Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Functional Mitral Valve Regurgitation, Pathophysiology, Leaflet ReModeling, and the Role of Imaging
- First Published: 25 February 2025
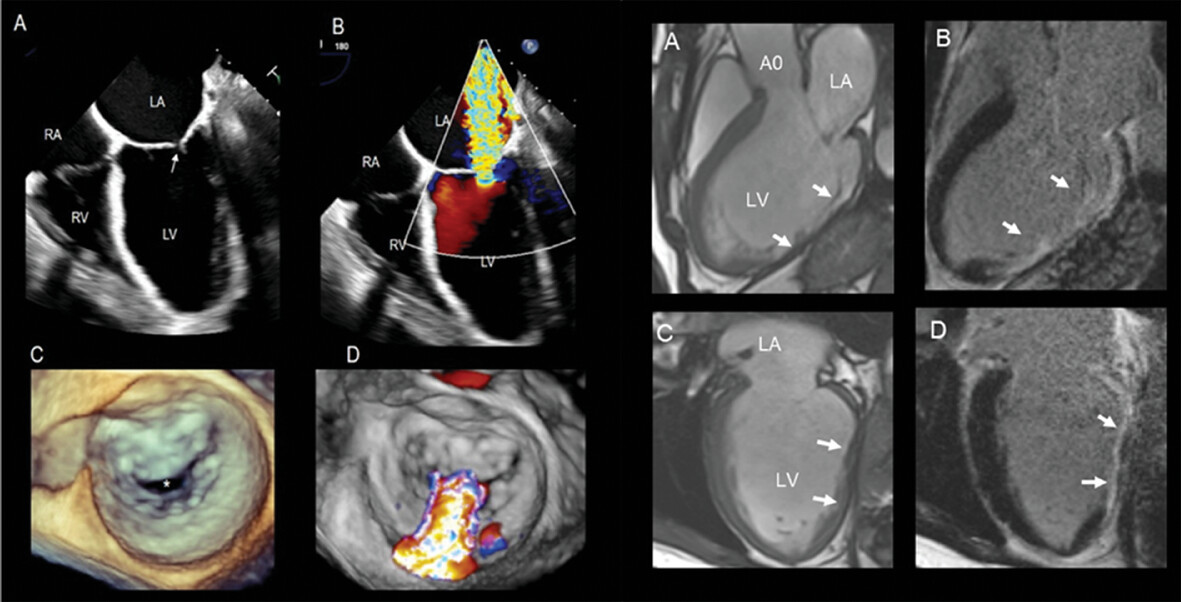
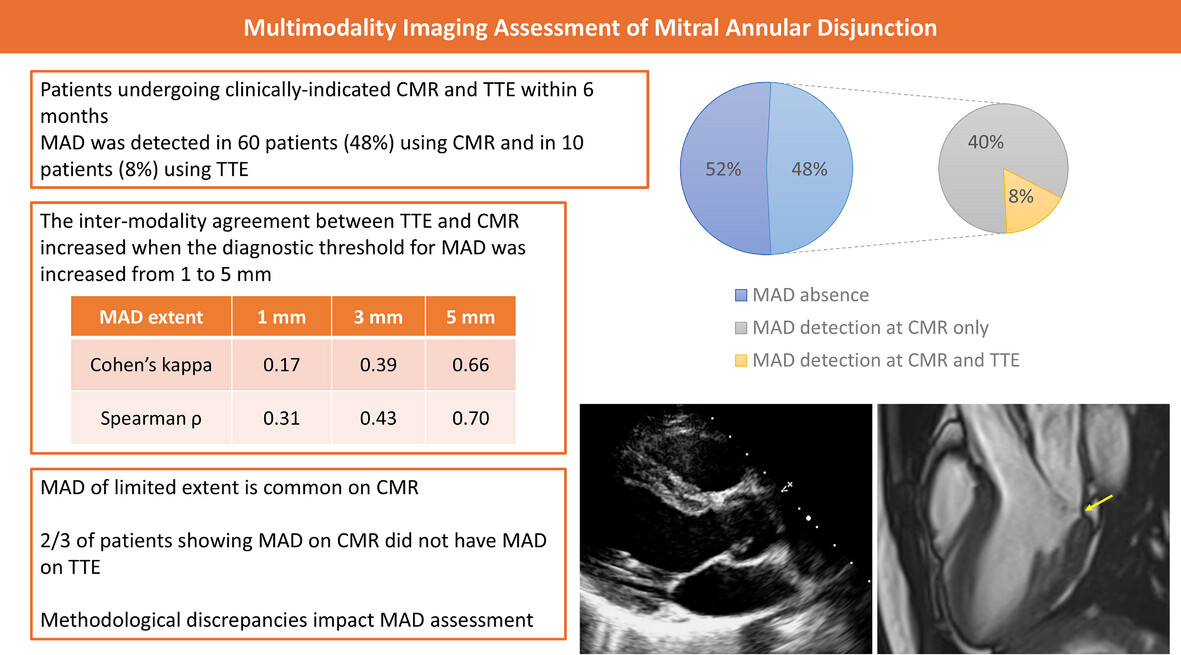
Functional mitral regurgitation (FMR) is a complex left ventricle (LV) and left atrium (LA) disorder with a multifactorial etiology. Regional and global LV dysfunction, extent and location of fibrotic myocardium and annulus enlargement are the leading causes of valve regurgitation. Echocardiography and CMR have a critical role in the comprehensive assessment of FMR.
