Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Simple, Rapid, and Large-Scale Fabrication of Multi-Branched Hydrogels Based on Viscous Fingering for Cell Culture Applications
- First Published: 15 September 2023
Front Cover: For fabricating organs, it is essential to form specific structures. In article 2300069, Kosuke Ino, Hitoshi Shiku and co-workers present a simple, rapid, and large-scale fabrication method for multi-branched hydrogels like vasculature. Vascular cells can be cultured in the multi-branched biomaterials, which will be useful to fabricate vascularized organs.
Back Cover
Targeted Delivery of Anticancer Drug Loaded Charged PLGA Polymeric Nanoparticles Using Electrostatic Field
- First Published: 15 September 2023

Back Cover: Pure Positive electrostatic charges (PPECs) are used for the delivery of drug-loaded (Paclitaxel) polymeric nanoparticles (DLNs) capped with negatively charged poly(lactide-coglycolide) (PLGA) and Poly (vinyl alcohol) PVA into the tumor site. In article 2300181, Mohammad Abdolahad and co-workers find that DLNs synthesized by PLGA show great attraction to PPECs due to their stable negative charges. Regarding deposition of the PVA on the surface of drug-loaded nanoparticles, opsonization will be decreased. PPECs have many potential clinical applications for advanced-targeted chemotherapy with the lowest discernible side effects.
Masthead
Reviews
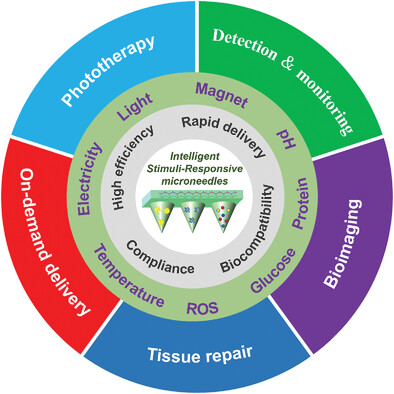
Advances in Intelligent Stimuli-Responsive Microneedle for Biomedical Applications
- First Published: 13 April 2023
Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Infected Wound Treatment
- First Published: 09 May 2023

Wound infections slow down the healing process and lead to complications such as septicemia, osteomyelitis, and even death. Chitosan-based hydrogels possess outstanding advantages for infected wound healing. In this review, the recent research progress of chitosan-based hydrogels for infected wound treatment is summarized. A concise assessment of current limitations and future trends is presented.
Promotion of ICD via Nanotechnology
- First Published: 28 April 2023
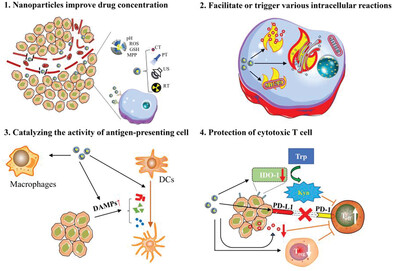
This review summarizes four leading strategies used to promote the therapeutic effects of immunogenic cell death (ICD) via nanotechnology, including increasing the localized concentration of an ICD inducer in tumor, inducing various intracellular reactions, catalyzing the activity of antigen-presenting cells, and protecting the function of cytotoxic T cells, together with an overview of the state-of-the-art clinical applications of ICD via nanotechnology.
Research and Application of Medical Polyetheretherketone as Bone Repair Material
- First Published: 23 April 2023
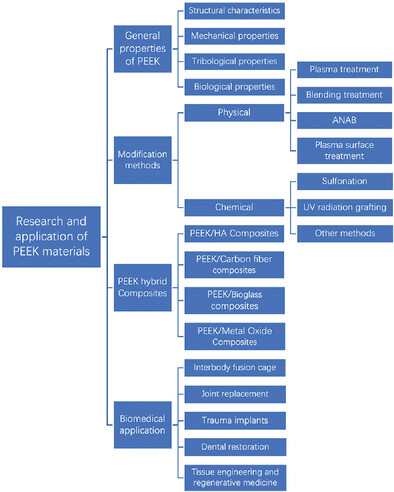
The general properties of Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) are discussed, which can be potentially used for bone repair due to its elastic modulus and good biocompatibility and chemical stability. The study also demonstrates about the modification methods of PEEK materials, and reviewed the biological applications in bone repair and optimization strategy, inspired by structure and compositions.
