Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Contents
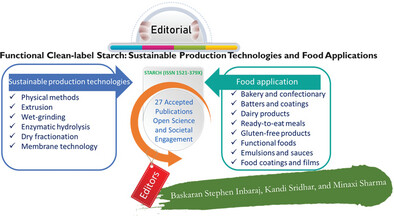
Guest Editorial
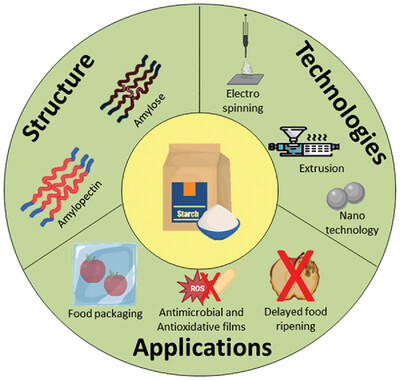
Functional Clean-Label Starch: Sustainable Production Technologies and Food Applications
- First Published: 08 July 2024
Review
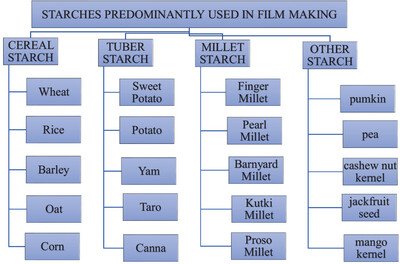
Starchy Films as a Sustainable Alternative in Food Industry: Current Research and Applications
- First Published: 06 May 2024
This review paper explores the unique chemical, physical, mechanical, thermal, and optical properties of starch as a biopolymer. It also focusses on the techniques utilized for transforming native starch into starch-based films and highlights recent insights into developing starch-based composite films. Furthermore, the review paper also critically discussespotential applications of starchy films in food packaging systems too.
Starch-Based Biodegradable Film from Fruit and Vegetable Waste and Its Standardization Modules Based on Neural Networks and Response Surface Methodology
- First Published: 25 October 2023
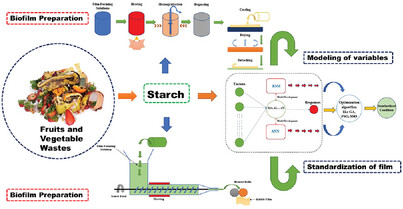
Starch extracted from fruits and vegetable wastes can be used to produce biofilm in food packaging materials. In order to cease throwing away valuable carbohydrates, especially starch, these should be incorporated into the concept of sustainable production. Response surface or artificial intelligence can be implemented for the standardization of biofilm.
Germinated Rice in Diabetes Management: Technological and Functional Changes
- First Published: 02 February 2024
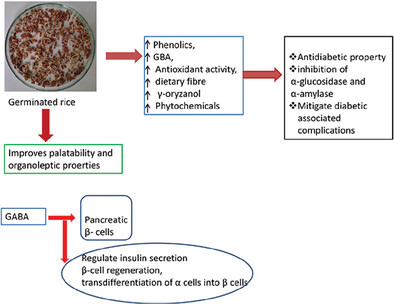
Germinated brown rice improves the palatability and organoleptic properties of brown rice thereby, making brown rice widely acceptable by the consumers. The bioactive compound in germinated rice helps in modulating blood glucose level and improves diabetic related health complications. Germinated rice can be promoted as staple food to manage diabetes.
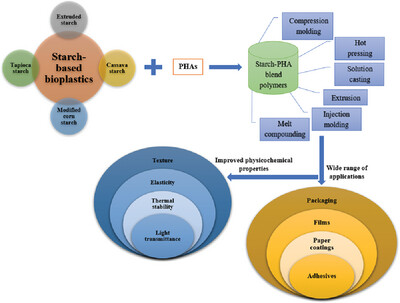
Starch-PHA Blend-Based Biopolymers with Potential Food Applications
- First Published: 28 January 2024
Role of Varieties of Starch in the Development of Edible Films—A Review
- First Published: 27 December 2023
Research Article
Relations Between Amylose Content and Physicochemical Properties of Starches from White and Red Sorghum Varieties
- First Published: 25 May 2024
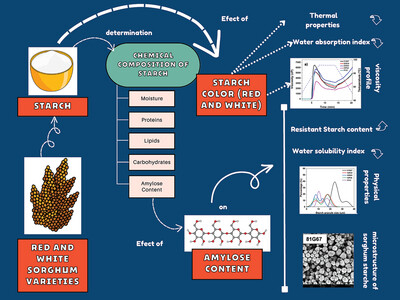
The present study investigated the relationship between the amylose content and the physicochemical properties of native starches of red and white sorghum. It was found that color sorghum starch had a relationship with thermal properties, viscosity, and water absorption index, but the amylose content determined the majority of the physicochemical properties of sorghum starches.
