Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Synthetic Substrates Specific to Activated Plasmin Can Monitor the Enzymatic Functional Status in Situ in Breast Cancer Cells
- First Published: 01 October 2013
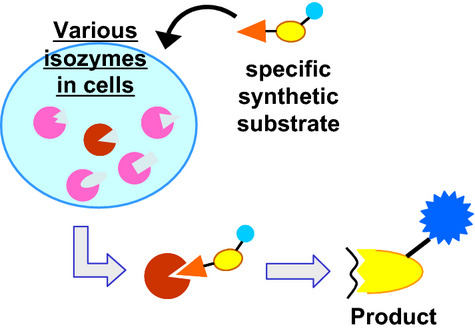
We designed synthetic substrates specific to target molecules to directly estimate enzymatic functionality in situ. It contains a probing unit, an organic fragment specific for enzyme-binding; and a reactive unit, a natural peptide subject to catalysis. In this study, activation of plasminogen to plasmin was examined in MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells, and the localization and function of plasmin were successfully visualized by fluorophore in the substrate. This would be the first time for activated plasmin at work in situ by direct observation.
Novel Fluorescently Labeled Peptide Compounds for Detection of Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein at High Specificity
- First Published: 09 April 2014
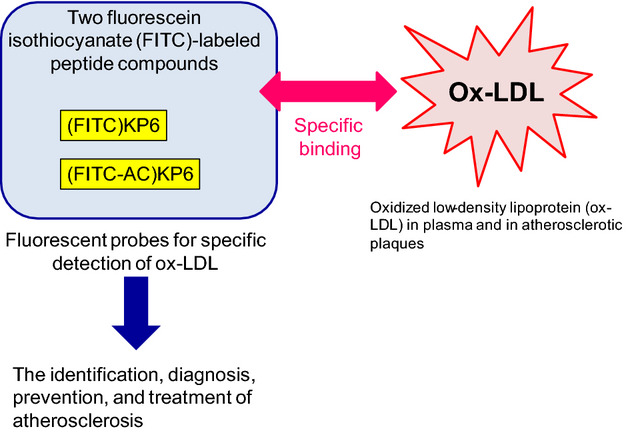
The probes for specific detection of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) in plasma and in atherosclerotic plaques are expected to be useful for the identification, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of atherosclerosis. We developed two fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled peptide compounds— (FITC)KP6 and (FITC-AC)KP6— bound with high specificity to ox-LDL in a dose-dependent manner. These compounds may be effective novel fluorescent probes for specific detection of ox-LDL.
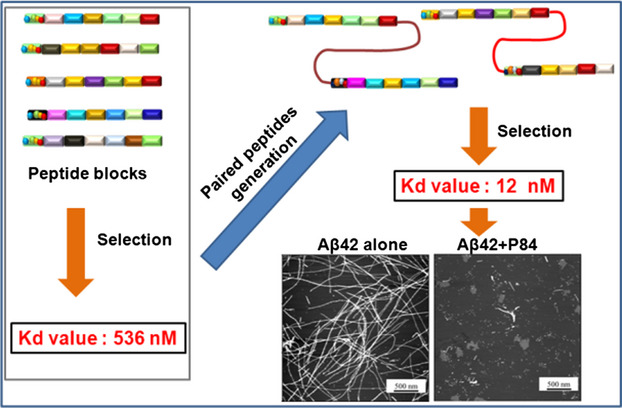
Strong Inhibition of Beta-Amyloid Peptide Aggregation Realized by Two-Steps Evolved Peptides
- First Published: 01 August 2014
Highly Stable, Fluorescence-Labeled Heptapeptides Substituted with a D-Amino Acid for the Specific Detection of Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Plasma
- First Published: 26 July 2014
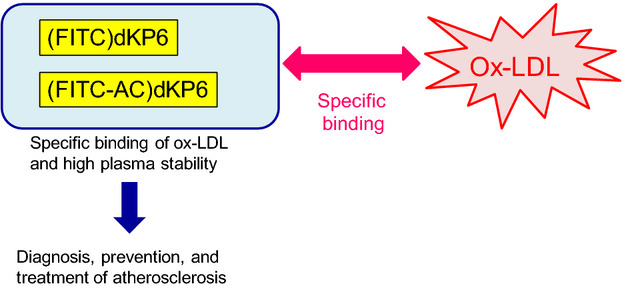
Probes that can detection oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) in plasma and in atherosclerotic plaques can be useful for to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of atherosclerosis. We developed two fluorescence-labeled heptapeptides substituted with a D-amino acid— (FITC)dKP6 and (FITC-AC)dKP6— with high plasma stability for specific detection of ox-LDL. These compounds may be useful as fluorescent probes for specific detection of ox-LDL.