INVITED REVIEW
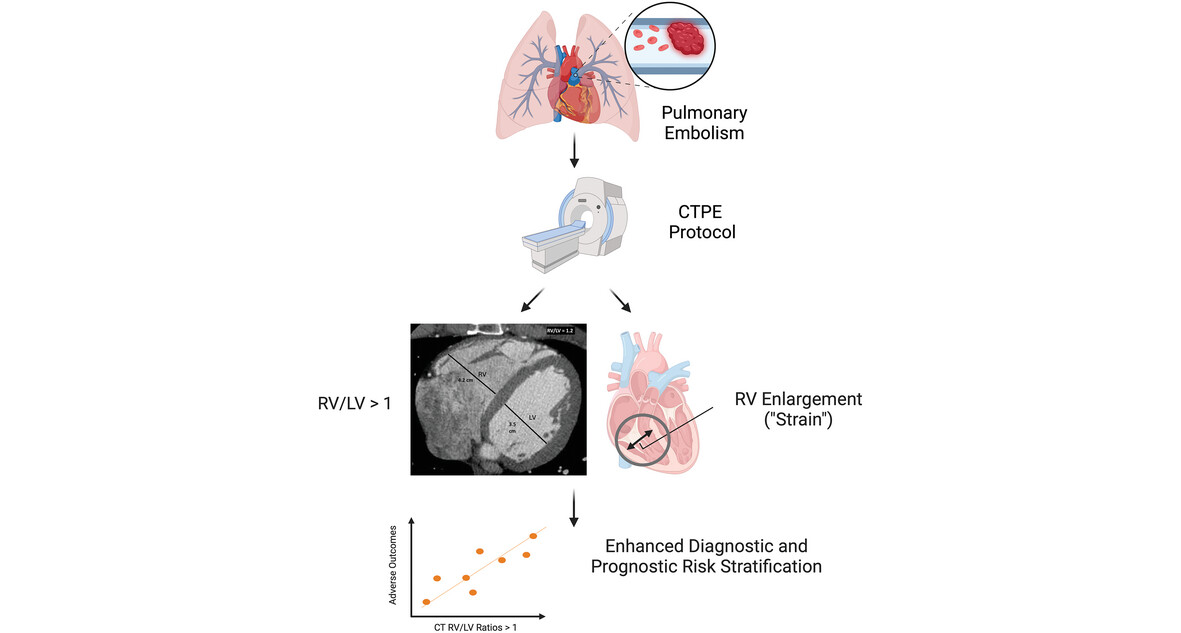
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of RV Strain Defined as RV/LV Ratio on Chest CT in Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Systematic Review
- First Published: 03 March 2025
REVIEW
Multimodality Imaging and Immune-Related Adverse Events During Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment: Where Do We Stand?
- First Published: 03 March 2025
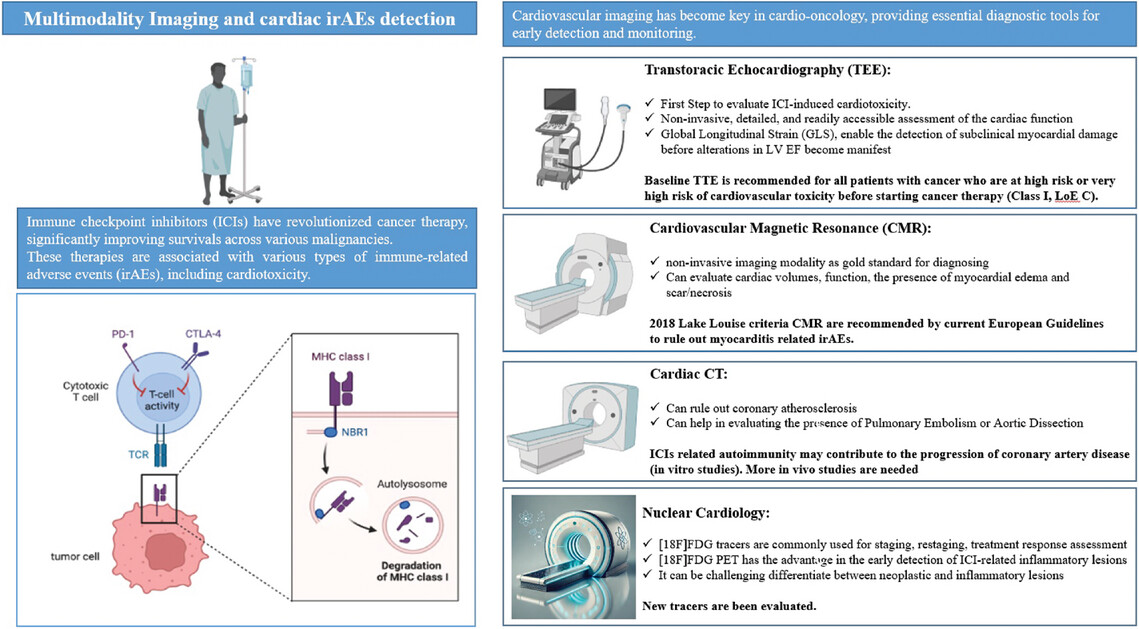
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy, significantly improving survivals across various malignancies, but may be associated with various types of immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Multimodality imaging, including transthoracic echocardiography, cardiac CT, cardiovascular magnetic resonance, and nuclear cardiology are fundamental diagnostic tools for the early detection of cardiotoxicity and monitoring.
