Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editor's Choice
Microscale Adaptation of In Vitro Transcription/Translation for High-Throughput Screening of Natural Product Extract Libraries
- Pages: 1331-1338
- First Published: 04 July 2015
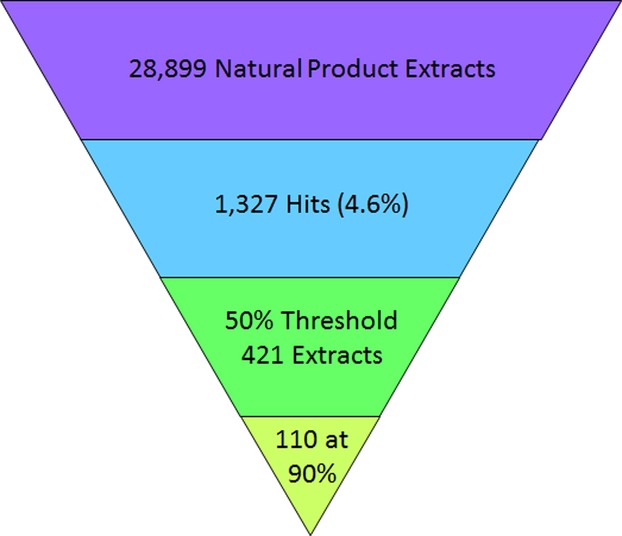
A coupled transcription/translation high-throughput screening assay was miniaturized and shown to be effective at detecting known classes of ribosome-inhibiting antibiotics. This luciferase-based assay was successfully applied to a natural product extract library of 30 000 compounds with a hit-rate of 4.6%, a %CV value of 8.5% and a Z’ value of 0.74. Selected hits were retested in triplicate to confirm authenticity, subjected to a secondary screen to remove luciferase inhibitors, and are moving forward in the discovery process..
Research Articles
Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Activity of (E,Z)-1-(dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-3-phenyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2-propen-1-ones
- Pages: 1339-1350
- First Published: 04 June 2015
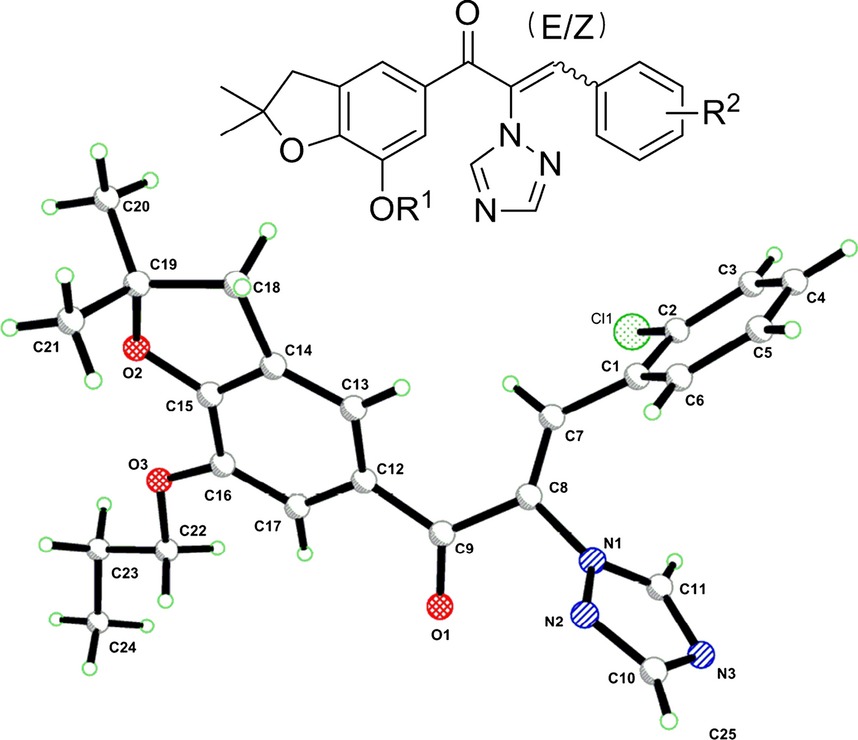
A series of (E,Z)-1-(dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-3-phenyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2-propen-1-ones were designed and synthesized, and their biological activities against tumor cell lines were evaluated in vitro. Compounds (E,Z)-C24 with para-nitro group exhibited the most consistently potent activities against three neoplastic cells, with IC50 ranging from 3.2 to 7.1 μm. Further researches showed that compounds (E,Z)-C24 could induce cell apoptosis and arrest cells cycle at the G2/M and S phases.
