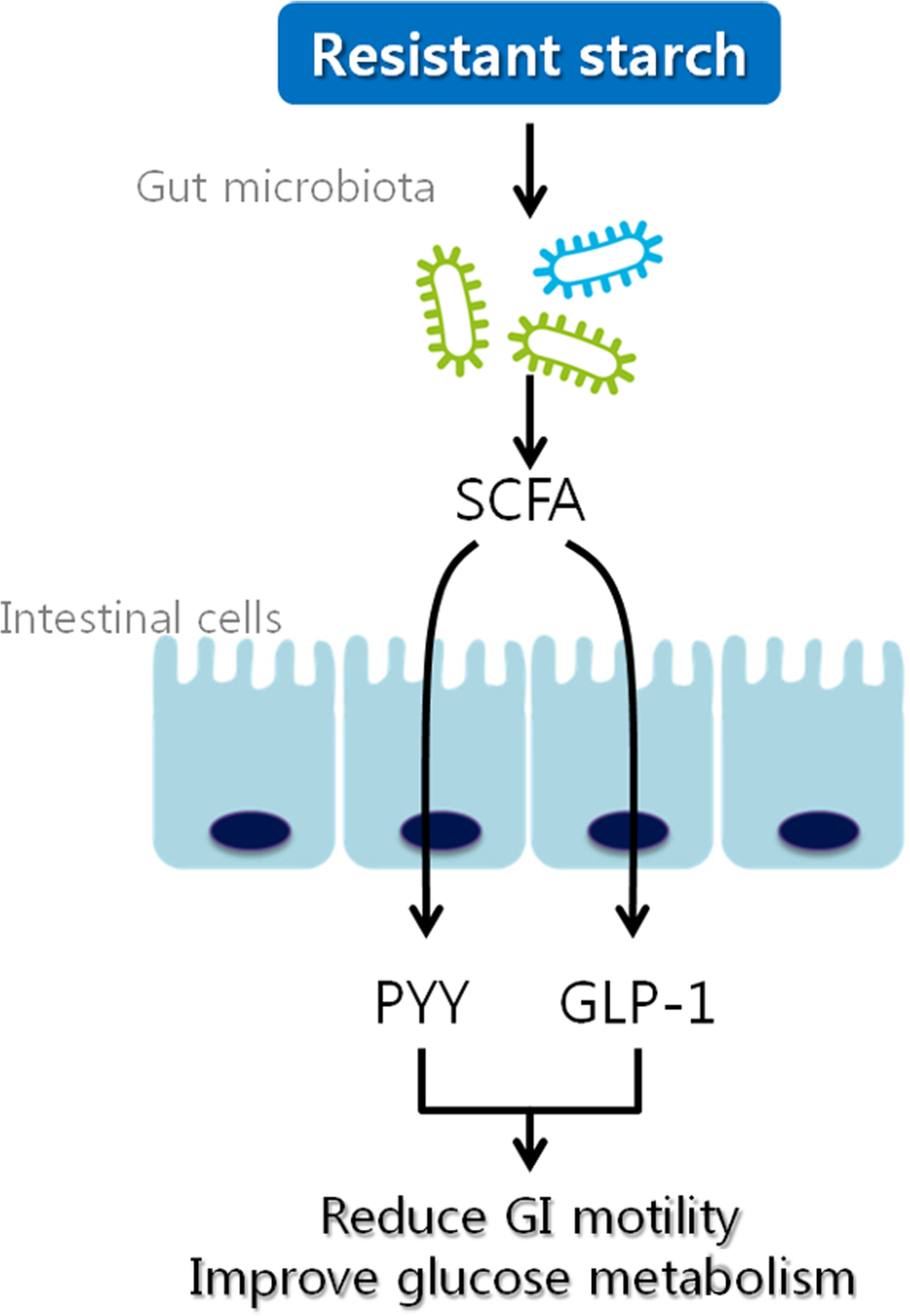
Resistant starch and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Clinical perspective
- Pages: 395-401
- First Published: 08 January 2024
Changing landscape of diabetes in Asia – What are the unmet needs?