INVITED REVIEW
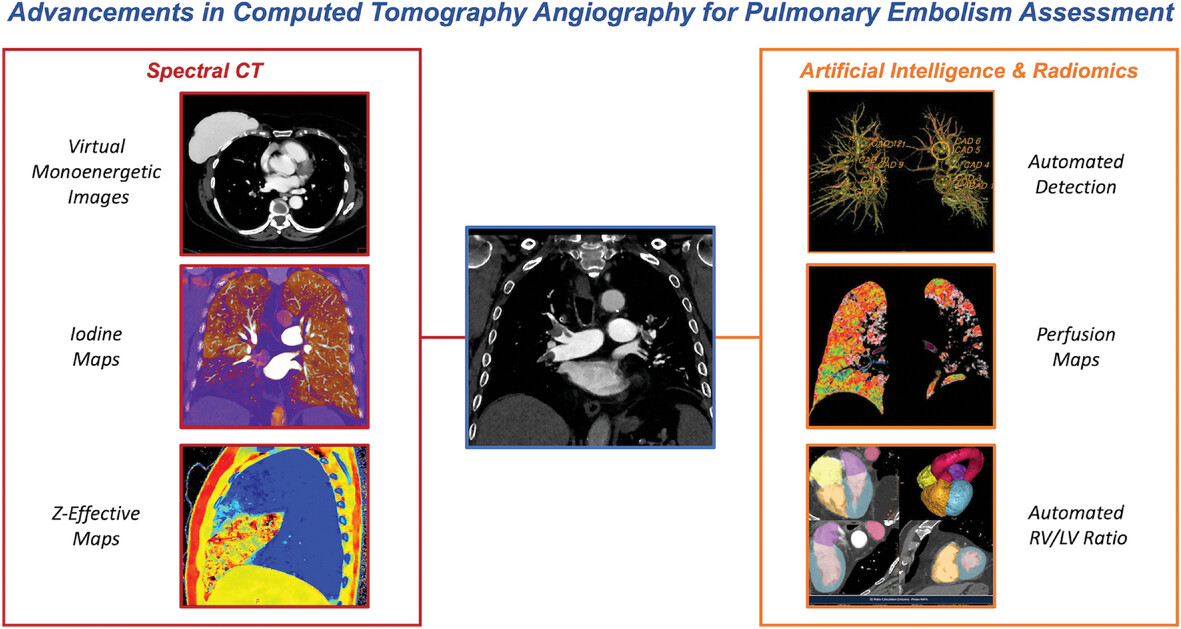
Advancements in Computed Tomography Angiography for Pulmonary Embolism Assessment
- First Published: 03 March 2025
CASE IMAGE
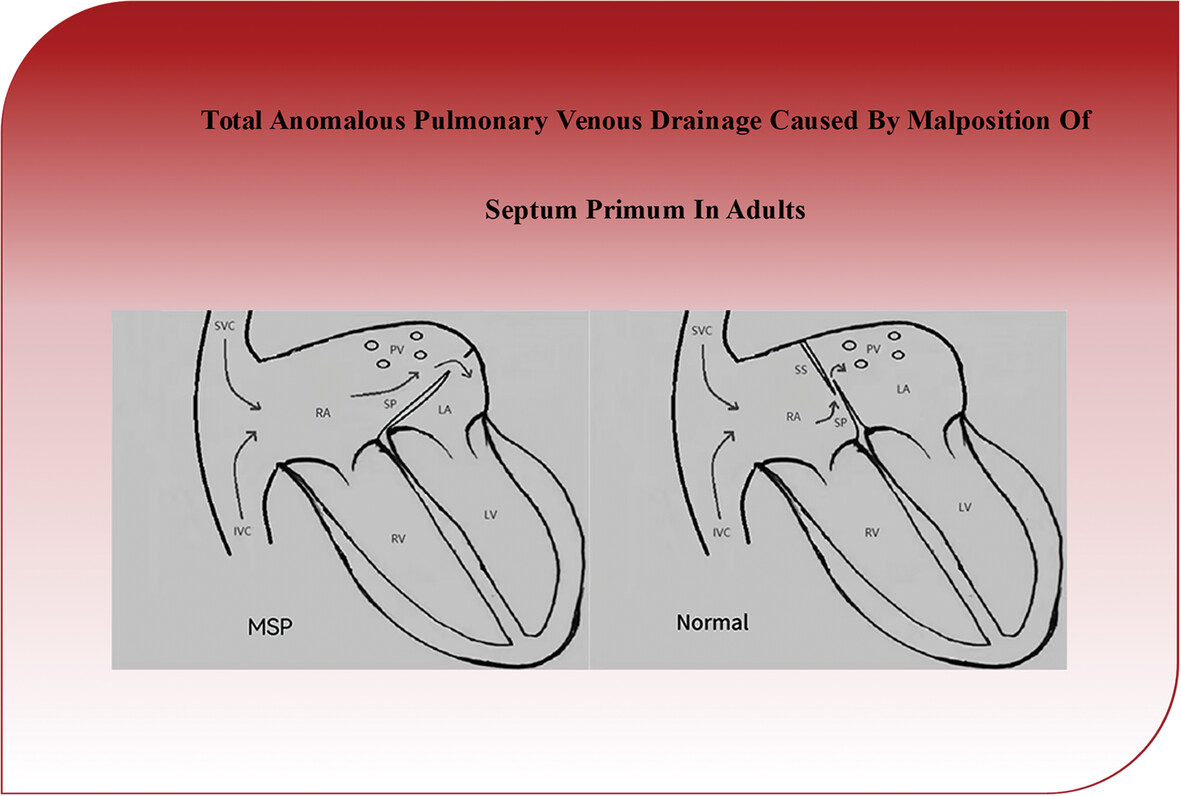
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Drainage Caused by Malposition of Septum Primum in Adults
- First Published: 03 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Myocardial Dysfunction and Risk of Long COVID in Patients Recovered From Mild and Moderate COVID-19
- First Published: 03 March 2025
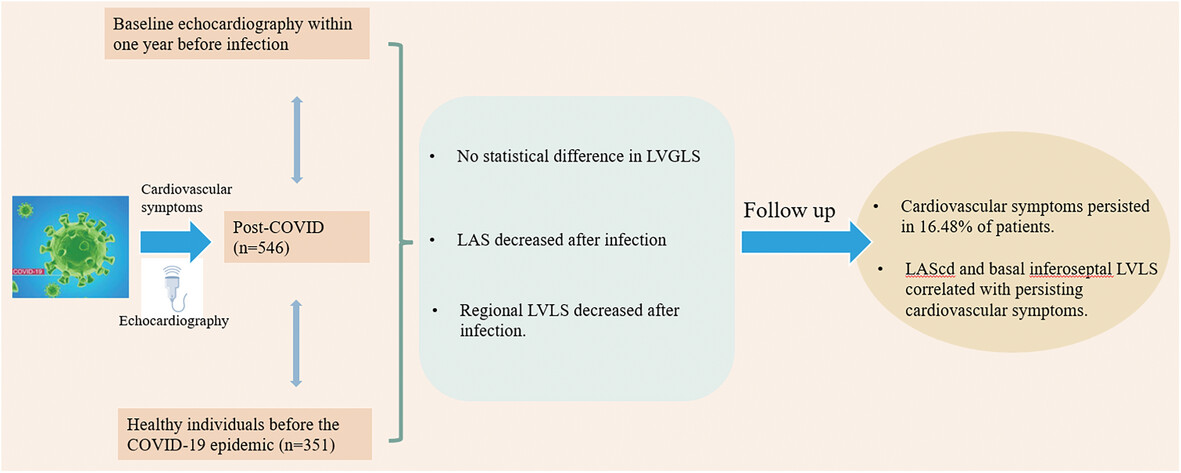
Patients who recovered from COVID-19 and presented to our hospital for echocardiography due to cardiovascular symptoms during the Omicron surge were retrospectively reviewed. Myocardial strains of 546 such recovered patients, both pre- and post-infection, were compared with those of COVID-19-free controls. Results indicated that post-infection, left ventricular global longitudinal strain (LVGLS) stayed constant, yet left atrial strain (LAS) and regional left ventricular longitudinal strain (LVLS) declined. After a 1-year follow-up, 16.48% of patients had persistent cardiovascular symptoms, which were linked to LA strain and basal inferoseptal LVLS.
