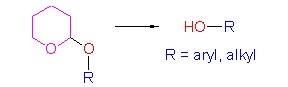Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Three-Component Cucurbit[6]uril Framework with 1:2 Host-Guest Motif and Dimeric Boric Acid (Chin. J. Chem. 5/2012)
- Page: 1005
- First Published: 15 May 2012
![Cover Picture: Three-Component Cucurbit[6]uril Framework with 1:2 Host-Guest Motif and Dimeric Boric Acid (Chin. J. Chem. 5/2012)](/cms/asset/a514cae4-1e84-491d-b78b-09578b63265a/mcontent.jpg)
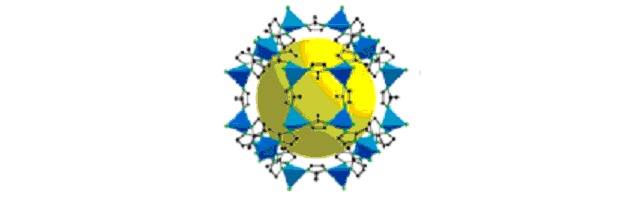
The cover picture shows a versatile approach combining different recognition modes to the construction of multicomponent complex supramolecular architectures. Recognition and assembly of macrocyclic host molecules are fundamental and crucial in the field of supramolecular research. Three-component cucurbit[6]uril framework with 1:2 host-guest motif and dimeric boric acid has been constructed. The 1:2 host-guest motif demonstrates both cation binding of imidazolium moiety and anion binding of sulfonate moiety for the first time. Incorporation of dimeric boric acid facilitates the formation of metal-free three-dimensional framework. More details are discussed in the article by Liu et al. on page 1022–1026.
Contents
Communications
Influence of Drying and Calcination on Remaining Amount and Immobile Character of Titanium on Titanium-pillared Montmorillonite
- Pages: 1017-1021
- First Published: 15 May 2012
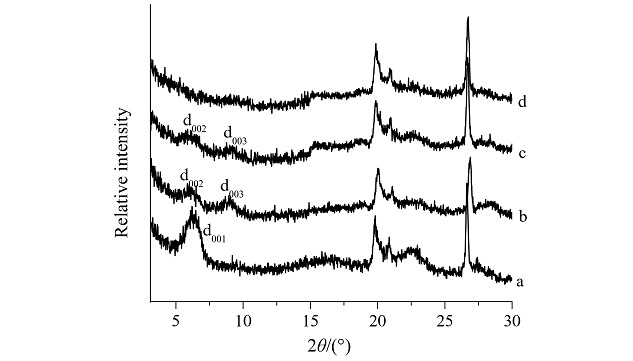
TIPMs were synthesized from TiCl and MMT in ethanol and then were dried or calcined at different temperatures to yield several samples. The spacing of the layers was enlarged from 14.2 Å up to 28.1 Å after intercalating and a gradual decrease of the peak intensity was also observed as the immobilization experiments were carried out, a situation owing to less homogeneous pillar distribution which means that partial pillars were destroyed in the process.
and MMT in ethanol and then were dried or calcined at different temperatures to yield several samples. The spacing of the layers was enlarged from 14.2 Å up to 28.1 Å after intercalating and a gradual decrease of the peak intensity was also observed as the immobilization experiments were carried out, a situation owing to less homogeneous pillar distribution which means that partial pillars were destroyed in the process.
Three-Component Cucurbit[6]uril Framework with 1:2 Host-Guest Motif and Dimeric Boric Acid
- Pages: 1022-1026
- First Published: 07 May 2012
![Three-Component Cucurbit[6]uril Framework with 1:2 Host-Guest Motif and Dimeric Boric Acid](/cms/asset/703268cc-0bad-4656-af2e-d490a557a994/mcontent.jpg)
Three-component cucurbit[6]uril framework with 1:2 host-guest motif and dimeric boric acid has been constructed. The 1:2 host-guest motif demonstrates both cation binding of imidazolium moiety and anion binding of sulfonate moiety for the first time. Incorporation of dimeric boric acid facilitates the formation of metal-free three-dimensional framework.