- Pages: 402-409
- First Published: 24 January 2024
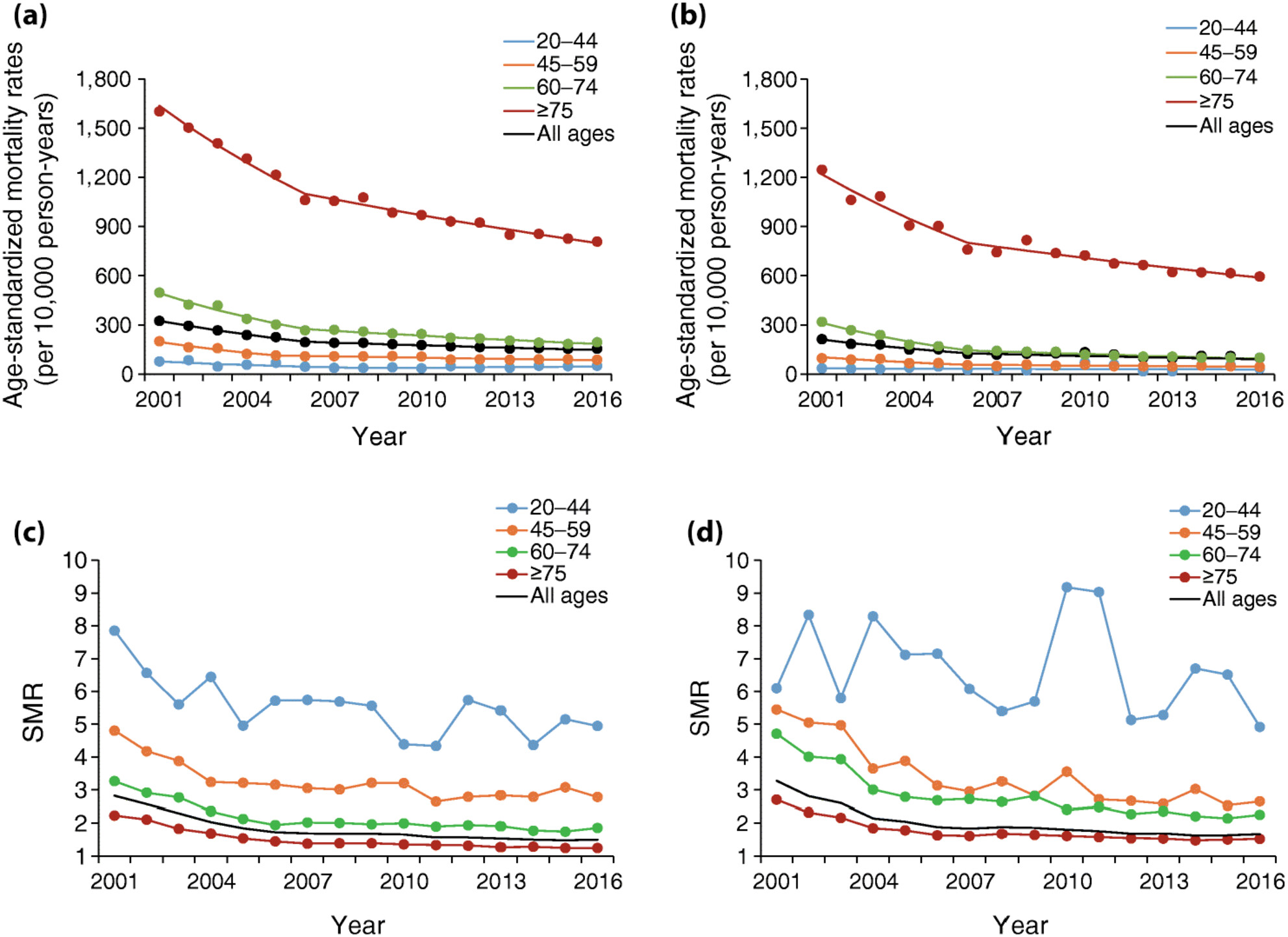
The mortality rates in people with type 2 diabetes have declined in high-income regions in Asia including Hong Kong but improved survival resulted in population aging and more people living with multiple morbidities. The increasing incidence of young-onset type 2 diabetes contributed to a growing number of people who are likely to develop major complications at an age when they are most economically productive. Monitoring of population-based data has revealed unmet needs in these subpopulations, where strategies tailored to their multifactorial needs are required to reduce morbidity and disability.
