Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Tumor-educated leukocytes mRNA as a diagnostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 737-745
- First Published: 21 January 2021
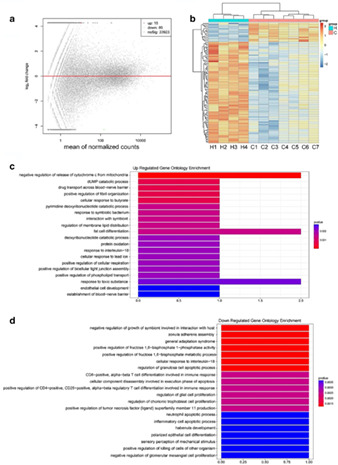
In the current study, we aimed to investigate the diagnostic and prognostic role of tumor-educated leukocytes (TELs) mRNA in NSCLC. We screened out GPX1, MAP3K7CL, BCL9L and PCSK7 using RNA-seq technology and validated their expression in a large cohort, followed by analysis for their diagnostic efficiency and predicting chemotherapy response assessment, thus providing the evidence of TELs GPX1, MAP3K7CL, BCL9L and PCSK7 as biomarkers for NSCLC.
Higher osimertinib introduction rate achieved by multiple repeated rebiopsy after acquired resistance to first/second generation EGFR-TKIs
- Pages: 746-751
- First Published: 21 January 2021
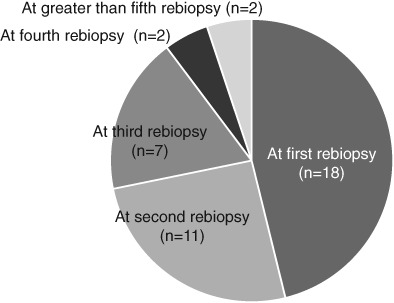
Times of rebiopsy in T790M positive patients. In 18 patients, T790M was positive at first rebiopsy. In 22 patients, T790M was positive at second or later rebiopsy. T790M detection rate increased from 36% to 80% by multiple repeated rebiopsy.T790M detection rate was increased by multiple repeated rebiopsy, achieving a higher osimertinib introduction rate. This higher introduction rate could contribute to better prognosis of EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients.
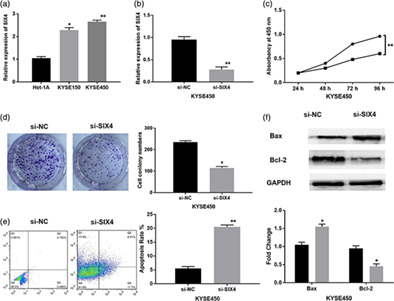
Upregulation of SIX4 indicates poor clinical outcome and promotes tumor growth and cell metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 752-759
- First Published: 22 January 2021
Patient prognostic scores and association with survival improvement offered by postoperative radiotherapy for resected IIIA/N2 non-small cell lung cancer: A population-based study
- Pages: 760-767
- First Published: 22 January 2021
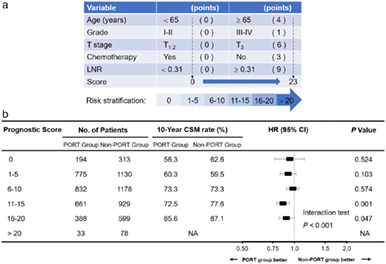
The role of postoperative radiotherapy for IIIA/N2 non-small cell lung cancer is unclear. Treatments for IIIA/N2 non-small cell lung cancer should be individualized. Patients who received postoperative radiotherapy had a lower CSM rate. The improved survival of patients receiving PORT was correlated with patient prognostic scores. Prognostic scores and clinical characteristics may be helpful in candidate selection for PORT.
Effects of periodontitis on postoperative pneumonia in patients with lung and esophageal cancer
- Pages: 768-774
- First Published: 24 January 2021
Tofacitinib overcomes an IFNγ-induced decrease in NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity via the regulation of immune-related molecules in LC-2/ad
- Pages: 775-782
- First Published: 24 January 2021
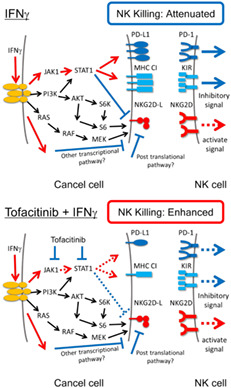
The JAK-STAT inhibitor tofacitinib blocks the IFNγ-induced transformation from an NK cell-sensitive phenotype to an NK cell-resistant one in IFNγ-reacted LC-2/ad cells, thereby implicating that tofacitinib may be a promising agent to overcome IFNγ-induced tumor immune escape, although it could be adapted to the limited number of NSCLC patients.
Symptom trajectories during chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and the function of prolonging low dose dexamethasone in promoting enhanced recovery after chemotherapy
- Pages: 783-795
- First Published: 25 January 2021
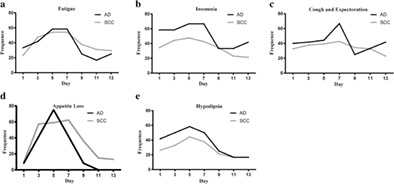
In our study, we identified the top five most frequently reported symptoms within a chemotherapy treatment cycle which were fatigue, insomnia, cough and sputum, appetite loss and hypodipsia. After intervention, we found that dexamethasone, with good tolerance, alleviated the symptom burden and improved the health-related quality of life (HRQOL) of patients.
Identification of small proline-rich protein 1B (SPRR1B) as a prognostically predictive biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma by integrative bioinformatic analysis
- Pages: 796-806
- First Published: 26 January 2021
Primary mediastinal germ cell tumors - A retrospective analysis of >30 years of experience in a single institution
- Pages: 807-813
- First Published: 27 January 2021
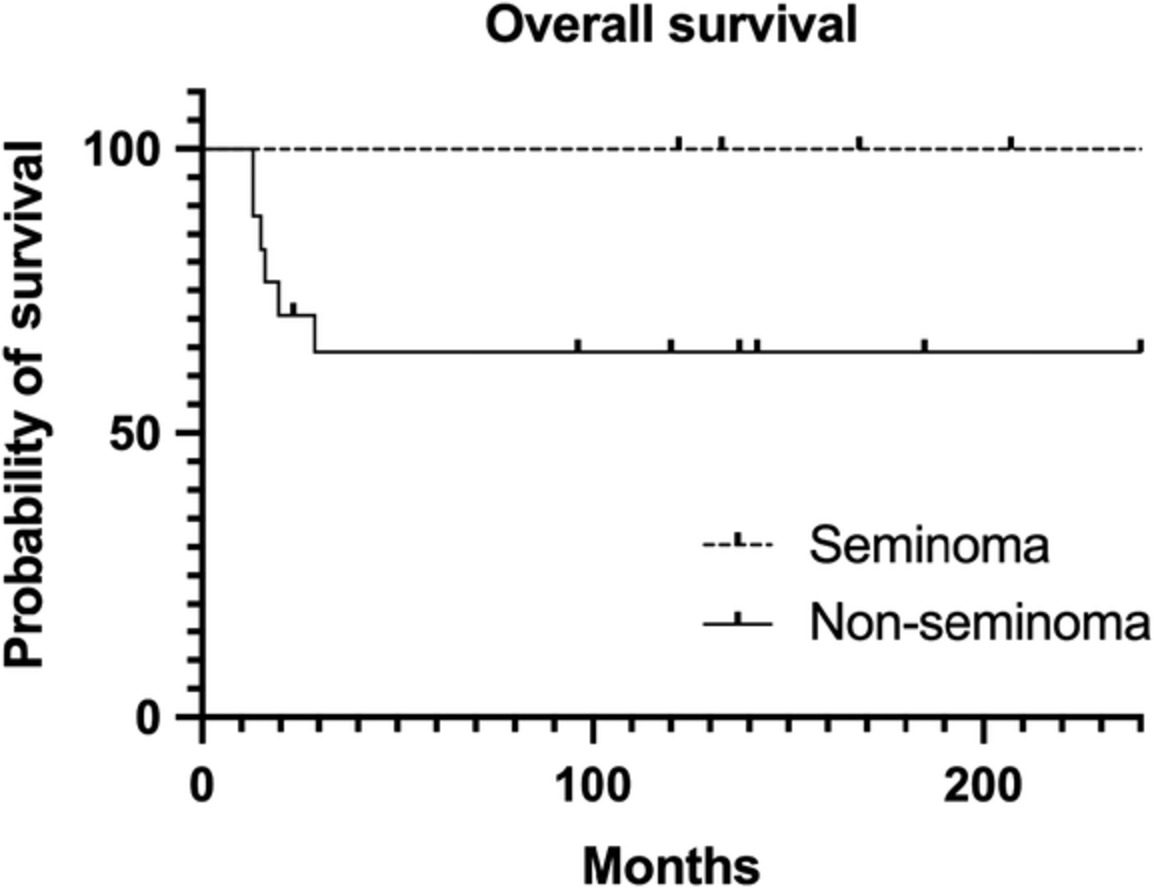
The clinical profiles and treatment outcomes of 22 patients (mean age of 29 years) with primary mediastinal germ cell tumors (GCT) treated at our hospital between 1983 and 2019 were examined in this retrospective study. The calculated 10-year overall survival rates were 100% in mediastinal seminoma and 64.7% in NSGCT. The clinical manifestations and biological behaviors during and/or after chemotherapy were complex and varied.
Clinical outcomes and radiation pneumonitis after concurrent EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and radiotherapy for unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 814-823
- First Published: 27 January 2021
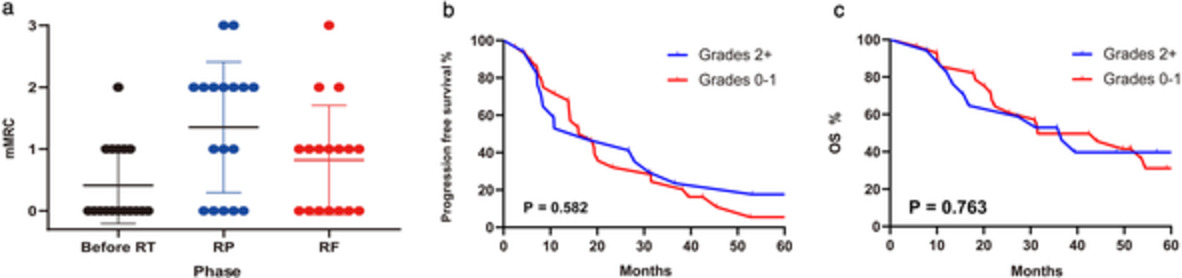
Our study evaluated the outcomes and radiation pneumonitis which occurred in patients following EGFR-TKI during interval radiotherapy. The results of combined EGFR-TKI and radiotherapy showed favorable survival in EGFR-mutant patients with inoperable stage III NSCLC, a higher incidence of mild to moderate radiation pneumonitis was observed and no grades 4-5 adverse events occurred.
