Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front Cover
- First Published: 31 December 2024

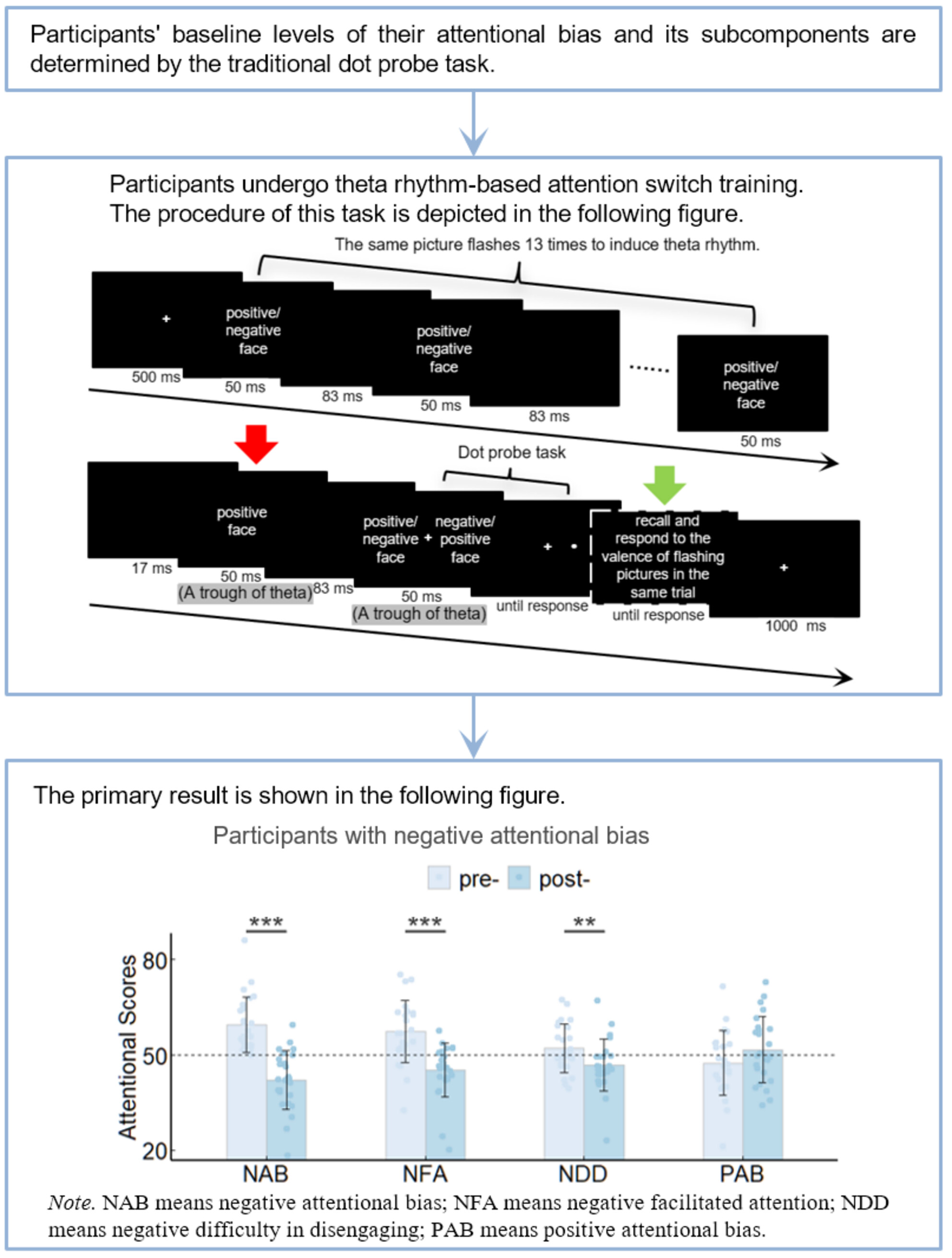
Cover image: The cover image is based on the article Theta Rhythm-Based Attention Switch Training Effectively Modified Negative Attentional Bias by Yifeng Wang et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.70157.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
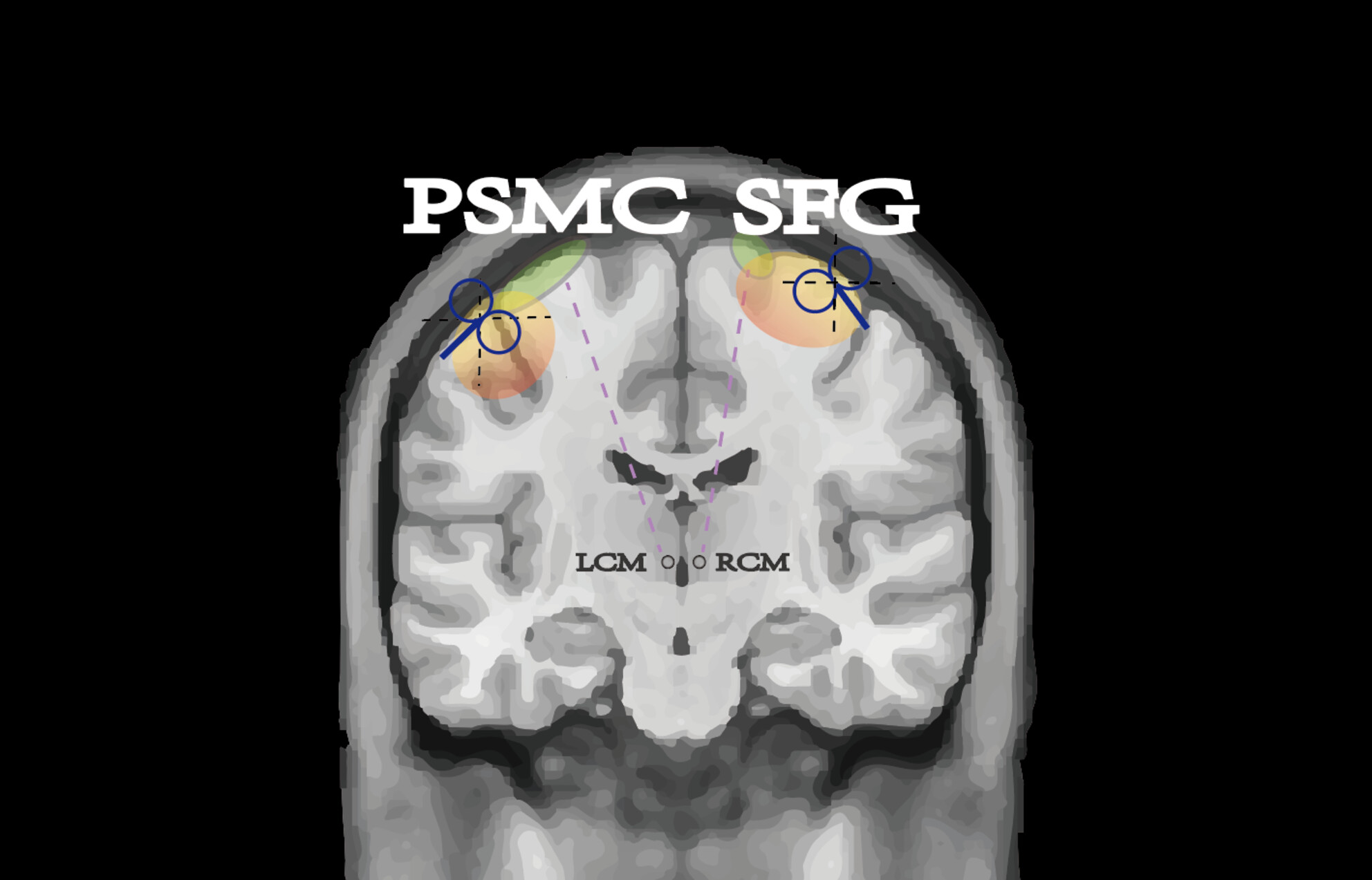
Utilizing Centromedian Thalamus Connectivity to Personalize Noninvasive Neuromodulation Targets
- First Published: 08 December 2024
REVIEW
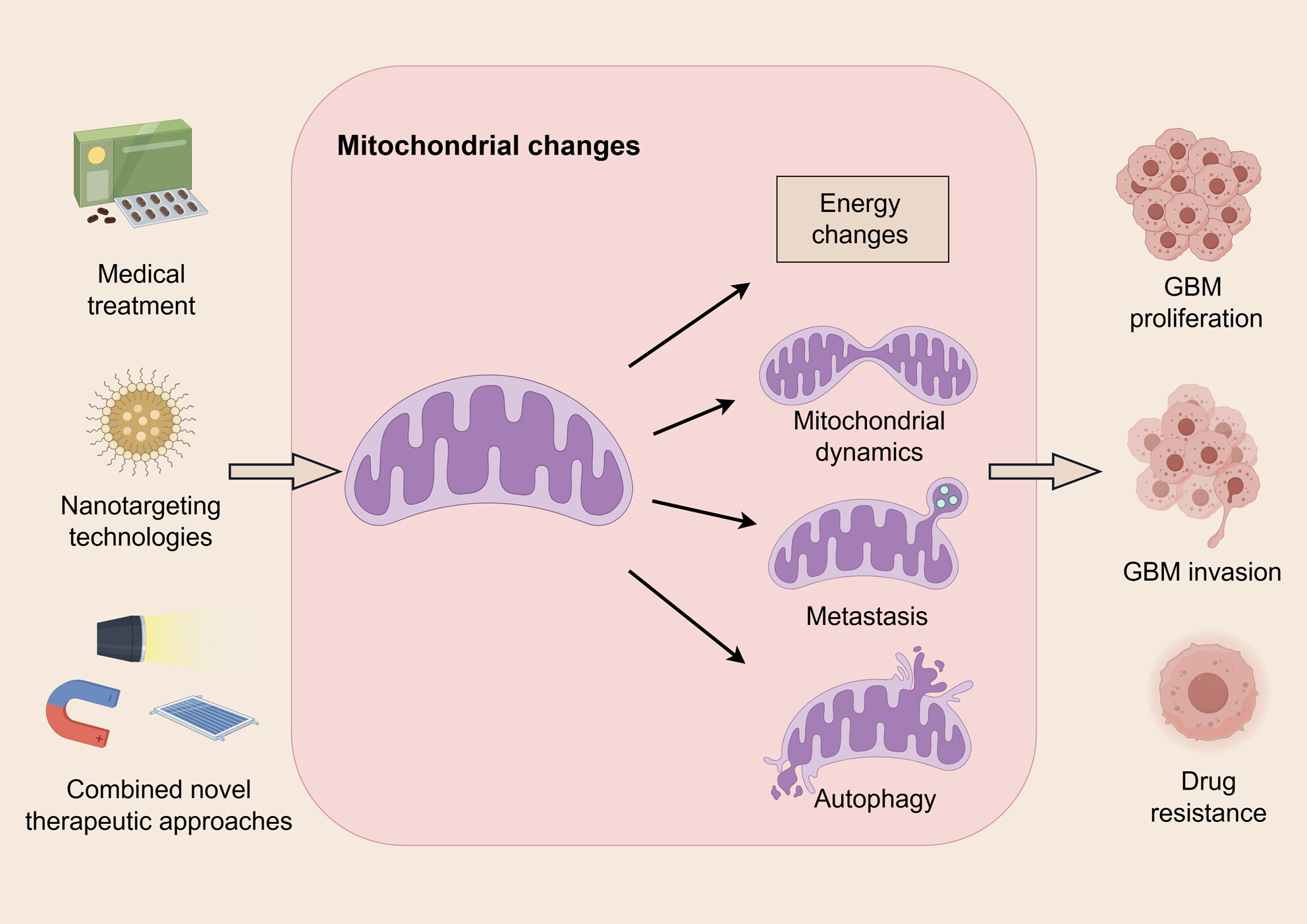
The Role and Applied Value of Mitochondria in Glioma-Related Research
- First Published: 05 December 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
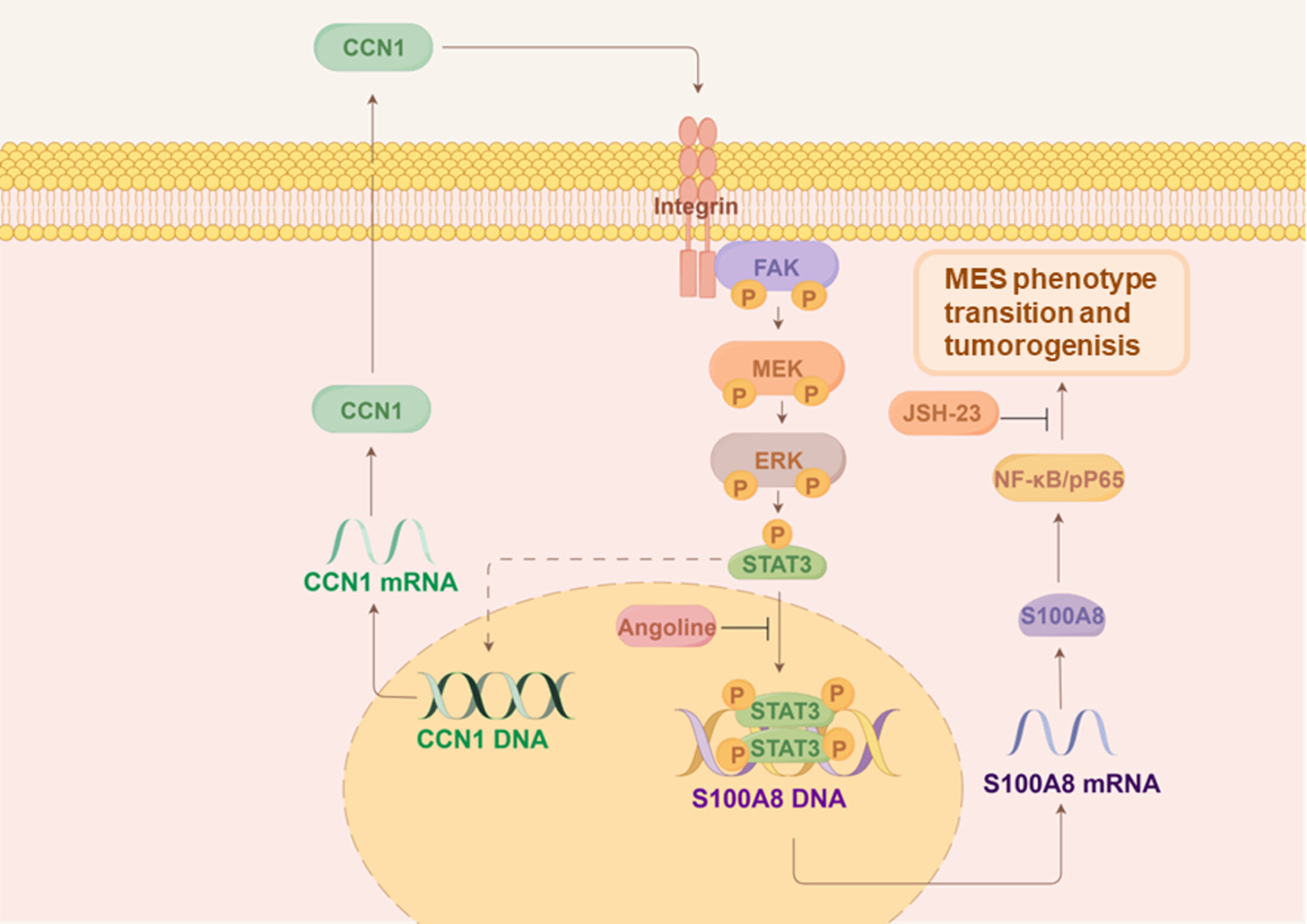
CCN1 Promotes Mesenchymal Phenotype Transition Through Activating NF-κB Signaling Pathway Regulated by S100A8 in Glioma Stem Cells
- First Published: 11 December 2024
Influence of TyG Index on Large Vascular Occlusive Stroke Following Endovascular Treatment
- First Published: 08 December 2024
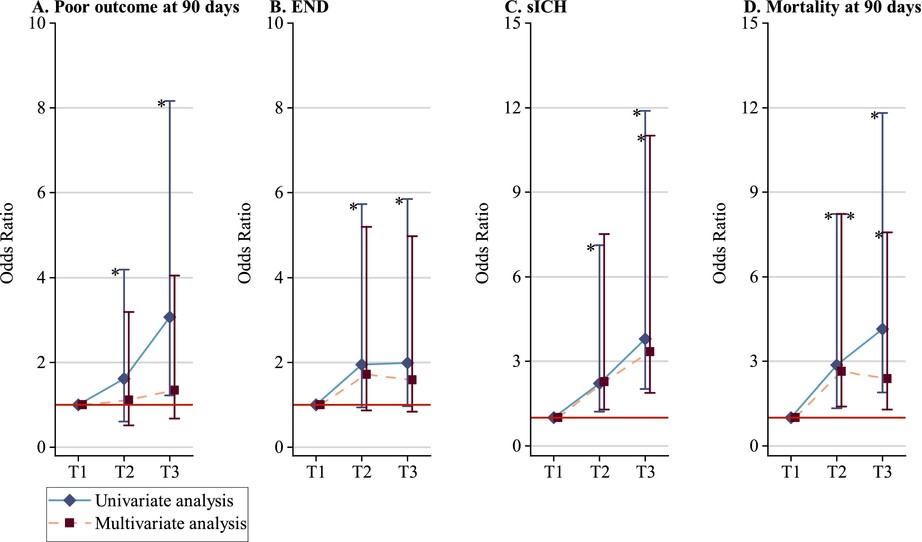
This single-center retrospective cohort study indicates that the triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index), as a marker of insulin resistance, was significantly linked to worse functional outcome, increased mortality at 90 days, and a higher risk of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) in patients with acute ischemic stroke postendovascular treatment. In addition, the TyG index was not significantly associated with early neurological deterioration (END).
Mef2c Exacerbates Neuron Necroptosis via Modulating Alternative Splicing of Cflar in Ischemic Stroke With Hyperlipidemia
- First Published: 08 December 2024
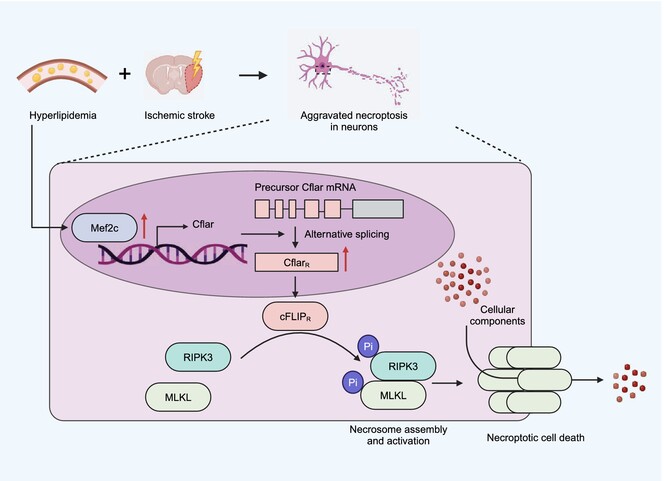
Hyperlipidemia is a common comorbidity of stroke, which exacerbated ischemic brain injury. We found that hyperlipidemia promoted alternative splicing of CflarR via upregulating Mef2c expression in ischemic neurons, thus aggravated neuron necroptosis and neurological deficits following ischemic stroke. This pathogenic splicing process is a promising target for hyperlipidemic stroke patients.
Impaired Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neuron GDNF Signaling Contributes to Perioperative Sleep Deprivation–Induced Chronicity of Postsurgical Pain in Mice Through Regulating Cholinergic Neuronal Activity, Apoptosis, and Autophagy
- First Published: 05 December 2024
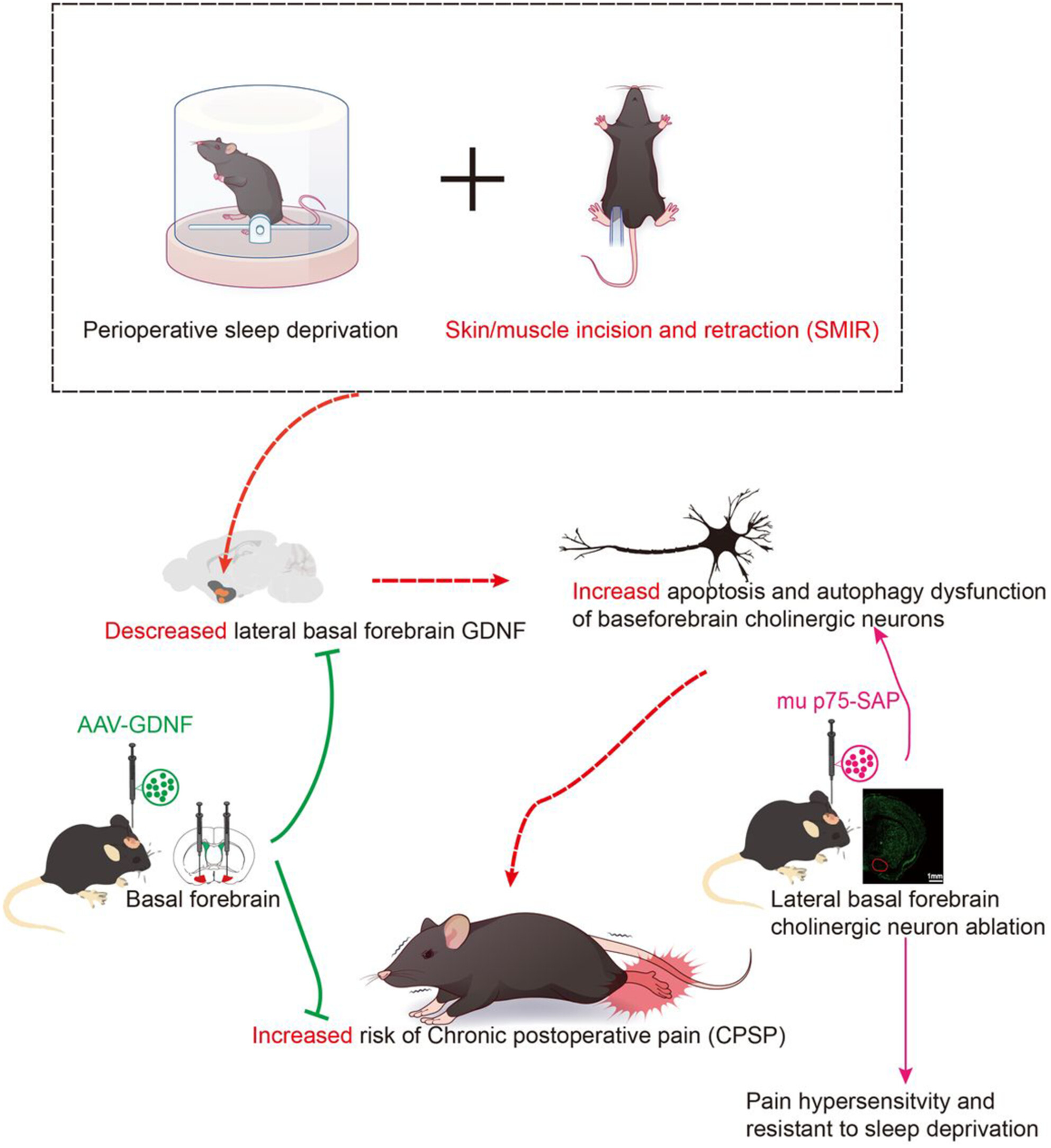
Surgery combined with perioperative sleep deprivation induces decreased GDNF in the lateral basal forebrain, which leads to enhanced apoptosis and autophagy dysfunction of cholinergic neurons and increased risk of chronic postsurgical pain. Normalizing GDNF levels by AAV-GDNF therapy rescues the deleterious effects of perioperative sleep deprivation. Selective lesion of the cholinergic neurons of lateral basal forebrain by mu p75-SAP decreases the pain threshold and abolishes the pain-enhancing effects of sleep deprivation.
