Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front Cover
- First Published: 04 December 2024

Cover image: The cover image is based on the article Lycium barbarum Extract Enhanced Neuroplasticity and Functional Recovery in 5xFAD Mice via Modulating Microglial Status of the Central Nervous System by Zhongqing Sun et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.70123.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
PTP1B Modulates Carotid Plaque Vulnerability in Atherosclerosis Through Rab5-PDGFRβ-Mediated Endocytosis Disruption and Apoptosis
- First Published: 08 November 2024
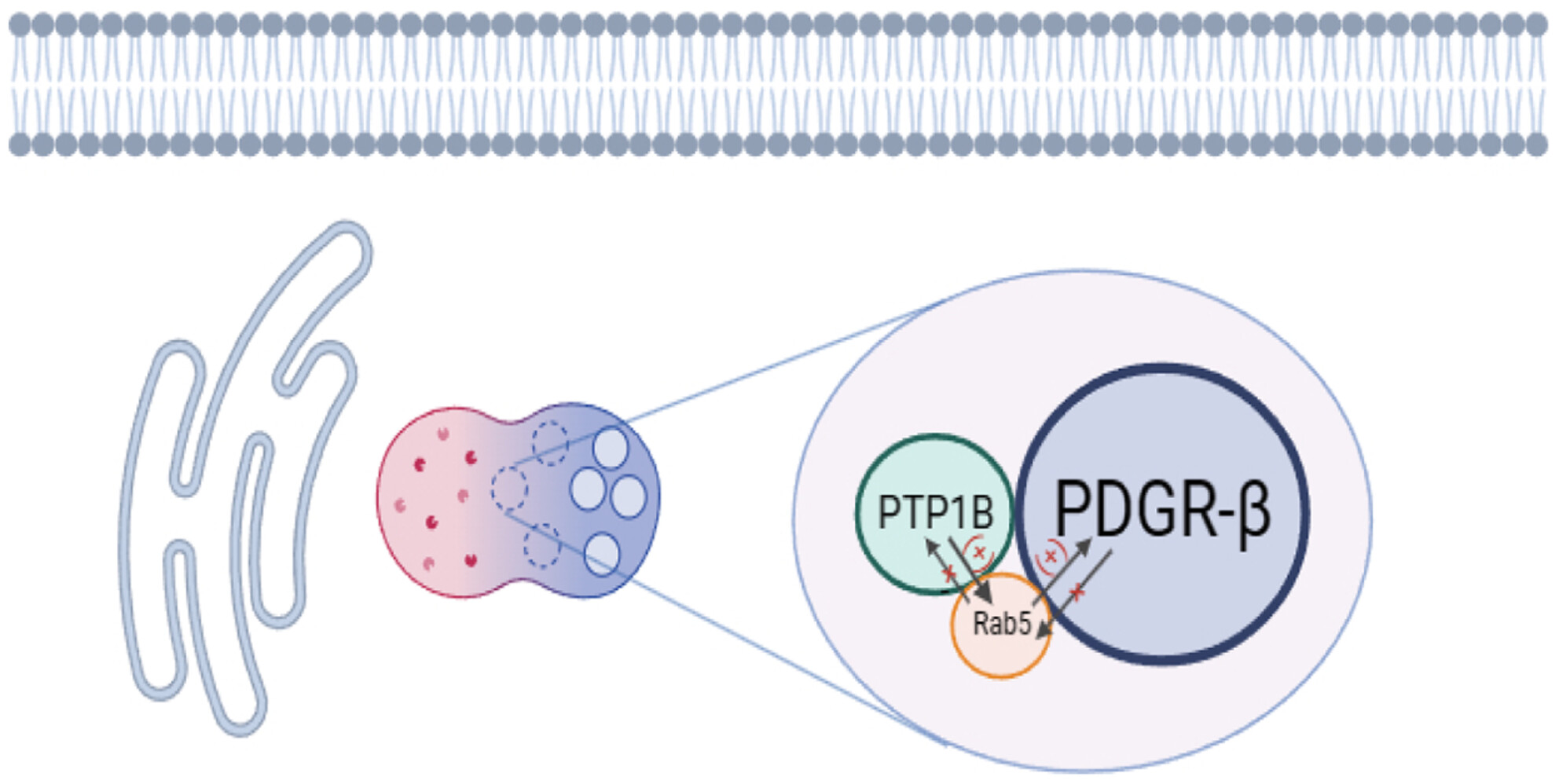
This study illustrates that PTP1B induces disruption in endocytosis and apoptosis of VSMCs through the Rab5-PDGFRβ pathway, suggesting a potential association with the heightened vulnerability of carotid plaques. Our results also present novel evidence supporting the potential use of PTP1B inhibitors in the treatment of vulnerable carotid plaques.
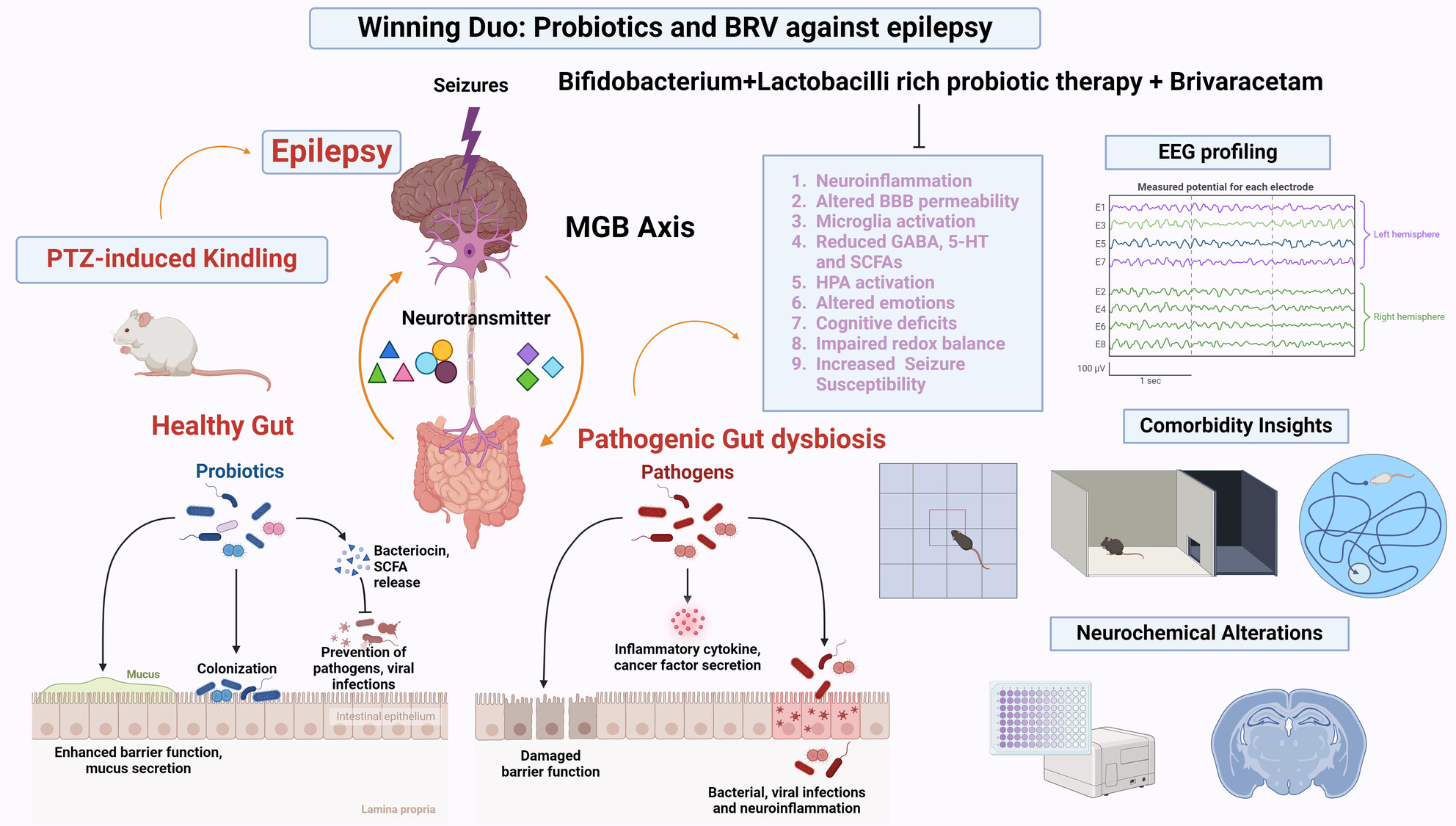
Probiotics by Modulating Gut–Brain Axis Together With Brivaracetam Mitigate Seizure Progression, Behavioral Incongruities, and Prevented Neurodegeneration in Pentylenetetrazole-Kindled Mice
- First Published: 29 October 2024
Construction of a Prognostic Model for Mitochondria and Macrophage Polarization Correlation in Glioma Based on Single-Cell and Transcriptome Sequencing
- First Published: 03 November 2024
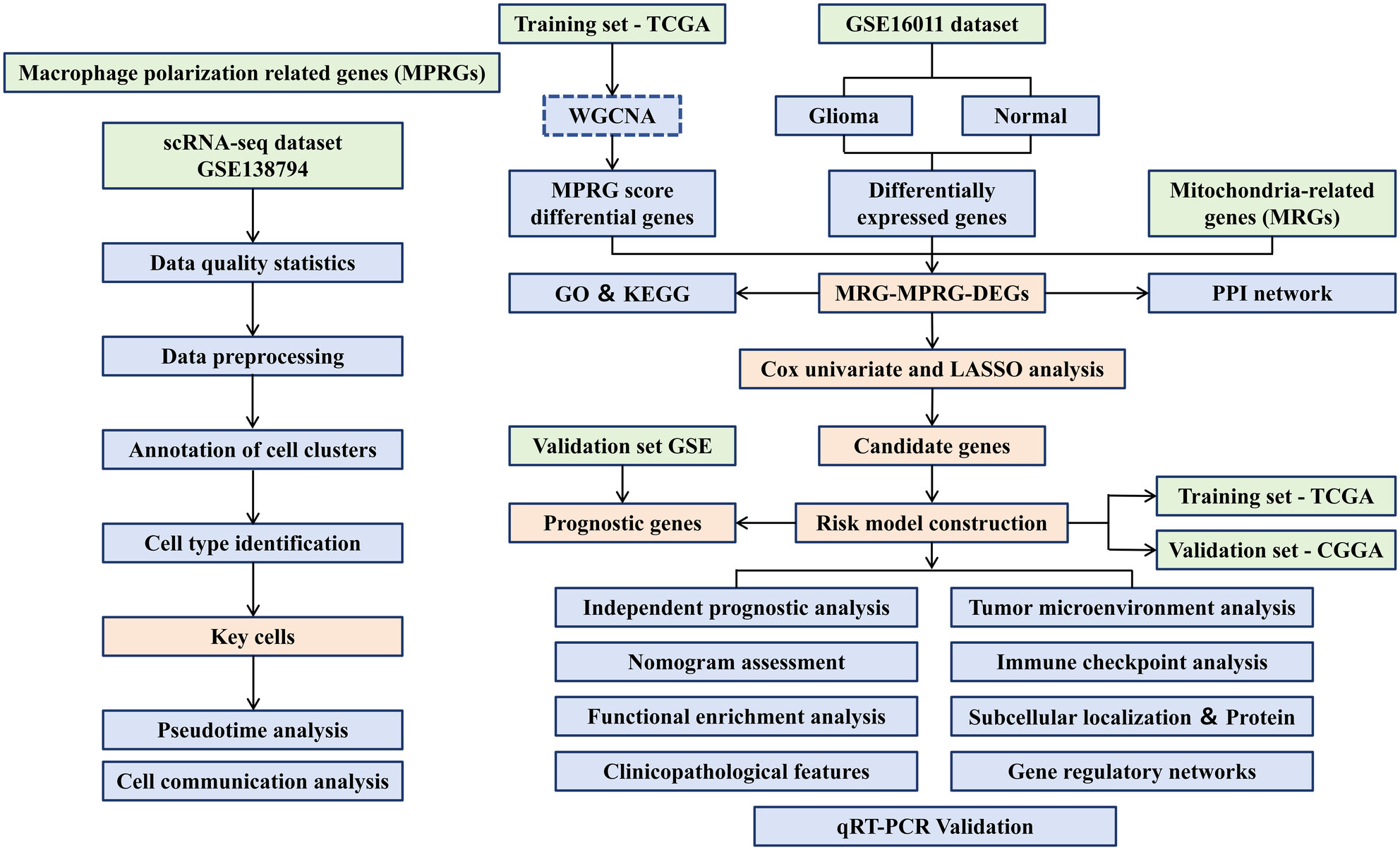
This study constructed a prognostic model for mitochondria and macrophage polarization correlation in glioma based on single-cell and transcriptome sequencing. Five genes associated with the prognosis of glioma (ECI2, MCCC2, OXCT1, SUCLG2, and CPT2) were revealed and then, validated using glioma tissues, providing novel insights into individualized treatment and prognosis.
Individualized rTMS Intervention Targeting Sleep Deprivation-Induced Vigilance Decline: Task fMRI-Guided Approach
- First Published: 13 November 2024
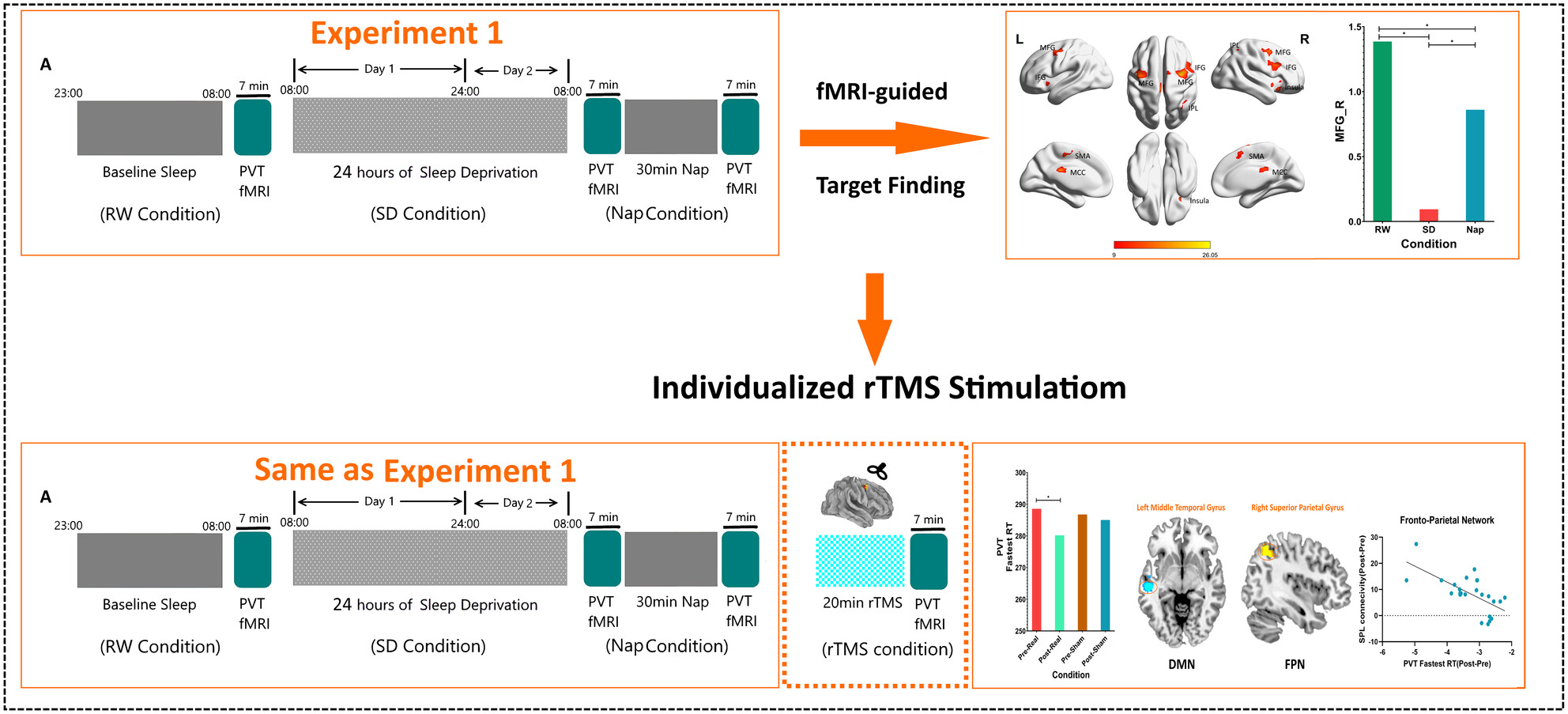
We recruited 50 healthy volunteers for two sleep deprivation experiments. In Experiment 1, each participant underwent a psychomotor vigilance task under three conditions: (1) after normal sleep, (2) after 30 h of sleep deprivation, and (3) after a subsequent 30-min nap, while undergoing functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). By analyzing the dynamic changes in task performance and brain responses across these conditions, we aimed to identify the optimal stimulation target. We discovered, for the first time, that the brain response in the right middle frontal gyrus exhibited the least recovery after a nap, leading us to select it as the stimulation target. In Experiment 2, using the same protocol (normal sleep, 30 h of sleep deprivation, 30-min nap), rTMS stimulation was applied after the nap. Subsequently, we found that individualized rTMS attenuated the sustained attention decline induced by sleep deprivation relative to napping alone. Thus, nap combined with personalized rTMS may facilitate the recovery of sustained attention following sleep deprivation by modulating neural activity in brain functional networks.
