Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
The ADA 2020 virtual poster hall
2020年ADA虚拟海报厅
- Pages: 778-780
- First Published: 04 August 2020
REVIEW ARTICLE
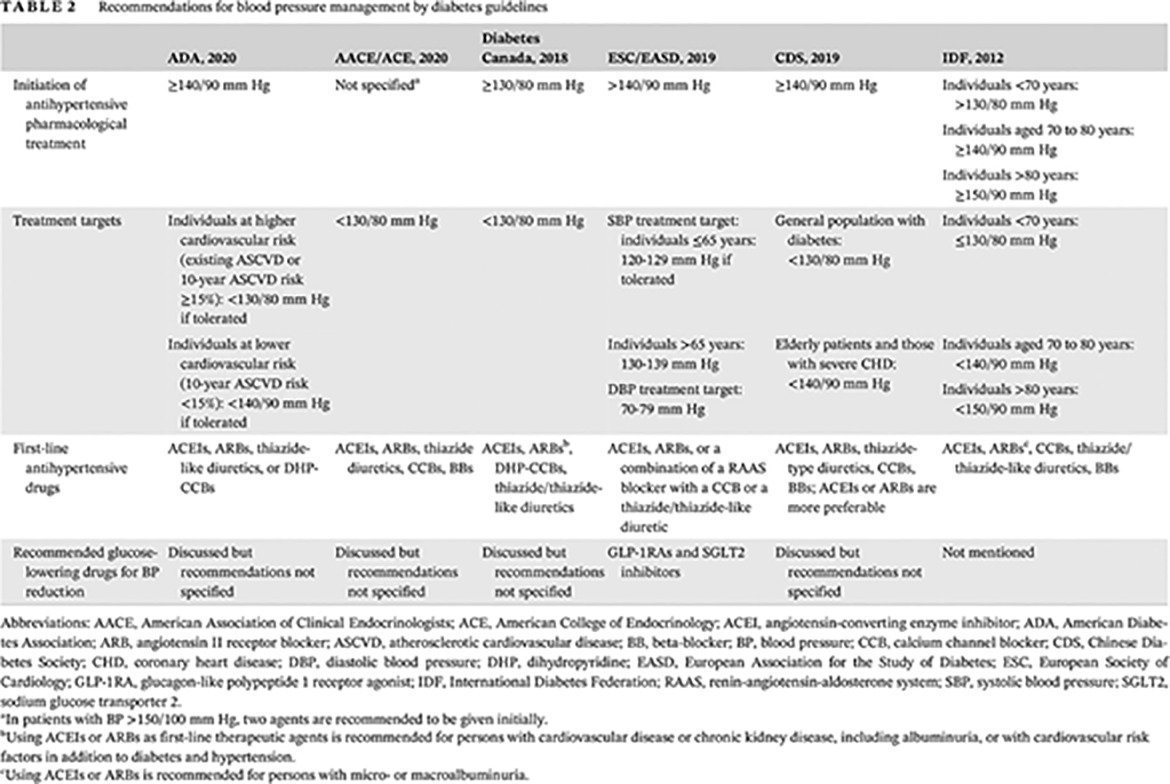
A comparative analysis of current blood pressure management guidelines in people with and without diabetes
糖尿病与非糖尿病人群各血压管理指南比较分析
- Pages: 781-790
- First Published: 29 May 2020
Highlights
- Recommendations from current guidelines of blood pressure (BP) management differ a great deal, especially BP thresholds for initiation of antihypertensive drug therapy and BP treatment targets in people with and without diabetes.