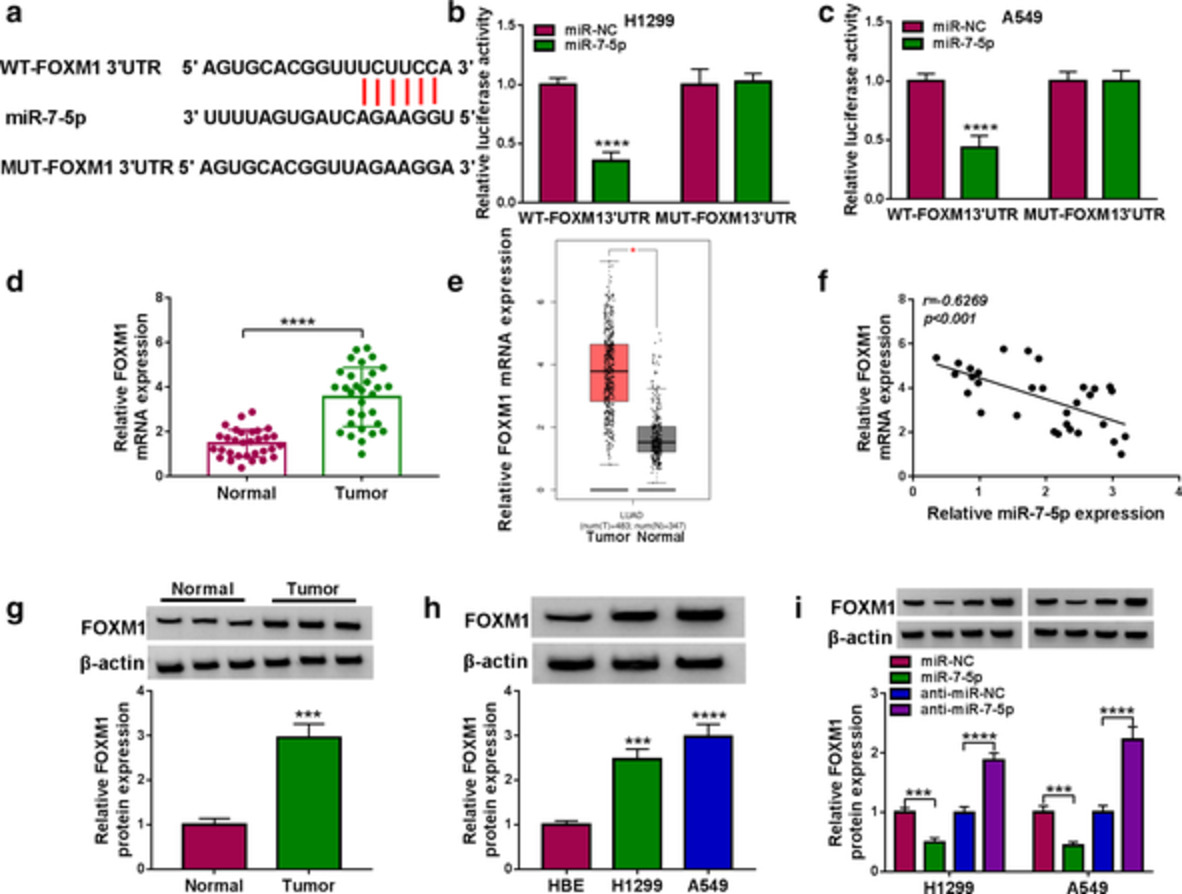
Propofol suppresses lung cancer tumorigenesis by modulating the circ-ERBB2/miR-7-5p/FOXM1 axis
- Pages: 824-834
- First Published: 27 January 2021
Preoperative predictors of restoration in quality of life after surgery for lung cancer
- Pages: 835-844
- First Published: 28 January 2021
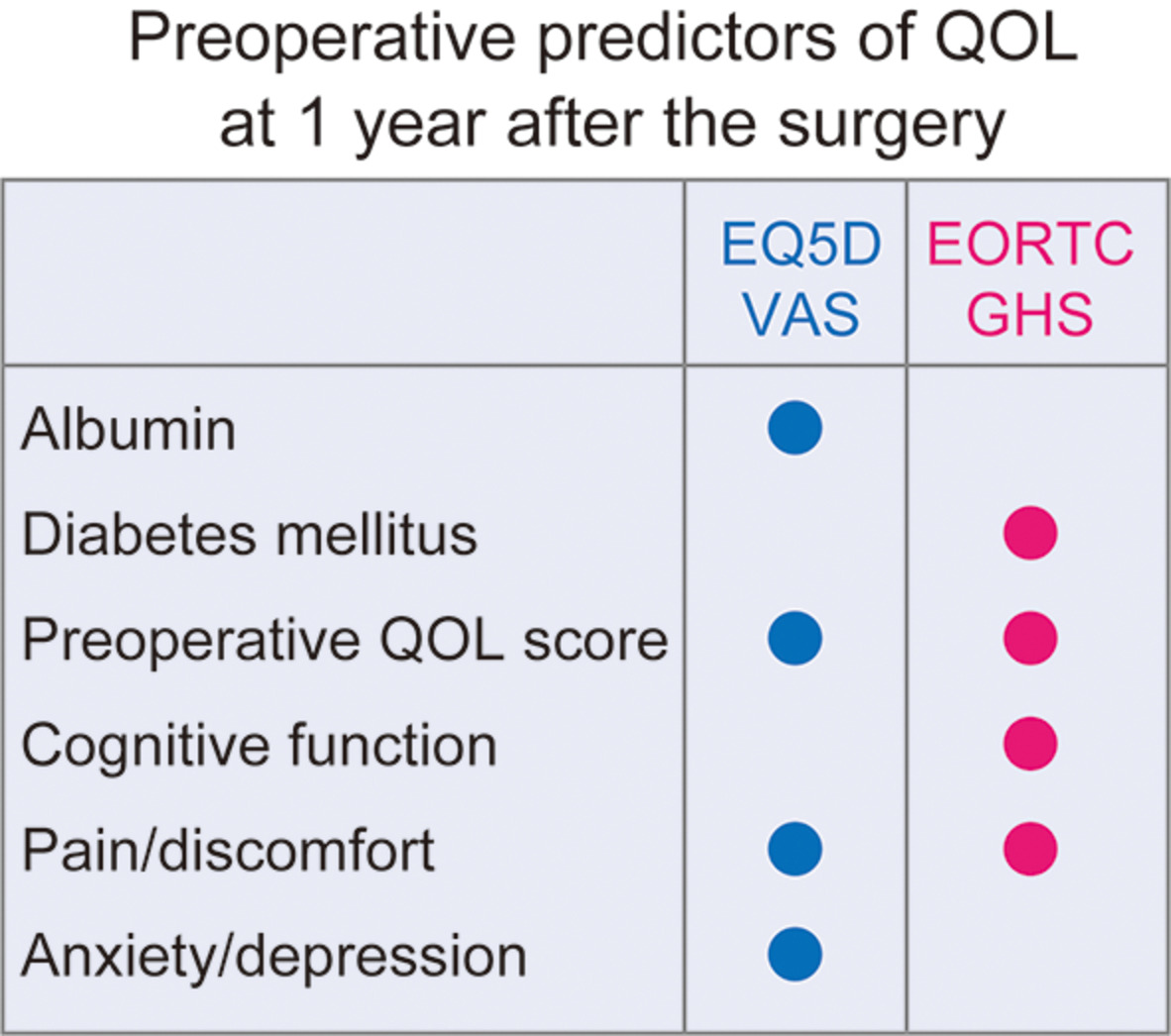
We investigated the preoperative predictors of QOL in surgical patients with lung cancer. General health status/QOL was measured by EQ-5D VAS and EORTC GHS scores. Multivariable linear regression analyses were used. Although each QOL measure detected some preoperative predictors, preoperative pain was a common predictor in both, one year after surgery. Predictors detected in this study were possible targets for patient/survivor care.
Prognostic impact of maximum standardized uptake value on 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging of the primary lung lesion on survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study
- Pages: 845-853
- First Published: 29 January 2021
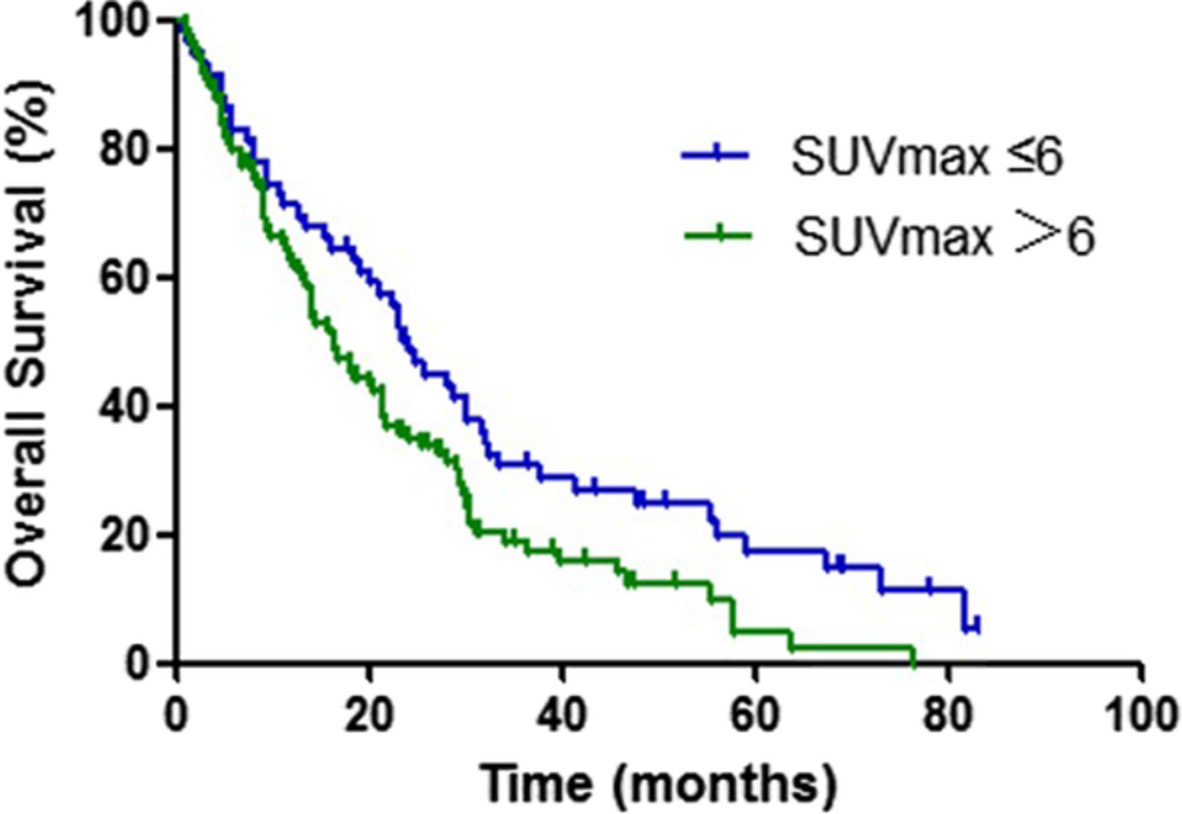
We performed a retrospective analysis of patients with advanced NSCLC who had undergone 18F-FDG PET/CT before systemic treatment between June 2012 and June 2016. The SUVmax of the primary lung lesion on PET/CT is significantly correlated with survival in treatment-naive patients with advanced NSCLC.
