Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Overview
Contents
Editorial
Forum
Scientific Highlights
Reviews
No Product Design without Process Design (Control)?†
- Pages: 723-729
- First Published: 28 April 2010
The importance and necessity of process design for product design is discussed for four selected examples in the field of crystallization, demonstrating the potential of process design and process control and thus the significance of the entire knowledge and understanding of a crystallization process to design a product with desired properties.
Prediction of Activity Coefficients for Uni-univalent Electrolytes in Pure Aqueous Solution
- Pages: 730-742
- First Published: 28 April 2010
The activity coefficients equations in the literature are tested with activity coefficients obtained by using the best extended Hückel equations for KCl, NaCl, RbCl, KBr, RbBr, CsBr, KI, RbI, KNO3, and KH2PO4 solutions at 298.15 K. These Hückel equations probably reproduce the best thermodynamic data from solutions of these electrolytes within experimental error up to the molality of the saturated solutions.
Research Articles
Closed-Loop Control of Reactive Crystallization. Part I: Supersaturation-Controlled Crystallization of L-Glutamic Acid
- Pages: 743-750
- First Published: 28 April 2010
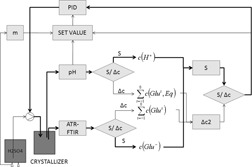
The feedback control policy of the reactive crystallization process was studied. The concentration of L-glutamic acid was determined from measured MID-IR ATR-FTIR spectra based on a multivariate model. The importance of the supersaturation level control at the nucleation moment and the effect of different supersaturation levels on the quality of the product crystals was studied using a 50-L crystallizer.
Closed-Loop Control of Reactive Crystallization PART II: Polymorphism Control of L-Glutamic Acid by Sonocrystallization and Seeding
- Pages: 751-756
- First Published: 28 April 2010
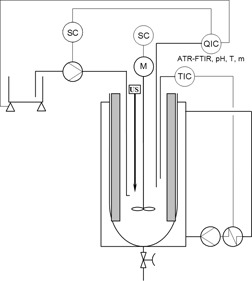
Attempts are made to control the mass fraction of the α-polymorph of L-glutamic acid in a semi-batch process during a controlled supersaturation. The impact of different nucleation methods is studied and results indicate that supersaturation-controlled sonocrystallization or supersaturation-controlled seeding can be used to control polymorphism. The novelty herein is the simplicity of the method directing the generation of a desired polymorph.
An Alternative Technology to Form Tablets
- Pages: 757-761
- First Published: 28 April 2010

The proof of concept of a freeze casting process is provided for the conversion of heat and/or pressure sensitive and difficult-to-tablet pharmaceutical ingredients into a solid tablet form. The new process produces high porous solid tablet bodies and their tensile strength and disslution rates are compared to commercially available tablets.
Estimation of Reliable Parameters for Solid-Liquid Equilibrium Description of Chiral Systems
- Pages: 767-774
- First Published: 28 April 2010
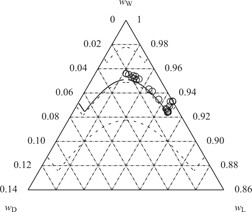
The knowledge of accurate solid-liquid phase equilibria serves as a basis for the design of crystallization processes. In this study, the predictive power of a multi-component gE model fed with limited experimental data was evaluated. The impact of uncertainties in the underlying experimental data and the obtained model parameters was of particular interest.
Quality-Controlled Reactive Crystallization of SrSO4 To Produce High-Valued Chemicals
- Pages: 775-779
- First Published: 28 April 2010
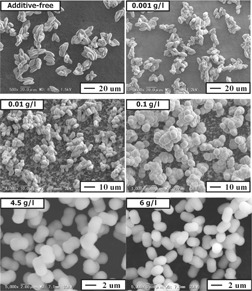
Precipitation of monodispersed SrSO4 particles was carried out in the presence of polyethylenimine (PEI), focusing on the influence of PEI dosage on crystal size distributions. PEI-assisted double jet techniques require no difficult controls of feeding rates, so this concept will be applicable to precipitation of other inorganic compounds for production of monodispersed nano-/microparticles.
Application of Classical Resolution for Separation of DL-Serine
- Pages: 780-786
- First Published: 28 April 2010
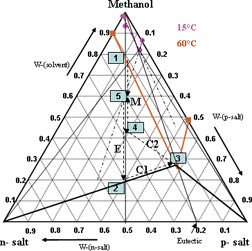
Resolution of the chiral compound-forming substance DL-serine via diastereomeric salt formation as the classical technique was investigated. Basic thermodynamic data like binary melting and ternary solubility phase diagrams were measured and discussed. A plan for a series of crystallization processes is suggested for the recovery of both n- and p-salts in pure form with a maximum possible yield.
Closed Crystalline Tubes as a Container System
- Pages: 787-790
- First Published: 28 April 2010
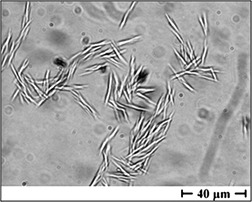
Closed hollow crystalline needles are produced based on a technique involving phase transformation of glucose monohydrate crystals into the anhydrate. The hollow nature of the needles and the uptake of a dye and a pharmaceutically active substance are demonstrated. The proof of concept for the use of such needles as a new drug delivery system is discussed.
Chromatography-Crystallization Hybrid Process for Artemisinin Purification from Artemisia annua
- Pages: 791-796
- First Published: 28 April 2010
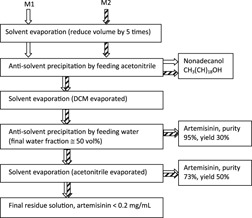
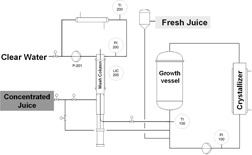
The feasibility of a chromatography-crystallization hybrid separation process for isolation and purification of artemisinin from the herbal plant Artemisia annua was studied based on the solubility and crystallization behavior of artemisinin. The suggested hybrid separation process might prove to be one of the most promising techniques for the separation of natural products from herbal plants.
Polyelectrolyte-Assisted Reactive Crystallization of SrSO4 to Obtain Monodispersed Nano/Micro-Particles
- Pages: 797-803
- First Published: 28 April 2010
Gypsum Crystallization in the Presence of Cr3+ and Citric Acid
- Pages: 804-811
- First Published: 28 April 2010