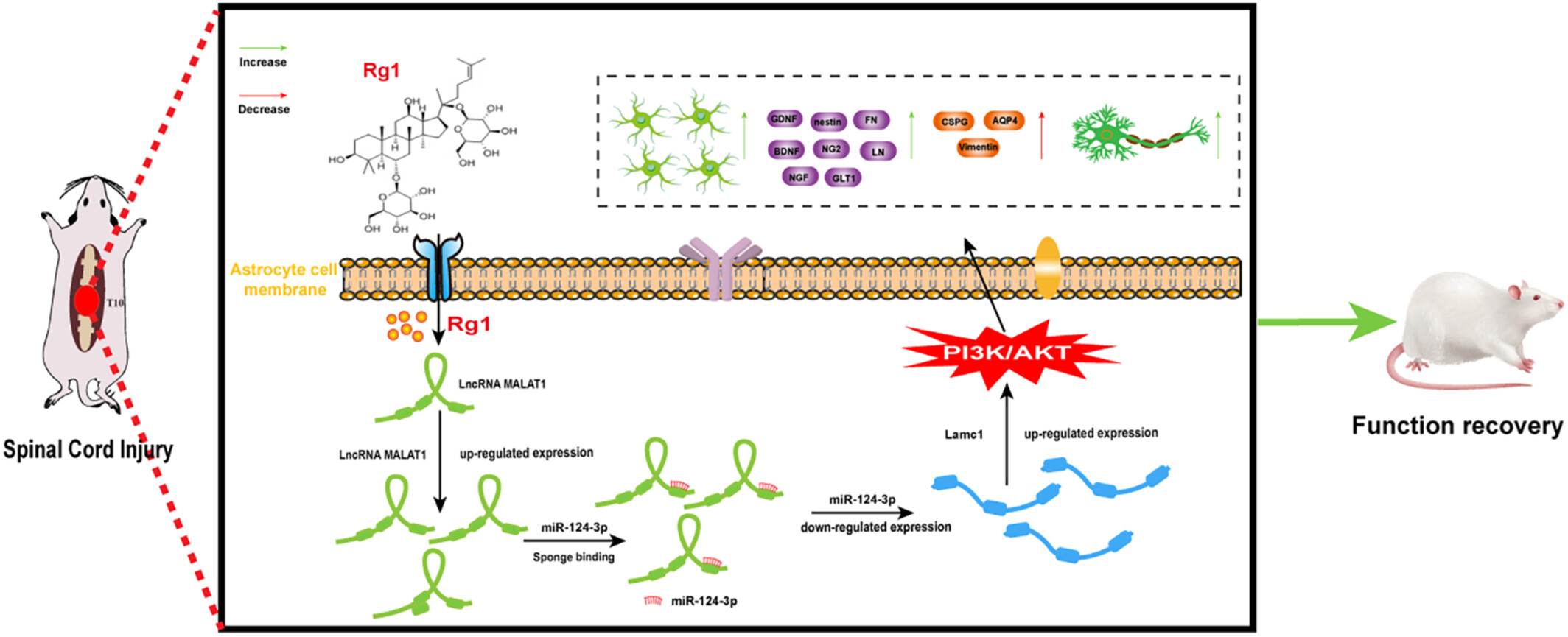
Ginsenoside Rg1 Regulates the Activation of Astrocytes Through lncRNA-Malat1/miR-124-3p/Lamc1 Axis Driving PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway, Promoting the Repair of Spinal Cord Injury
- First Published: 03 November 2024
Fasudil Alleviates Postoperative Neurocognitive Disorders in Mice by Downregulating the Surface Expression of α5GABAAR in Hippocampus
- First Published: 03 November 2024
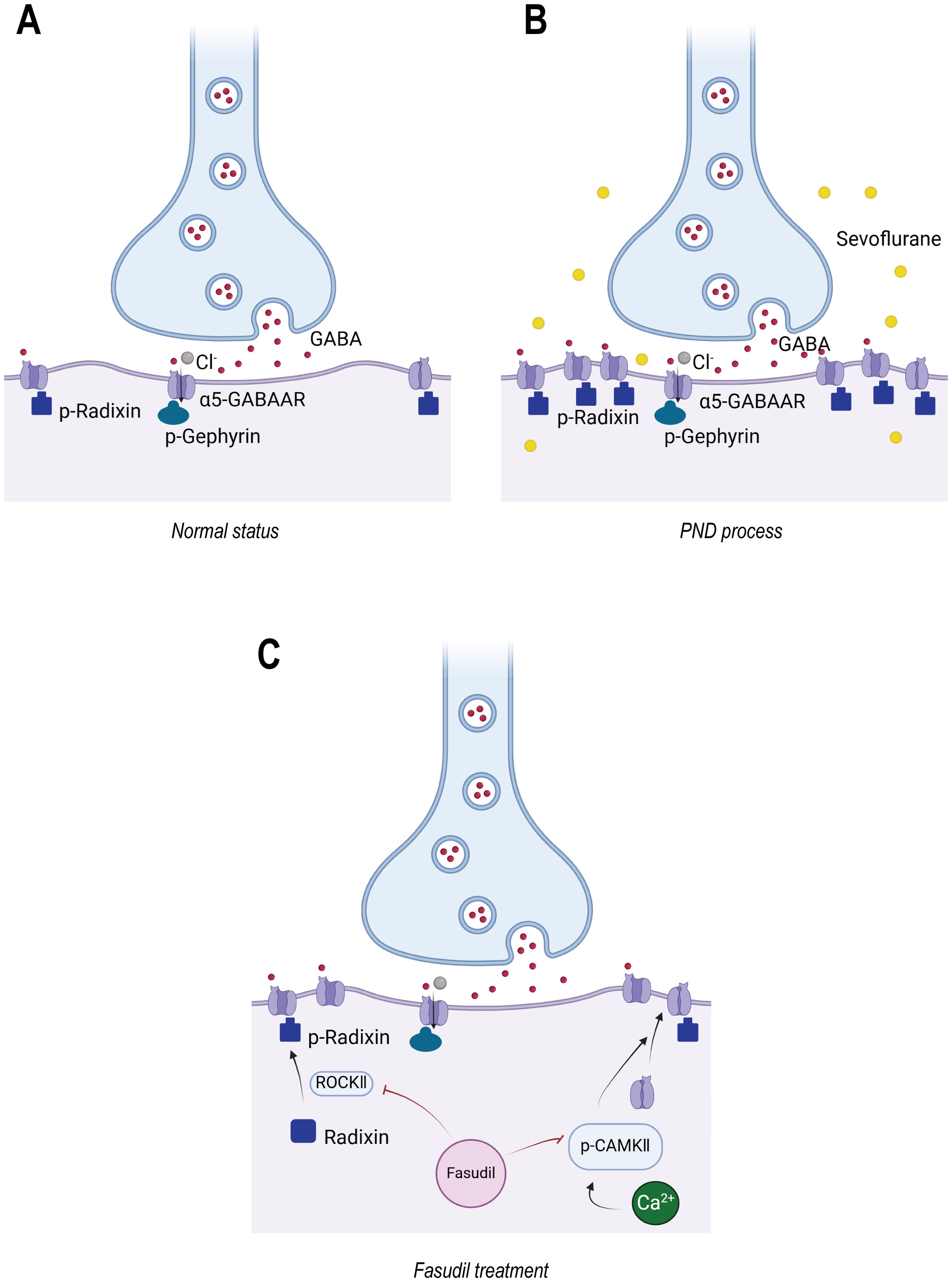
Anesthesia and surgery increase the calcium concentration in the hippocampus, increasing the phosphorylation of Camk2. Anesthesia and surgery activate the Radixin pathway, leading to increased phosphorylation of Radixin. The activation of these two pathways results in increased surface expression of α5GABAARs, ultimately leading to hippocampus-dependent memory impairment. Preadministration of the neuroprotective drug fasudil can inhibit the phosphorylation of the key molecules mentioned above, prevent the translocation of α5GABAARs to the cell surface, and thereby mitigate neurocognitive damage.
REVIEW
The early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: Blood-based panel biomarker discovery by proteomics and metabolomics
- First Published: 21 November 2024
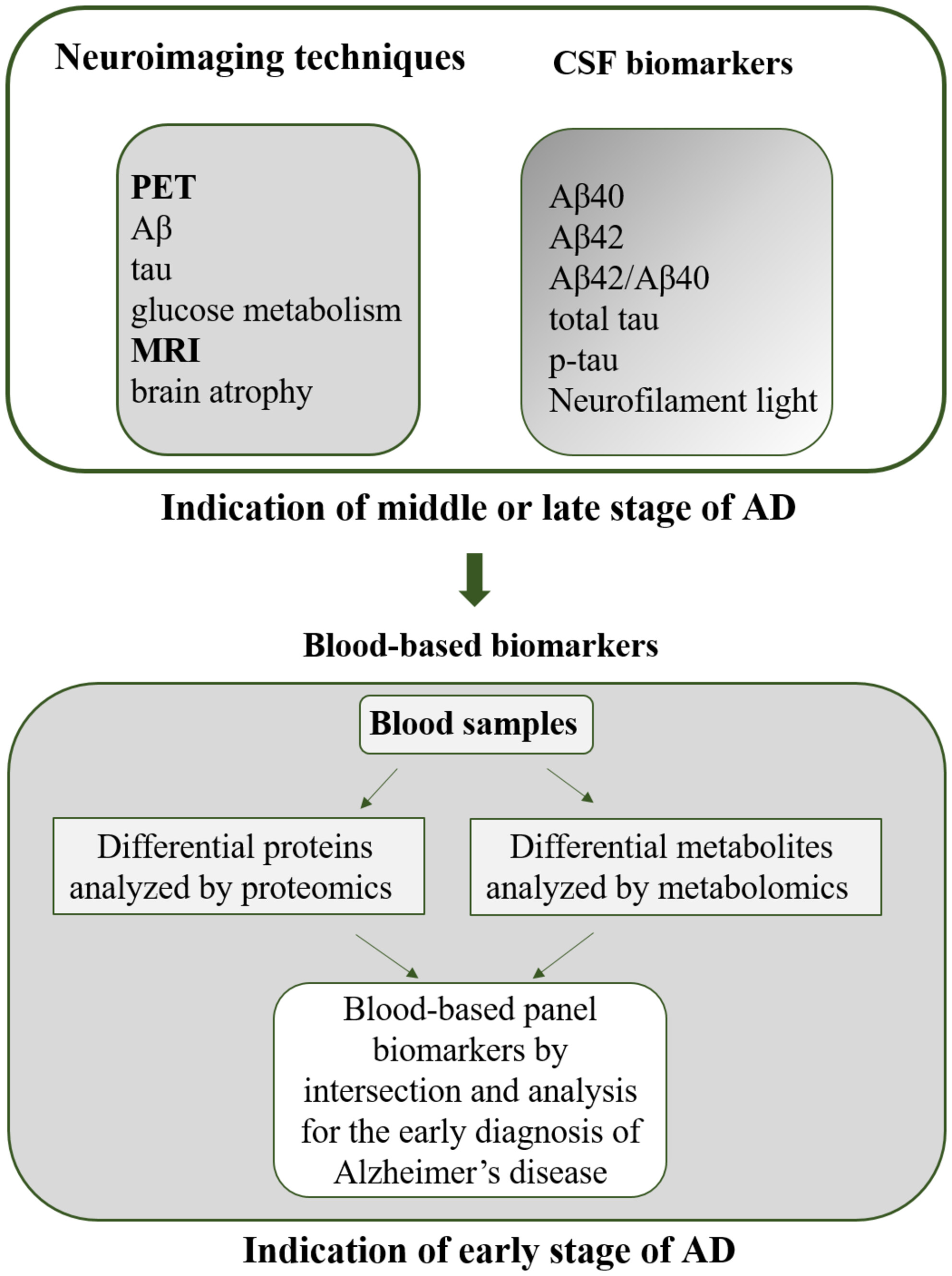
Because of CSF biomarkers identified by neuroimaging techniques in the middle or late stages of AD, blood is considered as the novel biomarker resource for the early diagnosis of AD. The accurate alternations in blood could predict AD. This paper discusses potential blood-based biomarkers identified by proteomics and metabolomics and future research direction for AD prediction, and provide an overview of early diagnosis and even promising therapeutic approaches for AD.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Orexin-A Attenuates the Inflammatory Response in Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting the ERK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Microglia and Astrocytes
- First Published: 07 November 2024
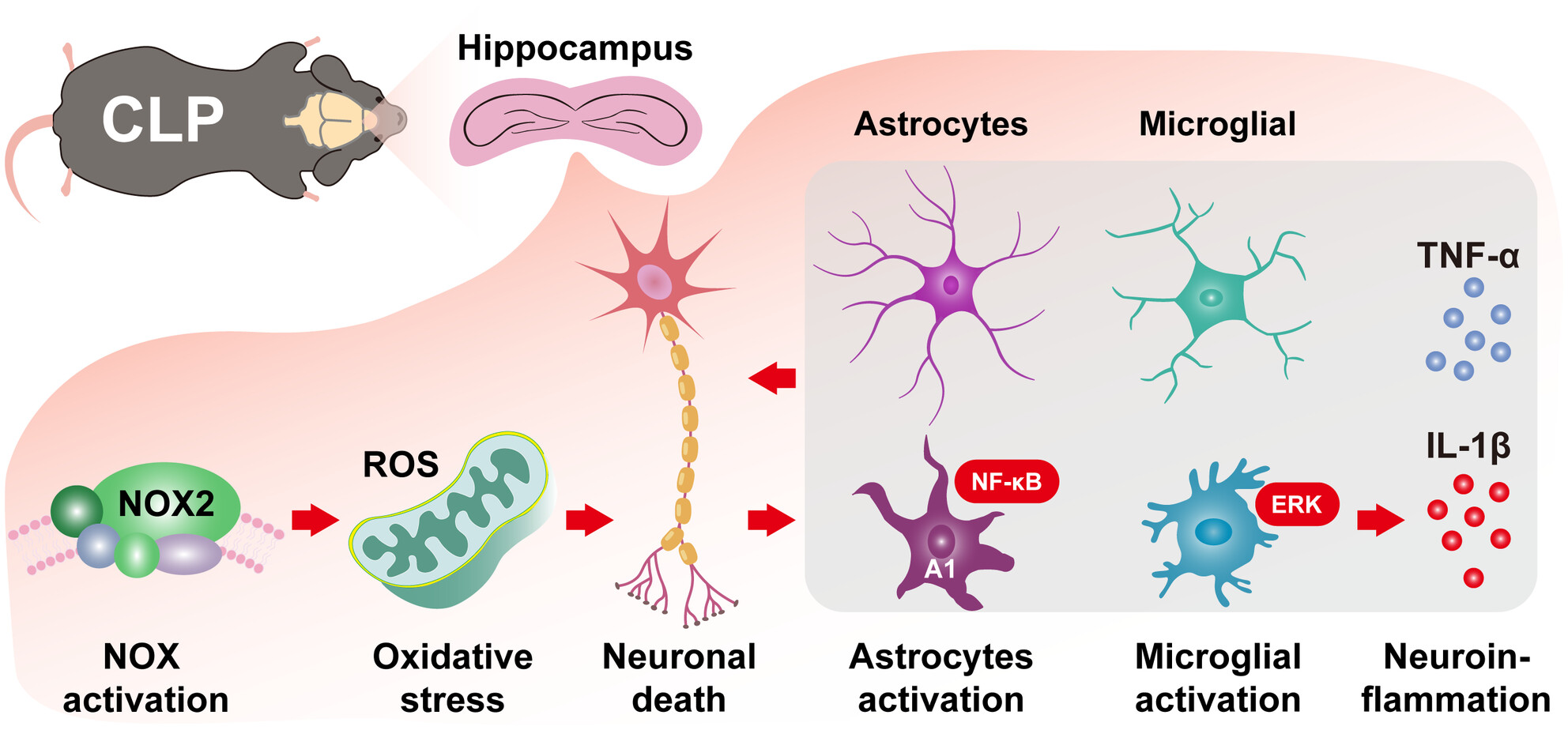
This graphic abstract provides an overview of the paper, focusing on the neuromodulatory effects of the neuropeptide orexin-A (OXA) in sepsis-associated encephalopathy. OXA reduces reactive oxygen species-induced oxidative stress by inhibiting NOX2 expression in hippocampal tissue. The main mechanism may be by inhibiting the activation of A1-type astrocytes and microglia with the NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway, which reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-1β and reduces neuronal apoptosis.
CB1 Receptor Activation Provides Neuroprotection in an Animal Model of Glutamate-Induced Excitotoxicity Through a Reduction of NOX-2 Activity and Oxidative Stress
- First Published: 04 November 2024
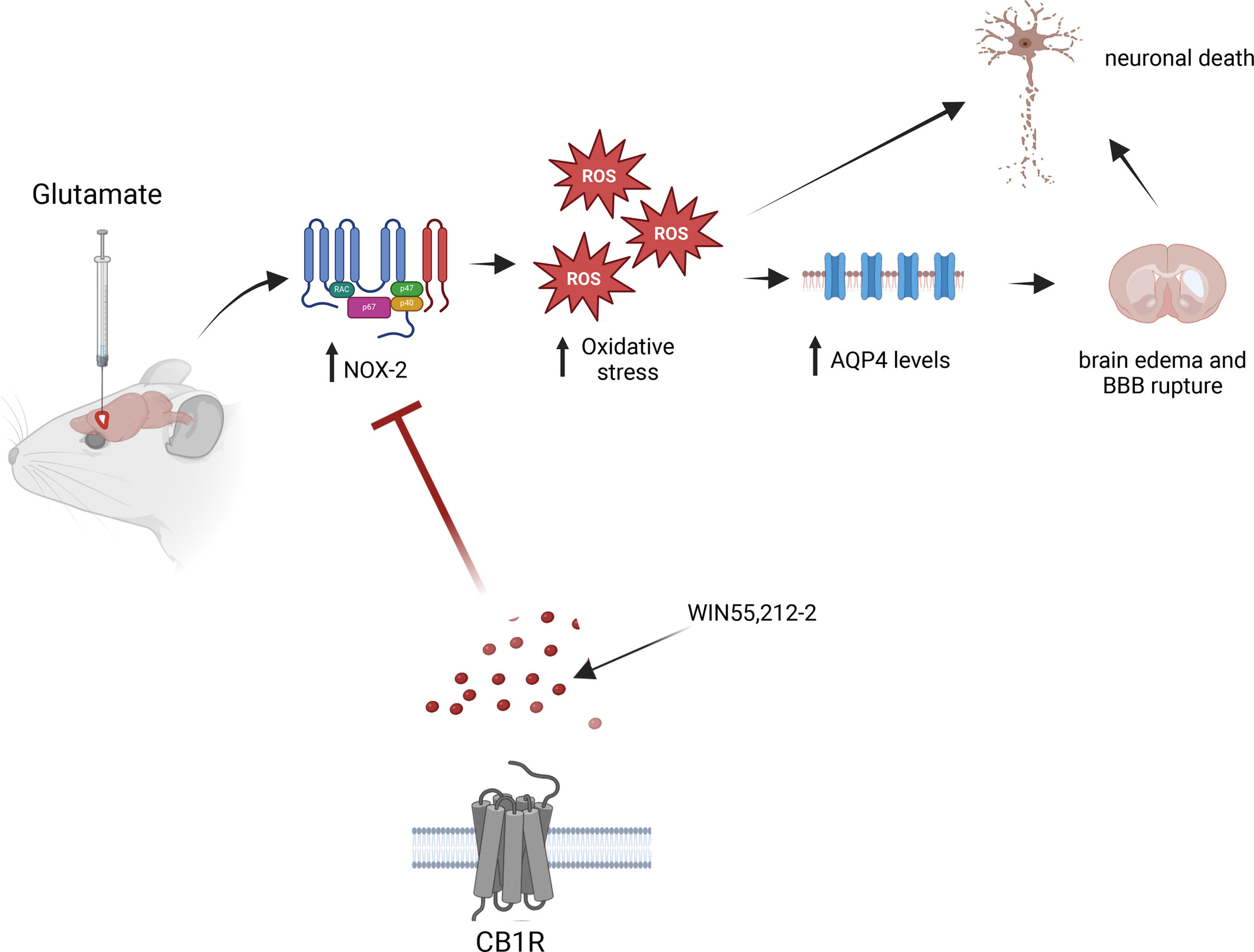
During excitotoxicity, reactive oxygen species, produced by NADPH-oxidase 2 (NOX-2), increases the levels of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) leading to the rupture of the blood–brain barrier and cerebral edema. This along with oxidative stress contributes to neuronal death. Stimulation of cannabinoid receptor type 1 receptors relieves oxidative stress by a reduction of NOX-2 activity and thus inhibits AQP4 increase, edema, and brain damage. The endocannabinoid system can be a therapeutic target for limiting brain damage.
Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals the Effects of rTMS on Neural Activity and Brain Connectivity After Experimental Stroke
- First Published: 04 November 2024
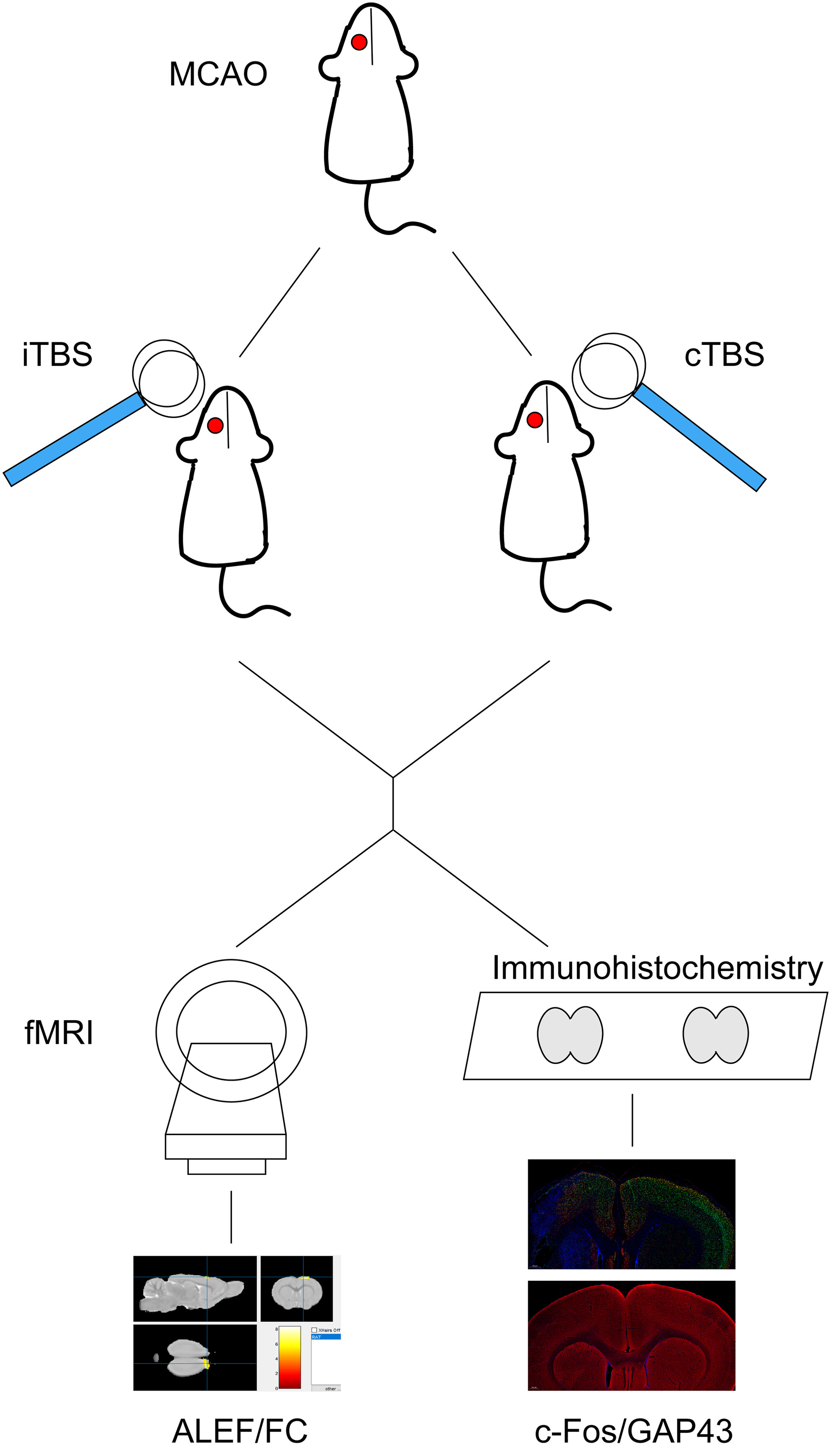
Intermittent and continuous theta burst stimulation were used to stimulate ipsilesional and contralesional hemisphere, respectively, during the subacute phase after stroke. Rs-fMRI was used to detect neuronal activity and functional connectivity, and immunohistochemistry was used to verify the results of rs-fMRI.