- High-level evidence from high-quality clinical studies is urgently needed to settle uncertainties on BP management recommendations.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
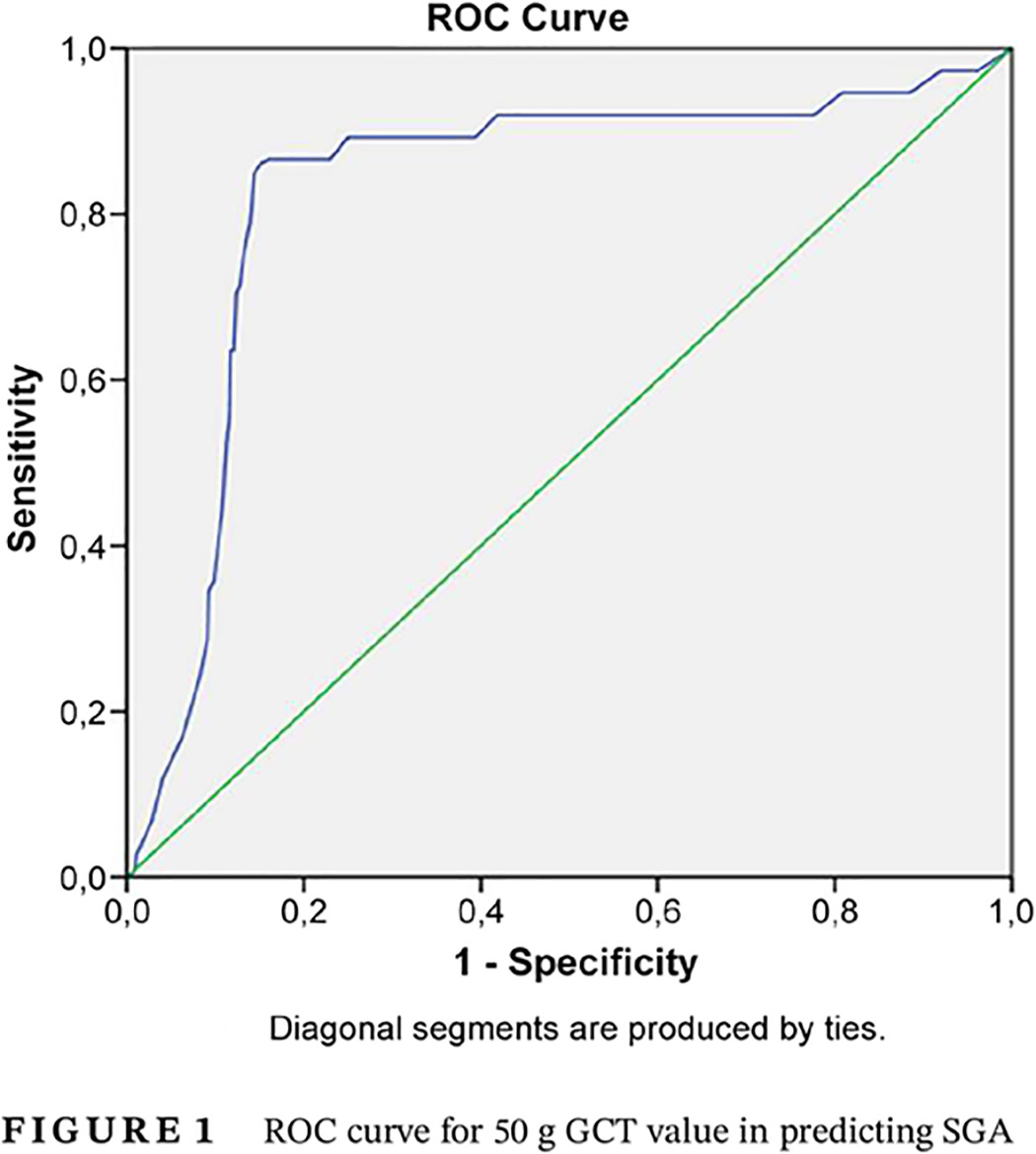
Use of the 50-g glucose challenge test to predict small-for-gestational-age neonates
50 g葡萄糖负荷试验在预测小于胎龄儿中的应用
- Pages: 791-797
- First Published: 29 May 2020
“High prepregnancy HbA1c is challenging to improve and affects insulin requirements, gestational length, and birthweight”
孕前高糖化血红蛋白在改善和影响胰岛素需求、孕周和出生体重方面具有挑战性
- Pages: 798-806
- First Published: 28 May 2020
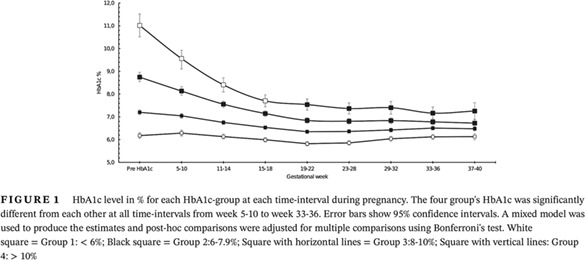
Highlights
- In this very large cohort of 530 pregnancies in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus, we found that high prepregnancy glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is a predictor for suboptimal glycemic control during pregnancy and that HbA1c only decreases until midpregnancy and then plateaus.
- In addition, a very high prepregnancy HbA1c is associated with shorter gestational length and lower birthweight z score, which is contrary to the common assumption of poor glycemic control leading to higher birthweight.
