Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 05 June 2023

A reflectional quantitative differential phase microscopy (RQDPM) based on polarized wavefront phase modulation and partially coherent full-aperture illumination is introduced for imaging thick and opaque samples. RQDPM utilizes the polarization-dependent characteristic of a phase-type spatial light odulator to divide the object wave into two identical copies with a certain shear distance. When loading different modulation images to the spatial light modulator, phase derivative images with different shearing directions and phase shifts can be obtained. Finally, the phase distribution of the sample is obtained.
For further details please visit the article by Ying Ma, Taiqiang Dai, Lan Yu, Lin Ma, Sha An, Yang Wang, Min Liu, Juanjuan Zheng, Liang Kong, Chao Zuo, and Peng Gao (e202200325).
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Point-of-care optical devices in clinical imaging and screening: A review on the state of the art
- First Published: 11 March 2023
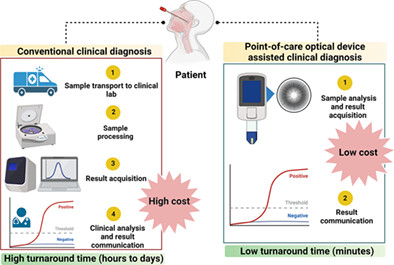
The use of point-of-care optical devices in healthcare allows fast clinical decisions with reduced turnaround time and resources, surpassing many critical steps in conventional diagnosis. Therefore, point-of-care optical device-assisted clinical diagnosis is preferred for resource-constrained settings, where implementation of early treatment options is often compromised. The review describes the potential applications of point-of-care optical devices in clinical imaging and screening and discusses the challenges and prospects related to the transferability of point-of-care optical research into the market.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Reflectional quantitative differential phase microscopy using polarized wavefront phase modulation
- First Published: 08 February 2023
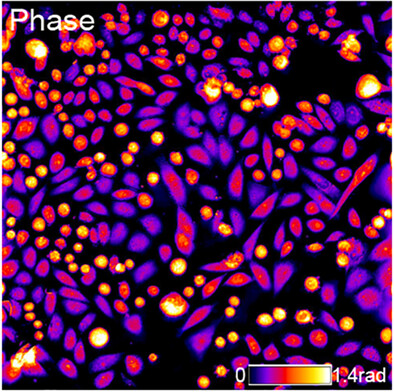
Transmission quantitative phase microscopy is unfit for opaque surfaces and turbid biological specimens. Herein, a reflectional quantitative differential phase microscopy based on polarized wavefront phase modulation and partially coherent full-aperture illumination is introduced for imaging thick and opaque samples.
Fluorescent polymer markers photoconvertible with a 532 nm laser for individual cell labeling
- First Published: 01 February 2023
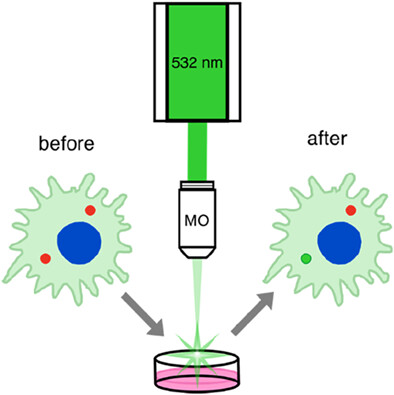
The photoconversion of fluorescent polymer labels with both pulsed and continuous-wave lasers with 532 nm-irradiation wavelength and different laser power densities were studied. The photoconversion process was described and its possible mechanism was proposed. The successful nondestructivity marker photoconversion inside RAW 264.7 monocyte/macrophage cells under continuous-wave laser with 532 nm irradiation wavelength was performed.
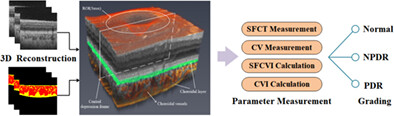
Choroidal vascularity index (CVI)-Net-based automatic assessment of diabetic retinopathy severity using CVI in optical coherence tomography images
- First Published: 12 January 2023
Serum Raman spectroscopy can be used to screen patients with early rheumatoid arthritis
- First Published: 06 January 2023
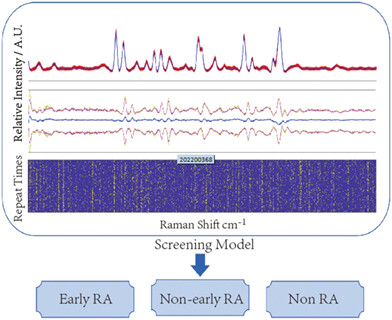
Raman spectroscopy was used to analyze the serum of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and to explore the screening value of Raman spectroscopy in patients with early RA. Fasting venous blood was collected for routine biochemical detection, and the remaining samples were tested by serum Raman spectroscopy. Support vector machine was used for model building and training.