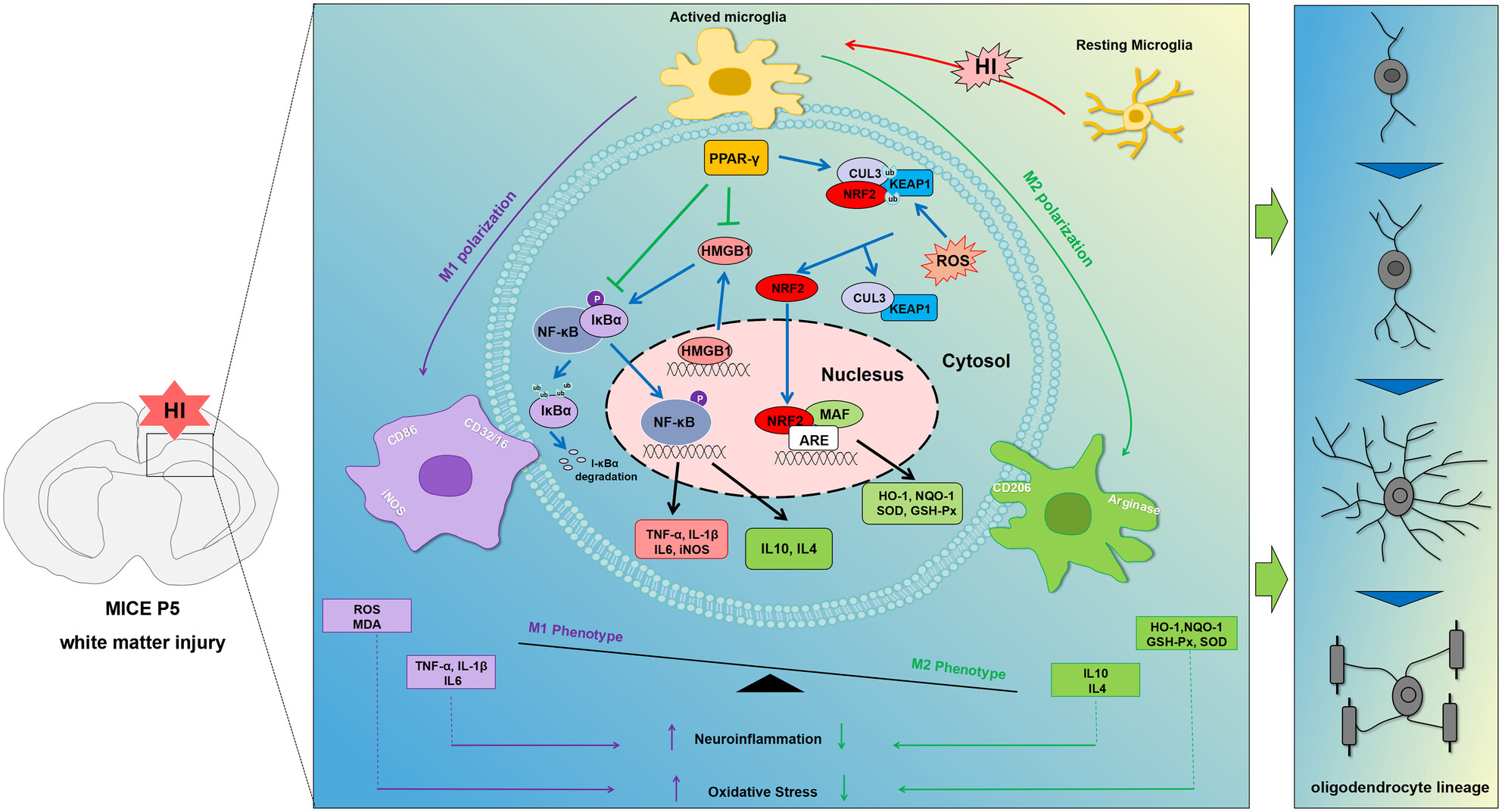
The Neuroprotective Mechanisms of PPAR-γ: Inhibition of Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Neonatal Mouse Model of Hypoxic-Ischemic White Matter Injury
- First Published: 04 November 2024
REVIEW
Border-Associated Macrophages: From Embryogenesis to Immune Regulation
- First Published: 04 November 2024
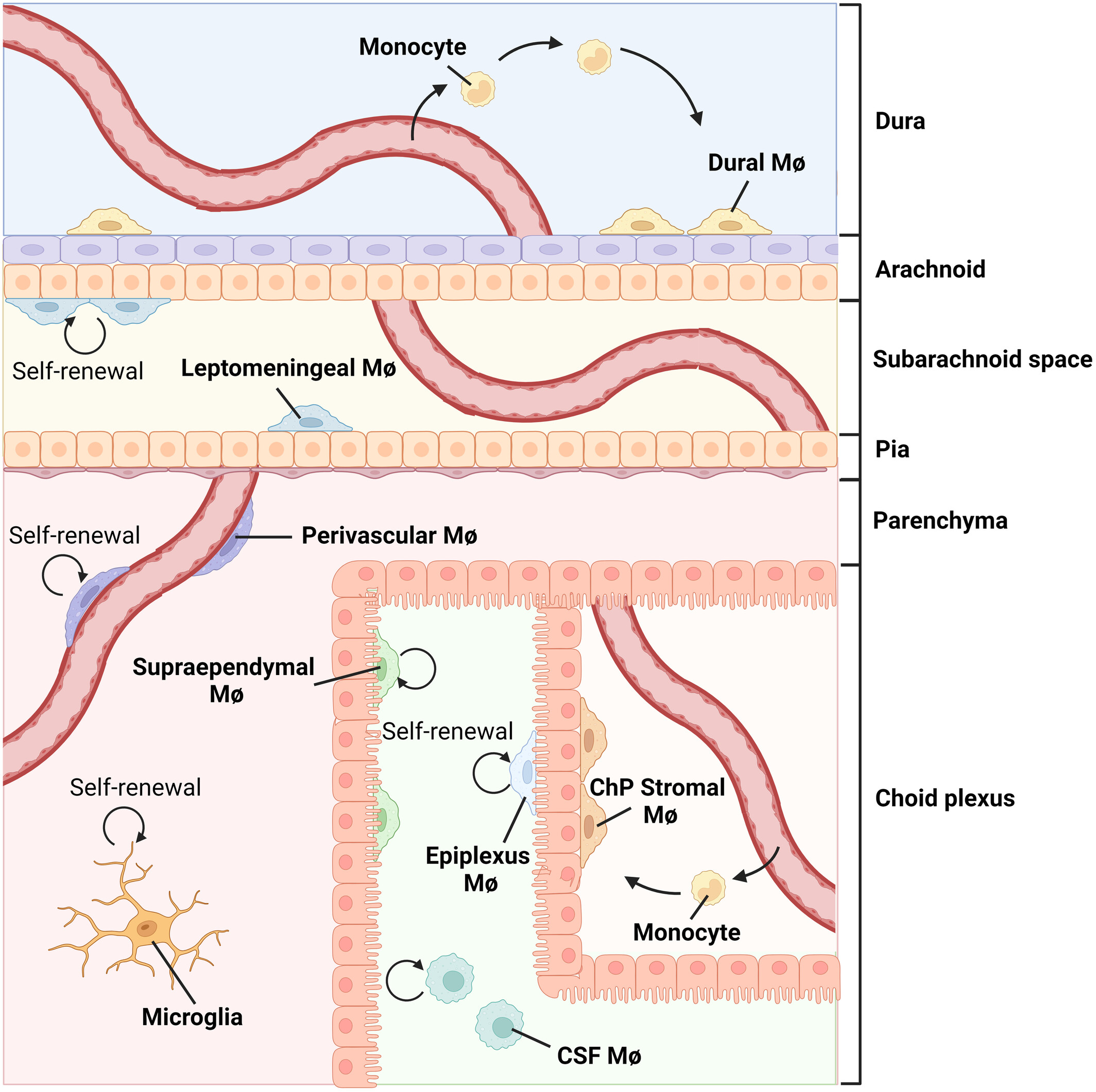
Border-associated macrophages (BAMs) are integral to the maintenance of brain homeostasis and the immune response to pathological conditions. This review addresses the ontogeny, replenishment, and microenvironmental regulation and transcriptomic heterogeneity of BAMs. Additionally, the roles of BAMs in sustaining brain homeostasis, conducting immune surveillance, and mediating responses to injury and neurodegenerative processes are critically examined.
CASE REPORT
Muscle Weakness in an Adult With 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome
- First Published: 04 November 2024

This case report provides the first evidence that coenzyme Q10 may improve muscle weakness in patients with 22q11.2DS. The patient's genetic copy number deletion mutation region mainly contains COMT, PRODH functional genes related with mitochondria dynamics. The level of L-arginine was significantly increased after treatment by coenzyme Q10 in serum.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Targeting Myeloperoxidase to Reduce Neuroinflammation in X-Linked Dystonia Parkinsonism
- First Published: 05 November 2024
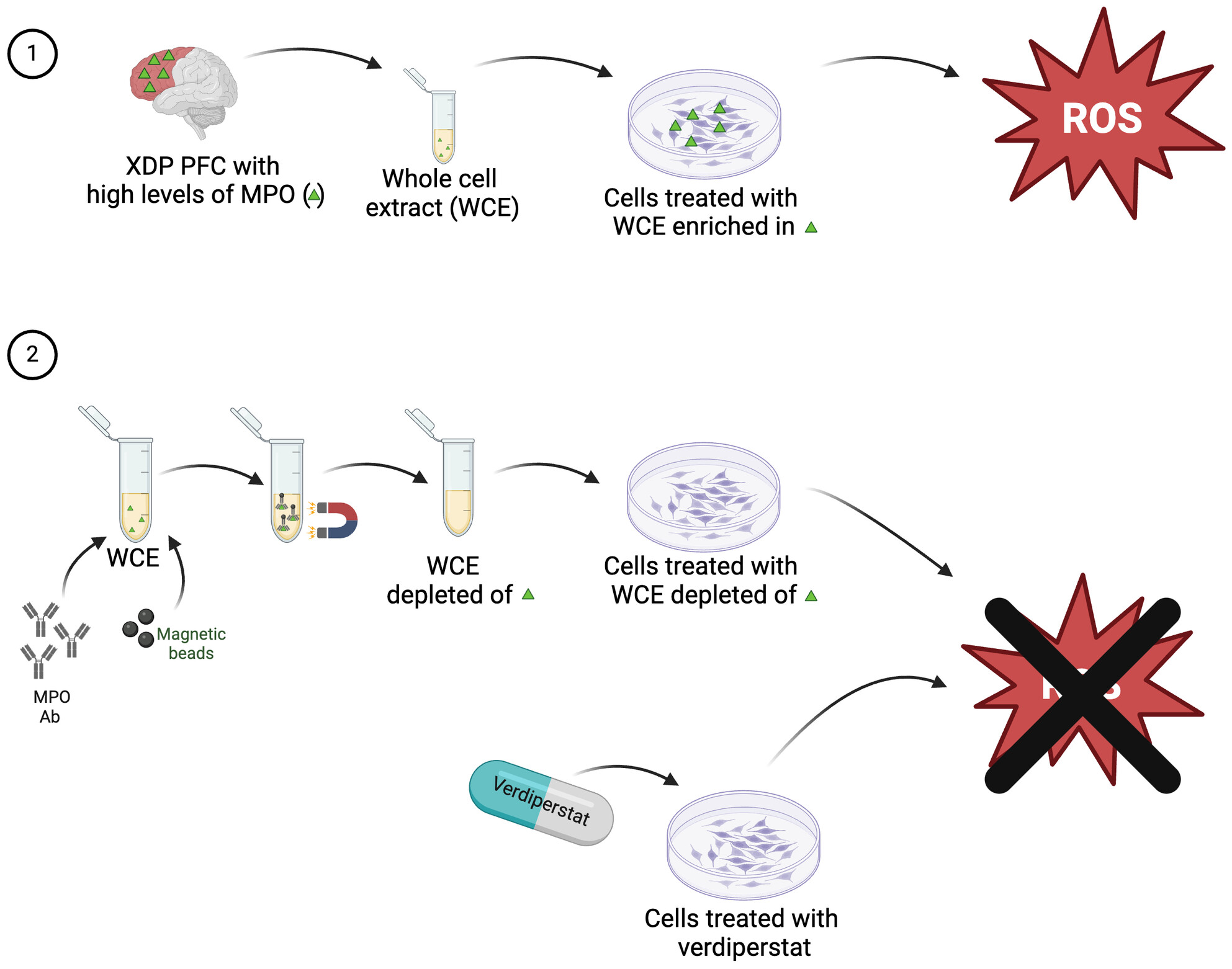
Myeloperoxidase activity is increased in X-linked dystonia parkinsonism (XDP) postmortem brain and caused an increase in oxidative stress. Decreasing MPO levels or inhibiting its activity significantly reduced reactive oxygen species in vitro, suggesting that targeting MPO may reduce oxidative stress in XDP.
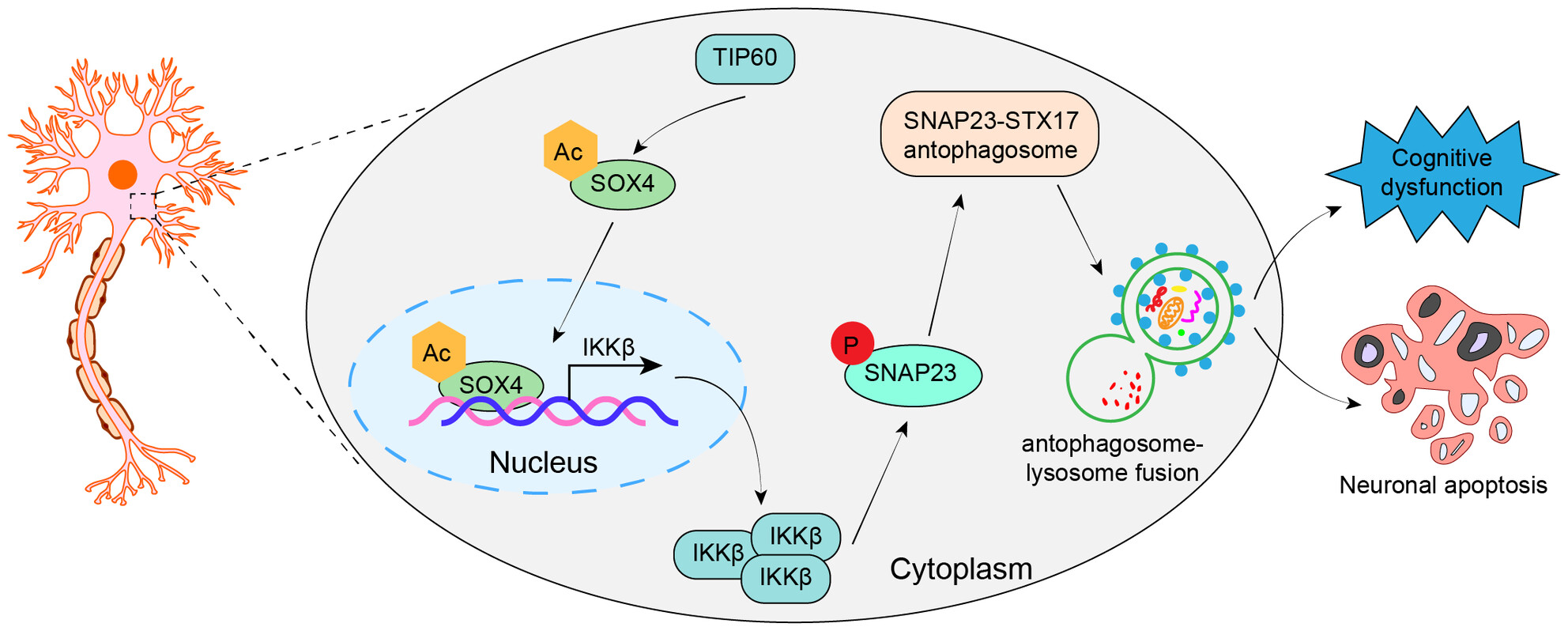
Lysine Acetyltransferase TIP60 Restricts Nerve Injury by Activating IKKβ/SNAP23 Axis-Mediated Autophagosome-Lysosome Fusion in Alzheimer's Disease
- First Published: 05 November 2024
The Optimal Radiotherapy Strategy for Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastasis: A Retrospective Analysis
- First Published: 05 November 2024
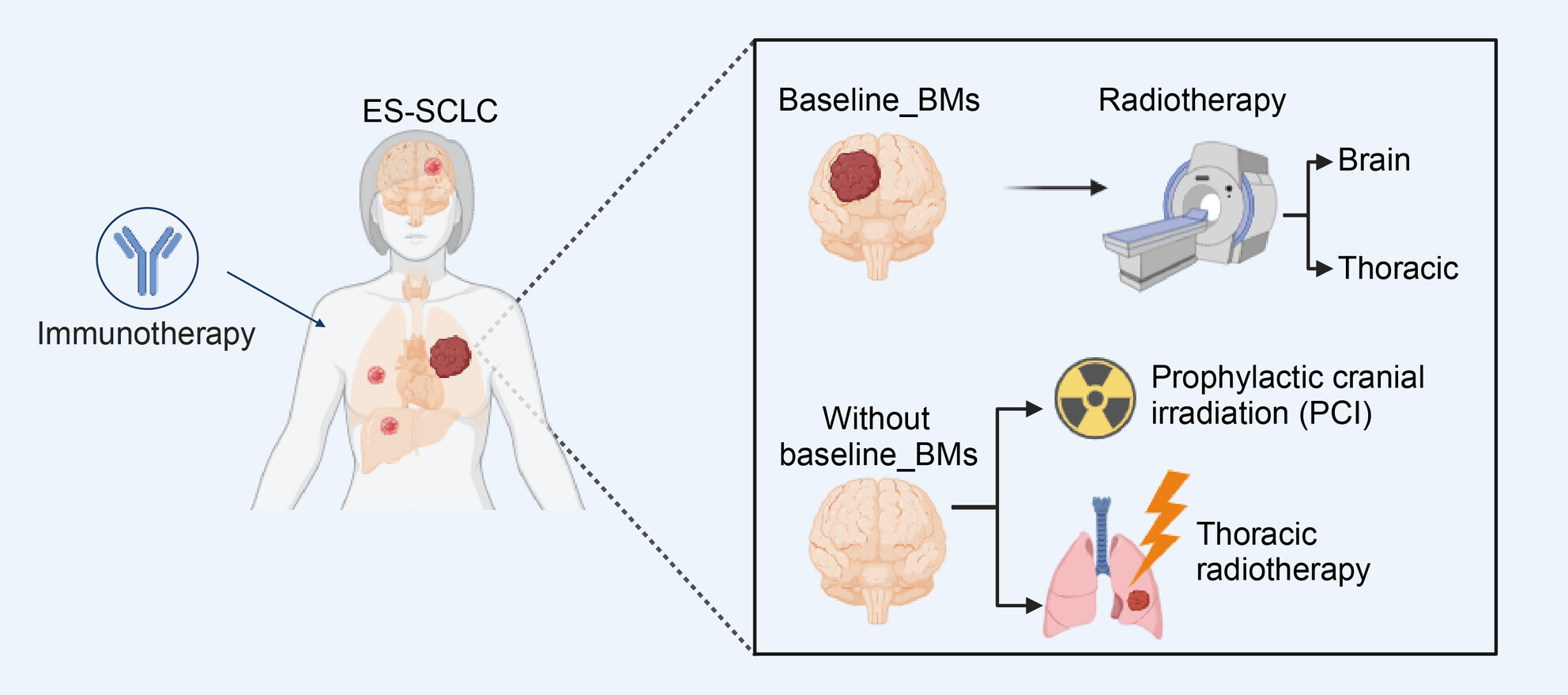
In a cohort of patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer undergoing immunotherapy, this study explored the role of radiotherapy and delve into brain metastases subgroup. Brain and thoracic radiotherapy were identified as favorable prognostic factors for survival in those with brain metastases. Moreover, prophylactic cranial irradiation and thoracic radiotherapy delayed intracranial progression in those initially without brain metastases. These findings underscore the pivotal role of local therapies in the management of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer during the immunotherapy era.