COMMENTARY
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
LIST OF REVIEWERS
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Predicting the Need for Pulmonary Venous Reintervention in Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection: The Role of Preoperative Echocardiographic Metrics
- First Published: 06 March 2025
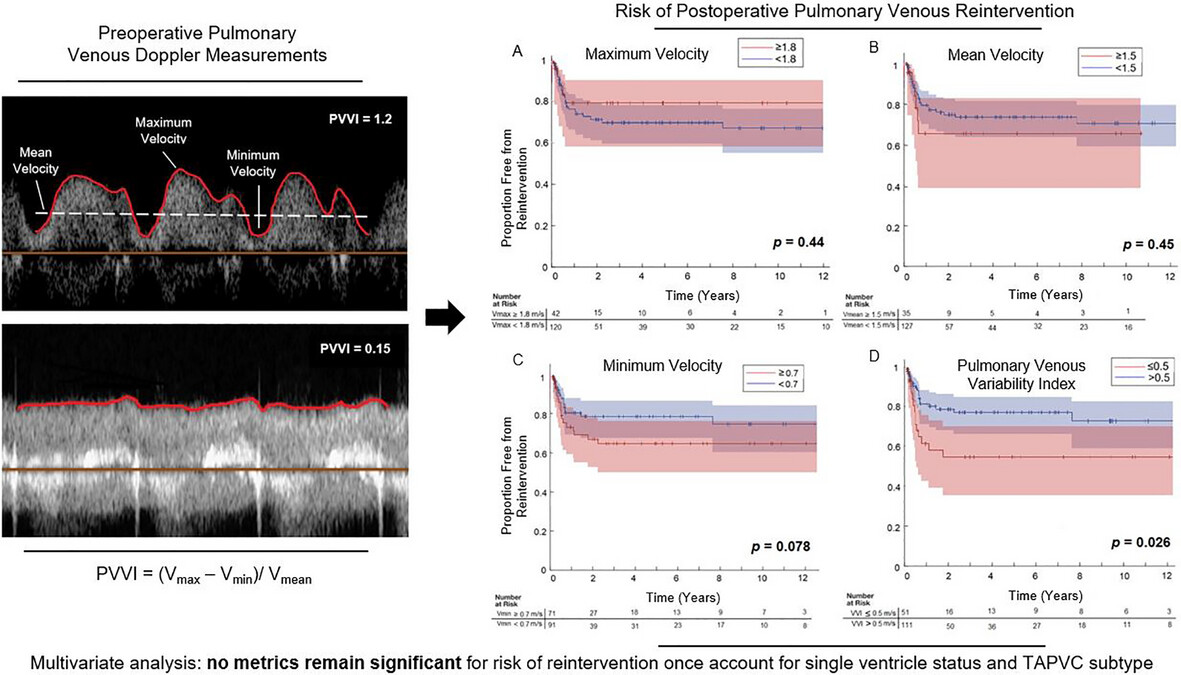
In patients with total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC), preoperative echocardiographic metrics were collected and used to calculate the pulmonary venous variability index (PVVI). PVVI ≤ 0.5 was the only measure predictive of catheter-based or surgical pulmonary venous reintervention after initial repair; however, this association was lost when single ventricle status and TAPVC subtype were incorporated into multivariate analysis .
CASE IMAGE
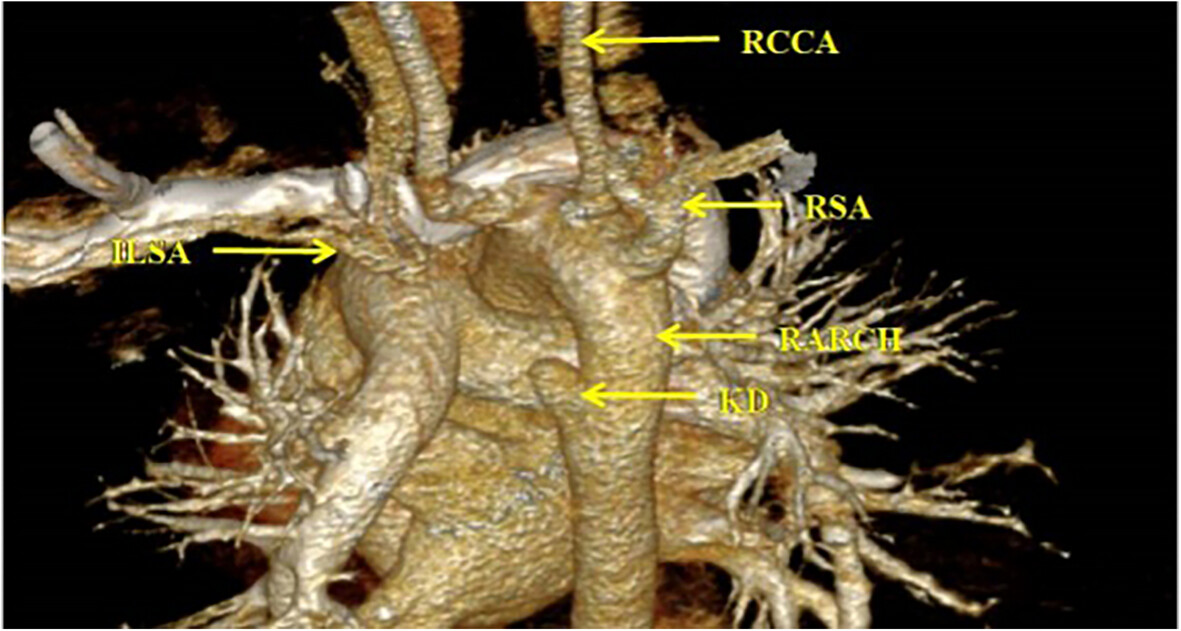
Right Aortic Arch With Kommerell Diverticulum and a Rare Type of Isolated Left Subclavian Artery
- First Published: 10 March 2025
COMMENTARY
Breathless Nights: How Obstructive Sleep Apnea Affects the Right Heart
- First Published: 11 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
CASE IMAGE
Multimodality Imaging Approach for a Transient Ischemic Stroke as a First Manifestation of Papillary Fibroelastoma
