Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLE
Research Progress on the Treatment of Geriatric Intertrochanteric Femur Fractures with Proximal Femur Bionic Nails (PFBNs)
- Pages: 2303-2310
- First Published: 09 July 2024
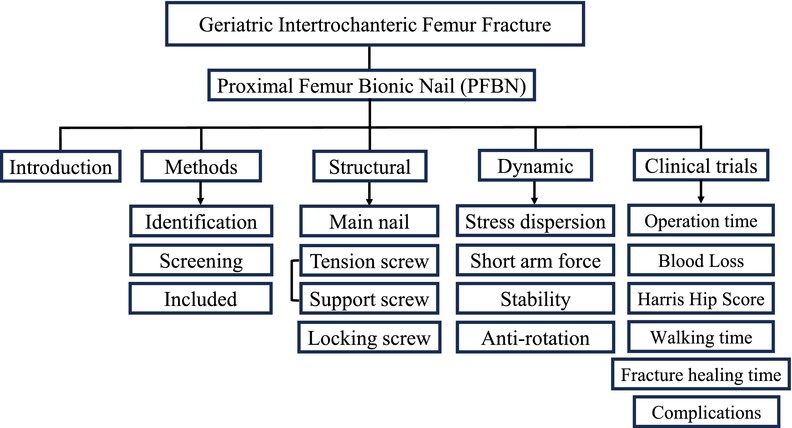
This article presents a comprehensive narrative review of literature pertinent to proximal femur bionic nails (PFBN), meticulously sourced from PubMed and other prominent databases. The review is structured around three pivotal facets: the structural characteristics of PFBN, its biomechanical dynamics, and clinical research findings. Notably, PFBN exhibits superior mechanical advantages compared to both InterTan and PFNA, an assertion that has been substantiated by clinical experimental data.
A New Tissue Engineering Strategy to Promote Tendon–bone Healing: Regulation of Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Tendon-derived Stem Cells
- Pages: 2311-2325
- First Published: 23 July 2024
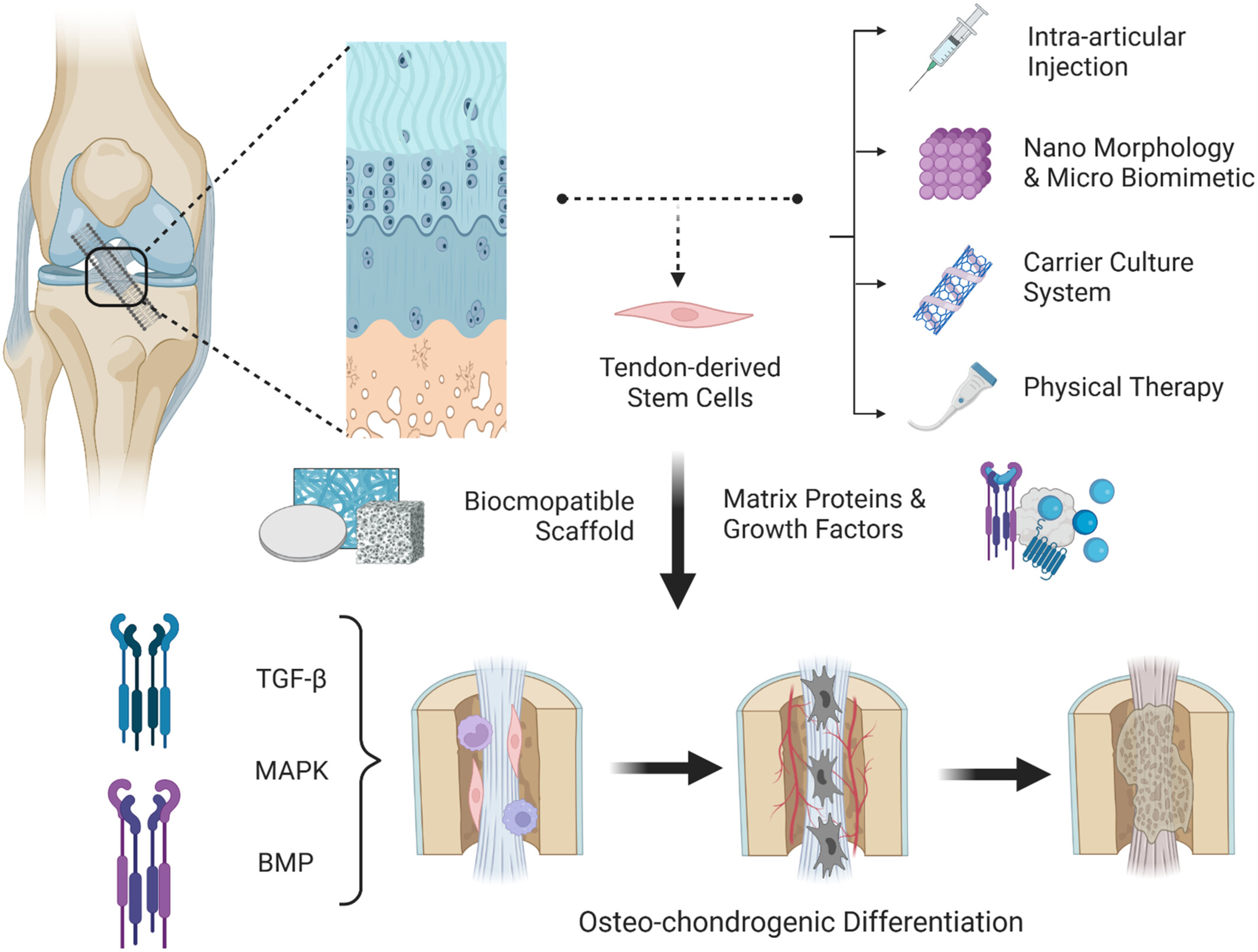
The graphical abstract outlines strategies for tendon-bone healing using tendon-derived stem cells (TDSCs). TDSCs, with high proliferation and differentiation capacities, are crucial for enthesis regeneration. Applications include injections, biomimetic systems, and physical therapy. Combining TDSCs with scaffolds and growth factors, guided by signaling pathways like TGF-β, promotes healing.
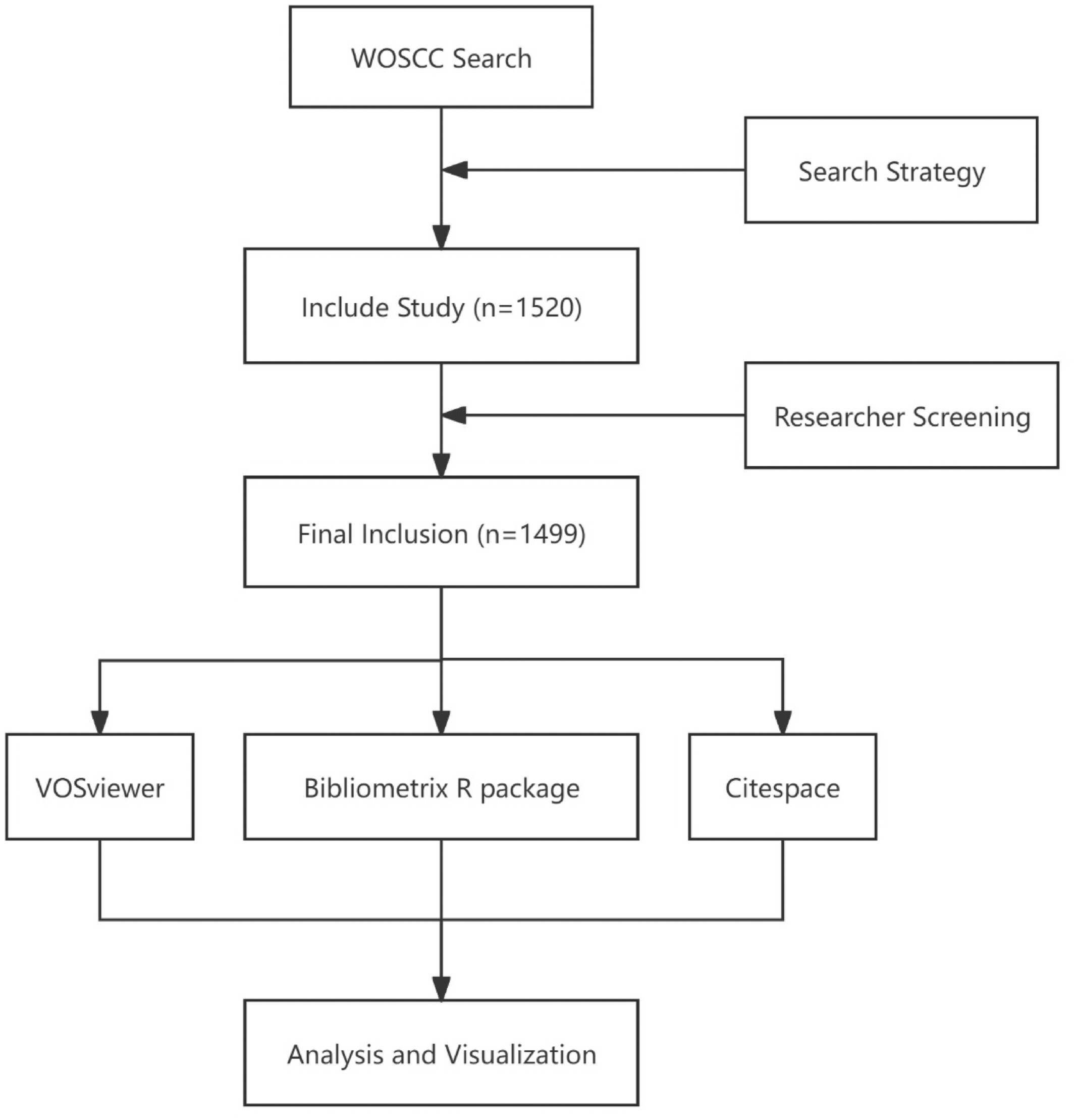
Knowledge Mapping of Macrophages in Osteoporosis: A Bibliometric Analysis (1999–2023)
- Pages: 2326-2343