Current Status and Trends in Nucleic Acids for Cancer Therapy: A Focus on Polysaccharide-Based Nanomedicines
- First Published: 22 May 2023
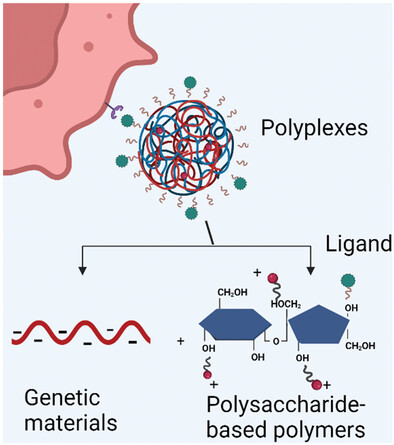
Polymers are employed in gene delivery as an alternative to lipid nanoparticles. Among polymeric materials, of particular interest there are those based on repetitive units of sugars, such as oligosaccharides-based polymers and polysaccharides. Carbohydrates-based polyplexes are widely investigated in preclinical studies and can be further translated into clinically-relevant nanomedicines for the delivery of therapeutic nucleic acids for cancer therapy.
Research Articles
Simple, Rapid, and Large-Scale Fabrication of Multi-Branched Hydrogels Based on Viscous Fingering for Cell Culture Applications
- First Published: 13 April 2023
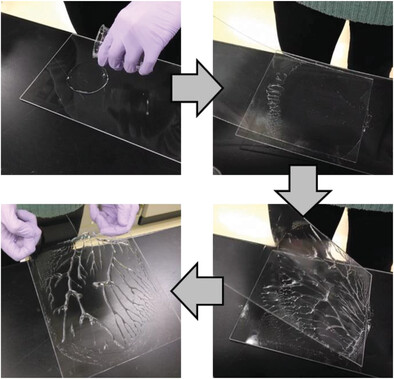
A simple, rapid, and large-scale fabrication process based on viscous fingering for forming multi-branched hydrogels for cell culture applications is proposed. In this study, only one solution and two substrates are used to form multi-branched structures within 1 min. In addition, the scaffolds are used for cell culture of vascular endothelial cells.
Targeted Delivery of Anticancer Drug Loaded Charged PLGA Polymeric Nanoparticles Using Electrostatic Field
- First Published: 03 July 2023
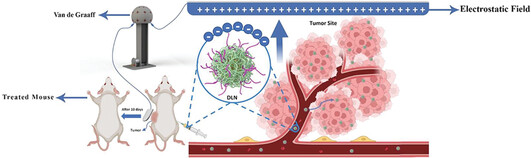
An external positive electrostatic charge applied to the drug-loaded polymeric (PLGA+PVA) nanoparticles introduce a new targeted approach to drug delivery. With an electrostatic patch applied on top of the skin, drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles are guided to the tumor region, the aim is decreasing required doses of PTX in mice with similar tumor destruction.
Frontispiece
Mechanomorphological Guidance of Colloidal Gel Regulates Cell Morphogenesis
- First Published: 15 September 2023

Colloidal Gels
In article 2300122, Lin and co-workers show that polyurethane based colloidal gels provide synchronized mechanomorphological guidance for the aggregation and organization of the cells to control their functional state in 3D microenvironment. Chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells and network formation of endothelial cells are promoted on these gel matrices.
Research Articles
Mechanomorphological Guidance of Colloidal Gel Regulates Cell Morphogenesis
- First Published: 04 May 2023
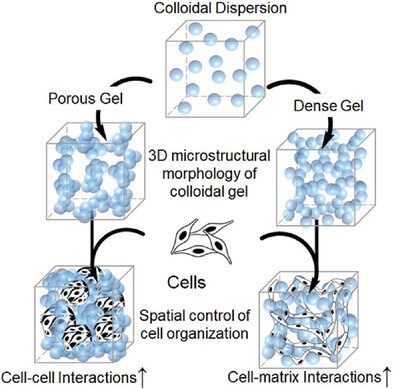
Colloidal gels are developed from the aggregation of ionic polyurethane colloids. The spatial organization of interconnected particles in the gel defines the microstructural morphology, which is engineered in a bidirectional manner with respect to gel mechanics. The mechanomorphology of the gels provides spatial guidance for cell organization through balanced cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions during endothelial morphogenesis and mesenchymal chondrogenesis.
Smart Design of Sensor-Coated Surgical Sutures for Bacterial Infection Monitoring
- First Published: 29 April 2023
PP/PE surgical sutures are functionalized with a conducting polymer using an approach that combines low-pressure plasma treatment with both chemical and electrochemical polymerizations. The obtained smart sutures allow real-time monitoring of bacteria growth through the detection of oxidation of specific metabolites, demonstrating that this is a promising approach to preventing bacterial infections.