A novel technique for preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules using a mixture of tissue adhesive and iohexol under computed tomography guidance: A 140 patient single-center study
- Pages: 854-863
- First Published: 29 January 2021
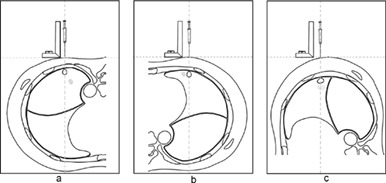
In this study, a technique for preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules with tissue adhesive and iohexol mixture was established and proved to be safe, easy to operate and efficient in clinical practice based on our experience. It is a suitable technique for promotion in localization of pulmonary nodules including multiple pulmonary nodules.
Effectiveness of EGFR-TKI rechallenge immediately after PD-1 blockade failure
- Pages: 864-873
- First Published: 31 January 2021
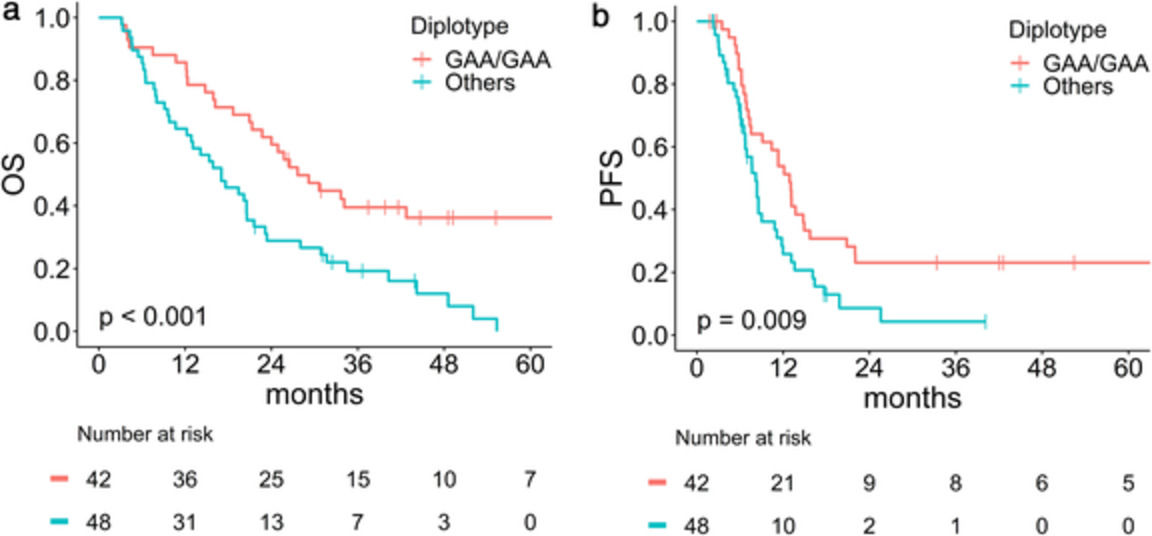
Prognostic significance of genetic variants in GLUT1 in stage III non-small cell lung cancer treated with radiotherapy
- Pages: 874-879
- First Published: 31 January 2021
Smoking status during first-line immunotherapy and chemotherapy in NSCLC patients: A case–control matched analysis from a large multicenter study
- Pages: 880-889
- First Published: 01 February 2021
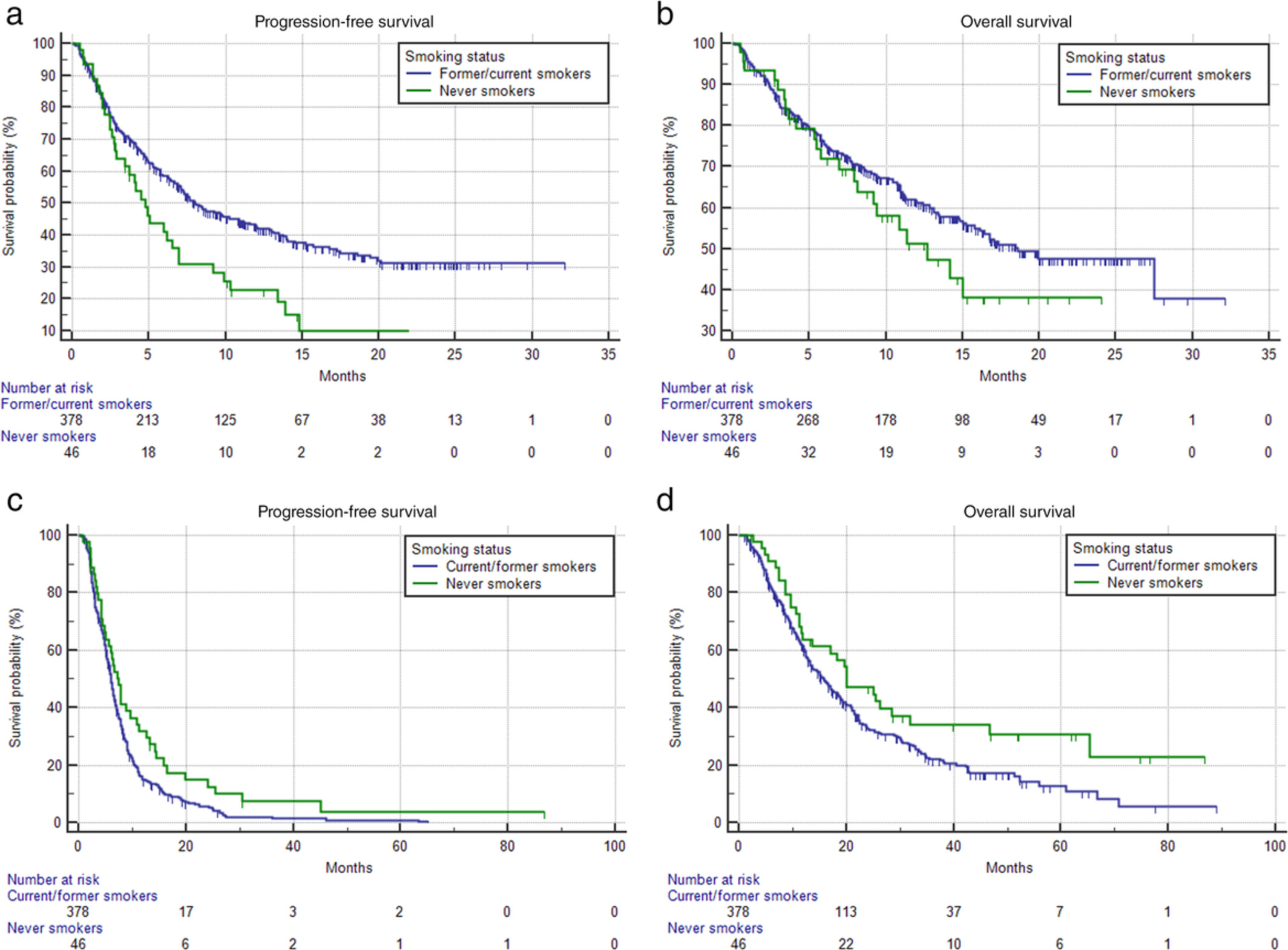
Improved outcome in tobacco smoking NSCLC patients following treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has previously been reported. Little is known regarding this association during first-line immunotherapy in patients with high PD-L1 expression. Clinical outcomes according to the smoking status of two large multicenter cohorts were compared in this study. Smokers with high PD-L1 expression ≥ 50% experienced improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) with first-line pembrolizumab. The opposite trend was found in NSCLC patients treated with first-line platinum-based chemotherapy.
Clinical impact of rebiopsy among patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinoma in a real-world clinical setting
- Pages: 890-898
- First Published: 02 February 2021
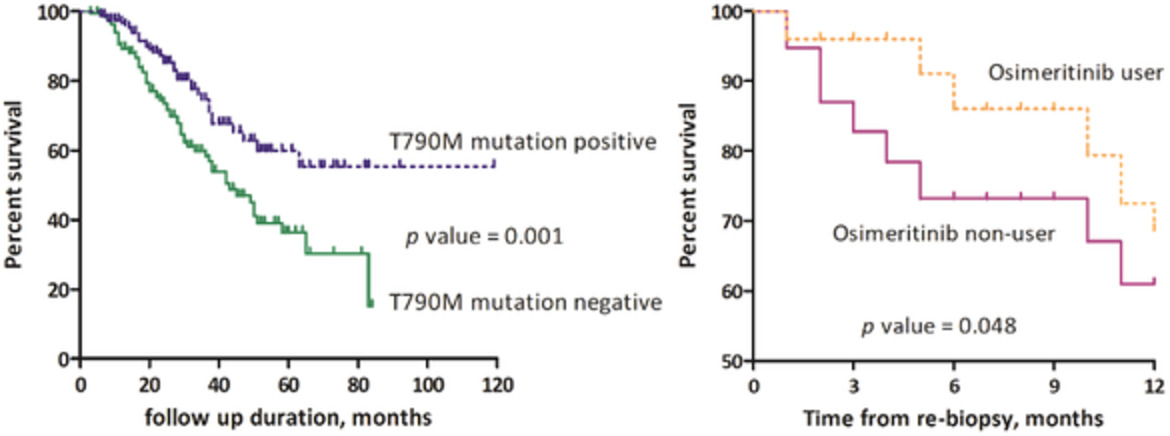
In this multicenter retrospective study, whereas exon 19 deletion, the absence of L858R, previous EGFR-TKI treatment duration and brain metastasis at initial diagnosis were associated with acquired T790M mutation, a previous EGFR-TKI treatment duration was independently associated with acquired T790M mutation. However, the acquired T790M mutation group had improved survival compared to the T790M mutation-negative group. In particular, the osimertinib user group had a better one-year survival than the nonuser group among patients with acquired T790M mutation.