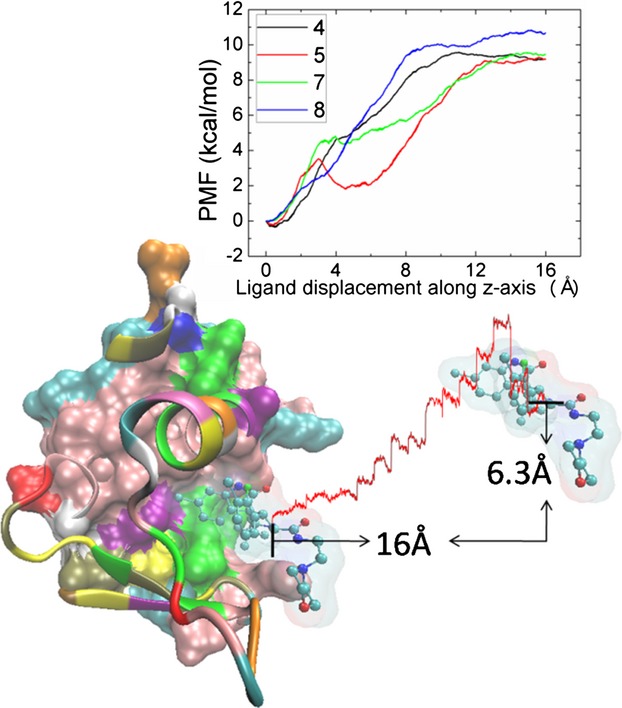
Characterizing the Free-Energy Landscape of MDM2 Protein–Ligand Interactions by Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulations
- Pages: 1351-1359
- First Published: 30 May 2015
Transmembrane Helix Assembly by Max–Min Ant System Algorithm
- Pages: 1360-1372
- First Published: 09 June 2015
A novel efficient algorithm called max–min ant system was designed for solving an assembly of transmembrane proteins. It show noticeably superior convergence performance compared to simulated annealing Monte Carlo and genetic algorithm. The algorithm gives a promising approach for solving structure with low-resolution data.
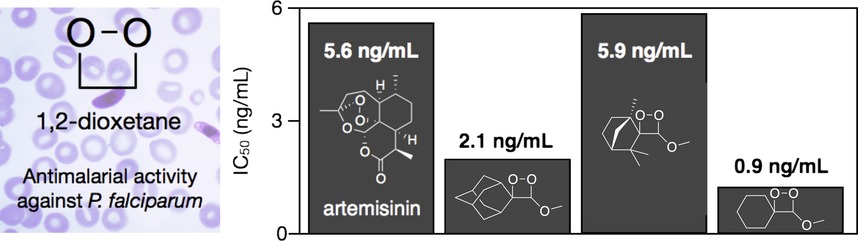
Antimalarial Effect of 3-Methoxy-1,2-Dioxetanes on the Erythrocytic Cycle of Plasmodium falciparum
- Pages: 1373-1377
- First Published: 30 May 2015
Research Letter
Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity of Silybin Conjugates with Salinomycin and Monensin
- Pages: 1378-1386
- First Published: 08 June 2015
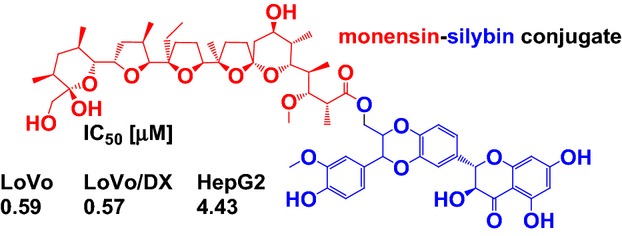
The conjugates of hepatoprotective natural compound silybin (SIL) and two natural polyether ionophores monensin (MON) and salinomycin (SAL) displayed interesting antiproliferative activity in various human cancer cells, including MDR cells at low micromolar concentrations. The anticancer activity is connected with high selectivity indexes (SI) and low toxicity against normal cells.
Research Articles
5-Arylaminouracil Derivatives: New Inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Pages: 1387-1396
- First Published: 09 June 2015
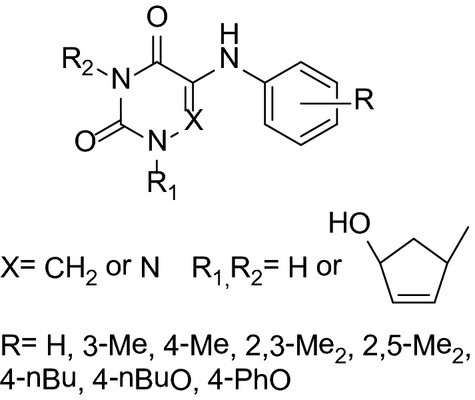
Three series of 5-arylaminouracil derivatives were synthesized and screened for potential antimicrobial activity. Most of compounds had a negative effect on the growth of the M. tuberculosis H37Rv strain, with 100% inhibition observed at concentrations between 5 and 40 μg/mL. Of those, 1-(4′-hydroxy-2′-cyclopenten-1′-yl)-3-(4‴-hydroxy-2‴-cyclopenten-1‴-yl)-5-(4″-butyloxyphenylamino)uracil proved to be the most active among tested compounds against the M. tuberculosis multidrug-resistant strain MS-115 (MIC90 5 μg/mL).