Full Papers
Solid-Phase Organic Synthesis of Aryl Vinyl Ethers Using Sulfone-Linking Strategy
- Pages: 1027-1030
- First Published: 10 April 2012
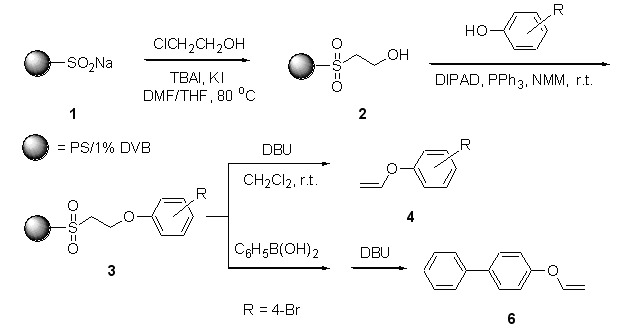
A novel facile solid-phase organic synthesis of aryl vinyl ethers by reaction of polystyrene-supported 2-phenylsulfonylethanol with phenols under Mitsunobu conditions and subsequent elimination reaction with DBU has been developed. The advantages of this method include straightforward operation, good yield and high purity of the products. Alternatively, a typical example of Suzuki coupling reaction on-resin was further applied to prepare 4-phenylphenyl vinyl ether for extending this method.
Stable Water-dispersed CdTe Nanocrystals Dependent on Stoichiometric Ratio of Cd to Te Precursor
- Pages: 1031-1039
- First Published: 07 May 2012
Microwave-assisted Ionothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8
- Pages: 1040-1044
- First Published: 10 April 2012
Synthesis, Crystal Structures and Electrochemical Properties of Complexes [M(ImH)4(tfbdc)(H2O)] (M=Co, Ni)
- Pages: 1045-1051
- First Published: 10 April 2012
![Synthesis, Crystal Structures and Electrochemical Properties of Complexes [M(ImH)4(tfbdc)(H2O)] (M=Co, Ni)](/cms/asset/654e75c1-b5f4-4341-9bea-5a3caa712a30/mcontent.jpg)
Two new isostructural compounds [M(ImH)4(tfbdc)(H2O)] (1: M=Co; 2: M=Ni) constructed by hydrogen bonding interactions have been obtained via the reaction of H2tfbdc, M(OAc)2·4H2O with ImH. The complexes were characterized by elemental analysis, IR spectra, thermogravimetric analysis, cyclic voltammetry and X-ray single crystal structure analysis. Electrochemical properties of the complexes 1 and 2 show that electron transfer of M(II) between M(III) in electrolysis is a quasi-reversible process.
Novel 1D Copper(II) Helical Chain Formed by Weak Coordination-driven Self-assembly: Synthesis, Structure, and Magnetic Property
- Pages: 1052-1056
- First Published: 07 May 2012
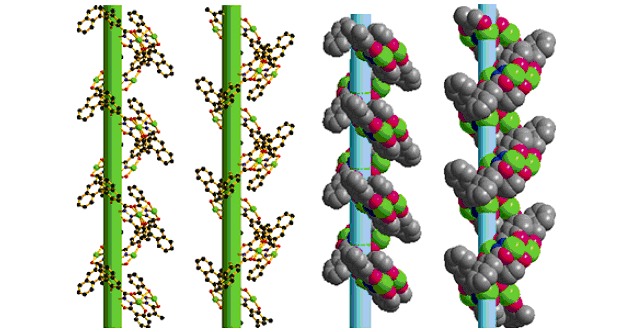
A novel 1D copper(II) helical chain is constructed through the connection of tetranuclear copper(II) units by weak coordination-driven self-assembly. The helical chains are packed in an alternating left-(M) and right-handed (P) chirality, the orientation of the helices was determined by the axial chirality of the ligand.
