Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
MINI REVIEW
Is video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy associated with higher overall costs compared with open surgery? Results of best evidence topic analysis
- Pages: 567-579
- First Published: 05 February 2021
- Is video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy associated with higher overall costs compared with open surgery? A review of the literature until May 2020 was performed, and 20 studies provided the most applicable evidence to evaluate this issue.
- Thoracoscopic lobectomy was associated with higher operative costs than open lobectomy, but lower indirect costs. It translated into lower overall costs for thoracoscopic than for open lobectomy in 10 studies, similar in seven, and higher in three studies.
- The worry that thoracoscopic lobectomy might be associated with increased total cost is thus not warranted, and should not be used as an excuse against the use of thoracoscopy in surgery for early stage lung cancers.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Comprehensive genomic profiling of Brazilian non-small cell lung cancer patients (GBOT 0118/LACOG0418)
- Pages: 580-587
- First Published: 13 December 2020
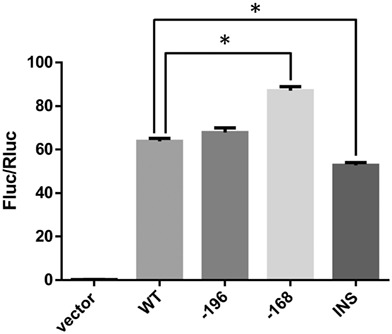
Two polymorphic mutations in promoter region of DNA polymerase β in relatively higher percentage of thymic hyperplasia patients
- Pages: 588-592
- First Published: 13 December 2020
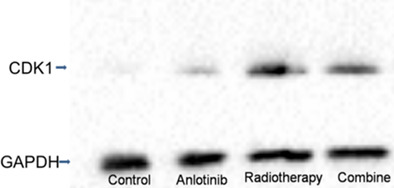
In vitro studies of H520 cell cycle and apoptosis by anlotinib combined with radiotherapy
- Pages: 593-602
- First Published: 12 January 2021
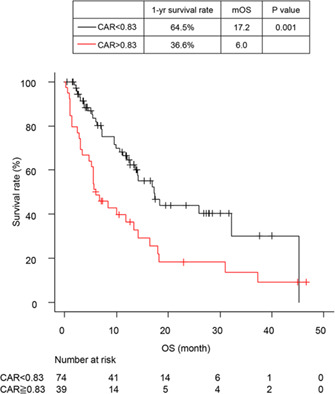
Clinical utility of the C-reactive protein:albumin ratio in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with nivolumab
- Pages: 603-612
- First Published: 12 January 2021
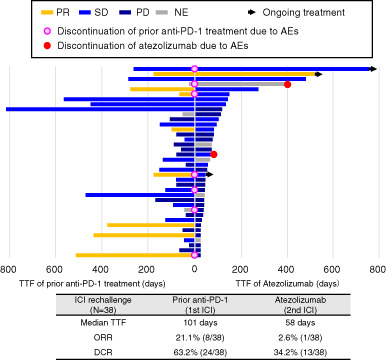
Real-world efficacy of atezolizumab in non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter cohort study focused on performance status and retreatment after failure of anti-PD-1 antibody
- Pages: 613-618
- First Published: 15 January 2021
Tumor LAG-3 and NY-ESO-1 expression predict durable clinical benefits of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 619-630
- First Published: 17 January 2021
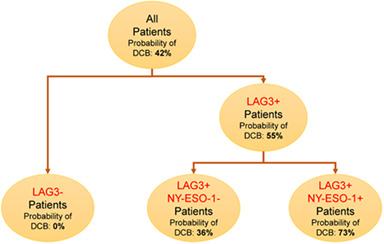
NY-ESO-1 or LAG-3 expression in patients with high PD-L1 expression was significantly associated with a favorable OS and PFS for immunotherapy in NSCLC. Moreover, LAG-3 and NY-ESO-1 co-expression was considered as a predictable marker for survival outcome and LAG-3 showed a good negative predictive value.