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Ursolic acid Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Prodrugs
- Pages: 1397-1404
- First Published: 16 June 2015
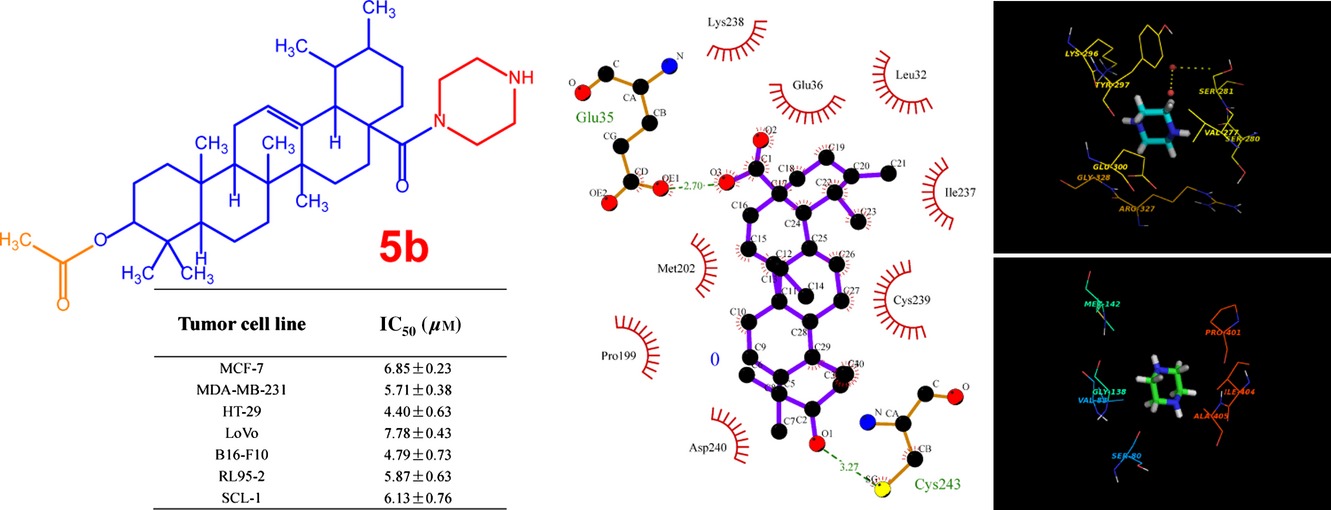
A series of UA piperazine derivatives were designed and synthesized to improve the anticancer activity and to explore the structure-activity relationships. The effects of the most potent compound 5b on cell proliferation, apoptosis induction and cell cycle were evaluated. Furthermore, we also analyzed the protein-ligand interaction with 5b by using molecular modelling studies.
Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Docking of Dihydropyrazole Sulfonamide Containing 2-hydroxyphenyl Moiety: A Series of Novel MMP-2 Inhibitors
- Pages: 1405-1410
- First Published: 09 June 2015
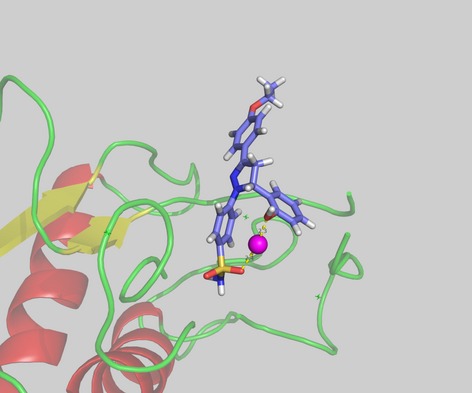
A series of dihydropyrazole sulfonamide derivatives containing 2-hydroxyphenyl moiety were designed and synthesized as antitumor agent to target the matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2). All of the synthesized compounds were examined by bioactivity assays, and structure-activity relationship analysis was also performed to discuss how structural changes could impact the bioactivity.
Comparative Analysis of Pharmacophore Features and Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships for CD38 Covalent and Non-covalent Inhibitors
- Pages: 1411-1424
- First Published: 15 June 2015
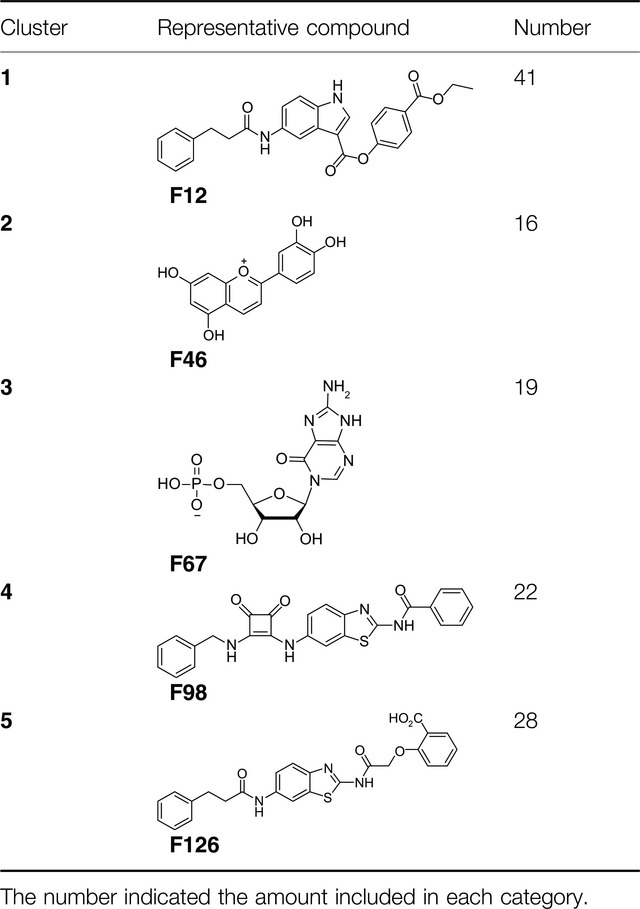
A comparative analysis of pharmacophore features and quantitative structure–activity relationships for CD38 inhibitors with systemic summarizations and analysis given about the binding characteristics and quantitative structure–activity relationships for known CD38 covalent and non-covalent inhibitors, which will be helpful for further CD38 inhibitors design.