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy as single treatment for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: A single institution analysis
- Pages: 899-905
- First Published: 02 February 2021
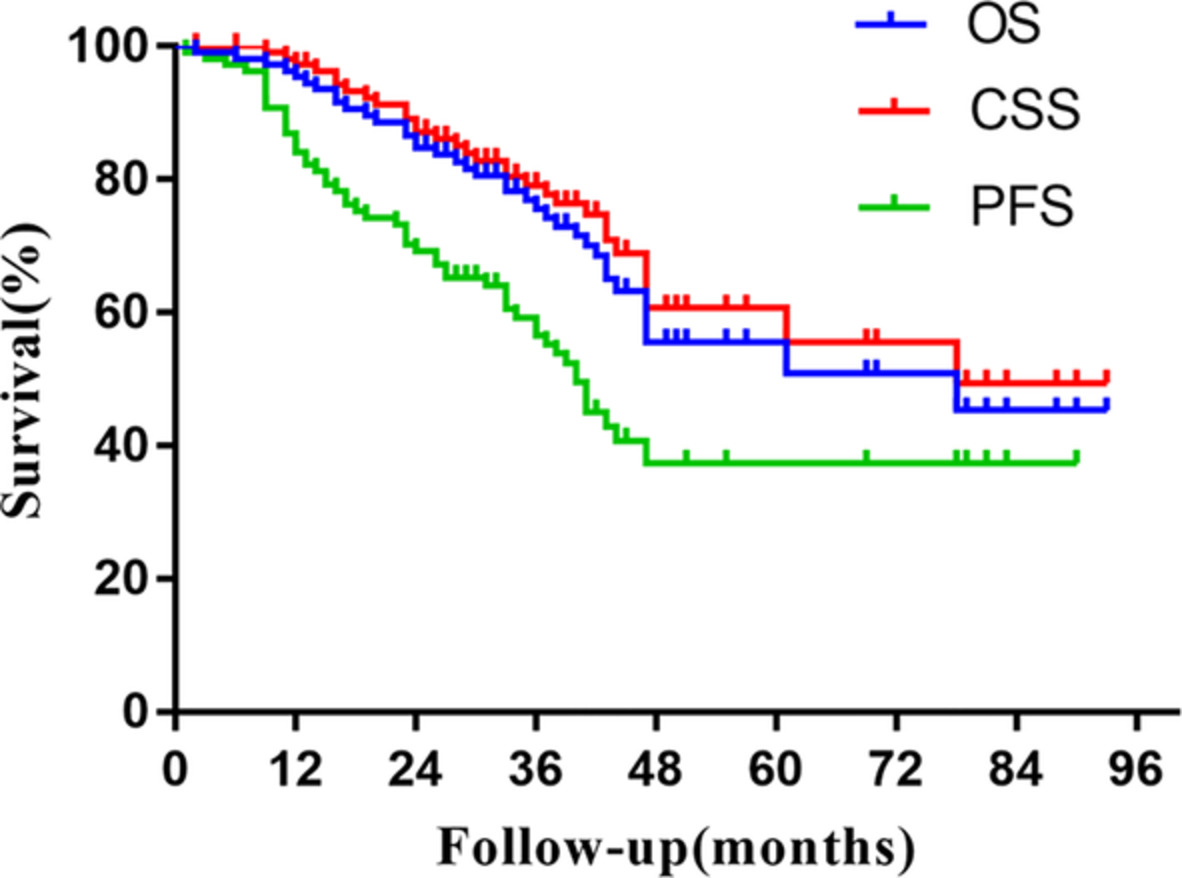
We retrospectively analyzed the survival outcomes and failure patterns of 109 early stage non-small cell lung cancer (ES-NSCLC) patients treated with SABR. The results showed that high survival rates can be achieved in patients with inoperable ES-NSCLC treated with SABR, which confirms previous results. However, among the 109 patients in the study, 45 (41%) failures were observed. Treatment with SABR may not be enough on its own. Prolonged surveillance and adjuvant therapy is needed.
Clinical influence of switching companion diagnostic tests for EGFR-TKs from Therascreen to Cobas v2
- Pages: 906-913
- First Published: 02 February 2021
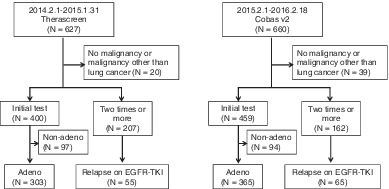
We examined the influence of changing the EGFR test among target PCR methods in 1228 patients in total. The detection rate of EGFR mutations was similar while the detection pattern for EGFR subtype mutations was slightly different between the two tests. In the future, switching companion diagnostic (CDx) tests from target PCR methods to NGS-based methods may lead to obvious changes in clinical practice.
The landscape of small cell lung cancer metastases: Organ specificity and timing
- Pages: 914-923
- First Published: 03 February 2021
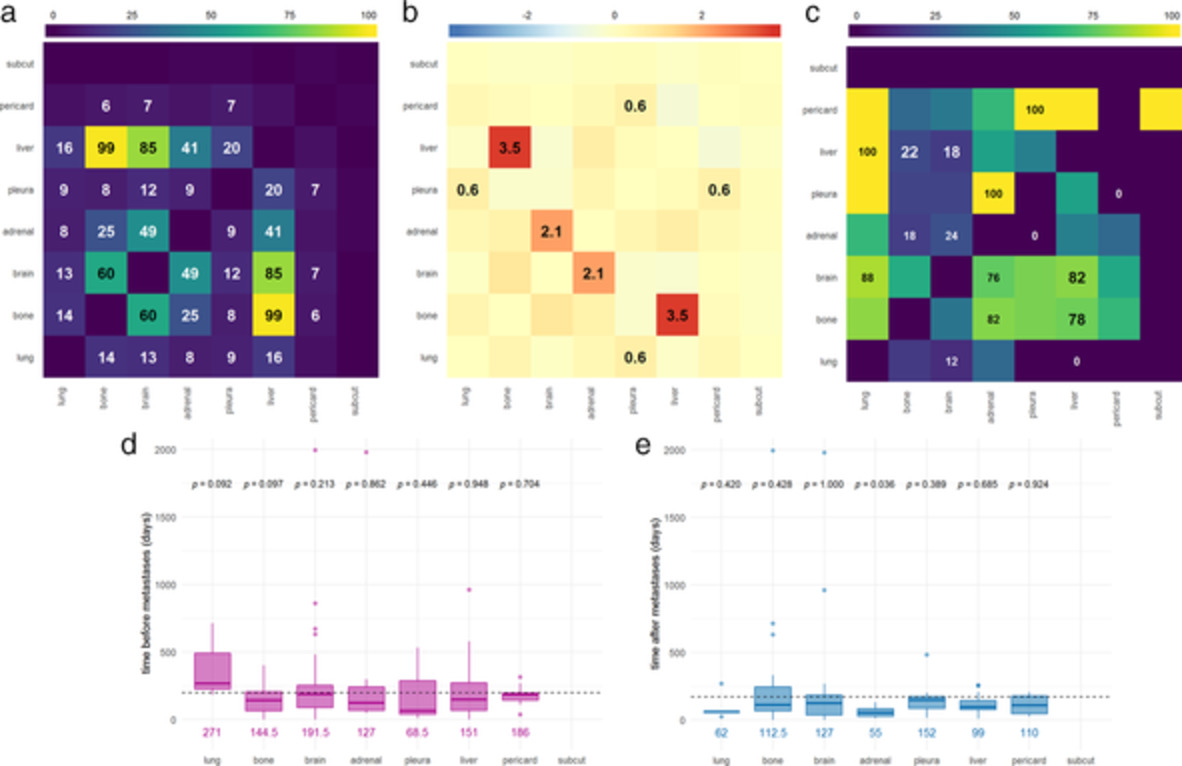
In this study, our aim was to examine the organ specificity and timing of blood-borne metastases in a comprehensive large cohort of Caucasian SCLC patients (n=1009). We report here that the onset of bone, brain, and pericardial metastases are late events, whereas adrenal gland and liver metastases occur earlier during tumor progression. We also show that several metastatic sites, such as bone and liver, and brain and adrenal gland intend to co-metastasize preferentially. Of note, however, no significant associations were observed with regards to the timing and organ preference of distant metastases when comparing central and peripheral primary tumors.