Roles of Basic Amino Acid Residues in the Activity of μ-Conotoxin GIIIA and GIIIB, Peptide Blockers of Muscle Sodium Channels
- First Published: 16 September 2014
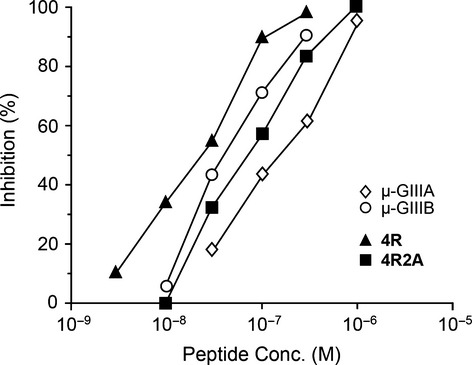
Seven analogs of μ-conotoxin GIIIA and two analogs of μ-conotoxin GIIIB were synthesized. The inhibitory effects on the twitch contractions of the rat diaphragm showed that the side chain guanidino group of Arg13 of μ-conotoxin GIIIA was important for the activity, whereas that of Arg19 has little role in the biological activity. The results on the analogs of μ-conotoxin GIIIB suggested that there was an appropriate molecular basicity for the maximum activity.
Changing Blue Fluorescent Protein to Green Fluorescent Protein Using Chemical RNA Editing as a Novel Strategy in Genetic Restoration
- First Published: 29 May 2015
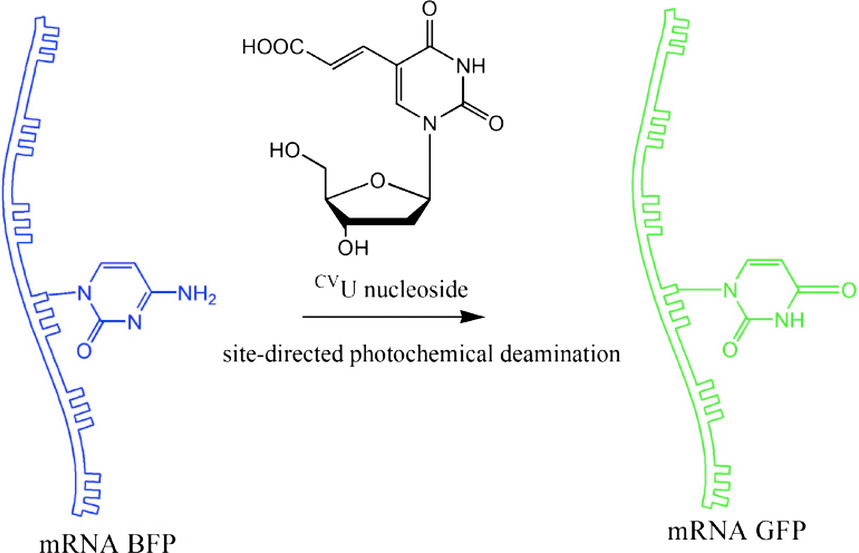
By using the transition from cytosine of BFP gene to uridine of GFP gene at position 199 as a model, we successfully controlled photochemical RNA editing to effect site-directed deamination of cytidine to uridine. Western-blotting and fluorescence-analysis results revealed that the transition-GFP protein was synthesized from mRNAs after site-directed RNA editing.