REVIEW
Ginsenoside Rg1: A Neuroprotective Natural Dammarane-Type Triterpenoid Saponin With Anti-Depressive Properties
- First Published: 06 December 2024
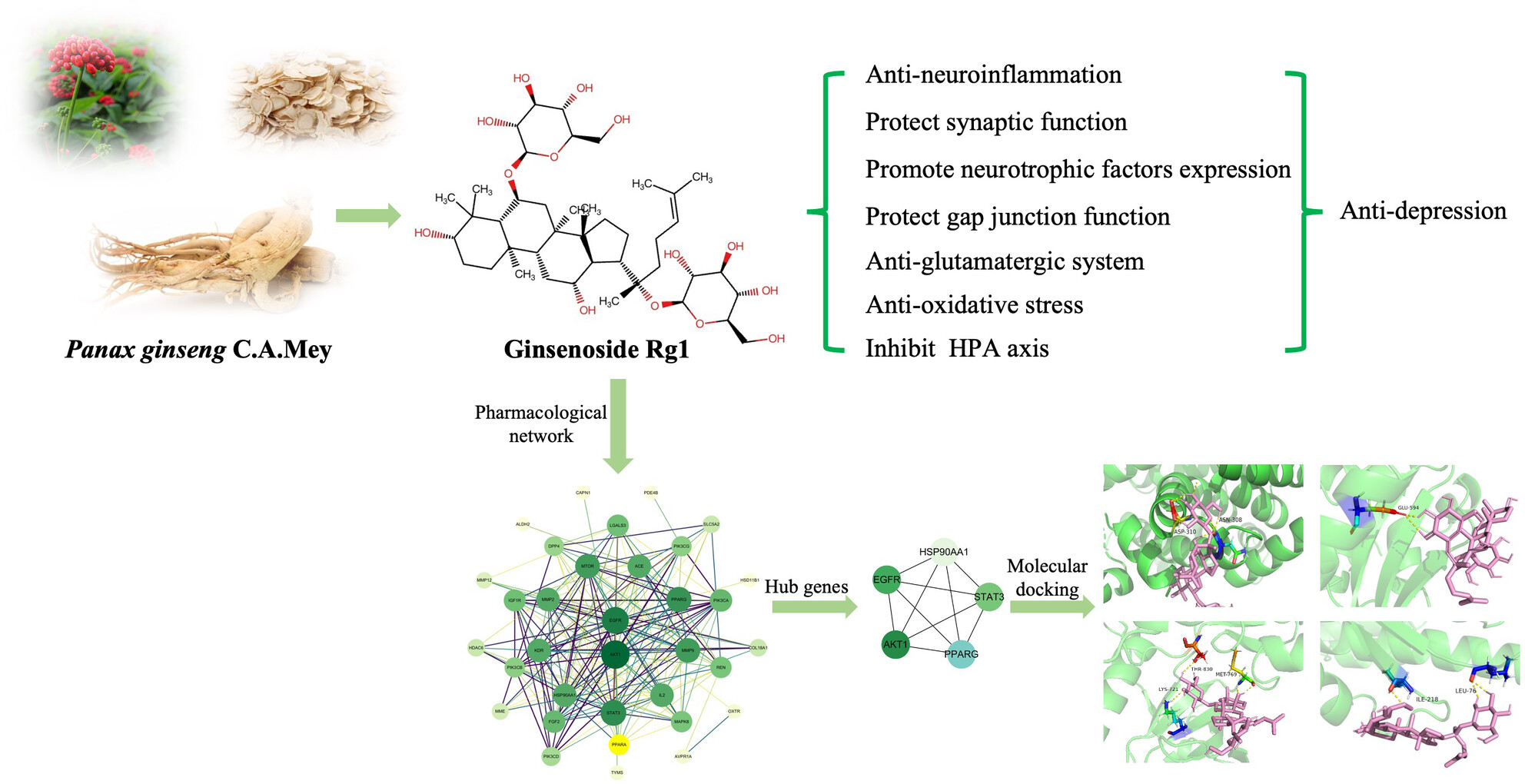
Rg1 exhibits antidepressant effects through diverse mechanisms, such as anti-inflammation, synaptic protection, neurogenesis promotion, brain-derived neurotrophic factor release, enhancement of astrocyte gap junction function, and regulation of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and antioxidative stress. Experimental studies validate Rg1's efficacy in depression treatment, with molecular docking analysis supporting its promising application prospects.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Combination of rs-fMRI, QSM, and ASL Reveals the Cerebral Neurovascular Coupling Dysfunction Is Associated With Cognitive Decline in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease
- First Published: 05 December 2024
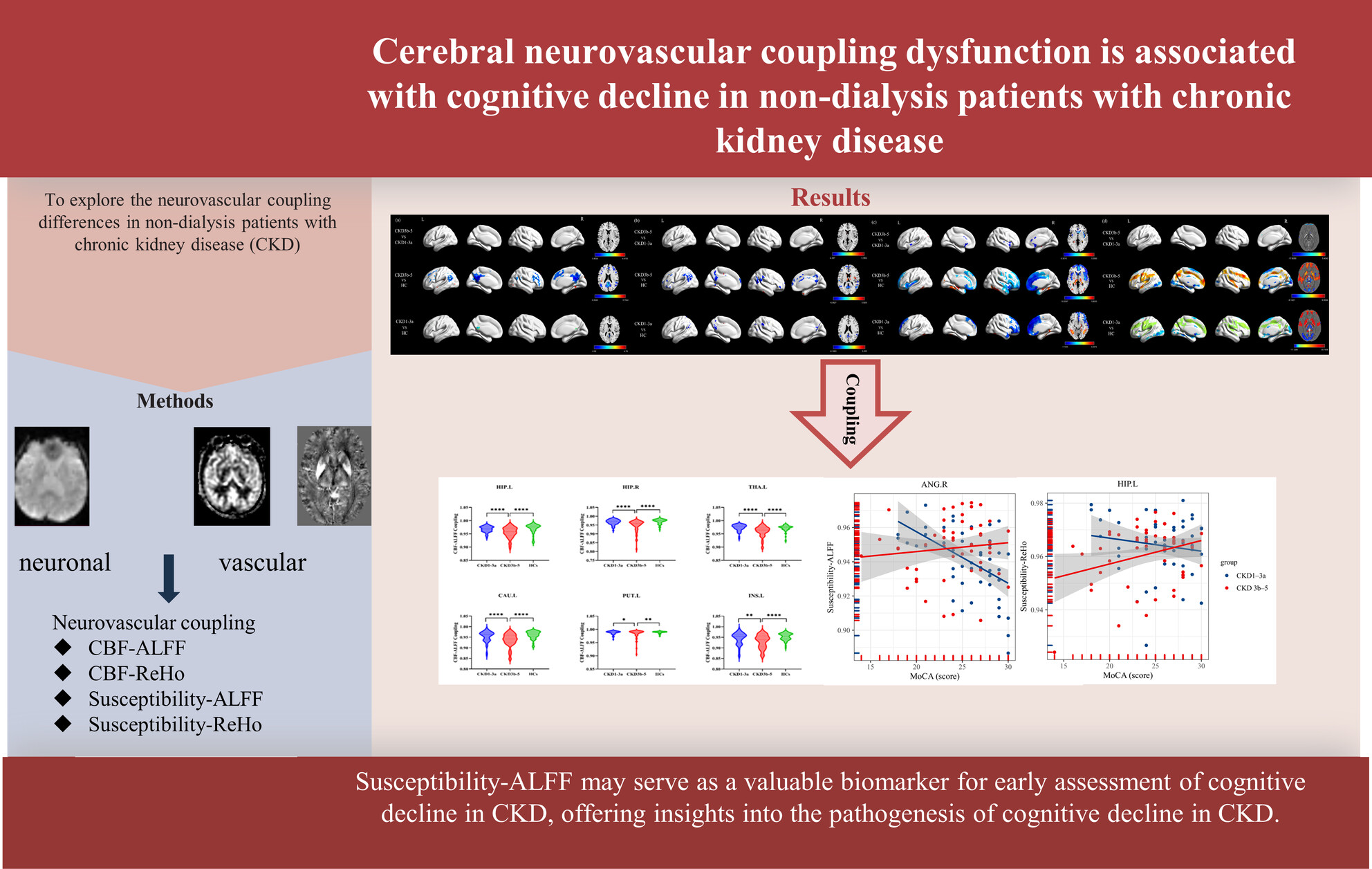
Susceptibility-ALFF may serve as a valuable biomarker for early assessment of cognitive decline in CKD, offering insights into the pathogenesis of cognitive decline in CKD. HC, healthy control; ALFF, amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations; ReHo, regional homogeneity; CBF, cerebral blood flow; ROI, region of interest.
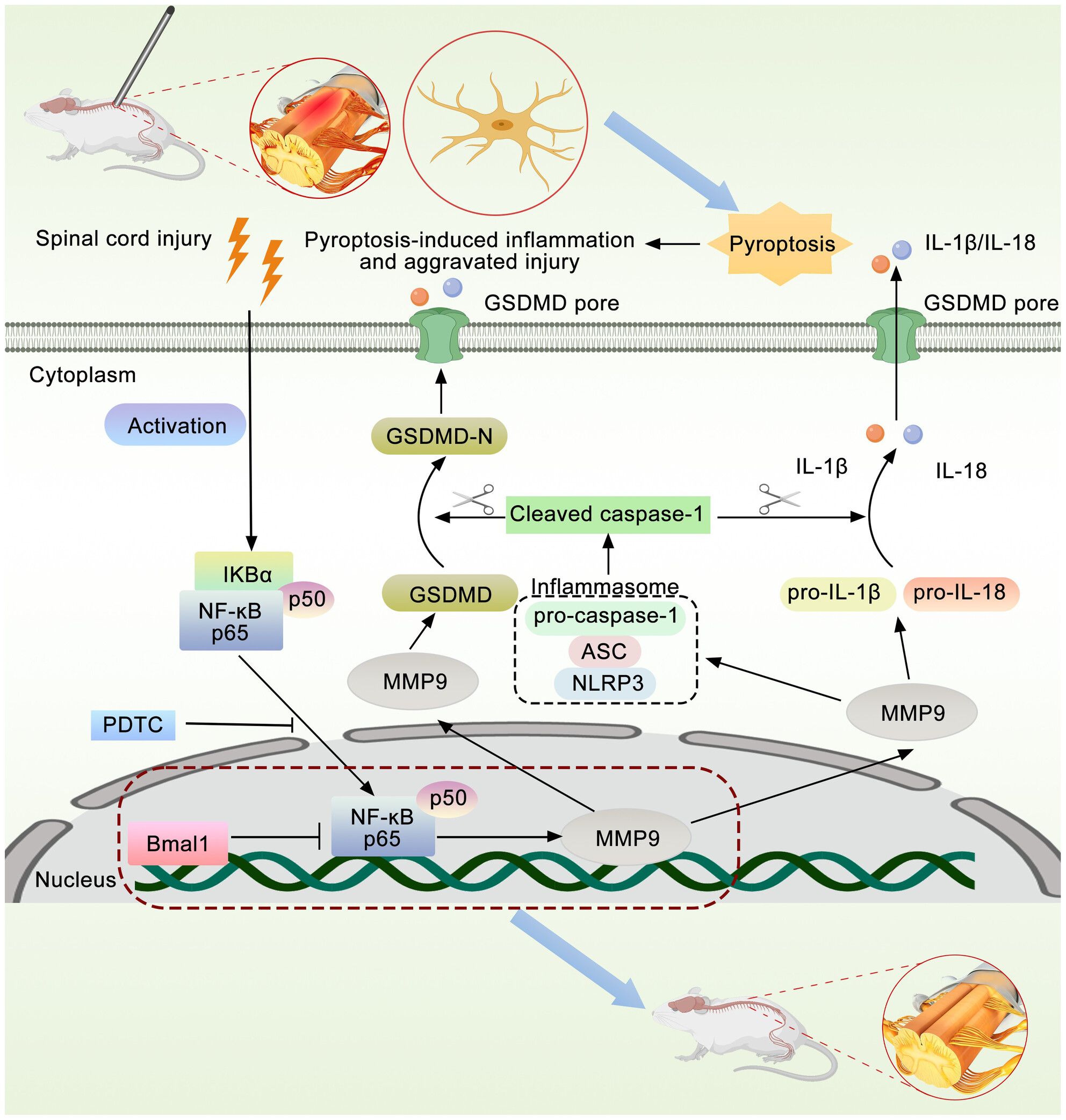
The Circadian Clock Gene Bmal1 Regulates Microglial Pyroptosis After Spinal Cord Injury via NF-κB/MMP9
- First Published: 08 December 2024
Integrating Neutrophil-To-Albumin Ratio and Triglycerides: A Novel Indicator for Predicting Spontaneous Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients
- First Published: 17 December 2024
REVIEW
The Oral–Gut–Brain Axis: The Influence of Microbes as a Link of Periodontitis With Ischemic Stroke
- First Published: 15 December 2024
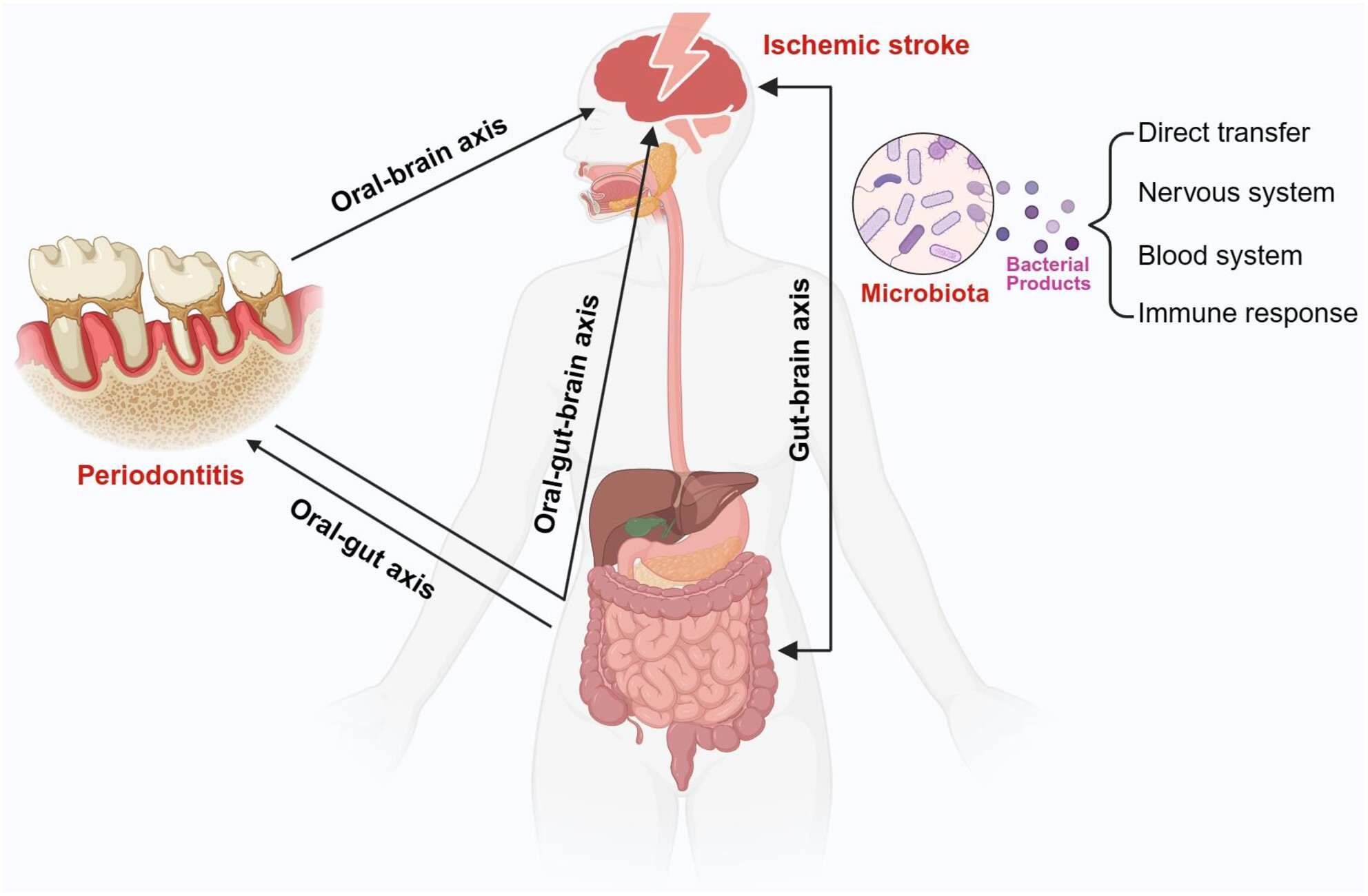
The underlying mechanism of oral–gut–brain axis between periodontitis and ischemic stroke could occur through the following pathways: (1) direct transfer of bacteria and their products via nervous or blood; (2) gut dysbiosis due to imbalanced oral microbiota; and (3) activation of inflammatory and immune responses activation by the secretion of inflammatory mediators.
Impact and Mechanisms of Action of BDNF on Neurological Disorders, Cancer, and Cardiovascular Diseases
- First Published: 09 December 2024
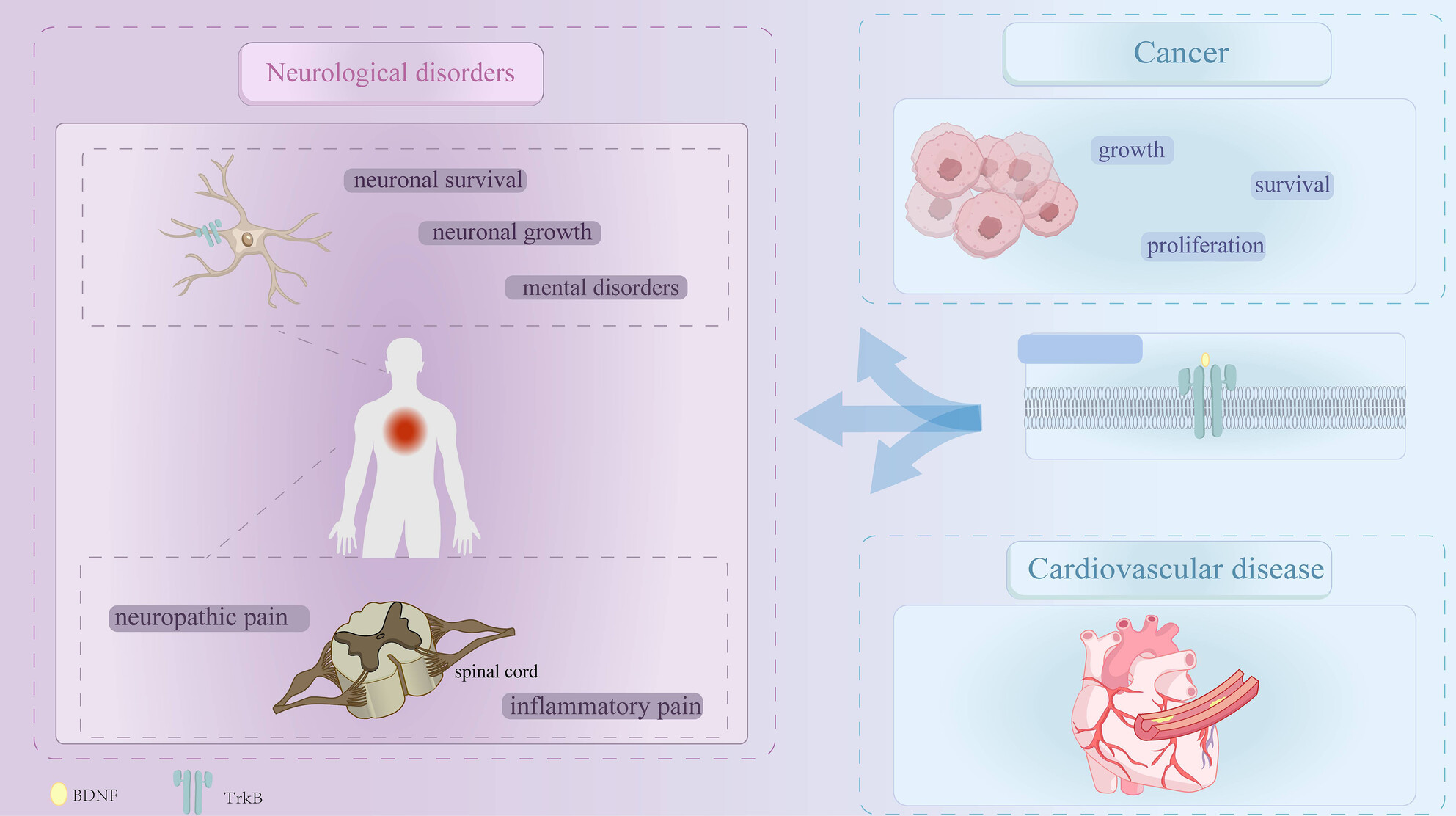
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is not only the main neurotrophic signal in the human body but also an important neuromodulator. BDNF and its receptors are widely distributed throughout the central nervous system. They promote neuronal survival and growth and protect neurons. They are considered to be the guiding mediators of central nervous system functional and structural plasticity. Reduced BDNF levels in the central and peripheral systems are closely related to various neurological diseases, including neuropathic pain, inflammatory pain, and mental illness. More and more studies have shown that BDNF can potentially increase the growth, survival, proliferation, and migration of cancer cells, affecting cancer development. When BDNF and its receptor tropomyosin receptor kinase B are missing in the signaling pathway, brain and cardiovascular diseases are also more likely to occur. This article focuses on summarizing and analyzing the effects of BDNF on neurological diseases, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases to clarify its effects on these diseases and provide new ideas and methods for the treatment of these diseases.
