Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Impact of Cell Loading of Recombinant Spider Silk Based Bioinks on Gelation and Printability
- First Published: 14 March 2022

Front Cover: Dragline silk proteins of the European Garden spider are the basis for recombinant spider silk proteins. Spider silk hydrogels are used as matrix for cell encapsulation and 3D bioprinting into stable scaffolds. With spider silk bioinks complex shapes can be printed such as a human aortic valve. This is reported by Annika Lechner, Vanessa T. Trossmann, and Thomas Scheibel in article number 2100390.
Back Cover
Synthesis and Incorporation of Quaternary Ammonium Silane Antimicrobial into Self-Crosslinked Type I Collagen Scaffold: A Hybrid Formulation for 3D Printing
- First Published: 14 March 2022
Back Cover: The project manufactures a unique 3D collagen membrane scaffold impregnated with a novel silane based quaternary ammonium antimicrobial crosslinked with Riboflavin in the presence of VE-TPGS to customise the membrane to fit in osseous defects caused by periodontal disease. The matrix features are somewhat similar to those in tissues of collagen matrices with antimicrobial capacity. This is reported by Cao Tong, Umer Daood, and co-workers in article number 2100326.
Masthead
Review
Advances in Field-Assisted 3D Printing of Bio-Inspired Composites: From Bioprototyping to Manufacturing
- First Published: 16 November 2021
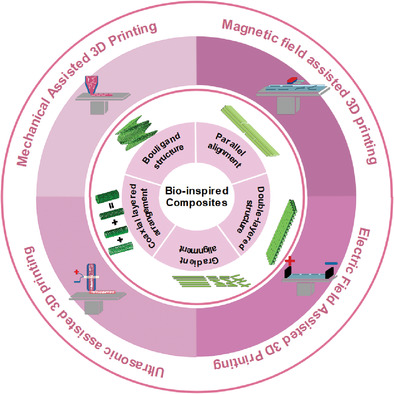
In this review, five typical reinforcement architectures within biocomposites are systematically outlined. It also describes in detail the potential of field-assisted 3D printing technology for manufacturing ingeniously reinforced architectures of biomaterials, fundamentally overcoming the limitations of conventional manufacturing methods. It paves the way for the design and preparation of next-generation high-performance, smart bio-inspired materials.
Research Articles
Impact of Cell Loading of Recombinant Spider Silk Based Bioinks on Gelation and Printability
- First Published: 09 December 2021
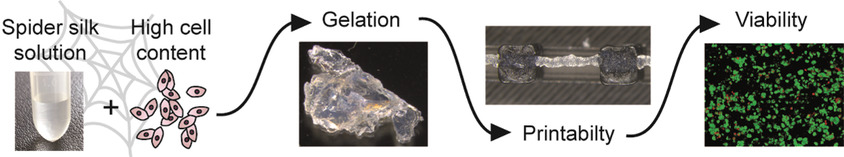
Spider silk based bioinks show high potential for biofabrication combining high biocompatibility with gentle cell encapsulation and reliable extrusion printing. In this study, valuable insights are gained concerning gelation and rheology of spider silk bioinks dependent on cell densities. Printability is optimized by understanding temperature-dependency of rheological behavior, used nozzle, and applied pressure.
Synthesis and Incorporation of Quaternary Ammonium Silane Antimicrobial into Self-Crosslinked Type I Collagen Scaffold: A Hybrid Formulation for 3D Printing
- First Published: 06 December 2021
The project manufactures a unique 3D collagen membrane scaffold impregnated with a novel silane based quaternary ammonium antimicrobial crosslinked with Riboflavin in the presence of VE-TPGS to customize the membrane to fit in osseous defects caused by periodontal disease. The matrix features are somewhat similar to those in tissues of collagen matrices with antimicrobial capacity.