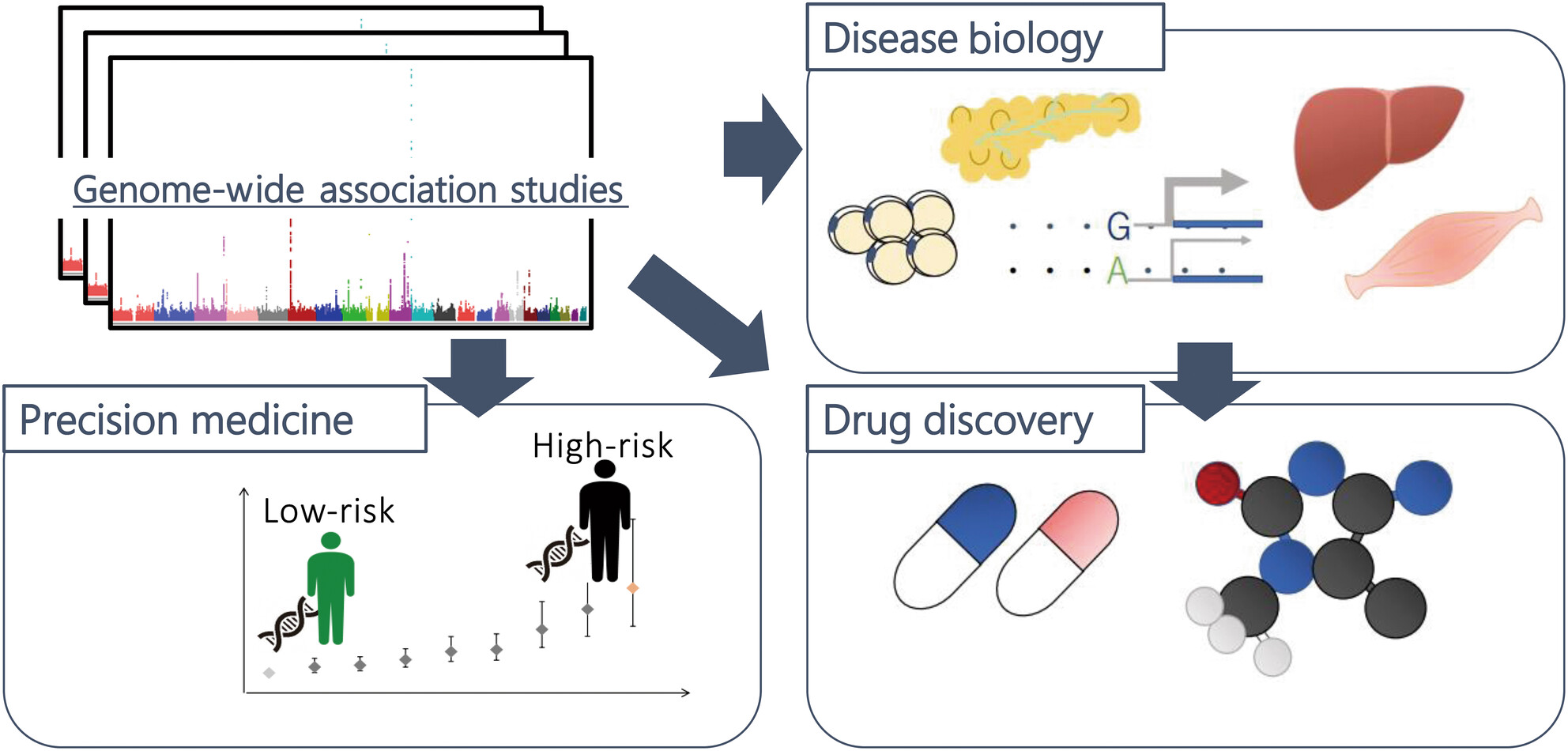
Perspectives on genetic studies of type 2 diabetes from the genome-wide association studies era to precision medicine
- Pages: 410-422
- First Published: 23 January 2024
Commentaries
Advancements and challenges in pancreatic islet transplantation: Insights from the Collaborative Islet Transplant Registry
- Pages: 423-425
- First Published: 08 January 2024
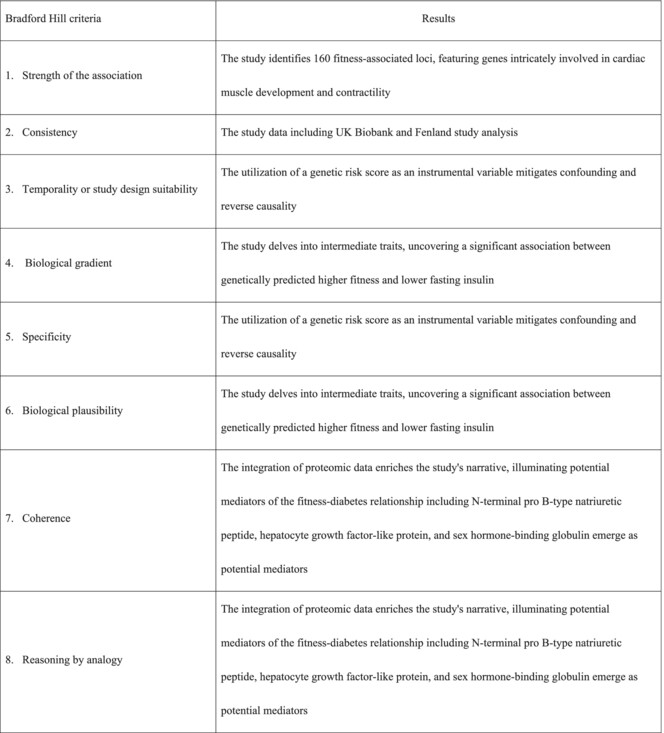