EXPRESSION OF CONCERN
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
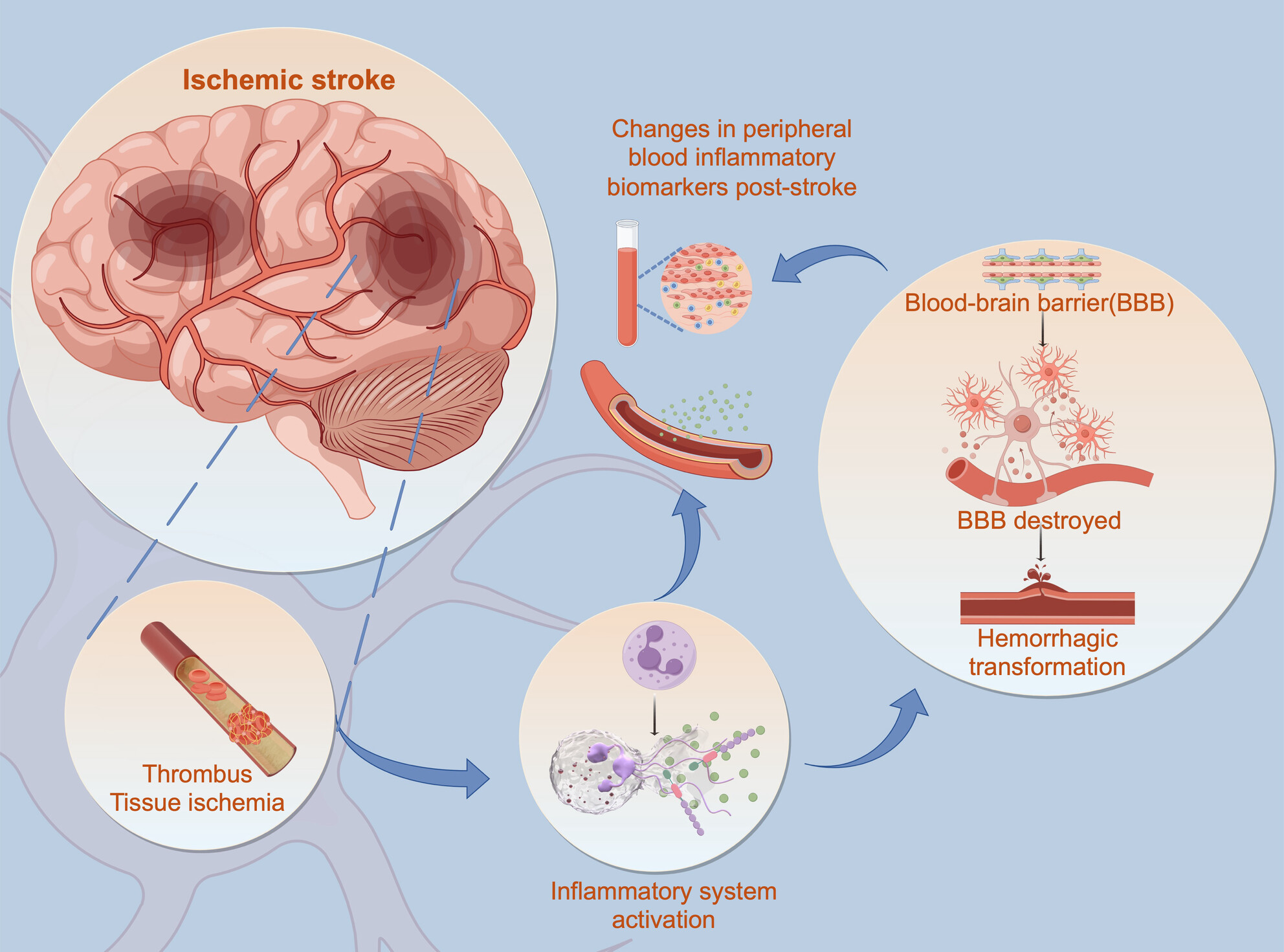
STING Activation in Macrophages and Microglia Drives Poststroke Inflammation: Implications for Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Interventions
- First Published: 19 December 2024
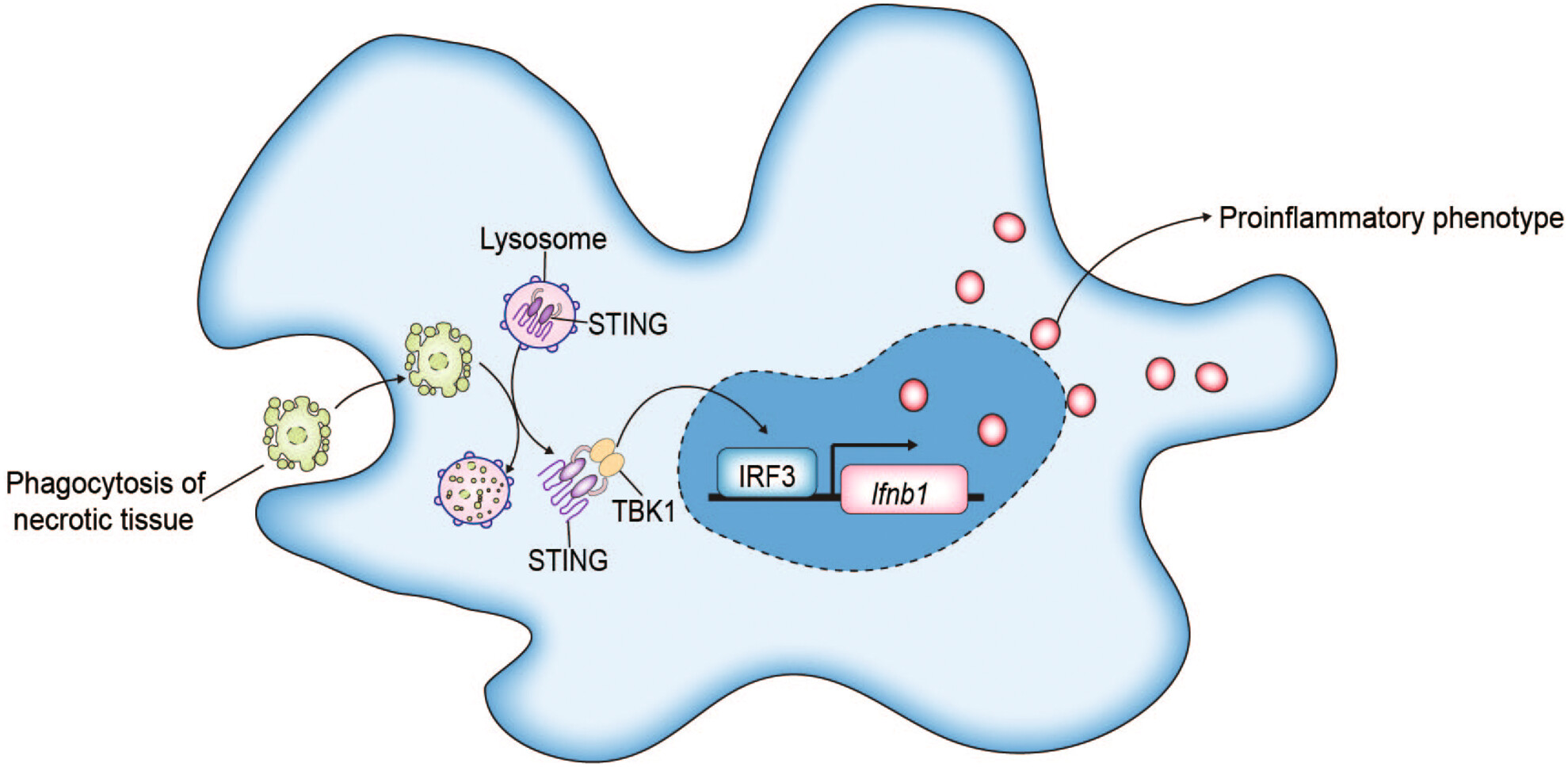
After stroke, macrophages and microglia transition from an anti-inflammatory to a proinflammatory phenotype due to lysosomal overload and impaired STING degradation. The activation of STING and the subsequent type I interferon signaling pathways results in the phenotypic transition of macrophages/microglia. Inhibiting STING can reverse the proinflammatory shift, thereby reducing poststroke neural inflammation and improving neurological outcomes.
Intraoperative Hypotension and Postoperative Newly Developed Cerebral Infarction in Patients With Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 09 December 2024
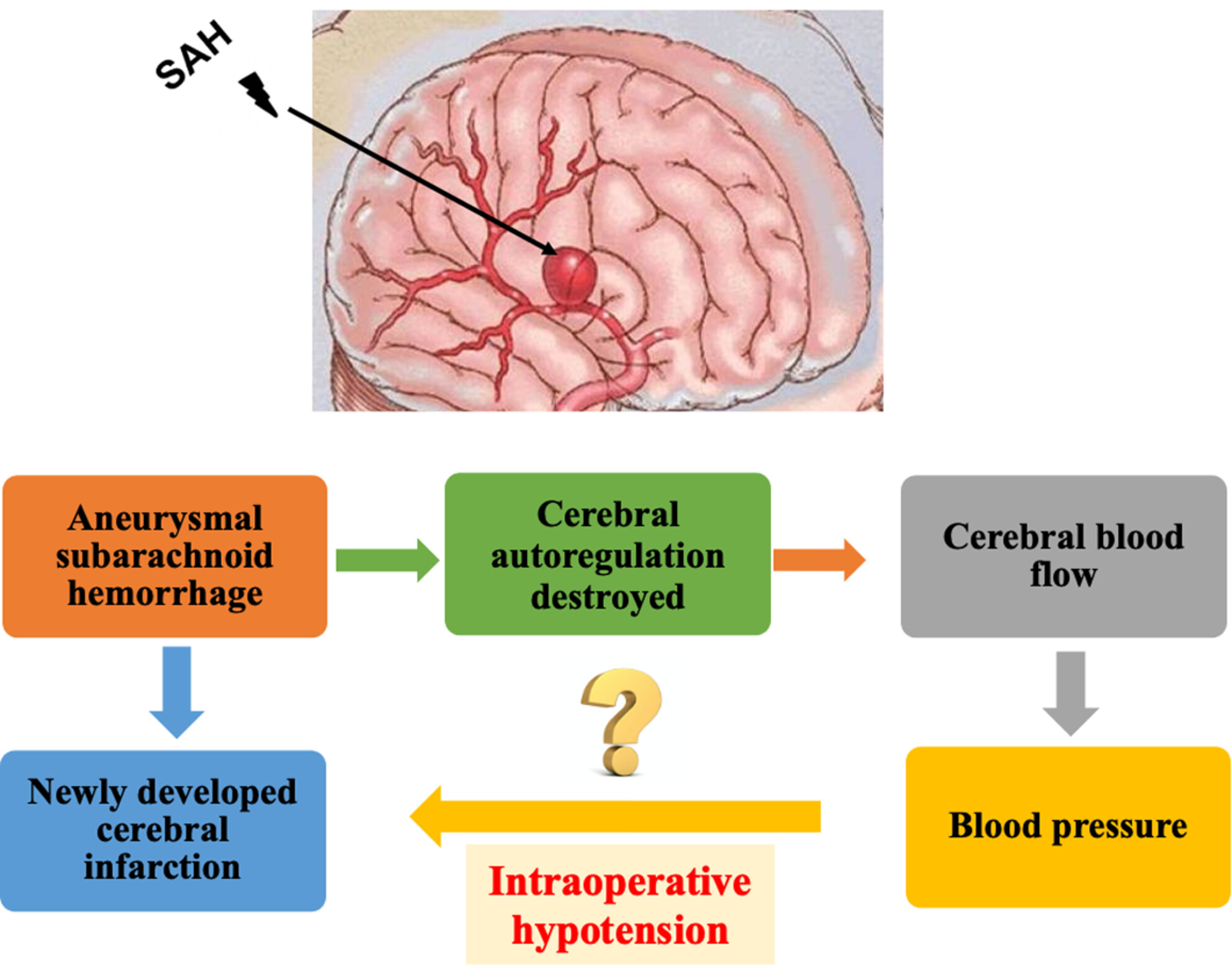
After aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, the cerebral autoregulation is destroyed, and the cerebral blood flow is dependent on blood pressure. Reliable recommendations on periprocedural blood pressure target are still lacking and remains inconclusive. This study aimed to investigate the association between intraoperative hypotension and newly developed cerebral infarction.
REVIEW
Potential and Challenges of Transcranial Photobiomodulation for the Treatment of Stroke
- First Published: 18 December 2024
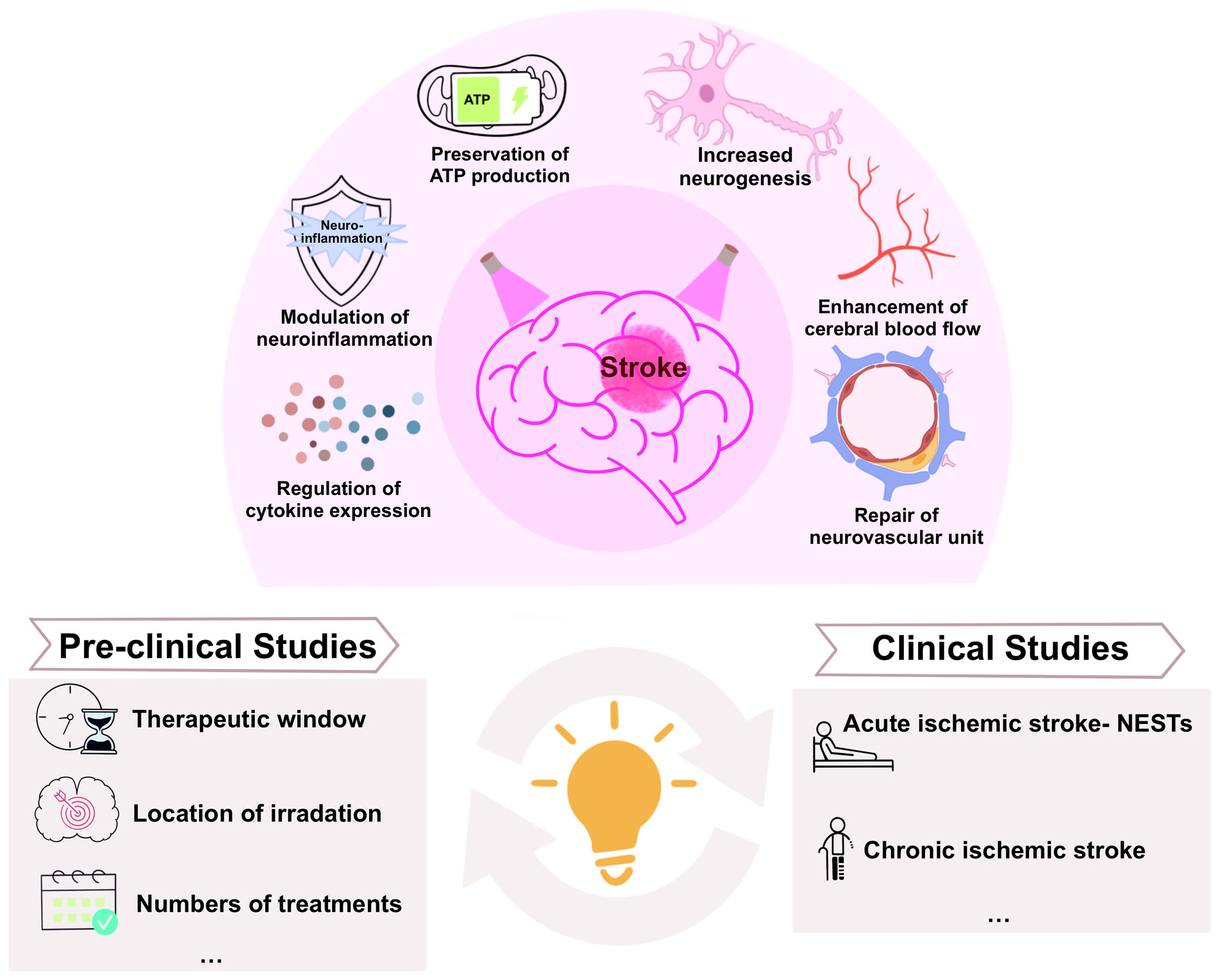
tPBM employs red or near-infrared light to enhance mitochondrial function, promote neurogenesis, and reduce neuroinflammation, offering potential benefits for stroke recovery. This review summarizes evidence from animal studies and clinical trials validating tPBM's efficacy and discusses translational challenges and future directions in treatment advancement.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Comparing Outcomes of Moyamoya Disease and Moyamoya Syndrome in a Real-World Scenario: A Cohort Study
- First Published: 09 December 2024
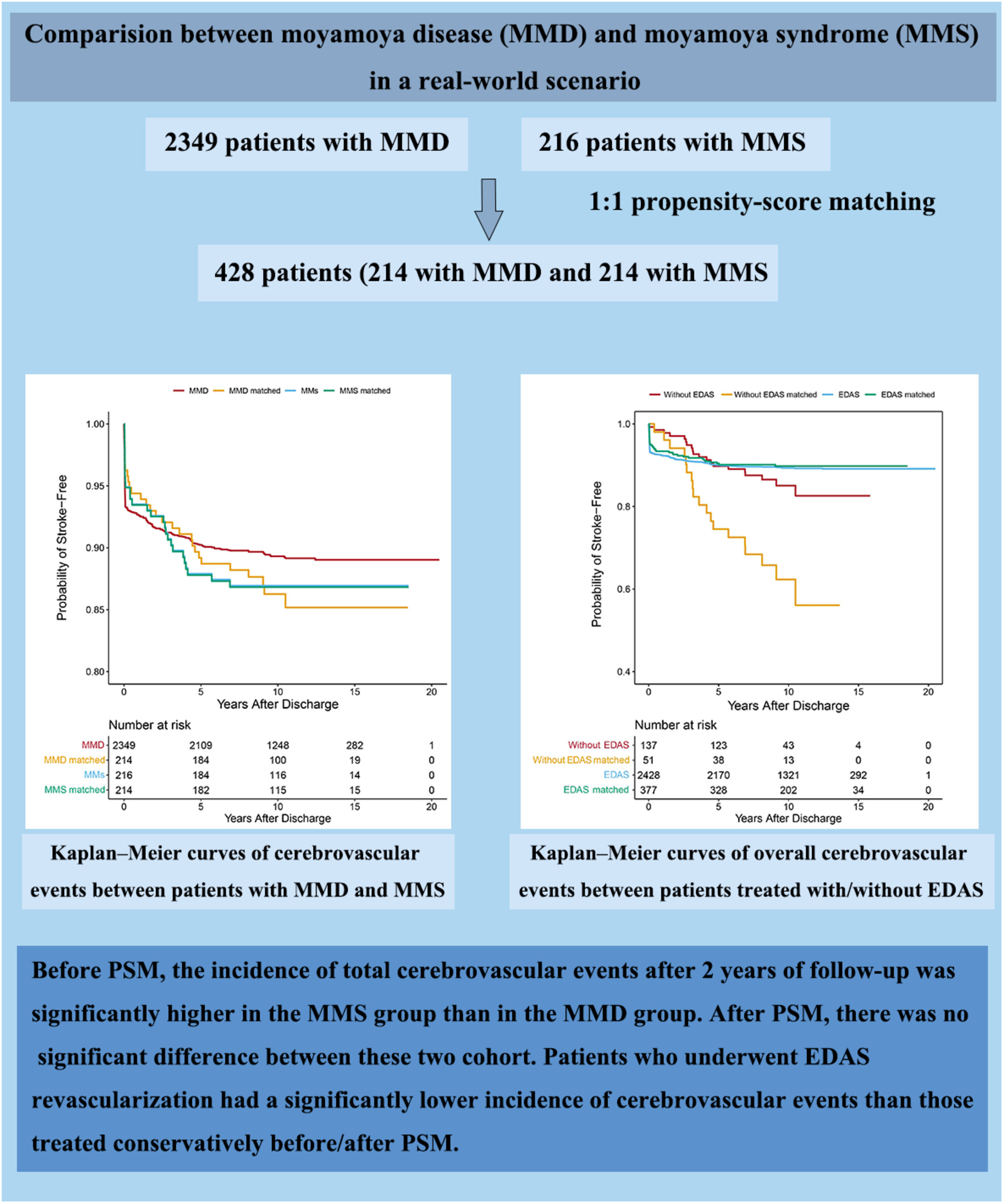
This real-world study revealed substantial clinical overlap between MMD and MMS. Both groups derived significant benefits from surgical revascularization, suggesting distinction may not be necessary to guide surgical management decisions. Optimizing preoperative status and preventing periprocedural complications may improve outcomes in these rare cerebrovascular conditions.
