Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Overview
Contents
Forum
Scientific Highlights
Scientific Highlights: Chem. Eng. Technol. 2/2010
- Pages: 196-197
- First Published: 28 January 2010
Reviews
Product Design and Process Engineering using the Example of Flavors
- Pages: 199-212
- First Published: 28 January 2010
In the food flavours industry, an exact knowledge of the physico-chemical properties of the flavor and carrier materials is important if process engineering measures are to be used to influence product properties. Recent progress in microencapsulation of flavors is discussed and a detailed discussion of the processes of spray drying, spray granulation, extrusion and multi-material nozzles, is provided.
Solid-state Materials and Methods for Hydrogen Storage: A Critical Review
- Pages: 213-226
- First Published: 28 January 2010
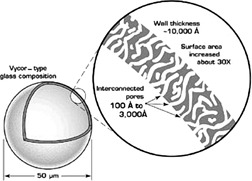
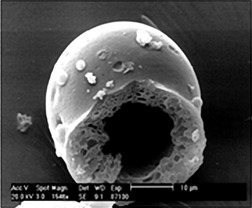
Hydrogen is important as a new source of energy for automotive applications. It is clear that efficient hydrogen storage is required to develop this technology. Hydrogen solid-state storage materials and methods including carbon based materials, metal hydrides, metal organic frameworks, hollow glass microspheres and capillary arrays, clathrate hydrates, metal nitrides and imides, doped polymer and zeolites, are critically reviewed.
Research Articles
Experimental Investigation of Performances of Microcapsule Phase Change Material for Thermal Energy Storage
- Pages: 227-230
- First Published: 28 January 2010

Microcapsule phase change material for thermal energy storage is prepared by a complex coacervation method with gelatin and acacia as wall materials and paraffin as core material in an emulsion system. The microencapsulated paraffin has a larger phase change latent heat, suitable phase change temperature, and better thermal stability, proving its great potential for thermal energy storage systems.
Effect of Ultrasound on SO2 Desorption from Sodium Alkali Desulphurization Regeneration Solution
- Pages: 231-236
- First Published: 28 January 2010
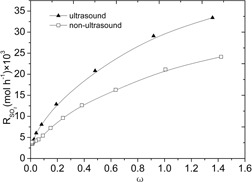
The application of ultrasound for the desorption of SO2 gas from sodium alkali desulphurization regeneration solution is reported. Ultrasound is seen to accelerate the SO2 release rate and the ultrasound enhancement effect is investigated by analyzing the compositions of desorption solutions at different pH values.
Coalescence of Water Droplets in Crude Oil Emulsions: Analytical Solution
- Pages: 237-243
- First Published: 28 January 2010
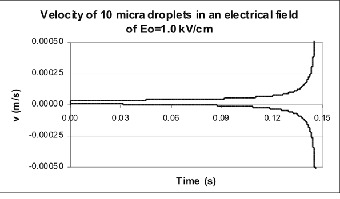
The equations of forces acting on the droplets in a water/crude oil emulsion submitted to an electrical field can be solved. Considering a pseudo-steady state, the equations enable the analytical calculation of the time between collisions and the velocities of the droplets. The influence of the operational variables (temperature, water content, and electrical field) on the separation of the phases may be analyzed and the crude-oil desalting process may be optimized.
Chitosan/titanate Nanotube Hybrid Membrane with Low Methanol Crossover for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells
- Pages: 244-250
- First Published: 28 January 2010
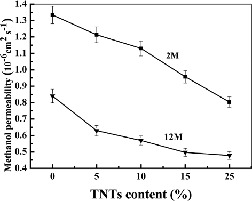
Titanate nanotubes were prepared by a hydrothermal method and incorporated into a chitosan matrix to fabricate chitosan/titanate nanotube hybrid membranes, which exhibited much lower methanol crossover and higher mechanical strength than the pure chitosan membrane. These hybrid membranes had the potential application of proton exchange membrane for direct methanol fuel cells.
A Case Study in the Pre-Calculation of Henry Coefficients
- Pages: 251-257
- First Published: 28 January 2010
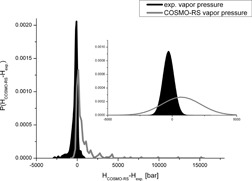
Gas solubilities represent the property data basis for absorption processes and are important in the design of gas-liquid reactors. We determine Henry coefficients as a measure of gas solubility by means of a series of computational approaches used in industrial practice and compare the results to experimentally determined values. Temperature-varied values for hydrocarbon-alcohol systems constitute the object of the study.
Computational Fluid Dynamics Study of a Styrene Polymerization Reactor
- Pages: 258-266
- First Published: 28 January 2010
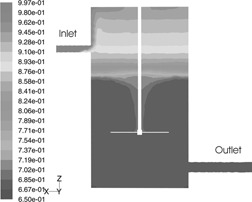
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is utilized to investigate the effect of mixing on styrene polymerization with a benzoyl peroxide initiator in a laboratory-scale continuous stirred-tank reactor equipped with a pitched-blade impeller. The CFD model is used to compute the monomer conversion as a function of the impeller speed and the residence time.
Effects of Operating Parameters on the Cinnamaldehyde Content of Extracted Essential Oil Using Various Methods
- Pages: 267-274
- First Published: 28 January 2010
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) of essential oils from commercial cinnamon bark was compared with essential oils that were obtained by hydrodistillation. Effects of operating parameters on extraction yield and composition of the extracted volatile oil were studied. In the hydrodistillation process, the effect of the pH of the solvent was also studied.
Sulfur Removal from Low-Sulfur Gasoline and Diesel Fuel by Metal-Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 275-280
- First Published: 28 January 2010
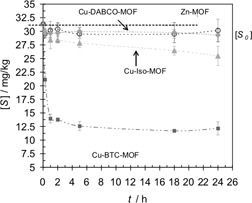
The reduction of the content of sulfur compounds in commercial gasoline and diesel fuels is a major concern of the petroleum, automotive and power generation industries. This is required to meet regulatory requirements and also to enhance the life-time of exhaust gas aftertreatment systems and sensors or fuel cell components. A series of metal-organic frameworks is investigated to determine their desulfurization capacity for commercial gasoline and diesel fuel.
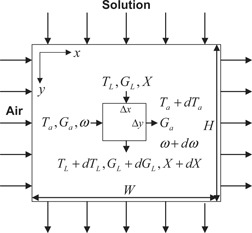
Heat and Mass Transfer between Air and Liquid Desiccant in Cross-flow Contact Systems
- Pages: 281-291
- First Published: 28 January 2010
Influence of a Lipid Phase on the Physical Properties of Spray-Dried Maltodextrin Powders
- Pages: 292-298
- First Published: 28 January 2010