The Neuroprotection of 1,2,4-Triazole Derivative by Inhibiting Inflammation and Protecting BBB Integrity in Acute Ischemic Stroke
- First Published: 05 November 2024
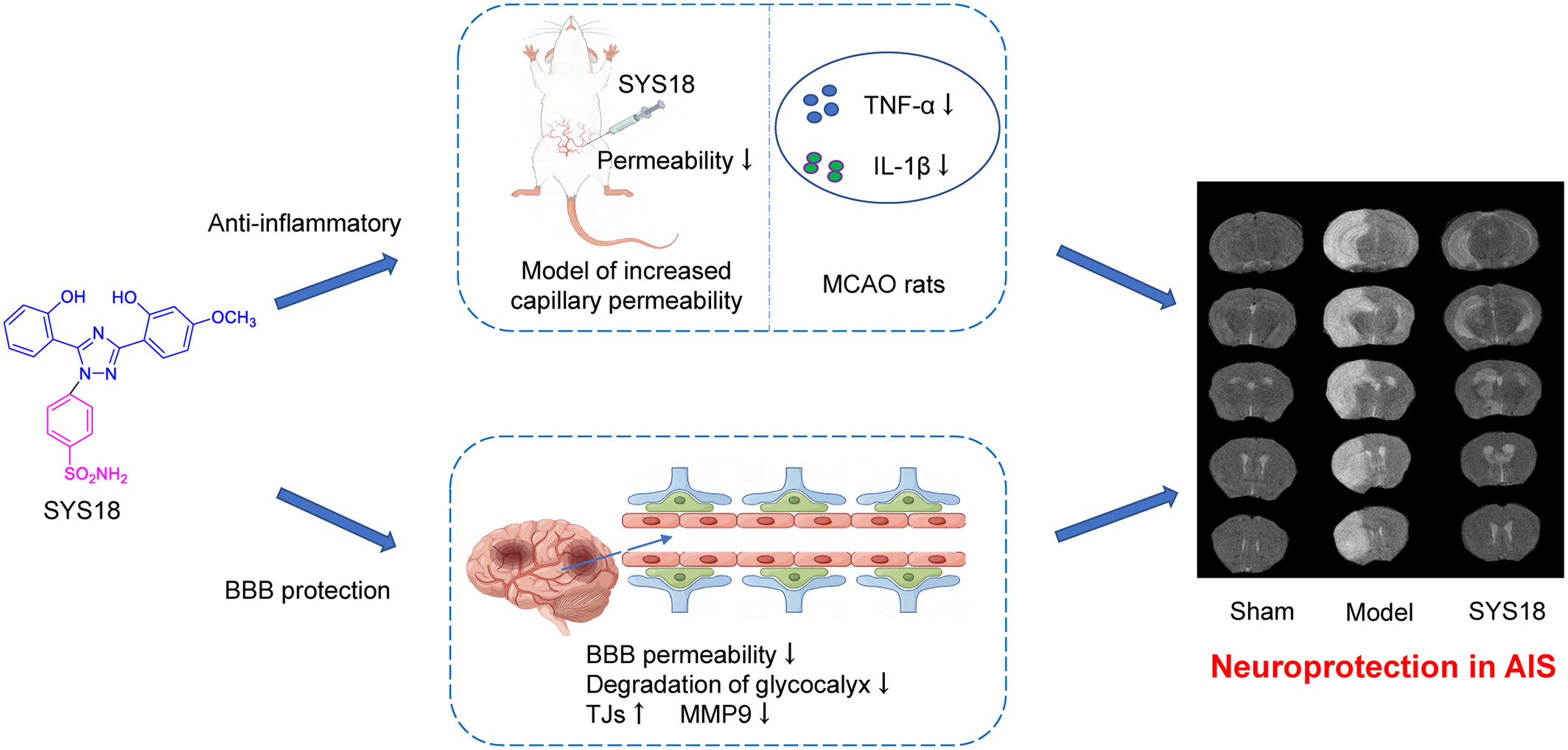
SYS18 has a certain therapeutic effect on acetic acid–induced acute inflammation. It protects the BBB integrity by decreasing the BBB permeability, inhibiting endothelial glycocalyx degradation, and regulating TJs and MMP-9 expression levels in AIS. SYS18 can alleviate neurological impairment by inhibiting inflammation and protecting the BBB integrity in AIS.
REVIEW
Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease Via the Regulation of the Gut Microbiota With Traditional Chinese Medicine
- First Published: 07 November 2024
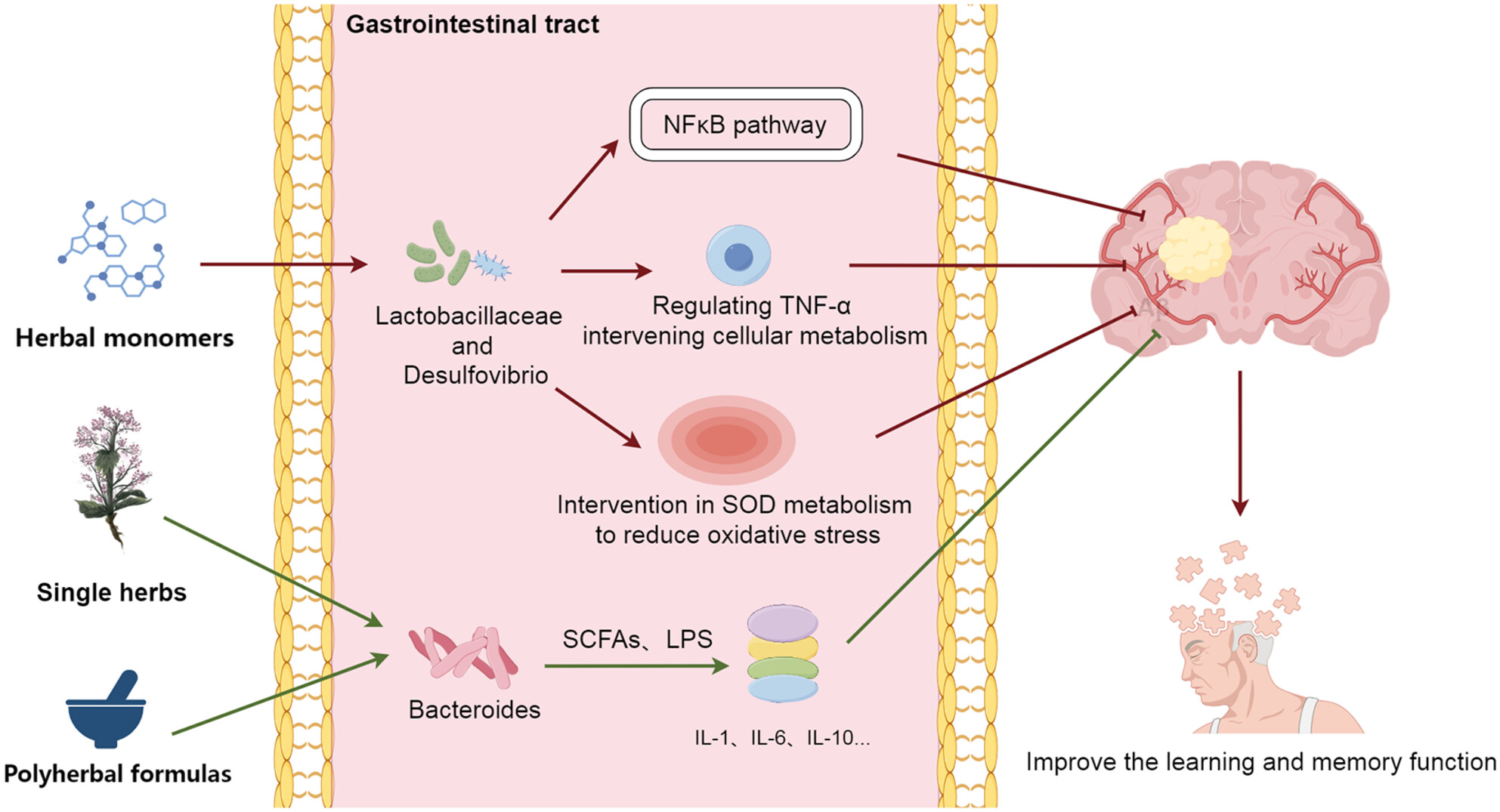
The microbiota–gut–brain axis plays an important role in the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In terms of treatment, it has been proven that traditional Chinese medicine are effective in AD by regulating the gut microbiota. And then gut microbiota and its metabolism may inhibit inflammatory response through tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL), the nuclear factor kappa-B pathway, and superoxide dismutase metabolism. The sedimentation of β-amyloid (Aβ) and learning and memory function of AD are finally influenced. It indicates that choosing appropriate Chinese medicine as the complementary treatment may be a better way to achieve satisfactory clinical efficacy in AD.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
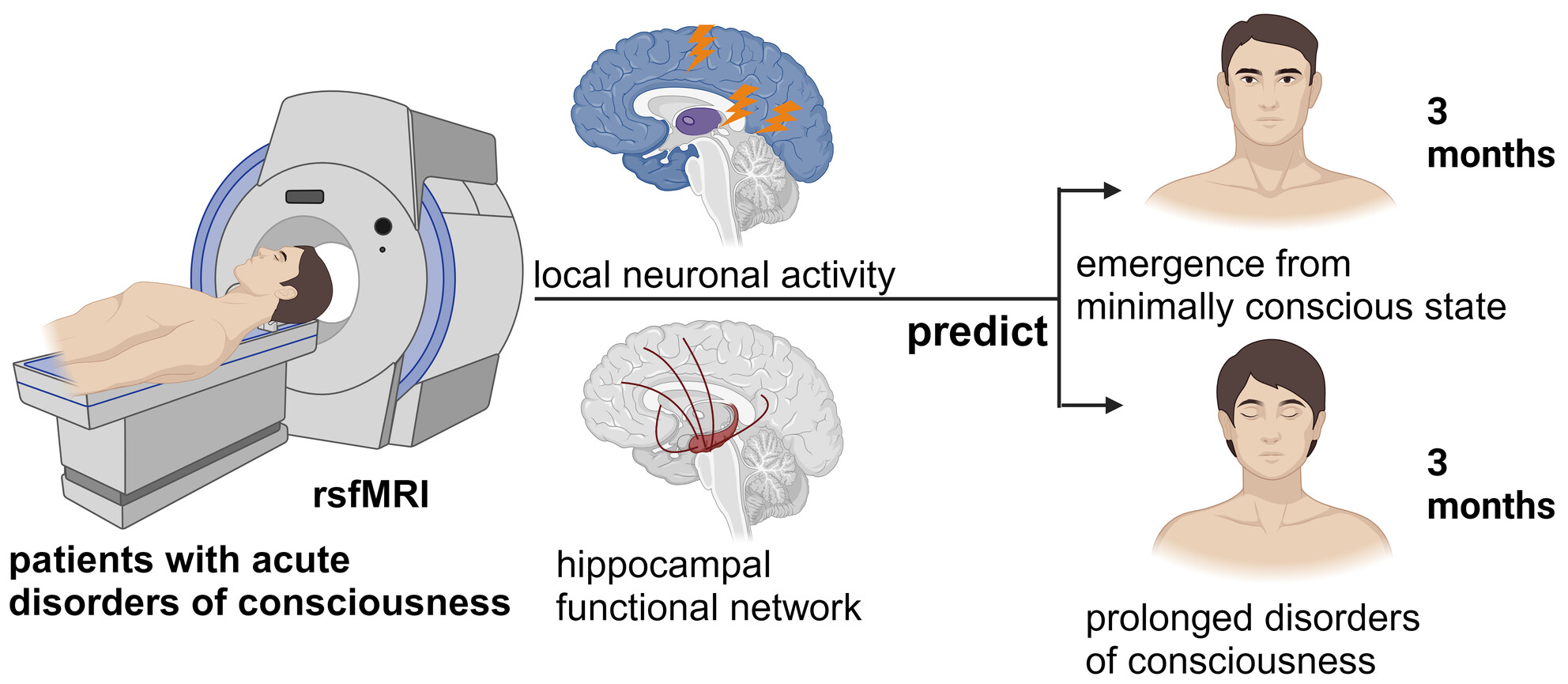
Local Neuronal Activity and the Hippocampal Functional Network Can Predict the Recovery of Consciousness in Individuals With Acute Disorders of Consciousness Caused by Neurological Injury
- First Published: 07 November 2024
Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Targeting Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex and Orbitofrontal Cortex on Somatic Symptoms in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Clinical Trial
- First Published: 08 November 2024
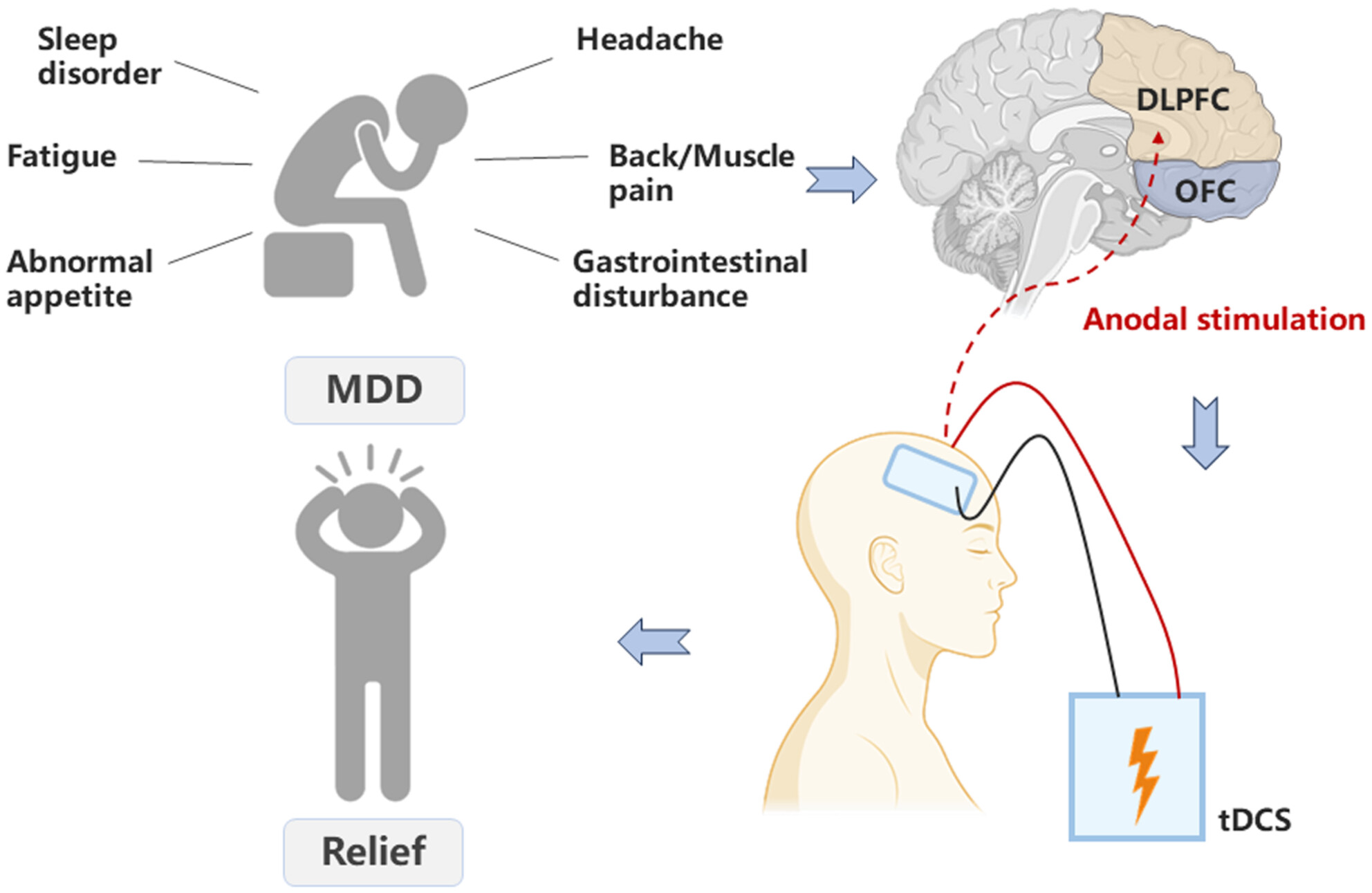
Somatic symptoms are common manifestations in MDD patients. However, there is a lack of research on tDCS for treating somatic symptoms in MDD. This study found tDCS targeting DLPFC significantly improved somatic symptoms in MDD patients, suggesting it an effective target of tDCS for somatic symptoms in MDD.
Postoperative Nodal Efficiency of the Lesional-Hemispheric Hand Motor Area Increasing Potentially Facilitated Motor Recovery for SMA Syndrome
- First Published: 12 November 2024
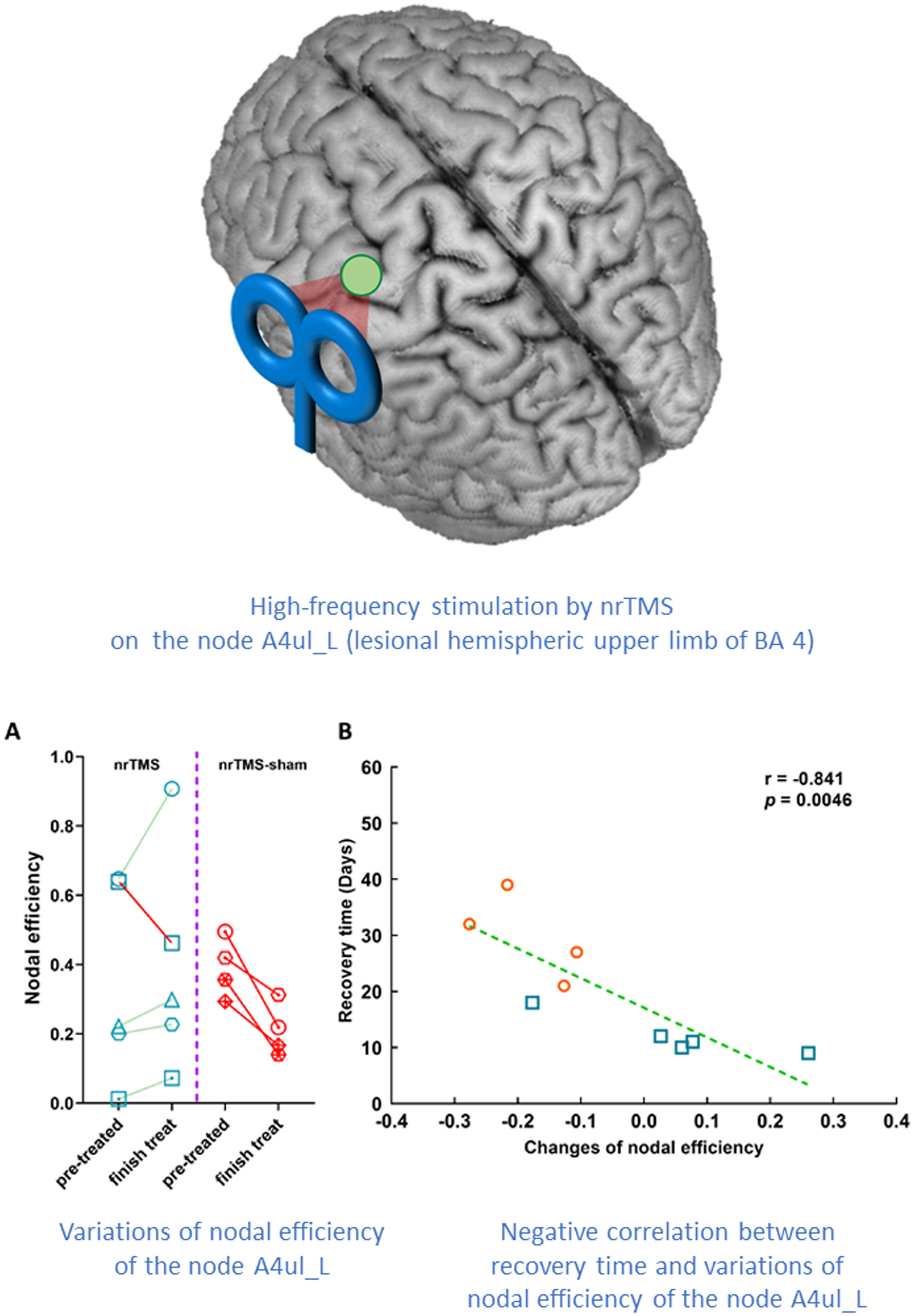
Hand-motor-related cortex on the lesional hemisphere (A4ul_L) increasing its nodal efficiency in postoperation was beneficial for SMA syndrome recovery. The A4ul_L may be a potential therapeutic target for SMA syndrome. Applying nrTMS with high-frequency stimulation on the node A4ul_L will increase its nodal efficiency, but sham-nrTMS won't. It may indicate that nrTMS stimulation may accelerate SMA syndrome recovery.