- First Published: 11 March 2025
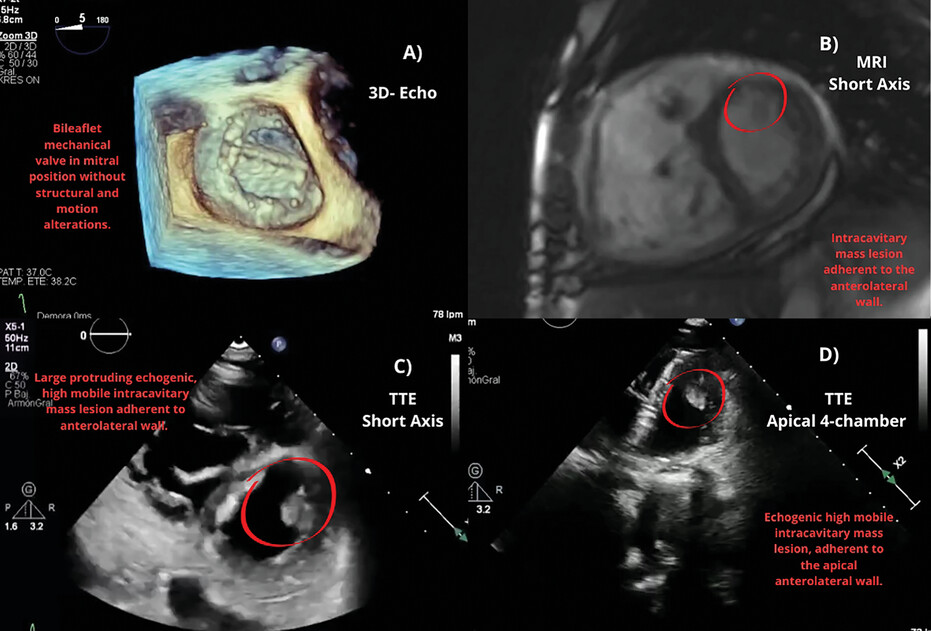
Take home messages
1. Despite being considered a benign tumor, the high reported incidence of embolic events increasingly warrants surgical resection, regardless of size, especially in patients with a history of cardiovascular risk factors.
2. Multimodal imaging evaluation plays a crucial role in distinguishing intracardiac masses, relying on the physician's ability to discern characteristic findings. Proper assessment leads to appropriate management decisions based on suggestive findings.
COMMENTARY
CASE IMAGE
INVITED REVIEW
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor–Related Myocarditis
- First Published: 11 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A New Method Using the Four-Chamber View to Identify Fetuses With Subsequently Confirmed Postnatal Aortic Coarctation
- First Published: 12 March 2025
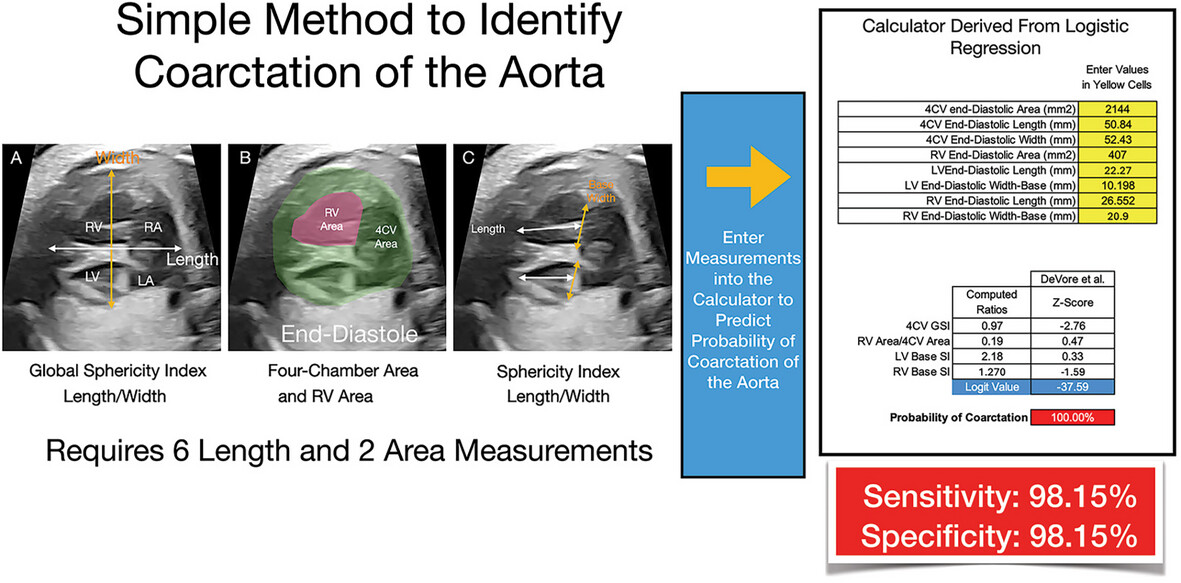
From a study of 54 fetuses with Coarctation of the Aorta and 54 with a false-positive diagnosis of Coarctation of the Aorta we developed a calculator that only required 8 end-diastolic measurements from the 4-chamber view to predict Coarctation of the Aorta with a Sensitivity of 98.15% and specificity of 98.15%.