Mulberry Leaves (Morus Rubra)-Derived Blue-Emissive Carbon Dots Fed to Silkworms to Produce Augmented Silk Applicable for the Ratiometric Detection of Dopamine
- First Published: 25 April 2023
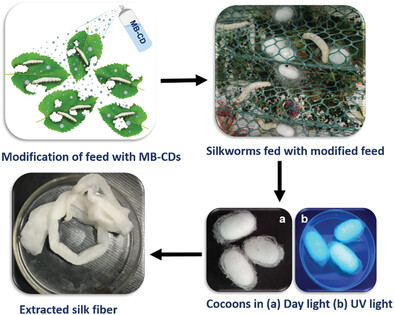
The possibility of blending carbon dots (CDs) with silk fibres (SF) is explored by directly feeding silkworms with a CD-modified diet. The major highlights of this study involve i) synthesis of CDs from the Morus rubra variant of mulberry leaves (MB-CDs) for the first time, ii) utilizing MB-CDs as fluorescent probes for Dopamine (DA) detection, iii) Feeding MB-CD-sprayed mulberry leaf diets to Bombyx mori variant of silkworms from their third instar to synthesize augmented SF, and iv) development of a novel, cost-effective method for the detection of DA by utilizing augmented SF.
Epsin Mimetic UPI Peptide Delivery Strategies to Improve Endothelization of Vascular Grafts
- First Published: 28 April 2023
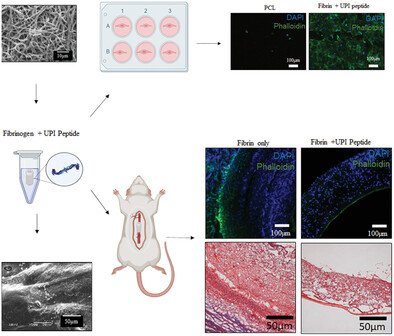
An epsin-mimetic UPI peptide can block internalization of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, which has promise for improving vascular graft endothelialization. This study shows that incorporation of UPI peptides into vascular grafts via a fibrin coating can promote endothelial cell attachment and migration in vitro and endothelialization in vivo. A low dose of the peptide also improves graft viability.
A 3D Bioprinted Nanoengineered Hydrogel with Photoactivated Drug Delivery for Tumor Apoptosis and Simultaneous Bone Regeneration via Macrophage Immunomodulation
- First Published: 23 April 2023
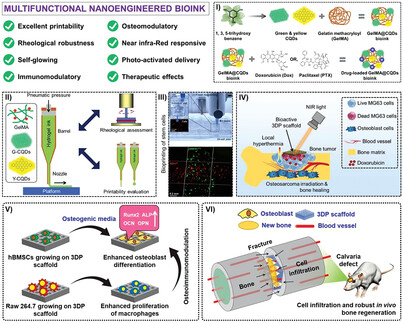
This work demonstrates using polyphenolic carbon quantum dots embedded in 3D bioprinted hydrogels with multi-faceted applications. The dynamic M2 macrophage polarization and light-controlled drug delivery synergistically promote bone regeneration via controlled osteosarcoma eradication and osteoblast differentiation.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Generation of Haploid Spermatids on Silk Fibroin-Alginate-Laminin-Based Porous 3D Scaffolds
- First Published: 28 April 2023
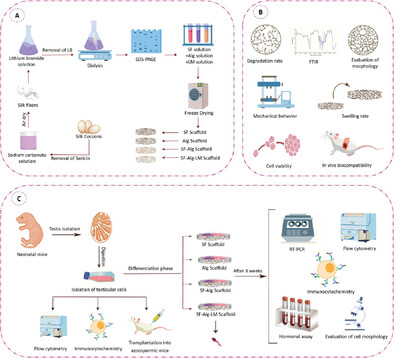
Biocompatible porous scaffolds that mimic the properties of extracellular matrices have great potential for cell proliferation and differentiation. The application of a composite system (Alg-SF-LM) can lead to the differentiation of SSCs and the progression of meiosis to elongated spermatid stage, paving the way for a novel infertility treatment landscape and various tissue engineering in the future.