Characterization of Spray Dried Starch Systems of Natural Antioxidant Compounds
- First Published: 02 February 2024

Spray dried starch molecular inclusion complexes with antioxidant molecules are prepared and characterized. The structural, morphological, and physical properties are determined. Results show that the molecular inclusion complexation technique via spray drying could be effectively applied in order to obtain powders with good quality and satisfactory functional characteristics.
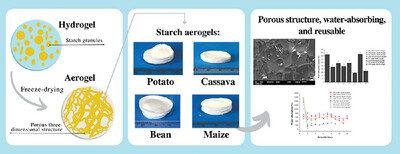
Water-Absorbent Biodegradable Aerogels Based on Potato, Cassava, Bean, and Maize Starches Applied in the Absorption of Chicken Exudate
- First Published: 19 April 2024
Morphological, Thermal, and Physicochemical Characteristics of Nano Starch from Cañihua (Chenopodium pallidicaule Aellen)
- First Published: 03 November 2023
Isolation and Characterization of Colon Targeting Starch from the Non-Conventional Source of Jharkhand, India
- First Published: 28 July 2023
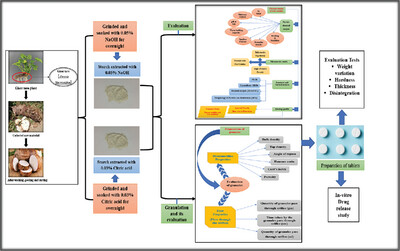
The delayed release starches from mankanda are isolated by using two different extraction media. Physicochemical, micromeritic, crystalline, thermal, rheological properties are determined, and the excipient property studies are explored in oral solid dosage form by in vitro dissolution studies which indicate its delayed release characteristics.
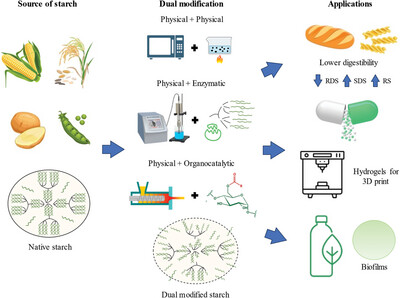
Dry Heat Treatment of Finger Millet Starch for Thin Films—Studies on Physicochemical, Mechanical, and Barrier Properties
- First Published: 05 September 2023

FMS modification via DHT: Spread 50 g FMS in a petri dish, heat at 120 °C for 4 h, cool naturally at 25 °C for 30 min. Mix 3 g modified starch with 30% w/w D-sorbitol in 100 mL, heat at 90 °C for 35 min with stirring. After cooling to 40 °C, degas starch solutions, fill Petri dishes with 25 mL of solution, and dry at 25 °C for 24 h.
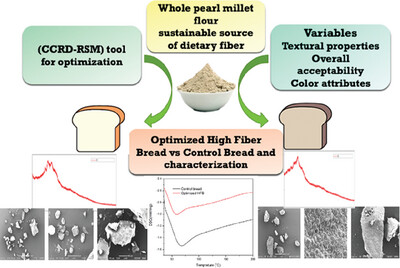
Modeling the Influence of Pearl Millet on High-Fiber Bread: An Investigation into Nutrition, Microstructure, Thermal Stability, Crystallinity, Rheology, and Glycemic Response
- First Published: 20 December 2023
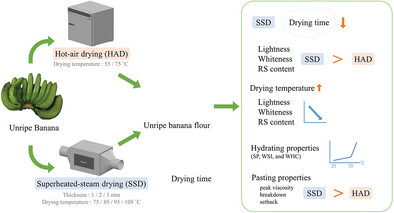
Sustainable Superheated Steam Drying of Unripe Banana (Musa acuminata cv. Hom Thong): Effects on Resistant Starch and Physicochemical–Functional Properties
- First Published: 10 August 2023
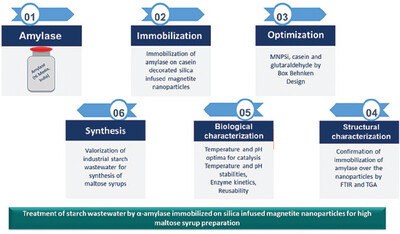
Treatment of Starch Wastewater by α-Amylase Immobilized on Silica Infused Magnetite Nanoparticles for Maltose Syrup Preparation
- First Published: 02 November 2023
Effects of Essential Oils and Ultrasonic Treatments on Properties of Edible Coatings and Their Application on Citrus Fruits
- First Published: 25 August 2023
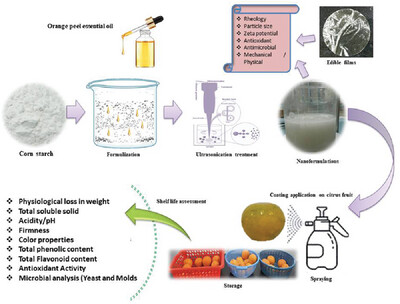
The graphical abstract image shows a schematic representation of developing corn starch based nano-formulations with orange peel, essential oils and ultrasonic treatments and their effects on the postharvest shelf life and characteristics of citrus fruits (Kinnow) at ambient temperature during 15 days of storage.