Global burden of noncommunicable diseases attributable to high fasting plasma glucose
高空腹血糖导致的全球非传染性疾病负担研究
- Pages: 807-818
- First Published: 29 May 2020
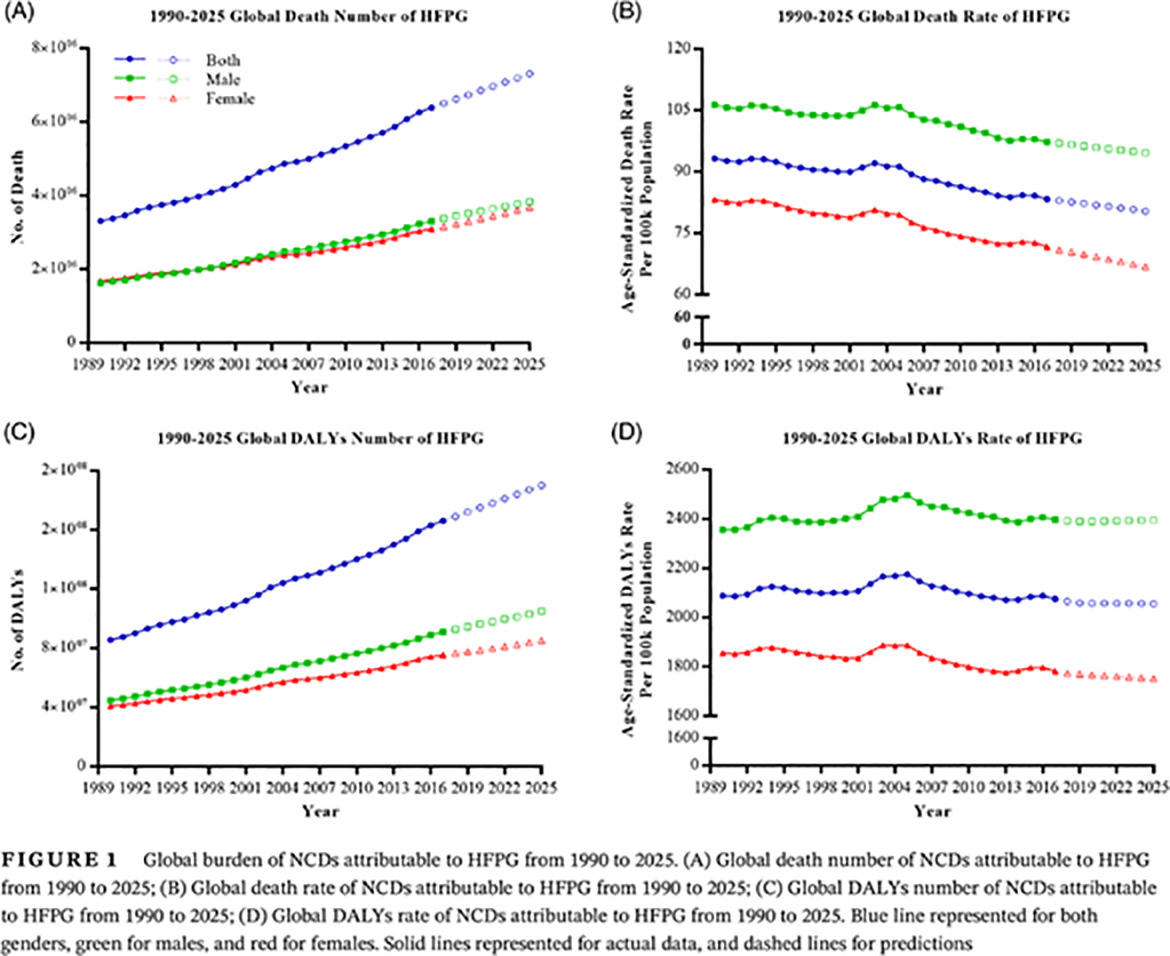
Highlights
- The burden of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) attributable to high fasting plasma glucose (HFPG) has increased significantly since 1990.
- Men and the elderly have a heavier burden of NCDs caused by HFPG.
- A higher burden of HFPG was found to be associated with a lower sociodemographic index.