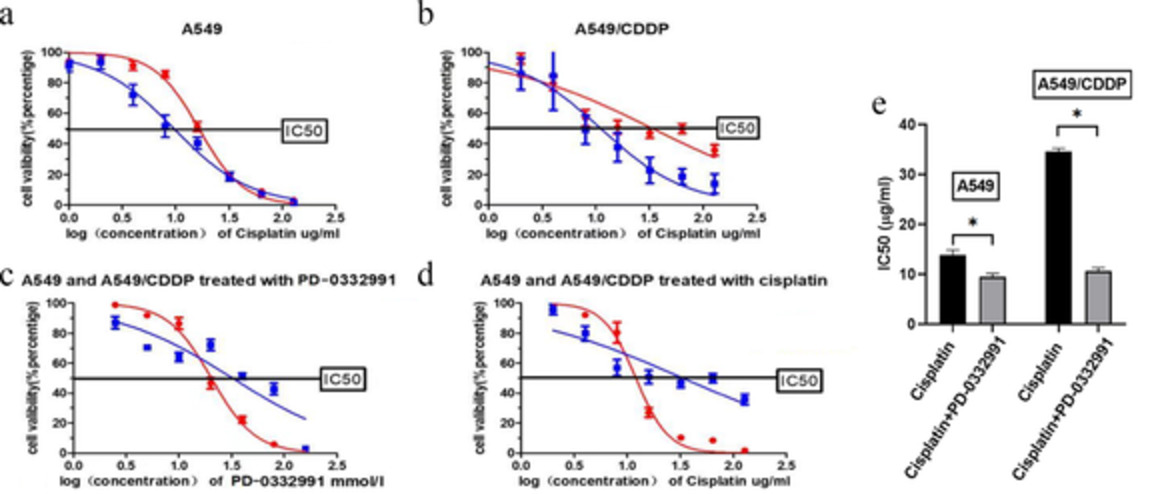
PD-0332991 combined with cisplatin inhibits nonsmall cell lung cancer and reversal of cisplatin resistance
- Pages: 924-931
- First Published: 03 February 2021
MicroRNA-210 targets FBXO31 to inhibit tumor progression and regulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and EMT in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 932-940
- First Published: 03 February 2021
miR-210 serves as an anti-ESCC miR via down-regulation of FBXO31 and regulation of EMT and Wnt signaling
Predictive factors of recurrence after resection of subsolid clinical stage IA lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 941-948
- First Published: 07 February 2021
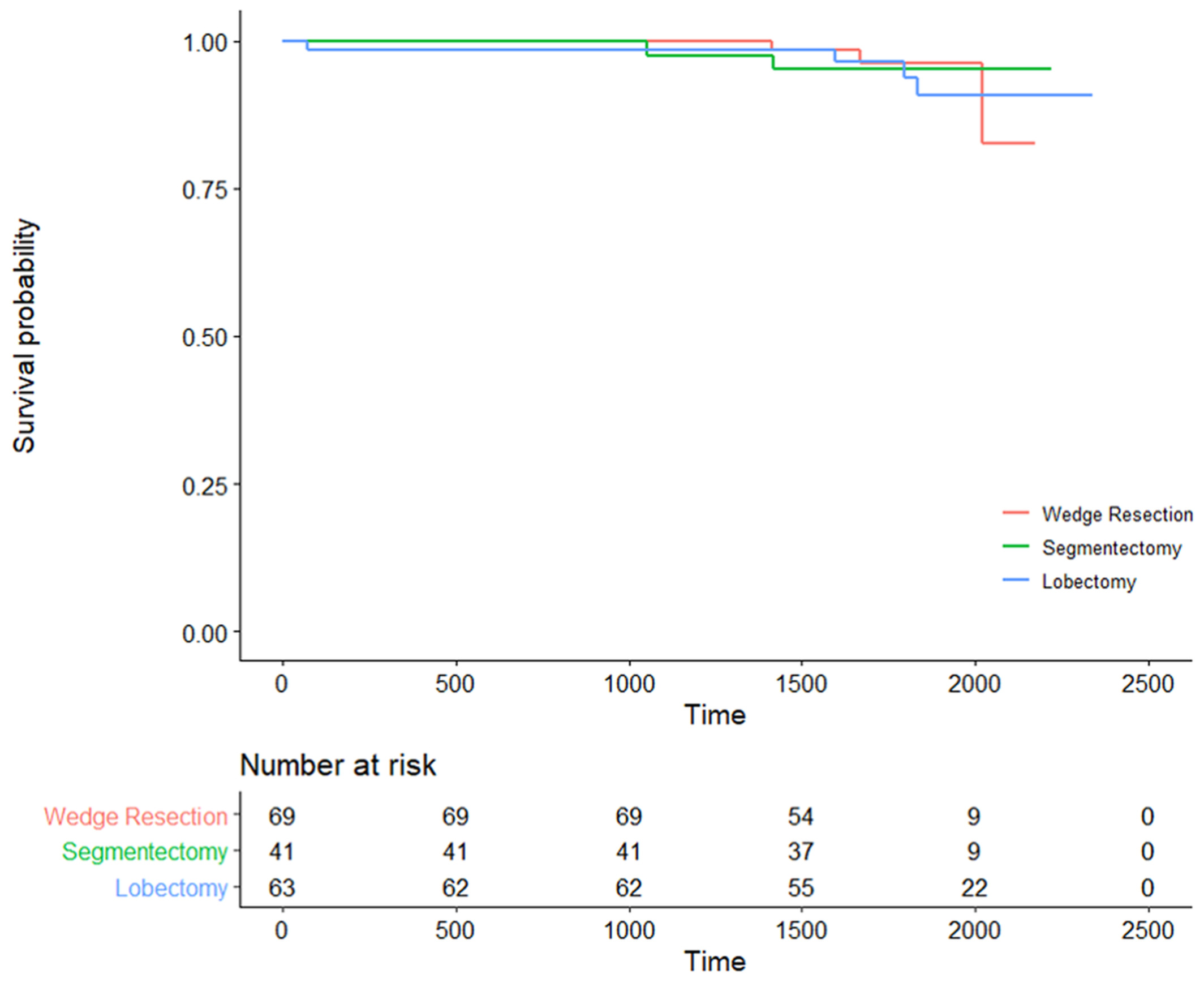
Highlights
- This study aimed to investigate risk factors related to recurrence in patients with clinical stage IA subsolid cancer who underwent either lobectomy or sublobar resection.
- The main results showed excellent surgical outcomes regardless of surgical procedure, subsolid nodule subtype and solid component size.
- Our results validate subjects eligible for sublobar resection recommended by the NCCN 2020 guideline and provide surgeons with a rationale for choosing a less extensive surgical alternative for clinical stage IA adenocarcinomas observed as subsolid nodules without compromising patient outcomes.
Effect of cyclooxygenase inhibitor use on immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 949-957
- First Published: 09 February 2021
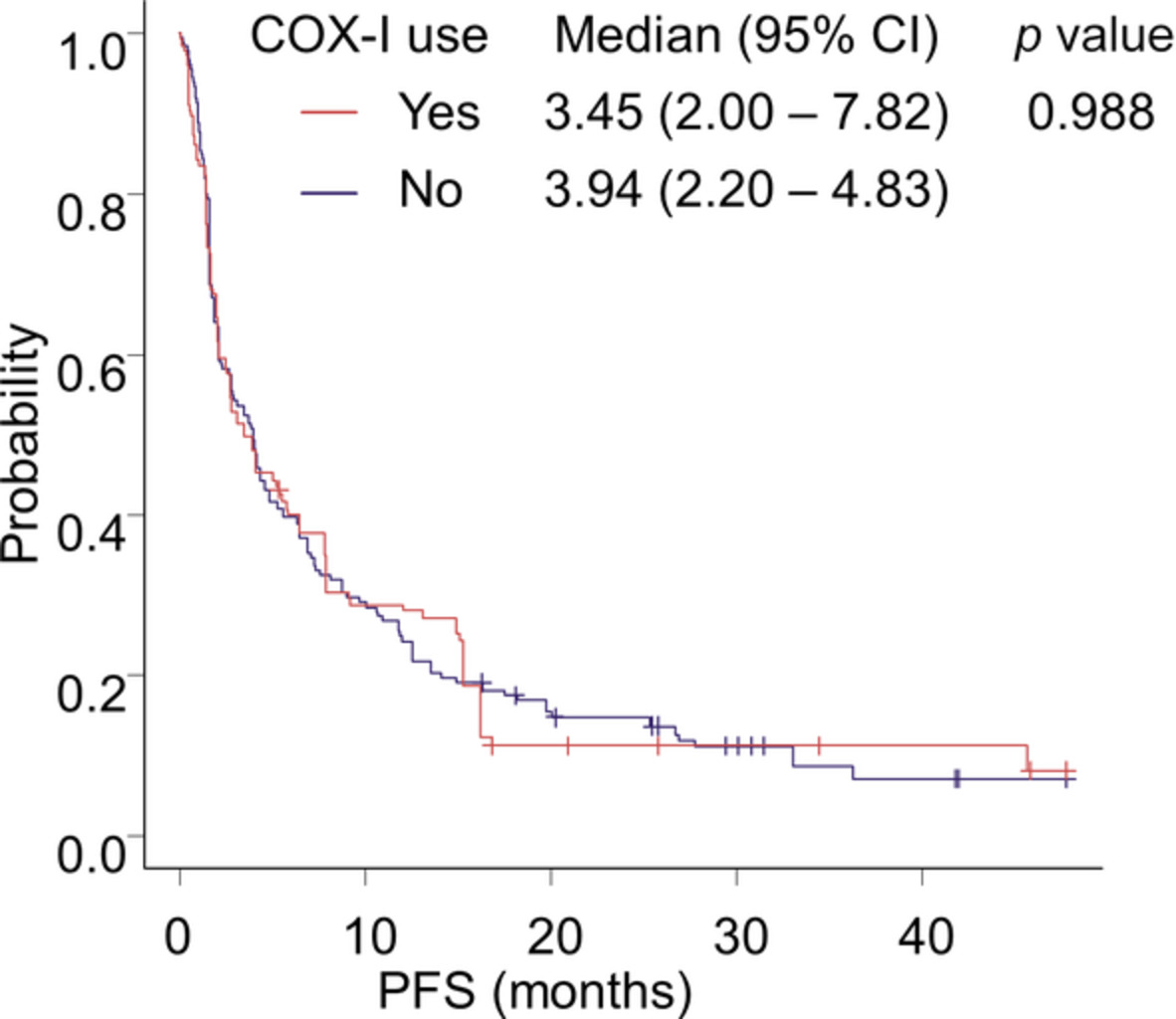
We retrospectively evaluated the relationship between cyclooxygenase inhibitor (COX-I) use and the efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We adjusted with as many factors as possible by inverse probability weighting estimated by propensity score. After adjustment, there was no additional or negative impact of COX-I use on the efficacy of ICIs in NSCLC.