Changes in Left Ventricular Function Assessed by 3D Echocardiography During Severe Central Hypovolemia in Healthy Humans
- First Published: 12 March 2025
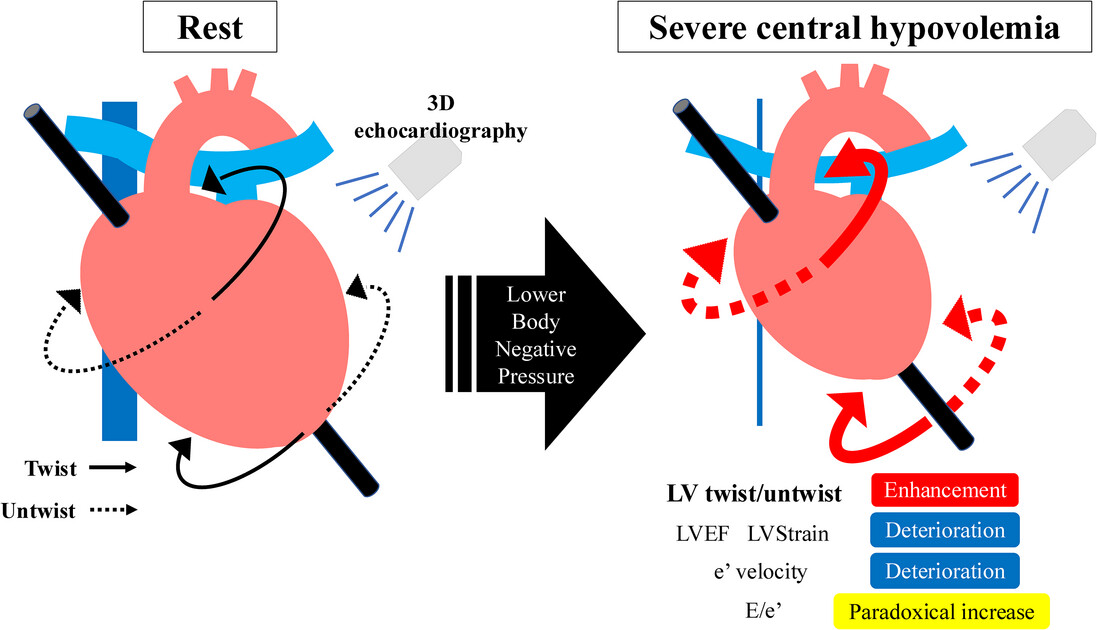
The purpose of the present study was to clarify the changes of left ventricular twisting and untwisting motions during severe central hypovolemia using 3D echocardiography. The present findings by three-dimensional (3D) echocardiography indicate that in healthy humans, LV twist/untwist function is enhanced during severe central hypovolemia. On the other hand, conventional echocardiographic indices for LV contractility, diastolic relaxation, and myocardial strain deteriorated. In particular, E/e’ paradoxically increased during severe central hypovolemia. These findings suggest that to accurately assess hemodynamic conditions, measurement of twist/untwist function may be useful in addition to conventional echocardiographic indices.
Right Atrial Function and Right Ventricular Diastolic Function and Their Relation With Exercise Capacity in OSAS
- First Published: 16 March 2025
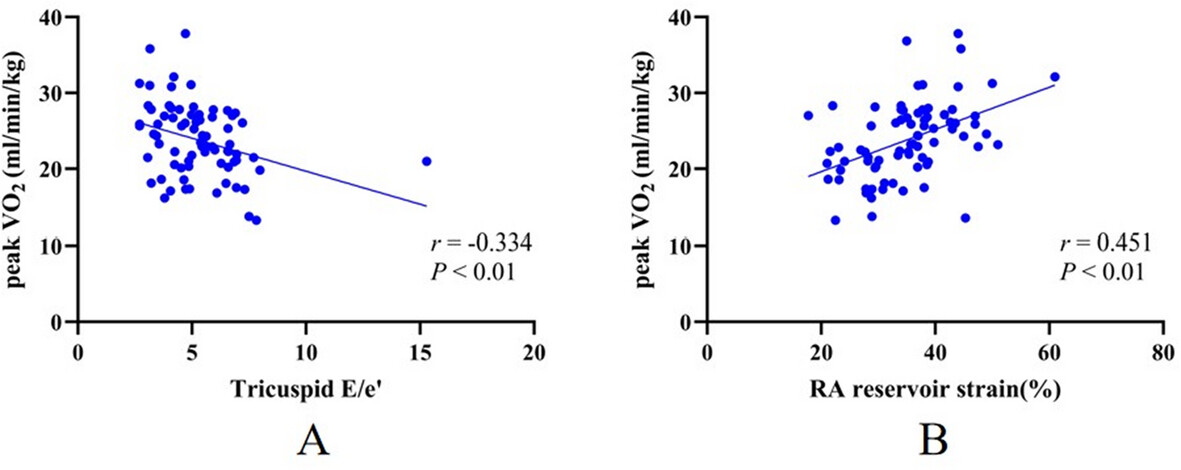
We found that patients with OSAS exhibit reduced right ventricular diastolic function and right atrial reservoir strain (RARS). Additionally, the TV E/e′ (Figure A) and RARS (Figure B) are correlated with peak VO2 in these patients, suggesting that the decline in exercise capacity in OSAS patients is related to RV diastolic function and RA function.