Polymer Architecture Effects on Poly(N,N-Diethyl Acrylamide)-b-Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-b-Poly(N,N-Diethyl Acrylamide) Thermoreversible Gels and Their Evaluation as a Healthcare Material
- First Published: 03 December 2021
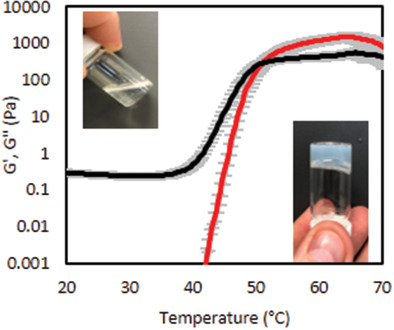
Poly(N,N-diethyl acrylamide) (PDEA) is a thermoresponsive polymer with a lower critical solution temperature. Herein PDEA-b-poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-b-PDEA is synthesized to give four block copolymers with varied molecular weight. Rheometry reveals that higher molecular weight PEG blocks are required to form thermoreversible gels. Furthermore, small-angle X-ray scattering elucidates clear differences in the nanostructure which can be linked to distinct rheology.
Inorganic–Organic Interpenetrating Network Hydrogels as Tissue-Integrating Luminescent Implants: Physicochemical Characterization and Preclinical Evaluation
- First Published: 30 November 2021
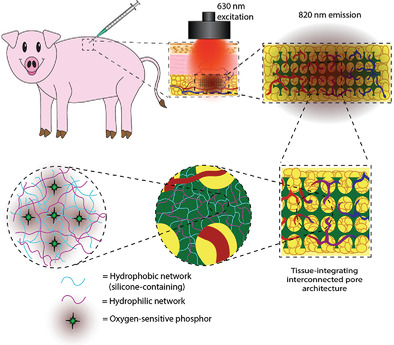
Interpenetrating network (IPN) hydrogels are fabricated with inorganic and organic networks as optical biosensors. Synergy between both polymer networks allows independent tuning of physicochemical properties while optimizing oxygen transport. IPN sensors with inverted colloidal crystal microarchitecture track tissue oxygen in real time for 76 days as subcutaneous implants in a porcine model, promoting tissue ingrowth and minimizing fibrotic encapsulation.
Biocompatible Polyurethane Conduit Grafted with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Loaded Hydrogel Repairs the Peripheral Nerve Defect in Rats
- First Published: 04 December 2021
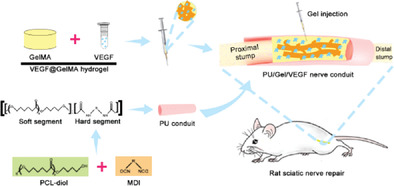
In the current study, a polyurethane conduit grafted with a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-loaded hydrogel (abbreviated as PU/Gel/VEGF conduit) is successfully fabricated, characterized in vitro, and used to repair the peripheral nerve defect in rats in vivo. The results collectively evidence that the PU/Gel/VEGF conduit could promote the process of peripheral nerve regeneration.
Development of Fluorescently Labeled, Functional Type I Collagen Molecules
- First Published: 01 December 2021
A Polyaniline Nanoparticles Crosslinked Hydrogel with Excellent Photothermal Antibacterial and Mechanical Properties for Wound Dressing
- First Published: 23 December 2021
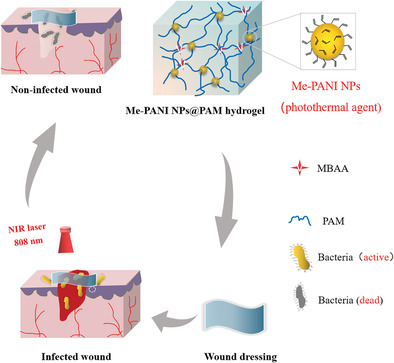
A novel NIR-responsive photothermal antibacterial hydrogel with excellent mechanical properties is prepared using double bond-ended polyaniline nanoparticles as the crosslinkers. The developed hydrogel has the potential for applications as a novel wound dressing to realize controlled treatment of bacterial infections and to accelerate the healing of skin wounds.