CASE REPORTS
A rare case of primary solitary endobronchial plasmacytoma
- Pages: 958-961
- First Published: 27 January 2021
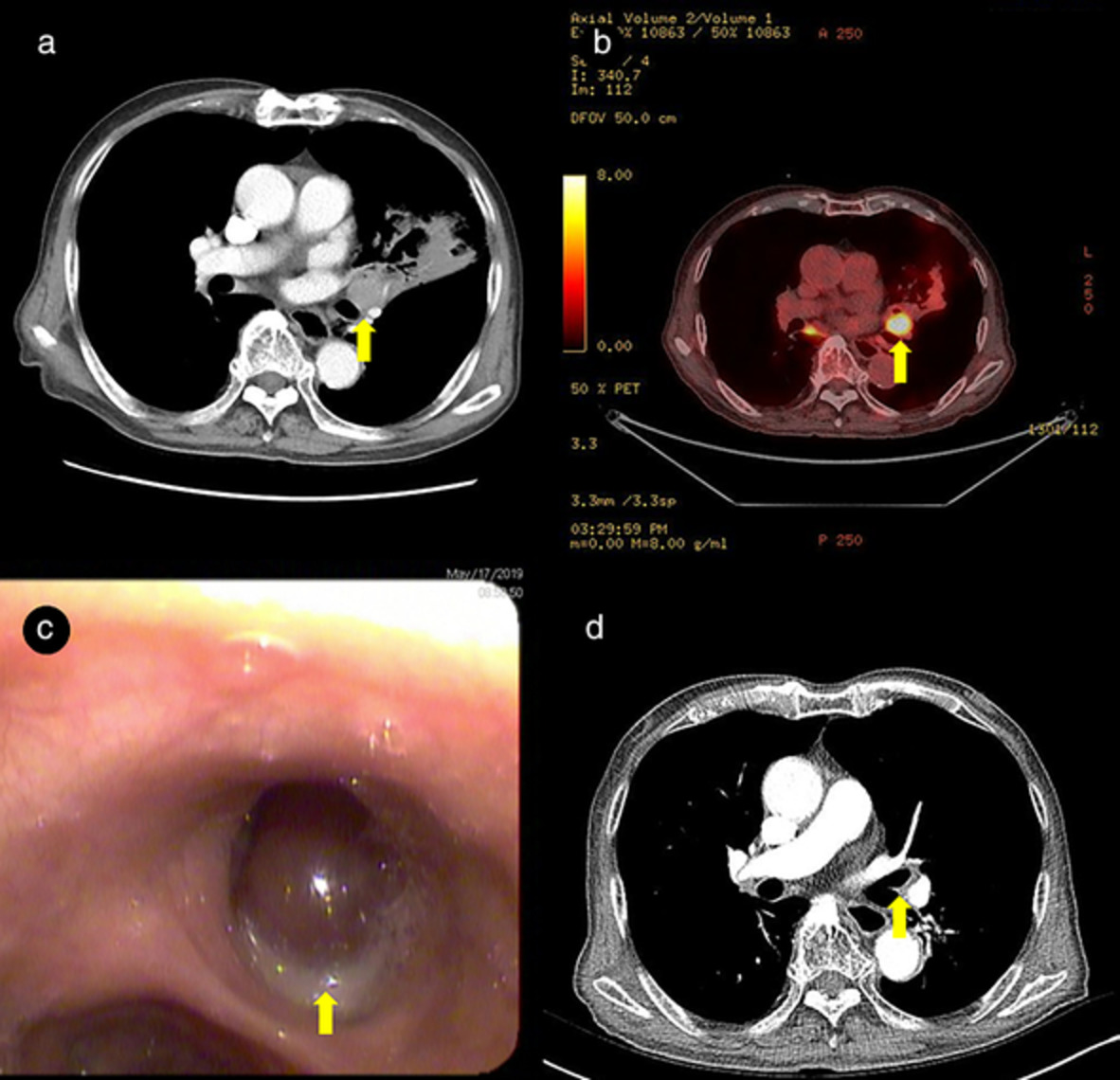
We present the case of an 86-year-old male ex-smoker who visited our outpatient clinic for an endobronchial mass in the left upper lobe of the lung. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy revealed a protruding mass in the left upper lobar bronchus; based on the bronchoscopic biopsy findings, a primary solitary endobronchial plasmacytoma was diagnosed.
ALK rearrangements as mechanisms of acquired resistance to osimertinib in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 962-969
- First Published: 27 January 2021
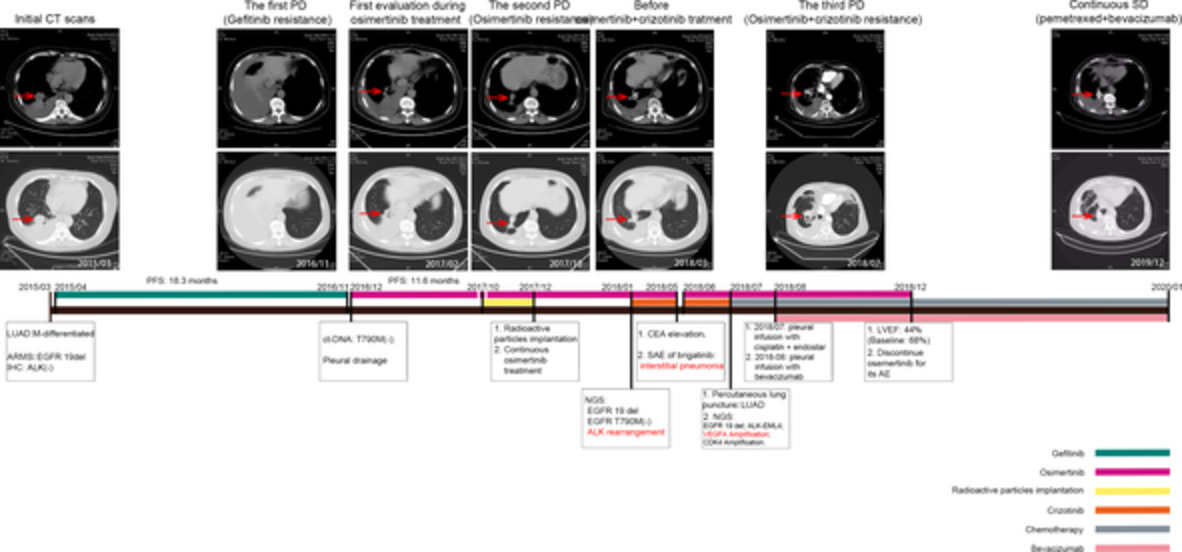
ALK rearrangement probably serves as a rare molecular mechanism underlying acquired resistance to osimertinib. The dual TKI treatment targeting EGFR and ALK might benefit osimertinib-resistant NSCLC patients induced by ALK rearrangement. VEGFA amplification might contribute to acquired resistance to combined osimertinib and crizotinib therapy, and chemotherapy plus bevacizumab might be an optimal treatment strategy.
Precise resection of multiple pulmonary nodules using a three-dimensional reconstruction model: A case report
- Pages: 970-973
- First Published: 27 January 2021
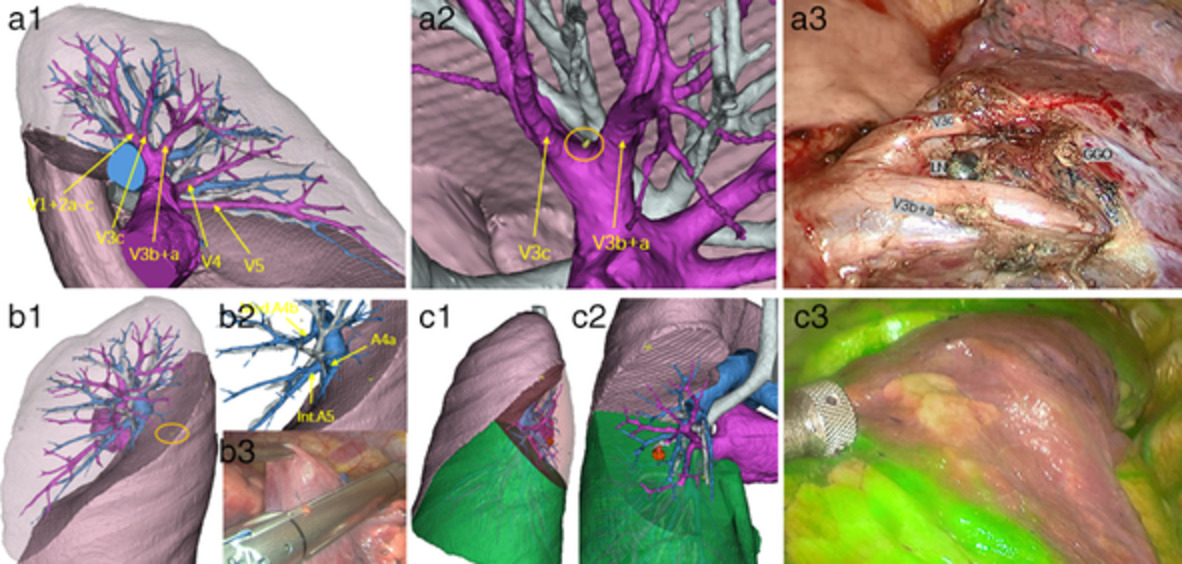
In this case, there was a very special small pulmonary nodule in the anterior segment of the right upper lung. Using 3D reconstruction, as it was difficult to carry out a conventional pulmonary wedge resection, we determined that the nodule was located exactly between the roots of V3c and V3b+a. Therefore, we used electrocautery to strip the lung tissue along the boundary of V3c and V3b+a during the operation, and successfully removed the nodule.
