Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover story: Eur. J. Immunol. 7'22
- First Published: 11 July 2022
Our cover features H&E staining of colon sections from RAG-1−/− mice after adoptive transfer of regulatory T cell-depleted CD4 T cells purified from Shn-3 deficient mice. Shn3 is a transcription factor expressed by activated T cells and supports the expression of Th2-type cytokines. In this autoimmune colitis model, Shn3-deficient T cells caused enhanced Th1 responses and exacerbated inflammation, and accelerated weight loss in the recipient mice. The image is taken from Cunha et al. (pp. 1077–1094), where the authors present the Th1-Th2 differentiation is controlled by Shn3 which is induced during a late phase of antigen stimulation and promotes GATA3 expression.
Issue Information
Contents
Forum
Issue Highlights
Obituary
Reinhold E. Schmidt: An exceptionally gifted physician and excellent scientist
- Pages: 1017-1018
- First Published: 11 July 2022
News & EFIS
A BRIEF HISTORY OF BELGIAN IMMUNOLOGY AND ITS SOCIETY
- Pages: 1019-1023
- First Published: 11 July 2022
Highlights
Reviews
Basic
Innate immune signaling and immunothrombosis: New insights and therapeutic opportunities
- Pages: 1024-1034
- First Published: 15 May 2022
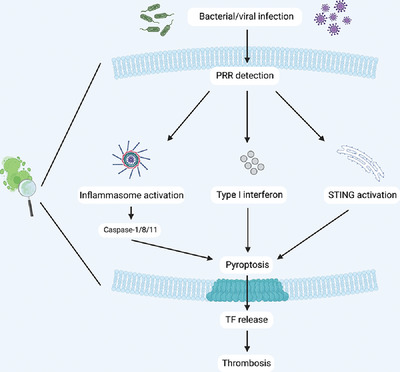
Detection of pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses, by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) triggers activation of components of immune cell defense pathways such as the inflammasome, type I interferon, and STING. This culminates in proinflammatory cell death, termed pyroptosis, and release of the coagulation activator, tissue factor (TF). This process of immune cell activation triggering coagulation, termed immunothrombosis, is a hallmark of coagulopathies such as sepsis and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Clinical
Intestinal homeostasis and inflammation: Gut microbiota at the crossroads of pancreas–intestinal barrier axis
- Pages: 1035-1046
- First Published: 27 April 2022
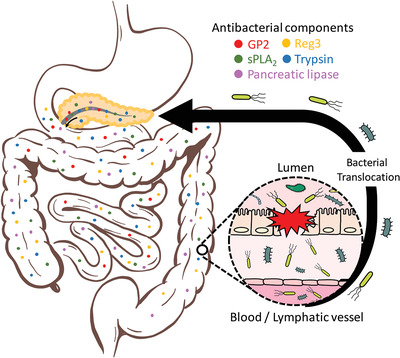
The pancreas plays a pivotal role in protecting the gastrointestinal tract from the breakdown of the mucosal barrier and the expansion of pathobionts that can lead to systemic disease. This crosstalk highlights the emerging concept of a pancreas-gut axis in the control of host responses to infection.
IL-13 in dermal type-2 dendritic cell specialization: From function to therapeutic targeting
- Pages: 1047-1057
- First Published: 02 June 2022

The differentiation and function of dermal CD11blow cDC2s requires the cytokine IL-13 and the transcription factors STAT6 and KLF4. Here, we discuss the properties of this skin-unique cDC2 population in the context of cDC2 heterogeneity across different tissues, the development of Th2 immune responses, and inflammatory skin disease.
Adaptive immunity
Short Communications
Basic
Polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 regulates the activation of mouse CD8 T cells
- Pages: 1058-1068
- First Published: 22 April 2022
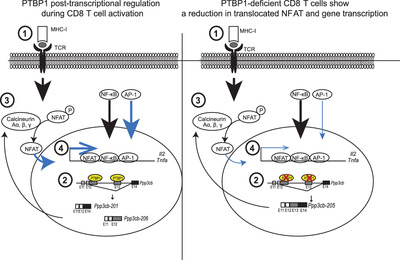
The RNA-binding protein PTBP1 is essential during early events following T-cell activation by regulating the alternative splicing of genes including that encoding calcineurin Aβ isoforms. These findings provide insight into how PTBP1 regulates gene expression essential for the optimal activation of T cells.
Human cDC1s display constitutive activation of the UPR sensor IRE1
- Pages: 1069-1076
- First Published: 13 April 2022
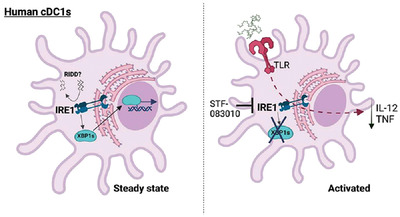
Human type 1 conventional dendritic cells (cDC1s) display constitutive activation of the IRE1/XBP1s axis of the UPR in steady state. Proinflammatory cytokine production by activated cDC1s is partly dampened upon inhibition of the IRE1 RNase domain, uncovering a role of the pathway in the biology of the human DC lineage.