Early Application of Quaternized Chitin Derivatives Inhibits Hypertrophic Scar Formation
- First Published: 09 December 2021
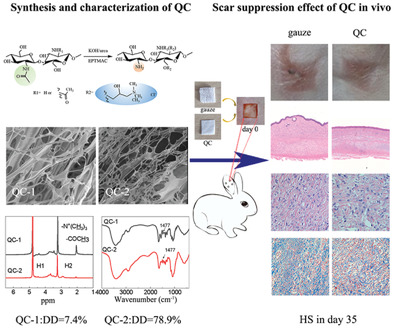
Early application of quaternized chitin inhibits hypertrophic scar formation in a rabbit ear model. Quaternized chitin suppresses inflammation and IL-6 expression in the early stage, then balances the synthesis and degradation of extracellular matrix during the remodeling phase. In addition, quaternized chitin with low deacetylation degree (7.4%) inhibits hypertrophic scar formation more effectively.
Cascade Tumor Therapy Platform for Sensitized Chemotherapy and Penetration Enhanced Photothermal Therapy
- First Published: 15 December 2021
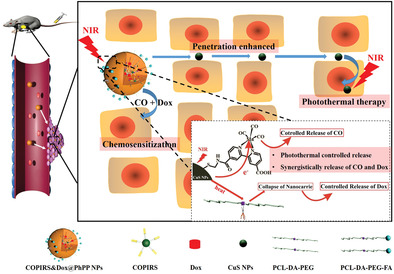
Under near infrared irradiation, carbon monoxide and doxorubicin are synergically released to achieve sensitized chemotherapy and heat is generated to achieve photothermal therapy. CuS nanoparticles (NPs) are also released and small-sized CuS NPs possess better tumor penetration and achieve penetration-enhanced photothermal therapy (PTT). Thus, cascade multistage cancer treatment of “combined PTT and chemotherapy sensitization”—“penetration-enhanced PTT” is achieved.
Fabrication of Resveratrol-Loaded Scaffolds and Their Application for Delaying Cell Senescence In Vitro
- First Published: 17 December 2021
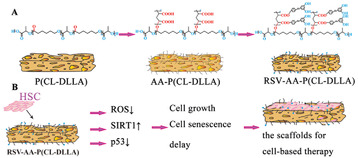
RSV-AA-P(CL-DLLA) is fabricated with the introduction of the functional carboxyl group–COOH) onto the surface of poly(ε-caprolactone/d,l-lactide) P(CL-DLLA)) and esterification of resveratrol with the modified surface. The synthetic scaffold is used to delay cell senescence in cell-based therapy tissue engineering.
Fabrication of a 3D Printed PCL Nerve Guide: In Vitro and In Vivo Testing
- First Published: 23 December 2021
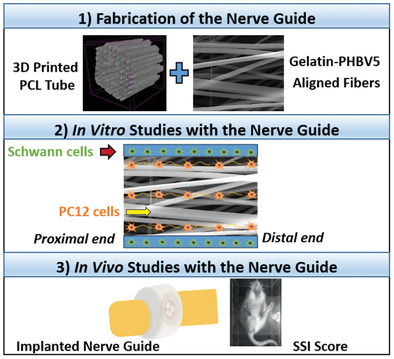
Fabrication of a biodegradable nerve guide is achieved by combining 3D printing and electrospinning techniques. Schwann cells seeded on 3D printed polycaprolactone conduit and PC12 cells seeded on the one side of the gelatin-poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) aligned fibers are used for in vitro studies. Biodegradable nerve guides are implanted in a 10 mm rat sciatic nerve injury and improved neuronal connections.
Peptide Modified Albumin–Paclitaxel Nanoparticles for Improving Chemotherapy and Preventing Metastasis
- First Published: 29 December 2021
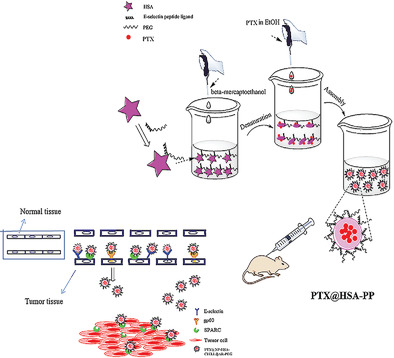
This study has developed a peptide modified albumin-paclitaxel nanoparticles for inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis. The preparation, characterization, and in vitro activity of the nanoparticles are investigated, and the in vivo efficacy for tumor growth/lung metastasis inhibition and metastasis prevention are respectively evaluated using 4T1 bearing nude mice and a B16-F10 model in C57BL/6 mice.