The knowledge of the physical properties of the instantaneous time (wetting) and flowability of samples containing different proportions of lipid fractions with different melting points can provide important information on the influence of the lipid phase in the agglomeration of powdered food, and is investigated in detail.
Synthesis of a Graphite Oxide Polyaniline Nano-Composite by an Electrochemical Method
- Pages: 299-304
- First Published: 28 January 2010
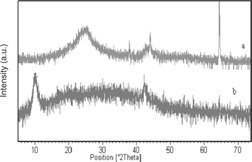
In order to produce a polyaniline graphite oxide nano-composite, electro-polymerization of aniline was performed within the graphite oxide layers via electrochemical treatment of aniline-intercalated graphite oxide in the supporting electrolyte. The polyaniline graphite oxide nano-composite was characterized by FTIR, XRD, TGA and SEM.
Continuous-Flow Surface Aeration Systems
- Pages: 305-314
- First Published: 28 January 2010
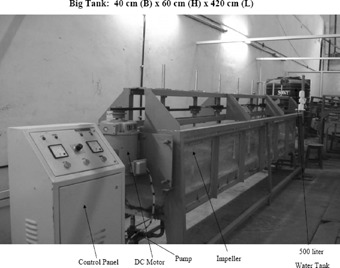
An aeration process in an activated sludge plant is a continuous-flow system. The efficiency of the surface aeration systems is governed by geometric and dynamic parameters. The objective of this study is the scale-up of laboratory results into field installation. The optimal geometric configuration of a continuous-flow surface aeration system is established.
Modeling of Particle Layer Detachment under Consideration of Transient Kinetic Effects
- Pages: 315-320
- First Published: 28 January 2010
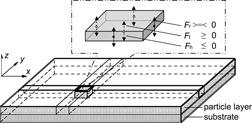
Particle layer detachment is extremely nonstationary concerning place and time, primarily due to changing conditions for the forces on the one hand and changes in the particle layer morphology on the other hand. A model and a simulation considering such transient kinetic effects on filter cake detachment are described and diverse computing results presented and discussed.
Mixing Agglomeration in a High-Shear Mixer with a Stirred Mixing Vessel
- Pages: 321-326
- First Published: 28 January 2010
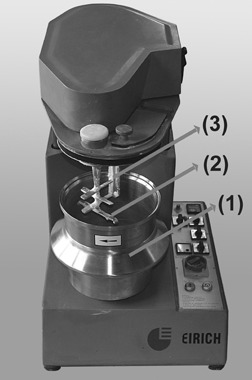
The agglomeration process in an Eirich-type high-shear mixer was investigated. Using a ceramic product, various influencing parameters, such as the agitator speed, vessel speed, or mixing tool, were investigated. The results will help the practical user to decide which parameters have to be considered for an optimum mixing agglomeration.
Experimental Study of the Mixing Time in a Jet-Mixed Gas-Liquid System
- Pages: 327-333
- First Published: 28 January 2010
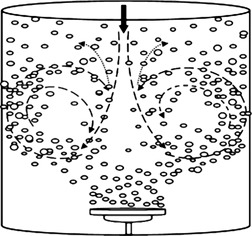
Previous studies on jet mixing have been limited to single liquid-phase mixing. Since the agitated gas-liquid vessels are widely used in chemical, biochemical and petroleum industries, the novelty of the present study is that it proposes the use of the jet fluid as a mixer in complex gas-liquid systems and attempts to experimentally investigate the jet mixing behavior in such systems.
High Temperature Cyclic Oxidation Resistance of Iron Chromium Base Alloys
- Pages: 334-340
- First Published: 28 January 2010

The cyclic oxidation behavior of an experimental stainless ferritic steel, without molybdenum and with copper-aluminum-titanium-lanthanum additions, developed for solid oxide fuel cell applications, was evaluated and compared with the oxidation behavior of commercial austenitic and ferritic stainless steels. For the cyclic oxidation tests, the steel samples were tested at temperatures ranging from 600 to 800 °C.
Roles of Pumps and Bypass in Chemistry Induced by Hydrodynamic Cavitation
- Pages: 341-346
- First Published: 28 January 2010