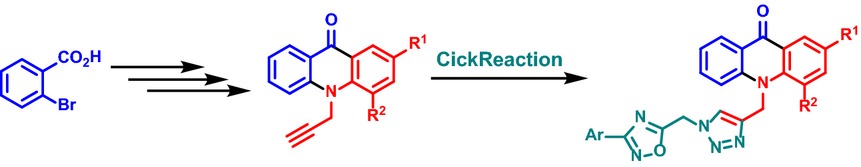
Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Docking Study of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: New Acridone-1,2,4-oxadiazole-1,2,3-triazole Hybrids
- Pages: 1425-1432
- First Published: 16 June 2015
Research Letter
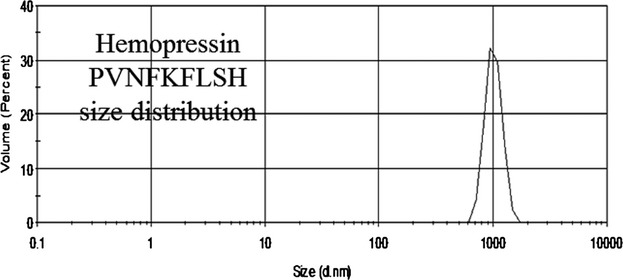
Site-specific Substitutions Eliminate Aggregation Properties of Hemopressin
- Pages: 1433-1437
- First Published: 24 June 2015
Research Articles
Integrating Pharmacophore into Membrane Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Improve Homology Modeling of G Protein-coupled Receptors with Ligand Selectivity: A2A Adenosine Receptor as an Example
- Pages: 1438-1450
- First Published: 15 June 2015
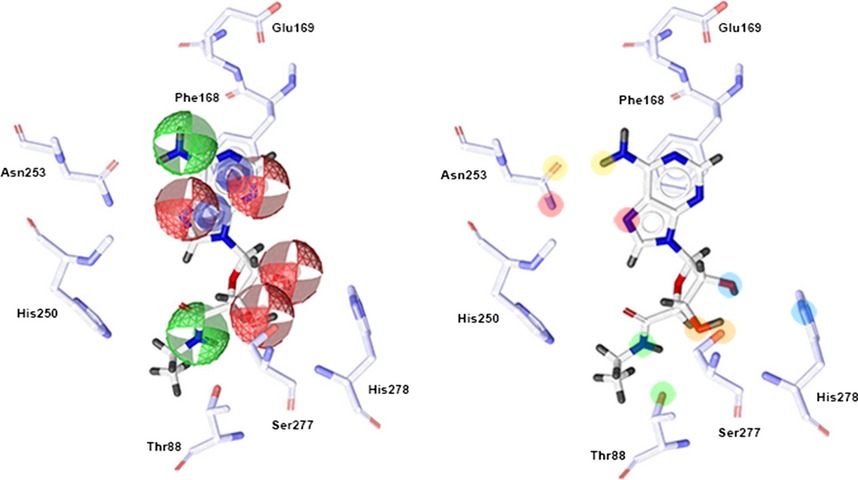
We propose a novel strategy by integrating pharmacophore and membrane MD simulations together to improve homology modeling of GPCRs with ligand selectivity. To validate this integrated strategy, the A2A adenosine receptor (A2AAR), whose structures in both active and inactive state have been established, has been chosen as an example. This integrated strategy can be further investigated in homology modeling and expand its applicability to other GPCR modeling, which should aid in the discovery of more effective and selective GPCR ligands.
Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of Novel Lipophilic Emodin Cationic Derivatives
- Pages: 1451-1457
- First Published: 24 June 2015
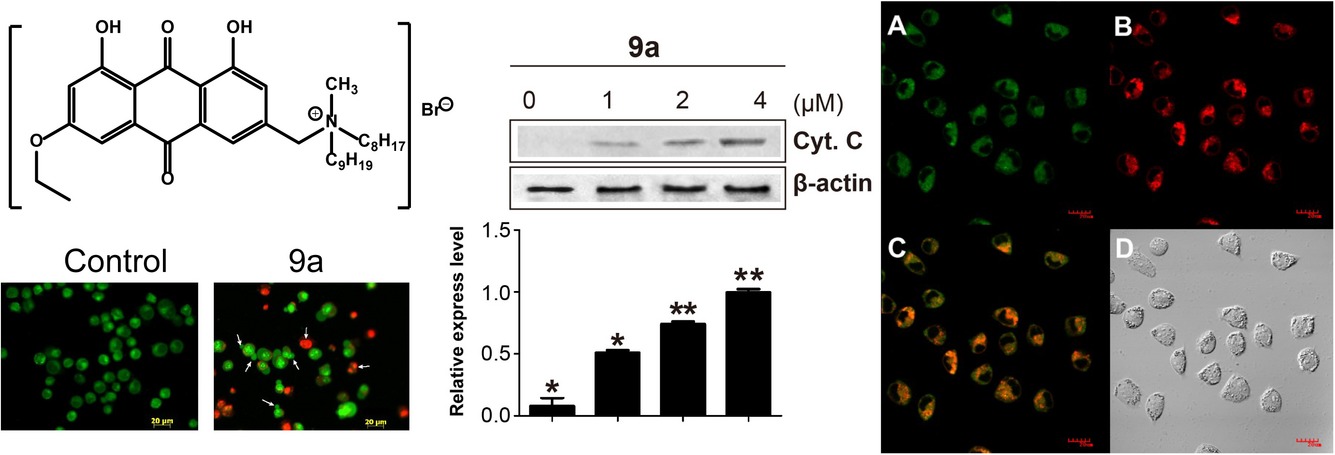
Seventeen novel emodin derivatives were synthesized and the cytotoxic activity were evaluated. Compound 9a with highest potency and low toxicity was selected to further investigate its detailed molecular mechanism. Compound 9a induced a loss of the mitochondrial transmemberane potential, an increase of reactive oxygen species, release of cytochrome c and activation of caspase 3 and 9.
Identification of Interaction Hot Spots in Structures of Drug Targets on the Basis of Three-Dimensional Activity Cliff Information
- Pages: 1458-1465
- First Published: 12 June 2015
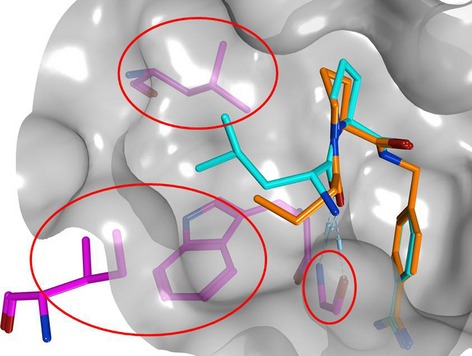
Three-dimensional activity cliffs derived from X-ray structures were systematically searched for recurrent interaction patterns that distinguished between highly and weakly potent compounds. For different drug targets, interaction hot spots were identified on the basis of detected interaction differences.
RNAi Silencing of IL-1β and TNF-α in the Treatment of Post-traumatic Arthritis in Rabbits
- Pages: 1466-1470
- First Published: 24 June 2015
We concluded that lentivirus-mediated RNA interference can knock down the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α in joint fluid and, in a synergistic effect when two siRNAs are co-transfected, ease cartilage degeneration. This may indicate a new direction for the use of gene silencing in the treatment of post-traumatic arthritis.
Synergy Potential of Indole Alkaloids and Its Derivative against Drug-resistant Escherichia coli
- Pages: 1471-1481
- First Published: 01 July 2015
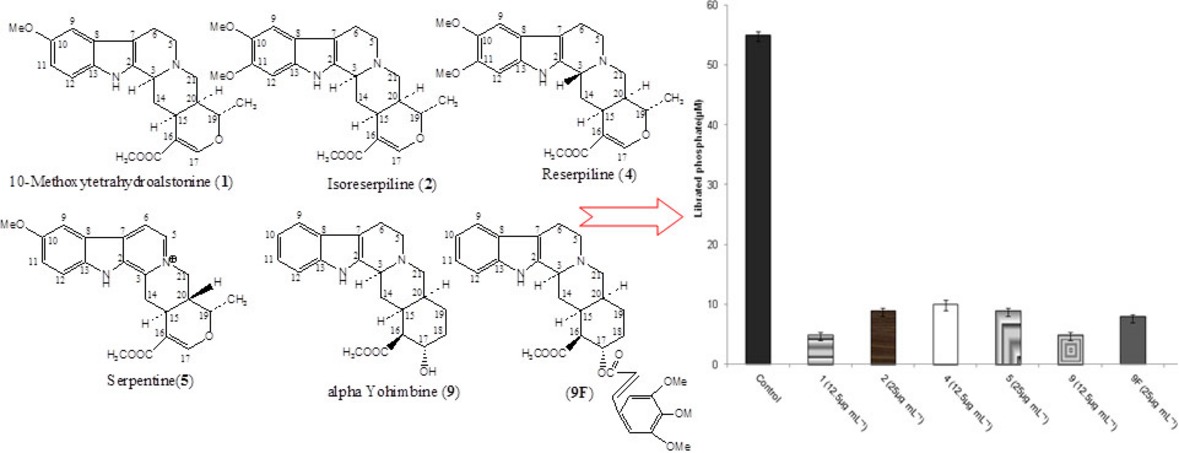
Synergy potential of the indole alkaloids, 1, 2, 4, 5, 9 and a semi-synthetic derivative 9F was deduced by inhibiting efflux pumps and down-regulation of the efflux pump genes. The in silico ADME analysis revealed that some of these alkaloids 1 and 9 are safe, nontoxic and possess good intestinal absorption, which makes them suitable leads for further drug development.