Reactive crystallization of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) was investigated at pH 3.5 and 65 °C in the presence of citric acid and Cr3+ ions. It was shown that crystal morphology, crystal size distribution, and filtration characteristics of gypsum were strongly affected by both ions. The change of morphology is related to the complex formation between Cr3+ ions and citric acid at high ion concentrations.
Drying of Pentaerythritol obtained from Batch Crystallization
- Pages: 812-820
- First Published: 28 April 2010

The influence of the process conditions, type of moisture (water, acetone, and ethanol), temperature, and pressure in the drying chamber, on the drying kinetics and the quality of the dried crystals of pentaerythritol obtained by batch crystallization from the aqueous solution was investigated in the laboratory-scale vacuum dryer.
Determination of Distribution Coefficients in 1-Ethyl-3-Methyl Imidazolium Chloride-Methylimidazole Mixtures by Zone Melting
- Pages: 821-826
- First Published: 28 April 2010
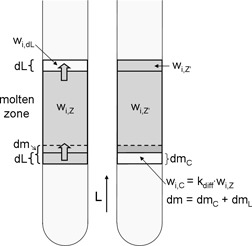
The differential distribution coefficient kdiff for crystallization of 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride (EMIMCl) out of EMIMCl-methylimidazole (MIM) mixtures was determined by the zone melting technique. For quantification of the MIM content after purification an analytical method with a combination of ion chromatography and UV/Vis detection was developed. kdiff was found to be 0.2.
Effect of Sonocrystallization on the Habit and Structure of Gemfibrozil Crystals
- Pages: 827-832
- First Published: 28 April 2010
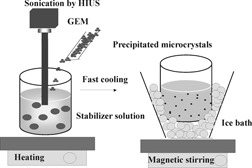
In the field of pharmaceutical preformulation, sonocrystallization is a possible way to modify the crystal habit and structure of the drugs. The aim was to present this crystallization procedure from the melt and solution applying melt emulsification and solvent diffusion methods in the case of Gemfibrozil as a model drug.
Insight into Crystallization Mechanisms of Polymorphic Hydrate Systems
- Pages: 833-838
- First Published: 28 April 2010
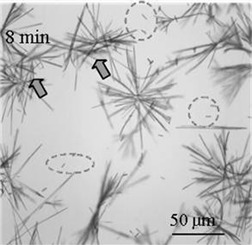
Polymorphic hydrate conversion from the unstable niclosamide monohydrate Ha to the stable niclosamide monohydrate Hb was observed during liquid-assisted ball milling in ethyl acetate-water mixture. When milled in water, the unstable niclosamide monohydrate Ha remained unchanged. In conclusion, the solvent has a significant effect on the dynamic form of the niclosamide monohydrate during ball milling.
Communication
Process Optimization of Filling Up Crystallization
- Pages: 845-850
- First Published: 28 April 2010
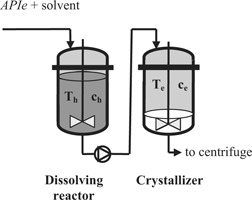
Filling up crystallization is a special cooling crystallization method in which fast cooling can be achieved in the first part of cooling profile. The optimization process for a filling up crystallization of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (APIe) is discussed, with the main goals being the production of a narrow crystal size distribution for the product.