Elevated circulating luteinizing hormone levels are associated with diabetic macroalbuminuria in Chinese men and postmenopausal women: A cross-sectional study
2型糖尿病男性和绝经后女性患者黄体生成素水平与晚期糖尿病肾病的关系:一项横断面研究
- Pages: 819-833
- First Published: 31 May 2020
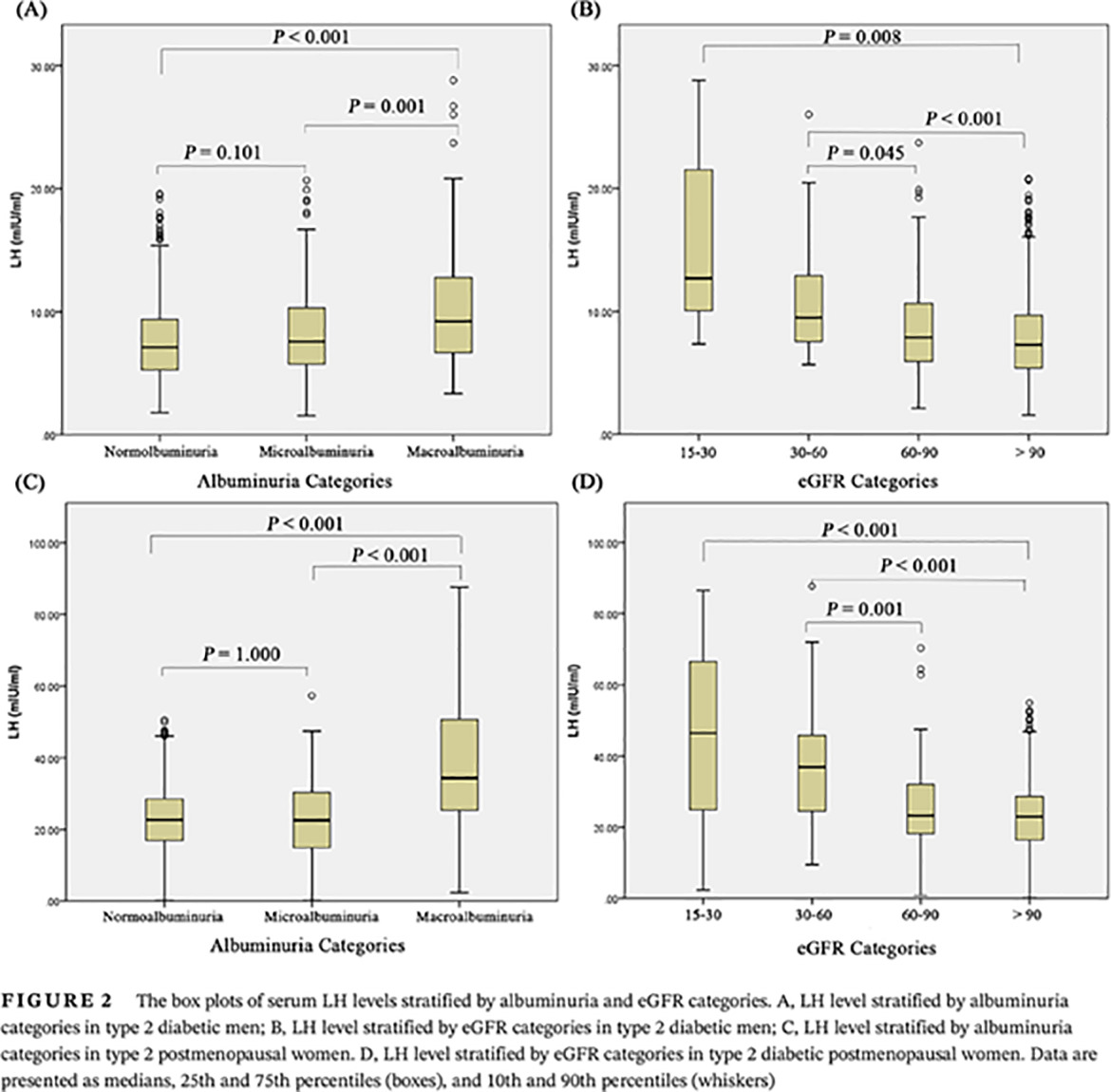
Highlights
- High luteinizing hormone (LH) levels are positively associated with established type 2 diabetic kidney disease (DKD) among Chinese men and postmenopausal women.
- The positive associations between LH and macroalbuminuria risk were independent of age, diabetes duration, or other metabolic factors.
- The increase of circulating LH may be a promising clinical factor for identifying established DKD.