- First Published: 09 July 2024
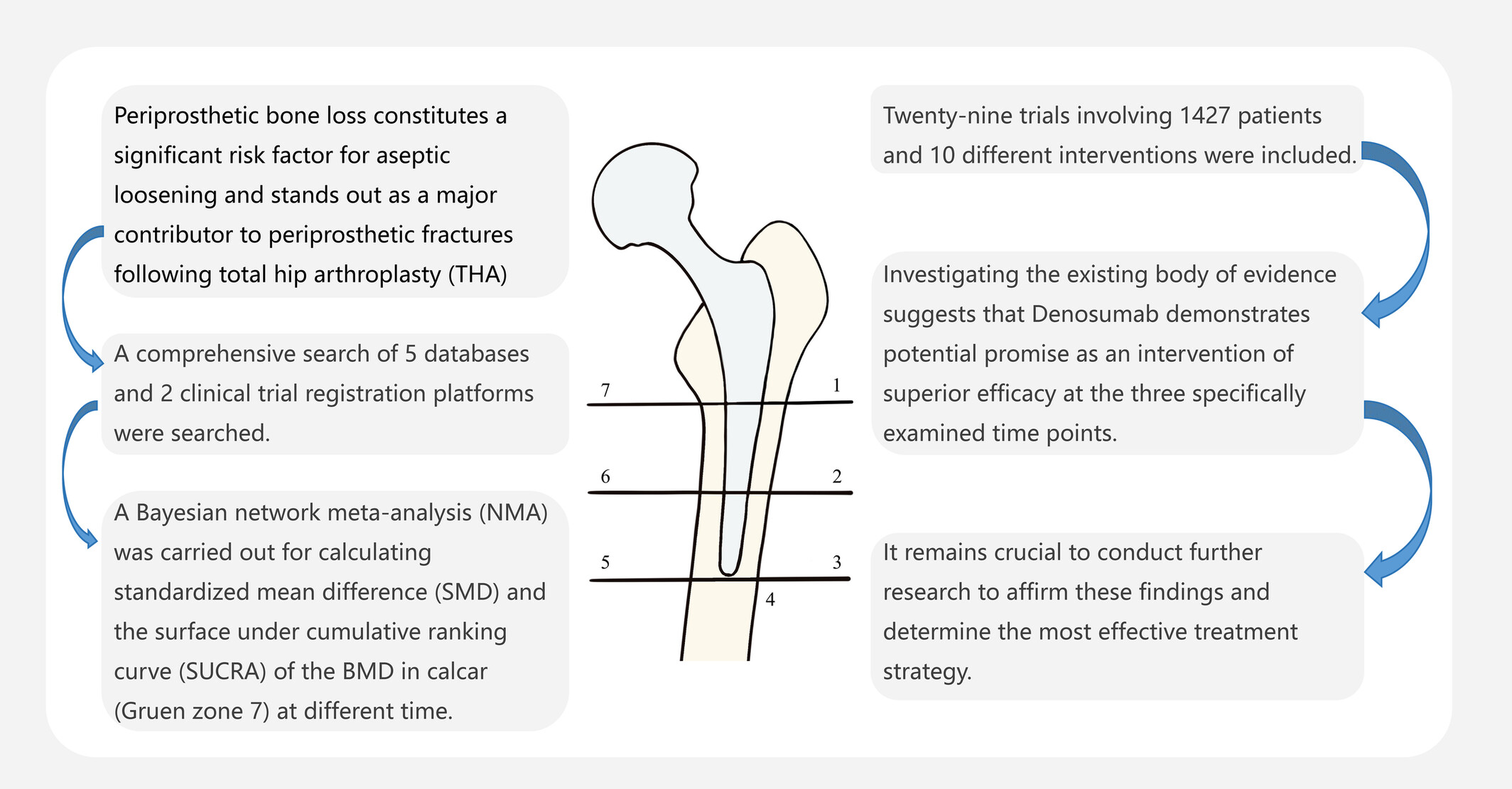
Comparing the Efficacy of Antiosteoporotic Drugs in Preventing Periprosthetic Bone Loss Following Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
- Pages: 2344-2354
- First Published: 26 July 2024
CLINICAL ARTICLE
Does Screw Number of Zero-profile Implants in Fusion Segment Influence Intervertebral Stability?
- Pages: 2355-2363
- First Published: 19 June 2024

In zero-profile Implant selection, two screw and four screw implants provide comparable immediate, medium, and long-term stability. The fusion rates and clinical outcomes of both implants were identical. However, the two screw implant was inferior to the four screw implant in subsidence prevention. Therefore, patients with a high risk of subsidence should receive a four-screw implant rather than a two-screw implant.
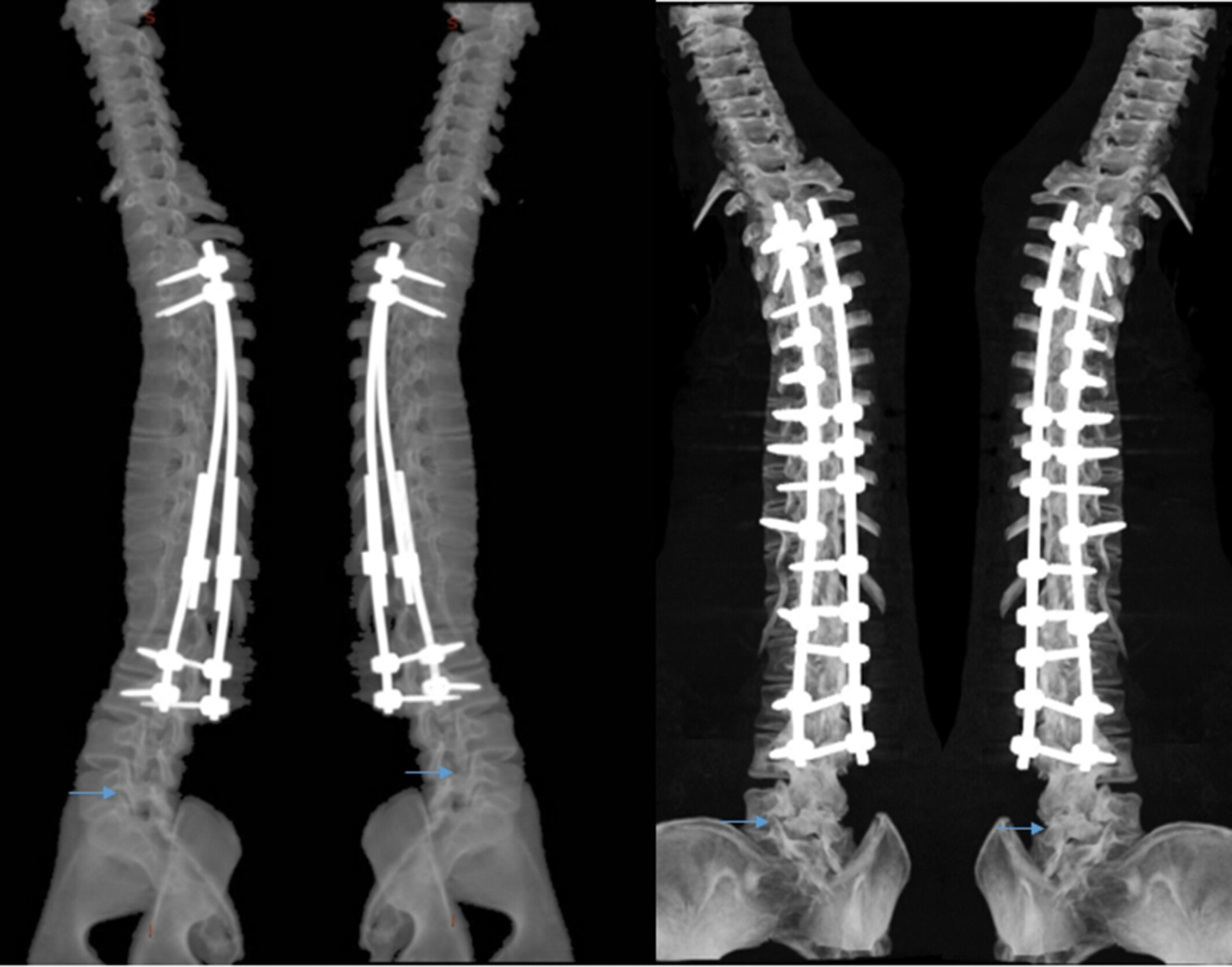
Application of Multi-Rod Constructs for the Revision of Thoracolumbar Fractures
- Pages: 2364-2371
- First Published: 09 July 2024
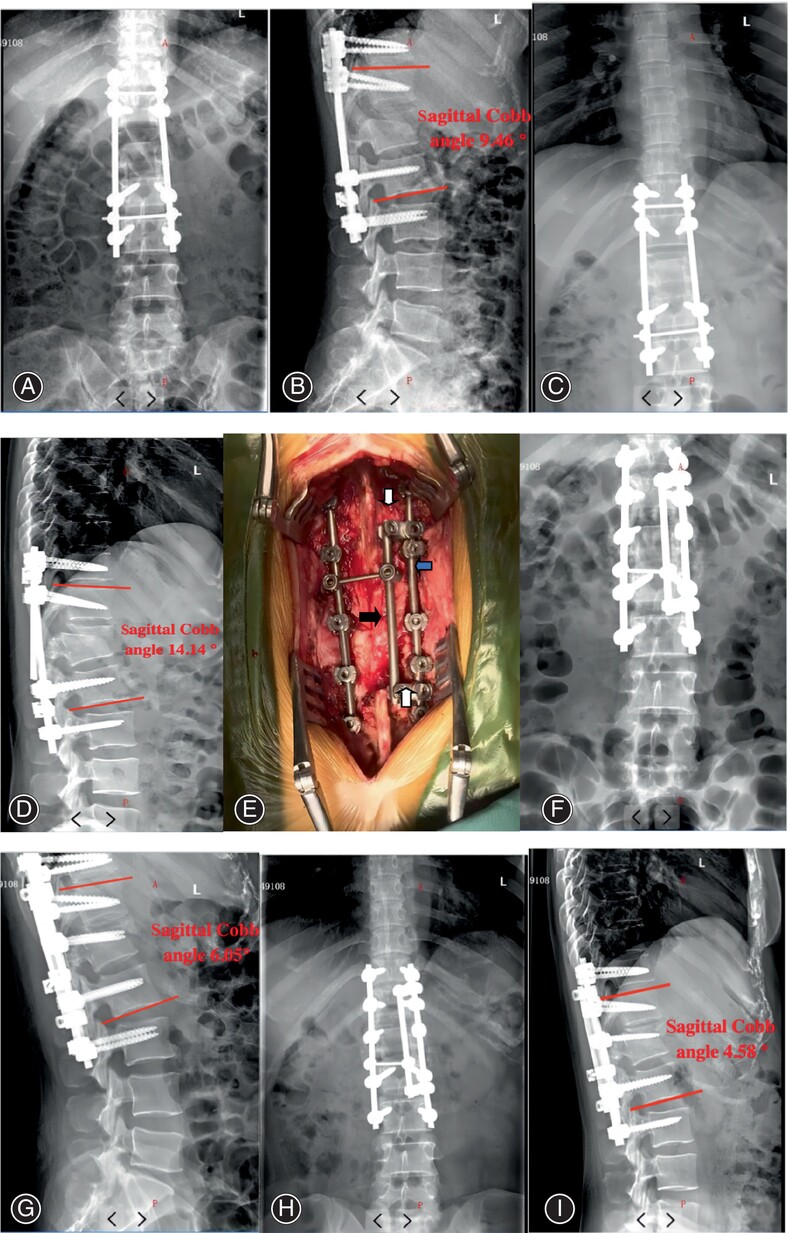
Multi-rods technique can be used in the revision of fracture rod after operation of severe thoracolumbar fracture. After all, the operation is simple and easy, and the clinical outcome of short-term follow-up is good. In addition, there is no failure of internal fixation, and it is possible to avoid anterior revision surgery. The deficiency of this paper lies in the small sample size and short follow-up time, and whether the multi-rods technique can stand the test remains to be tested by time and more research.
