Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Titelbild Chem. Ing. Tech. 3/2023
- Page: 297
- First Published: 22 February 2023

Computer keyboard and laboratory glass in blue light. Science concept. Copyright: isak55@Shutterstock
Editorial
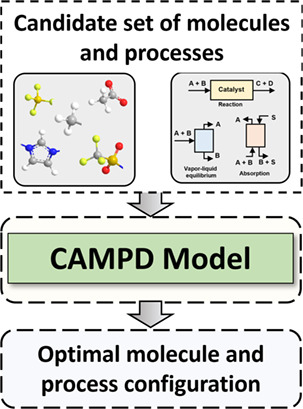
Computer-Aided Molecular and Process Design
- Page: 299
- First Published: 22 February 2023
Inhalt
Aus den Gesellschaften
Essays
How to Decarbonize Our Energy Systems: Process-Informed Design of New Materials for Carbon Capture
- Pages: 309-314
- First Published: 03 January 2023
Decarbonisation from a variety of industrial and power emission sectors highlights a marked need for capture technologies. Advanced tailored sorbent-based technologies offer higher capture capacities than the state-of-the-art systems. The PrISMa project addresses this challenge by integrating materials design with process design and environmental considerations.
Reviews
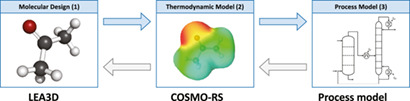
An Overview of Computer-aided Molecular and Process Design
- Pages: 315-333
- First Published: 30 January 2023
The choice of enabling materials in sustainable chemical processes directly influences the overall performance. Computer-aided molecular and process design is the perfect tool to determine the optimal process configurations, operating conditions, and material structures. It's current state-of-the-art is discussed here.
Research Articles
A Workflow for Crystallization Process Design with Simultaneous Process Optimization and Solvent Selection based on the Perturbed-Chain Statistical Associating Fluid Theory
- Pages: 334-343
- First Published: 16 January 2023
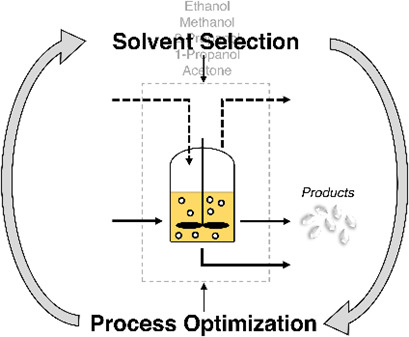
This work presents a perturbed-chain statistical associating fluid theory (PC-SFAT)-based solvent selection and process optimization workflow for solution crystallization processes with readily executable computational tools that are usable with minimal expertise. The application of the workflow is illustrated via a case study on aspirin crystallization.
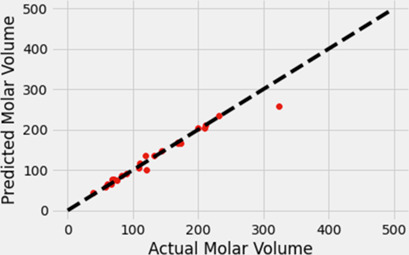
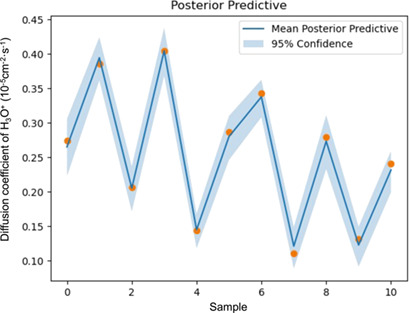
Predicting Material Properties of Methane Hydrates with Cubic Crystal Structure Using Molecular Simulations
- Pages: 344-352
- First Published: 22 December 2022
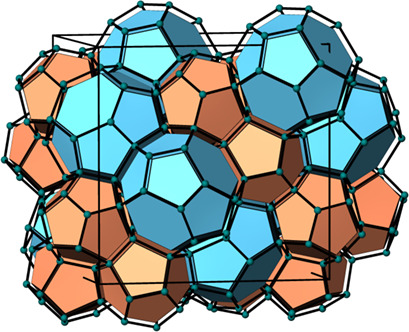
Molecular simulations are used to calculate energy profiles of the cavities in methane hydrates and to derive thermodynamic material parameters. The aim is to obtain non-measurable material parameters comparatively easily in this way and thus to be able to parameterize material data models more universally.