Malignant pleural mesothelioma in a patient with pneumothorax: A cumbersome subtype both clinically and pathologically
- Pages: 974-977
- First Published: 02 February 2021
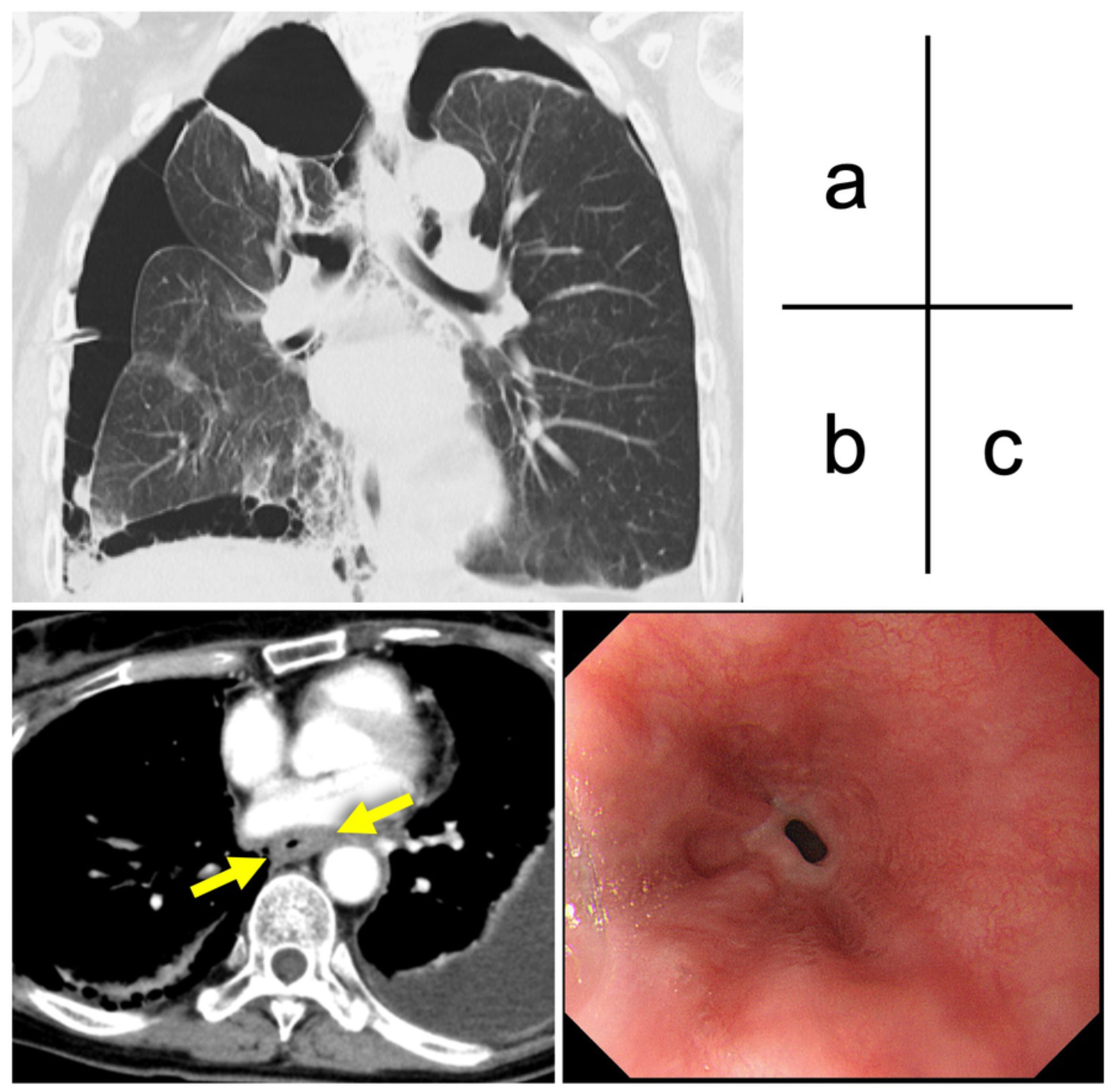
A 62-year-old woman with a surgical history of recurrent bilateral pneumothorax was admitted to our hospital with severe dysphagia. Under a tentative diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM), chemotherapy was instituted but the patient died of severe exhaustion. Autopsy was performed and a final diagnosis of MPM was made.
Dramatic intracranial response to tepotinib in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring MET exon 14 skipping mutation
- Pages: 978-980
- First Published: 03 February 2021
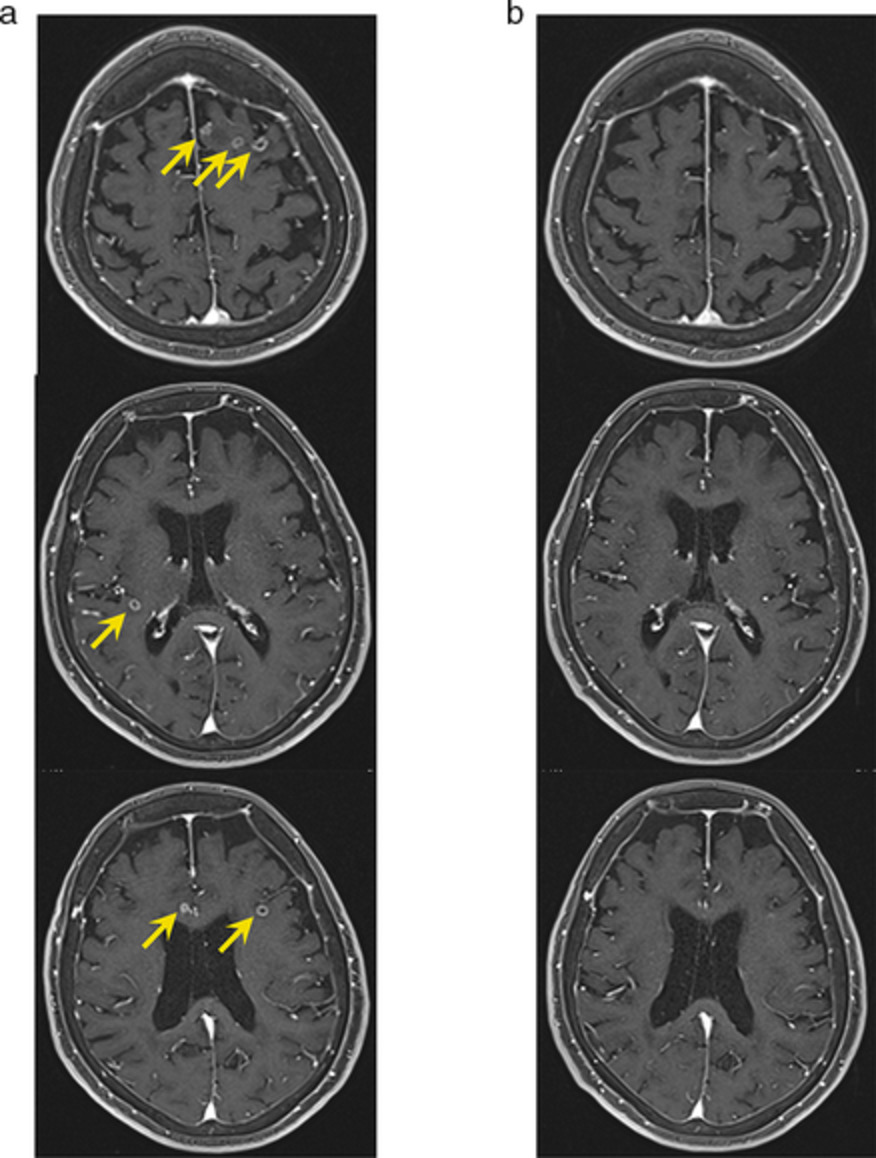
In the previous clinical trials, patients with symptomatic brain metastases (BMs) from lung cancer harboring METex14del were excluded. We report a case of dramatic intracranial response to tepotinib in a patient with symptomatic BMs from lung adenocarcinoma harboring METex14del. Tepotinib might be a therapeutic option for lung cancer patients with symptomatic multiple BMs harboring METex14del.
Pleural mesothelioma: When echo-endoscopy (EUS-B-FNA) leads to diagnosis in a minimally invasive way
- Pages: 981-984
- First Published: 03 February 2021
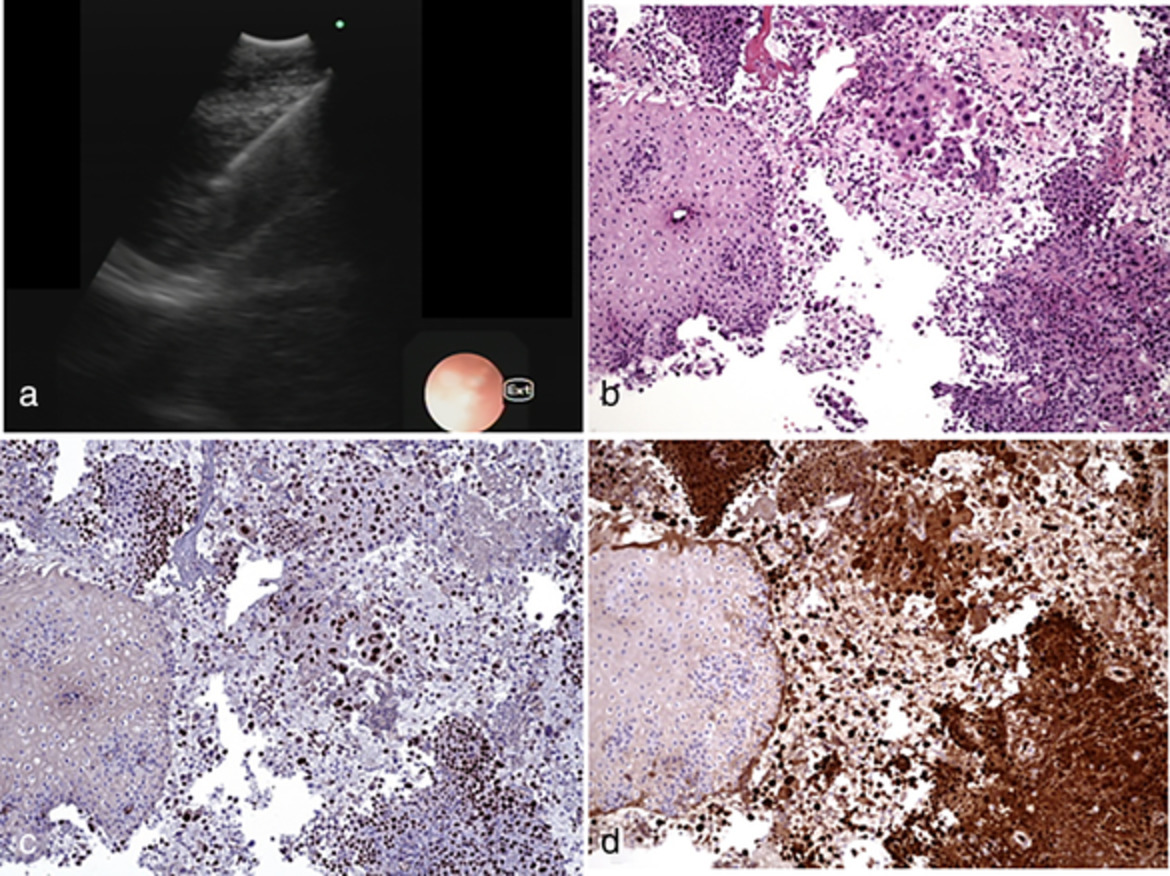
We present a rare case of MPM successfully diagnosed via EUS-B-FNA. The use of EUS-B-FNA and EBUS-TBNA for pleural sampling is unusual because the standard approach to pleuropathy is a pleural effusion analysis followed by thoracoscopy or image-guided pleural biopsy. However, when one or more pleural lesions are near to the central airway or esophagus, EUS-B FNA and/or EBUS-TBNA should be considered and one of them chosen because of their simplicity and safety.