Bongkrekic Acid Analogue, Lacking One of the Carboxylic Groups of its Parent Compound, Shows Moderate but pH-insensitive Inhibitory Effects on the Mitochondrial ADP/ATP Carrier
- First Published: 29 May 2015
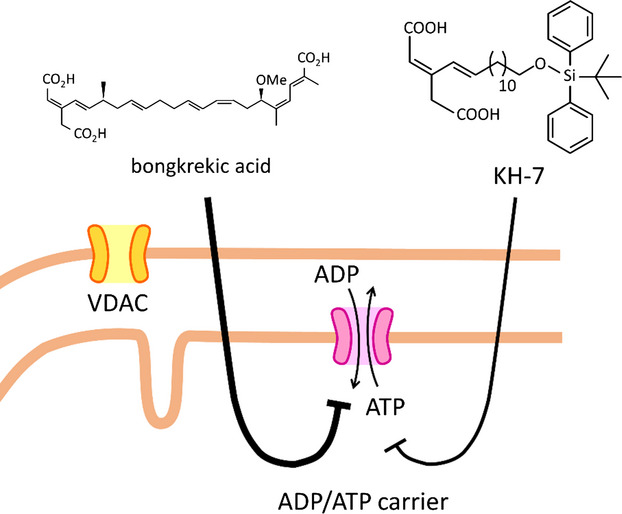
Inhibitory effects of 17 bongkrekic acid analogues derived from the intermediates obtained during its total synthesis, on the mitochondrial ATP/ATP carrier were examined. One compound, KH-7, lacking one of the carboxylic groups of its parent compound, showed moderate but pH-intensive inhibitory effects on the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier.
A Splicing Reporter Tuned to Non-AG Acceptor Sites Reveals that Luteolin Enhances the Recognition of Non-canonical Acceptor Sites
- First Published: 08 September 2015
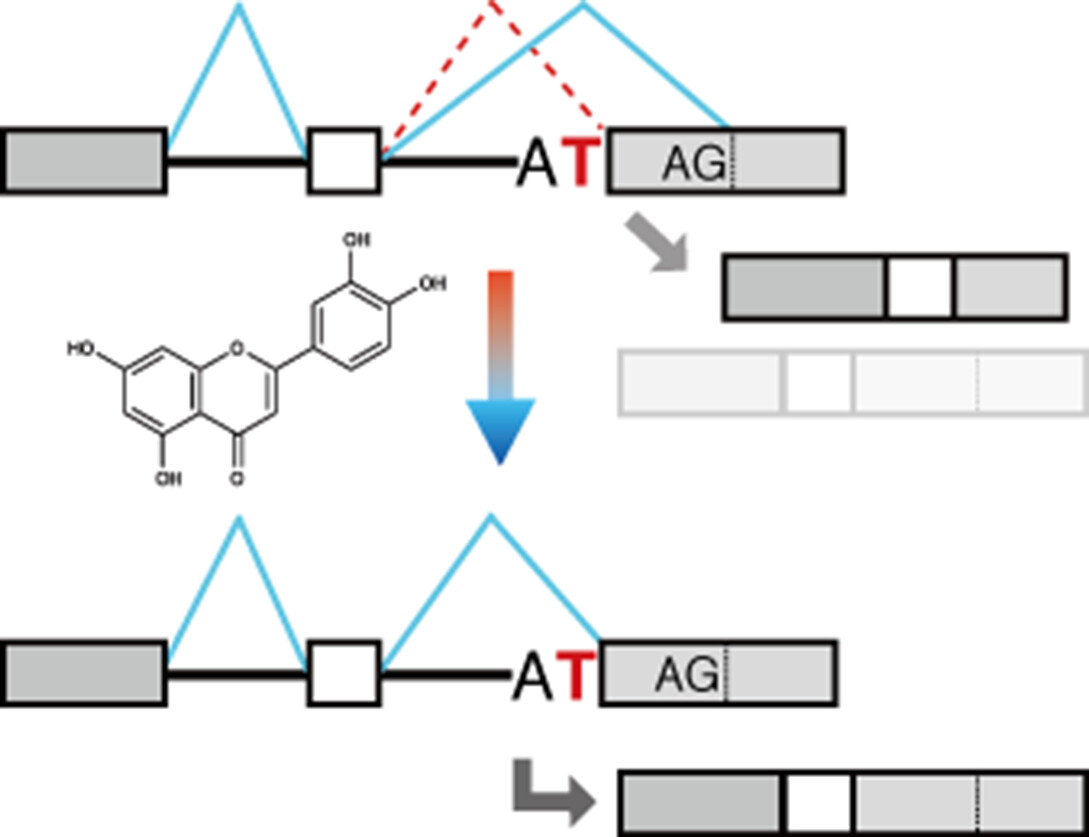
To find compounds that restore splicing at the mutated acceptor site, we constructed a splicing reporter gene. Addition of a modified polypyrimidine tract to the reporter gene mediated splicing at adjacent non-canonical acceptor sites, including the original mutated site. Certain flavons such as luteolin and apigenin enhanced aberrant splicing at the original non-canonical acceptor site of the reporter gene.