Design and Analysis of Charge-Reduced Refrigerant Cycles Using R290
- Pages: 353-362
- First Published: 03 January 2023
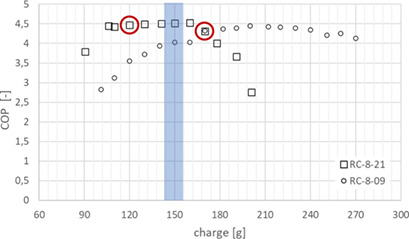
The article presents an evaluation method using an experimental and simulation-based analysis of refrigerant circuits to generate more reliable design knowledge for low refrigerant charge applications. The results show promising steps towards a reliable prediction of capacity, coefficient of performancet, and refrigerant charge for circuits with 100 g to 300 g of propane.
Using Artificial Neural Networks to Predict Physical Properties of Membrane Polymers
- Pages: 363-367
- First Published: 22 November 2022
From Molecules to Heat-Integrated Processes: Computer-Aided Design of Solvents and Processes Using Quantum Chemistry
- Pages: 368-380
- First Published: 30 November 2022
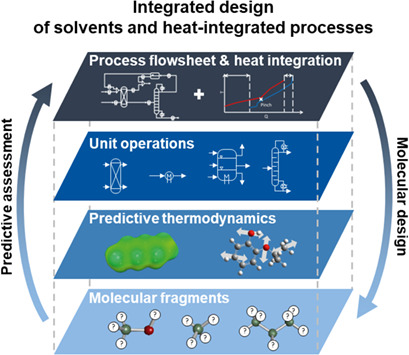
The integrated design of solvents and processes links molecular structures to process performance by predictive assessment across multiple scales. The presented method solves the inverse problem by combining process flowsheet optimisation including heat integration with molecular design. Thereby, we can select molecules that are optimal regarding process-level objectives.
Rather the Rule than the Exception: Non-Convex Pareto Sets and their Navigation in Distillation Processes
- Pages: 381-390
- First Published: 29 November 2022
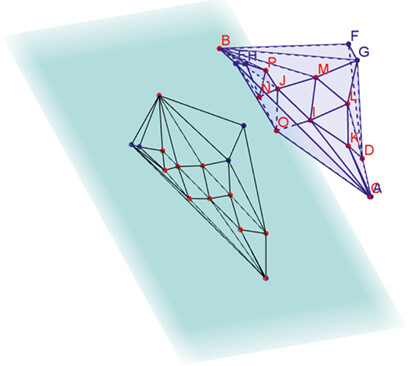
Novel algorithms for exploring Pareto sets are applied to distillation processes. Product purities are maximised while total heat duties are minimised. The illustrated Pareto set consists of both convex (blue dots) and non-convex (red dots) regions. This article shows how such Pareto sets can be navigated interactively using a ray tracing technique.
Simultaneous Optimization of Process Design and Solvent in a Flowsheet Simulator
- Pages: 391-404
- First Published: 18 November 2022
To solve the simultaneous process and fluid optimization problem for industrial applications, the two-stage CoMT-CAMD approach is implemented in CHEMASIM, the in-house flowsheet simulator of BASF SE. The required modifications of the method and the extension of the user interface of CHEMASIM results are presented for single and multiobjective optimization problems of process-fluid selection and design.