Deciphering the causal tapestry between cardiorespiratory fitness and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 426-428
- First Published: 19 January 2024
Articles
Basic Science and Research
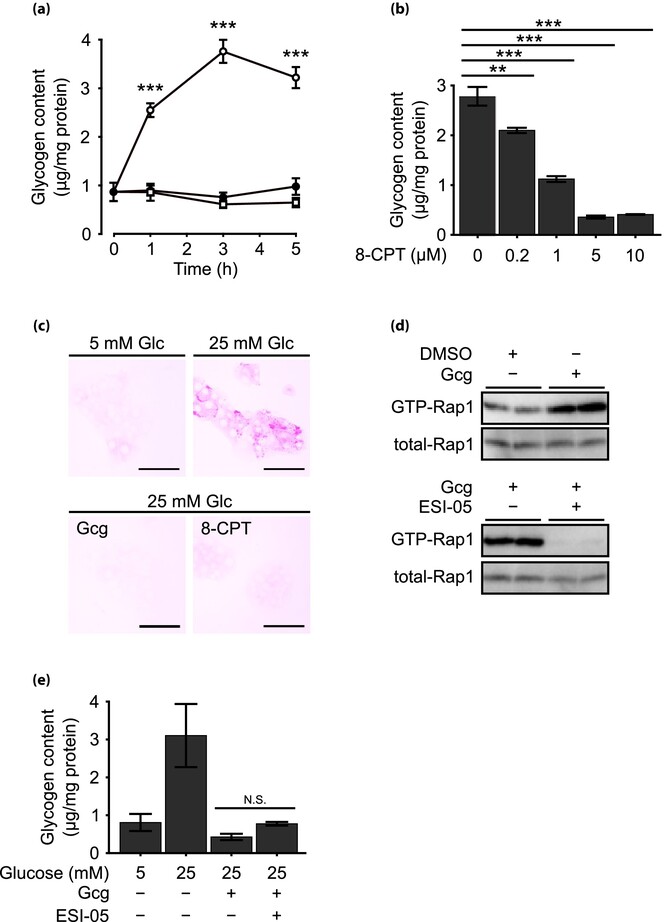
Epac2 activation mediates glucagon-induced glucogenesis in primary rat hepatocytes
- Pages: 429-436
- First Published: 19 January 2024
Clinical Science and Care
Short-term recovery of insulin secretion in response to a meal is associated with future glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients
- Pages: 437-448
- First Published: 27 December 2023
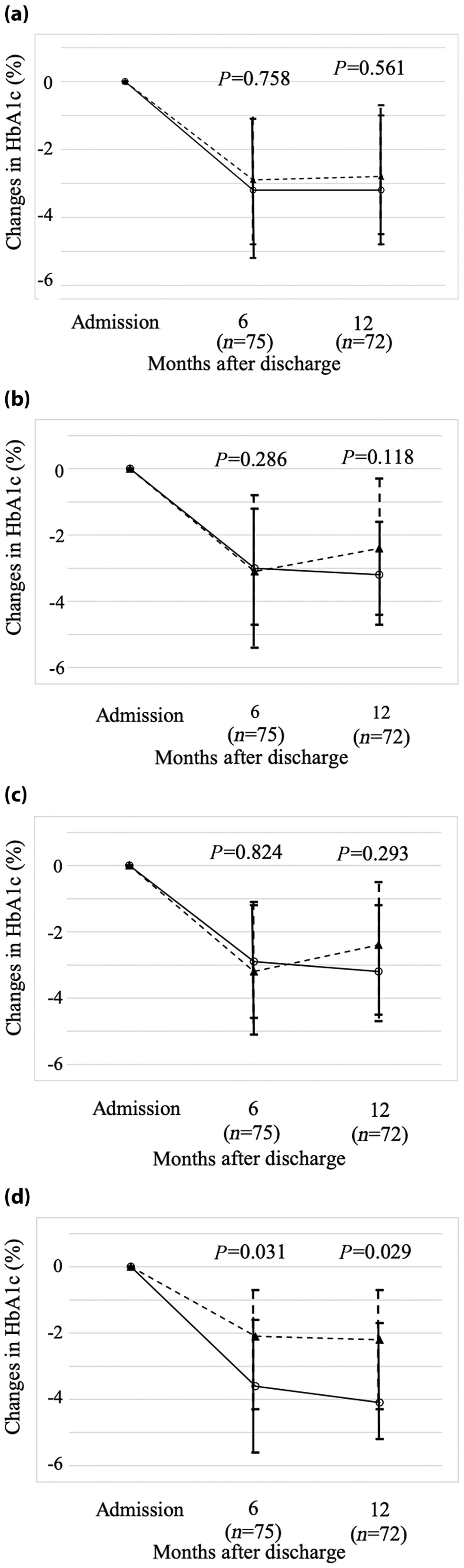
We investigated the association between short-term recovery of insulin secretion during hospitalization and clinical background or future glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. According to our results, short-term recovery of insulin secretion in response to a meal during hospitalization might predict future glycemic control.