In Vivo RNAi Efficacy of Palmitic Acid-Conjugated Dicer-Substrate siRNA in a Subcutaneous Tumor Mouse Model
- First Published: 22 January 2016
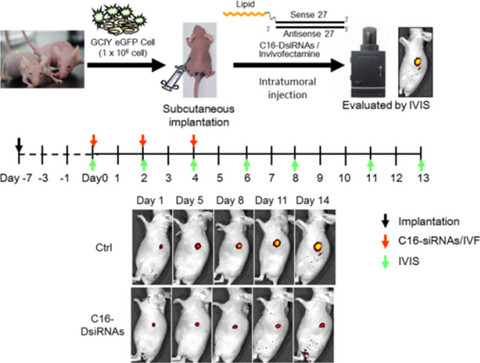
We designed palmitic acid-conjugated Dicer-substrate 27-nt short interfering RNAs (C16-Dsi27RNAs) and investigated theirin vivo RNA interference effects in a subcutaneous tumor mouse model. C16-Dsi27RNAs had potent gene silencing activity against both enhanced green fluorescent protein and vascular endothelial growth factor as target genes in a subcutaneous tumor mouse model generated from GCIY-eGFP cells administered by intratumoral injection.
Chemical RNA Editing for Genetic Restoration: The Relationship between the Structure and Deamination Efficiency of Carboxyvinyldeoxyuridine Oligodeoxynucleotides
- First Published: 27 November 2015
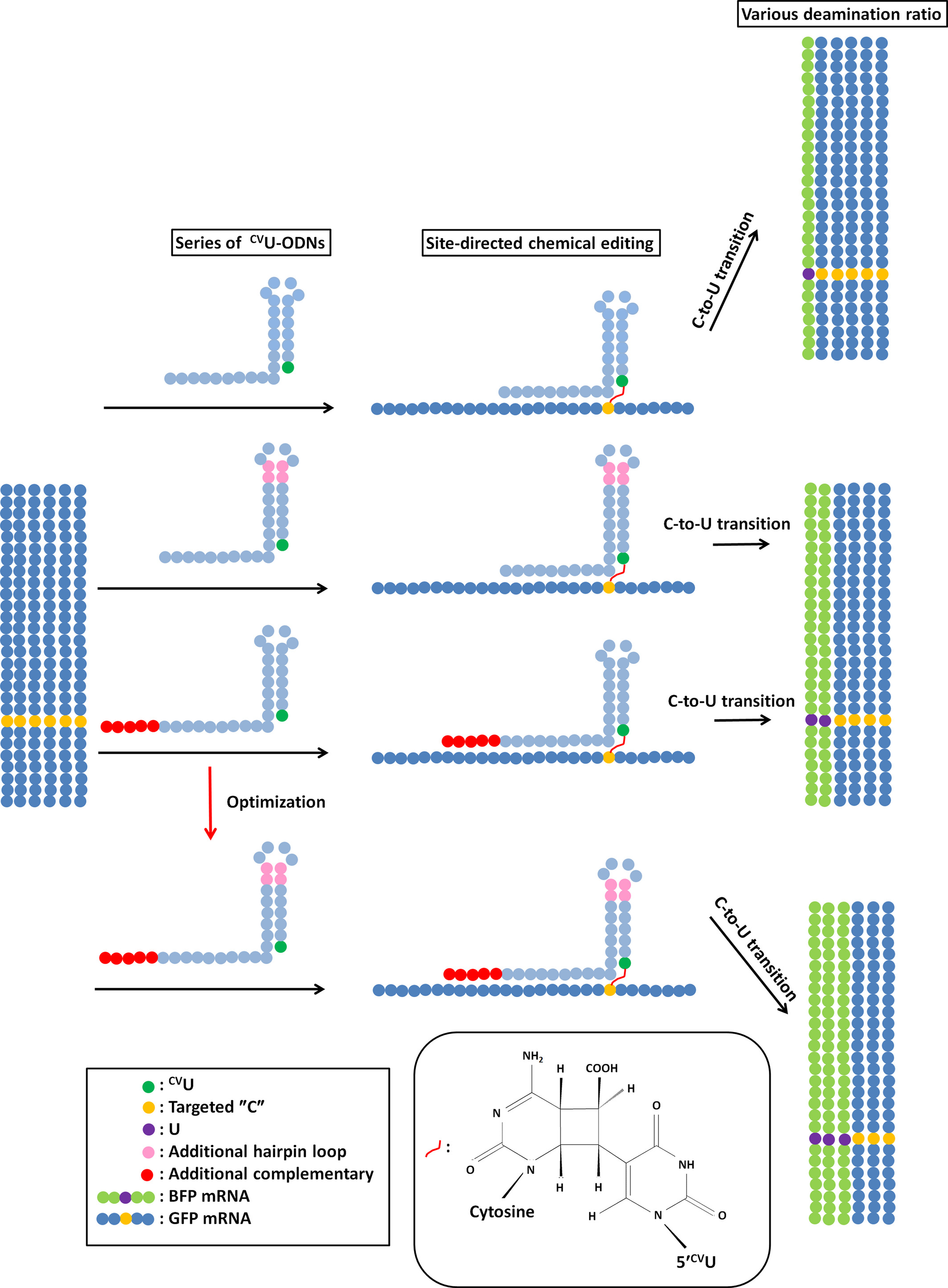
To optimize the CVU-containing-ODN structures, we investigated the dependence of the deamination efficiency on the effector CVU-containing ODN's complementary