HSP90 inhibition overcomes EGFR amplification-induced resistance to third-generation EGFR-TKIs
- Pages: 631-642
- First Published: 20 January 2021
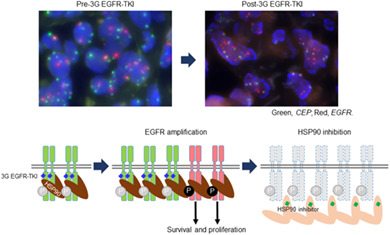
Third-generation EGFR-TKIs overcome EGFR T790M-meditated resistance. However, amplified EGFR confers resistance to third-generation EGFR-TKIs. Inhibiting HSP90, a chaperon for EGFR, suppresses the proliferation of EGFR-amplified cells by degrading EGFR in vitro, providing a preclinical rationale for the use of HSP90 inhibitors to overcome the EGFR amplification-meditated resistance.
Crizotinib for recurring non-small-cell lung cancer with EML4-ALK fusion genes previously treated with alectinib: A phase II trial
- Pages: 643-649
- First Published: 20 January 2021
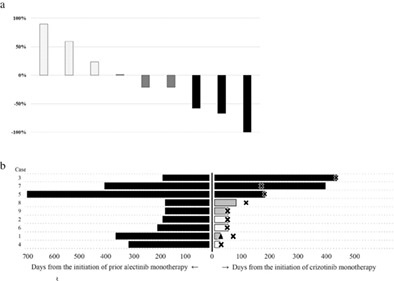
We evaluated the efficacy and safety of crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer refractory to alectinib. We included nine patients and stipulated an overall response rate (ORR) of 50% and a lower limit of interest of 15%. The ORR was 33.3%, failing to meet the criteria. However, the treatment showed efficacy alongside tolerable adverse effects.
HN1L promotes invasion and metastasis of the esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 650-658
- First Published: 20 January 2021
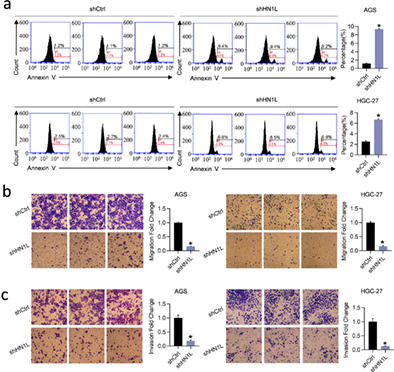
This study investigated the expression level of HN1L in AEG and adjacent nontumor tissues and further explored the correlation between HN1L expression and clinical parameters, confirming the regulatory effect of HN1L on the malignant proliferation of AEG. We found that knockdown of HN1L could effectively inhibit tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis, which indicates that HN1L may be a potential therapeutic target for AEG patients.