Research Articles
Thermosensitive Microneedles Capable of On Demand Insulin Release for Precise Diabetes Treatment
- First Published: 27 April 2023
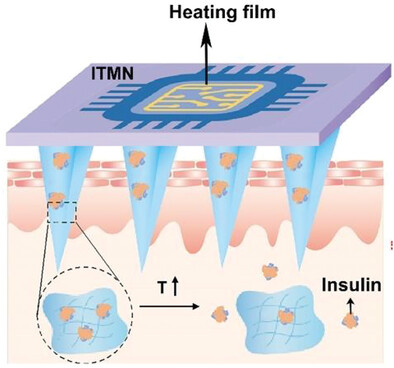
An insoluble thermosensitive microneedle (ITMN) is designed to control the release of insulin by adjusting the temperature in response to the glucose concentration, enabling effective regulates blood glucose and precise treatment of diabetes. It has the potential to form an integrated and precise closed-loop treatment for diabetes, which is of great importance in diabetes management.
Silk Meshes Coated with Chitosan-Bioactive Phytochemicals Activate Wound Healing Genes In Vitro
- First Published: 18 May 2023
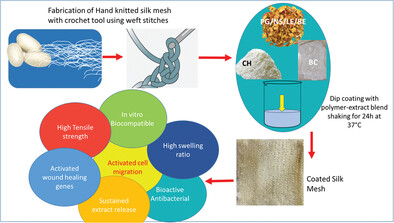
The sustainable bioactive composite knitted silk meshes carrying phytochemicals are mechanically strong, hydrophilic, biocompatible, and nontoxic. The meshes are antibacterial , activate cell migration and express wound healing genes . These coated meshes can be suitable candidates for hernia repair as well as regeneration in other load bearing applications.
Large Polyacrylamide Hydrogels for Large-Batch Cell Culture and Mechanobiological Studies
- First Published: 02 May 2023
An improved method to produce hydrogels with tunable elastic moduli for cell culture studies is presented. This method avoids the costly and labor-intensive need for chemically treating glass coverslips and produces much larger surfaces, suitable for preparing cells in sufficient numbers for protein analyses. Examples of mechanosensing by multiple cell types illustrate the improvised utility of these gels.
Immunogenic Potential and Therapeutic Efficacy of Multi-Epitope Encapsulated Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Mediated Urinary Tract Infections
- First Published: 09 May 2023
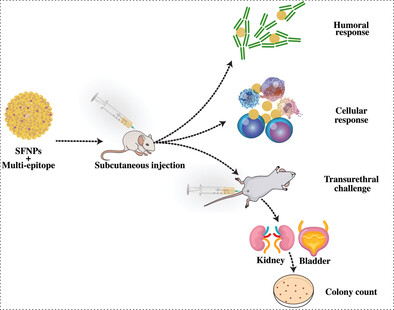
The development of an effective vaccine can prevent urinary tract infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa). A novel multi-epitope candidate is designed and encapsulated in silk fibroin nanoparticles (SFNPs). Immunization of mice with the multi-epitope-SFNPs induces significant immune responses. The multi-epitope-SFNPs protect mice against experimental infection with P. aeruginosa, demonstrating the therapeutic potential of the vaccine candidate.
Folate Functionalized and Evodiamine-Loaded Pluronic Nanomicelles for Augmented Cervical Cancer Cell Killing
- First Published: 10 May 2023
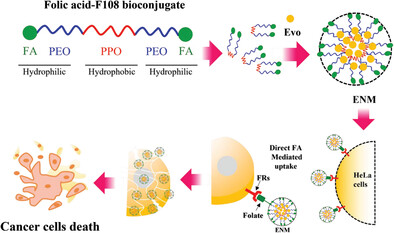
In this study, folate functionalized and evodiamine (Evo) loaded pluronic nano micelles (ENM) is synthesized and characterized, aiming to enhance delivery and anticancer activity of Evo. ENM enhances cellular uptake, induces cytotoxicity and apoptosis, inhibits migration, reduces colony formation, and alters the expression of apoptotic genes. Therefore, designed ENM could be potential targeted delivery system for Evo.
Enhancing the Activity of Surface Immobilized Antimicrobial Peptides Using Thiol-Mediated Tethering to Poly(ethylene glycol)
- First Published: 11 May 2023
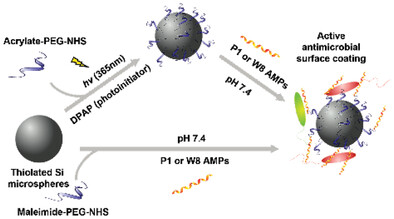
The efficiency and antibacterial activity of thiol-mediated immobilization strategies for the coupling of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) is assessed through a one-step thiol–maleimide, or a two-step thiol–ene “photo-click” approach. It is demonstrated that both methods offer versatile platforms to tether AMPs while preserving their activity; however, the thiol–ene “photo-click” minimizes competitive interactions, allowing for higher AMP loading and prolonged antibacterial activity.