Fabrication and characterization of porous tissue-mimicking optical phantoms as a tool for optical sensor validation
- First Published: 03 February 2023
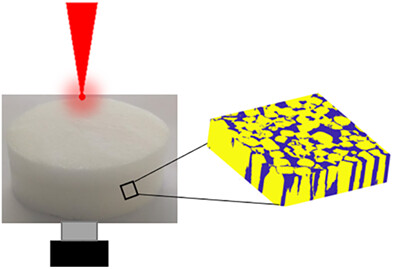
Many biological tissues, such as lungs, leaves, and fruit, have a well-connected porous network structure that promotes gas exchange. Spectroscopic techniques are increasingly used for the non-destructive monitoring of such biological tissues and hence, tissue-mimicking optical phantoms are needed during the design and optimization of novel optical setups. This paper presents porous PDMS phantoms with tunable optical and microstructural properties to mimic the features of biological tissue as a tool for optical sensor validation.
Photoacoustic (532 and 1064 nm) and ultrasonic coscanning microscopy for in vivo imaging on small animals: A productized strategy
- First Published: 14 February 2023
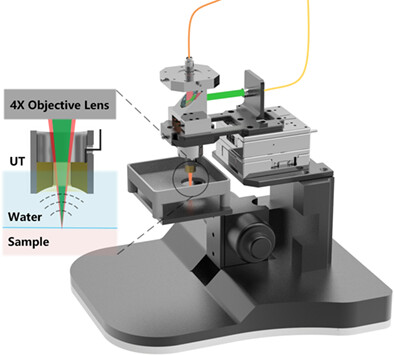
A productized strategy of photoacoustic (532 and 1064 nm) and ultrasonic coscanning microscopy for in vivo imaging on small animals is developed to help life science practitioners build a stable photoacoustic microscopy platform. A 532 nm laser: image blood vessels and pigments in label-free manner, whereas 1064 nm laser: image pigments and some novel probes developed for NIR-II windows. Ultrasound: assist photoacoustic imaging to accurately locate its imaging site in tissues.
Normalized mutual information of fNIRS signals as a measure for accessing typical and atypical brain activity
- First Published: 21 February 2023
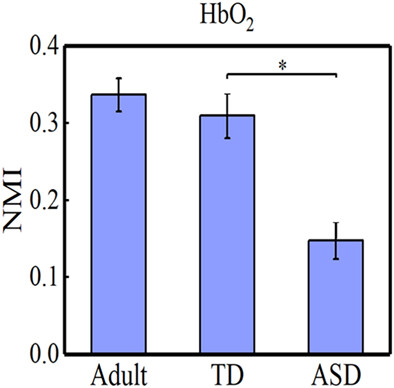
Spontaneous hemodynamic fluctuations were recorded from bilateral temporal lobes with functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), typically developing (TD) children, and young healthy (YH) adults. The normalized mutual information (NMI) was calculated between the left and right hemispheres for each group, showing that NMI was significantly higher for TD children than children with ASD, and higher for YH adults than TD children.
Effect of camera distance and angle on color of diverse skin tone-based standards in smartphone photos
- First Published: 11 February 2023
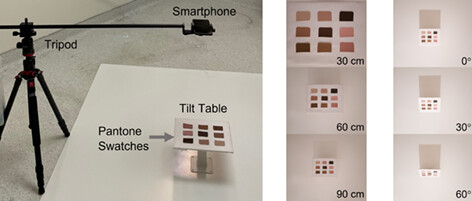
In medical photography, accurate capture of color is critical for clinical decision-making. Through standardized experiments of changing one parameter at a time, we quantified the effect of distance, angle, illumination, flash, and file format on color of a standard of diverse skin tones. By demonstrating the extent to which each variable affects color, these findings highlight the importance of developing clear guidelines for medical photography.
Intraoperative application of optical coherence tomography for lung tumor
- First Published: 08 February 2023
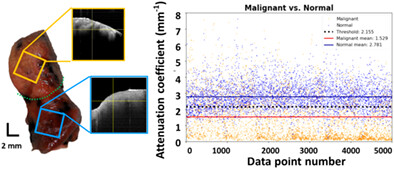
On-site instant determination of benign or malignant tumors for deciding the types of resection is crucial during pulmonary surgery. We designed a portable spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) system to do real-time scanning intraoperatively for the distinction of fresh tumor specimens in the lung. After OCT-imaged reconstruction, the qualitative morphology of OCT and histology among malignant, benign, and normal tissues was compared. In addition, through analysis of the quantitative data, a discrete difference in optical attenuation coefficients around the junctional surface was shown by the data processing.
Application of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to detect biochemical changes in blood serum of obese patients
- First Published: 03 March 2023
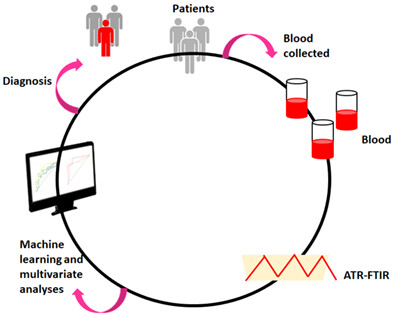
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of blood are difficult to differentiate by simple statistical tests, mainly when this technique is used for a diagnostic approach. Consequently, it is necessary to use multivariate analyses. Here, we presented the possibility of distinguishing blood collected from obese and healthy patients by FTIR in combination with principal component analysis. Furthermore, we showed that it is possible to correlate blood biochemical parameters with individual FTIR peaks.