Does undiagnosed diabetes mitigate the association between diabetes and cognitive impairment? Findings from the ELSI-Brazil study
未诊断的糖尿病是否减轻了糖尿病和认知损害之间的关联?巴西ELSI研究的结果
- Pages: 834-843
- First Published: 01 June 2020
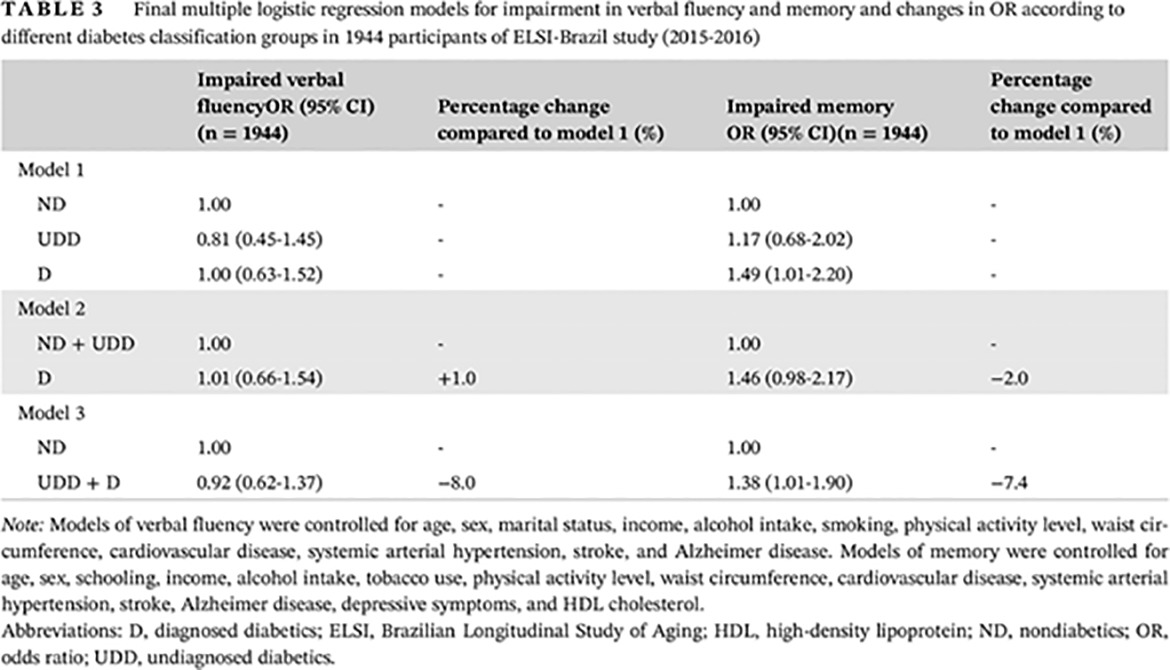
Highlights
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with impaired memory but not with verbal fluency.
- The association between diabetes and impaired memory becomes not significant by combining undiagnosed and nondiabetics in the same category.
- Including undiagnosed diabetics and diabetics in the same category attenuates the association between diabetes and impaired memory.
COMMENTARIES
New insights into the older hypoglycemic agents in type 2 diabetes therapy
对2型糖尿病治疗中使用的老降糖药的新见解
- Pages: 844-847
- First Published: 07 August 2020
Is it time to ban sulfonylureas?
现在是时候不用磺脲类药物了吗?
- Pages: 848-850
- First Published: 07 August 2020
RESEARCH LETTERS
Diabetes mellitus association with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis
糖尿病与冠状病毒病2019(COVID-19)的严重程度和死亡率的关联:汇总分析
- Pages: 851-855
- First Published: 16 July 2020
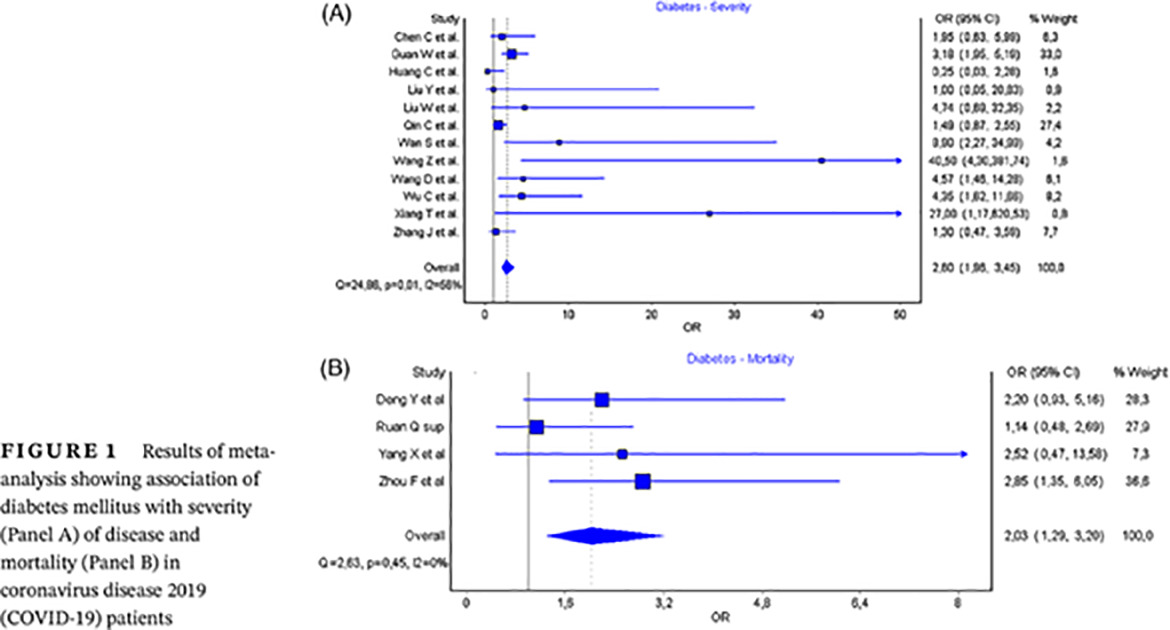
Highlights