Comparative effects of fixed-dose mitiglinide/voglibose combination and glimepiride on vascular endothelial function and glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 449-458
- First Published: 27 December 2023
Low-dose aspirin for prevention of cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A real-world nationwide cohort study
- Pages: 459-467
- First Published: 21 December 2023
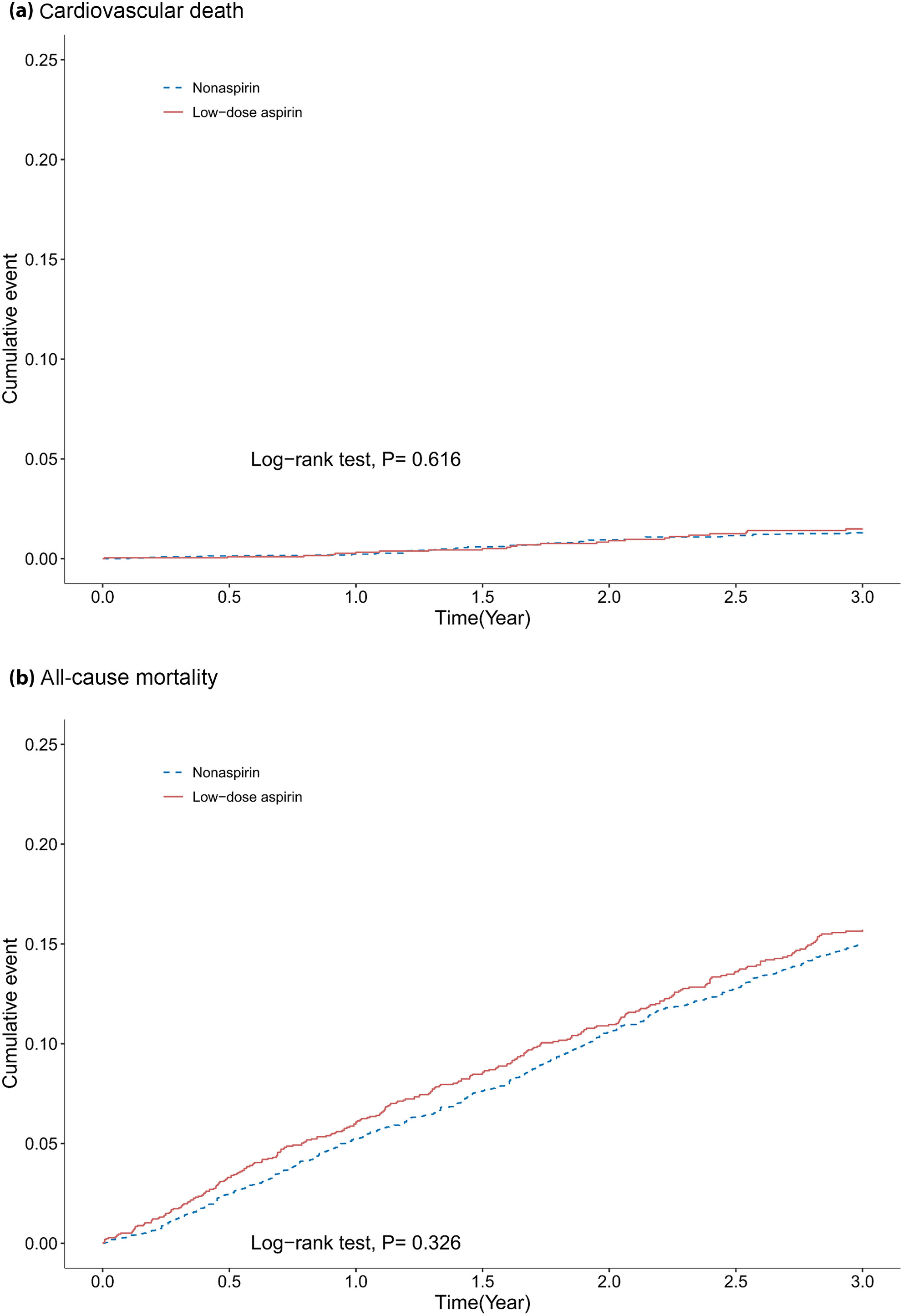
This retrospective population-based cohort study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of low-dose aspirin for primary prevention in patients with diabetes and pre-end-stage renal disease. This study showed that low-dose aspirin did not reduce cardiovascular mortality, nor increase the risk of major bleeding and renal disease progression. These findings do not support the use of aspirin for primary prevention in this high-risk population.