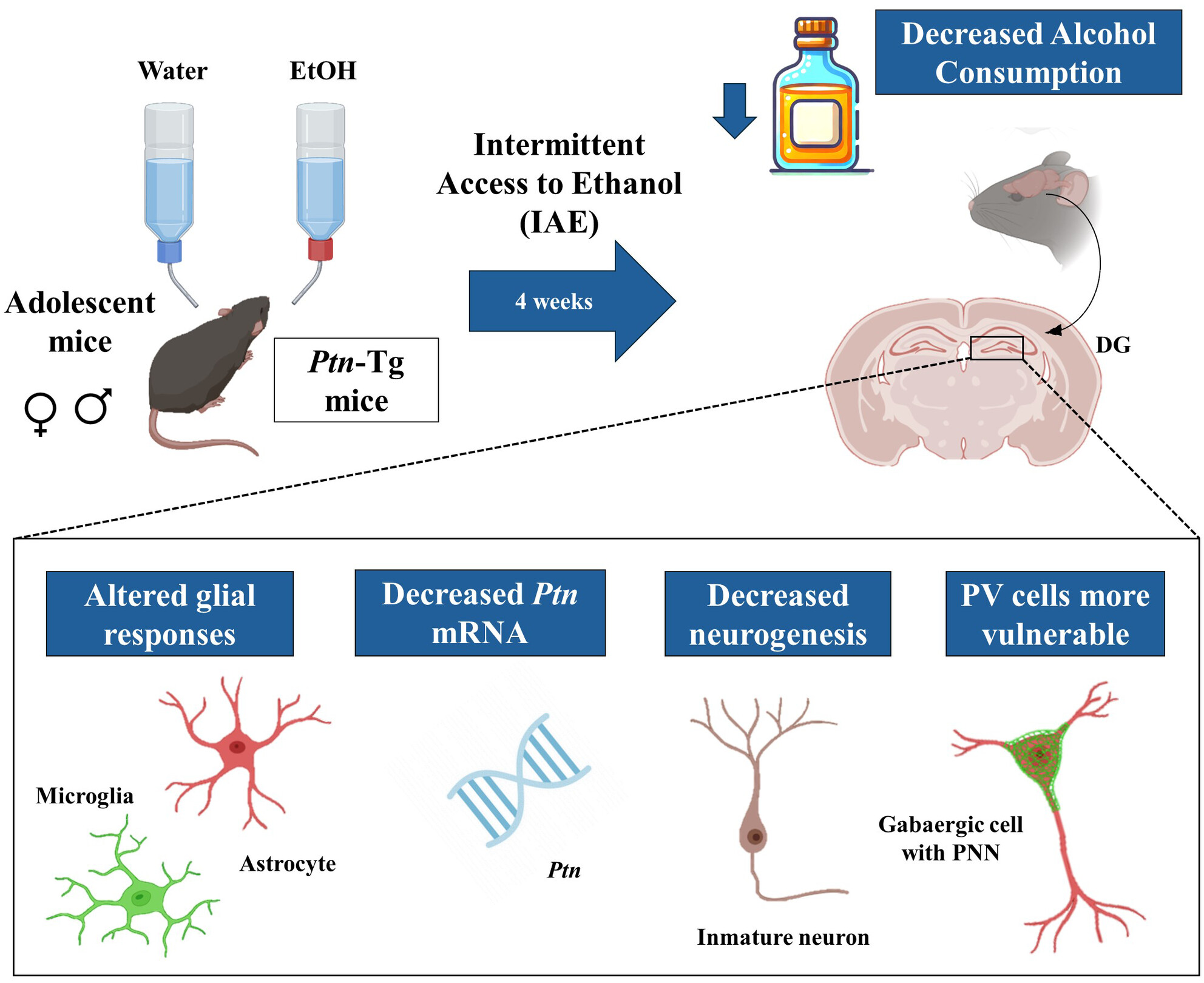
Pleiotrophin Overexpression Reduces Adolescent Ethanol Consumption and Modulates Ethanol-Induced Glial Responses and Changes in the Perineuronal Nets in the Mouse Hippocampus
- First Published: 09 December 2024
REVIEW
The Compelling Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling in Multiple Sclerosis: Role of BDNF Activators
- First Published: 09 December 2024
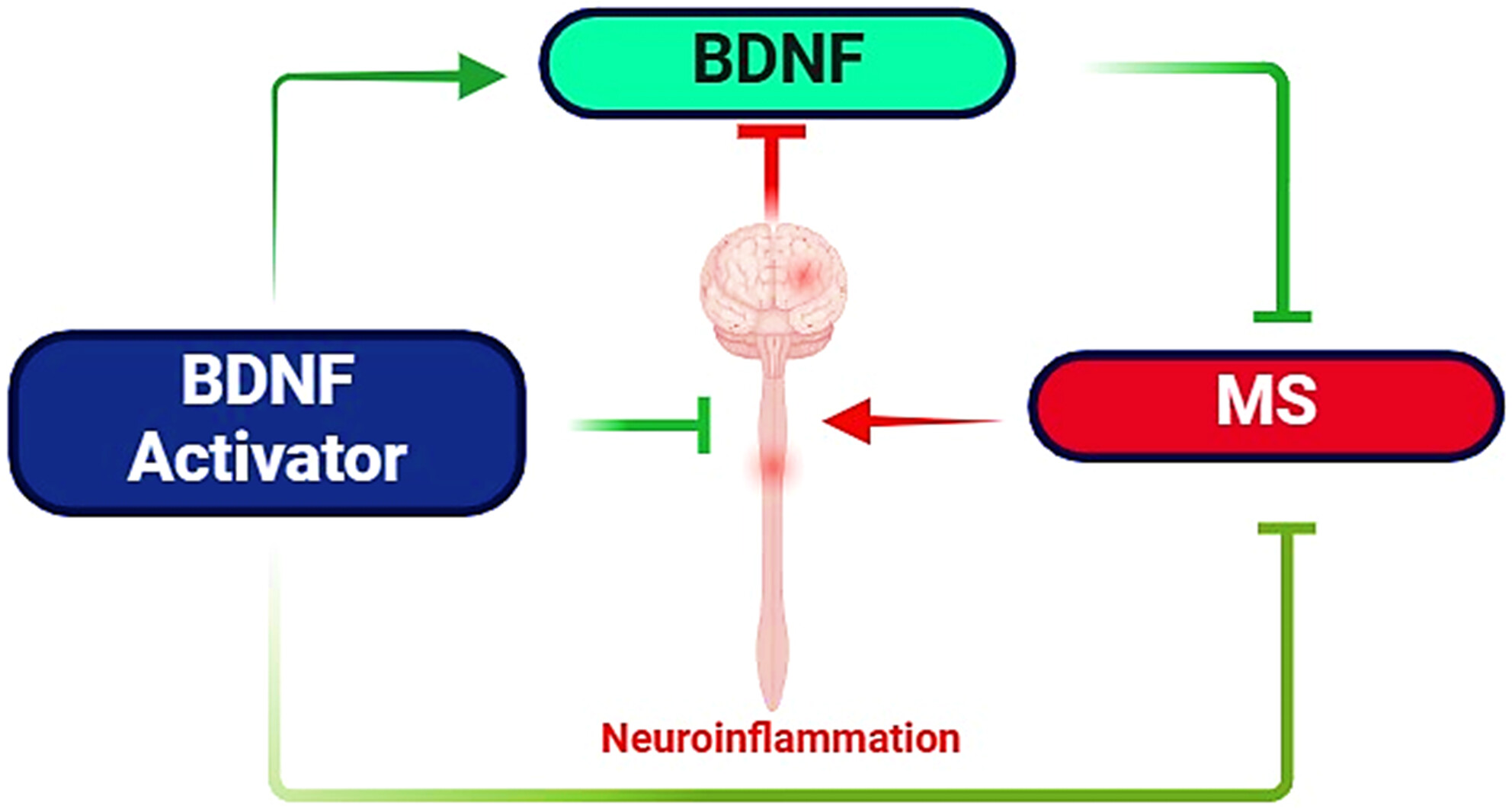
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is crucial for neuronal survival and plasticity in the CNS, acting through NTRK2/TRKB receptors. It also plays a role in inhibiting microglial activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine release. This review examines the controversial BDNF levels in multiple sclerosis (MS) stages and explores how BDNF signaling and its modulators influence MS pathogenesis and outcomes.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A Novel Compound Ligusticum Cycloprolactam Alleviates Neuroinflammation After Ischemic Stroke via the FPR1/NLRP3 Signaling Axis
- First Published: 09 December 2024
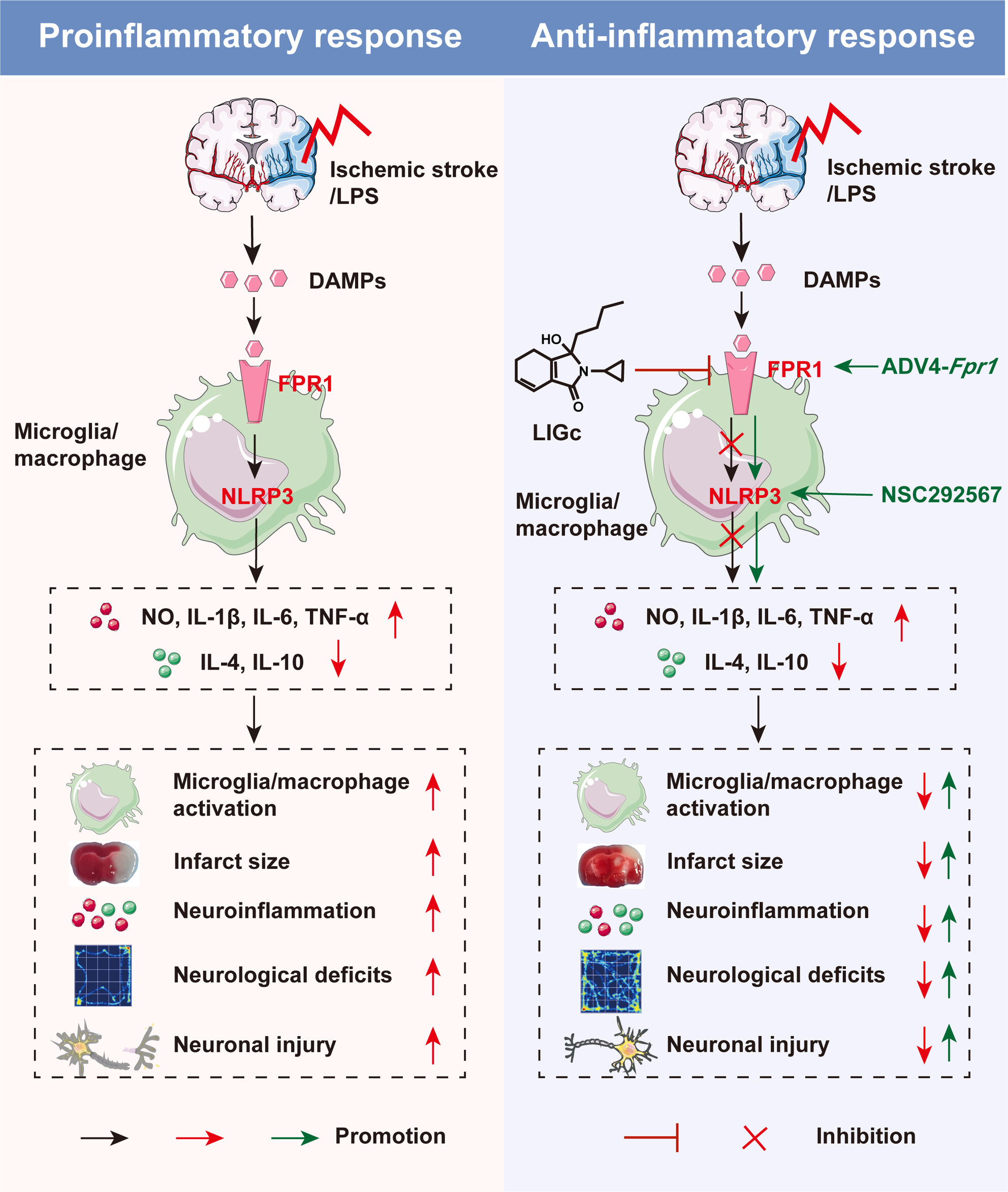
The anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective mechanisms of the novel drug LIGc in models of neuroinflammation and cerebral ischemic injury involve its ability to downregulate the expression of the FPR1/NLRP3 signaling pathway in microglia/macrophages. This regulation facilitates the transformation of these cells into an anti-inflammatory phenotype, leading to inhibition of pro-inflammatory factor release and promotion of anti-inflammatory factor production.
Caffeine's Neuroprotective Effect on Memory Impairment: Suppression of Adenosine A2A Receptor and Enhancement of Tyrosine Hydroxylase in Dopaminergic Neurons Under Hypobaric Hypoxia Conditions
- First Published: 13 December 2024
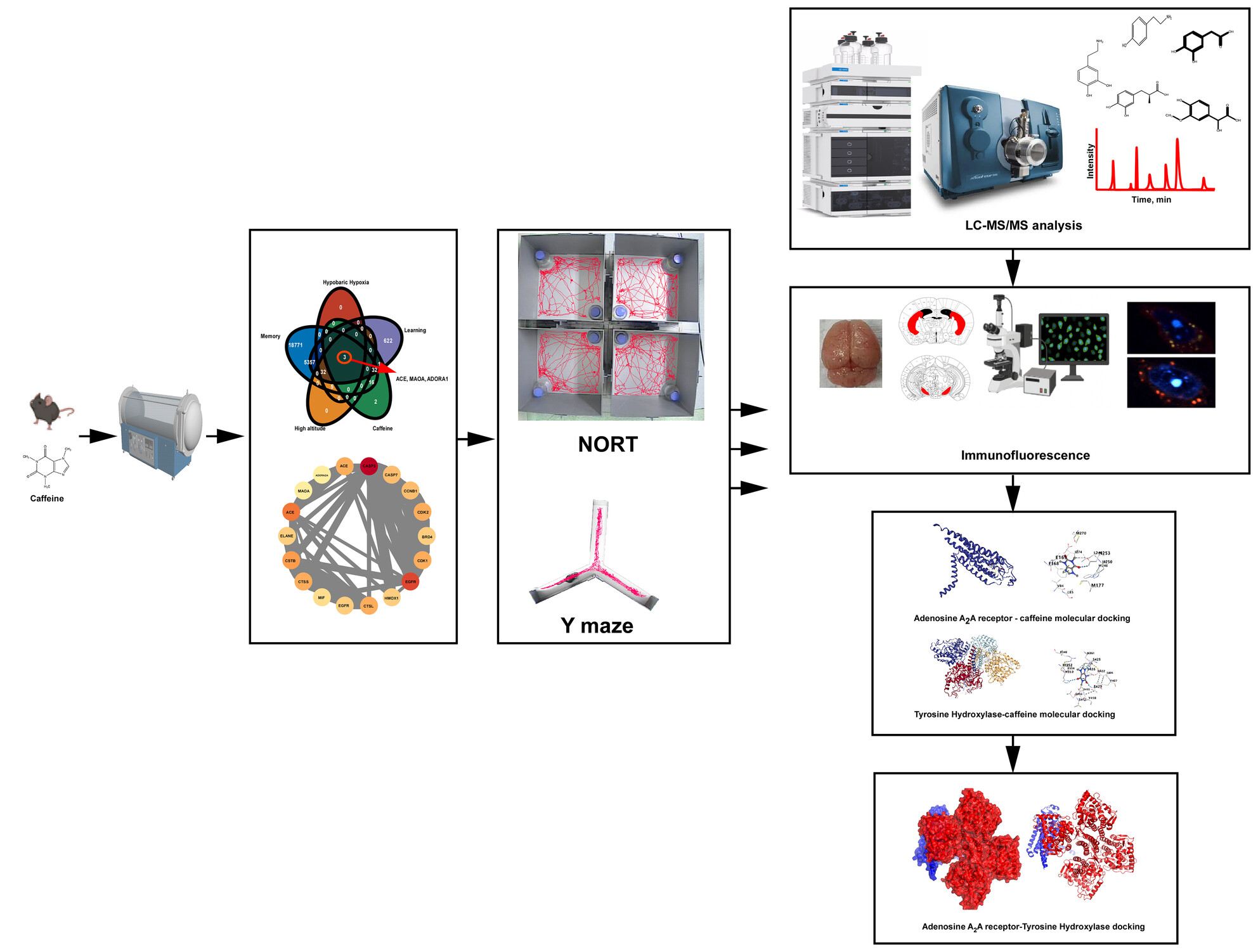
Administering caffeine preventively to mice can alleviate memory deficits caused by hypobaric hypoxia conditions. The possible mechanism is that caffeine inhibits A2A receptors, thereby promoting the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase, which in turn affects the release of dopamine and dopamine metabolism.
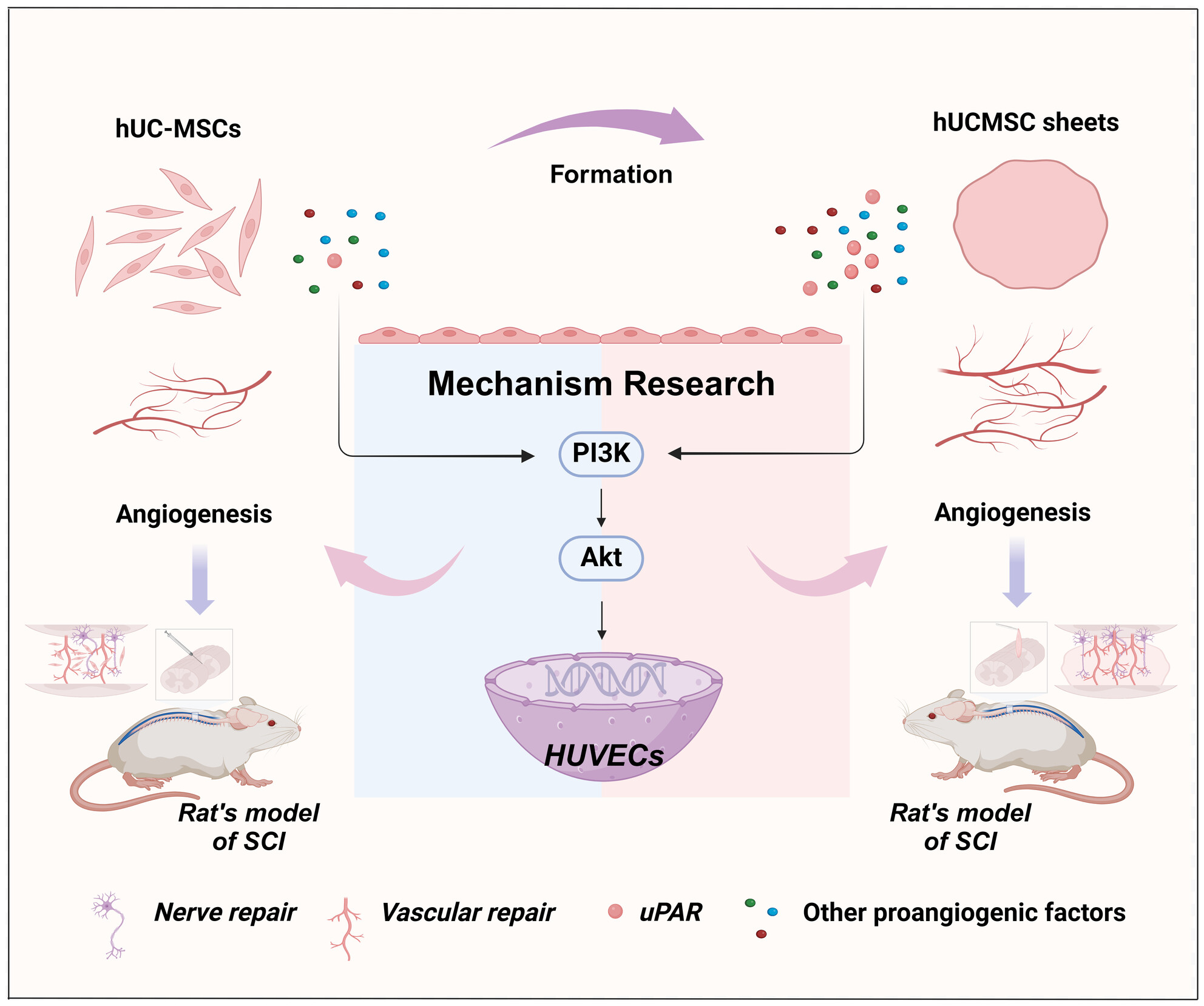
Cell Sheets Formation Enhances Therapeutic Effects of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Spinal Cord Injury
- First Published: 13 December 2024
Reproductive Toxicity Induced by Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis From 2004 to 2023 Based on the FAERS Database
- First Published: 13 December 2024
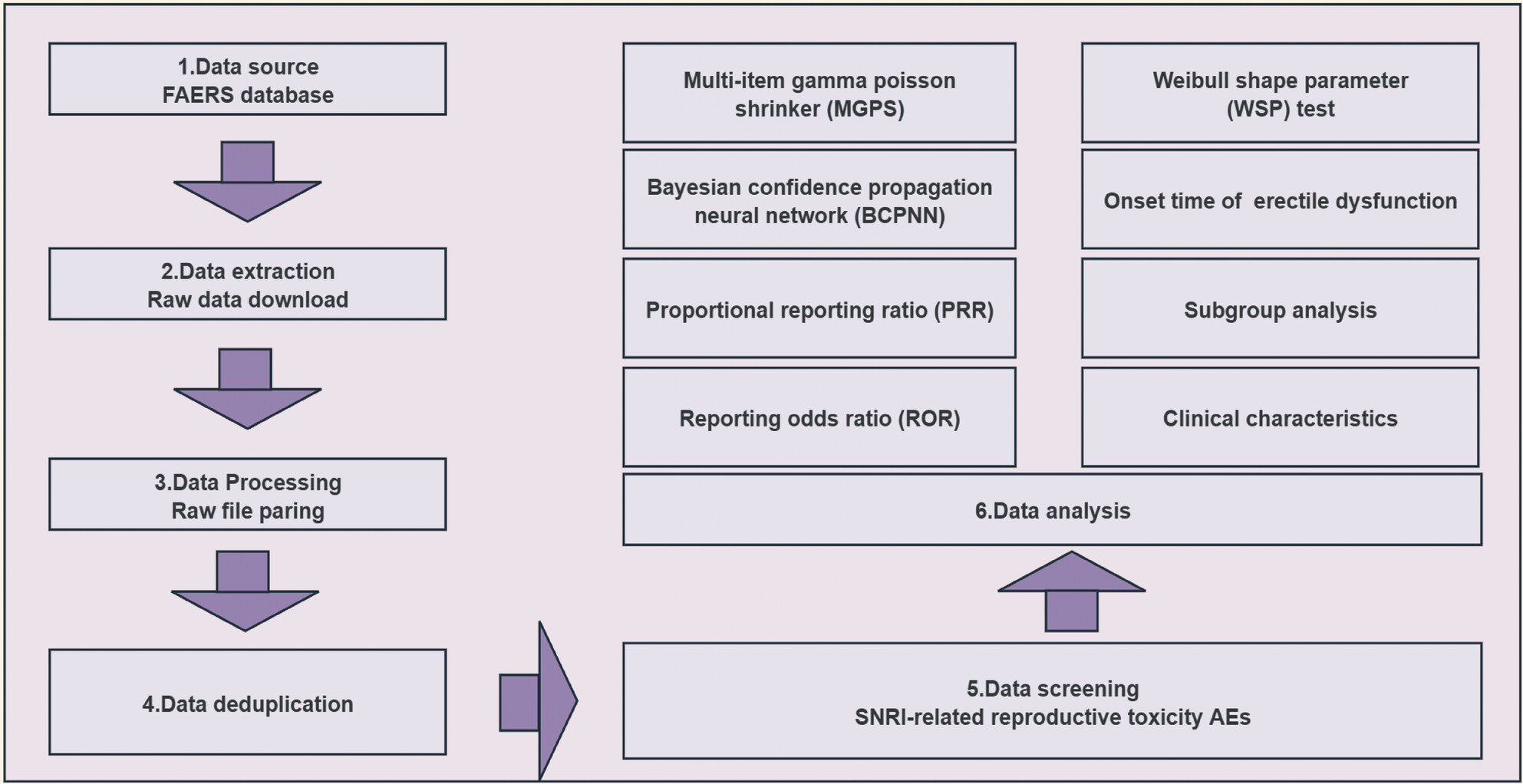
A comprehensive analysis of the large-scale real-world FAERS database was conducted to evaluate the relationship between SNRIs and adverse reproductive system events. In patients treated with SNRIs, males should focus on erectile dysfunction and retrograde ejaculation, while females should be alert to potential associations with ovarian cysts.