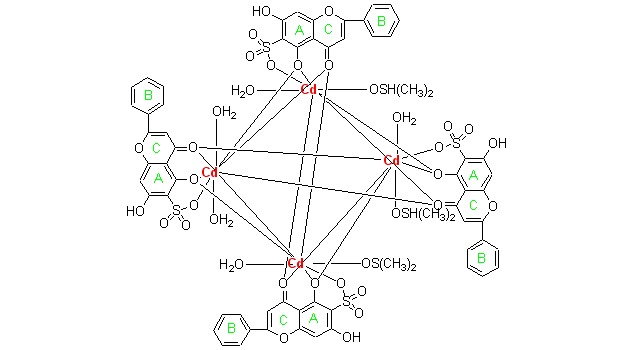
Crystal Structure and Photoluminescence of a Tetranuclear Cadmium Complex
- Pages: 1057-1062
- First Published: 07 May 2012
Solvothermal Synthesis and Crystal Structures of Two Manganese Complexes [Mn(II)(acac−)2(4,4′-bipy)]n (bipy=4,4′-bipyridine) and [Mn(III)(acac−)3]·4CO(NH2)2
- Pages: 1063-1068
- First Published: 10 April 2012
![Solvothermal Synthesis and Crystal Structures of Two Manganese Complexes [Mn(II)(acac−)2(4,4′-bipy)]n (bipy=4,4′-bipyridine) and [Mn(III)(acac−)3]·4CO(NH2)2](/cms/asset/717cade6-6446-4195-82e5-0338d5dc8b2a/mcontent.jpg)
The two special manganese complexes [Mn(II)(acac−)2(4,4′-bipy)]n (bipy=4,4′-bipyridine) (The left one, complex 1) and [Mn(III)(acac−)3]·4CO(NH2)2 (acacH=acetylacetone) (The right one, complex 2) were synthesized in the same strategy by solvothermal method. The complex 1 consists of one-dimensional infinite coordination chain, but complex 2 is located in the 14-membered carbamide ring formed by hydrogen bonds among the free carbamides.
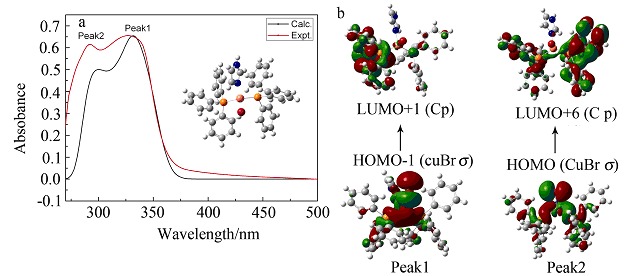
A New Copper(I) Complex Based on Imidazole and Triphenylphosphine Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, Third-Order NLO, and Fluorescence Properties
- Pages: 1069-1074
- First Published: 07 May 2012
Facile Synthesis of 3-Substituted Isoquinolines Derivatives via Microwave-assisted Tandem Three-component Coupling Cyclization
- Pages: 1075-1082
- First Published: 07 May 2012
Synthesis and Anti-tumor Evaluation of Novel C-37 Modified Derivatives of Gambogic Acid
- Pages: 1083-1091
- First Published: 07 May 2012
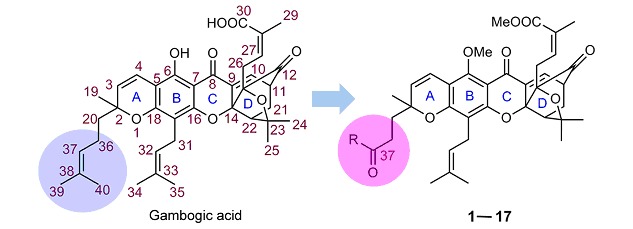
17 novel C-37 modified derivatives of GA were synthesized by a regioselective chemical strategy and evaluated for their in vitro anti-tumor activities against A549, HCT-116, BGC-823, HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cell lines. Among them, 11 compounds were found to be more potent than GA against some cancer cell lines. The structure-activity relationship (SAR) was also discussed.