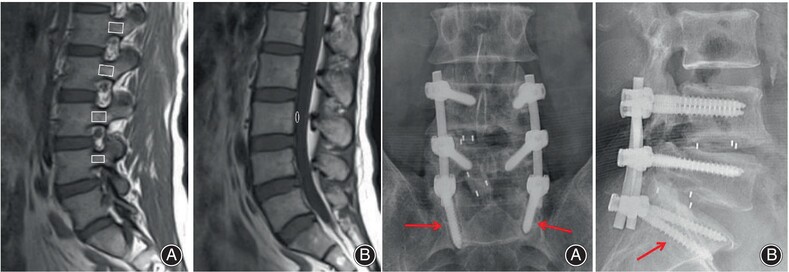
Novel MRI-Based Pedicle Bone Quality Score Independently Predicts Pedicle Screw Loosening after Degenerative Lumbar Fusion Surgery
- Pages: 2372-2379
- First Published: 09 July 2024
Efficacy and Safety of Fruquintinib-Based Treatment in Patients with Refractory Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcoma after Developing Resistance to Several TKIs: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- Pages: 2380-2390
- First Published: 18 July 2024
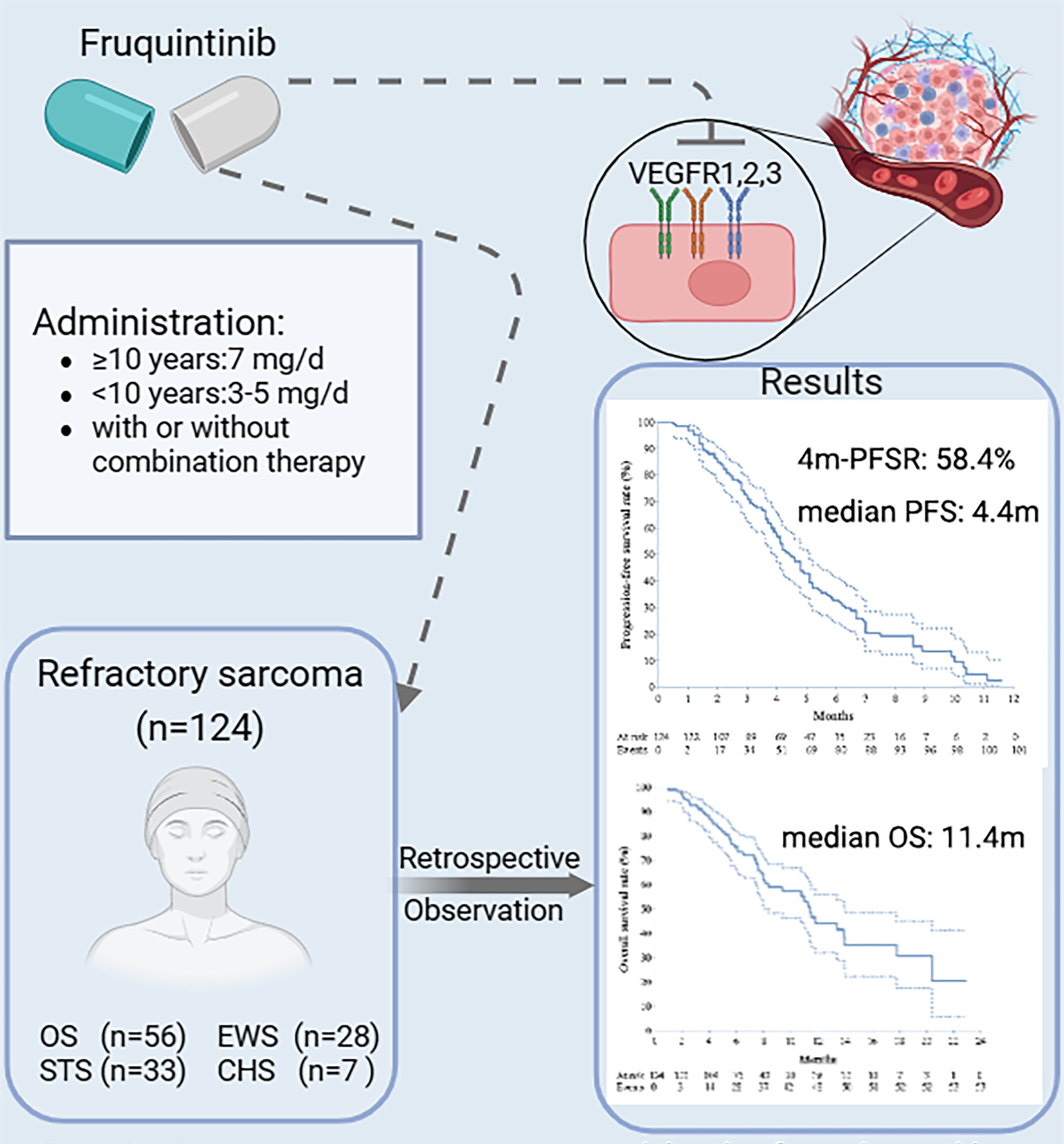
We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 124 patients with refractory sarcoma after they had developed several lines of resistance to TKIs and who received fruquintinib-based treatment. Fruquintinib may be a potential option for patients with refractory sarcoma after developing several lines of TKI resistance, with a satisfactory efficacy and safety profile in combination therapy.
Modified Tracheal Traction Exercise Reduces the Incidence of Dysphagia in Patients with Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
- Pages: 2391-2400
- First Published: 18 July 2024
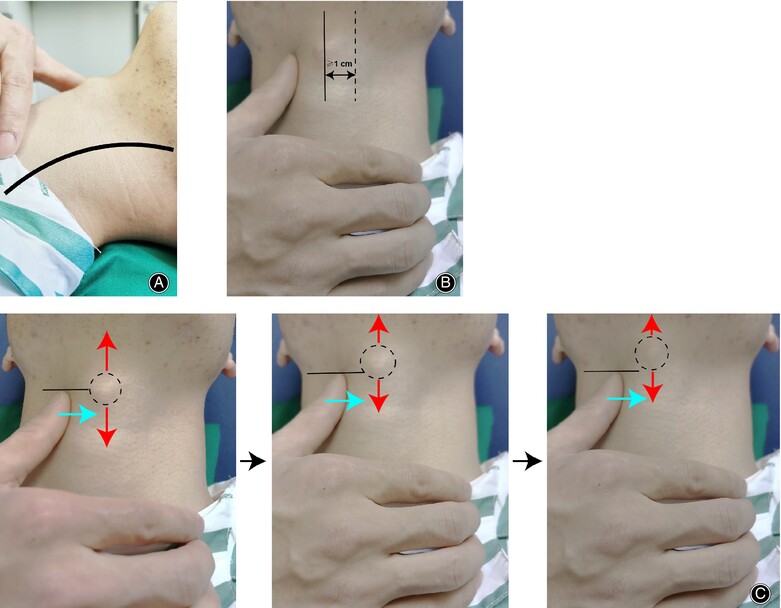
The procedure of modified tracheal traction exercise (MTTE). The patient is in supine position and a U-shaped neck cushion is used to achieve cervical hyperextension. The operator confirms the location of thyroid cartilage, and then the thyroid cartilage is pushed to the left side at least 1 cm across the midline of the anterior neck. Before returning to the starting position, this status should be held for 5 s, swallowing when the pushing is performed.