Nano Silver Imprinted Starch-co-Polymethylmethacrylate Sandwiched Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocomposite Films for Packaging Application
- First Published: 27 April 2024
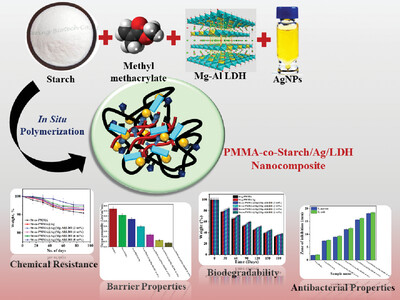
St-co-PMMA@Ag/(Mg-Al)LDH nanocomposite films fabricated by in situ polymerization approach show improved thermal stability, chemical resistance, biodegradability, and antibacterial properties by the virtue of AgNPs and LDH. The exfoliation of LDH platelets offers an eight-fold enhancement in oxygen barrier properties which is of importance in packaging applications.
Pasting Characteristics and In Vitro and In Vivo Digestibility of Low-, Medium-, and High-Amylose Types of Mung Bean Flour after Heat-Moisture Treatment
- First Published: 14 February 2024
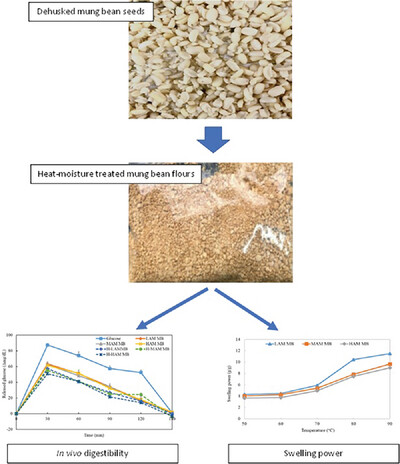
Mung bean flours varying amylose content are heat-moisture treated at 100℃ for 6h. The HMT forms the starch granules being more stable to continuous heating and agitation, lower swelling power and higher solubility and produces more RS content, resulting in lower blood glucose response and glycemic index.
Immobilization of Xylanase onto Starch Nanoparticles: A Reusable and Robust Nanobiocatalyst for Juice Clarification
- First Published: 04 September 2023
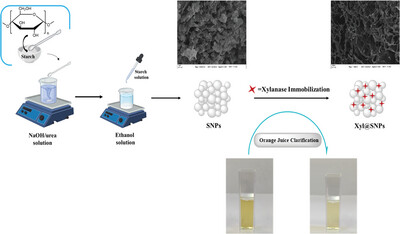
This study focuses on the synthesis and characterization of starch nanoparticles (SNPs) as a carrier material for xylanase (Xyl) immobilization. Changes in particle morphology, crystal structure, and molecular properties of synthesized SNPs are analyzed using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometry, and infrared spectrometry methods. Moreover, the biochemical properties (optimum pH, optimum temperature, and reusability) of immobilized Xyl are investigated.
Effect of Soluble Potato Starch on the Pregelatinization Properties of Non-Conventional Elephant Foot Yam Starch
- First Published: 10 September 2023
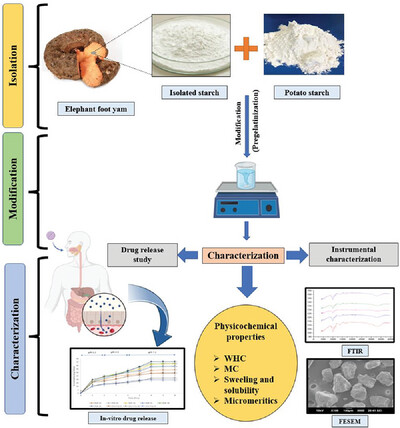
Elephant foot yam starch is mixed with soluble potato starch, thermally modified, and characterized for physicochemical, micromeritic properties, and structural evaluation. Morphological assessment is also conducted. Adjuvant properties of the modified starches are studied through in vitro dissolution analysis in oral solid dosage forms.