Thalamic Volumes and Functional Networks Linked With Self-Regulation Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder
- First Published: 10 November 2024
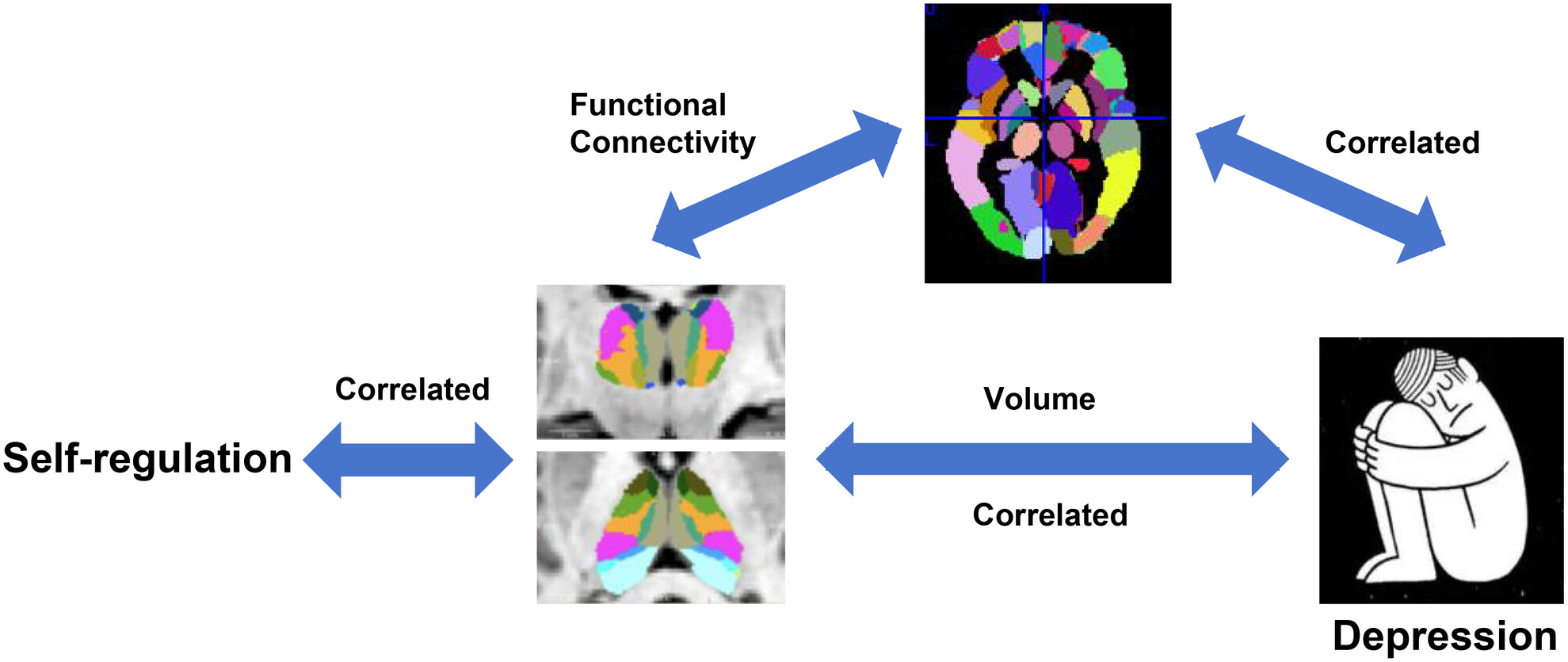
Inter-network functional connectivity of the orbital part of the right superior frontal gyrus and left supplementary motor area mediated the relationship between self-regulation and depression. Self-regulation could impact depressive symptoms via regulating inter-network functional connectivity of thalamic subnuclei. Thalamic functional subnetworks could predict the self-regulation and depressive severity of depressed individuals.
Static and Dynamic Functional Network Connectivity in Parkinson's Disease Patients With Postural Instability and Gait Disorder
- First Published: 10 November 2024
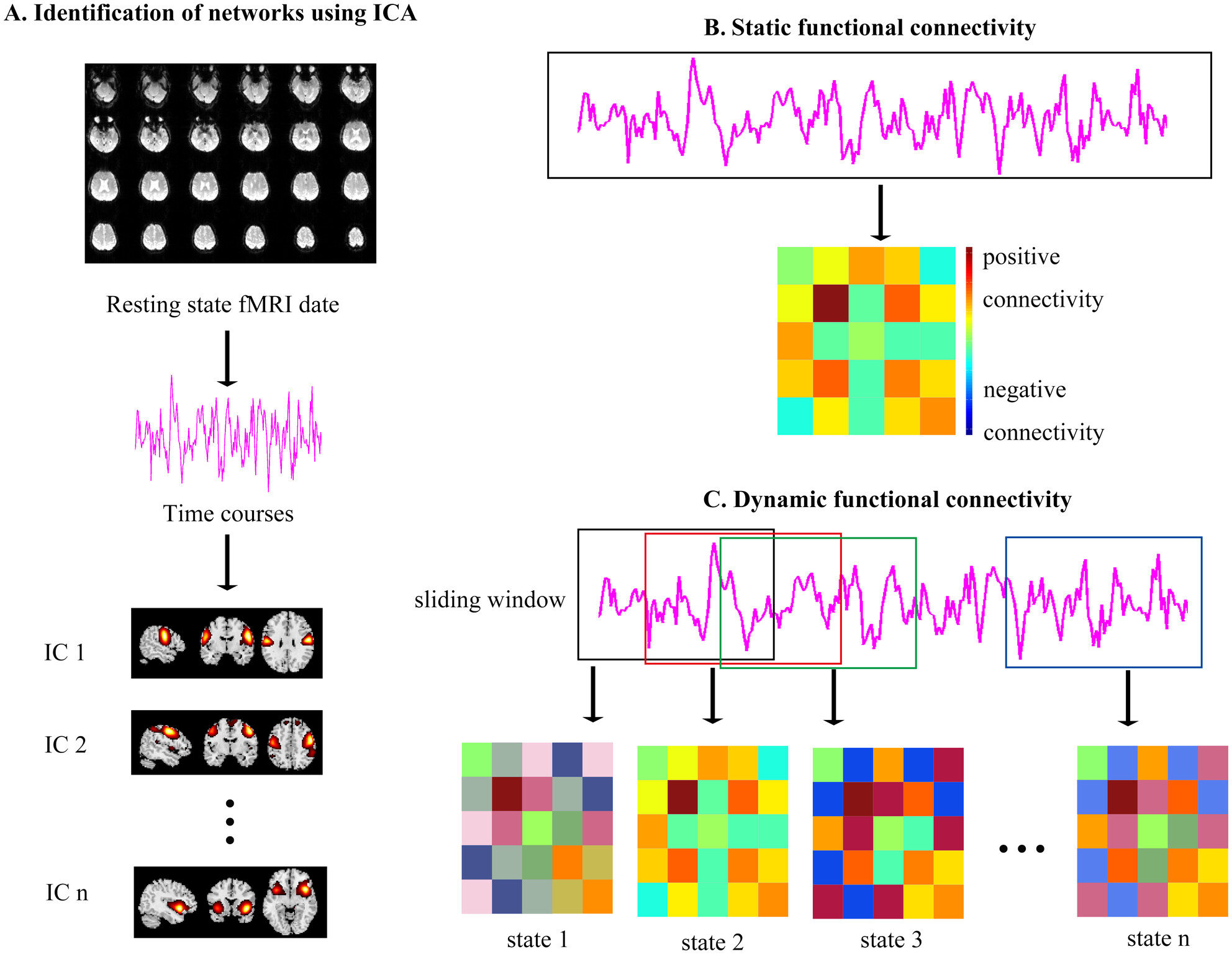
We first compared the DFNC and SFNC of the three networks and examined their associations with tremor symptoms. PIGD-PD patients were more likely to remain in the condition of sparse connection. The enhanced connection between the cerebellum and cognitive networks is considered a type of dynamic compensation.
REVIEW
Antisense oligonucleotides as a precision therapy for developmental and epileptic encephalopathies
- First Published: 11 November 2024
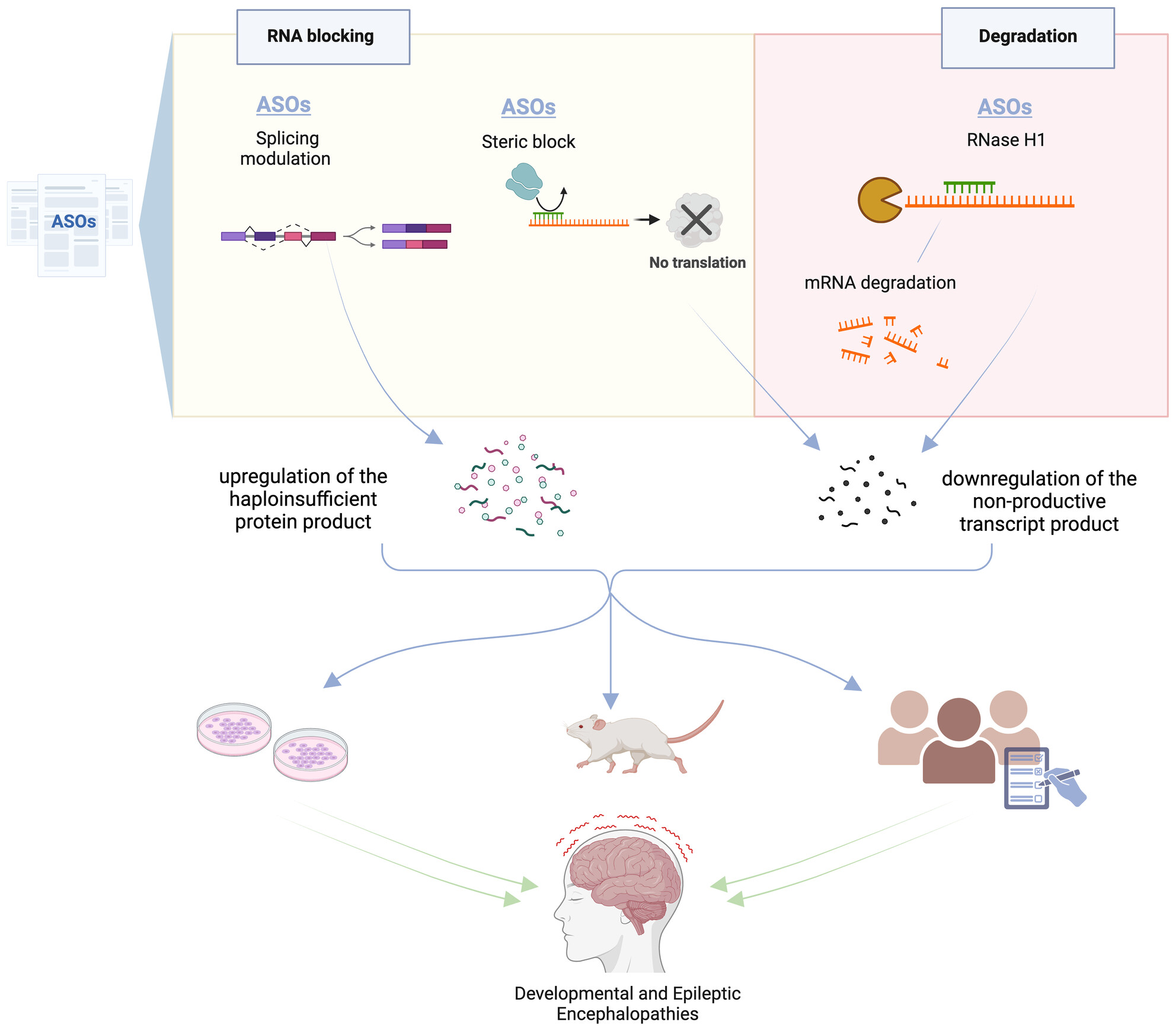
ASOs have led to important advancements in mRNA regulation for treating developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs). The mechanisms of action may vary: RNA function blocking could be obtained by modulating alternative splicing or through steric hindrance; similarly, RNA degradation could be obtained through RNase H1. However, upregulation of the final haploinsufficient protein product can also be achieved. Pre and clinical studies pave the way for potential innovative therapies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Automated Hematoma Detection and Outcome Prediction in Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury
- First Published: 12 November 2024
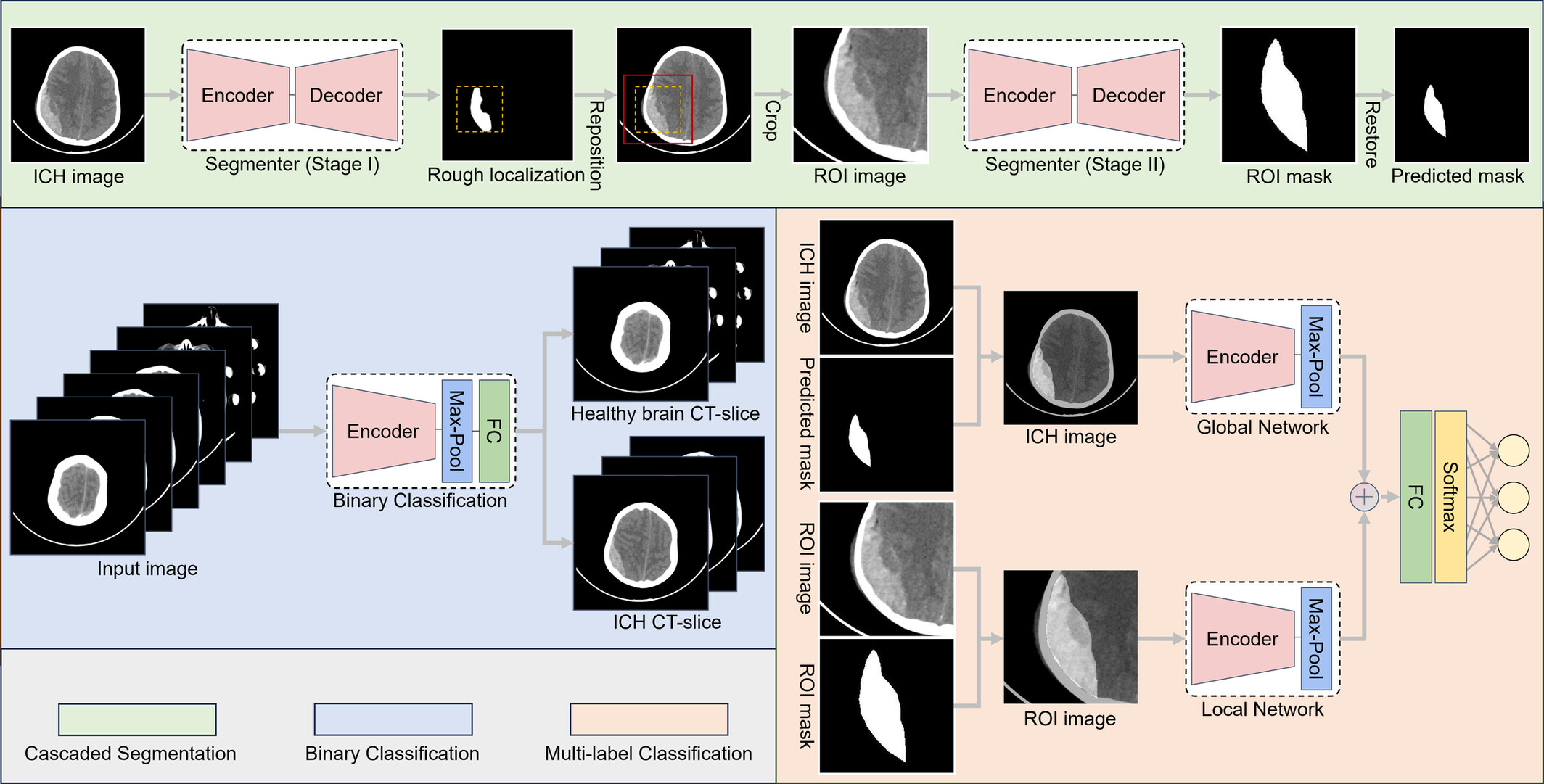
Our study aims to automatically classify and segment CT images of patients with traumatic brain injury using a deep learning model. Based on the automatic classification and segmentation, volume and subtype characteristics of the hematoma were extracted and combined with other clinical information to predict in-hospital mortality.