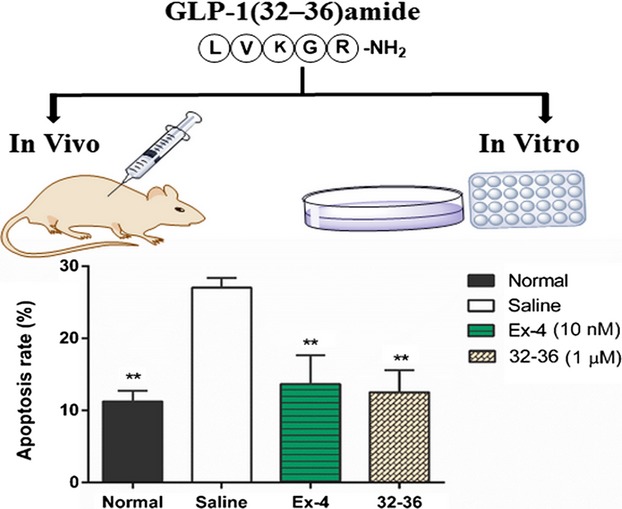
Novel Pentapeptide GLP-1 (32–36) Amide Inhibits β-Cell Apoptosis In Vitro and Improves Glucose Disposal in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice
- Pages: 1482-1490
- First Published: 14 July 2015
Design, Synthesis and Molecular Docking Studies of Novel Indole–Pyrimidine Hybrids as Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors
- Pages: 1491-1500
- First Published: 14 July 2015
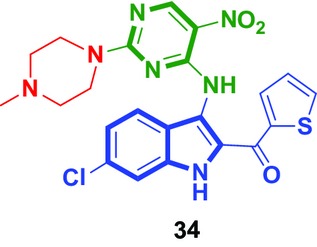
A series of novel indole-pyrimidine hybrids were synthesized. All newly synthesized compounds were evaluated for their antiproliferative and tubulin polymerization inhibitory activities. The most promising compound 34 showed more potent and broad-spectrum cytotoxic activities with the IC50 values ranged from 5.01 to 14.36 μm against four cancer cell lines and also displayed the most potent anti-tubulin activity (IC50 = 11.2 μm).
Ligand Efficiency Outperforms pIC50 on Both 2D MLR and 3D CoMFA Models: A Case Study on AR Antagonists
- Pages: 1501-1517
- First Published: 22 July 2015