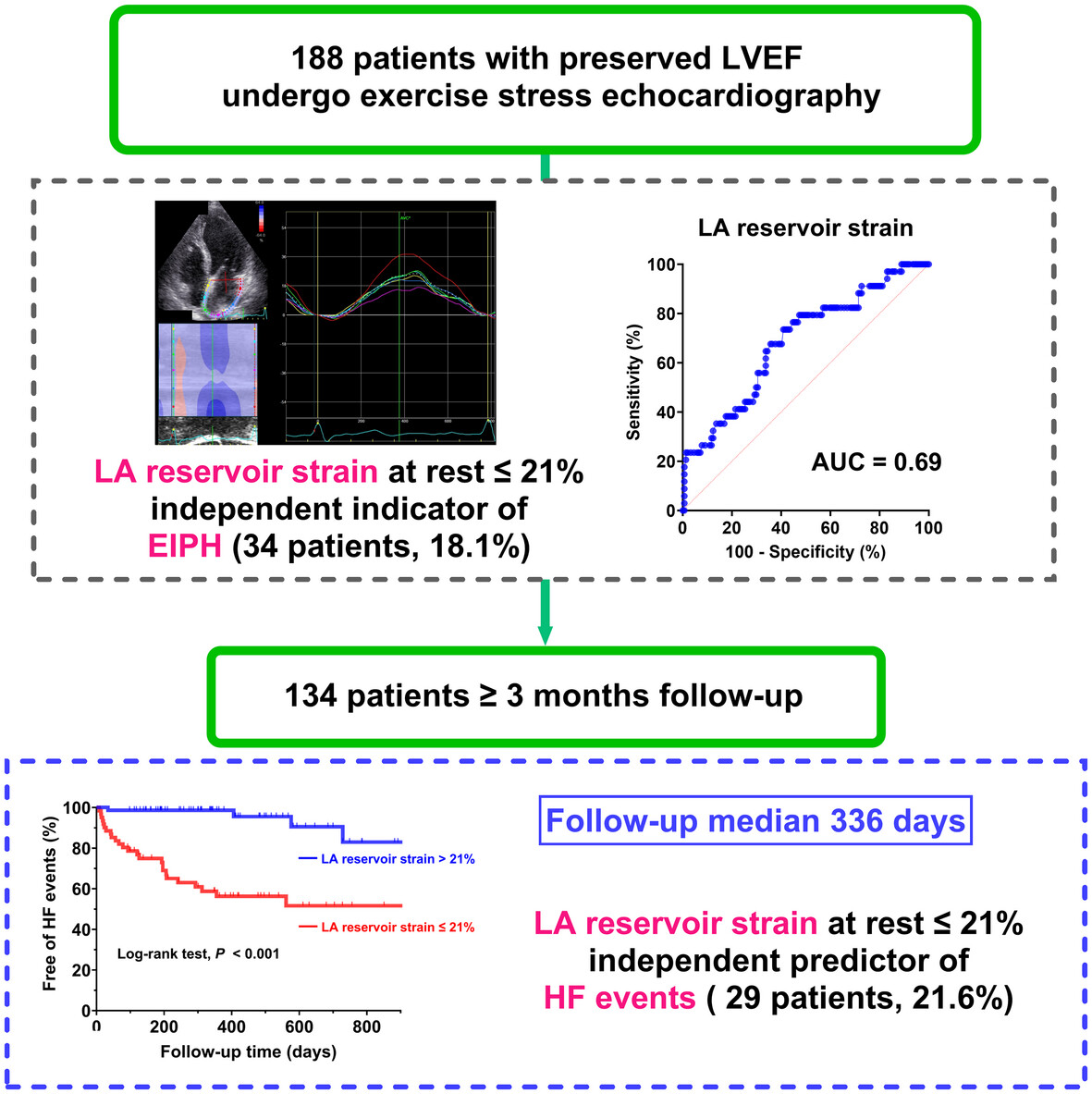
Impaired Left Atrial Reservoir Strain Causes Exercise-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients With Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction
- First Published: 20 March 2025