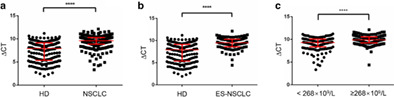
Tumor-educated platelet SNORD55 as a potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 659-666
- First Published: 21 January 2021
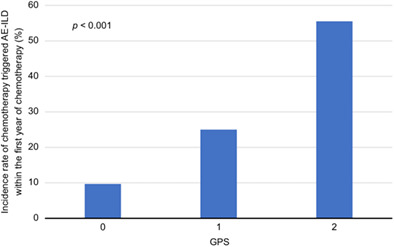
Glasgow Prognostic Score predicts chemotherapy-triggered acute exacerbation-interstitial lung disease in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 667-675
- First Published: 21 January 2021
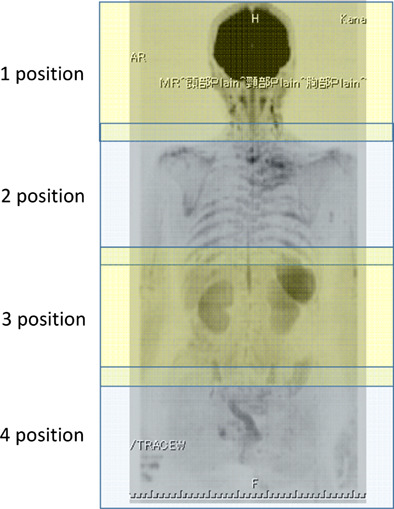
Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background suppression (DWIBS) is effective and economical for detection of metastasis or recurrence of lung cancer
- Pages: 676-684
- First Published: 21 January 2021
CASE REPORTS
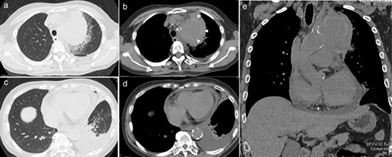
Ruptured pseudoaneurysm of the thoracic aorta mimicking lung cancer: A case report
- Pages: 685-689
- First Published: 09 January 2021
Early-onset interstitial pneumonitis in a patient with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with crizotinib and osimertinib
- Pages: 690-692
- First Published: 12 January 2021
Both crizotinib and osimertinib had an adverse effect of interstitial pneumonitis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment. Here, we report a 60-year-old male patient with advanced non-small cell lung cancer resistant to osimertinib. Crizotinib was used in combination with osimertinib due to elevated mesenchymal epithelial transition (MET) copy number amplification, but an early-onset interstitial pneumonitis occurred within two days.
Coexistence of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma and invasive adenocarcinoma: Gene mutation analysis
- Pages: 693-698
- First Published: 14 January 2021
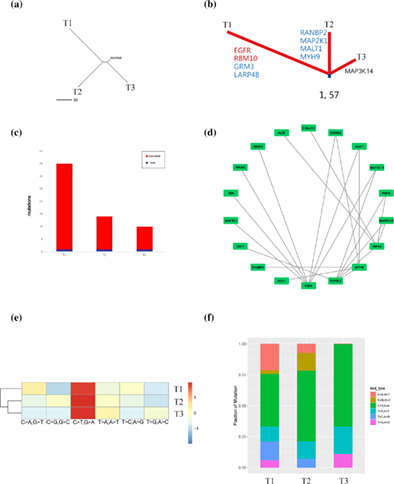
We analyzed the origin and evolution of lung adenocarcinoma based on the WES results of MPLC in one individual. Analysis of the WES results reflects a progressive genomic evolution at the single nucleotide level, which we believe supports the lung adenocarcinoma model from AAH to MIA and ADC. Meanwhile, we explored possible potential driver genes and therapeutic targets.
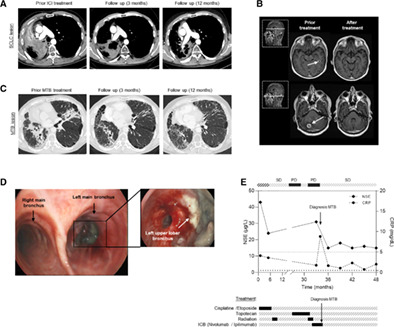
Long-term remission of small cell lung cancer after reactivation of tuberculosis following immune-checkpoint blockade: A case report
- Pages: 699-702
- First Published: 17 January 2021
How far will minimally invasive thoracic surgery go? Uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic lingulectomy with 1 cm incision complicated by a mediastinal lingual artery: A case report
- Pages: 703-706
- First Published: 18 January 2021
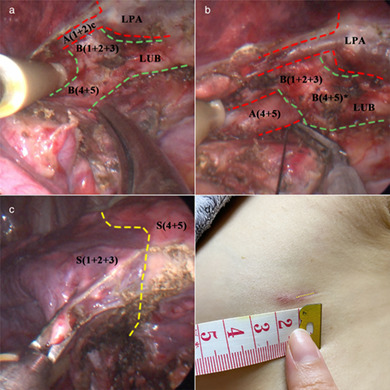
This is a report of a 36-year-old female with a ground-glass nodule in the left lingual segment determined on computed tomography (CT) who successfully underwent 1 cm incision uniportal thoracoscopic lingulectomy. This procedure is technically safe and feasible in selected patients and produces better cosmetic results than traditional thoracoscopic surgery.