A Facile Synthesis of Enantiomerically Pure (R)-6-Arylbinols
- Pages: 1092-1096
- First Published: 07 May 2012
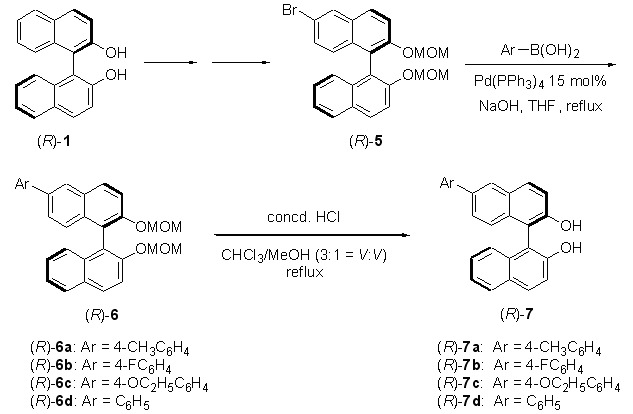
This work reported a convenient method for the preparation of enantiomerically pure 6-aryl-2,2′-dihydroxy-1,1′-binaphthyl derivatives starting from the commercially available (R)-2,2′-hydroxy-1,1′-binaphthyl [(R)-1] via bromination, hydrolysis and Suzuki cross coupling reaction. This novel synthetic method was characterized with high regioselectivity, simple operation, mild reaction conditions, and excellent yield (up to 73%). On the other hand, we synthesized the target unknown compounds, which were confirmed by IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, MS and elementary analysis.
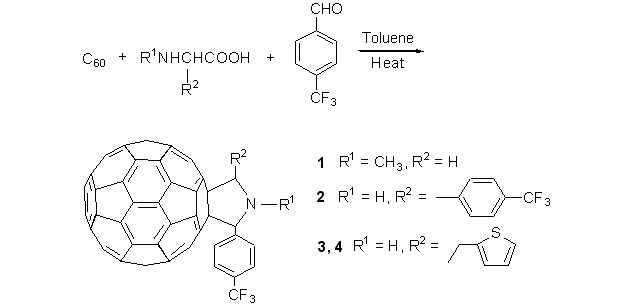
Synthesis, Characterization, Optical and Electrochemical Properties of Fulleropyrrolidines Containing Trifluoromethyl Group
- Pages: 1097-1101
- First Published: 07 May 2012
Determination of Uric Acid in Human Urine by Ion-exclusion Chromatography with UV Detection Using Pure Water as Mobile Phase
- Pages: 1102-1104
- First Published: 07 March 2012
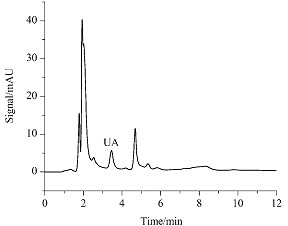
A simple, rapid and accurate ion-exclusion chromatographic method coupled with a UV detector for the determination of uric acid in human urine samples has been developed. The separation was carried out on an ion-exclusion column using only pure water as mobile phase. The detection wavelength was 254 nm and urine sample was injected directly without any pretreatment. Furthermore, the retention behavior of uric acid on the ion-exclusion column was researched when pure water and 1 mmol·L−1 HCl were used as mobile phase, respectively. The stability of uric acid was also further investigated within 28 d. The proposed ion-exclusion chromatographic method has been used for the determination of uric acid in human urine.
Synthesis, Characterization, and Highly Selective Ethylene Dimerization to 1-Butene of [O−NX]Ni(II) Complexes
- Pages: 1105-1113
- First Published: 07 May 2012
An Efficient Palladium and Bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-based System for Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling under Aqueous and Aerobic Condition
- Pages: 1114-1118
- First Published: 10 April 2012
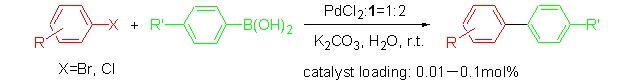
A novel PdCl2/bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-based ligand (1) catalytic system, which is water-soluble and air-stable, has been successfully synthesized and applied to Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. In the presence of catalytic amount of PdCl2/1 system, arylboronic acids can couple with a wide range of aryl halides, including aryl bromides and aryl chlorides. The reactions proceed under mild conditions (aqueous and aerobic conditions) to give excellent yields, and a wide range of functionalities is tolerated.