REVIEW
Stroke-Induced Renal Dysfunction: Underlying Mechanisms and Challenges of the Brain–Kidney Axis
- First Published: 12 November 2024

After a stroke, multiple pathways in the neurohumoral system are activated. At the same time, the blood–brain barrier is compromised, and pro-inflammatory substances are released from the brain into the bloodstream, consequently activating the peripheral inflammatory immune response. As an acute injury, stroke triggers renal hemodynamic disturbances and an acute ischemic state in the kidney, thereby promoting the development of AKI or CKD.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
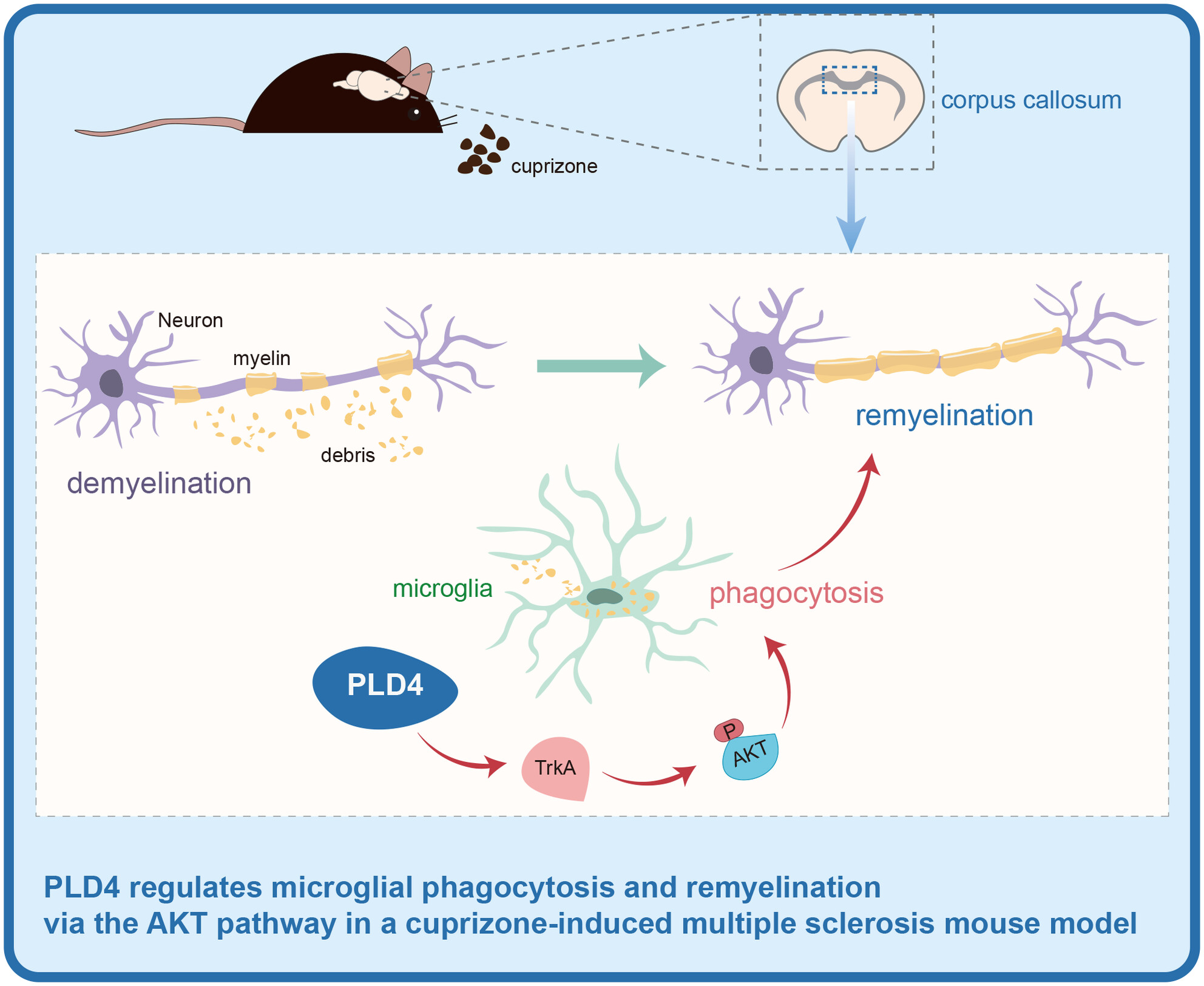
Phospholipase D Family Member 4 Regulates Microglial Phagocytosis and Remyelination via the AKT Pathway in a Cuprizone-Induced Multiple Sclerosis Mouse Model
- First Published: 15 November 2024
REVIEW
Endothelial Dysfunctions in Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown in Alzheimer's Disease: From Mechanisms to Potential Therapies
- First Published: 15 November 2024
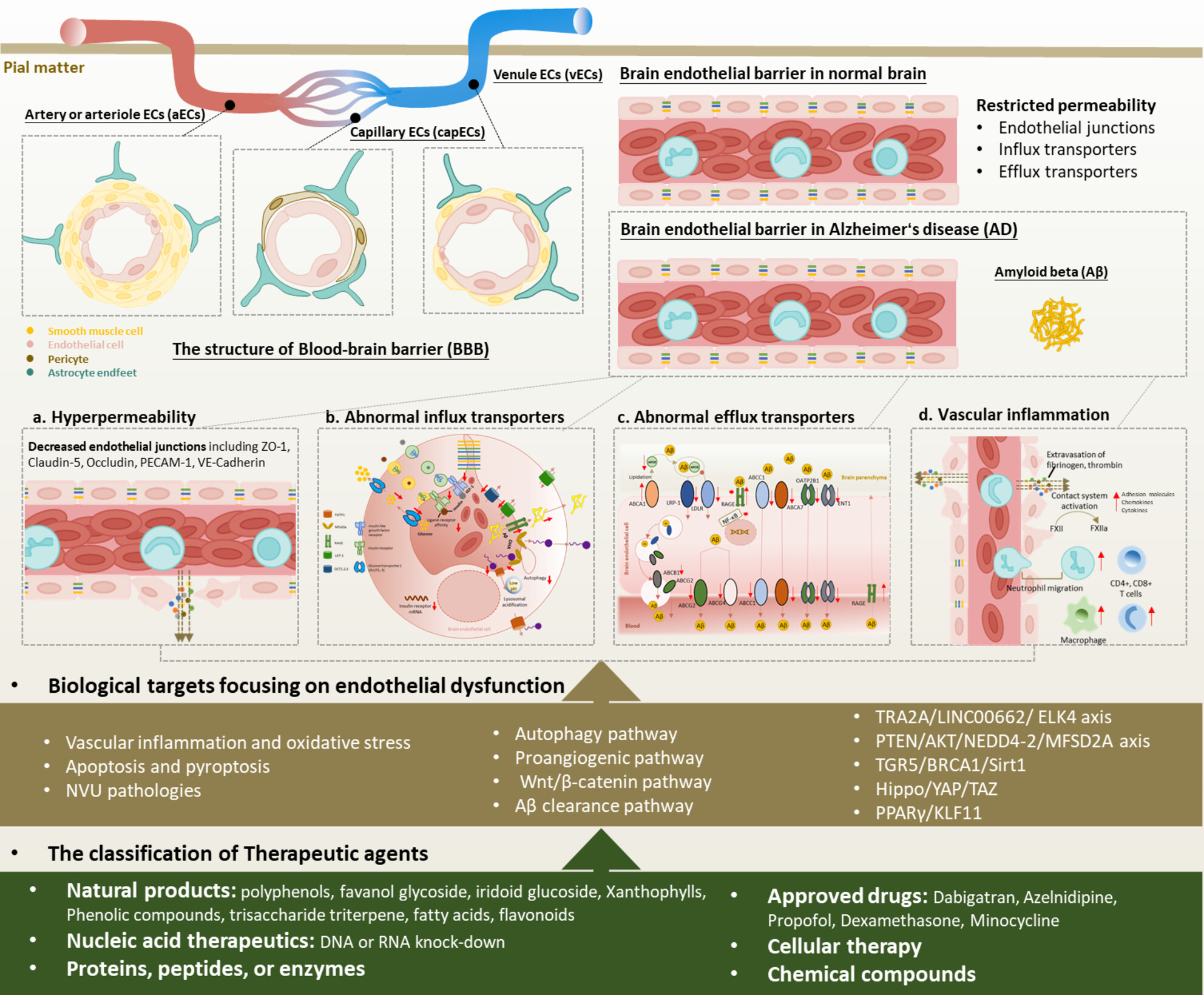
Blood–brain barrier (BBB) works as a crucial structure separating central nervous system (CNS) and circulating system. The highly organized endothelial junctions and transporters strictly restricts substance exchange across BBB to maintain the homeostasis of CNS. In Alzheimer's disease, BBB breakdown has been widely detected, featured as a series of brain endothelial cell (BEC) pathologies, including increased permeability, abnormal levels and functions of influx and efflux transporters, as well as inflammatory and oxidative profile. The goal for BEC-targeting treatment in AD is to maintain the integrity of BBB and accelerate the clearance of brain-derived Aβ species through BBB. BEC-targeting treatment for AD mainly focuses on regulating a series of pathological processes including inflammation, oxidative stress, autophagy, apoptosis, and several signaling such as angiogenic and Wnt/β-catenin pathway, as well as modulating Aβ clearance pathway and so on. Targeting various BEC pathologies have shown therapeutic potentials in protecting BBB and improving cognitive functions in AD.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Steroids' Neuroprotective Potential in Severe Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: Experimental and Clinical Exploration of NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibition
- First Published: 17 November 2024
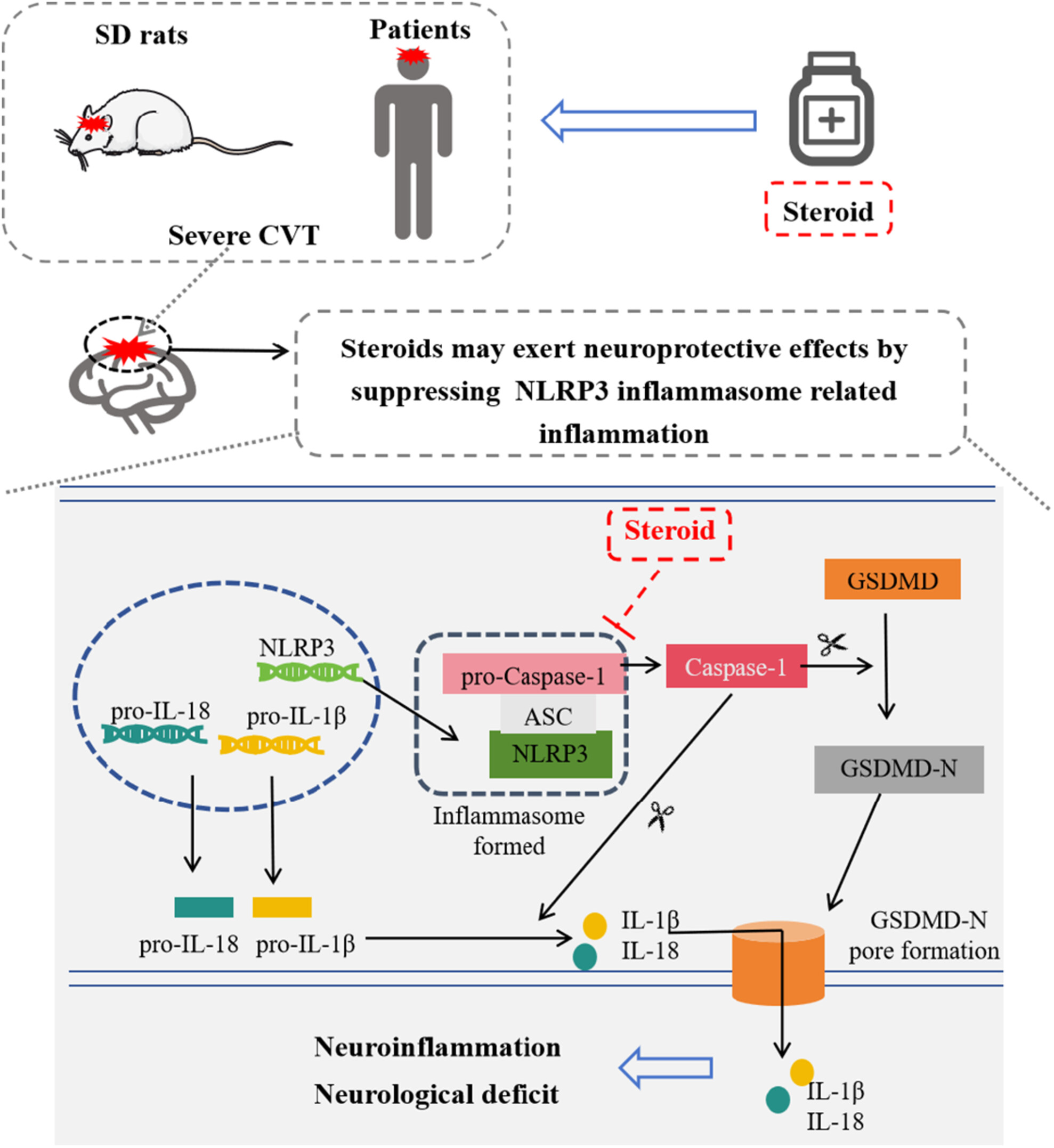
The NLRP3 inflammasome exhibited a strong correlation with neurological injury in severe CVT, both in rats and patients. The neuroprotective benefits of steroid treatment in severe CVT-associated brain injury were possibly attributed to its ability to suppress NLRP3 inflammasome-induced inflammation.
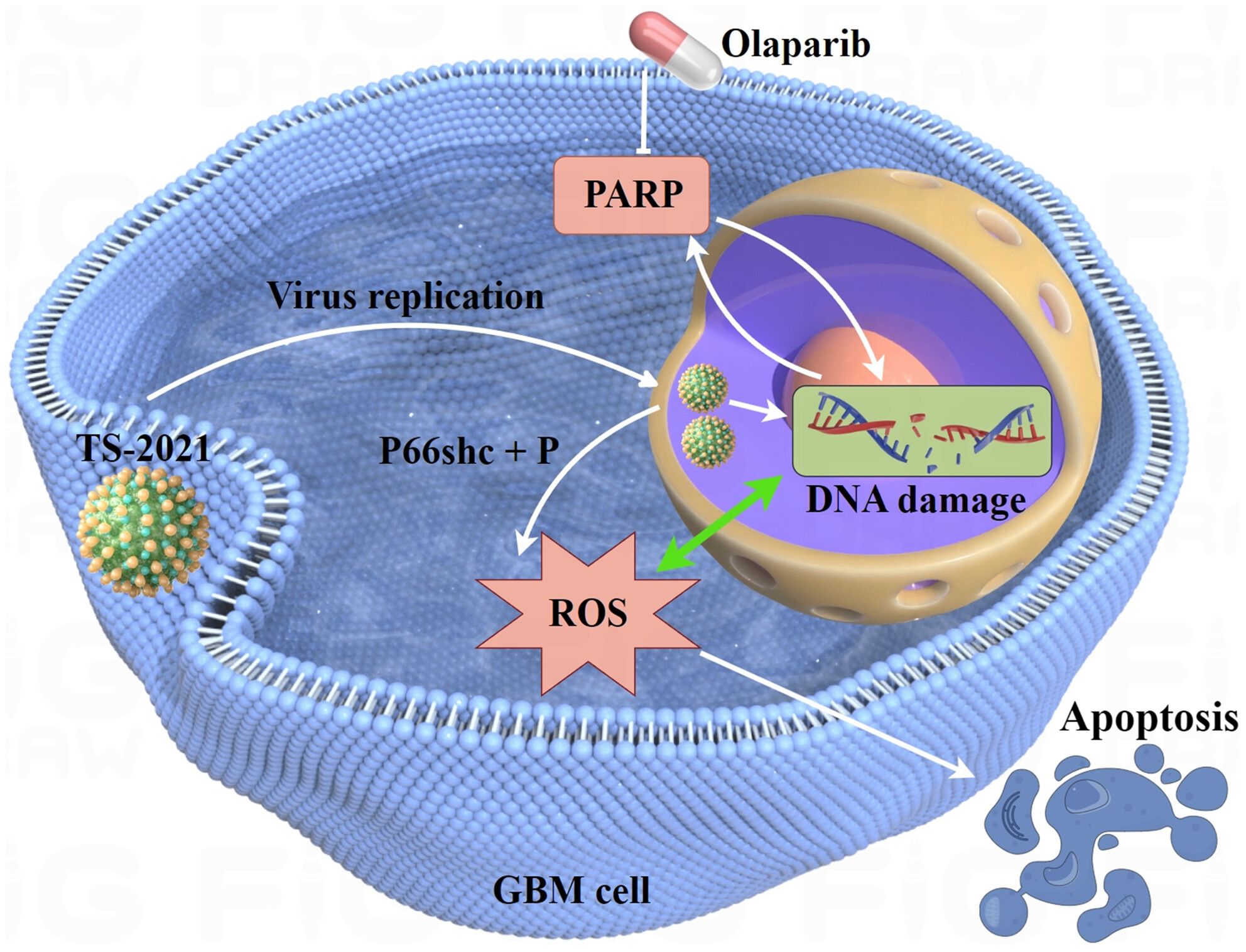
Olaparib Enhances the Efficacy of Third-Generation Oncolytic Adenoviruses Against Glioblastoma by Modulating DNA Damage Response and p66shc-Induced Apoptosis
- First Published: 18 November 2024
Magnetic Resonance-Guided Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy Using Dual-Wavelength Dual-Output Laser Within Two Probe Trajectories for Treatment of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
- First Published: 21 November 2024
Selective Inhibition of P2Y1 and P2Y12 Receptor Signal Pathways in Platelet Aggregation in Transgenic Cell Lines and Rats by Potassium 2-(1-Hydroxypentyl)-Benzoate, Puerarin and Salvianolic Acid B
- First Published: 19 November 2024
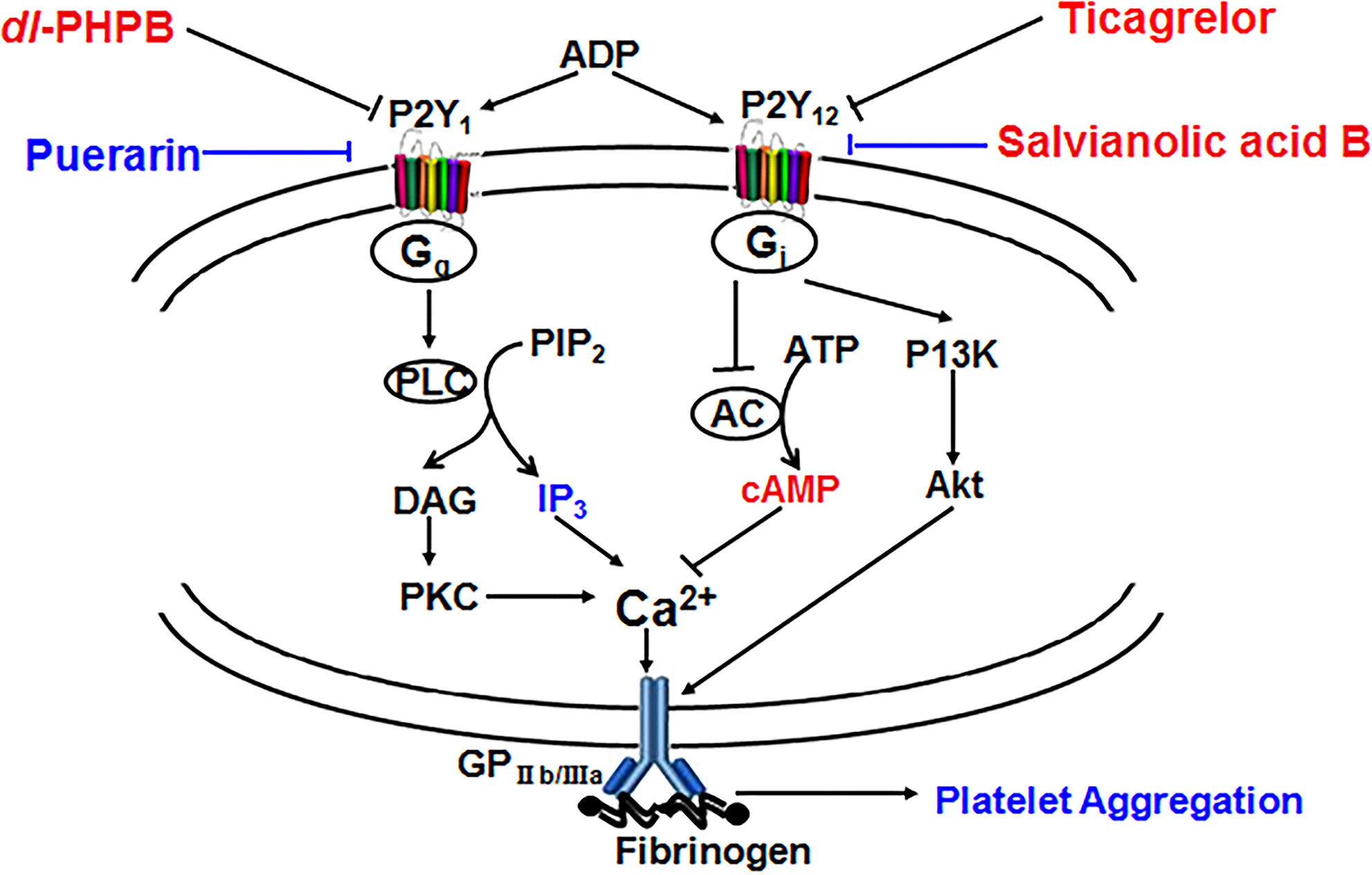
Dl-PHPB and puerarin inhibit the Gq-PLC-IP3-Ca2+ signal transduction pathway, reduce IP3 and intracellular [Ca2+]i and decrease platelet aggregation via acting on P2Y1 receptor. However, salvianolic acid B, like ticagrelor, inhibits the Gi-AC-cAMP signal transduction pathway, enhances cAMP and decreases platelet aggregation via acting on P2Y12.