Molecular immunology and signaling
Research Article
Basic
Schnurri 3 promotes Th2 cytokine production during the late phase of T-cell antigen stimulation
- Pages: 1077-1094
- First Published: 01 May 2022
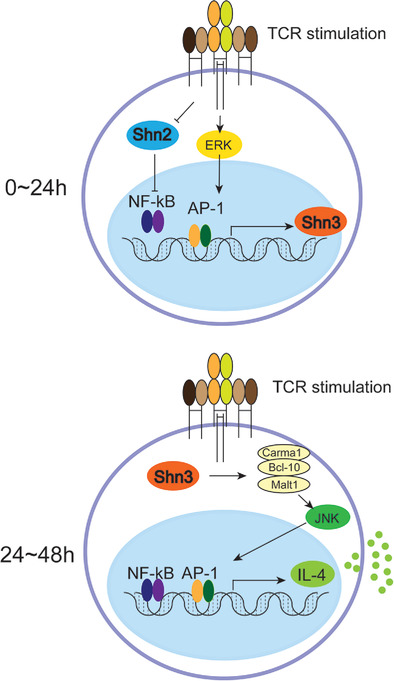
Earlier studies showed that antigen receptor signal strength can dictate Th1/Th2 polarization. Prolonged antigen receptor signaling induces the expression of a transcription factor, SHN-3, which is required for initial Th2-cell differentiation. Loss of SHN-3 expression causes a reduction in IL-4 production and causes Th1-dominant in vivo immune responses.
Immunity to infection
Research Article
Basic
Hobit and Blimp-1 regulate TRM abundance after LCMV infection by suppressing tissue exit pathways of TRMprecursors
- Pages: 1095-1111
- First Published: 07 April 2022
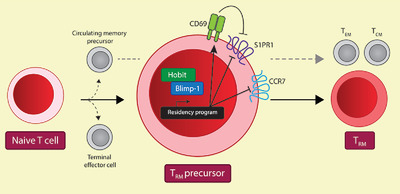
Tissue-resident memory T cells (Trm) permanently lodge themselves in peripheral tissues to capture invading pathogens. We found that the transcription factors Hobit and Blimp-1 already acted in Trm precursors to suppress tissue-exit pathways. Our findings imply that establishment of the Trm lineage requires lodgment of their precursors early after infection.
Short Communication
Clinical
Host transcriptomic signatures of tuberculosis can predict immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV patients
- Pages: 1112-1119
- First Published: 09 April 2022
Research Article
Clinical
Anti-IFN-α/-ω neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients correlate with downregulation of IFN response and laboratory biomarkers of disease severity
- Pages: 1120-1128
- First Published: 13 April 2022
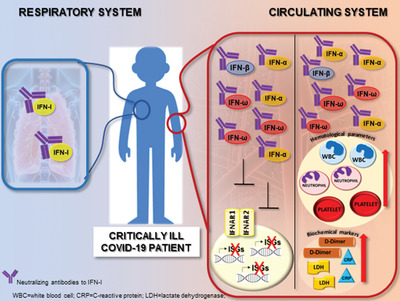
Autoantibodies capable of neutralizing multiple IFN-α subtypes and IFN-ω can be found in severe COVID-19 patients, preferentially males. Anti-IFN-I neutralizing antibodies (NAB) positive patients present a defective IFN response and have raised levels of biochemical and hematological parameters predictive of severe COVID-19.
Allergy and inflammation
Research Articles
Clinical
Mesenchymal stromal cells-derived small extracellular vesicles modulate DC function to suppress Th2 responses via IL-10 in patients with allergic rhinitis
- Pages: 1129-1140
- First Published: 12 April 2022
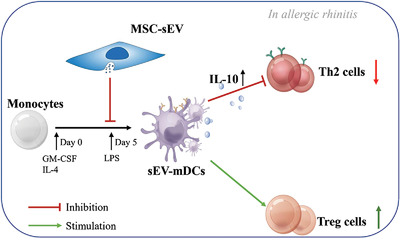
MSC-sEV regulated the differentiation and function of dendritic cells in allergic rhinitis. Peripheral monocytes treated with GM-CSF, IL-4, and LPS differentiated into dendritic cells. DCs treated with MSC-sEV inhibited the type 2 immune response from allergic rhinits. sEV-mDC exhibited a regulatory phenotype by the production of IL-10 and induced Treg cells. GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, LPS: lipopolysaccharide, mDCs: mature dendritic cells, MSC: mesenchymal stromal cells, sEV: small extracellular vesicles, Treg: regulatory T.