REVIEW
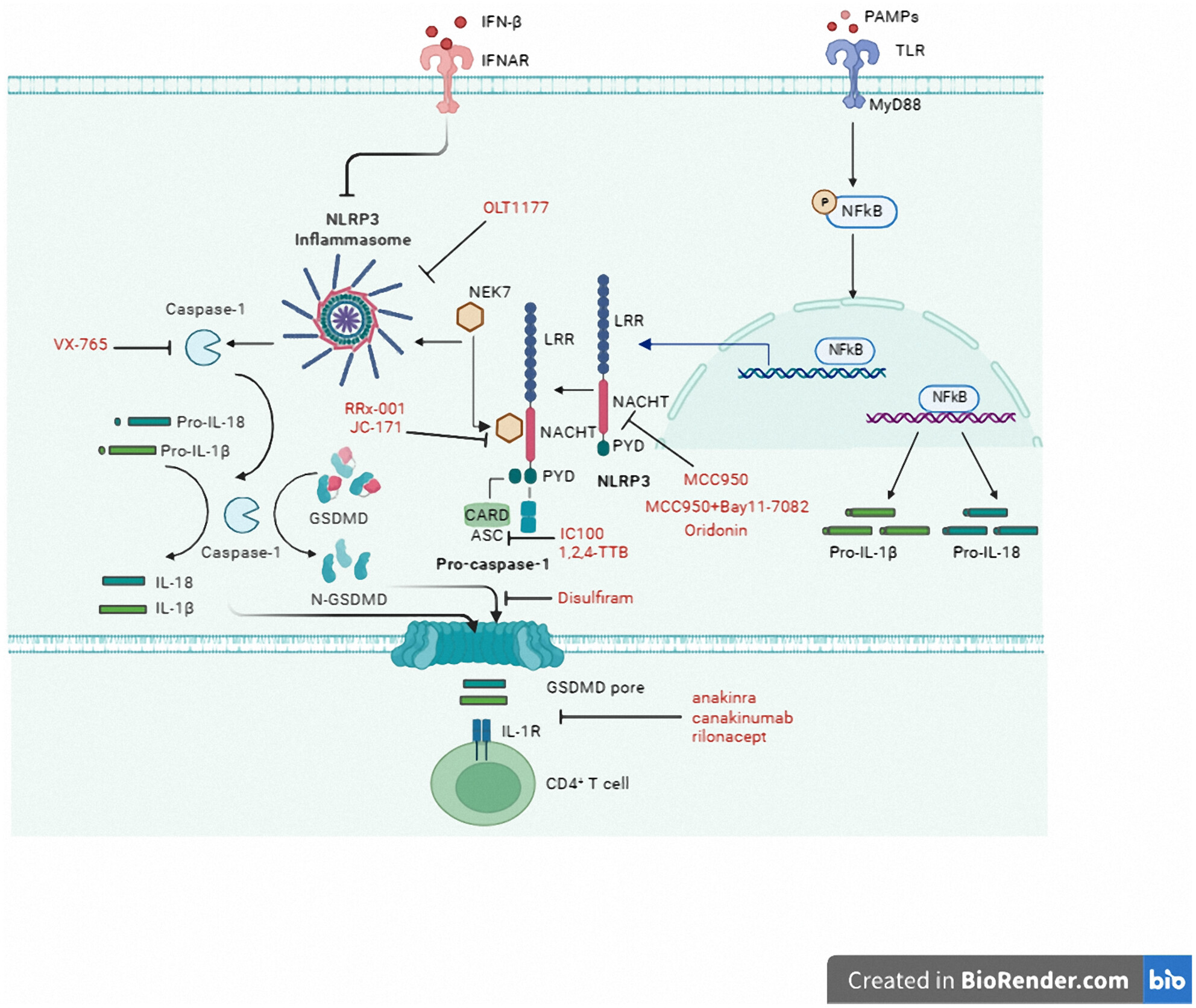
Microglial Mayhem NLRP3 Inflammasome's Role in Multiple Sclerosis Pathology
- First Published: 17 December 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Transplantation Reduces White Matter Injury in a Fetal Goat Model
- First Published: 17 December 2024
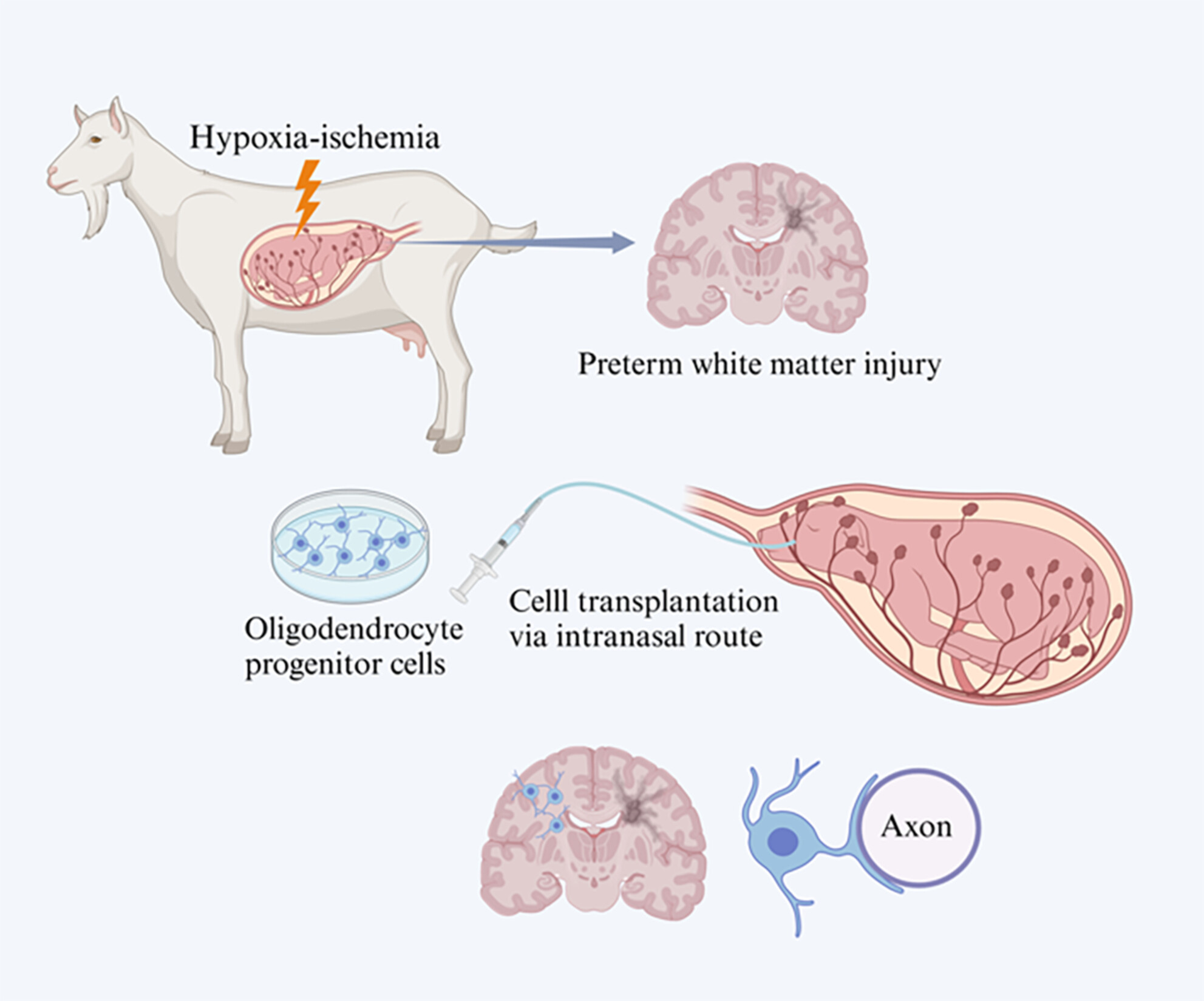
Preterm white matter injury (PWMI) is the most common type of brain injury in preterm infants. In this study, human OPCs (hOPCs) were administered to a fetal goat model of PWMI. Exogenous hOPCs can differentiate into mature oligodendrocytes in fetal goats and alleviate hypoxia-ischemia-induced PWMI.
Altered Hippocampal Subfields Functional Connectivity in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Patients With Residual Dizziness: A Resting-State fMRI Study
- First Published: 17 December 2024
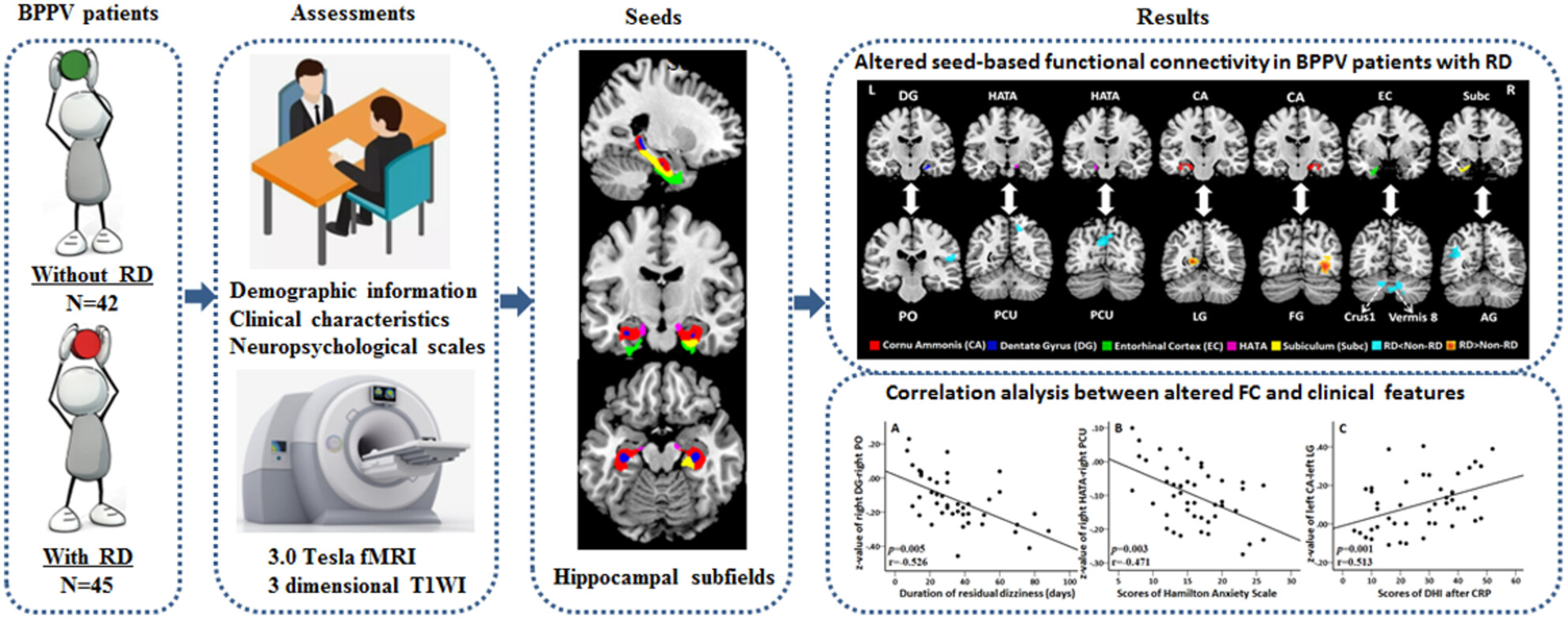
BPPV patients with RD showed altered FC between hippocampal subfields and brain regions involved in spatial orientation and navigation, vestibular and visual processing, as well as emotional regulation. These findings offer novel insights into the pathophysiological mechanisms in BPPV patients with RD following successful CRP.
Exploring the Synergistic Effects of Erinacines on Microglial Regulation and Alzheimer's Pathology Under Metabolic Stress
- First Published: 17 December 2024

Erinacines enhance microglial ramification and alleviate Alzheimer's disease pathology in a metabolically stressed model. This study reveals novel mechanisms, including histone deacetylase inhibition, supporting erinacines as a promising therapeutic for Alzheimer's, particularly in cases complicated by metabolic dysfunction.
Functional Segregation-Integration Preference Configures the Cognitive Decline Against Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: An MRI Study
- First Published: 17 December 2024
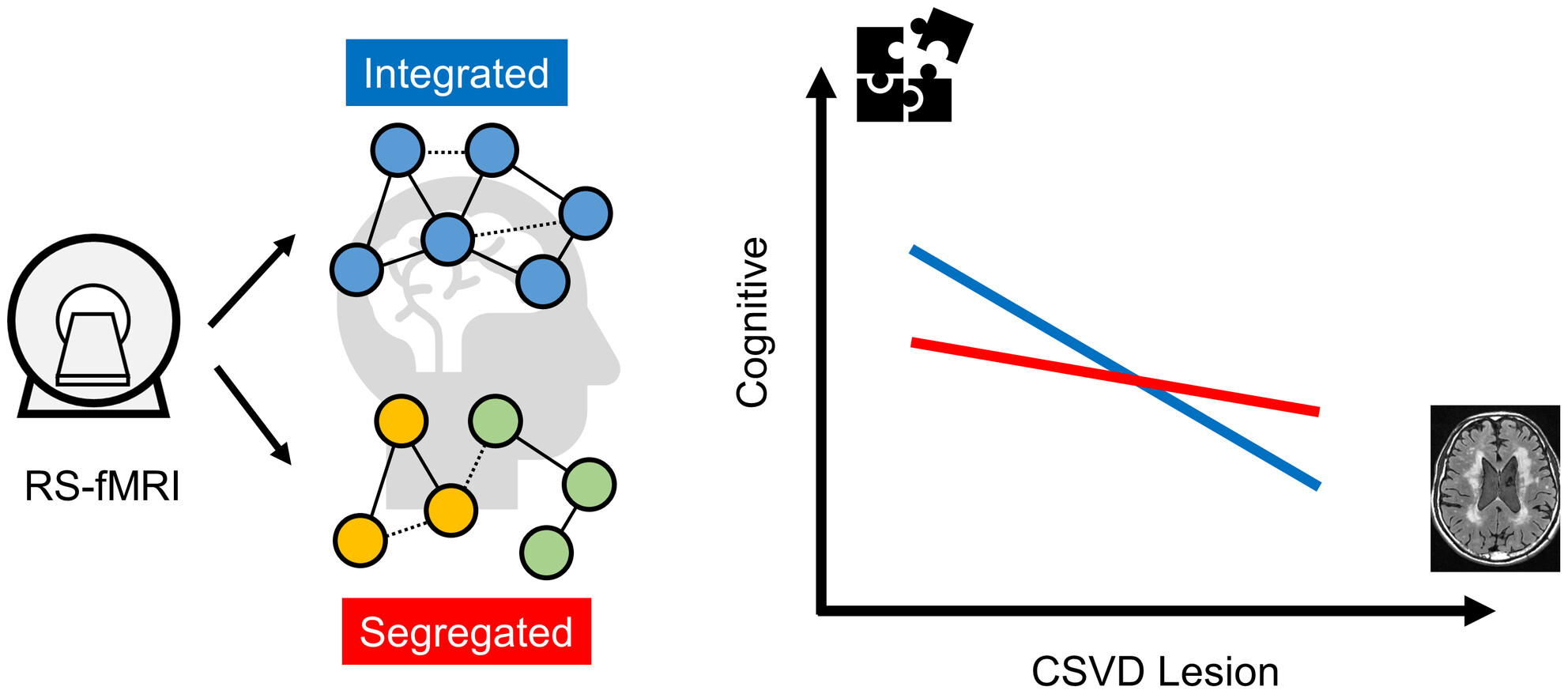
This study emphasizes the impact of functional segregation-integration preference on the cognitive outcome of cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD). Compared to segregated resting-state network, integrated one was found to contribute to cognitive resilience against mild and moderate damage from CSVD. Cognitive cross-overs exist for several domains before severe damage stages.