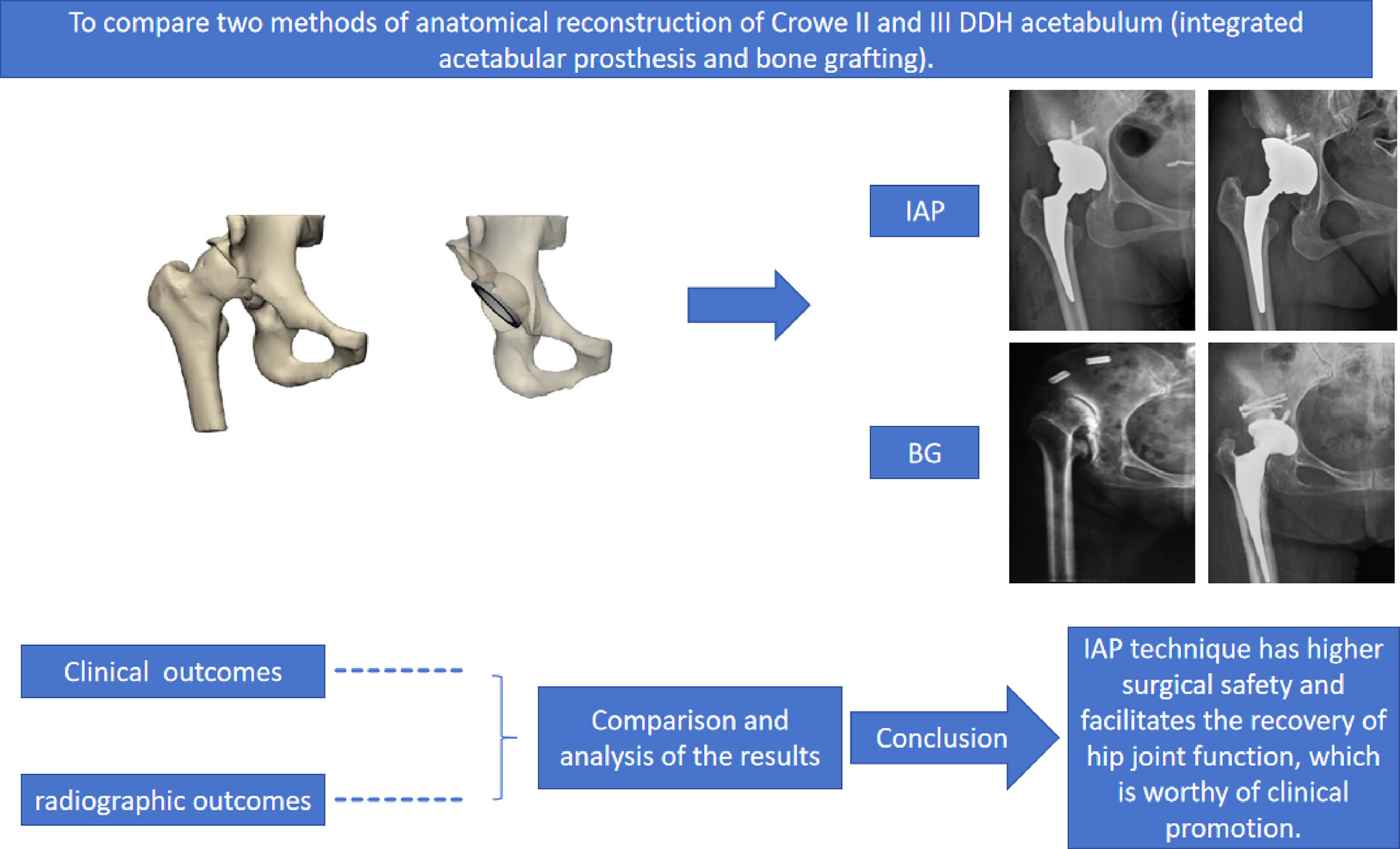
Integrated Acetabular Prosthesis Versus Bone Grafting in Total Hip Arthroplasty for Crowe Type II and III Hip Dysplasia: A Retrospective Case–Control Study
- Pages: 2401-2409
- First Published: 23 July 2024
Comparison of the Effects of Posterior Cervical Fixation or Posterior Cervical Fixation Extending to the Upper Thoracic Region on Cervical Sagittal Alignment
- Pages: 2410-2418
- First Published: 23 July 2024

This figure illustrates the changes in various spinal angles and the statistical significance of these changes across C2-T2, C3-C6, and Subaxial-T2 surgical groups. The left panel shows the mean changes in different spinal angles (units) for each group. The right panel displays the p-values of these changes, indicating their statistical significance (C2-T2: Blue; C3-C6: Orange; Subaxial-T2: Green).
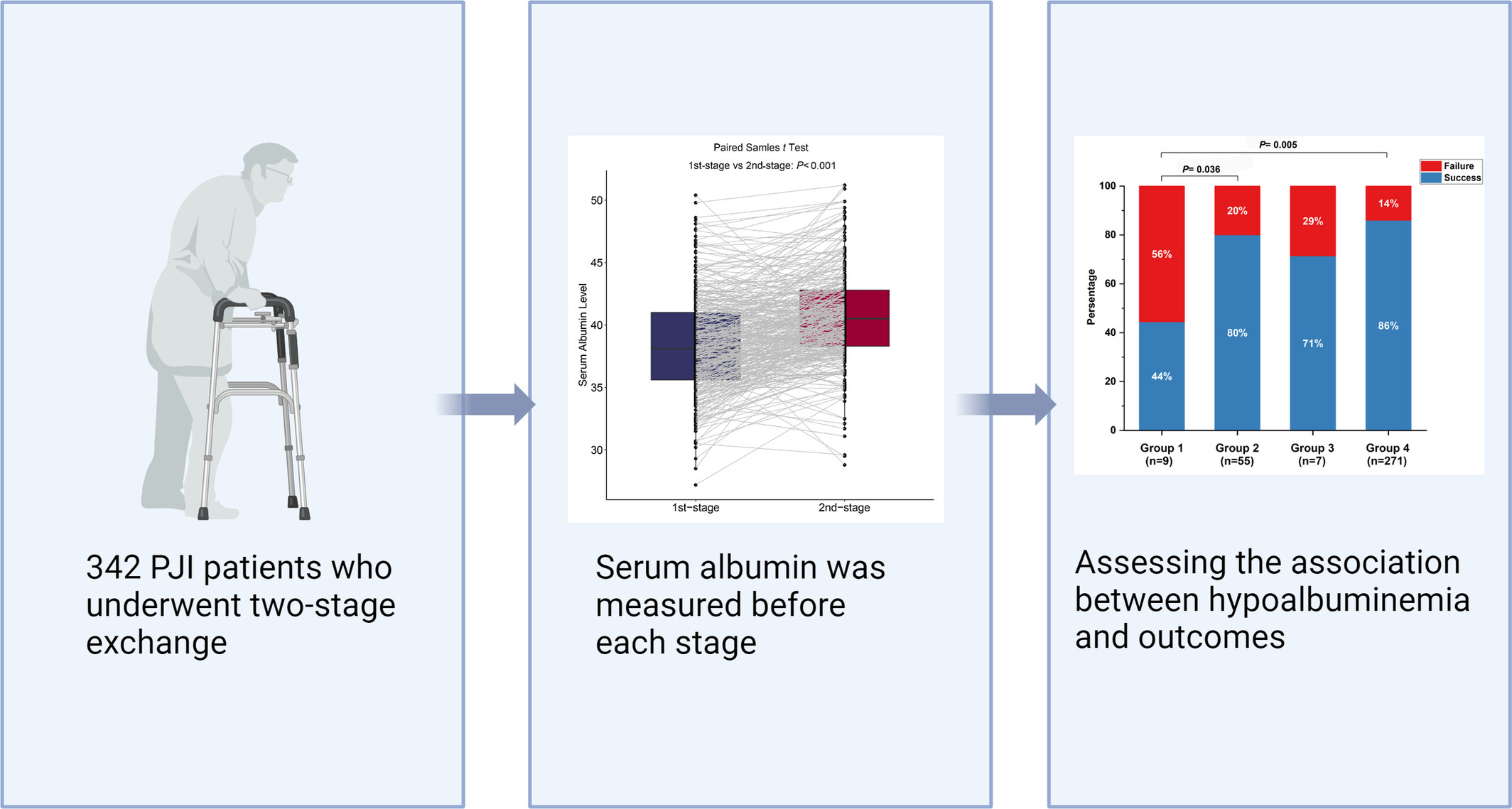
Hypoalbuminemia is Highly Prevalent in Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection and Strongly Associated with Treatment Failure
- Pages: 2419-2427
- First Published: 25 July 2024
CT Anatomical Analysis of C4 Pedicle and Lateral Mass in Children Aged 0–14 in Southern China
- Pages: 2428-2435
- First Published: 26 July 2024
We measured eight indicators, including the size and angle of the C4 vertebral arch and lateral mass, in 513 children who underwent cervical CT examinations at our hospital. We employed the aggregate function for statistical analysis, conducted t-tests for difference statistics, and utilized the least squares method for regression analysis.
A Novel Deformity Correction Manipulation System for Better Correction of Large Thoracic Scoliosis
- Pages: 2436-2446
- First Published: 27 July 2024
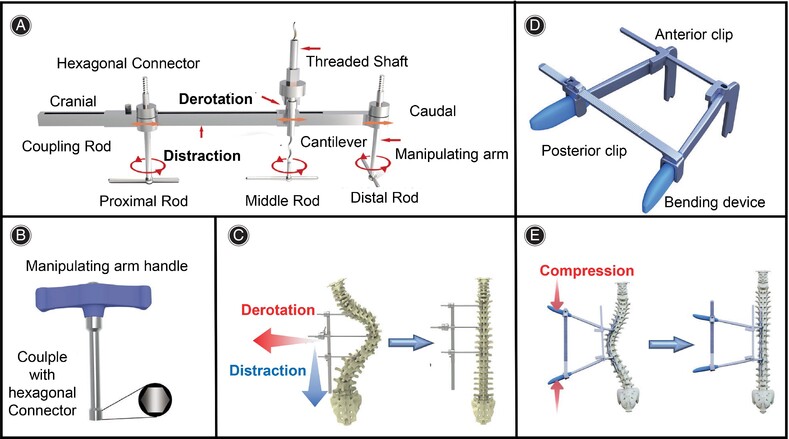
Deformity correction manipulation system (DCMS). (A) Multiple-screw linkage distraction reducer (MLDR) system: cranial and caudal manipulating arms are designed to perform distraction force and the middle cantilever manipulating arms with threaded shaft are designed to perform lifting force for derotation. Together they are connected to a coupling rod by couplers. The manipulating arms are attached to proximal, apical, and distal regions of the spine via three provisional rods. (B). Manipulating handle couples with the hexagonal connector to regulate the manipulating arms. (C) Schematic diagram of the MLDR system. (D) In situ cantilever bending (ISCB) system: traditional two-rod bending devices were attached to the spine. Two adjustable and removable clips were connected to the lever arms of the rod-bending device. The anterior clip is designed to stabilize the system and the posterior clip is designed to modulate the degree of compression. (E) Schematic diagram of the ISCB system.