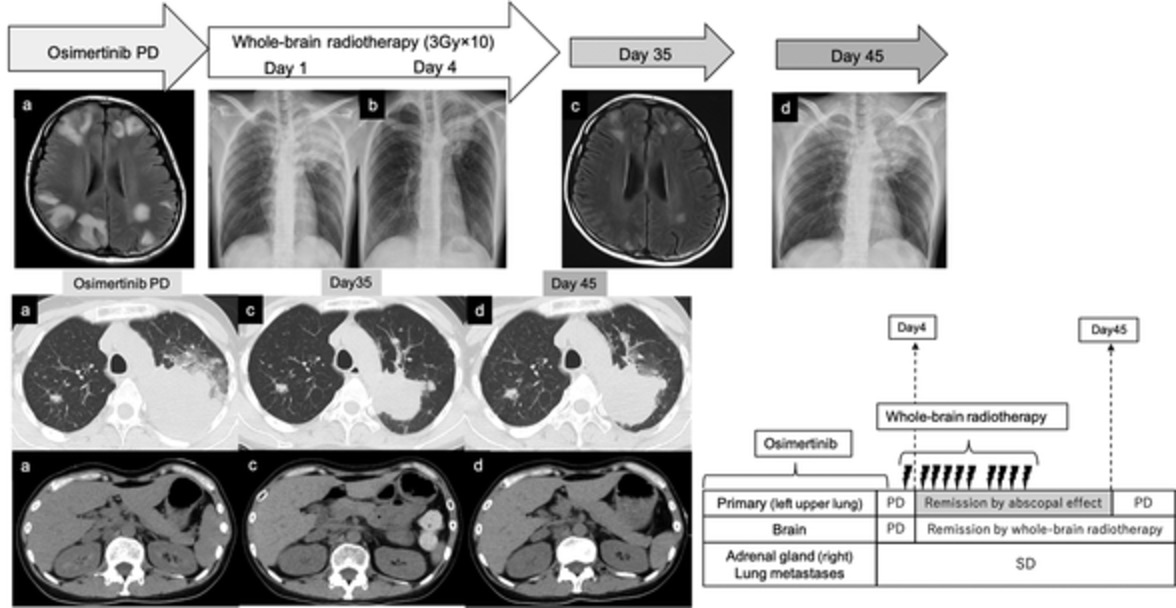
Reproducible abscopal effect in a patient with lung cancer who underwent whole-brain irradiation and atezolizumab administration
- Pages: 985-988
- First Published: 03 February 2021
Long-term response to afatinib in an elderly patient with uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 989-992
- First Published: 03 February 2021
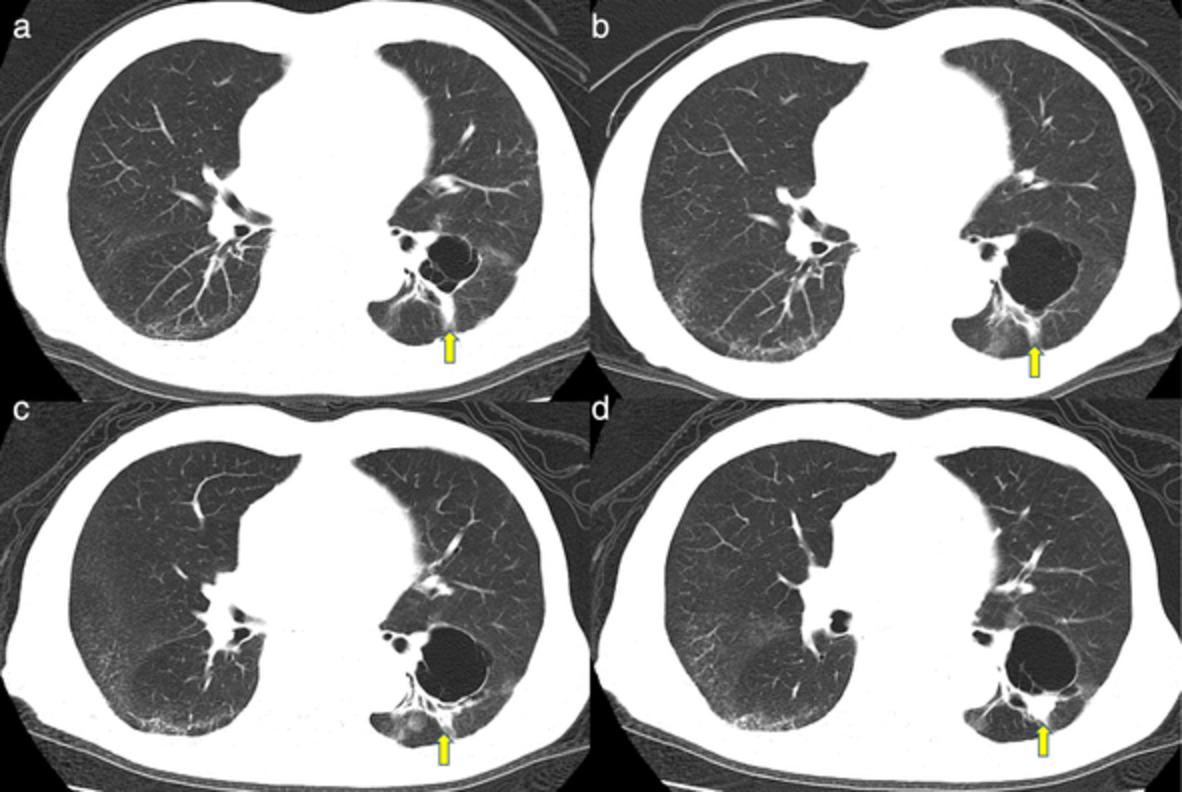
A large number of compound mutations have been observed in patients with uncommon EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC. Compound mutation-induced cells are most susceptible to afatinib, suggesting the efficacy of afatinib in clinical practice. Afatinib may be administered to elderly patients with appropriate dose adjustments
Lipolymph node presenting as a pulmonary nodule: A case report
- Pages: 993-994
- First Published: 10 February 2021
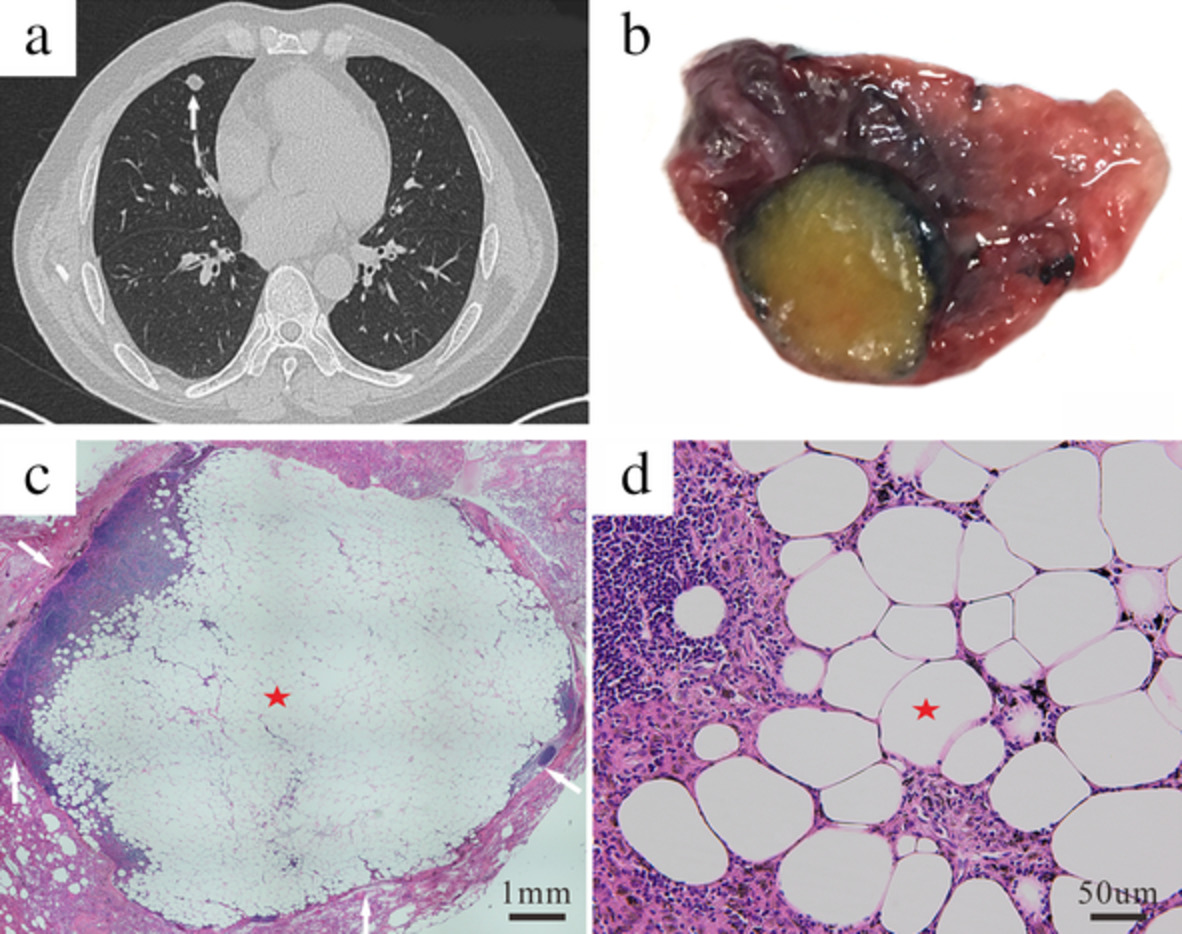
Lipolymph nodes are defined as enlargement of lymph nodes caused by abnormal accumulation of fat, due to mature, benign adipocytes within lymph node capsules. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of a lipolymph node in the lung. Although rare and benign, lipolymph nodes should be considered in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary nodules.