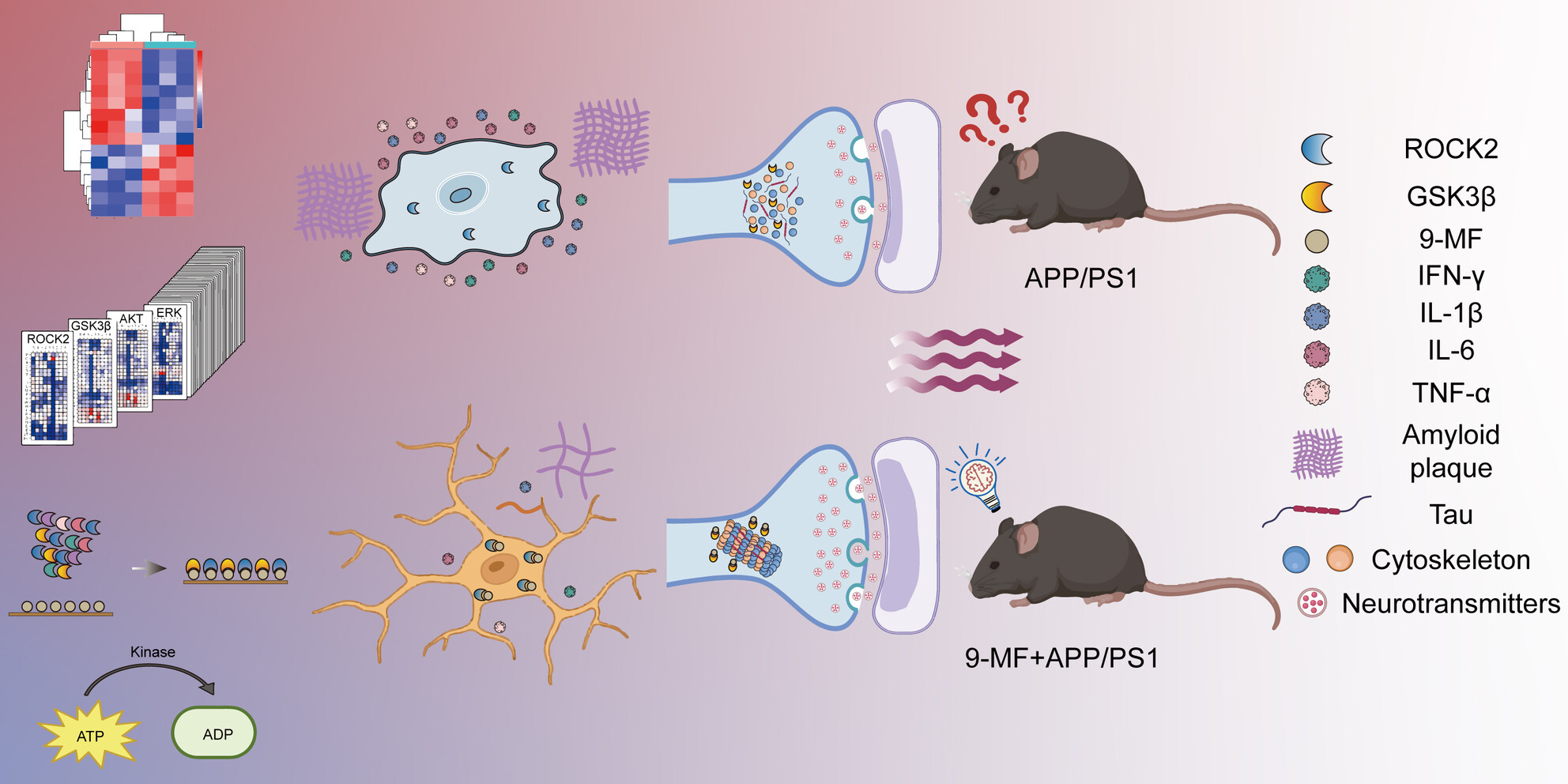
9-Methylfascaplysin Prevents Neuroinflammation and Synaptic Damage via Cell-Specific Inhibition of Kinases in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice
- First Published: 19 November 2024
The Abnormal Proliferation of Midbrain Dopamine Cells From Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Is Induced by Exposure to the Tumor Microenvironment
- First Published: 19 November 2024
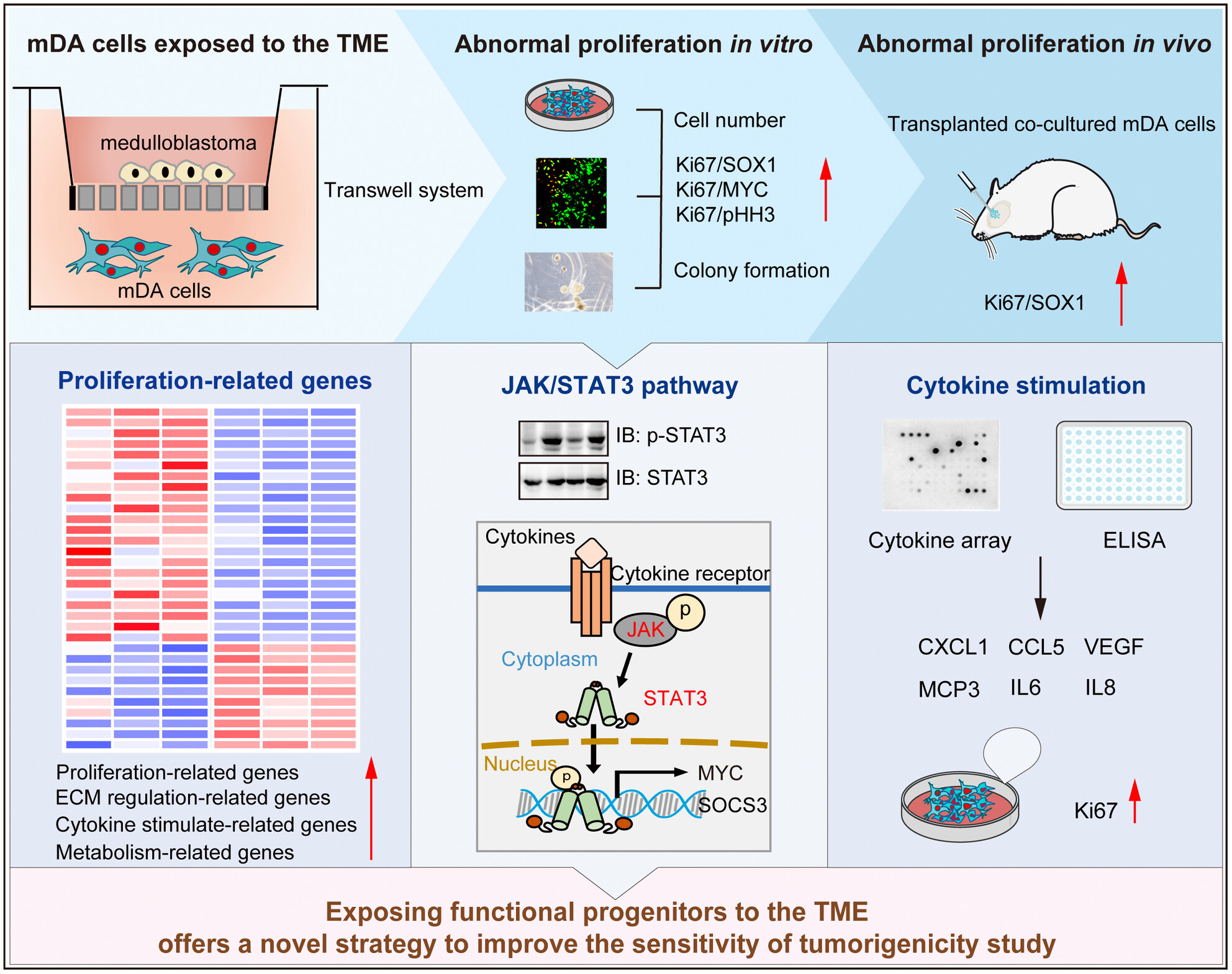
mDA cells exposed to the tumor microenvironment induced abnormal proliferation in vitro and in vivo, which was ascribed to the hyperactivation of proliferation-related genes, the JAK/STAT3 pathway, and cytokine stimulation. It suggests that exposing functional progenitors to the TME offers a novel strategy to improve the sensitivity of tumorigenicity study.
Lycium barbarum Extract Enhanced Neuroplasticity and Functional Recovery in 5xFAD Mice via Modulating Microglial Status of the Central Nervous System
- First Published: 20 November 2024
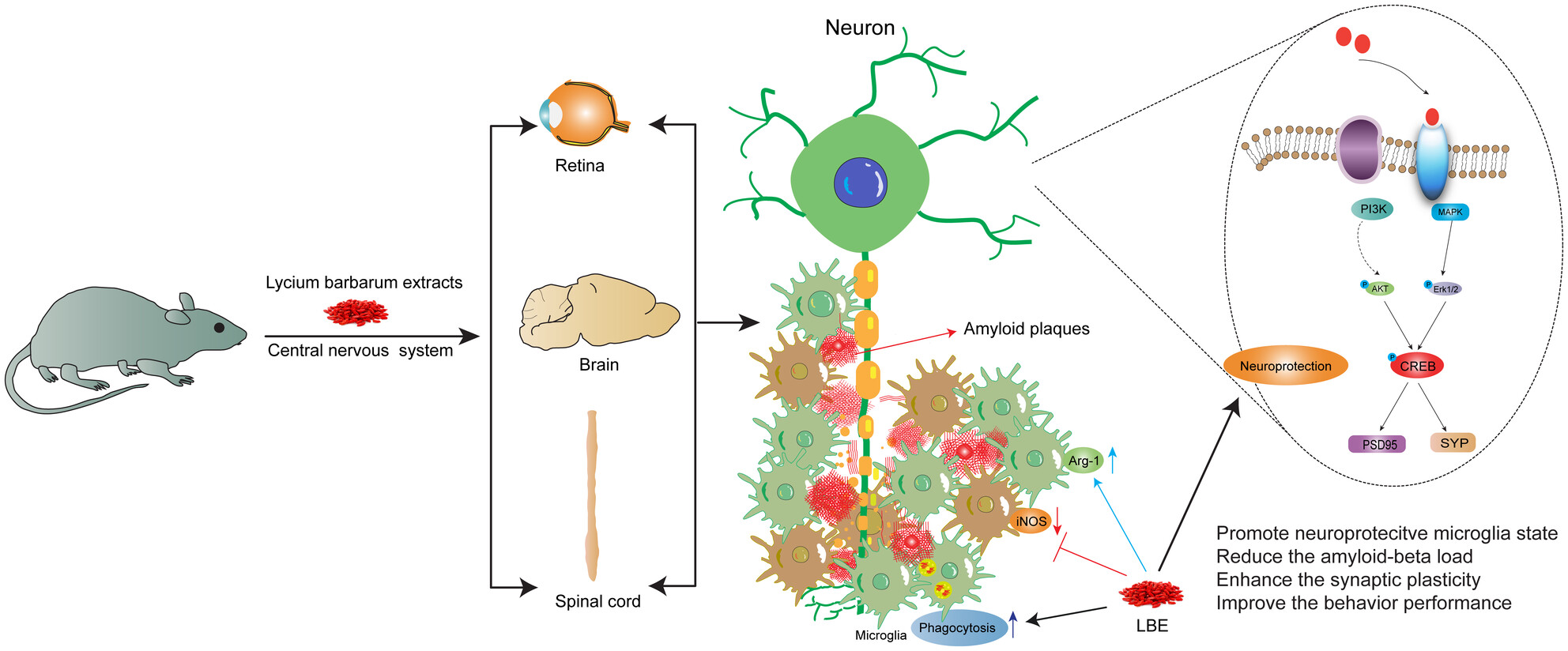
LBE administration preserved cognition, movement, and visual function in 5xFAD mice. It reversed systemic inflammation and reduced Aβ load by enhancing microglial phagocytosis through modulating microglia into a neuroprotective state, thereby ameliorating the neurological pathology of the CNS (brain, spinal cord, and retina).
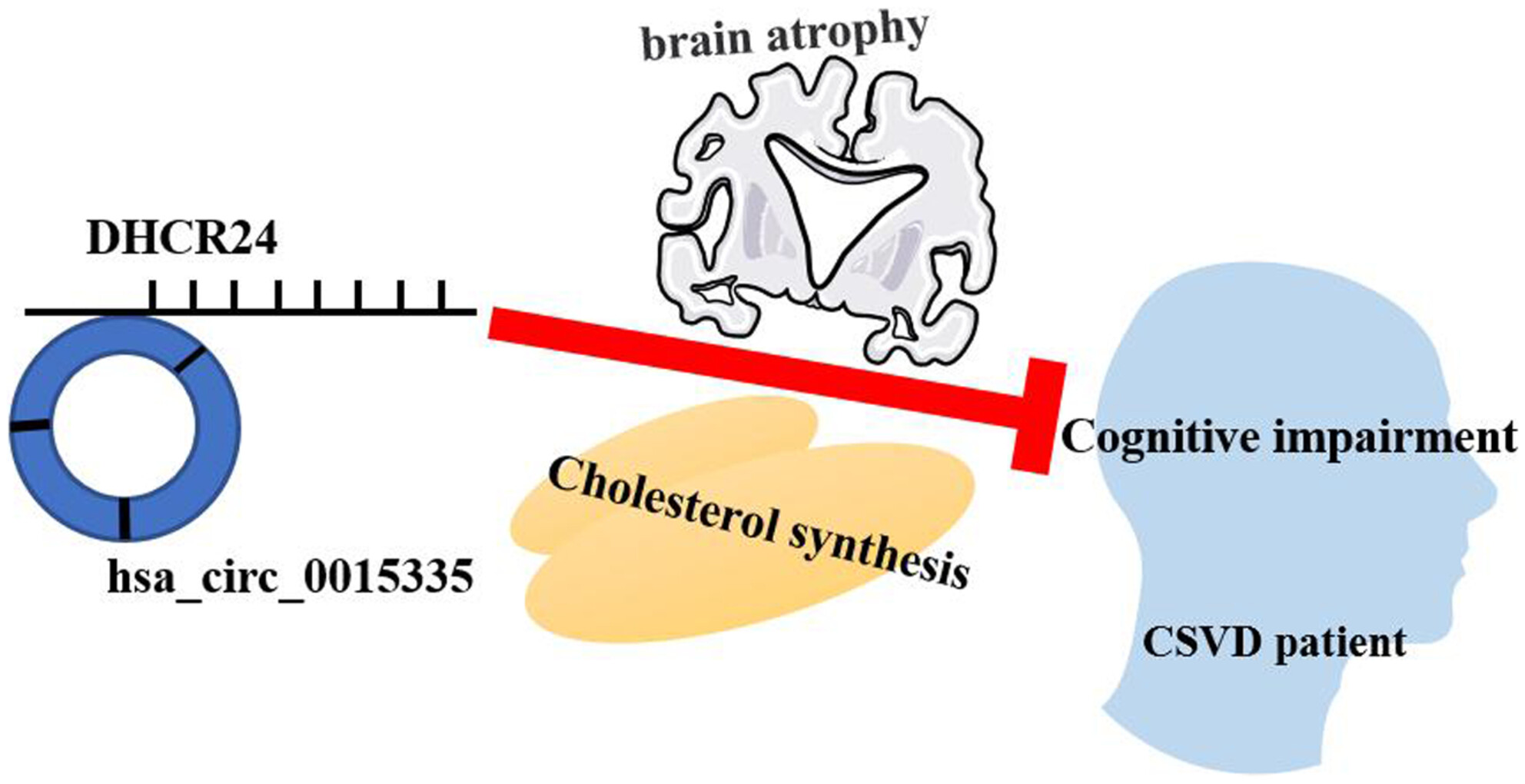
Interaction Between DHCR24 and hsa_circ_0015335 Facilitates Cognitive Impairment in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Patients
- First Published: 22 November 2024
Novel Insights Into the Causal Effects and Shared Genetics Between Body Fat and Parkinson Disease
- First Published: 22 November 2024
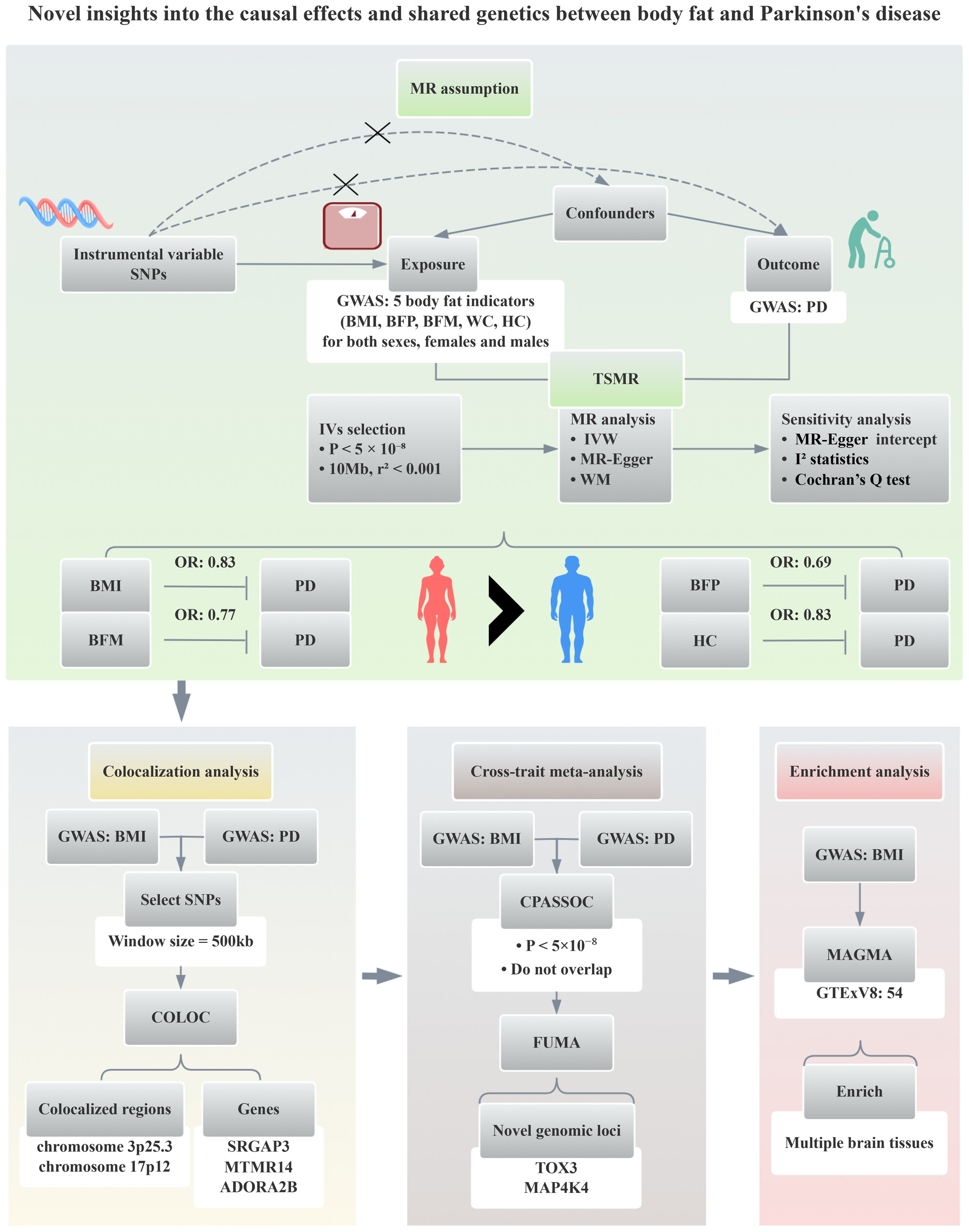
Our two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis suggested that except waist circumference, higher body mass index (BMI), body fat percentage, body fat mass, and hip circumference were protective against Parkinson disease (PD), and were more pronounced in females than in males. Colocalization analysis highlighted two colocalized regions shared by BMI and PD. Cross-trait meta-analysis successfully identified 10 novel genomic loci. They pointed to some genes as possible players, including SRGAP3, MTMR14, ADORA2B, TOX3, and MAP4K4. Enrichment analysis showed that BMI-associated genetic variants were enriched in multiple brain tissues.