Tegafur-uracil-induced pericardial effusion during adjuvant chemotherapy for resected lung adenocarcinoma: A case report
- Pages: 707-710
- First Published: 18 January 2021
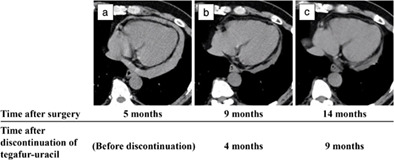
This is a rare case report of tegafur-uracil-induced pericardial effusion that mimics a malignant pericardial effusion in a patient with primary lung cancer. In cases of pericardial effusion without symptoms and no suspicious metastatic lesions in other organs, we should be concerned about tegafur-uracil-induced pericardial effusion, and short-term follow-up after discontinuation of tegafur-uracil should be recommended.
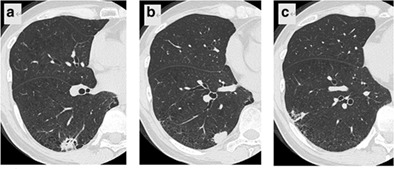
Synchronous triple primary lung cancer with three different histological subtypes in the same lobe: A case report
- Pages: 711-714
- First Published: 20 January 2021
Transformation from adenocarcinoma to squamous cell lung carcinoma with MET amplification after lorlatinib resistance: A case report
- Pages: 715-719
- First Published: 21 January 2021
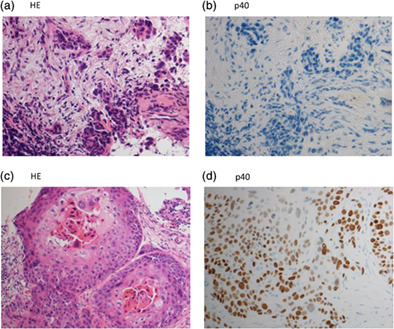
Little has been reported on acquired resistance mechanisms to lorlatinib. Here, we report a case of a patient with ALK-positive lung adenocarcinoma that acquired resistance to lorlatinib during treatment for brain metastasis and showed histological transformation to squamous cell carcinoma with MET amplification. We also review the previous literature on the resistance mechanism to ALK inhibitors.
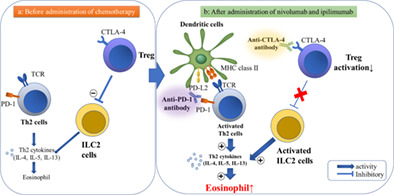
Immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced eosinophilic pneumonia: A case report
- Pages: 720-724
- First Published: 21 January 2021
STUDY PROTOCOL
Novel prospective umbrella-type lung cancer registry study for clarifying clinical practice patterns: CS-Lung-003 study protocol
- Pages: 725-731
- First Published: 12 January 2021
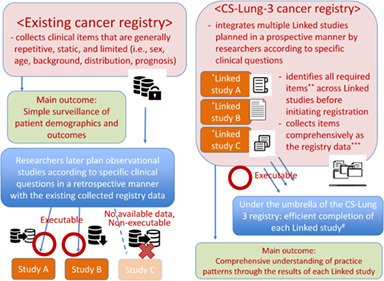
We constructed an umbrella-type lung cancer patient registry (CS-Lung-003) integrating multiple related prospective observational studies (linked studies) that reflect clinical questions about lung cancer treatment. Under this single registry, researchers collaborate on patient registration and data provision for their own and other studies.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Response to: Estimated direct costs of non-small cell lung cancer by stage at diagnosis and disease management phase: A whole-disease model
- Pages: 732-733
- First Published: 06 January 2021