Synthesis, Characterization and Ethylene Oligomerization Behavior of Neutral Nickel Complexes Bearing N-Fluorinated Phenyl Salicylaldiminato Chelate Ligands
- Pages: 1119-1126
- First Published: 07 March 2012
Synthesis and Cyclization of 8-Formyl-2-(phenoxymethyl)quinoline-3-carboxylic Acids
- Pages: 1127-1132
- First Published: 07 May 2012
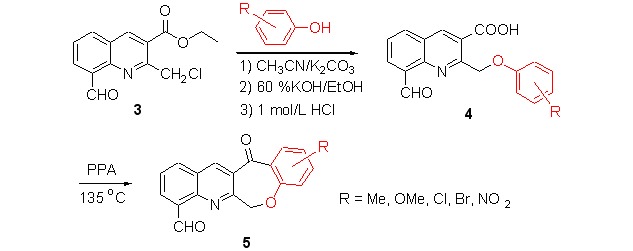
A facile synthesis of a series of new quinoline-8-carbaldehyde compounds, namely 8-formyl-2-(phenoxymethyl)quinoline-3-carboxylic acids (4a–4h) and 13-oxo-6,13-dihydro-[1]benzoxepino[3,4-b]quinoline-8-carbaldehyde (5a–5g) is described, featuring the one-pot synthesis reaction of ethyl 2-(chloromethyl)-8-formylquinoline-3-carboxylate (3) with substituted phenols followed by the intramolecular cyclization reaction via the treatment with polyphosphoric acid (PPA).
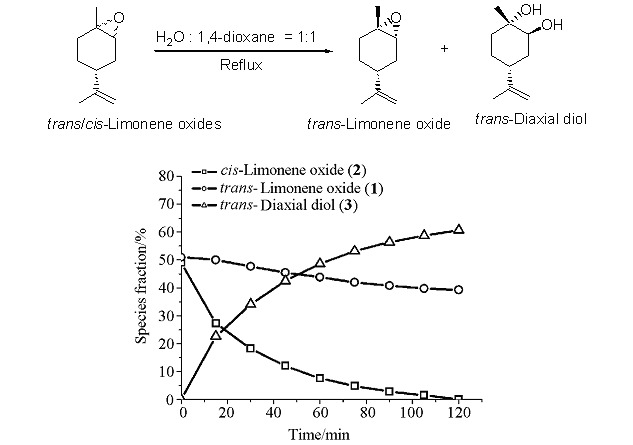
Water-Promoted Kinetic Separation of trans- and cis-Limonene Oxides
- Pages: 1133-1136
- First Published: 07 March 2012
Rapid Determination of Costunolide and Dehydrocostuslactone in Human Plasma Sample and Chinese Patent Medicine Xiang Sha Yang Wei Capsule Using HPLC-DAD Coupled with Second-order Calibration
- Pages: 1137-1143
- First Published: 10 April 2012
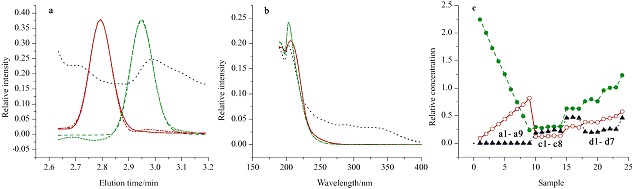
Normalized elution (a) as well as spectral (b) profiles for costunolide and dehydrocostuslactone, in XSYW captual sample which are true and resolved by the ATLD algorithm, and resolved normalized concentrtion (c) profiles for costunolide and dehydrocostuslactone in spiked plasma sample and XSYW capsule sample, respectively. The dash-dot-dot and long dash lines represent the actual spectral profiles of costunolide and dehydrocostuslactone. The solid and medium dash lines represent the resolved spectral profiles of costunolide and dehydrocostuslactone. The dotted lines represent the profile of the background. Hollow circles stand for costunolide, solid circles mean dehydrocostuslactone and solid trigon represent background.