First-in-Human Study of BAT4406F, an ADCC-Enhanced Fully Humanized Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody in Patients With Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders
- First Published: 26 November 2024
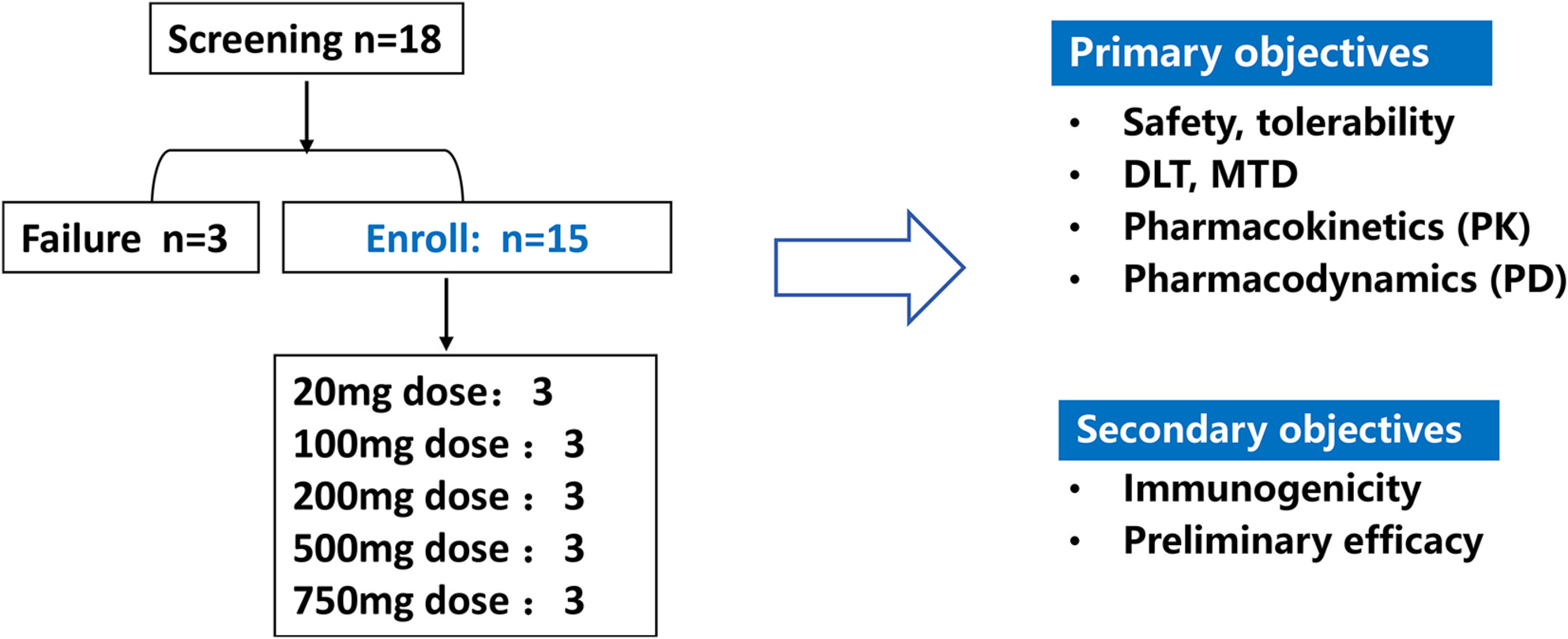
This is the first-in-human dose-escalation Phase I study of BAT4406F, a fully humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody with enhanced ADCC effect. The safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics, immunogenicity, and preliminary efficacy of BAT4406F injection on Chinese neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) patients were investigated.
Brain Morphometric Alterations in Focal to Bilateral Tonic–Clonic Seizures in Epilepsy Associated With Excitatory/Inhibitory Imbalance
- First Published: 24 November 2024
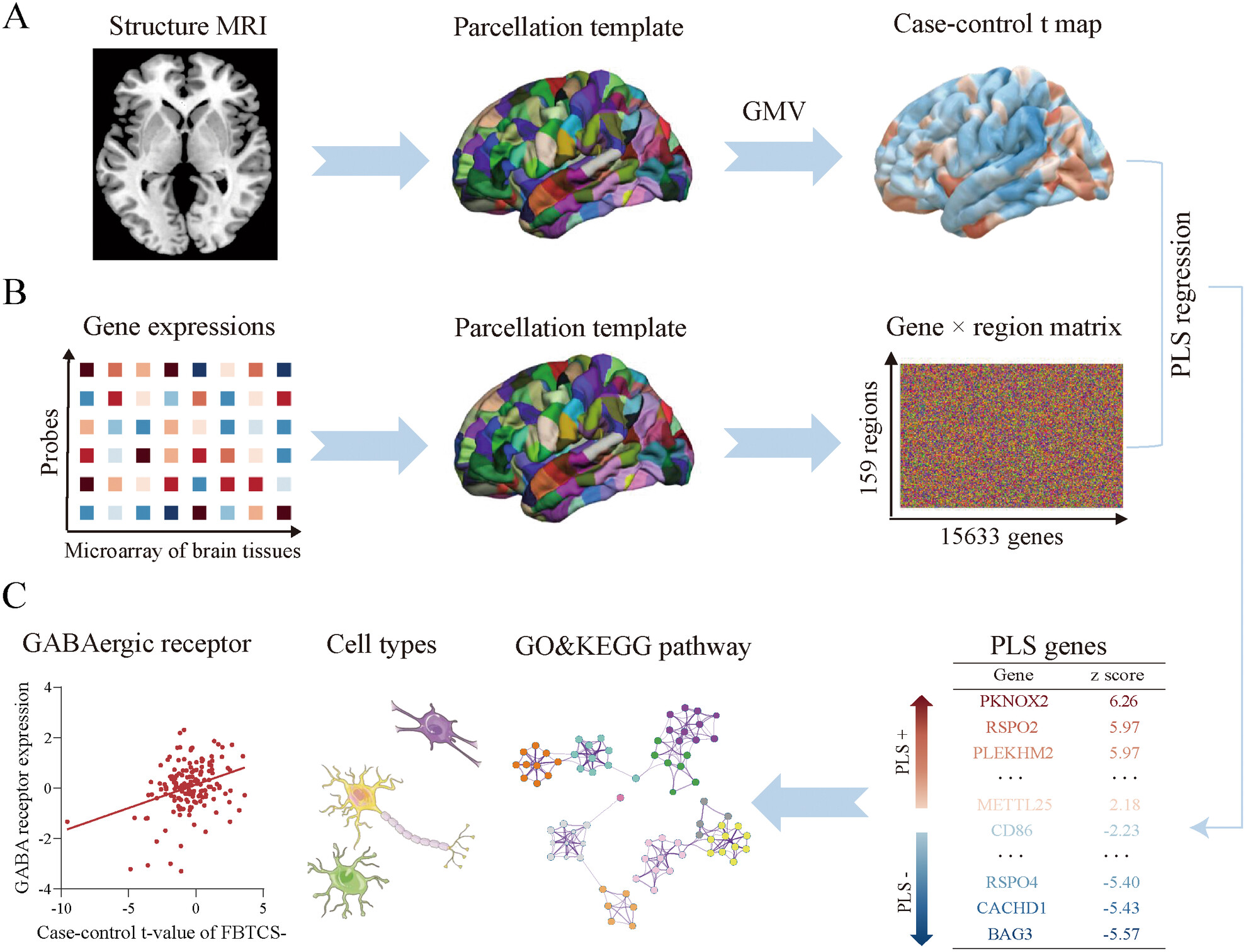
Schematic diagram of methodology. (A) T1-weighted image of each subject was parcellated into 322 cortical and subcortical regions, and gray matter volume of each region was computed by Freesurfer. Then regional case–control differences were estimated. (B) Gene expression profiles of each region (left hemisphere only) were extracted from AHBA database and obtained 159 × 15,633 regional gene matrix. (C) PLS regression was applied to link case–control t-values and gene expression data. Then, pathway enrichment analysis and cell type assignment were conducted on the gene list of first component of PLS to identify different biological pathway and cell types between groups. Additionally, the GABAergic atlas was used to explore the relationship between inhibitory neurotransmitter and morphometric alterations. AHBA, Allen Human Brain Atlas; PLS, partial least squares.
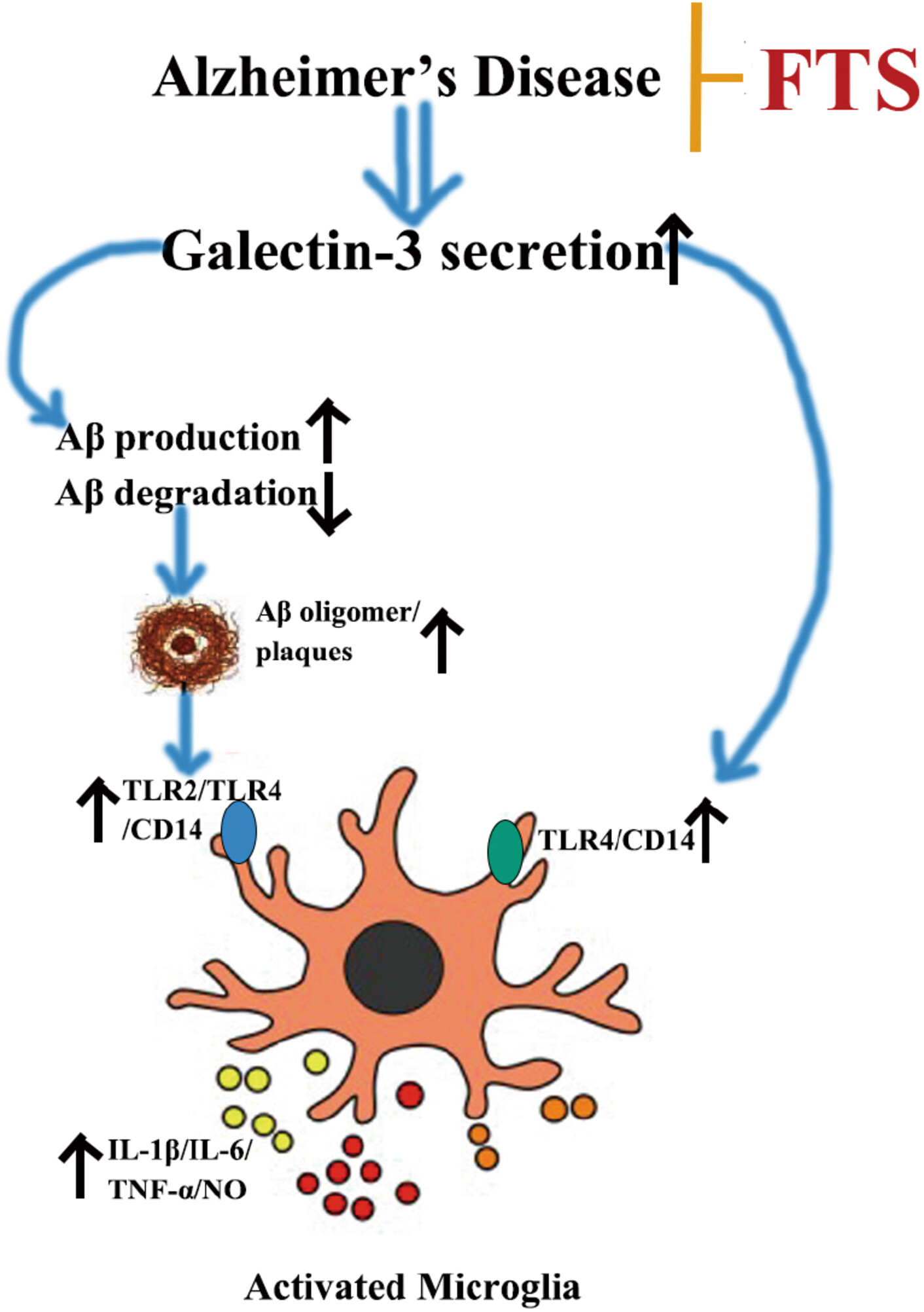
Farnesylthiosalicylic Acid Through Inhibition of Galectin-3 Improves Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer Disease via Multiple Pathways
- First Published: 26 November 2024
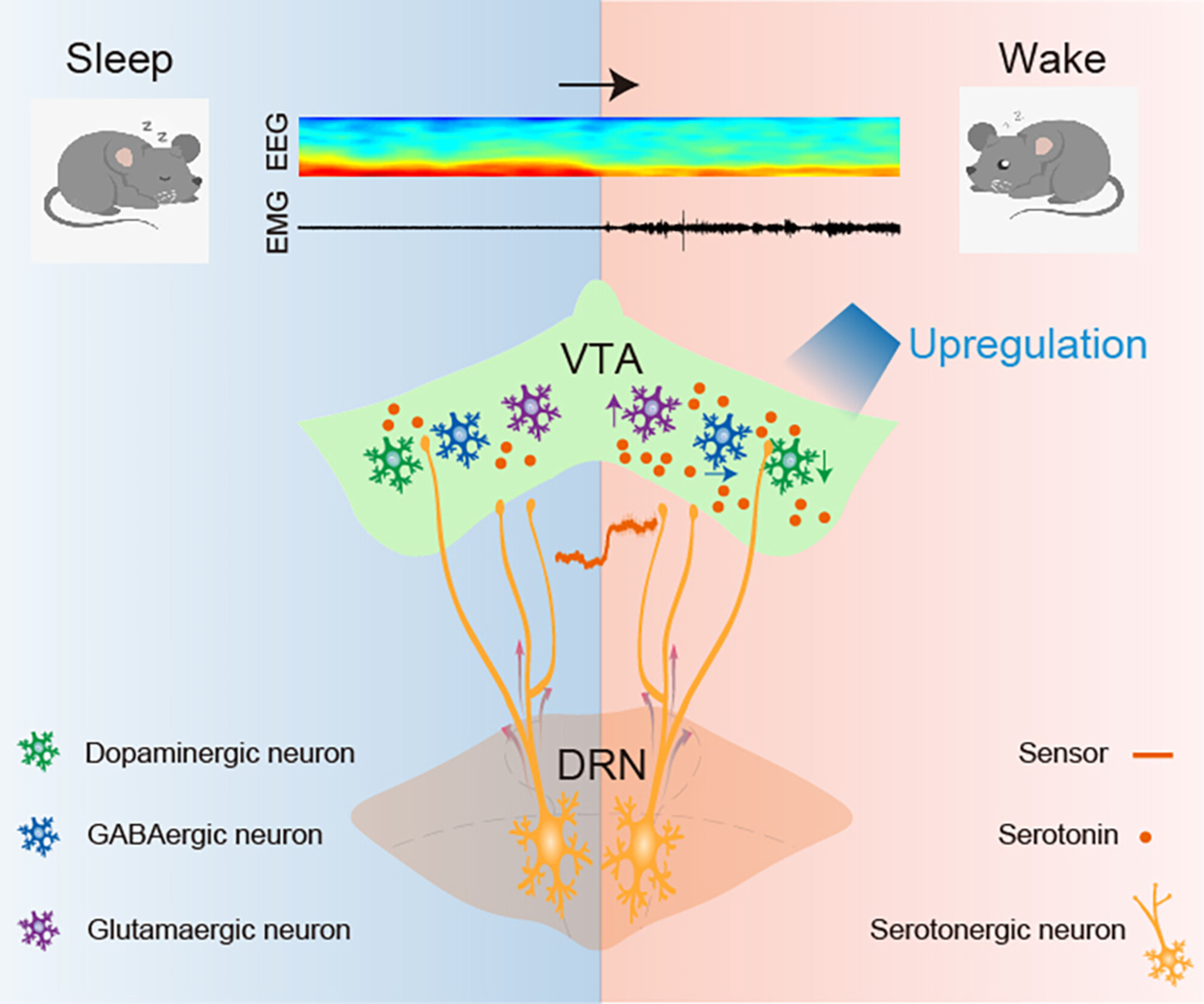
Dorsal Raphe Serotonergic Neurons-Ventral Tegmental Area Neural Pathway Promotes Wake From Sleep
- First Published: 26 November 2024
E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Ring Finger Protein 2 Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Stabilizing Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Through Monoubiquitination
- First Published: 30 November 2024
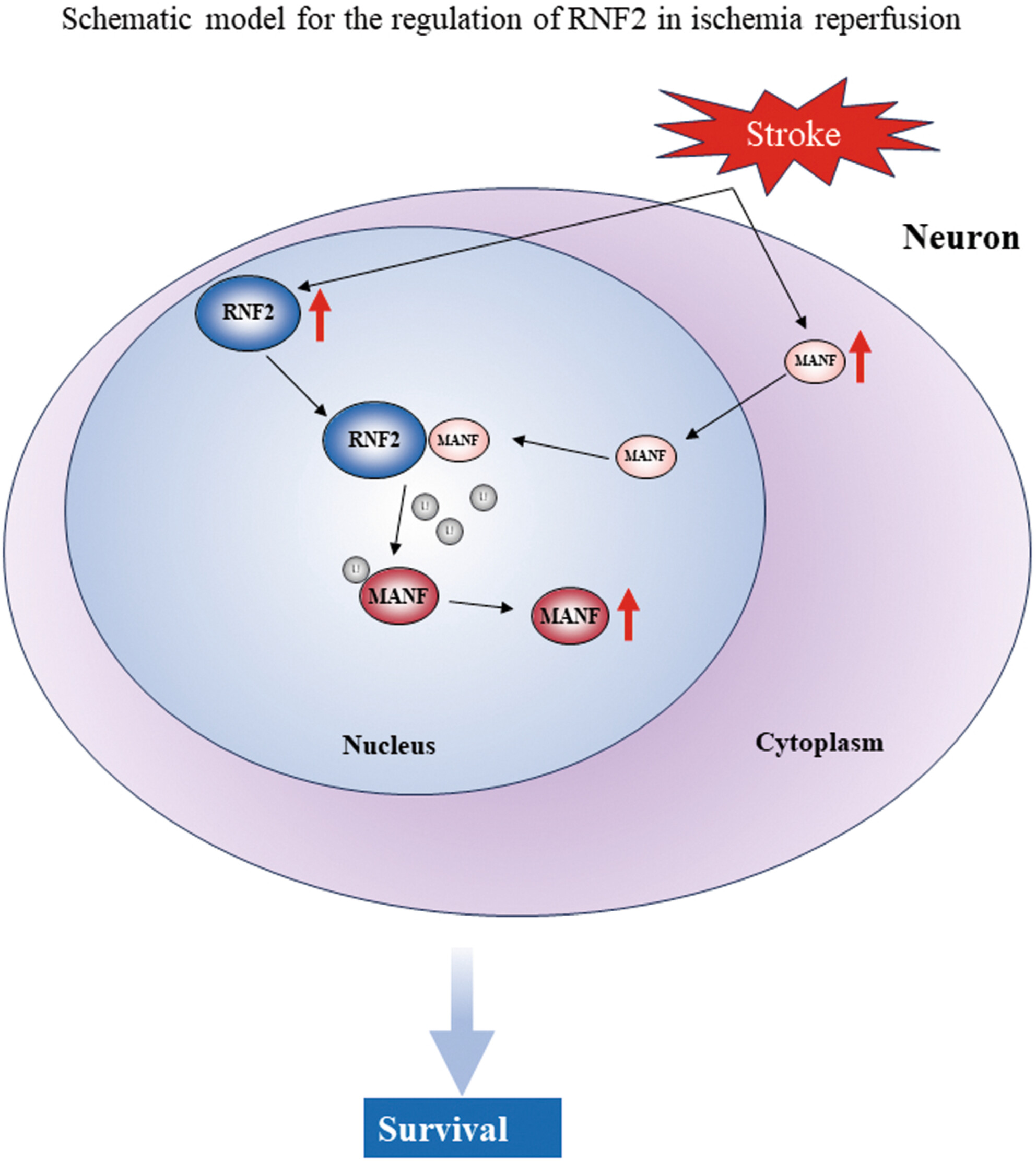
RNF2 was upregulated in the ischemia–reperfusion brain, as well as in nerve cells treated with OGD/R or TM. RNF2 inhibited cell apoptosis. RNF2 promoted MANF nuclear transport. RNF2 monoubiquitinated MANF and stabilized MANF protein level. RNF2 inhibits cell apoptosis dependently on MANF, which can be reversed by recombinant human MANF.
FNIRS-Based Energy Landscape Analysis to Signify Brain Activity Dynamics of Individuals With Depression
- First Published: 01 December 2024
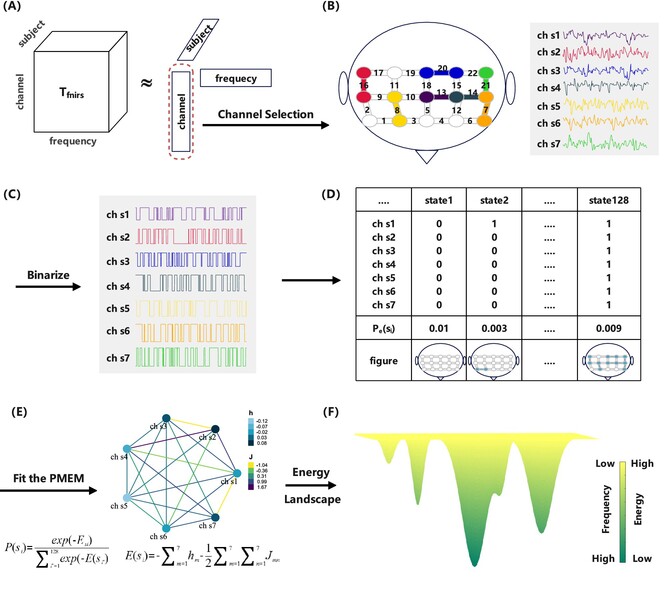
Our study uses energy landscape analysis to investigate the brain dynamics of patients with major depression (MDDs) under task conditions. The experiments show that brain networks in MDDs show more restraint and less freedom, which is associated with depressive symptoms such as negative emotional bias and rumination.