- There are ~ 2-fold increased odds of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and a ~ 2-fold increased risk of odds of mortality in patients with history of diabetes mellitus compared to those without diabetes mellitus.
- Patients with a history of diabetes mellitus should be closely monitored if they get infected with COVID-19.
Results of meta-analysis showing association of diabetes mellitus with severity (Panel A) of disease and mortality (Panel B) in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients
Effect of gender on transition of normo- to microalbuminuria under angiotensin receptor blocker therapy in diabetes
血管紧张素受体拮抗剂治疗的糖尿病患者中性别对于正常白蛋白尿向微量白蛋白尿转变的影响
- Pages: 856-859
- First Published: 04 August 2020
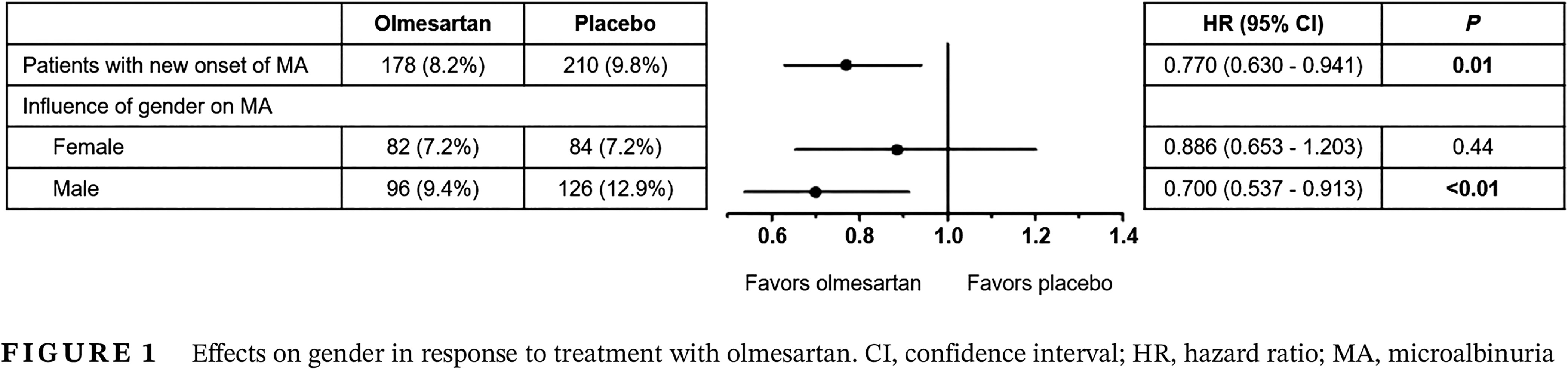
Highlights
- In normoalbuminuric diabetic patients at low cardiovascular risk, the risk of transition from normo- to microalbuminuria is lower in women, despite the nonprotective effects of the angiotensin receptor blocker olmesartan.
- Additional methods of assessment of albuminuria in clinical studies (eg, measurements of albumin and creatinine excretion rate) should be implemented or the actually accepted higher urine albumin creatinine ratio (UACR) cutoff values for microalbuminuria in women reconsidered.