Efficacy and Safety of Bone Wax Application at Different Time Points to Reduce Postoperative Blood Loss in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial
- Pages: 2447-2453
- First Published: 28 July 2024
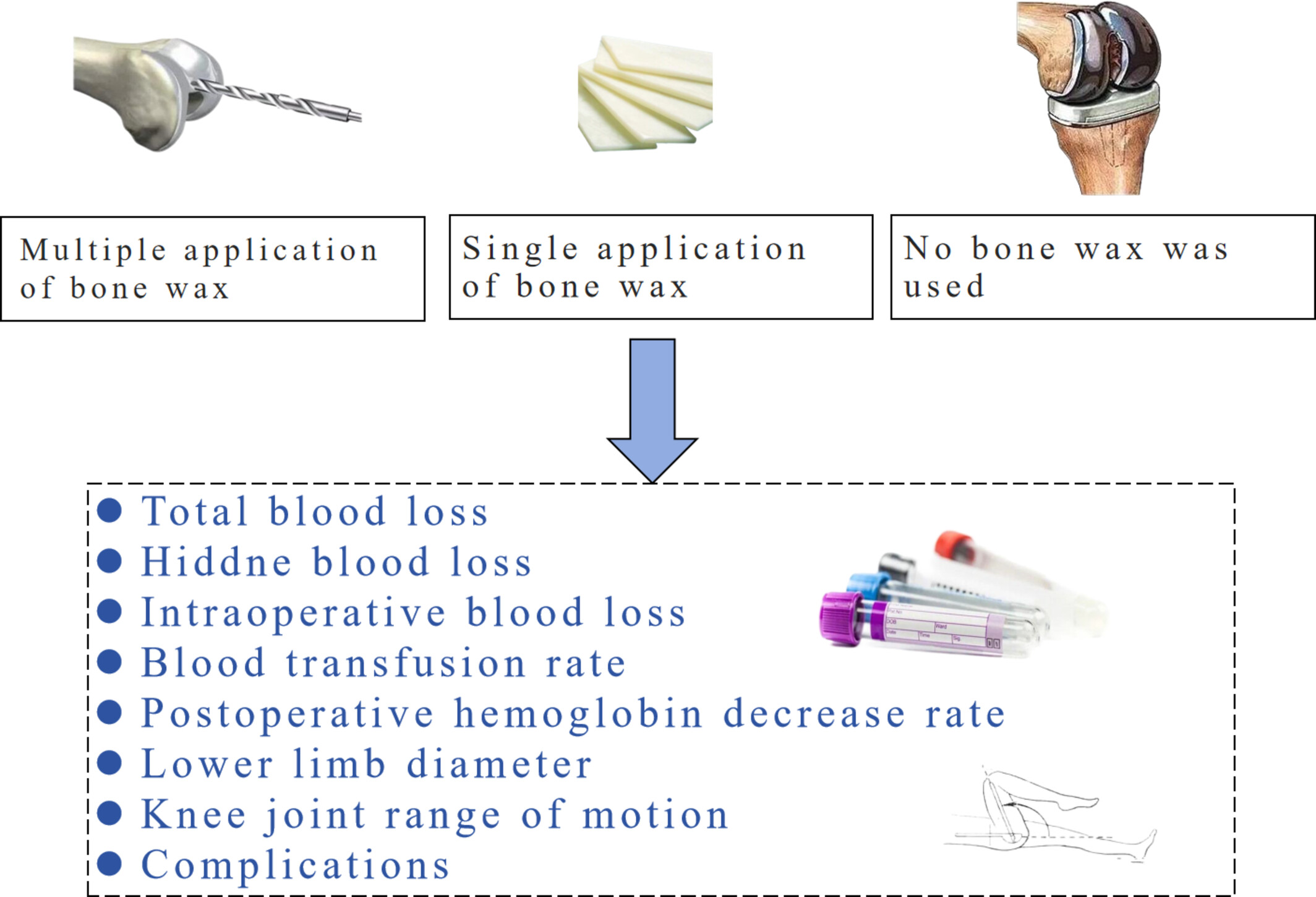
In addition to surface hemorrhage of cancellous bone after large-area osteotomy, intramedullary hemorrhage after the knee joint is also a major cause of postoperative bleeding after total knee arthroplasty (TKA). This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of bone wax application at different time points during prone hemorrhage to reduce perioperative blood loss. Finally, it was found that the use of bone wax in TKA can safely and effectively reduce perioperative blood loss and the rate of decrease in hemoglobin, and multiple use steps during surgery, when blood loss is prone to occur, can produce more significant hemostatic effects.
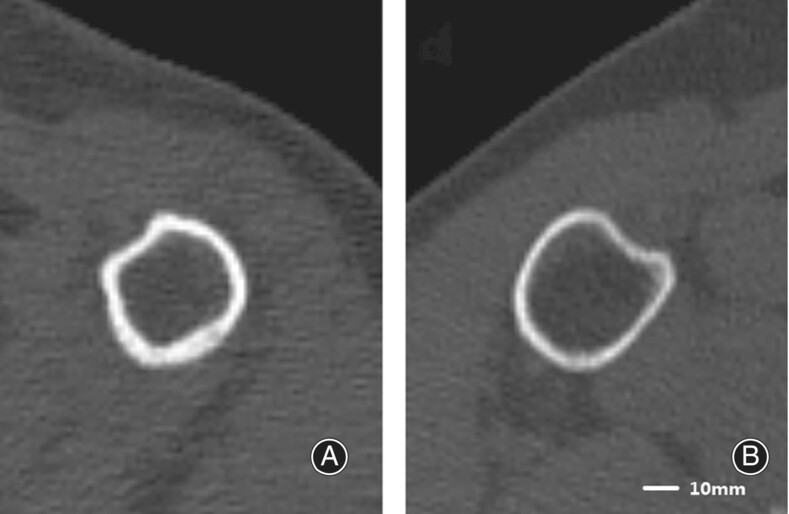
Atypical Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture Might be Considered a Distinct Subtype of Atypical Femoral Fracture: A Retrospective Study
- Pages: 2454-2463
- First Published: 28 July 2024
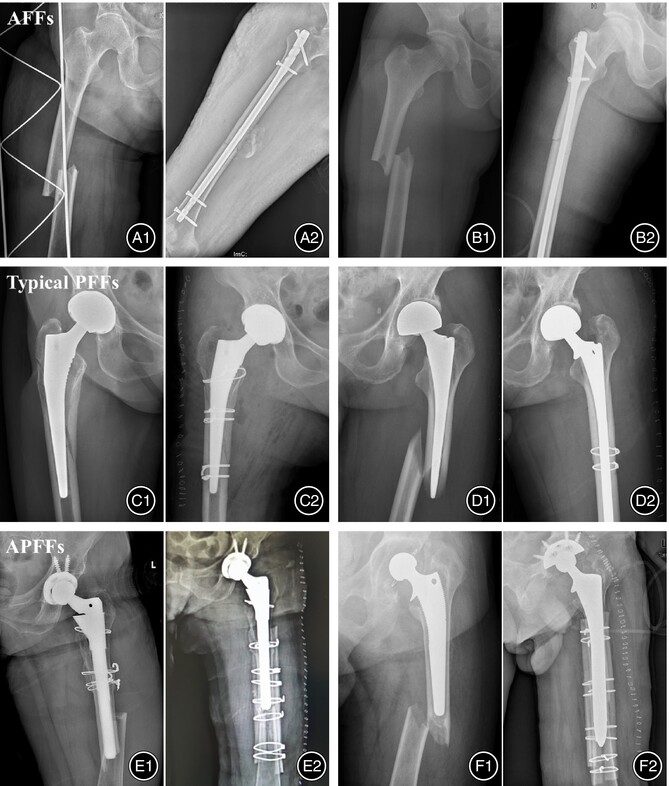
APFFs not only fulfilled the mandatory and major diagnostic criteria for AFF but also had many clinical characteristics, ways of managing, and prognoses distinguishing them from typical PFFs but resembling AFFs; hence, the diagnostic criteria for AFF might be revised to incorporate APFF as a distinct subtype of the condition.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Radiomics Based on Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging for the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Compression Fractures
- Pages: 2464-2474
- First Published: 09 July 2024
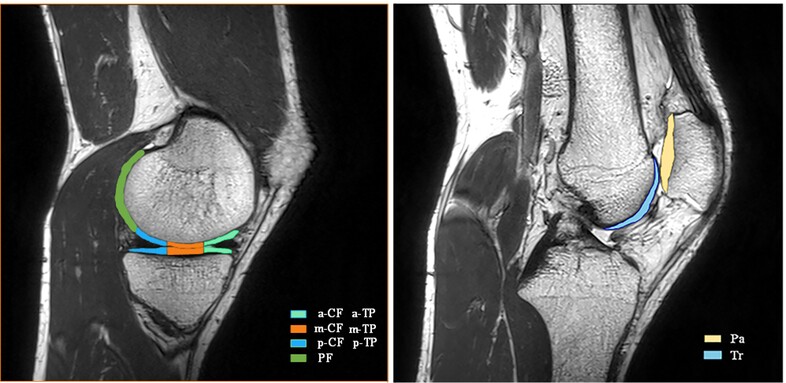
In the Acute Phase of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture: Quantitative Assessment of Matrix Changes and Correlation between Different States of Meniscus and Adjacent Cartilage
- Pages: 2475-2487
- First Published: 02 August 2024
Biomechanical Effects of Different Prosthesis Types and Fixation Ranges in Multisegmental Total En Bloc Spondylectomy: A Finite Element Study
- Pages: 2488-2498
- First Published: 05 August 2024
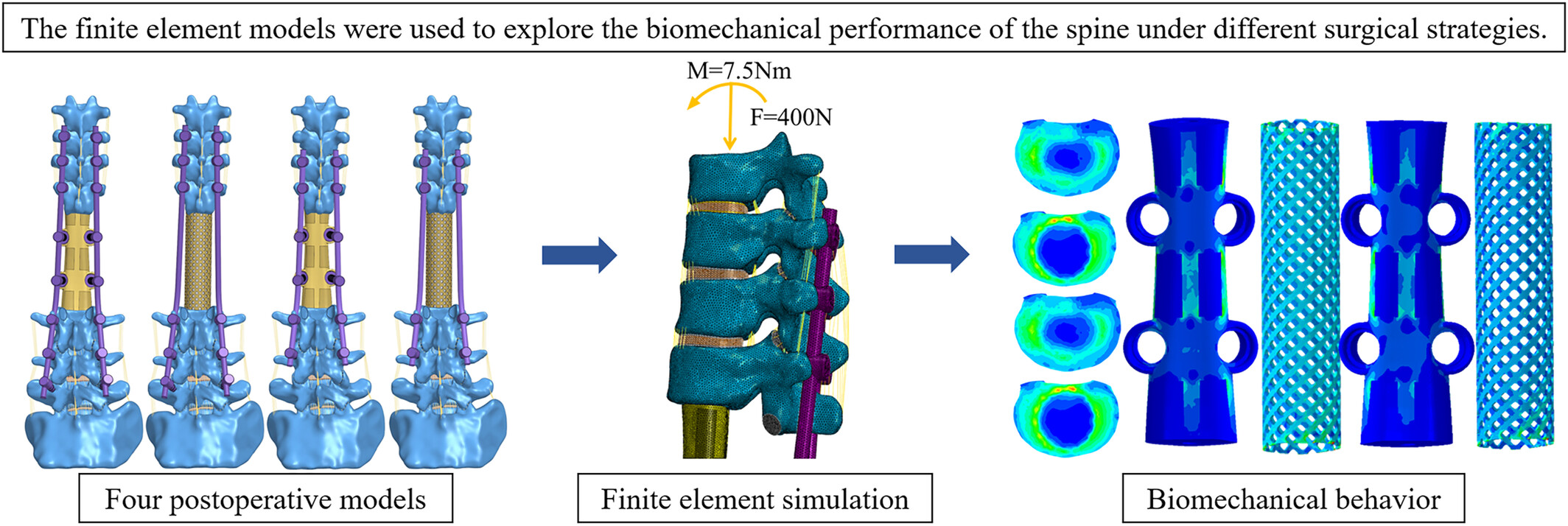
In multi-segmental total en bloc spondylectomy, the surgical strategy of using 3D-printed artificial prosthesis for anterior column support and pedicle screws for posterior fixation at both upper and lower levels, respectively, may achieve good postoperative stability and reduce the risk of complications.