Development and validation of a prediction model for self-reported hypoglycemia risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal cohort study
- Pages: 468-482
- First Published: 19 January 2024
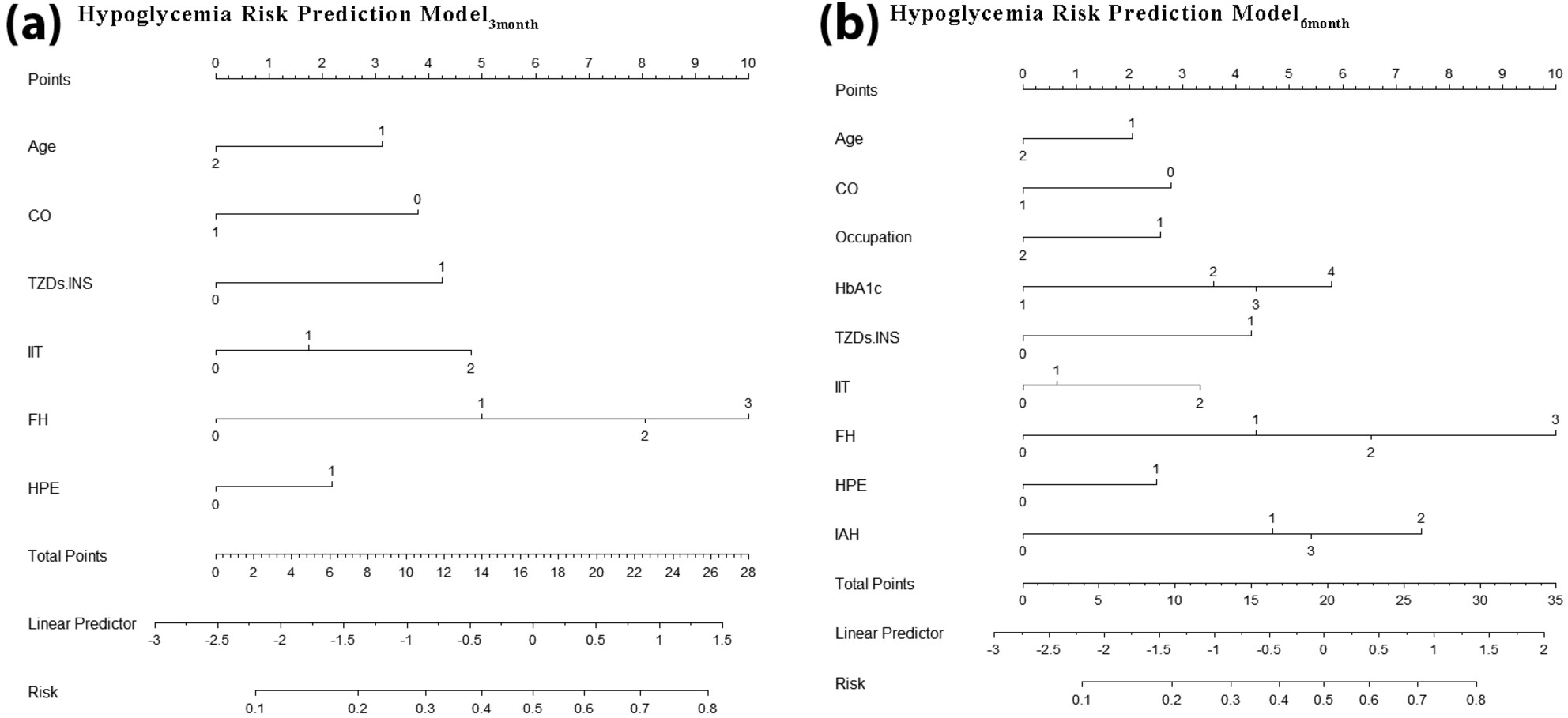
The study developed 3 and 6 month hypoglycemia risk prediction models for patients with type 2 diabetes, and visualized the use of the models by nomograms. Age, central obesity, intensive insulin therapy, frequency of hypoglycemia in the past year and hypoglycemia prevention education entered both model3month and model6month. The study found that risk factors of hypoglycemia were different in the different stages, suggesting that a dynamic assessment of the risk of hypoglycemia was needed.