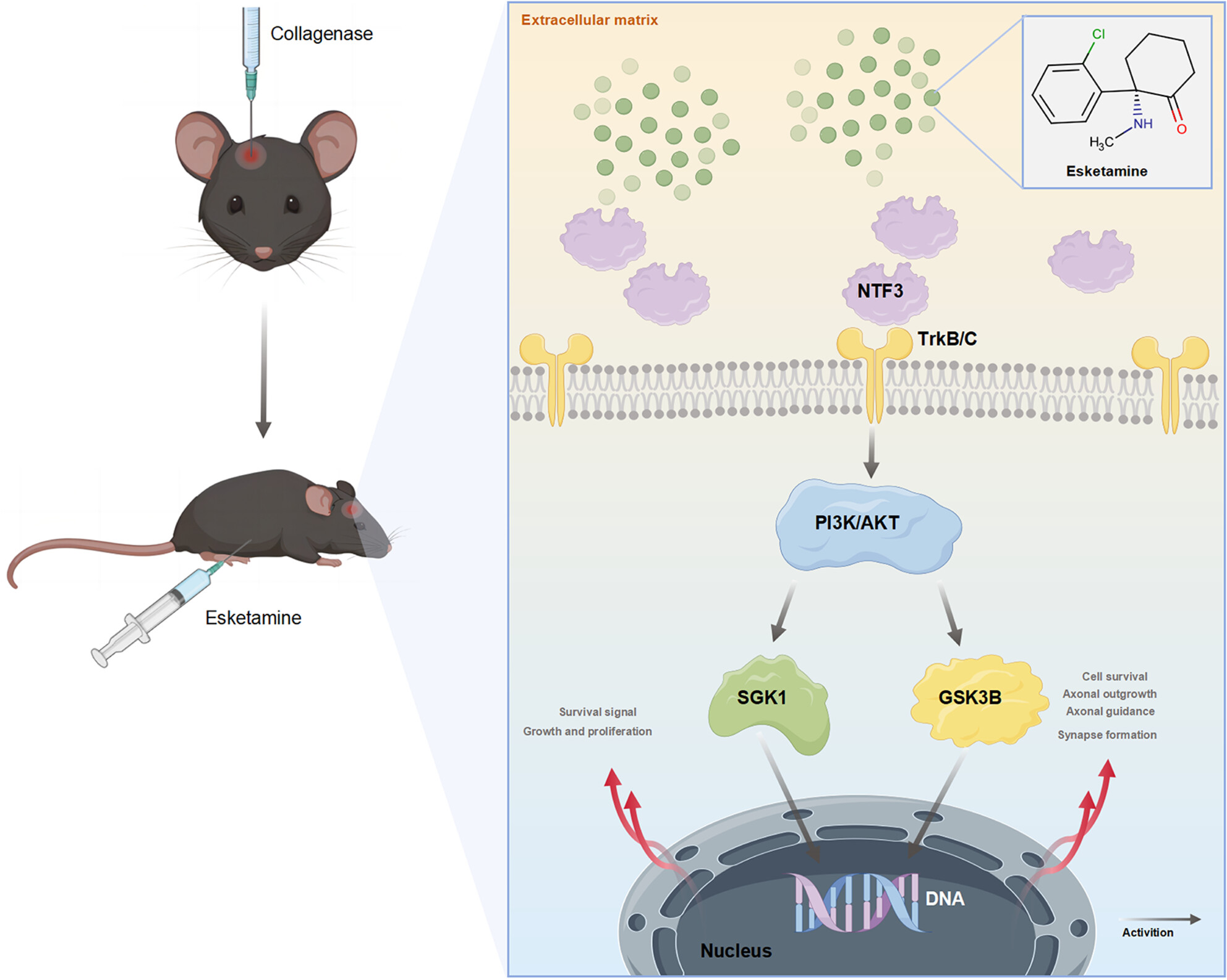
Esketamine Provides Neuroprotection After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice via the NTF3/PI3K/AKT Pathway
- First Published: 17 December 2024
REVIEW
tsRNAs: A Prospective, Effective Therapeutic Intervention for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- First Published: 17 December 2024
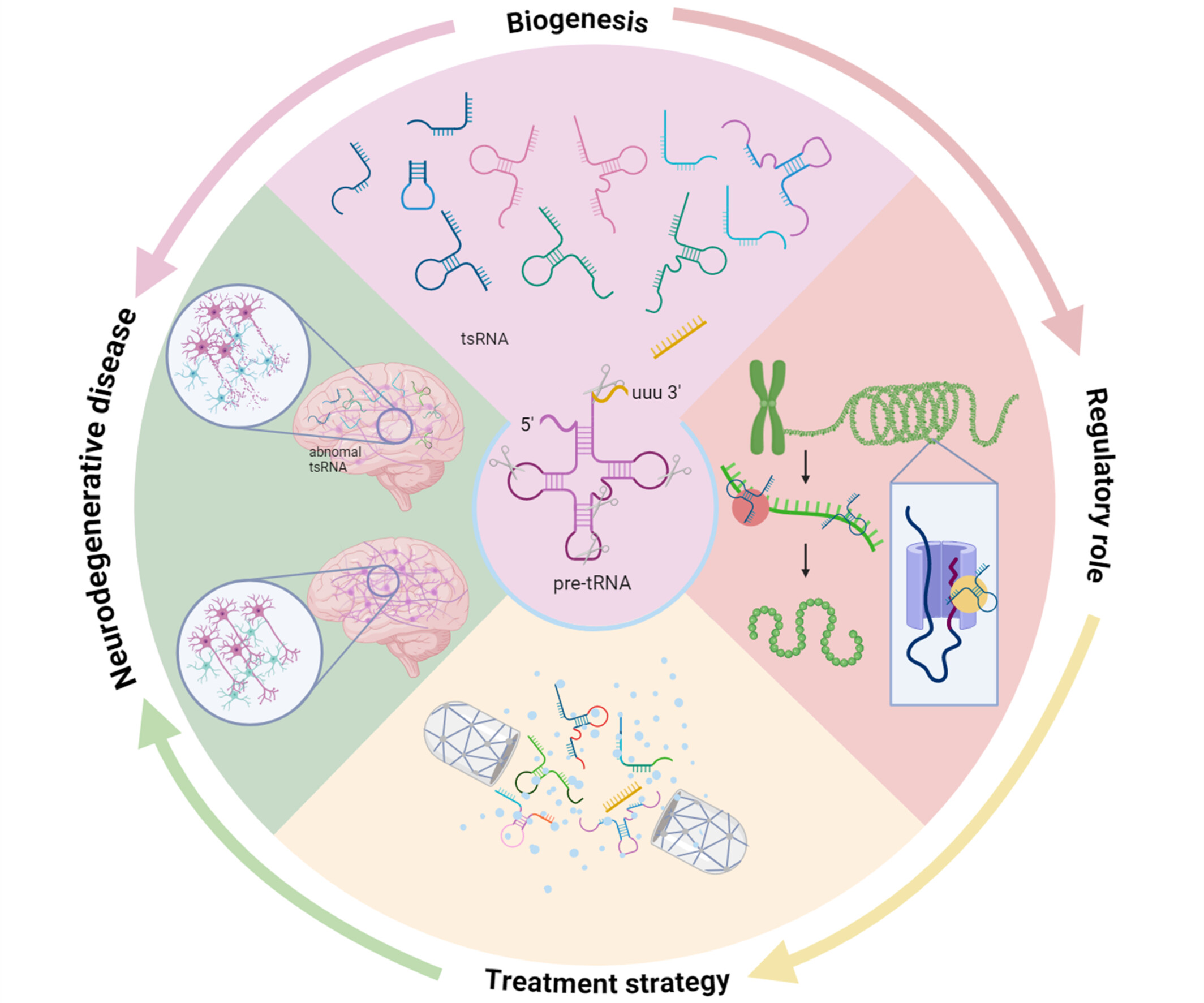
Transfer RNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs) are generated through the cleavage of transfer RNAs. tsRNAs modulate gene expression through transcriptional and translational mechanisms. tsRNAs are implicated in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders. tsRNAs have potential applications as nucleic acid therapeutics for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Interleukin-3 Modulates Macrophage Phagocytic Activity and Promotes Spinal Cord Injury Repair
- First Published: 19 December 2024
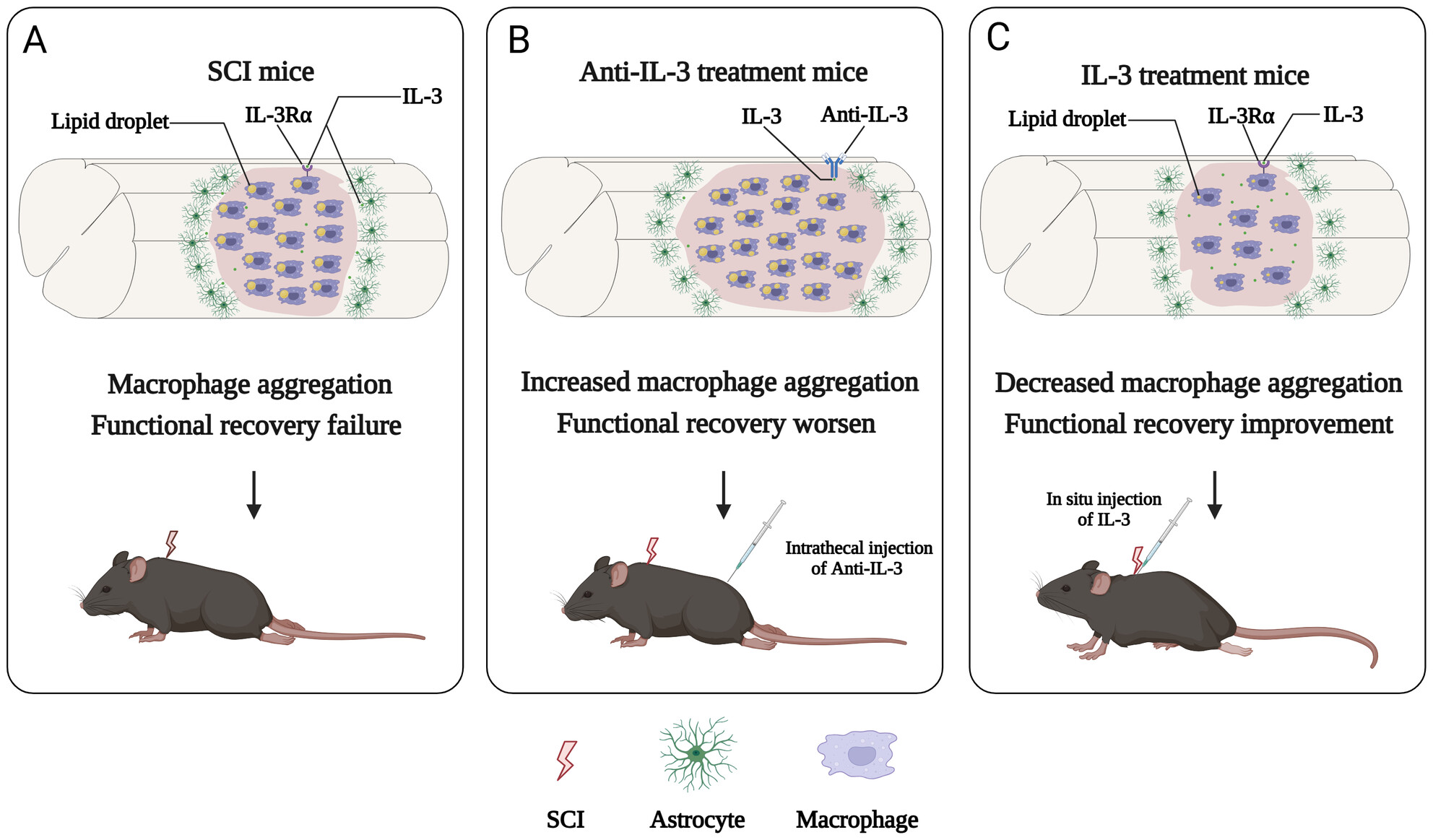
IL-3 modulates macrophage phagocytic activity and promotes SCI repair. (A) After SCI, IL-3 is secreted by astrocytes surrounding the lesion core, while foamy macrophages filled with lipid droplets gather in the injury center, contributing to the failure of functional recovery in mice. (B) Blockage of IL-3 leads to increased aggregation of macrophage and lipid droplets at the injury core, resulting in the expansion of the lesion area and worsened locomotor function in mice. (C) Administration of IL-3 results in a significant decrease in macrophage accumulation and promotes the clearance of lipid droplets by macrophages at the injury site, accompanied by enhanced functional recovery.
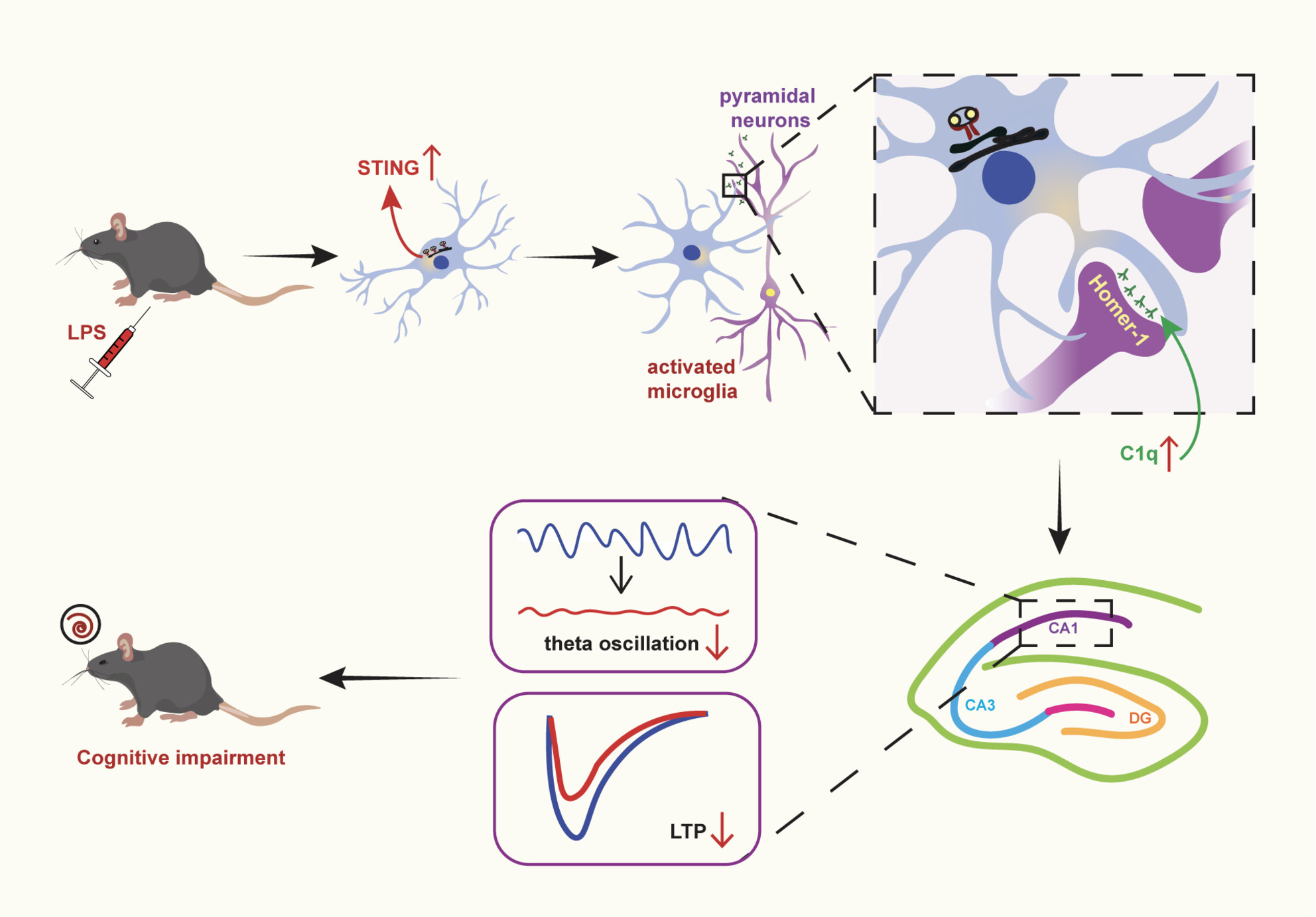
STING Driving Synaptic Phagocytosis of Hippocampal Microglia/Macrophages Contributes to Cognitive Impairment in Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy in Mice
- First Published: 19 December 2024
Causal Relationships Between Epilepsy, Anti-Epileptic Drugs, and Serum Vitamin D and Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Bidirectional and Drug Target Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 20 December 2024
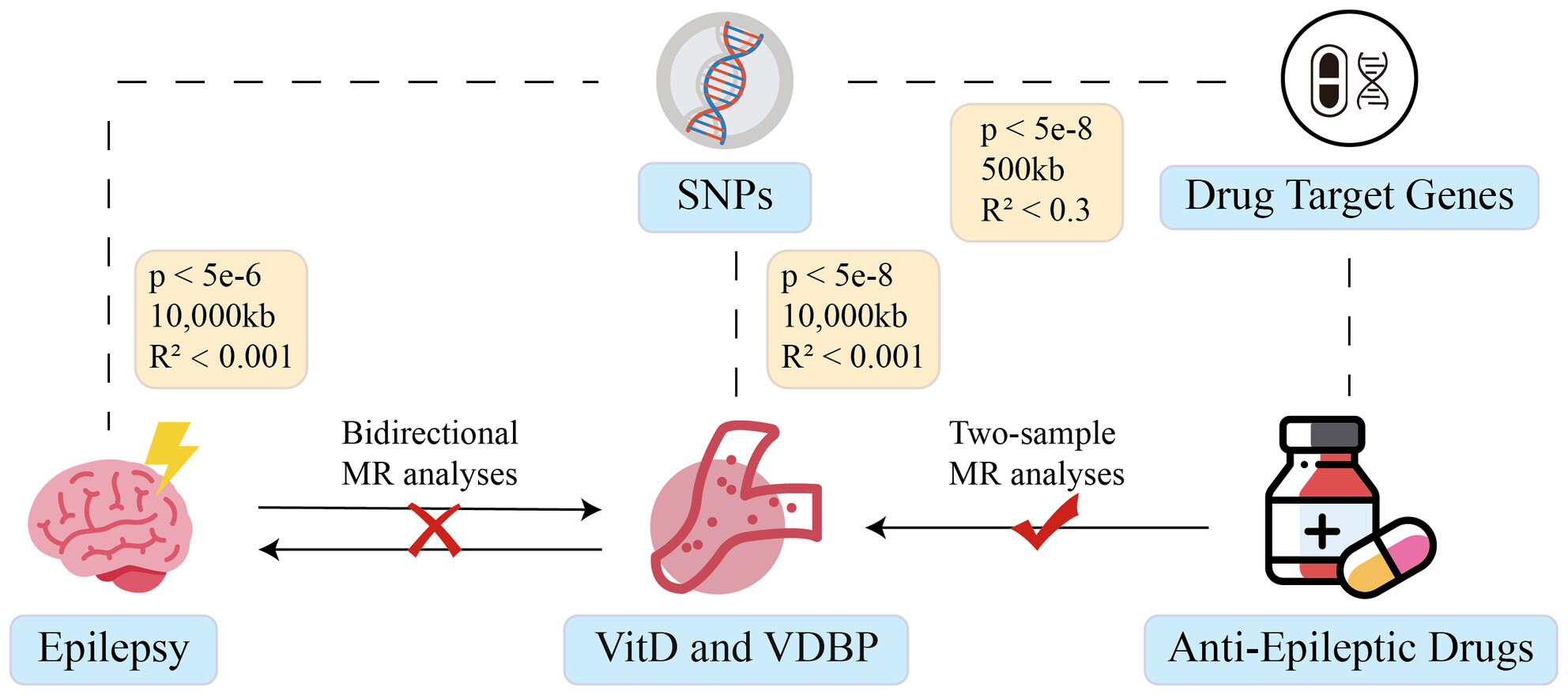
The study utilized single nucleotide polymorphisms from genome-wide association studies as instrumental variables and employed Mendelian Randomization to uncover causal relationships between epilepsy and both vitamin D and vitamin D-binding protein. Additionally, the findings support that anti-epileptic drugs reduce serum vitamin D levels without affecting vitamin D-binding protein.
Theta Rhythm-Based Attention Switch Training Effectively Modified Negative Attentional Bias
- First Published: 20 December 2024
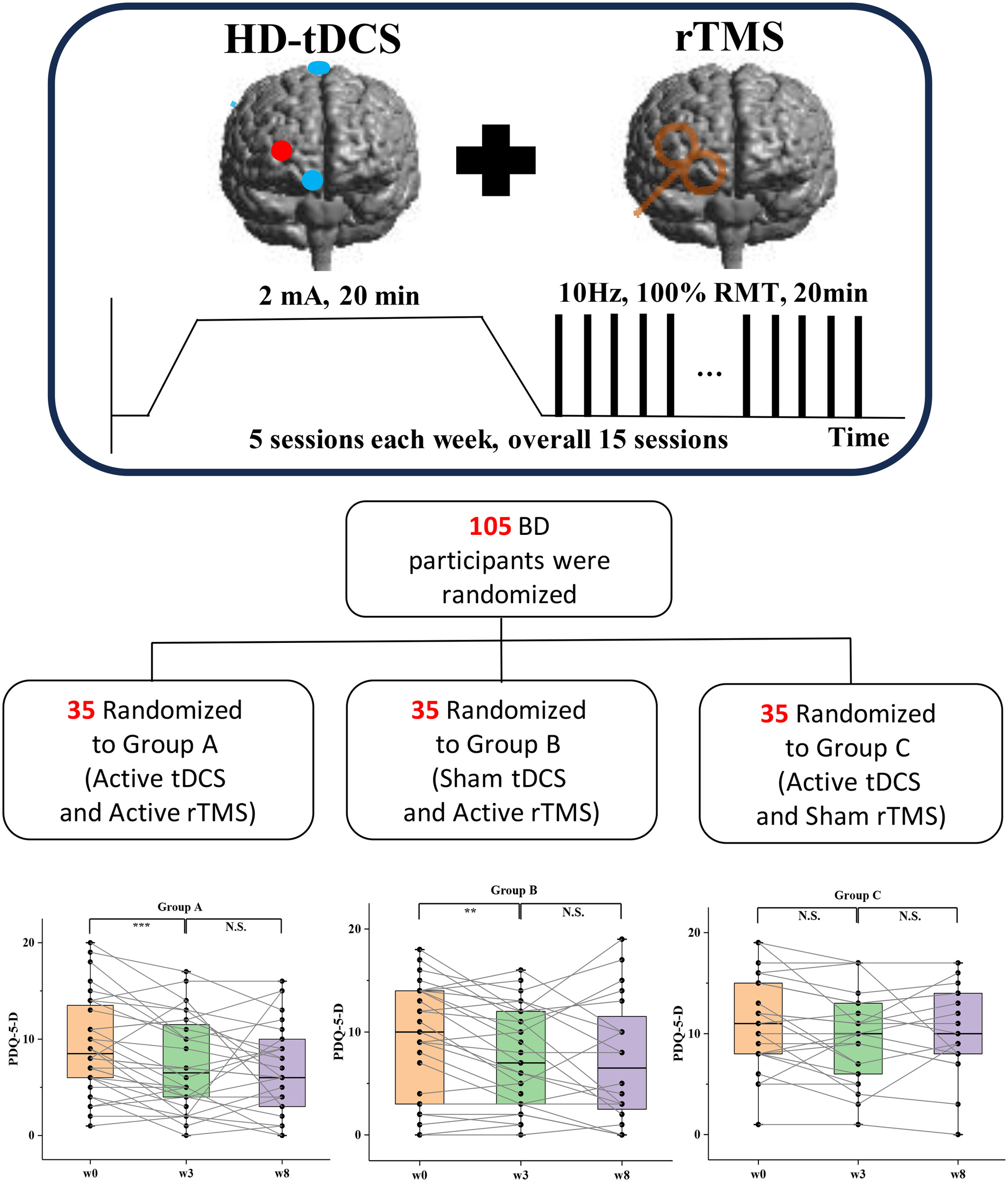
Cognitive Remediation in Patients With Bipolar Disorder: A Randomized Trial by Sequential tDCS and Navigated rTMS Targeting the Primary Visual Cortex
- First Published: 20 December 2024
The Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: A Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 23 December 2024
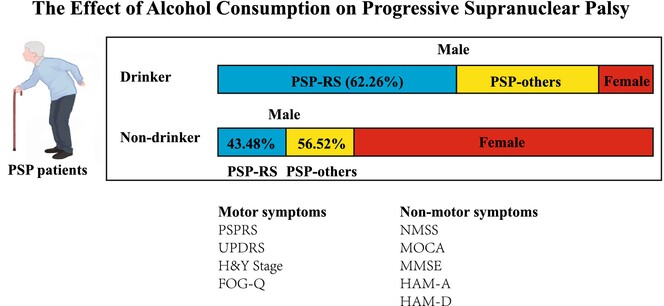
An evaluative analysis conducted at our center on PSP patients has uncovered a significant association between alcohol consumption and more pronounced clinical symptoms. Specifically, heavy alcohol consumption exacerbates motor symptoms and accelerate cognitive decline, particularly in visuospatial and executive abilities, memory, and language functions. This correlation is particularly pronounced among male patients.