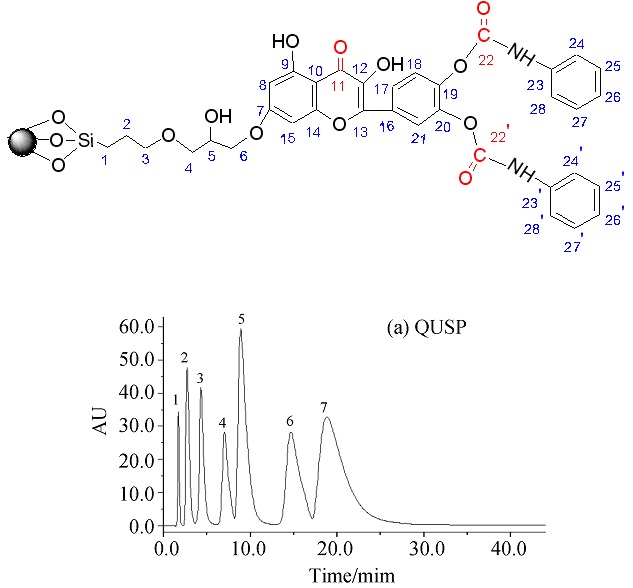
Preparation and Characterization of a New Quercetin-bonded Stationary Phase for High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- Pages: 1144-1154
- First Published: 07 May 2012
A Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Immunosensor for Determination of 1-Pyrenebutyric Acid Based on the Bifunctionality of Nafion/Gold Nanoparticles Composite Electrode
- Pages: 1155-1162
- First Published: 07 May 2012
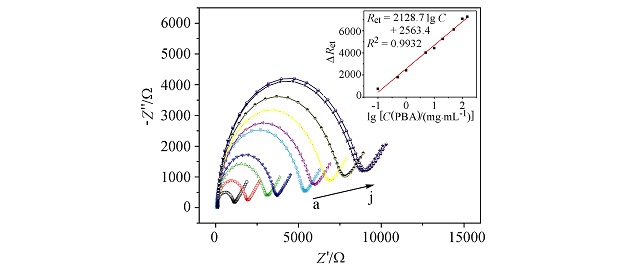
A simple, highly sensitive, and label-free EIS immunosensor for the detection of 1-pyrenebutyric acid was reported based on the bifunctionality of nano-Au/Nafion composite electrode. The results demonstrated that the synergistic effect was obtained by the Nafion film and gold nanoparticles composite electrode, which significantly enhanced the sensitivity of the nano-Au/Nafion immunosensor for 1-pyrenebutyric acid determination.
Facile Fabrication of a Graphene-based Electrochemical Biosensor for Glucose Detection
- Pages: 1163-1167
- First Published: 07 May 2012
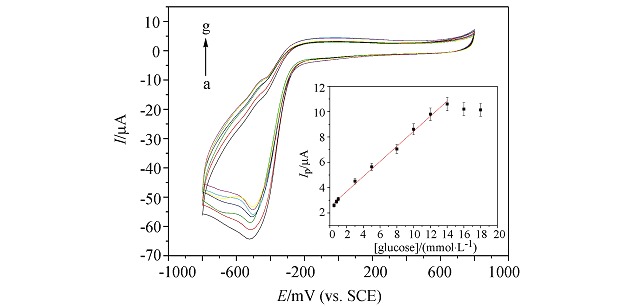
A simple and effective glucose biosensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase (GOD) in graphene (GR)/Nafion film was constructed. The GR/Nafion film provides a favorable microenvironment for GOD immobilization and promotes the direct electron transfer between the electrode substrate and GOD. The as-prepared biosensor exhibits the enhanced performances for glucose detection, such as a wider linear range, satisfying detection limit, good reproducibility and long-term stability.
Photoelectrochemical Immunosensor Array Based on Thioglycolic Acid Capped CdS Quantum Dots for Multiplexed Detection of Veterinary Drug Residues
- Pages: 1168-1176
- First Published: 10 April 2012
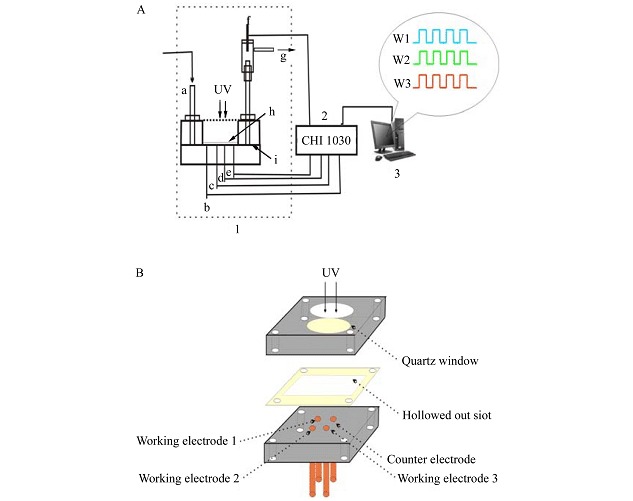
A photoelectrochemical immunosensor array for multiplexed detection of CB, RAC and CAP was demonstrated based on the photoelectrochemical effects of CdS quantum dots. All experimental results indicate that the immunosensor array system has potential application to practical, effective and high throughput analysis of veterinary drugs.