NLRP3 inflammasome triggers interleukin-37 release from human monocytes
- Pages: 1141-1157
- First Published: 16 April 2022
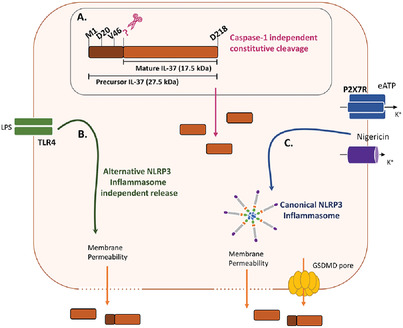
A. In human monocytes, IL-37 cleavage occurs constitutively but not at positions D20 or V46. B. Long-term LPS stimulation induces mature IL-37 release independently of alternative NLRP3 inflammasome but dependent on membrane permeability. C. Mature IL-37 release is mediated by canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation, gasdermin-D, and membrane permeability.
Immunodeficiencies and autoimmunity
Research Articles
Basic
A dormant T-cell population with autoimmune potential exhibits low self-reactivity and infiltrates islets in type 1 diabetes
- Pages: 1158-1170
- First Published: 07 April 2022
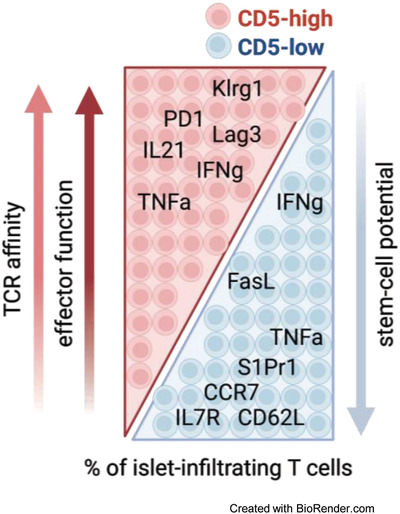
Low level of CD5 expression identified phenotypically dormant T cells with autoimmune potential, which was revealed upon cell transfer. Transcriptional signature indicated stem-cell memory-like phenotype and was similar to low-affinity insulin-specific T cells, suggesting that TCR affinity guides autoimmune T-cell fate decisions and stem-like capacity.
Clinical
Follicular helper T cell signature of replicative exhaustion, apoptosis, and senescence in common variable immunodeficiency
- Pages: 1171-1189
- First Published: 13 May 2022
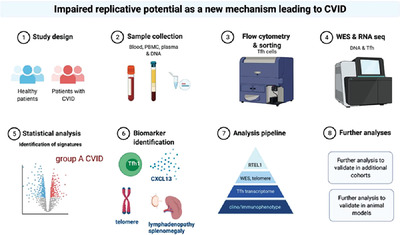
Patients with common variable immunodeficiency with no previous genetic diagnosis presenting additionally one autoimmune symptom were compared to healthy subjects. Circulating follicular helper T (Tfh) cells were analyzed for their phenotype and function by flow cytometry, while their transcriptome was determined with RNA seq. Genetic analysis was performed by WES and validated by Sanger Sequencing. An integrated pipeline led to the identification of a cluster of patients characterized by a Th1 Tfh signature, elevated plasma CXCL13 levels, shortened telomeres, and enlarged lymph nodes and spleen. Rare monoallelic mutations in RTEL1 were identified as a possible common denominator. Further analyses revealed Tfh replicative exhaustion as a possible underlying mechanism.
Technical report
An optimized platform for efficient siRNA delivery into human NK cells
- Pages: 1190-1193
- First Published: 13 April 2022

The molecular networks that regulate natural killer (NK) cell functions are not completely understood. Here, we present a workflow for efficient delivery of siRNA into human NK cells without compromising viability. This methodology represents a promising approach for rapidly interrogating gene functions in primary human NK cells.
Notes and Insights
SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells are generated in less than half of allogeneic HSCT recipients failing to seroconvert after COVID-19 vaccination
- Pages: 1194-1197
- First Published: 07 April 2022
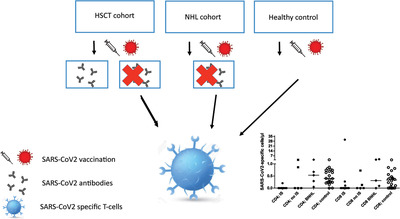
Little is known about the cellular immune response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients after HSCT and B-NHL with iatrogenic B-cell aplasia. In nonseroconverted HSCT patients, induction of specific T-cell responses was assessed. The majority of allogeneic HSCT patients not showing humoral responses to vaccination also fail to mount antigen-specific T-cell responses.
Antibody response to herpes simplex virus-1 is increased in autoimmune encephalitis
- Pages: 1198-1200
- First Published: 08 April 2022