sequence length and hairpin loop length. We found that the deamination efficiency reached its maximum values with a complementary sequence length slightly more than 14 nt and hairpin loop length of 9 nt.
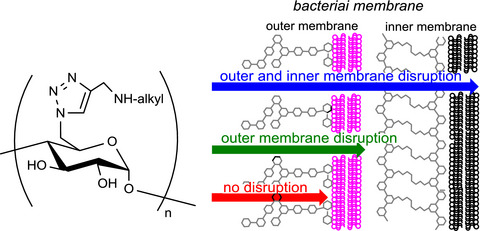
Syntheses and structure–membrane active antimicrobial activity relationship of alkylamino-modified glucose, maltooligosaccharide, and amylose
- First Published: 04 April 2017
Identification and structure–activity relationship of purine derivatives as novel MTH1 inhibitors
- First Published: 12 November 2016
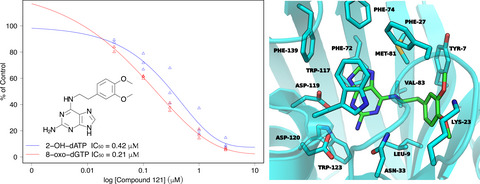
A series of compounds belonging to the purine scaffold have been screened for MTH1 inhibitory activity, and several new inhibitors with potency in the submicromolar range have been discovered. The structure activity relationship of these compounds has been analyzed, and their associated binding modes to MTH1 have been predicted using molecular docking. These studies have provided insights for the development of highly potent MTH1 inhibitors.