Soluble and Green-light-emitting Oligo(9-fluorenylideneacetic acid): Electrosynthesis and Characterization
- Pages: 1177-1184
- First Published: 10 April 2012
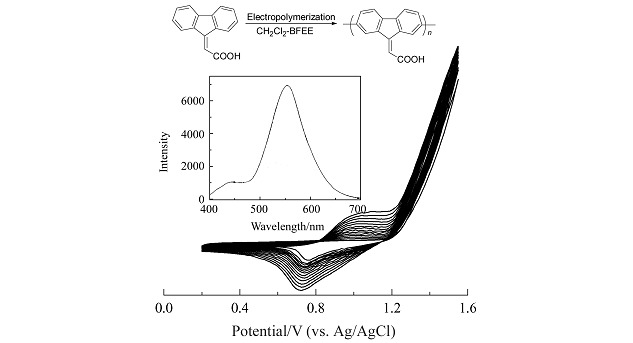
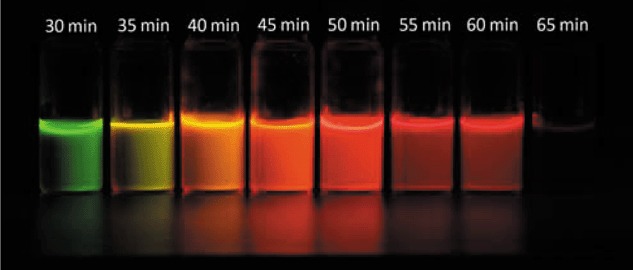
A novel semiconducting oligo(9-fluorenylideneacetic acid) (OFYA) with good redox activity and stability was successfully electrosynthesized by direct anodic oxidation of 9-fluorenylideneacetic acid (FYA) in CH2Cl2 containing boron trifluoride diethyl etherate (BFEE) as the supporting electrolyte. The as-formed OFYA film exhibited good solubility in common solvents and green light-emitting property with maximum emission at 555 nm.
Note
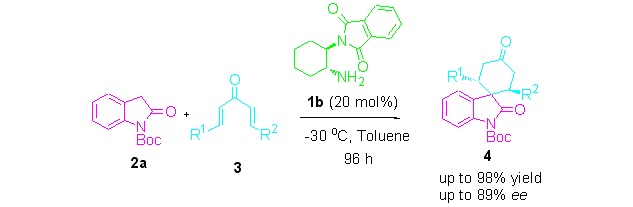
Asymmetric Double Michael Reaction Catalyzed by Simple Primary Amine Catalysts: A Straightforward Approach to Construct Spirocyclic Oxindoles
- Pages: 1185-1188
- First Published: 10 April 2012
Simple and Efficient Method for Deprotection of Tetrahydropyranyl Ethers by Using Silica Supported Sodium Hydrogen Sulphate
- Pages: 1189-1191
- First Published: 29 February 2012
Erratum
Erratum: DFT Studies of Ag-Loading Intrinsic and Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
- Page: 1192
- First Published: 15 May 2012





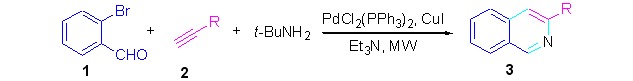
![Synthesis, Characterization, and Highly Selective Ethylene Dimerization to 1-Butene of [O−NX]Ni(II) Complexes](/cms/asset/233e3f6c-9b90-4b4e-a13e-0c64c4779465/mcontent.jpg)