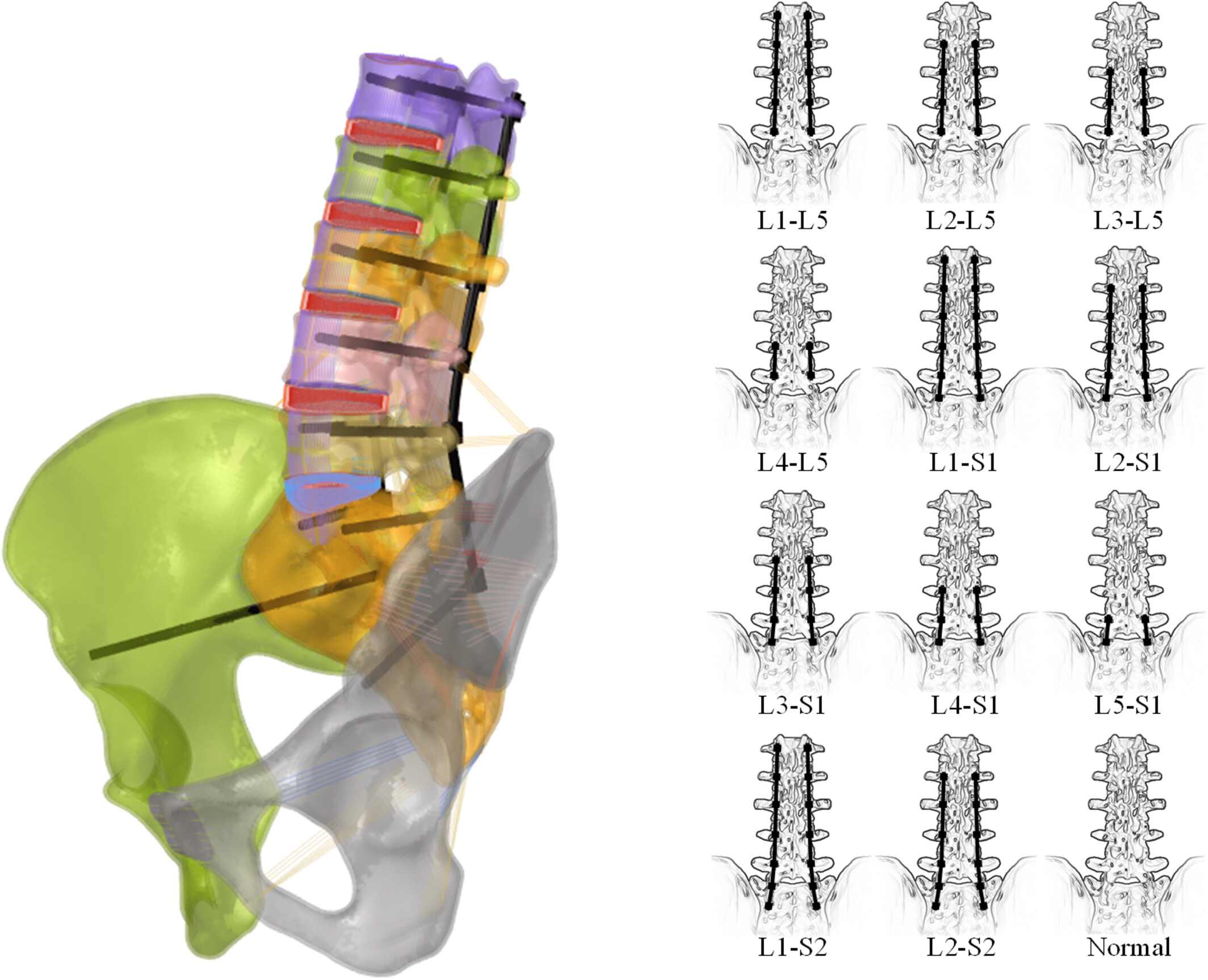
Biomechanical Effects of Multi-segment Fixation on Lumbar Spine and Sacroiliac Joints: A Finite Element Analysis
- Pages: 2499-2508
- First Published: 08 August 2024
Age-related Differences in Volumetric Bone Mineral Density, Structure, and Bone Strength of Surgical Neck of Humerus in Postmenopausal Women
- Pages: 2509-2516
- First Published: 08 August 2024
A Study on Imaging Risk Factors for Hip Osteoarthritis
- Pages: 2517-2525
- First Published: 21 August 2024
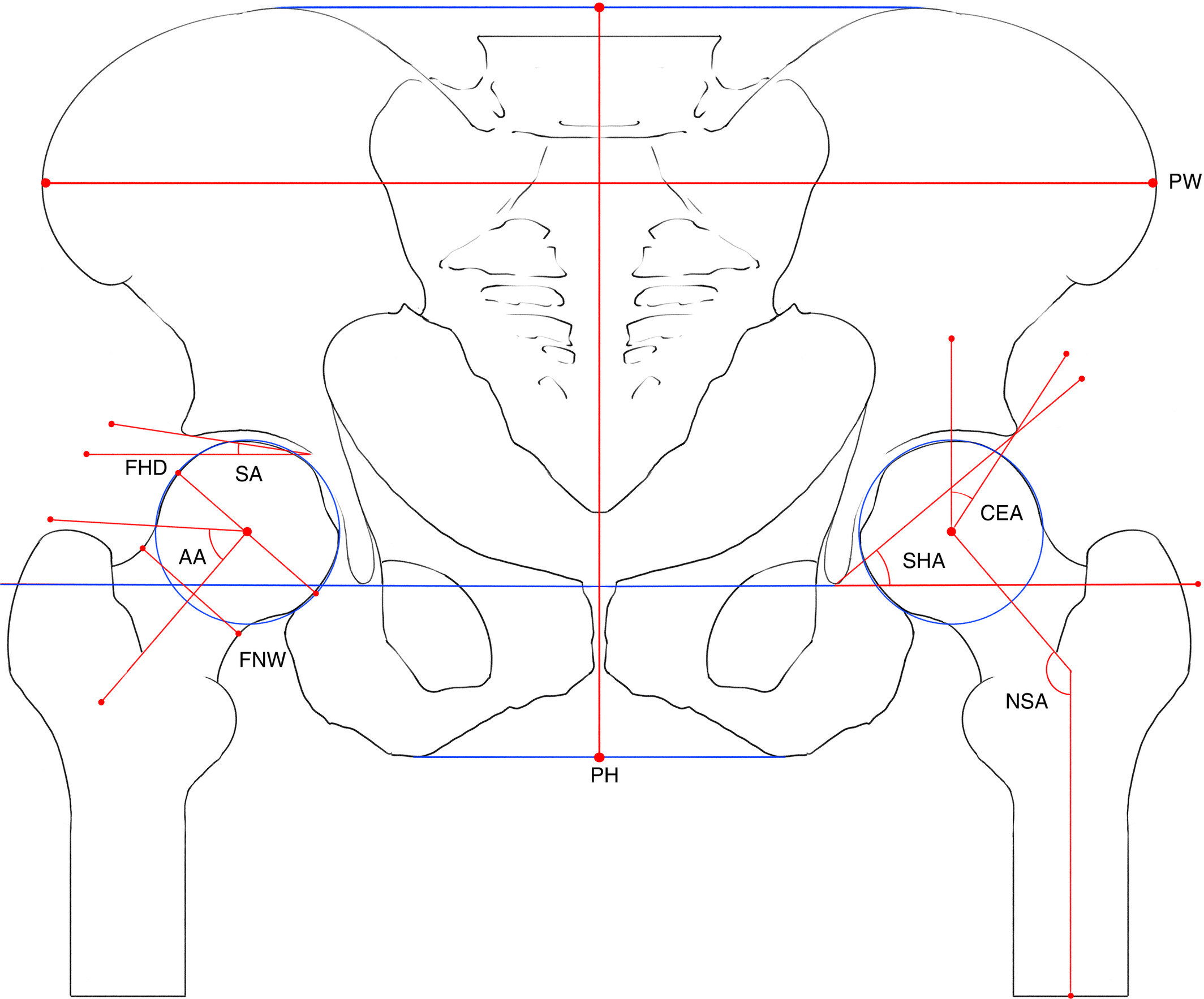
The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between 10 radiographic parameters measured via anteroposterior pelvic X-ray radiography and hip osteoarthritis (HOA). We found that in patients without significant hip dysplasia, a larger SA, wider femoral neck, nonspherical femoral head, pistol grip deformity, and smaller PW were risk factors for HOA.