Development of a Microfluidic Formatted Ultrasound-Controlled Monodisperse Lipid Vesicles' Hydrogel Dressing Combined with Ultrasound for Transdermal Drug Delivery System
- First Published: 13 May 2023
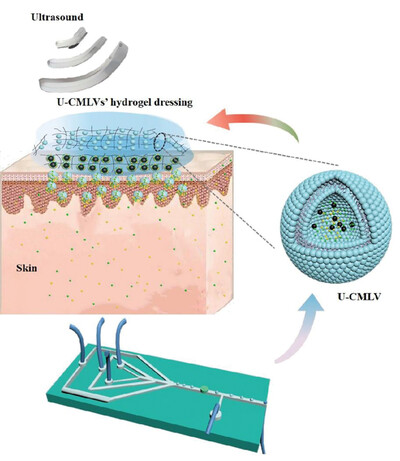
An ultrasound-controlled monodisperse lipid vesicles' (U-CMLVs') hydrogel dressing is described. The U-CMLVs formed by microfluidic have the characteristics of high drug encapsulation efficiency, quantitative encapsulation of ultrasonic response materials, controllable size, and uniform distribution. It combines different frequencies and powers ultrasound to compose a transdermal drug delivery system to achieve deep, controllable, efficient, and safe drug delivery.
The Effect of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Collagen Incorporated with Exo-Polysaccharides Derived from Rhodotorula mucilaginosa sp. on Burn Healing
- First Published: 29 April 2023
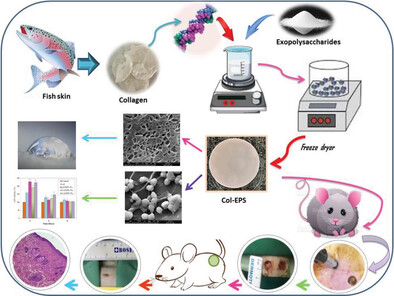
Here exo-polysaccharide (EPS)-incorporated marine-derived collagen scaffolds are fabricated for burn wound healing applications. Instrumental characterizations do not indicate a significant difference in physical properties. However, in vitro and in vivo biological studies show higher cell biocompatibility and accelerated wound healing rate in EPS-incorporated collagen scaffolds.
Development of a Silk Fibroin-Small Intestinal Submucosa Small-Diameter Vascular Graft with Sequential VEGF and TGF-β1 Inhibitor Delivery for In Situ Tissue Engineering
- First Published: 01 June 2023
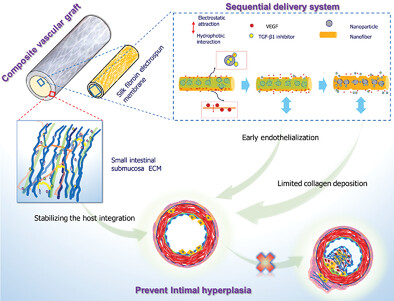
A small-diameter vascular graft is fabricated by integrating an electrospun silk fibroin membrane with decellularized small intestinal submucosa. The graft sequentially releases VEGF and TGF-β1 inhibitors to promote rapid endothelialization and limit collagen deposition and provides a mechanical structure for stabilizing the integration process with degradation. This bioengineered graft aims to prevent intimal hyperplasia and facilitate vascular regeneration.
SOCS1-KIR Peptide in PEGDA Hydrogels Reduces Pro-Inflammatory Macrophage Activation
- First Published: 20 June 2023
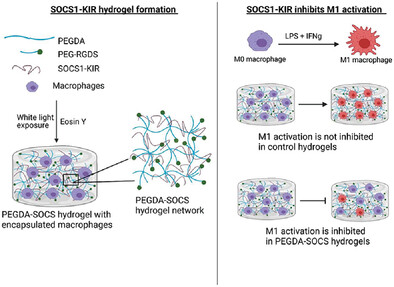
Reducing pro-inflammatory macrophage activation is conducive to inhibiting inflamed chronic wounds. Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins can be utilized to target the JAK/STAT pathway, which in turn reduces inflammatory signaling. This study introduces a PEGDA hydrogel platform to investigate a peptide mimicking the kinase inhibitory region of SOCS (SOCS1-KIR) as an effective therapeutic for macrophage manipulation.