Simulation of Compression Heat Pump Cycles Using NH3/H2O Mixtures to Estimate Their Working Domains
- Pages: 405-415
- First Published: 22 November 2022
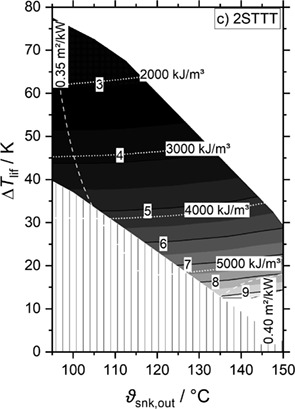
The working domain of different NH3/H2O heat pump cycles is investigated to provide temperatures up to 150 °C. An algorithm is developed, which maximizes coefficient of performance and volumetric heat capacity and minimizes compressor discharge temperature for given external temperatures and internal pressure limits.
COSMO-CAMPED – Solvent Design for an Extraction Distillation Considering Molecular, Process, Equipment, and Economic Optimization
- Pages: 416-426
- First Published: 29 November 2022
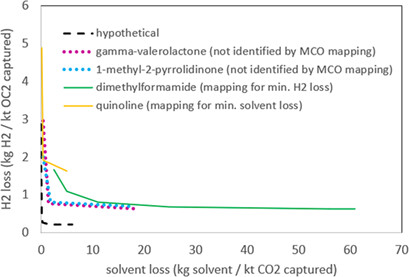
Ex-Ante Optimal Design of Sustainable Phase Change Materials for Latent Heat Storage
- Pages: 427-437
- First Published: 17 November 2022
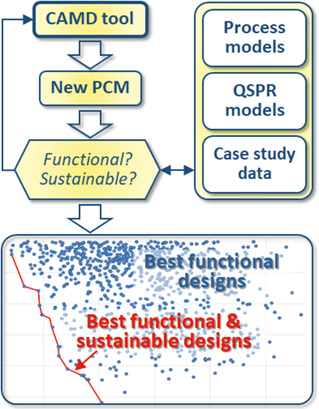
This work proposes a systematic framework to search for phase change materials that are sustainable-by-design without compromise on their functional performance. Computer-aided molecular design tools, a simple process simulation model, and QSPR models are applied to predict thermophysical properties, ecotoxicity and climate change indicators.
A Fragrance Prediction Model for Molecules Using Rough Set-based Machine Learning
- Pages: 438-446
- First Published: 02 November 2022
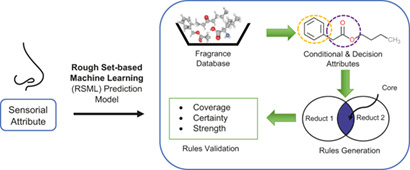
Fragrance is a desirable and often essential attribute in various consumer products. To predict fragrance attributes of molecules, a novel machine learning based methodology has been developed. Rough set-based machine learning is used to link fragrance to molecular structure. The factors affect the perception of fragrance has also been analysed.
Computer-Aided Design of Crosslinked Polymer Membrane Using Machine Learning and Molecular Dynamics
- Pages: 447-457
- First Published: 07 October 2022
A novel computer-aided crosslinked polymer design framework is proposed, in which machine learning and molecular dynamics are integrated for the design of an optimal polymer structures. Two case studies are presented to illustrate the application of the proposed CAPD framework, and the optimized results are verified.
A Multi-Criteria Study of Optimal Working Fluids for High Temperature Heat Pumps
- Pages: 458-466
- First Published: 05 December 2022
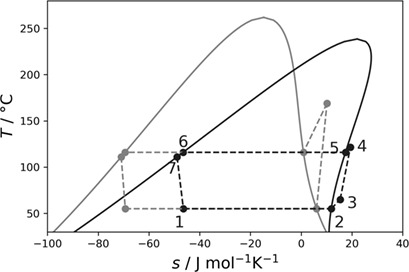
Suitable working fluids for high temperature heat pumps are identified from a COMT-CAMD approach. PC-SAFT and a realistic model for the ideal gas heat capacity are applied as thermodynamic model. Results are presented for a one-stage and a two-stage heat pump cycle. Cyclobutane and butene isomers are identified as promising working fluids.
Vorschau
Überblick
Überblick Inhalt: Chem. Eng. Technol. 3/2023
- Page: 471
- First Published: 22 February 2023