Effect of Sclerosis Bands in Femoral Head Necrosis on Non-Vascularized Fibular Grafting—A Finite Element Study
- Pages: 2526-2538
- First Published: 02 September 2024
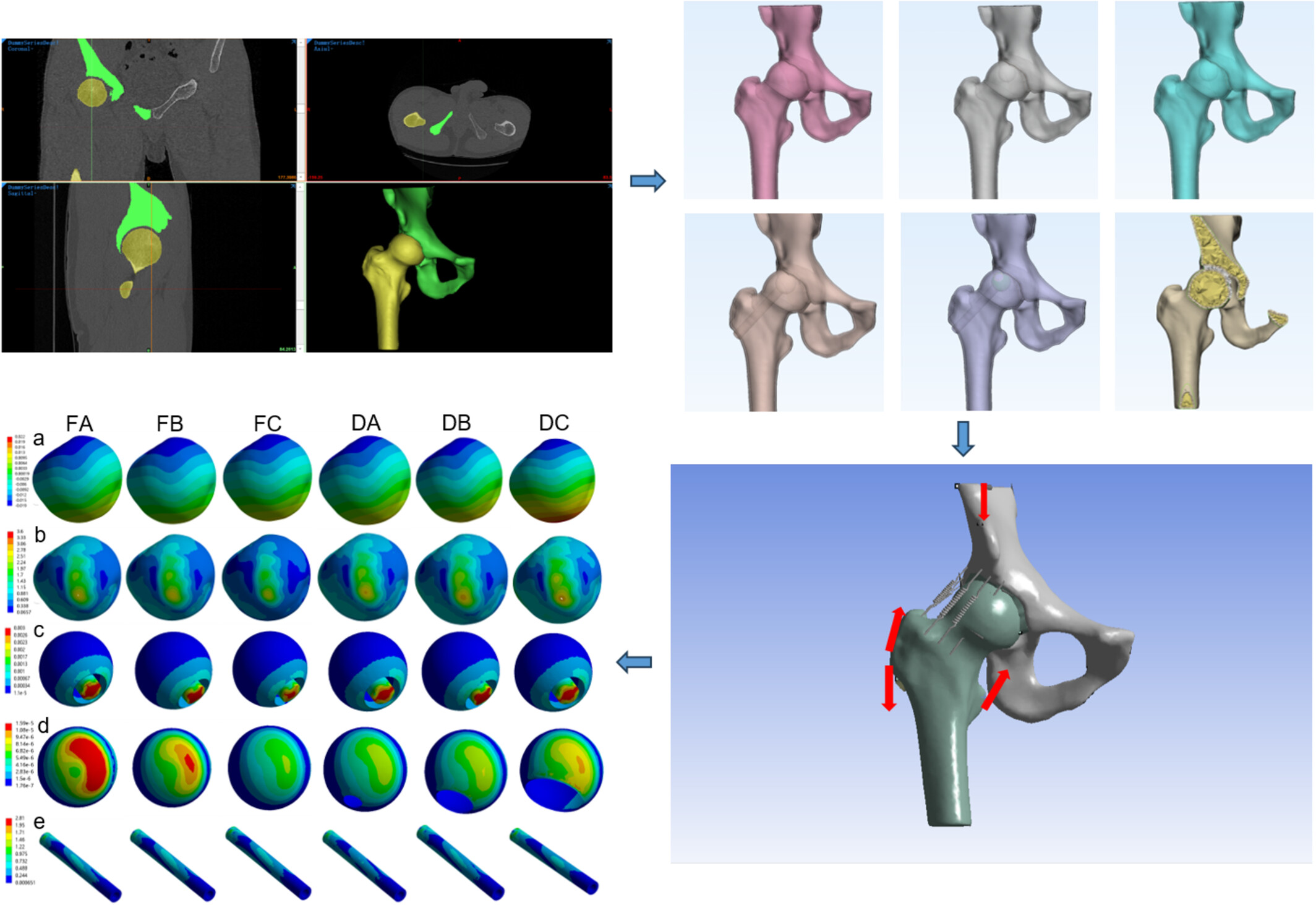
This study simulated the stress and displacement distribution on the surface of the femoral head after non-vascularized fibular grafting surgery using a finite element model. The results indicated that the sclerosis band in the anterolateral region plays a mechanical supporting role for the femoral head after non-vascularized fibular grafting surgery. This suggests that during non-vascularized fibular grafting surgery, the sclerosis band in the anterolateral area should be avoided, as its removal may lead to the risk of early collapse postoperatively.
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE
Biplane Reduction: A Novel Technique for Restoring Fibula Length in Maisonneuve Fracture
- Pages: 2539-2545
- First Published: 10 July 2024
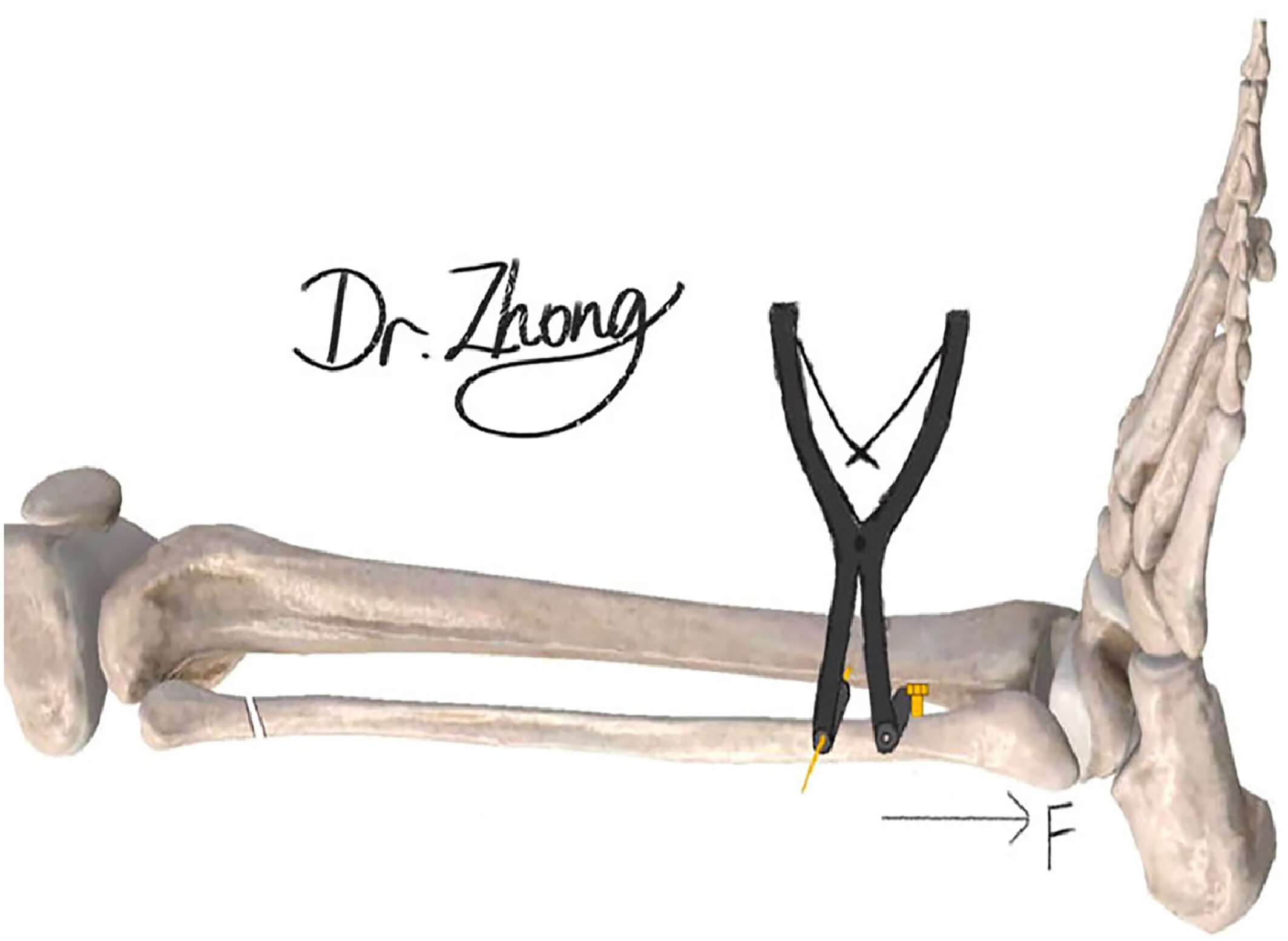
The anterolateral incision of the anterior edge of the fibula was made slightly arcually inward from approximately 8 cm above the level of the ankle joint to the level of the ankle joint. The skin and fascia were cut layer by layer. The extensor support band was cut open and the anterior tibial muscles were pulled medially to expose the inferior tibiofibular commissure and distal fibula. During the operation, the inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis was completely separated, and the interosseous membrane was torn. The inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis joint was fully cleaned, parallel to the coronal plane of the ankle joint, and a 2.0 mm Kirschner wire was inserted vertically on the tibial shaft 8 inches above the level of the ankle joint, 0.5–1.0 inches away from the anterior edge of the fibula, and approximately 7 feet above the level of the ankle joint, perpendicular to the coronal plane of the ankle joint, a common screw was placed vertically on the fracture piece of the distal fibula; the distance between the two was approximately 1.0 mm. A Kirschner needle retractor was placed between the Kirschner needle and screw, and a stretching technique was used to restore the length of the fibula. Taking the length of the contralateral fibula as a reference, intraoperative fluoroscopy showed that after the fibula length recovered well, a 2.0 mm Kirschner wire was used to temporarily fix the inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis, and a 3.5 mm metal cortical bone screw was inserted to fix the inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis at approximately 2.0 cm and 4.0 cm above the level of the ankle joint.
The Application of Bidirectional Rapid Reductor in Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for the Treatment of Proximal Humeral Fractures: A Case Series
- Pages: 2546-2551
- First Published: 12 August 2024
This study suggests that the bidirectional rapid reductor is effective in the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) treatment of proximal humeral fractures (PHFs). This device not only aids in achieving or maintaining reduction during MIPO surgery but also reduces operation and exposure times.