Effects of Wet-Milling Extraction Methods on Nutritional, Functional, and Structural Properties of Barnyard Millet Starch
- First Published: 27 November 2023
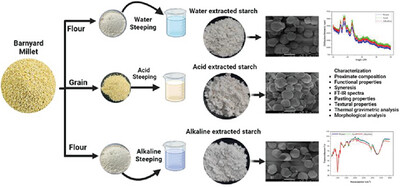
In the present study, the effects of different wet milling extraction methods (water, acidic, and alkaline) on the physical, structural, thermal, and functional properties of barnyard millet starch. The results show that the alkaline method yields significantly higher yield of starch with good amylose content and functional properties such as water binding capacity, oil binding capacity, higher color attributes (whiteness), thermal stability, textural properties, and lowest particle size as compared to other extracted starch. The results of the FESEM microstructure show polygonal, spherical, and rounded shapes of starch granules. Present study reveals that the alkaline method is the most potential to extract starch from barnyard millet with good quality and functional properties for food application.
Effects of Starch-Lipid Complexes on Quality and Starch Digestibility of Wheat Noodles
- First Published: 01 March 2024
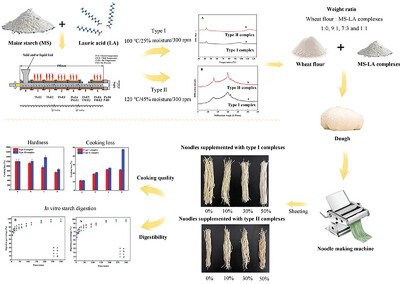
Starch-lipid complex with different crystalline forms (type I and type II) are prepared by extrusion-cooking. The partial substitution of wheat flour by complexes increases cooking loss and elasticity and decreases the hardness of cooked wheat noodles. Noodles made with type II complex are more resistant to amylolysis than those made with type I complex.
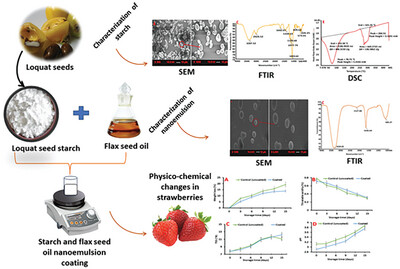
Exploring the Structural, Thermal, and Protective Potential of Loquat Seed Starch and Flax Seed Oil Nanoemulsion Coating on Strawberry
- First Published: 05 February 2024
Acid Hydrolyzed Pearl Millet Starch Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization
- First Published: 09 November 2023

Acid hydrolysis leads to starch nanoparticle formation. The size of nanoparticles is controlled by the use of synthesis conditions. Pearl millet starch nanoparticles are elliptical, and irregular in shape with a rough surface due to partially damaged granules. Conversion of native starch to nanostarch helps to improve its properties for further applications.
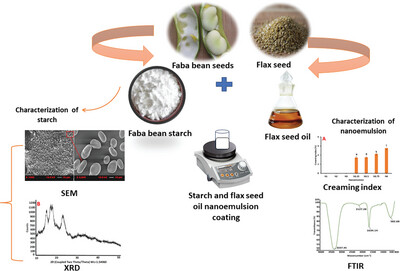
Structural and Thermal Properties of Faba Bean Starch and Flax Seed Oil Nanoemulsion: Effect of Processing Conditions on Nanoemulsion
- First Published: 09 February 2024
Modified Starch from Mango Pickling Industry Waste: Comparison of Physical and Chemical Modification
- First Published: 15 May 2024
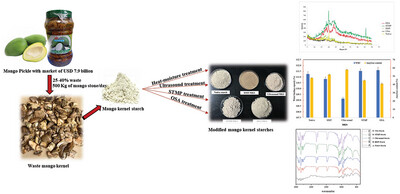
Mango pickling is a very big industry in India generating 500 kg of waste kernels per day. To provide sustainable solution to the waste, starch is extracted from kernels. To broaden the range of extracted starch applications, detailed characterization of native starch and modified starch is done for versatile utility.