The quality by design approach for optimization of slayer exciter based low power portable atmospheric plasma jet on bactericidal efficacy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- First Published: 08 March 2023
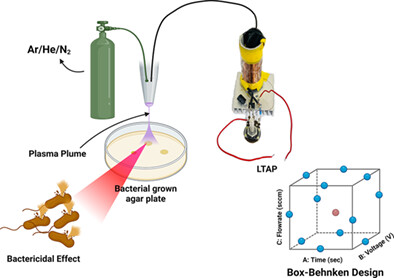
This article presents a simple, portable, economical design of low-temperature atmospheric plasma (LTAP) for the bactericidal of Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria. Input parameters to the LTAP, such as type of input gas, gas flow rate, input DC voltage, output frequency, plasma exposure time, and probe distance, are optimized using quality by design approach, Box–Behnken design of experiments, and response surface graphs for high bactericidal efficacy.
Prostate cancer tissue classification by multiphoton imaging, automated image analysis and machine learning
- First Published: 20 February 2023
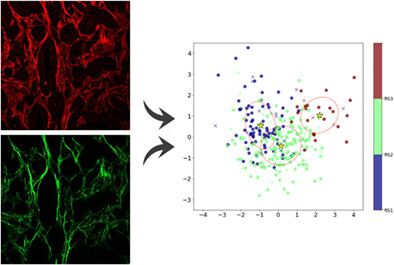
Multiphoton imaging of prostate tumour samples allows us to obtain quantitative parameters leading to specific tumour aggressiveness signatures. An automated image analysis recognises and quantifies the stromal fibre and neoplastic cell regions in the images and provides a set of metrics to distinguish between non-neoplastic tissue and carcinoma areas by linear discriminant analysis and random forest with good accuracy. The results show the importance of the stromal parameters as additional criteria for a more accurate diagnosis.
Fluorescence attenuated by a thick scattering medium: Theory, simulations and experiments
- First Published: 08 March 2023
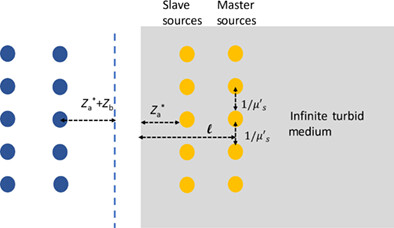
In vivo fluorescence imaging is greatly influenced by tissue scattering. This article presents a diffusion model of isotropic point sources imbedded in a scattering slab, representing fluorophores within a tissue. The model is compared with Monte Carlo simulations and measurements of a fluorescent slide measured through tissue-like phantoms showing a good fit. In addition, a counterintuitive behavior of the fluorescence intensity can be seen where the intensity decay has an inverse correlation to reduced scattering coefficient.
Depth-resolved attenuation mapping of the human ovary and fallopian tube using optical coherence tomography
- First Published: 14 March 2023
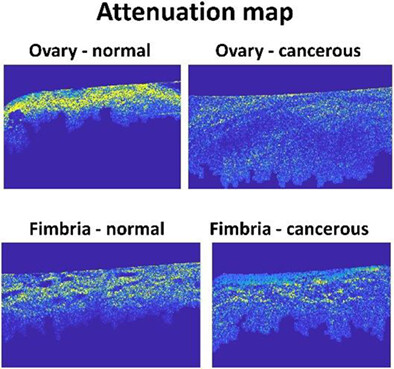
Freshly excised human ovaries and fallopian tubes were imaged with miniaturized optical coherence tomography (OCT) probe. Pixel-wise attenuation coefficients of ovaries and fallopian tubes were calculated from OCT images. Statistical features from attenuation maps showed statistically difference between cancerous ovaries, infundibula, and fimbriae and normal ones.
Classification method based on Siamese-like neural network for inter-species blood Raman spectra similarity measure
- First Published: 11 March 2023

A novel Siamese-like neural network is proposed for blood species identification, which could achieve high accuracy with relatively smaller training dataset. It addresses the inability of existing methods to detect the species not represented in the training dataset. Moreover, it realizes the function of model update training and reinforcement training. When new training data is added, training can be continued on the basis of the original model.
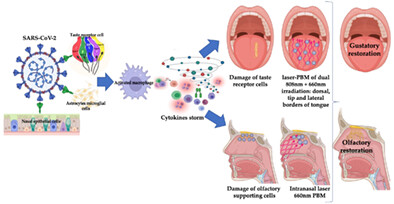
Can photobiomodulation restore anosmia and ageusia induced by COVID-19? A pilot clinical study
- First Published: 16 March 2023