Simultaneous Single-Position Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation under O-Arm Navigation for Modified MISDEF Type II Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: Case Series and Surgical Technique
- Pages: 2552-2561
- First Published: 19 August 2024
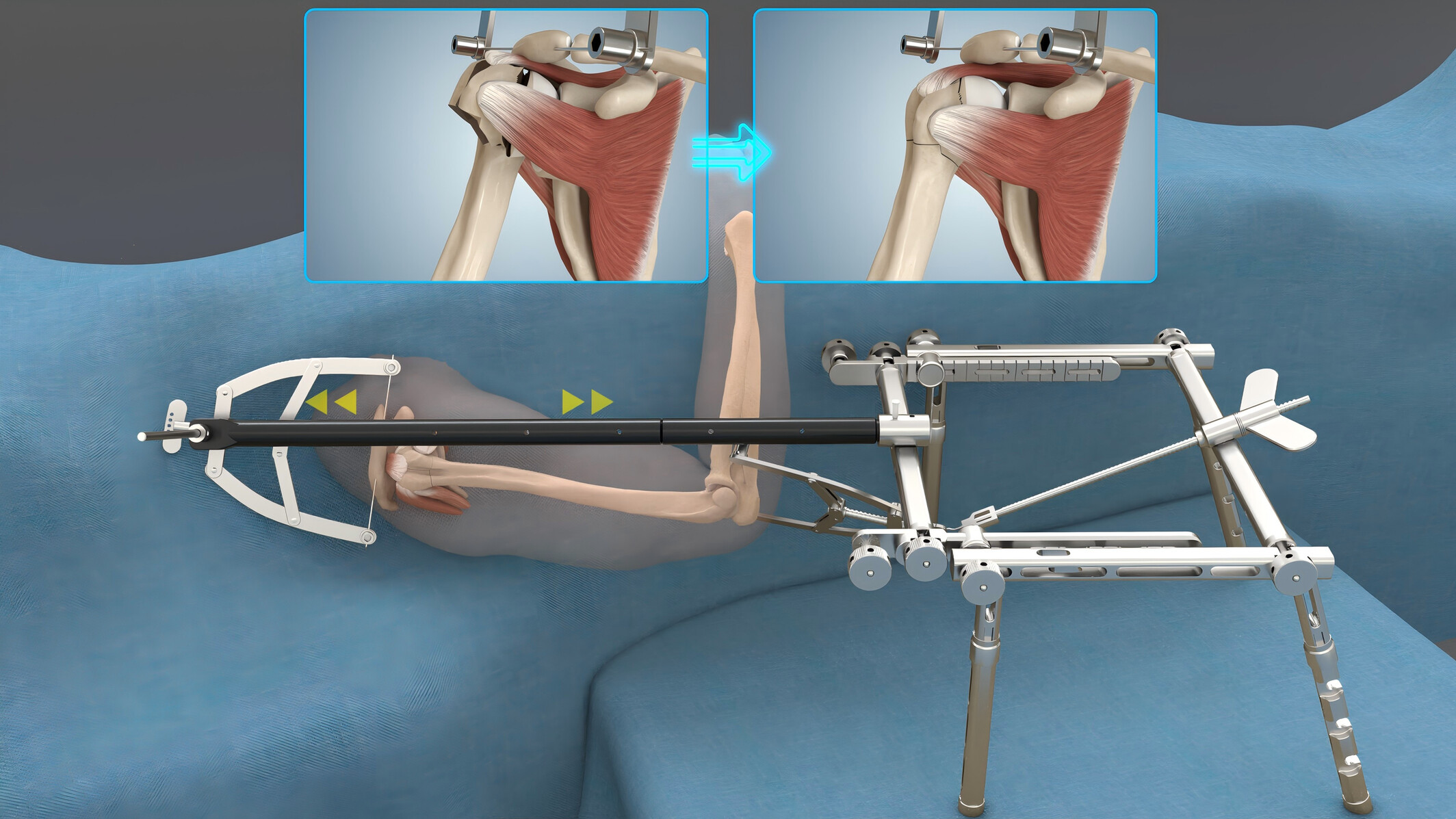
OLIF 360 technology is used to perform the OLIF procedure and percutaneous pedicle screw fixation in a single position simultaneously. We report on a case series and describe navigated OLIF 360 in treating ADS, which has shown encouraging surgical outcomes with good spinal imbalance correction and indirect decompression.
A Modified Fixation Method for Talonavicular Arthrodesis in the Treatment of Müller-Weiss Disease: The Use of the Shape-Memory Alloy Staple as an Adjunct
- Pages: 2562-2568
- First Published: 27 August 2024
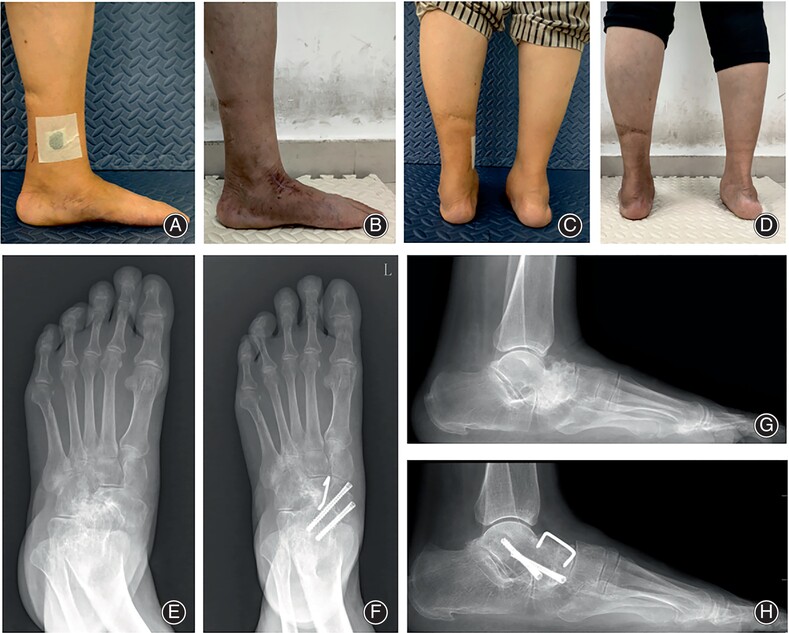
Using the SMA staple as an adjunct alongside screws in talonavicular arthrodesis surgery to treat MWD provides good clinical outcomes. We took the method of putting the SMA staple on the basis of the existing screws. The study emphasizes the importance of a better place for orthopedic implants to assist bone healing, and the efficacy of the SMA staple in clinical applications was further evaluated. Therefore, for surgical interventions targeting MWD, this modified fixation method presents a promising option.
CASE REPORT
Bilateral Spondylolysis of Lumbar Vertebra Secondary to Long Spinal Fusion for Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature
- Pages: 2569-2573
- First Published: 07 August 2024
Extra-Articular Abscess Expansion as a Specific Complication of Septic Arthritis of the Shoulder Joint: Report of Three Cases with Extension of the Infection through the Biceps Groove Producing a Large Abscess
- Pages: 2574-2581
- First Published: 02 September 2024
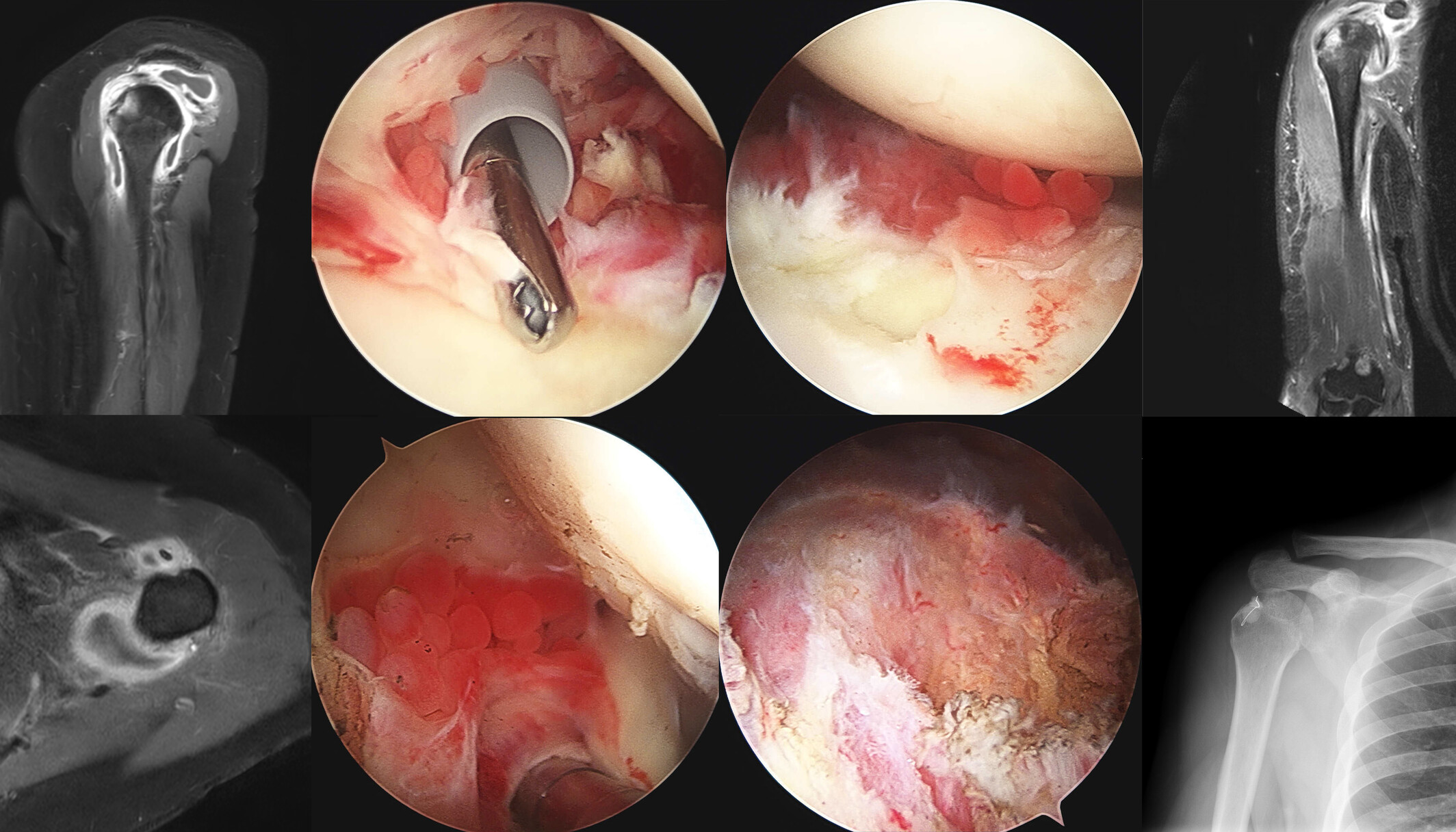
Septic arthritis of the shoulder joint can extend to the upper arm through the biceps tendon groove and cause an abscess. Arthroscopic debridement with through irrigation and open drainage of the extra-articular abscess extension to the upper arm improved both the shoulder pain and abscess completely. Also, acute osteomyelitis of the tuberosity should be considered in patients with long-standing refractory septic arthritis of the shoulder joint who have continued pain and uncontrolled laboratory findings after initial treatment.
CORRECTION
Correction to “Diagnostic Value of MRI Lamellated Hyperintense Synovitis in Periprosthetic Infection of Hip”
- Pages: 2582-2583
- First Published: 22 July 2024