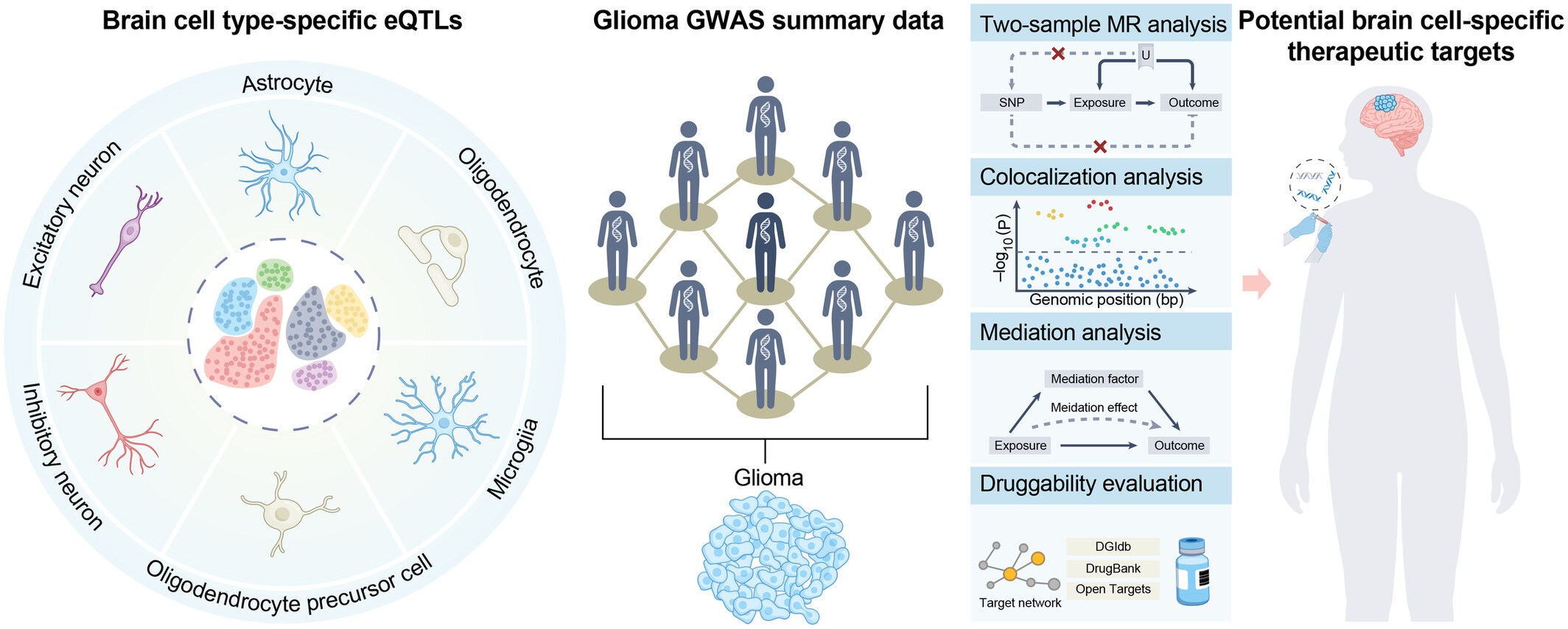
Identification of Brain Cell Type-Specific Therapeutic Targets for Glioma From Genetics
- First Published: 25 December 2024
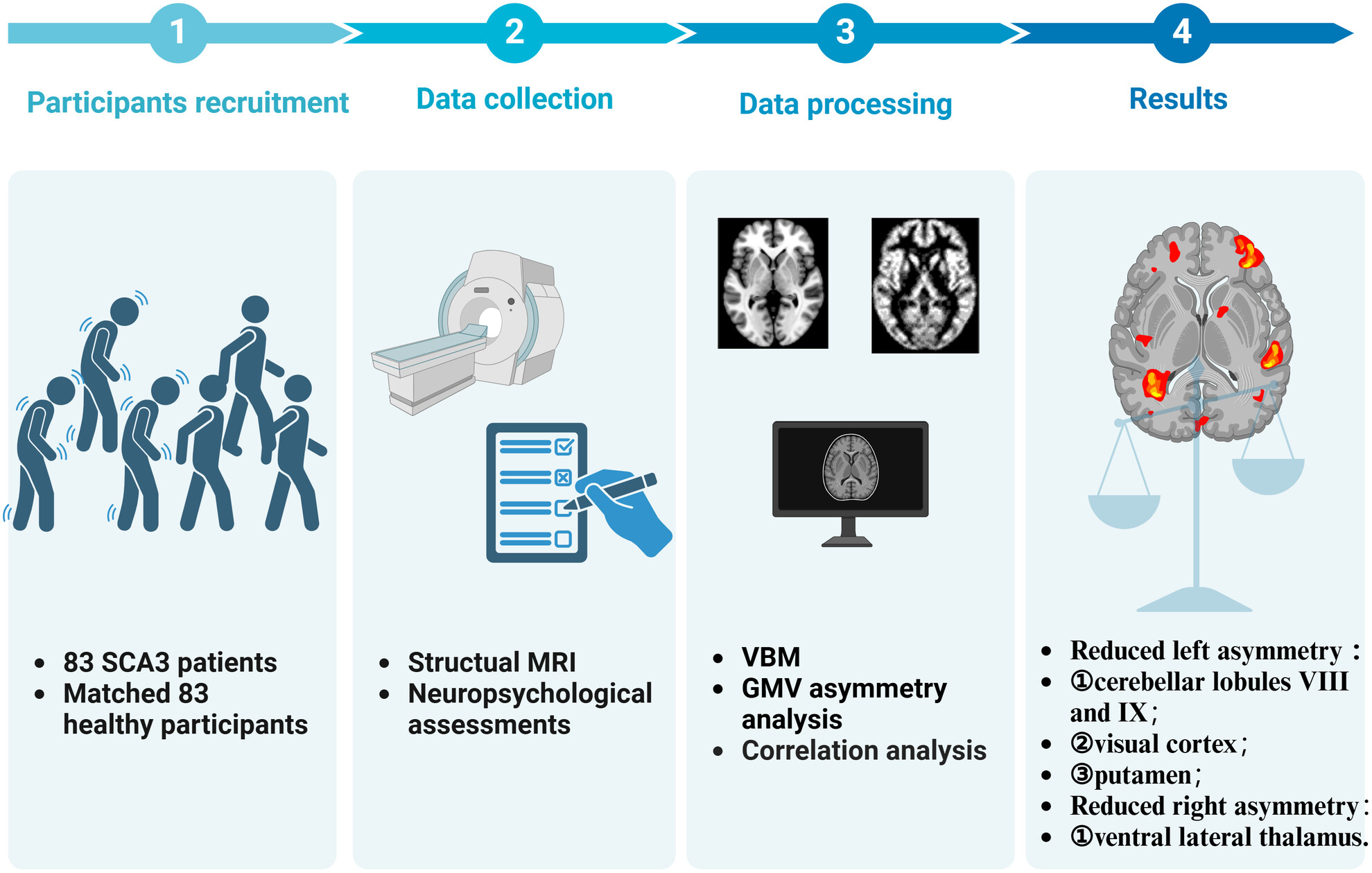
Gray Matter Asymmetry Alterations in Patients With Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Comparison Study
- First Published: 25 December 2024
Altered Cognitive Networks Connectivity in Parkinson's Disease During the Microlesion Period After Deep Brain Stimulation
- First Published: 25 December 2024
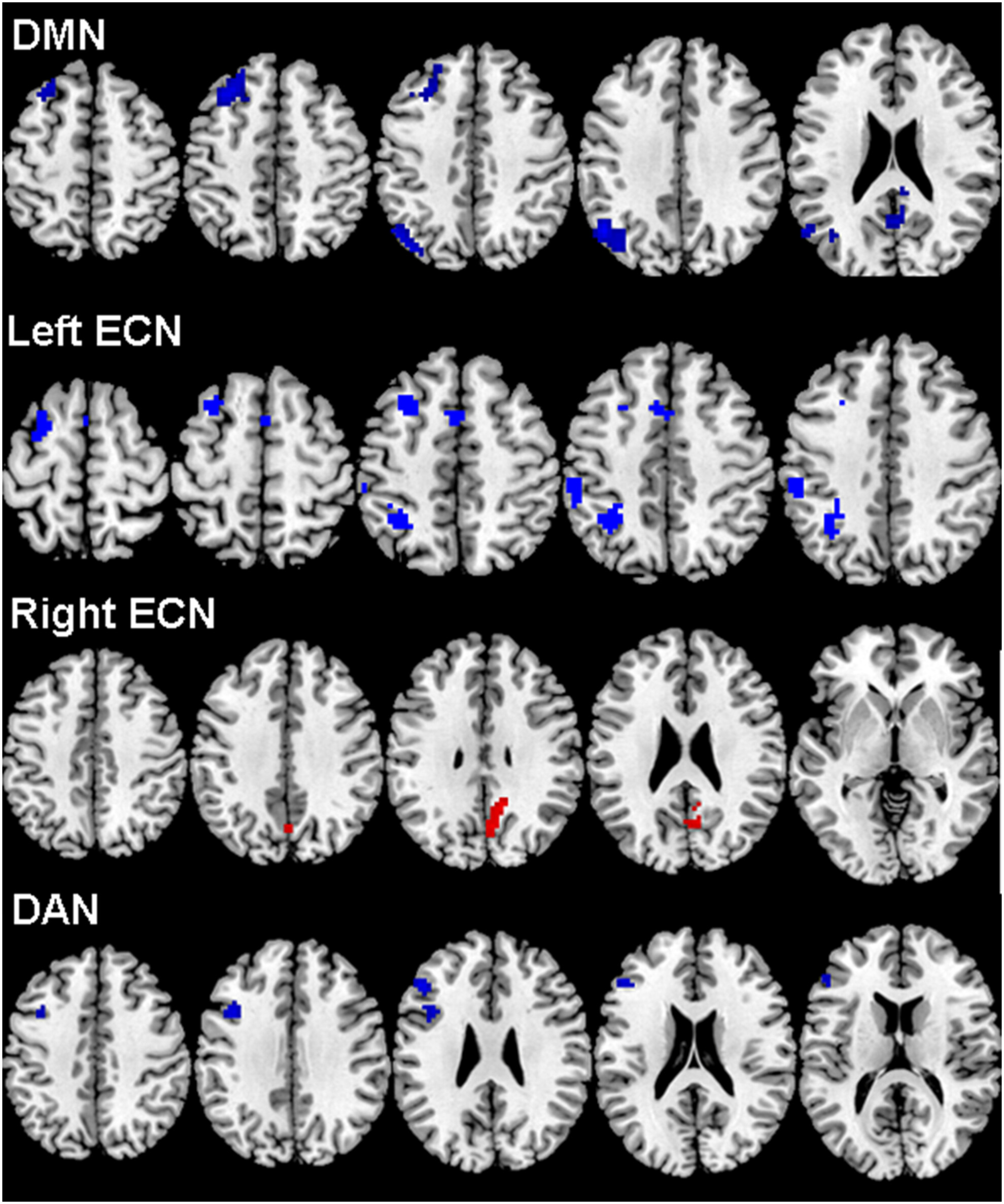
Seeds-based functional connectivity analysis revealed significant alterations in cognitive networks during microlesion period after deep brain stimulation. Functional connectivity within the three major networks of the default mode network, executive control network, and dorsal attention network showed a widespread decline after surgery.
The JNK Signaling Pathway Regulates Seizures Through ENT1 in Pilocarpine-Induced Epilepsy Rat Model
- First Published: 25 December 2024
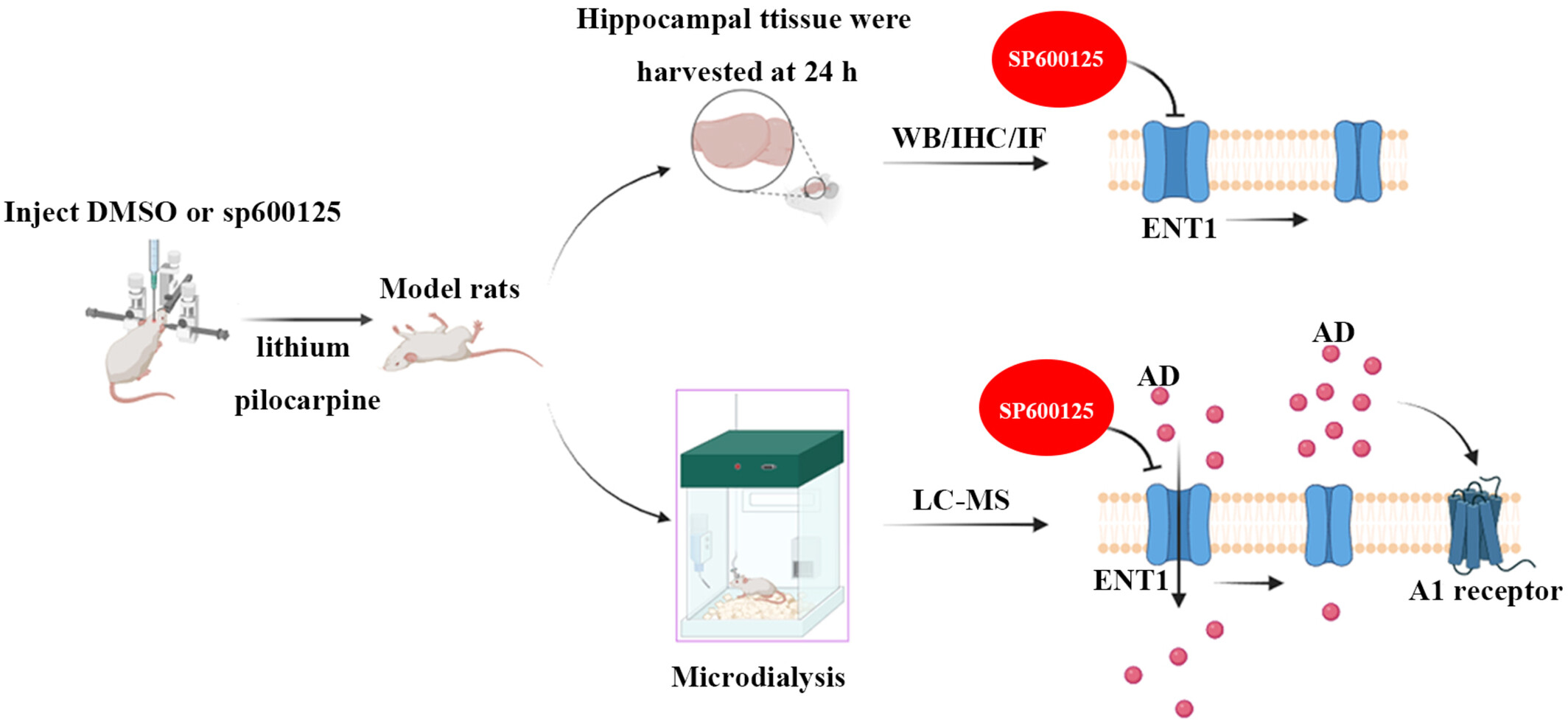
The JNK-specific inhibitor SP600125 can specifically inhibit the JNK signaling pathway, reduce the expression of the ENT1 transporter, and reduce the seizure intensity in experimental rats. The mechanism is related to the transport of adenosine from the extracellular space to the intracellular space by ENT1 during epileptic states. Inhibition of ENT1 can increase the concentration of adenosine in the extracellular fluid of the hippocampus. The increase in adenosine can inhibit the release of glutamate by acting on the A1 receptor of the presynaptic membrane.
Gender Differences in Dendritic Damage, Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, and Cognitive Impairment During Aging Processes
- First Published: 26 December 2024
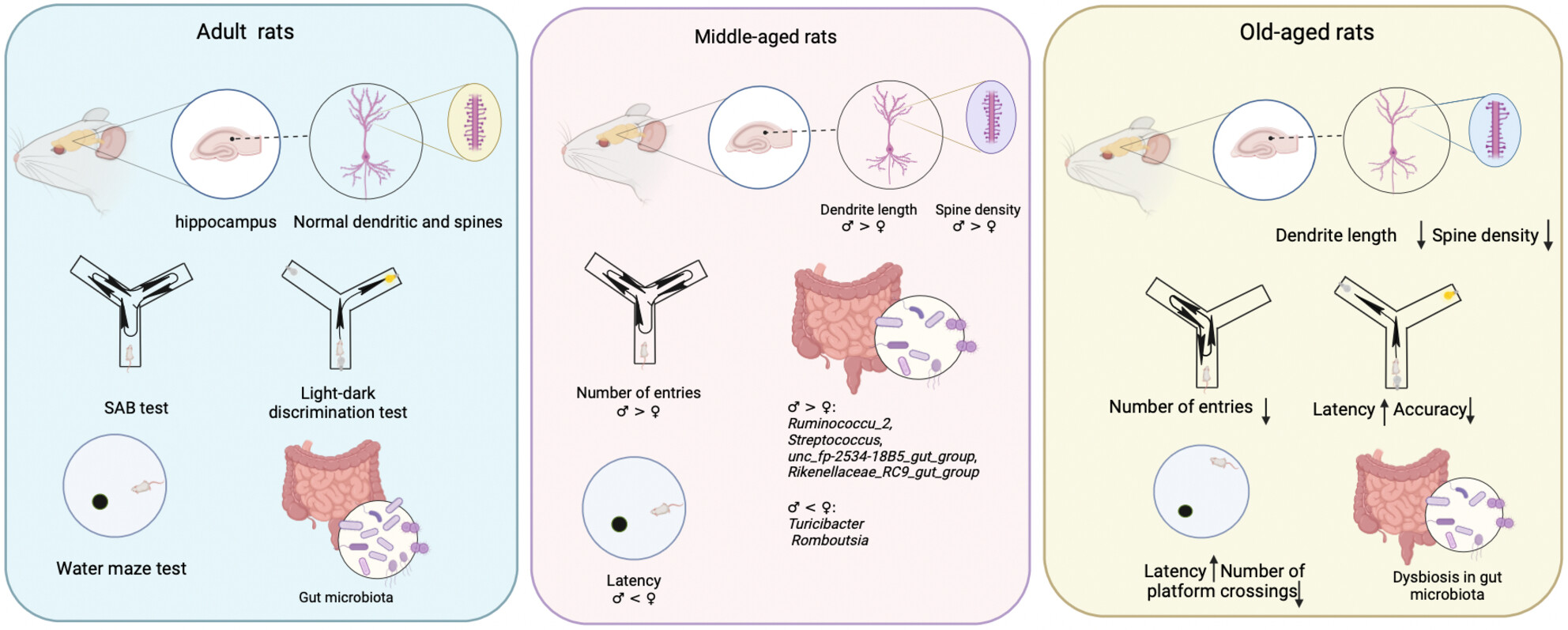
The present study showed the cognitive ability of old-aged rats was decreased than adult and middle-aged rats; males have better cognitive ability than females in middle-aged rats. The neuronal dendritic structures of the hippocampus were damaged to different degrees during aging, and spine loss occurred in females rather than males in middle-aged rats. In addition, the microbial diversity of gut microbiota was significantly decreased in old-aged male rats; some specific bacteria of microbiota communities were changed with aging.
Annexin A1 Mitigates Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in a Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy Model by Enhancing the Expression of Occludin and Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1)
- First Published: 27 December 2024
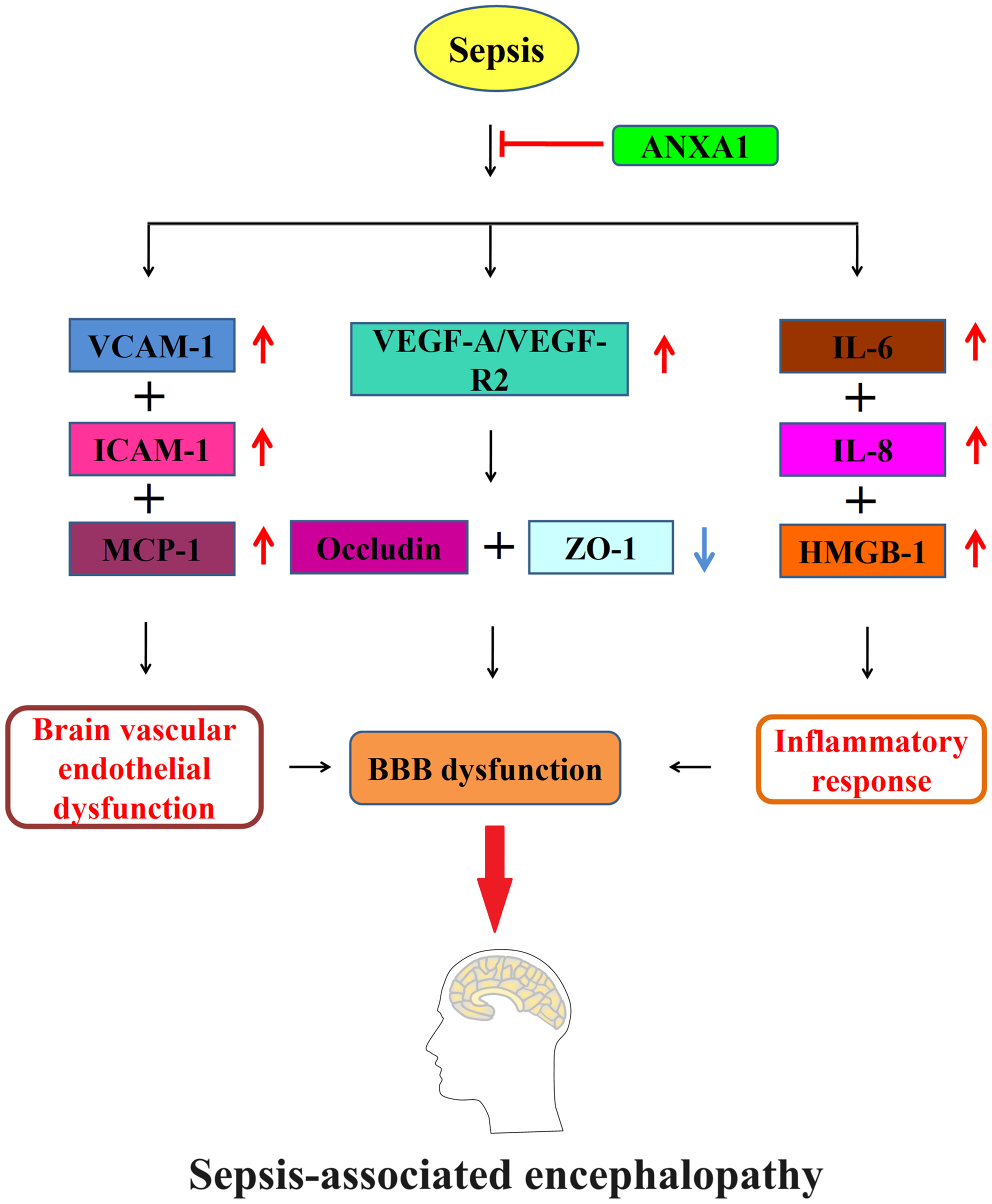
Reduced expression of ANXA1 was observed in the brain cortex of septic mice. ANXA1 deficiency led to a decreased 7-day survival rate and exacerbated neurobehavioral changes induced by CLP. Furthermore, ANXA1 deficiency worsened BBB dysfunction in septic mice, with this effect being mediated through occludin and ZO-1. The protective effects of ANXA1 are mediated by the VEGF-A/VEGF-R2 signaling pathway.