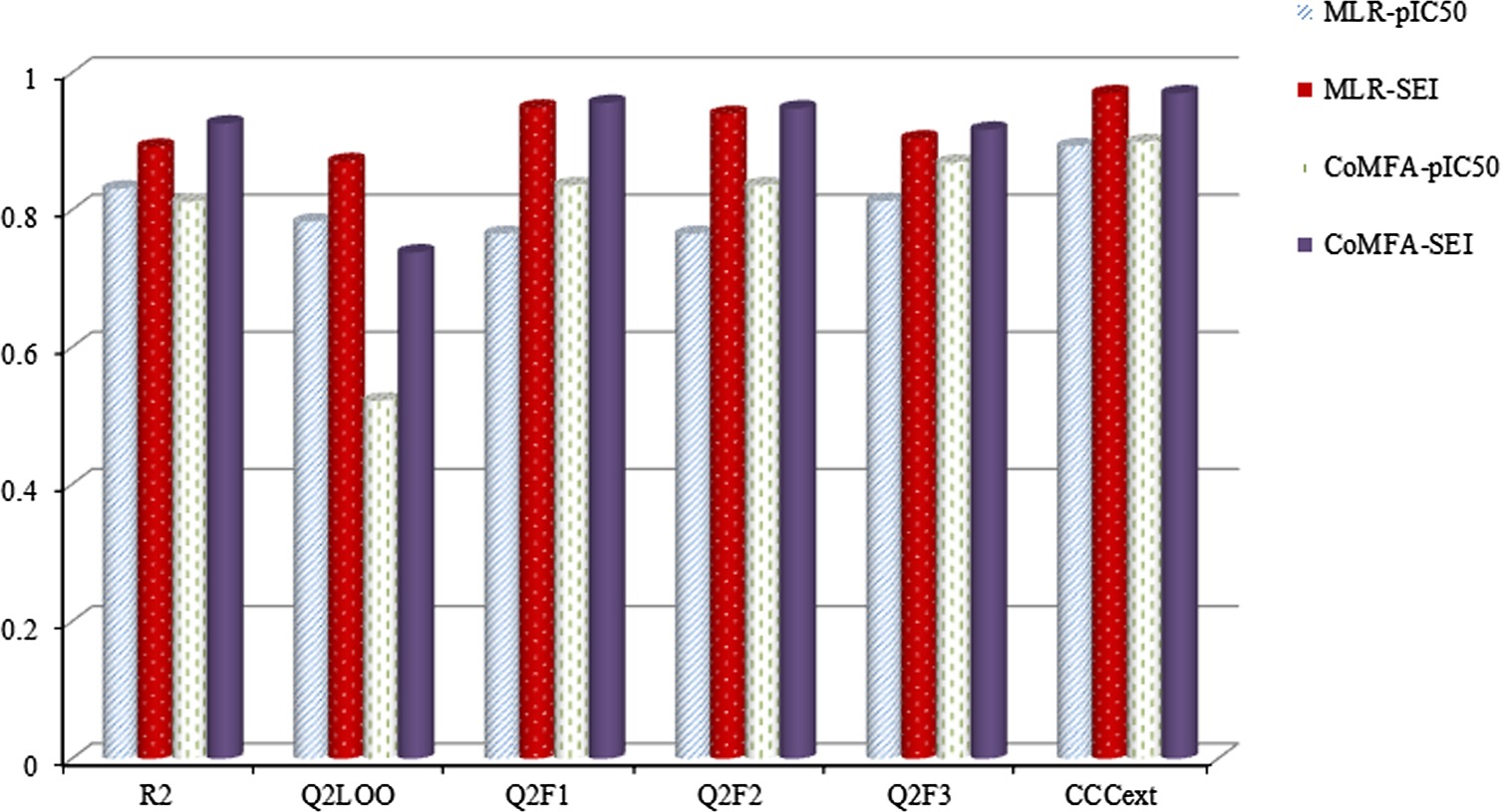
We expanded the application of the ligand efficiency SEI to MLR and CoMFA modeling to investigate the relationships between the hydantoin derivatives and AR antagonist activities. The obtained results indicate that the SEI-based models outperform the pIC50-based models with higher stability, robustness, and predictive abilities. We put forward our opinion that SEI can incarnate the relationships between bioactivities and molecular structures better than pIC50, in nature. SEI could be a more rational parameter to be optimized in the drug discovery.
Discovery of Novel Peptidomimetics as Irreversible CHIKV NsP2 Protease Inhibitors Using Quantum Mechanical-Based Ligand Descriptors
- Pages: 1518-1527
- First Published: 25 July 2015
Characterization of a Pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidine Inhibitor of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 2 and 5 and Aurora A With Pro-Apoptotic and Anti-Angiogenic Activity In Vitro
- Pages: 1528-1540
- First Published: 22 July 2015