Enhanced Bone Regeneration Using a ZIF-8-Loaded Fibrin Composite Scaffold
- First Published: 28 December 2021
Here a hydrogel for skull bone defects, which is composed of fibrin and zeolite imidazole framework-8 (ZIF-8), is reported. Results show that this hydrogel enhances ectomesenchymal stem cells (EMSCs) osteogenic through activating piezo 1 in vitro. Implantation experiments with rats with millimeter-scale cranial defects reveal that, after 12 weeks, the hydrogels promote regenerative growth of bone tissue.
Complement Activation Dramatically Accelerates Blood Plasma Fouling On Antifouling Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) Brush Surfaces
- First Published: 27 December 2021
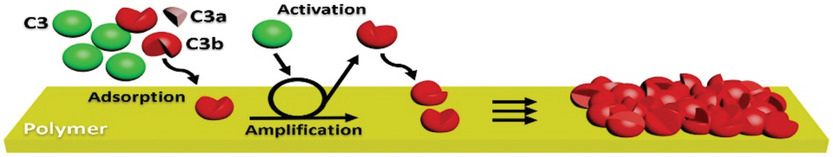
Blood plasma fouling on antifouling poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (poly(HEMA)) brushes is dramatically increased and accelerated for some donors due to activation of the complement system. The alternative complement pathway plays a significant role in the fouling on poly(HEMA) through the “tick-over” generation of C3b that can bind poly(HEMA) and trigger an amplification loop.
Chitosan/Gelatin Composite Nonwoven Fabric Scaffold Seeding Minimal Function Unit of Skin for Functional Skin Regeneration
- First Published: 03 January 2022
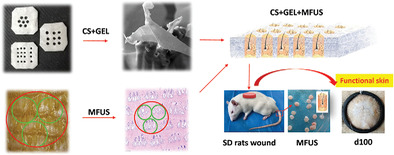
Traditional engineered skin, using “seed cells” as a bioactive source maybe not efficient enough. Here a new strategy is shown for constructing functional tissue-engineered skin with Chitosan/gelatin non-woven fabric seeding Minimal Functional Unit of Skin (MFUS) as the source of bioactivity. This study proposes a new strategy for the clinical treatment of large full-thickness skin defects with intact functional skin.
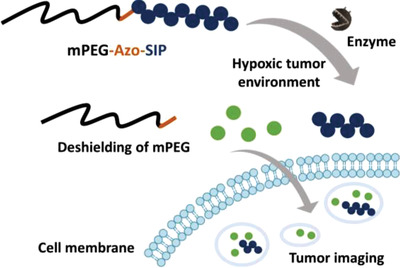
Hypoxia-Activated Fluorescent Probe Based on Self-Immolative Block Copolymer
- First Published: 04 January 2022
Chondroitin and Dermatan Sulfate Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting and Cartilage Regeneration
- First Published: 13 January 2022
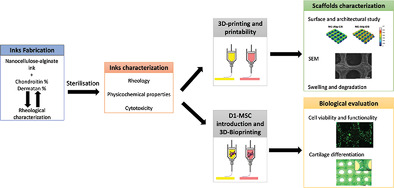
Bioinks based on nanocellulose-alginate-chondroitin sulfate (NC-Alg-CS) and nanocellulose-alginate-dermatan sulfate (NC-Alg-DS) have been developed for 3D bioprinting and cartilage regeneration. The addition of both CS and DS to the NC-Alg bioink improves its characteristics in terms of rheology and embedded D1-MSC viability and functionality. Furthermore, differentiation to cartilage is promoted on NC-Alg-CS and NC-Alg-DS scaffolds.