Clinical Insights Into Default Mode Network Abnormalities in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: Unraveling Axonal Injury Through Functional, Structural, and Molecular Analyses
- First Published: 26 December 2024

This study explores the relationship between mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) and disruptions in the default mode network (DMN) using a multimodal approach. Through functional connectivity analysis, diffusion tensor imaging, and gene expression profiling, the research highlights the role of diffuse axonal injury in DMN abnormalities, particularly in the middle cingulate cortex (MCC). The study suggests potential therapeutic targets for neuromodulation, such as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), to mitigate cognitive and emotional disturbances associated with mTBI.
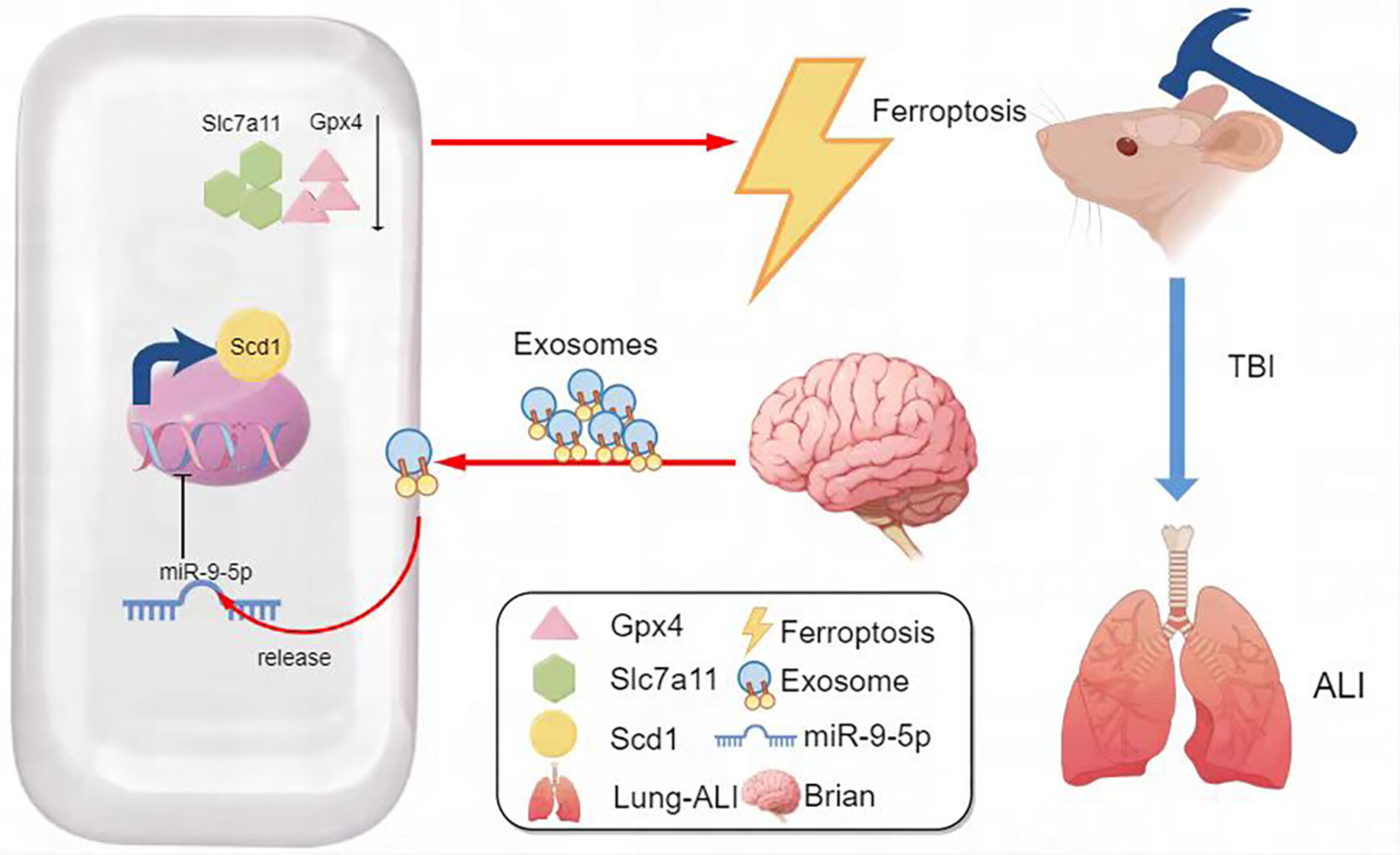
Brain-Derived Exosomal miR-9-5p Induces Ferroptosis in Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Targeting Scd1
- First Published: 26 December 2024
Structural and Functional Projections of the Nucleus Basalis of Meynert and Their Changes After Cognitive Training in Individuals With Mild Cognitive Impairment
- First Published: 26 December 2024
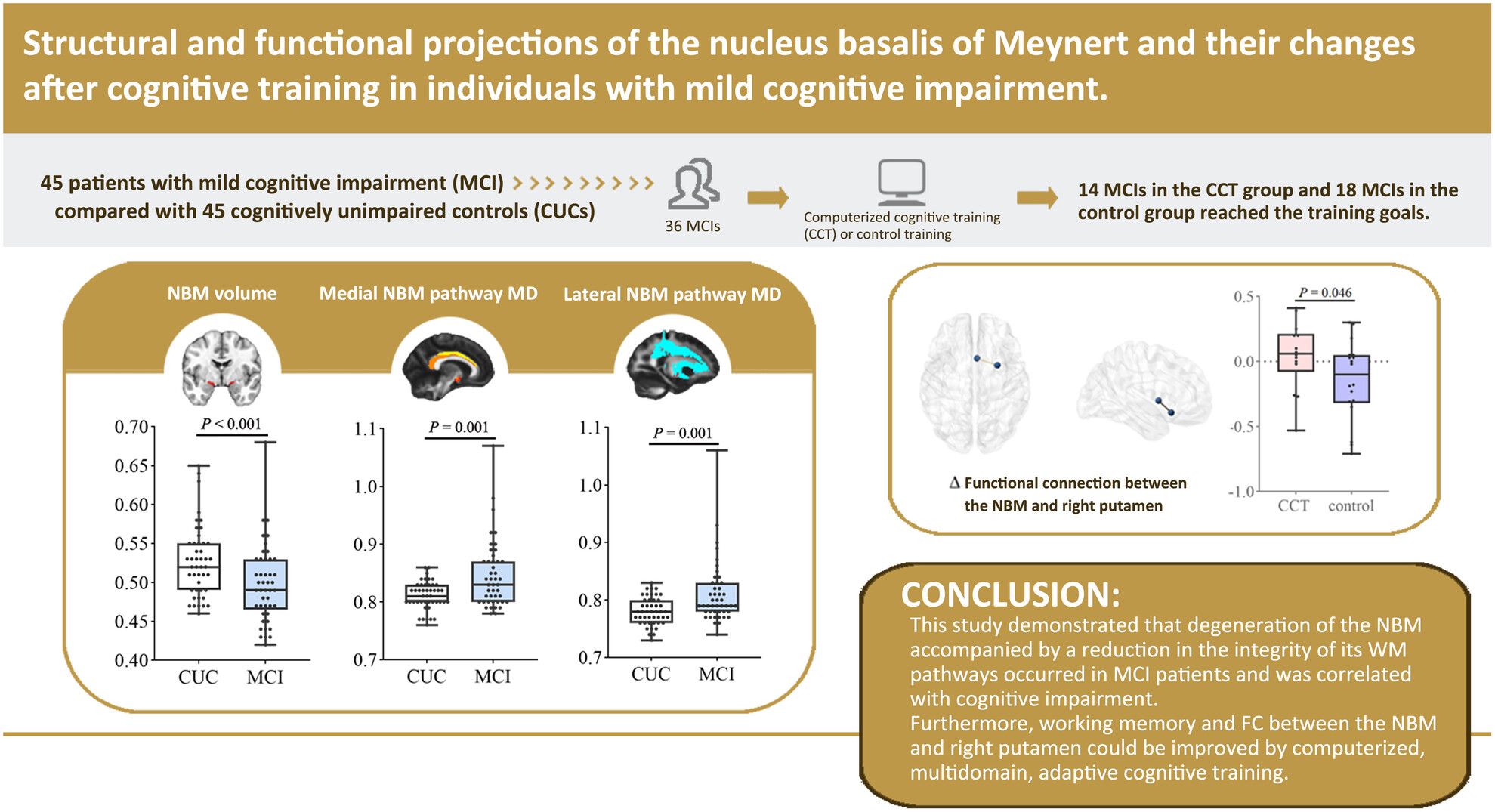
This study demonstrated that degeneration of the NBM accompanied by a reduction in the integrity of its WM pathways occurred in MCI patients and was correlated with cognitive impairment. Furthermore, working memory and FC between the NBM and right putamen could be improved by computerized, multidomain, and adaptive cognitive training.
Elevated Activity in Left Homologous Music Circuits Is Inhibitory for Music Perception but Mediated by Structure–Function Coupling
- First Published: 26 December 2024
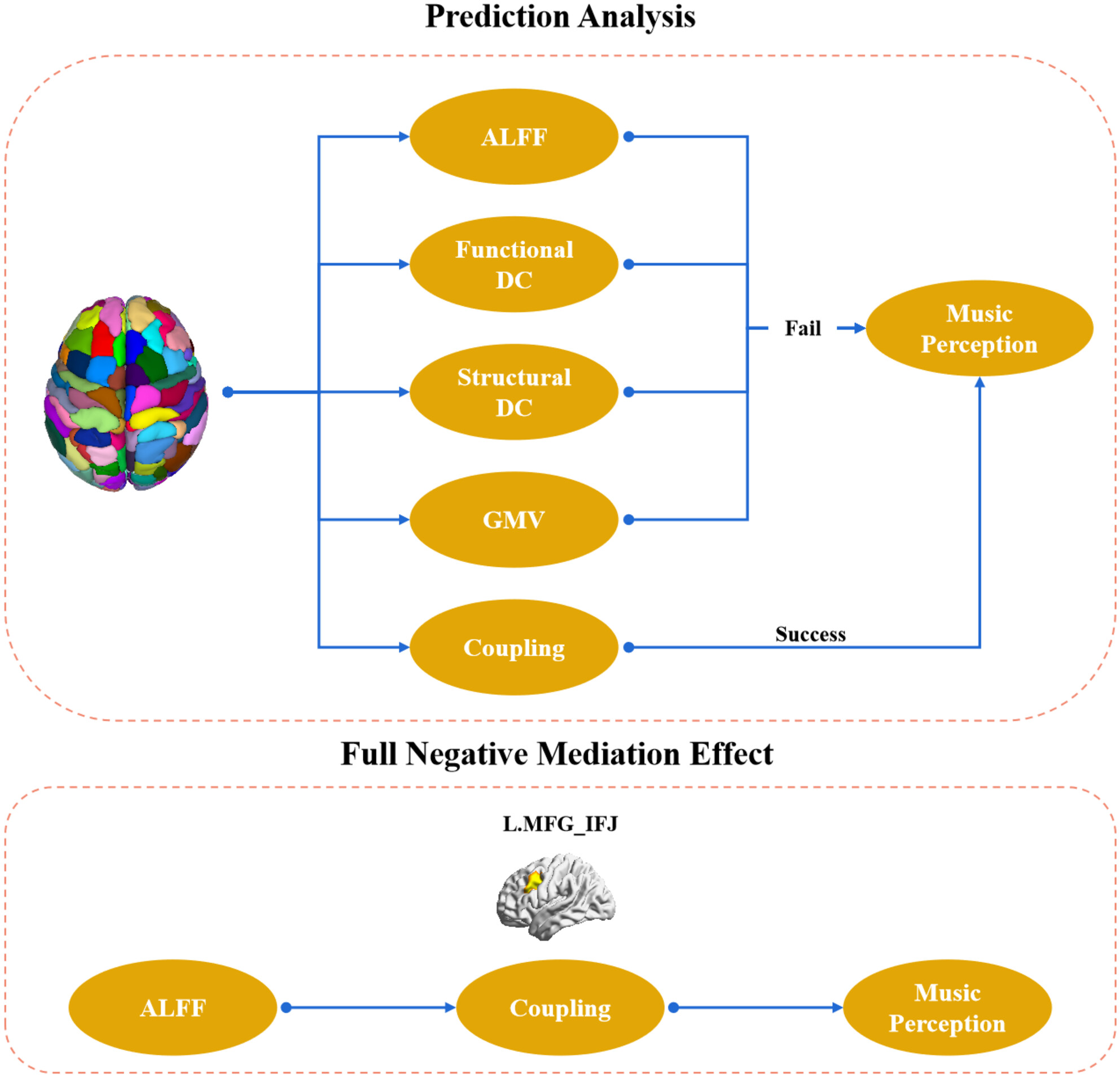
We found structure–function coupling, rather than gray matter volume, spontaneous regional neural activity (ALFF) or uni-modal regional connectivity profile (degree centrality) could predict music perception. Further, structure–function coupling of left middle frontal gyrus (L.MFG), a region that is homologous to typical music circuits, fully mediated the negative link between ALFF of L.MFG and MBEA score.
REVIEW
Targeting Remyelination in Spinal Cord Injury: Insights and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
- Pages: 1-15
- First Published: 26 December 2024
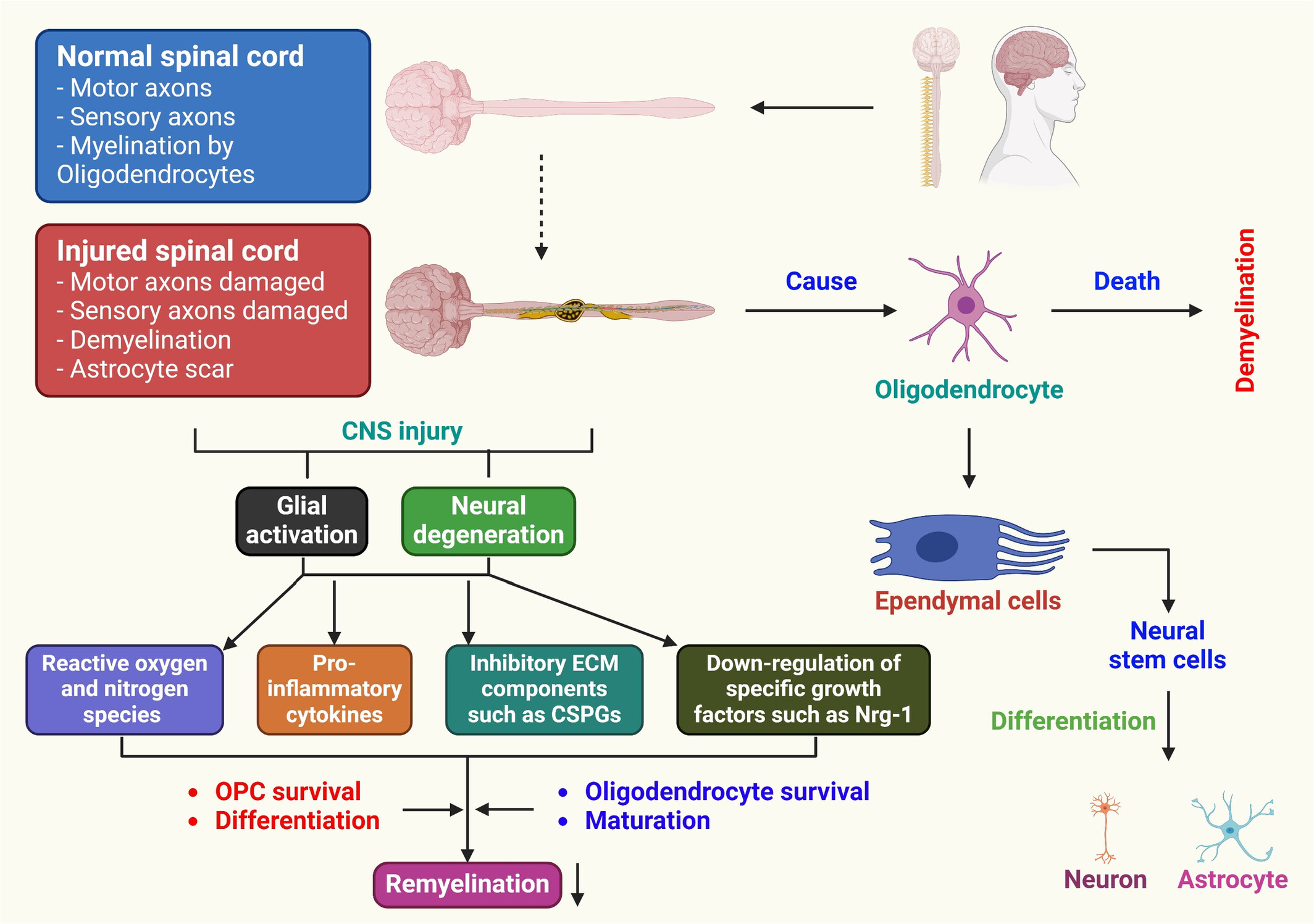
Exploring the potential targeted therapy of remyelination after spinal cord injury: The review demonstrates the possibility of stimulating oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation, differentiation, and myelin sheath formation in both in vitro and in vivo SCI models through molecular pathway modulation and pharmacological agents. Targeted therapies have shown promising results in improving remyelination, providing hope for functional recovery in SCI patients.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
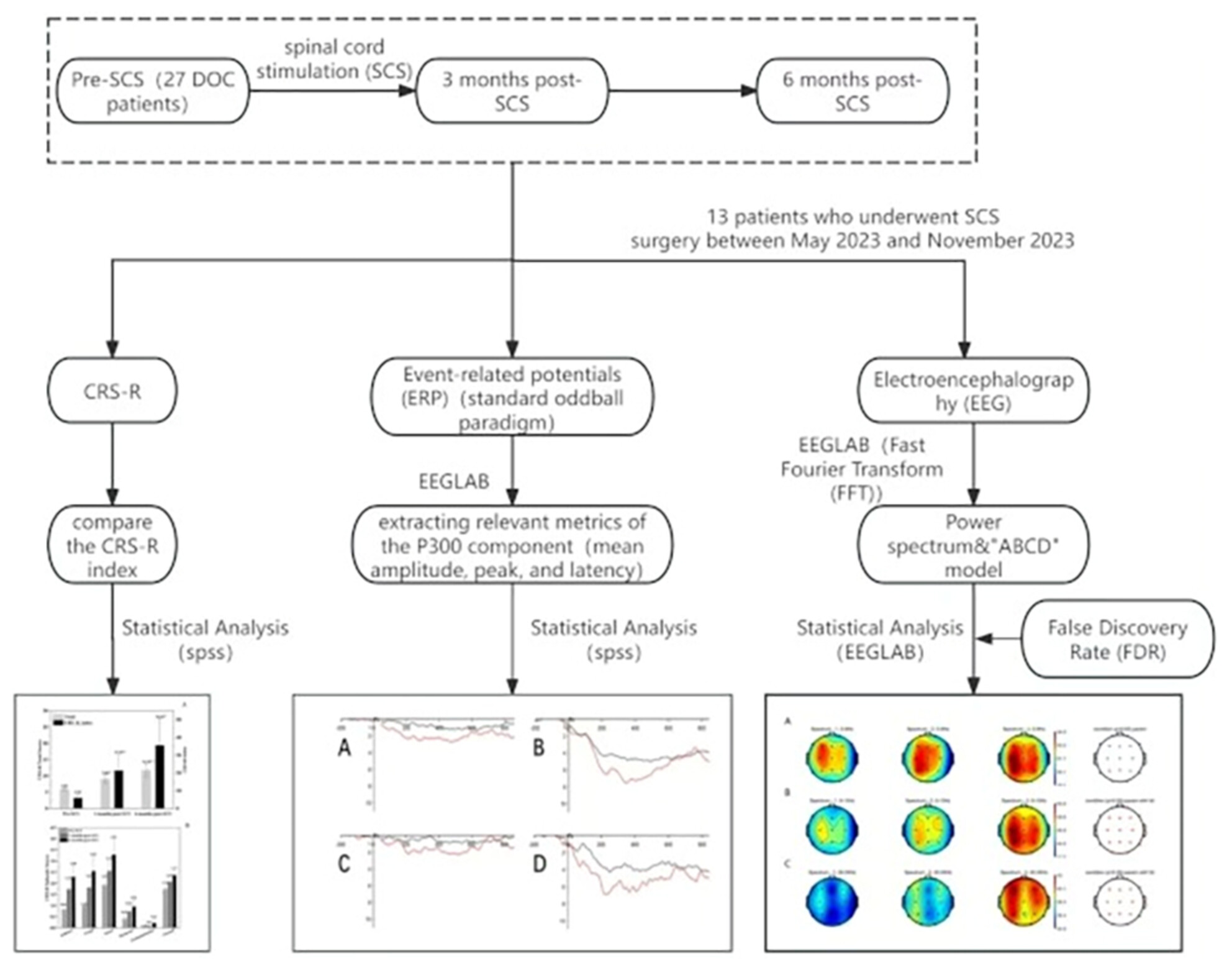
Spinal Cord Stimulation for Prolonged Disorders of Consciousness: A Study on Scalp Electroencephalography
- First Published: 30 December 2024