![Characterization of a Pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidine Inhibitor of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 2 and 5 and Aurora A With Pro-Apoptotic and Anti-Angiogenic Activity In Vitro](/cms/asset/b196d624-31b1-42cc-b921-296ef80e861f/cbdd12618-toc-0001-m.jpg)
We introduce novel pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidine 2i, which preferentially inhibits CDK2, CDK5 and aurora A. Treatment with 2i causes the downregulation of cyclins A and B and the dephosphorylation of histone H3 at Ser10, induces apoptosis in HCT-116 cancer cells and reduces angiogenesis-like activity in endothelial cells.
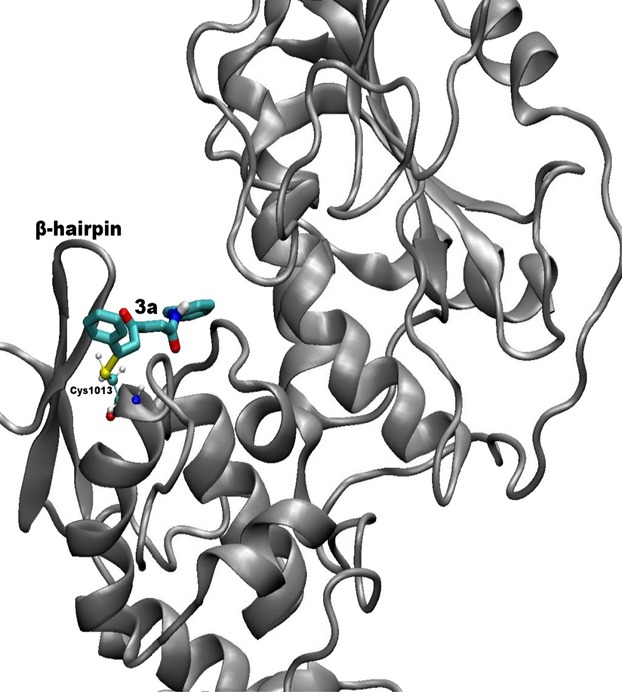
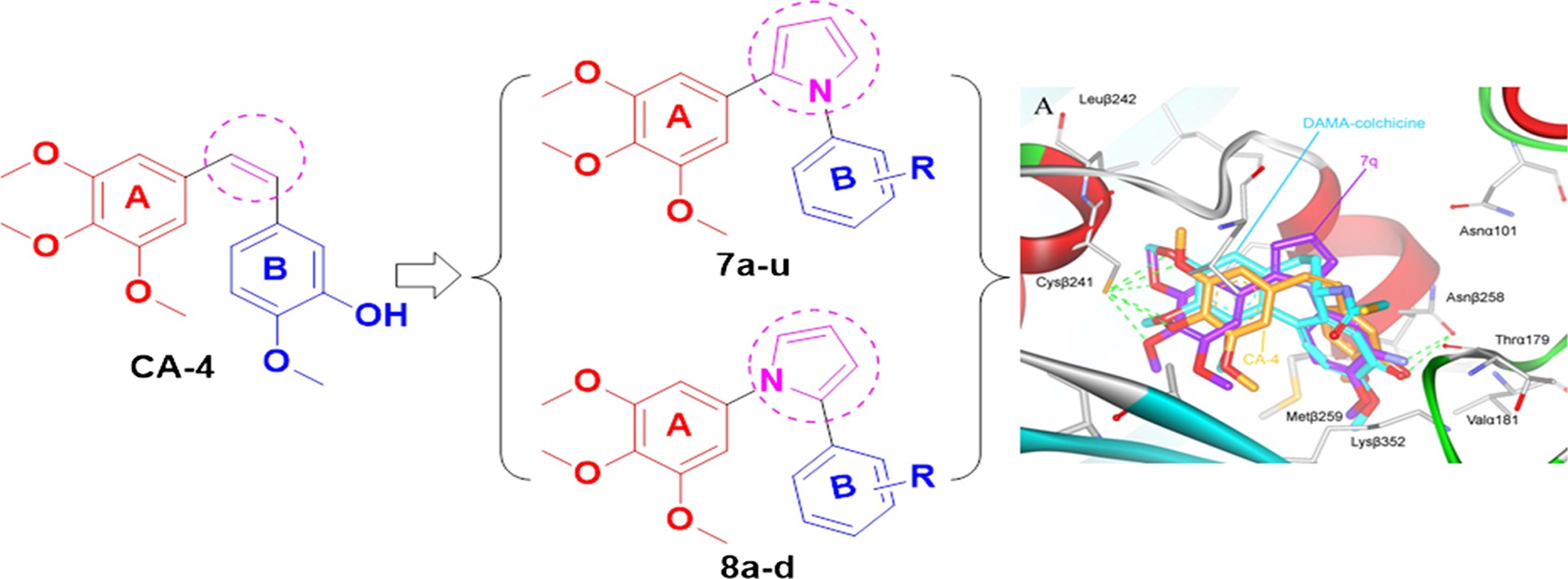
Synthesis and Biological Evaluations of 1,2-Diaryl Pyrroles as Analogues of Combretastatin A-4
- Pages: 1541-1547
- First Published: 22 July 2015
Research Letter
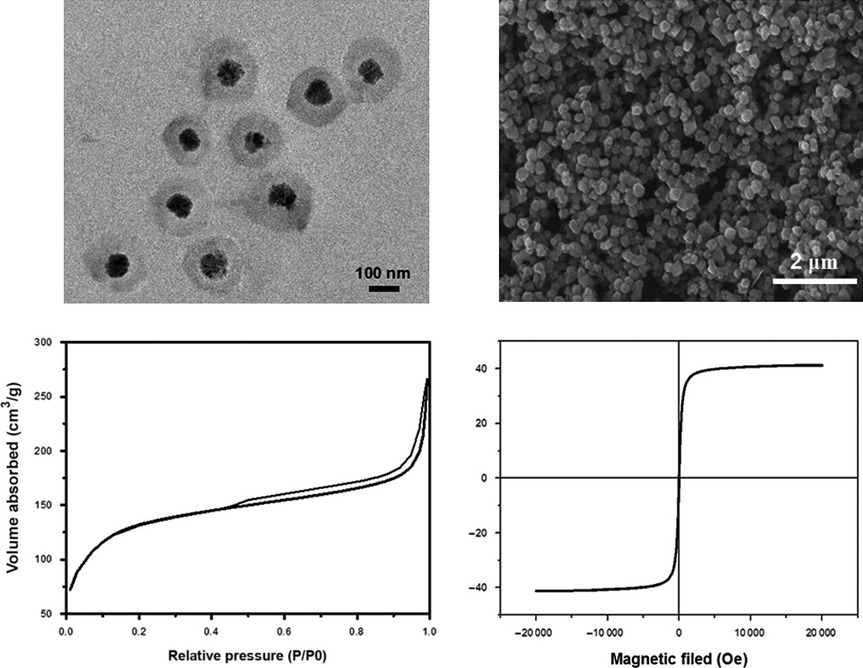
Facile Synthesis of Core–shell Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for pH-sensitive Anticancer Drug Delivery
- Pages: 1548-1553
- First Published: 28 July 2015