Inverted U-shaped associations between serum uric acid and fasting - plasma glucose level in non-diabetic, pre-diabetic, and diabetic adults: A population-based study in China
- Pages: 483-490
- First Published: 18 December 2023
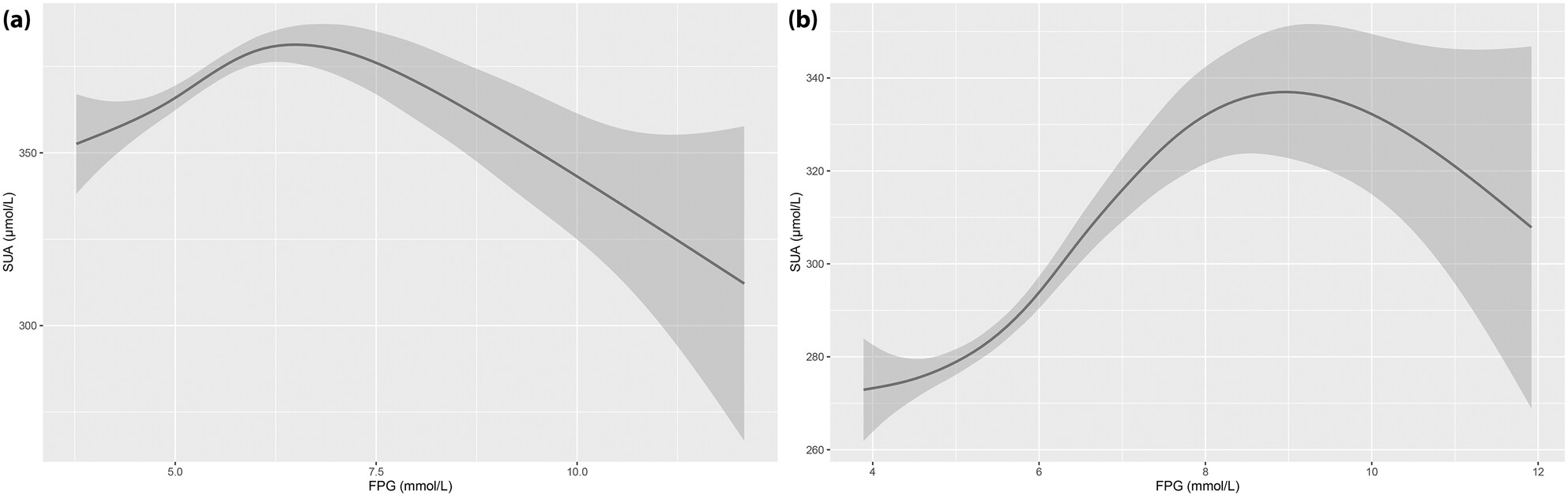
The current findings support the hypothesis that SUA levels might be involved in the early, rather than advanced, stages of glucose metabolism disorder. Patients with pre-diabetes and newly diagnosed diabetes might be at a higher risk of hyperuricemia. The findings are of great significance for the management of diabetes.
Estimated small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonobese populations
- Pages: 491-499
- First Published: 18 December 2023
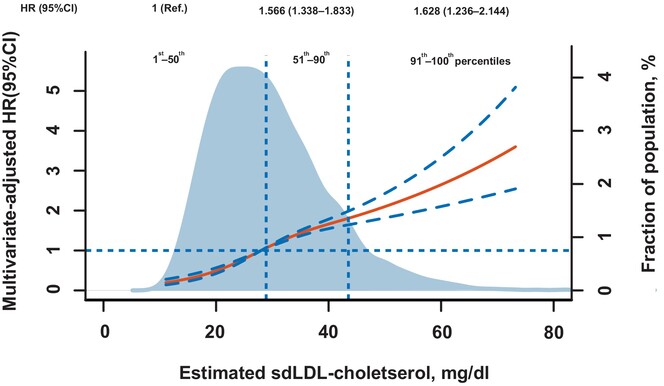
Estimated small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol was positively associated with the risk of developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, independent of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The predictive value of estimated small dense low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol was stronger than that of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and estimated large buoyant low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Comparing the screening methods for gestational diabetes mellitus before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review
- Pages: 500-516
- First Published: 16 December 2023
This study aims to compare the screening methods for gestational diabetes mellitus before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. The new screening methods for GDM had poor sensitivity, which resulted in many misdiagnosed pregnant women. It also prompts reflection on the post-pandemic era. OGTTs remain the gold standard, and there must be future planning so that future pandemics or emergencies do not significantly alter the effectiveness of screening practices for GDM.
Letter to the Editor
Comment on the article titled “Association of the triglyceride-glucose index with subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A retrospective cross-sectional study”
- Pages: 517-518
- First Published: 20 October 2023